A Study on the Sustainable Development of Water, Energy, and Food in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. The Characteristics of Water-Energy-Food Resources in China
4. Modeling the Water-Energy-Food System in China and Testing Its Effectiveness
4.1. Model Design
4.1.1. Causality Diagram of China’s Water-Food-Energy System
- (1)
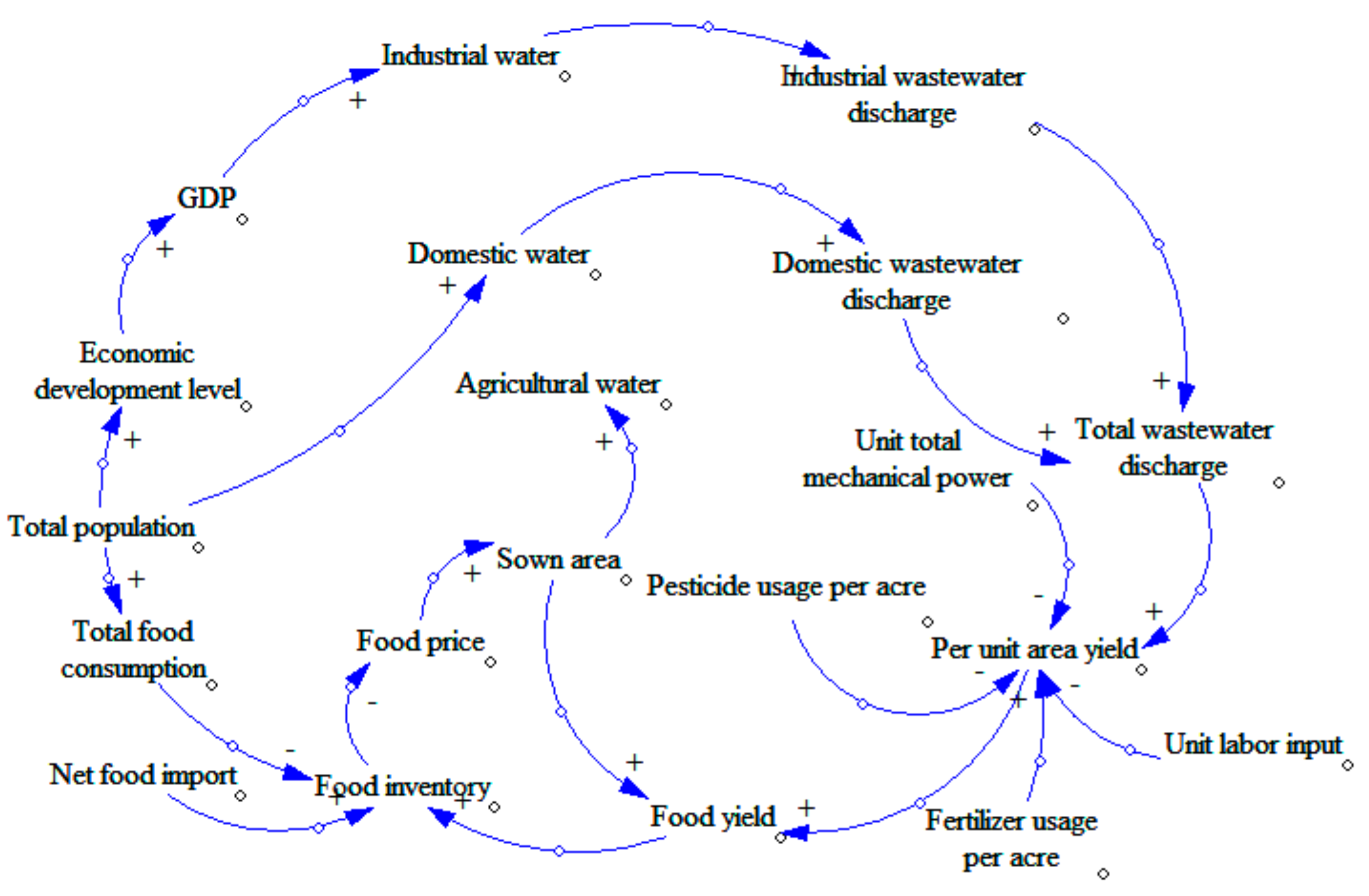
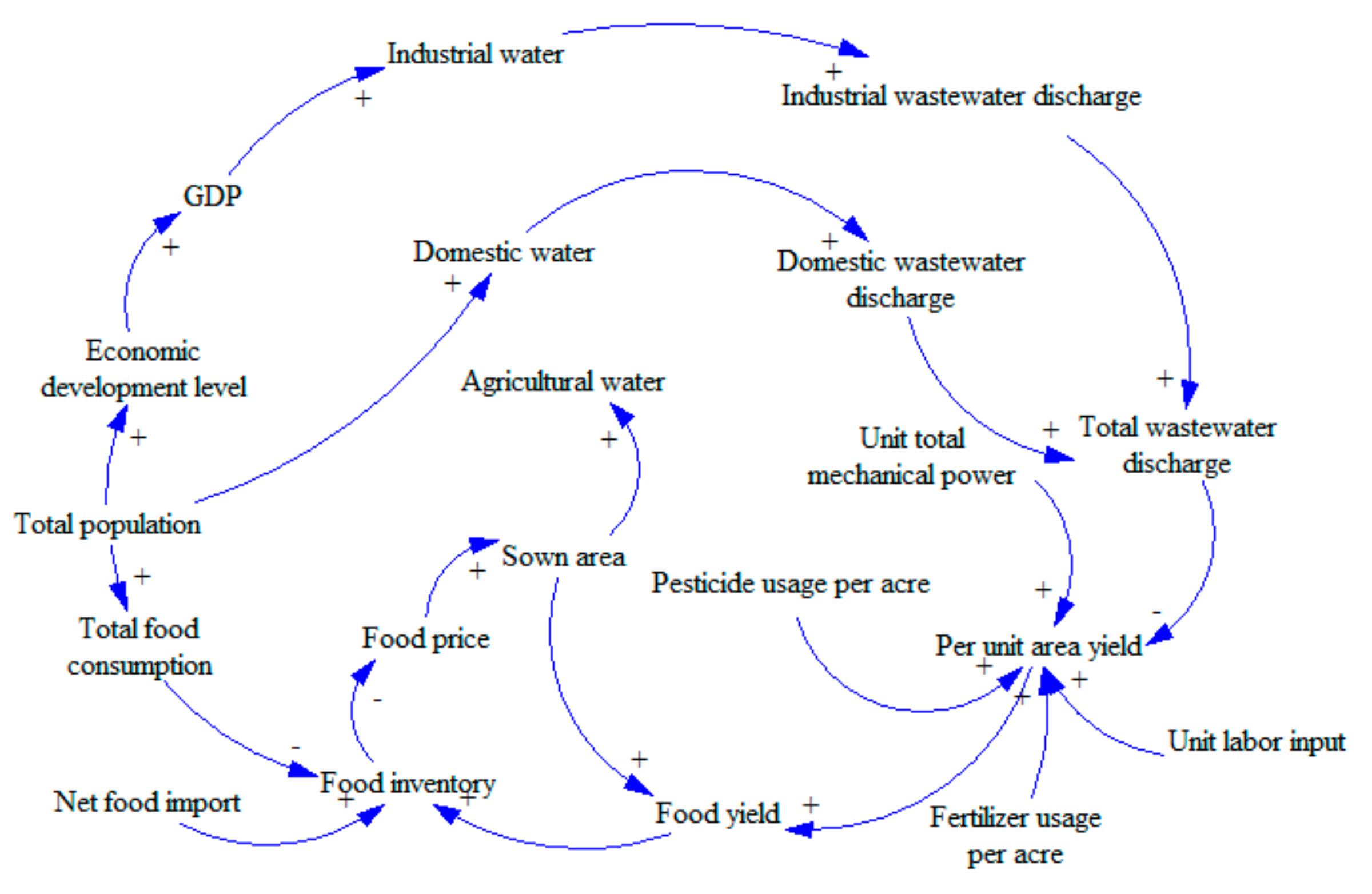
- Water subsystem (see Figure 1). We will study the water subsystem from the perspective of water consumption. We will consider industrial water, agricultural water, domestic water, and ecological water. These factors also have a circular feedback relationship with changes in population and energy consumption. There are three loops in Figure 1.Loop 1: GDP—Industrial pollution control investment—Industrial wastewater pollution control investment—Industrial wastewater discharge—Total wastewater discharge—Death rate—Annual death population—Total population—Economic development level—GDP.Loop 1 is a positive feedback loop. With the increase in GDP, the industrial pollution control investment will be increased as well as the industrial wastewater pollution control investment. As a result, the wastewater processing capacity will be increased, and the industrial wastewater discharge will be decreased. With less pollution, the environment will be friendlier, and the death rate will decline. The economic development level will gradually increase, leading to an increase in GDP, which forms a positive feedback loop.Loop 2: Total population—Domestic water—Domestic wastewater discharge—Total wastewater discharge—Total pollutant discharge—Death rate—Annual death population—Total population.Loop 2 is a negative feedback loop. With the increase in total population size, the consumption of domestic water will increase, leading to an increase in wastewater emission. The increase in wastewater emission will cause increased pollution, leading to a higher death rate. As such, the total population size will decrease, implying that it is a negative feedback loop.Loop 3: Total population—Economic development level—GDP—Industrial water—Industrial wastewater discharge—Total wastewater discharge—Total pollutant discharge—Death rate—Annual death population—Total population.Loop 3 is a negative feedback loop. The increase in total population will raise the economic development level, causing increased GDP. The increase of GDP will lead to the development of industry, causing increases in the consumption of industrial water. Thus, there will be more wastewater emissions, causing environmental degradation. The deteriorated environment will then affect the health of human beings, leading to a decrease in the total population size, which forms a negative feedback loop.
- (2)
- Food subsystem (see Figure 2). The subsystem of food resources will be studied from the perspective of food inventory. We will explore the cyclical feedback relationship between variables including food consumption, food production, net food imports and food inventory, and the changes in the population and pollution emissions.Loop: Food yield—Food inventory—Food price—Sown area—Food yield.This loop is a negative feedback loop. With the increases in food yield, the food inventory increases, which will lead to the decline of food prices. When the market price drops, farmers will reduce the sown area, leading to decreased food yield, which forms a negative feedback loop.
- (3)
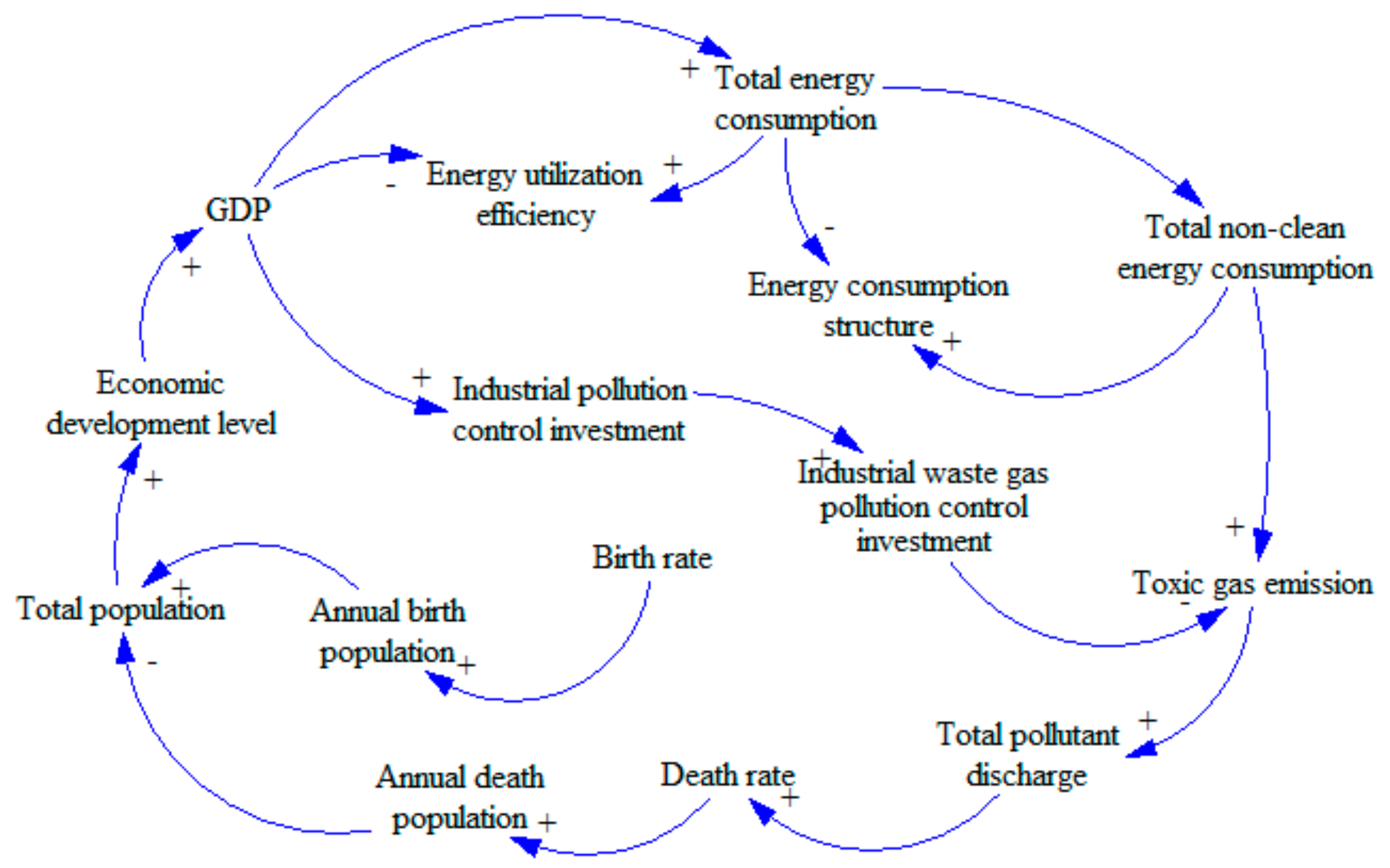
- Energy subsystem (see Figure 3). The energy resource subsystem will be studied from the perspective of energy consumption structure. We will explore the circular feedback relationship between variables including consumption of non-clean energy, investment in the control of waste gas pollution and emission of pollutants, and the total energy consumption and level of economic development.Loop: Economic development level—GDP—Total energy consumption—Total non-clean energy consumption—Toxic gas emission—Total pollutant discharge—Death rate—Annual death population—Total population—Economic development level.This loop is a negative feedback loop. Increasing economic development level will lead to increased GDP. The increase in GDP will lead to an increase in total energy consumption. As the main type of energy, more non-clean energy will then be consumed, leading to an increase in toxic gas emission. The polluted air will cause higher death rate, leading to a decrease in total population. Less population will slow economic growth [34], which forms a negative feedback loop.
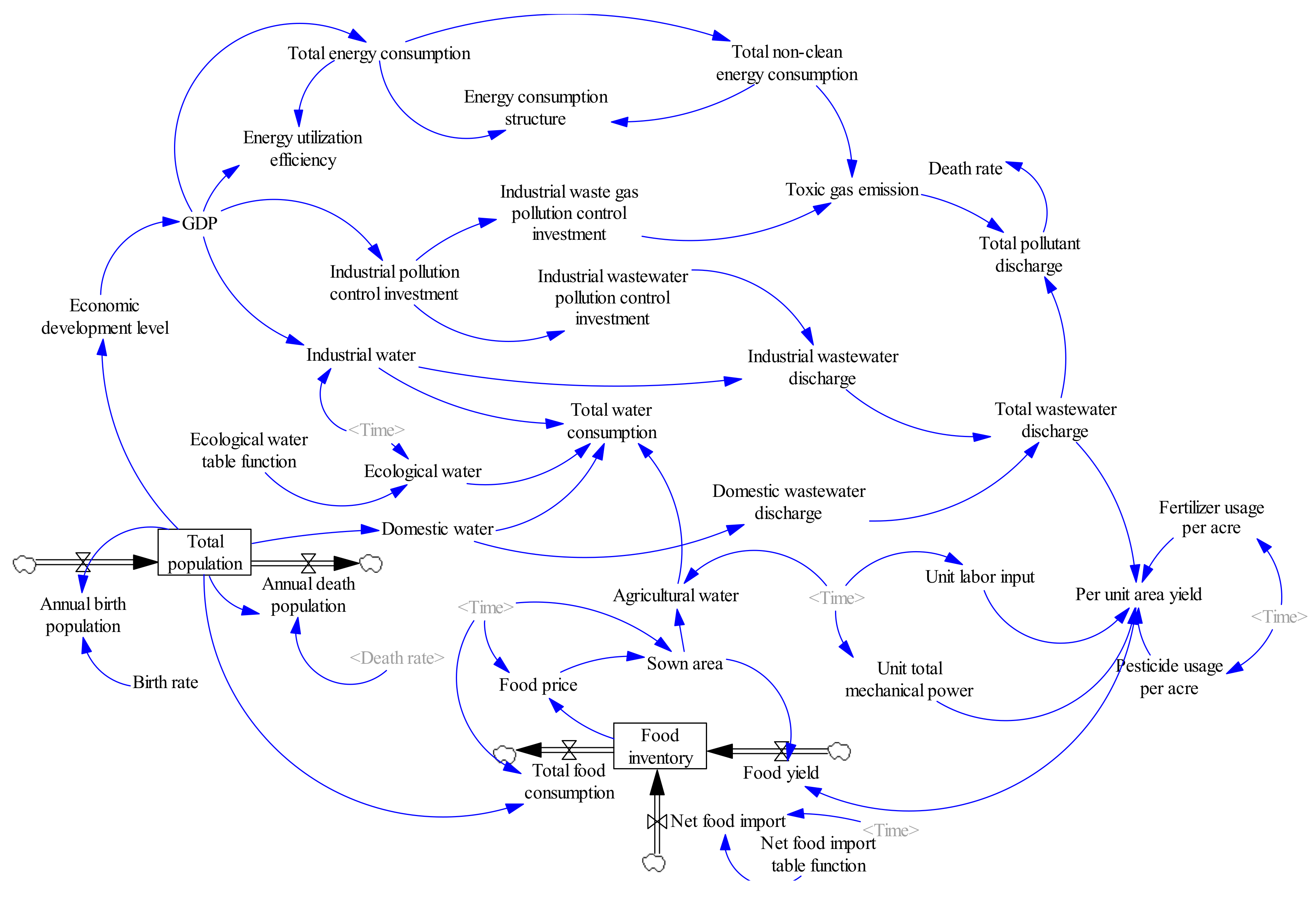
4.1.2. Stock-Flow Diagram of China’s Water-Food-Energy System
4.2. Initial Parameters and Equations of the Water-Energy-Food System in China
4.3. Model Test
5. Simulation, Prediction, and Scenario Analysis
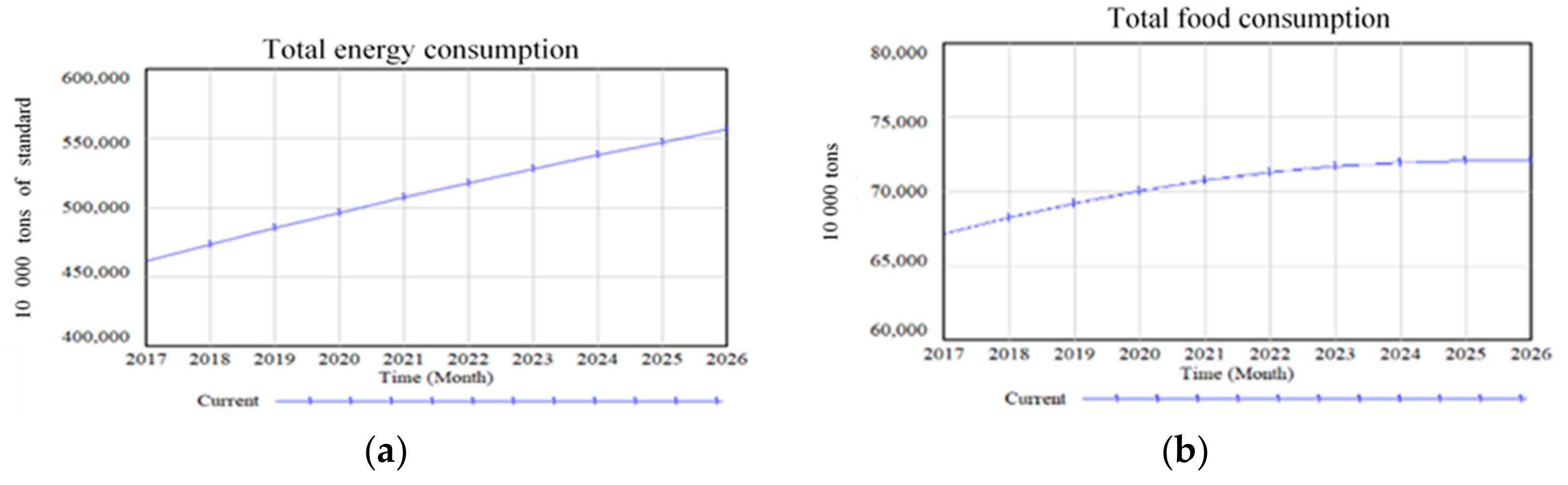
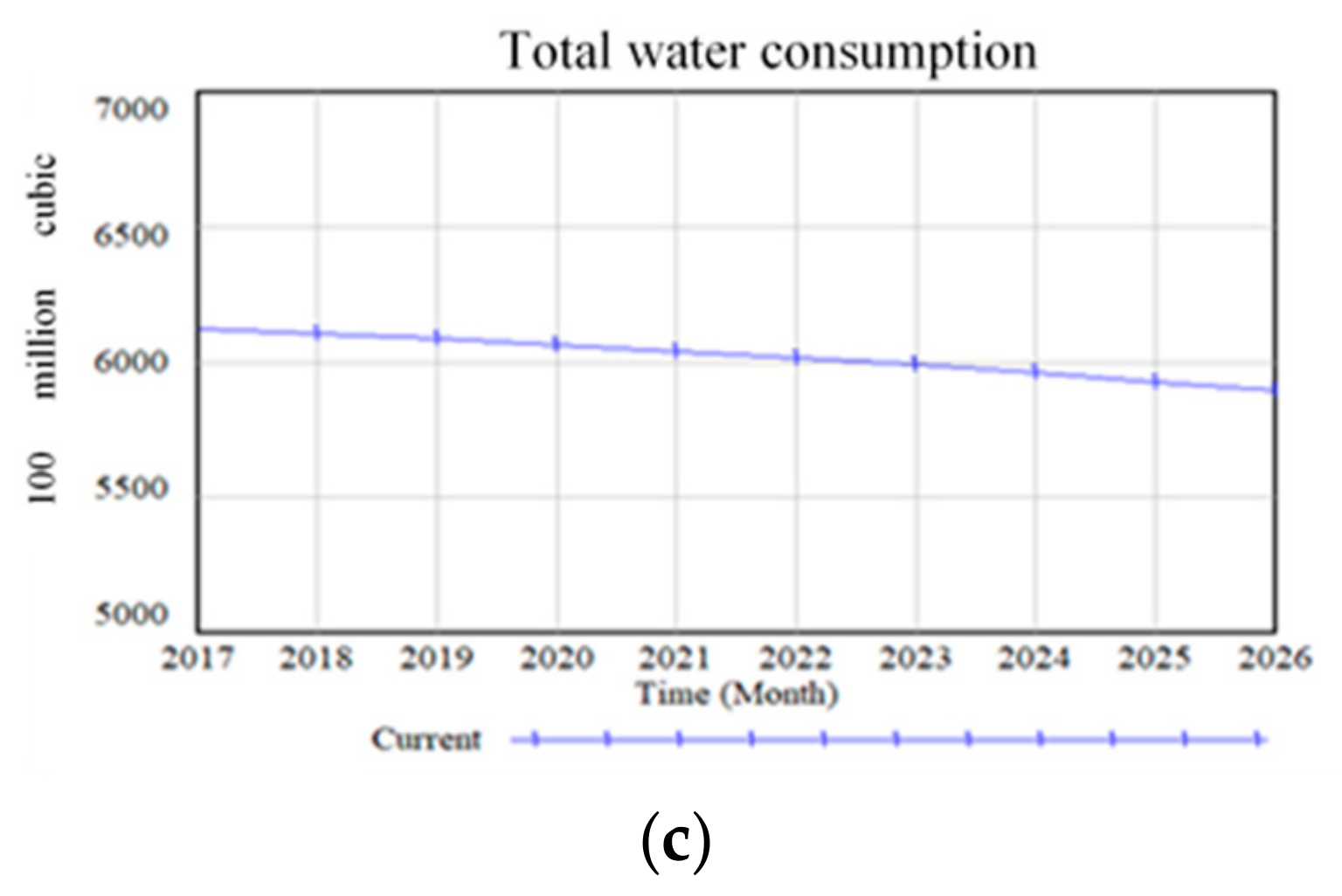
5.1. Simulation and Prediction
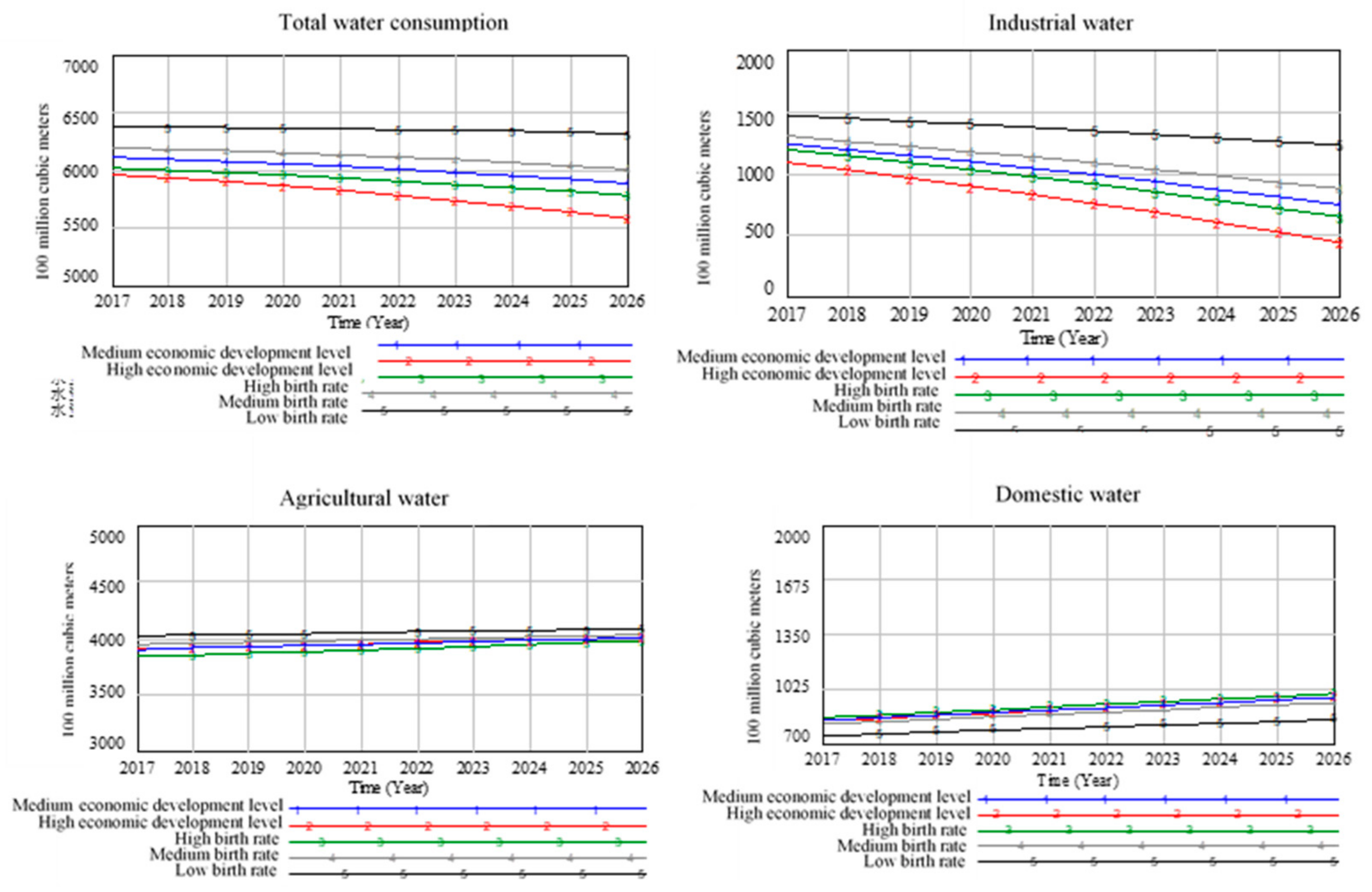
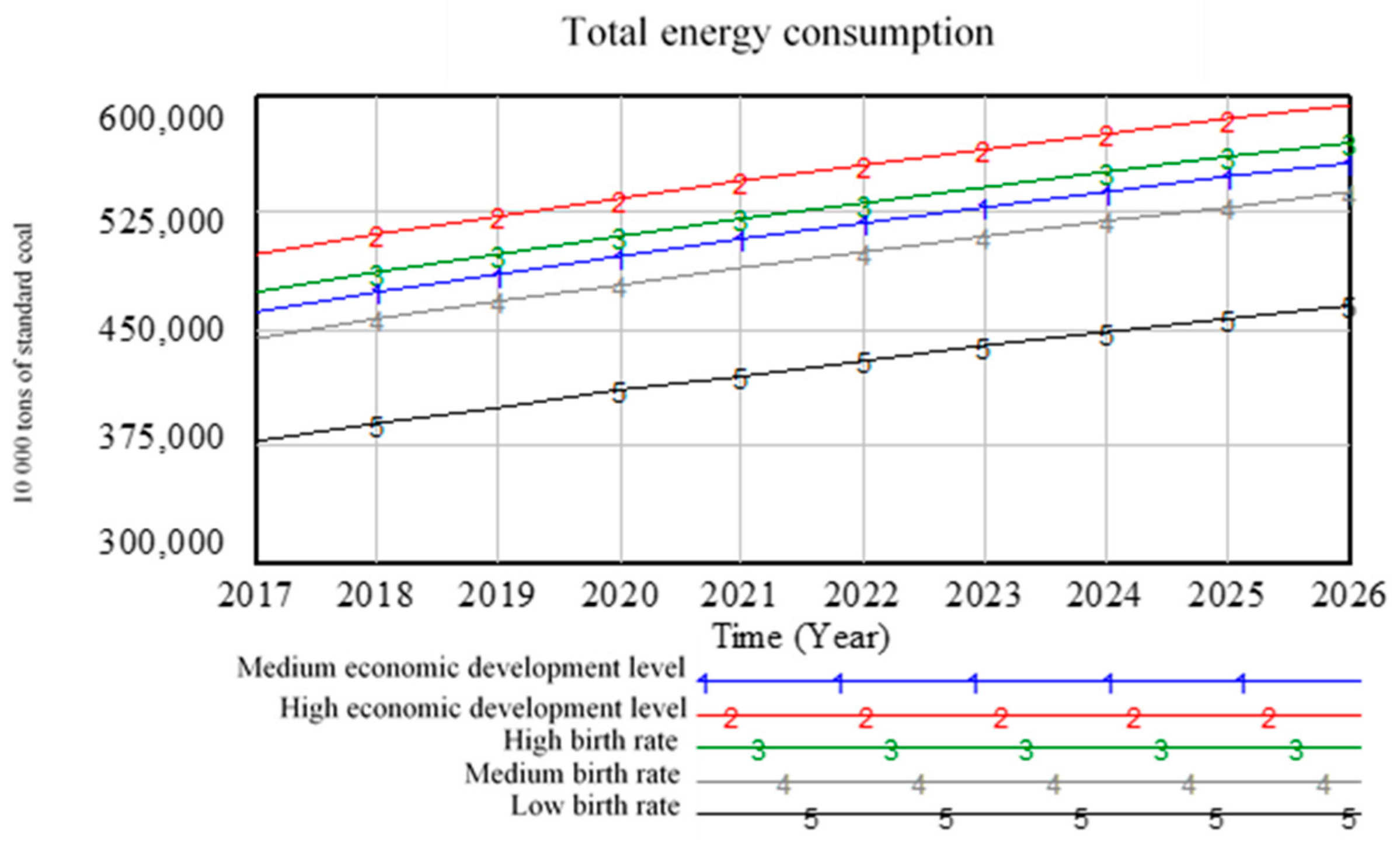
5.2. Scenario Analysis
5.2.1. Analysis Results of Water Resource Subsystem Scenario
5.2.2. Analysis Results of Energy Subsystem Scenario
5.2.3. Scenario Analysis Results of Food Subsystem
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Notation | Variable Meaning | Variable Type | Function Type | Mathematical and Logical Relational Expressions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IWPCI | Industrial wastewater pollution control investment | Auxiliary variable | Linear function | IWPCI = − 37.907 + 0.573 307*IPCI |
| DW | Domestic water | Auxiliary variable | Linear function | DW = − 1 982.63 + 0.020 282*TP |
| IWGPCI | Industrial waste gas pollution control investment | Auxiliary variable | Linear function | IWGPCI = 21.066 6 + 0.283 667*IPCI |
| TNEC | Total non-clean energy consumption | Auxiliary variable | Linear function | TNEC = − 1966.344 + 0.88*TEC |
| GDP | GDP | Auxiliary variable | Linear function | GDP = − 11 241.1 + 1.389 8*EDL |
| DR | Death rate | Auxiliary variable | Linear function | DR = 5.740 43 + 0.001 809*TPD |
| UTMP | Unit total mechanical power | Auxiliary variable | Linear function | UTMP = −659.672 + 0.332 272*Time |
| FUPA | Fertilizer usage per acre | Auxiliary variable | Linear function | FUPA = − 21 214.1 + 10.803*Time |
| PUPA | Pesticide usage per acre | Auxiliary variable | Linear function | PUPA = − 698.659 + 0.355 335*Time |
| TFC | Total food consumption | Rate variable | Piecewise function | TFC = IF THEN ELSE(Time ≤ 2007, − 45 323.4 + 0.734 912*TP, − 1.708 61e + 006 + 18.361*TP − 2.892e − 010*TP^3) |
| IW | Industrial water | Auxiliary variable | Piecewise function | IW = IF THEN ELSE(Time ≤ 2010,991.106 + 0.001 851*GDP − 1.805e − 009*GDP^2,1 760.3 − 0.000 613*GDP) |
| AW | Agricultural water | Auxiliary variable | Piecewise function | AW = IF THEN ELSE(Time ≤ 2000, 3 644.82,919.601 + 0.026 062*SA) |
| SA | Sown area | Auxiliary variable | Piecewise function | SA = IF THEN ELSE(Time ≤ 2004, 4.035 72e + 006 − 1 962.98*Time, 21 801.3*FP^0.175125) |
| ULI | Unit labor input | Auxiliary variable | Piecewise function | ULI = IF THEN ELSE(Time ≤ 2003, 3.262, 268.065 − 0.132 077*Time) |
| FP | Food price | Auxiliary variable | Piecewise function | FP= IF THEN ELSE(Time ≤ 2005, 3 871.46 + 0.475*FI − 2.03e − 005*FI^2, − 18 616.2 + 2 909.44*LN(FI)) |
| IPCI | Industrial pollution control investment | Auxiliary variable | Logarithmic function | IPCI = − 2 147.66 + 205.301*LN(GDP) |
| TEC | Total energy consumption | Auxiliary variable | Logarithmic function | TEC = − 1.462 49e + 006 + 141 032*LN(GDP) |
| DWD | Domestic wastewater discharge | Auxiliary variable | Exponential function | DWD = EXP(8.739 99 − 2 042.77/DW) |
| PUAY | Per unit area yield | Auxiliary variable | Multivariate linear function | PUAY = 5 649.83 − 71.401*UTMP − 601.068*ULI + 2.545*FUPM − 19.47*PUPM + 0.774*TWD |
| TGE | Toxic gas emission | Auxiliary variable | Multivariate linear function | TGE = − 173 447 − 420.831*IGPCI + 2.481*TNEC |
| IWD | Industrial wastewater discharge | Auxiliary variable | Multivariate linear function | IWD = 71.006 + 0.115 316*IW − 0.009 569*IWPCI |
| EDL | Economic development level | Auxiliary variable | Multivariate linear function | EDL = 2.045 06e + 007 − 248.913*TP + 5.492e − 009*TP^3 |
| ECS | Energy consumption structure | Auxiliary variable | \ | ECS = TNEC/TEC |
| EUE | Energy utilization efficiency | Auxiliary variable | \ | EUE = TEC/GDP |
| TWC | Total water consumption | Auxiliary variable | \ | TEC = IW + AW + DW + EW |
| TWD | Total wastewater discharge | Auxiliary variable | \ | TWD = IWD + DWD |
| TPD | Total pollutant discharge | Auxiliary variable | \ | TPD = TWD + TGE |
| TP | Total population | Stock variable | \ | TP = INTEG(ABP − ADP, 123626) |
| ABP | Annual birth population | Flow variable | \ | ABP = TP*BR/1000 |
| ADP | Annual death population | Flow variable | \ | ADP = TP*DR/1000 |
| NFI | Net food import | Flow variable | \ | NFI = Net food import table function(time) |
| EW | Ecological water | Auxiliary variable | \ | EW = Ecological water table function(time) |
| FY | Food yield | Flow variable | \ | FY = PUAY*SA/10,000 |
| FI | Food inventory | Stock variable | \ | FI = INTEG(FY + NFI − TFC, 9106.45) |
| BR | Birth rate | Constant | \ | 12.7725 |
References
- Allan, T.; Keulertz, M.; Woertz, E. The water–food–energy nexus: An introduction to nexus concepts and some conceptual and operational problems. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2016, 31, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Jun, B.; Yuanchun, Z.; Miaomiao, L. Research progress of regional environmental risk management: From the perspectives of food-energy-water nexus. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2018, 28, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, J. Collapse: How Societies Choose to Fail or Succeed, 1st ed.; Viking Penguin: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Saidi, M.; Elagib, N.A. Towards understanding the integrative approach of the water, energy and food nexus. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazilian, M.; Rogner, H.; Howells, M.; Hermann, S.; Arent, D.; Gielen, D.; Steduto, P.; Mueller, A.; Komor, P.; Tol, R.S.J.; et al. Considering the energy, water and food nexus: Towards an integrated modelling approach. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 7896–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, H.; Alrahaife, S.A.; El Hajj, R.; Lohr, K.; Mengoub, F.E.; Farajalla, N.; Fritzsche, K.; Jobbins, G.; Özerol, G.; Schultz, R.; et al. A Nexus Approach for the MENA Region—From Concept to Knowledge to Action. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keliang, W.; Li, Y.; Baochen, Y.; Yunhe, C. Energy Economic Efficiency, the Energy Environmental Performance and Regional Economic Growth. J. Manag. Sci. 2013, 26, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z. Empirical study on the coodinated development of China’ s enegry-economy-environment(3E). Economist 2009, 12, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Hu, Z.; Tang, L. The Geographic Distribution Characters and Dynamic Evolution for the Coordination Degree of Energy-Economic-Environmental (3E) in China. Econ. Geogr. 2013, 33, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenchao, L.; Lixin, T.; Dan, H. Research on SD Model of Economics-Energy-Environment Sustainable Development—Take China for Example. Chin. J. Syst. Sci. 2014, 22, 54–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hongwei, S.; Deliang, P. Coordinate horizontal Spatial Distribution and dynamic Evolution of Economy-Energy—Environment system in China. Inq. Econ. Issues 2017, 3, 5–13. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Renjun, X.; Zhi, D.; Xiuting, L.; Jichang, D. The System Dynamics Model of Energy Sustainable Development in Xinjiang. Manag. Rev. 2014, 26, 31–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Duncan, I.; Reedy, R.C. Drought and the water–energy nexus in Texas. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wallington, K.; Shafiee-Jood, M.; Marston, L. Understanding and managing the food-energy-water nexus—Opportunities for water resources research. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 111, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandone, D.; Peri, M.; Baldi, L.; Tanda, A. The impact of energy and agriculture prices on the stock performance of the water industry. Water Resour. Econ. 2018, 23, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lili, Z.; Zhou, H.; Xiuting, L. A System-dynamics-based Research on the Sustainable Development of Xinjiang’s Tourist Industry. Manag. Rev. 2014, 26, 37–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guijun, L.; Daohan, H.; Yulong, L. Research on Water-Energy-Food Input-Output Efficiency Evaluation in Different Areas of China. Comp. Econ. Soc. Syst. 2017, 3, 144–154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Haiyan, W.; Lu, L.; Fangting, Y.; Jun, M. System Dynamics Modeling of China’s Grain Forecasting and Policy Simulation. J. Syst. Simul. 2009, 21, 3079–3083. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wichelns, D. The water-energy-food nexus: Is the increasing attention warranted, from either a research or policy perspective? Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 69, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Huang, D.; Sun, C.; Li, Y. Developing interpretive structural modeling based on factor analysis for the water-energy-food nexus conundrum. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ding, T.; Wang, H.; Yu, X. Research on Total Factor Productivity and Influential Factors of the Regional Water–Energy–Food Nexus: A Case Study on Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijun, L.; Yulong, L.; Xiaojing, J.; Lei, D.; Daohan, H. Establishment and Simulation Study of System Dynamic Model on Sustainable Development of Water-Energy-Food Nexus in Beijing. Manag. Rev. 2016, 28, 11–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, C.; Peng, X.; Jianping, W. Overview of water-energy-food system and its enlightenment to China. Water Resour. Dev. Res. 2016, 2016, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Amorim, W.S.; Valduga, I.B.; Ribeiro, J.M.P.; Williamson, V.G.; Krauser, G.E.; Magtoto, M.K.; De Andrade Guerra, J.B.S.O. The nexus between water, energy, and food in the context of the global risks: An analysis of the interactions between food, water, and energy security. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2018, 72, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaoming, P.; Xiaokang, Z.; Yu, W.; Guiqin, J. Study on water-energy-food collaborative optimization for Yellow River basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2017, 28, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z. Research of Energy Consumption, Economic Growth and Energy Demand Forecast on China. Manag. Rev. 2011, 23, 38–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Djehdian, L.A.; Chini, C.M.; Marston, L.; Konar, M.; Stillwell, A.S. Exposure of urban food–energy–water (FEW) systems to water scarcity. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namany, S.; Al-Ansari, T.; Govindan, R. Optimisation of the energy, water, and food nexus for food security scenarios. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019, 129, 106513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, O.; Stewart, R.A.; Richards, R.G. Addressing the water-energy-climate nexus conundrum: A systems approach. In Proceedings of the 7th International Congress on Environmental Modelling and Software, San Diego, CA, USA, 15–19 June 2014; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Vesselinov, V.V. Integrated modeling approach for optimal management of water, energy and food security nexus. Adv. Water Resour. 2017, 101, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; He, W.; Shen, J.; Degefu, D.M.; Yuan, L.; Kong, Y. Coupling and Coordination Degrees of the Core Water–Energy–Food Nexus in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiguang, F. Prediction Analysis of Population, Cultivated Land and Grain in China Based on the ARIMA Model. Territ. Nat. Resour. Study 2014, 4, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Mu, L. Study on GM(1,1) Model Optimized Based on Genetic Algorithm for the Energy Consumption Forecast. China Manag. Informationization 2009, 12, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Jin, L. Research on system dynamic mechanism of population development and economic growth. Popul. Dev. 2017, 23, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.W. Industrial Dynamics a Major Breakthrough for Decision Makers. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1958, 36, 37–66. [Google Scholar]
- Sterman, J. System Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Eng. Syst. Div. Camb. 2002. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1721.1/102741 (accessed on 5 April 2002).
- Rehan, R.; Knight, M.A.; Unger, A.J.A.; Haas, C.T. Development of a system dynamics model for financially sustainable management of municipal watermain networks. Water Res. 2013, 47, 7184–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.Y.; Chen, S.Q.; Zhang, L.X. System dynamics modeling for urban energy consumption and CO2 emissions: A case study of Beijing, China. Ecol. Model. 2013, 252, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gafy, I.K. System Dynamic Model for Crop Production, Water Footprint, and Virtual Water Nexus. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 4467–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.; Wang, Z. Emergy synthesis and simulation for Macao. Energy 2008, 33, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

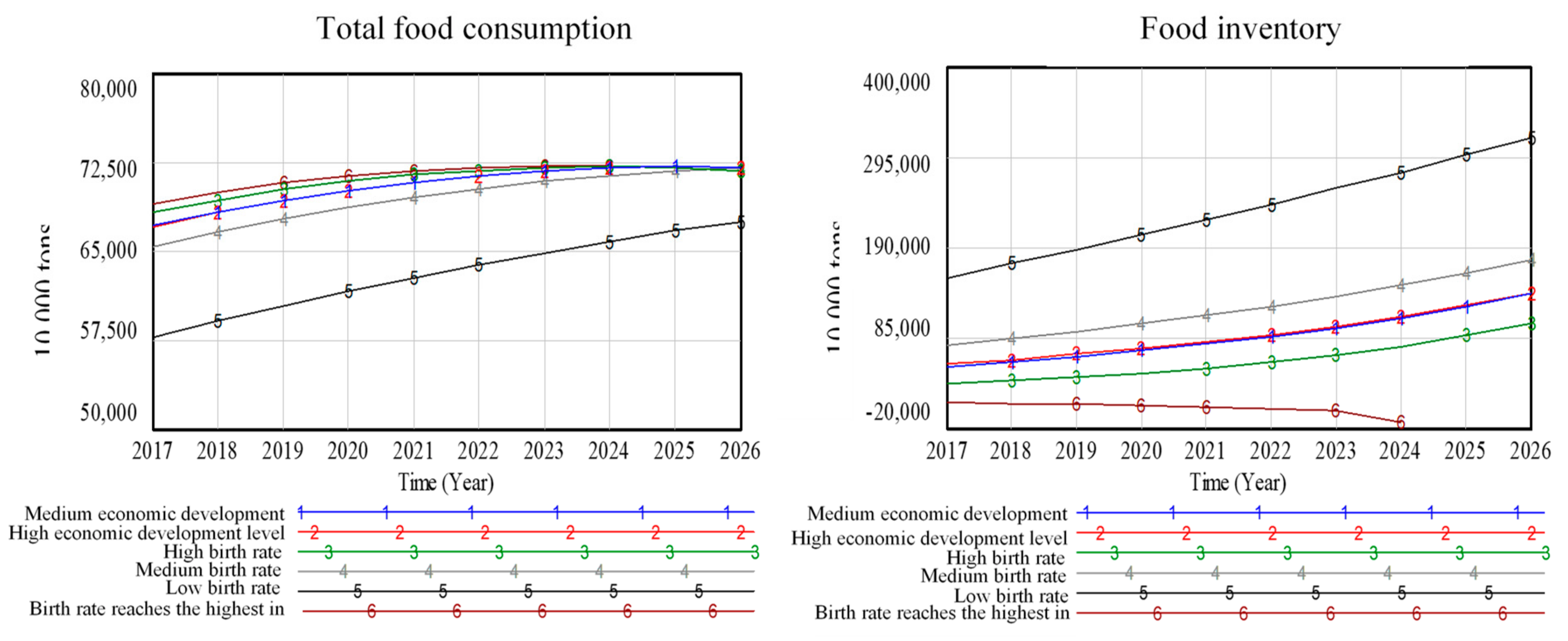
| Category | Scenario | Meaning | Parameter Setting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Population scenario | Low birth rate | The population target for the 13th five-year plan will not be met, and the fertility rate is low | The birth rate was set at 10.94‰ (according to the 2018 birth rate) |
| Median birth rate | The population target for the 13th five-year plan will be met. The population target of 1.42 billion will be reached by 2020 | The birth rate is set at 12.3‰ | |
| High birth rate | The response to the “two-child” policy is strong, exceeding the target of the 13th five-year plan | The birth rate is set at 13‰ | |
| Economic scenario | Medium economic development level | Affected by the trade friction between China and the United States, it is impossible to step into the ranks of high-income countries by 2020 | Keep the current level of economic development |
| High economic development level | The economic goal of the 13th Five-Year Plan is achieved, and China enter the ranks of high-income countries in 2020 | GDP per capita is increased by 30% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, L.; Chang, Y.; Ju, X.; Xu, F. A Study on the Sustainable Development of Water, Energy, and Food in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193688
Jin L, Chang Y, Ju X, Xu F. A Study on the Sustainable Development of Water, Energy, and Food in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(19):3688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193688
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Lei, Yuanhua Chang, Xianwei Ju, and Fei Xu. 2019. "A Study on the Sustainable Development of Water, Energy, and Food in China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 19: 3688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193688
APA StyleJin, L., Chang, Y., Ju, X., & Xu, F. (2019). A Study on the Sustainable Development of Water, Energy, and Food in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(19), 3688. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16193688




