Spatio-Temporal Characterization Analysis and Water Quality Assessment of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Background and Case Study
2.2. Data Collection and Preparation
2.3. Multivariate Statistical Methods
2.4. Water Quality Index
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatio-temporal Characterization of Water Quality Indicators
3.1.1. Toxic Metals
3.1.2. Easily Treated Indicators
3.1.3. Other Indicators
3.2. Statistical Analyses
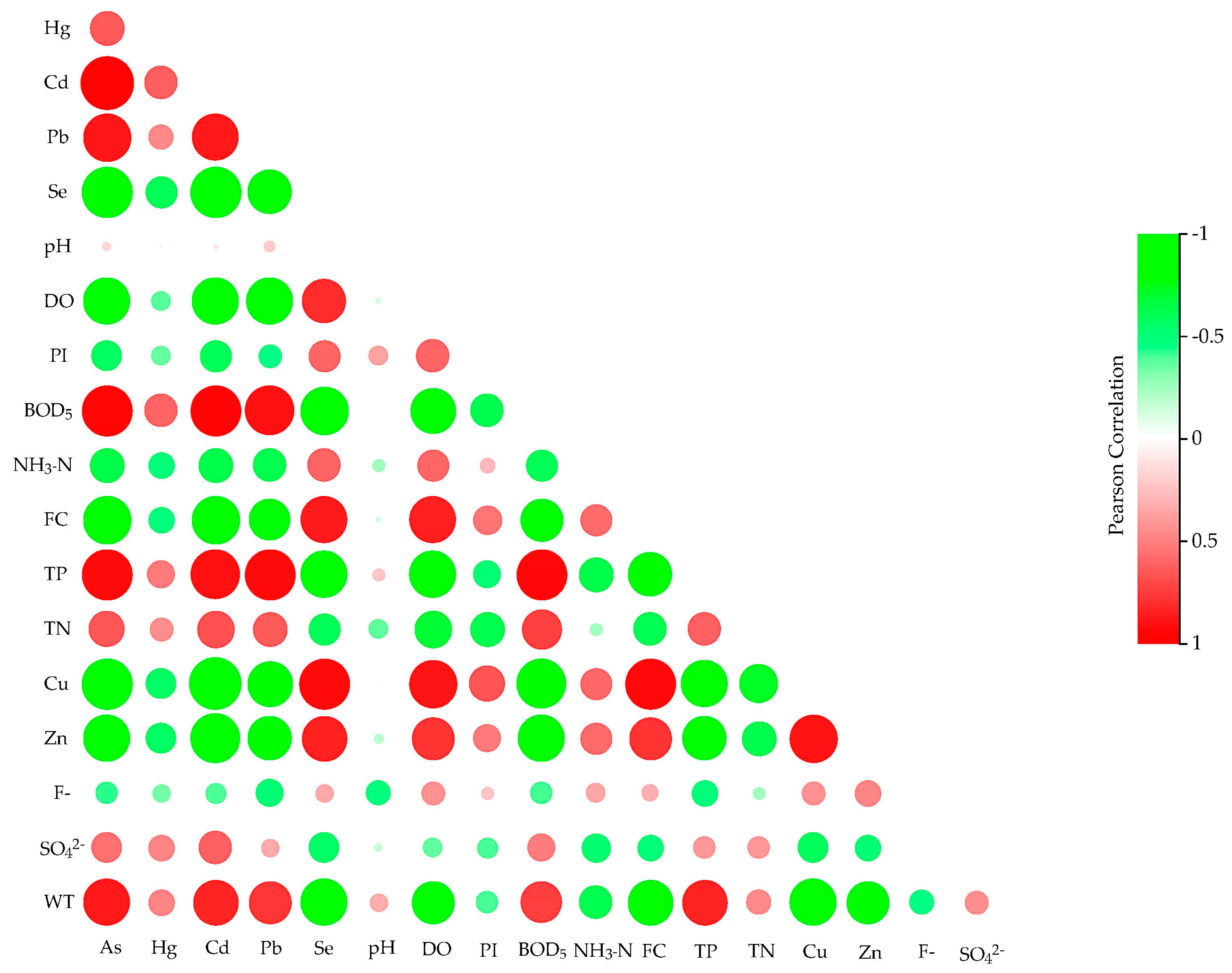
3.2.1. Correlation Analysis
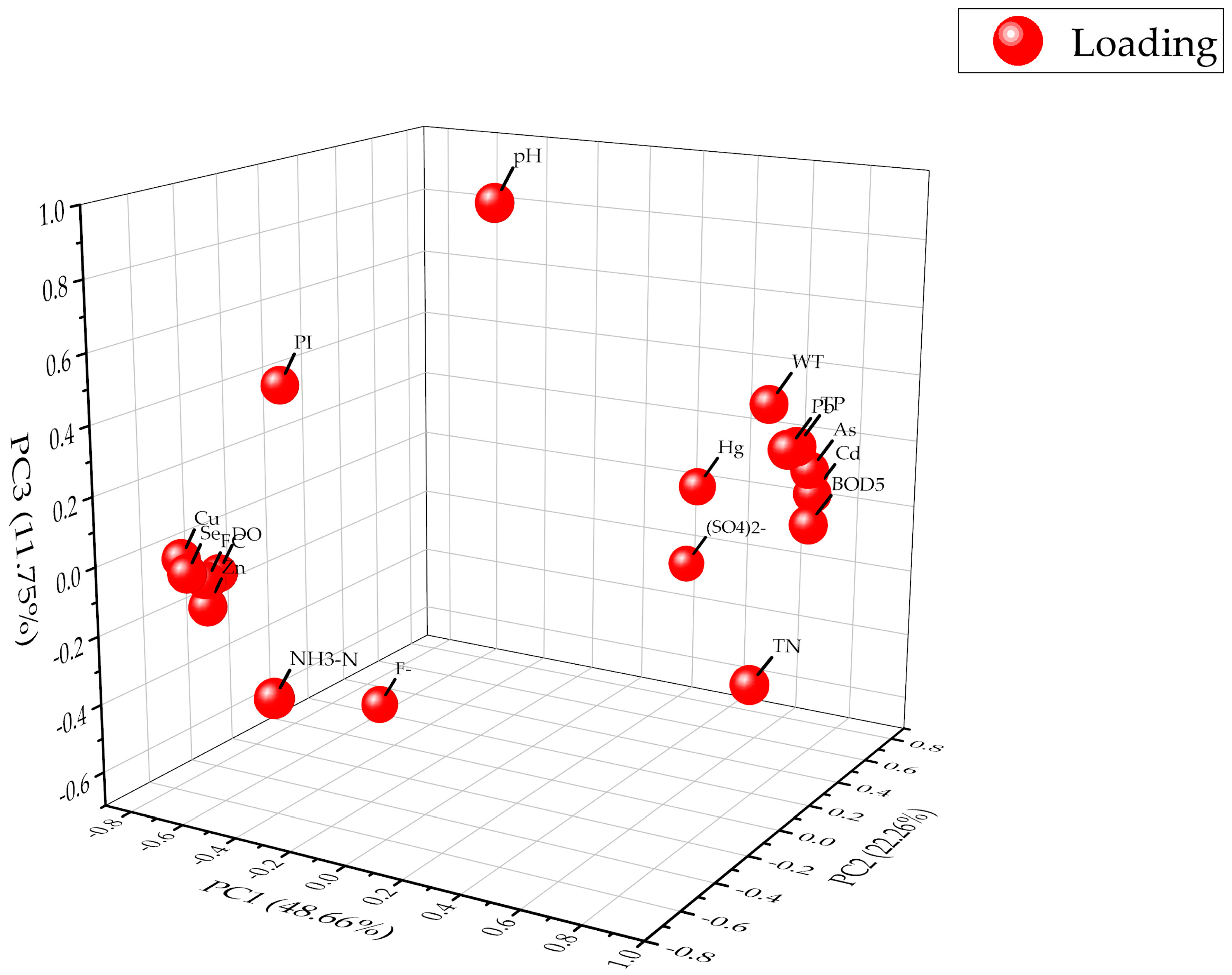
3.2.2. Principal Component Analysis
3.3. Water Quality Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vorosmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, A.K.; Mahato, M.K. Assessment of groundwater quality of pratapgarh district in india for suitability of drinking purpose using water quality index (wqi) and gis technique. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 4, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Han, G.L.; Liu, M.; Yang, K.H.; Li, X.Q.; Liu, J.K. Distribution, sources, and water quality assessment of dissolved heavy metals in the jiulongjiang river water, southeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Ma, R.H.; Hu, M.Q.; Luo, J.H.; Li, J.; Liang, Q.C. Combining citizen science and land use data to identify drivers of eutrophication in the huangpu river system. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mazumder, M.A.J.; Al-Attas, O.; Husain, T. Heavy metals in drinking water: Occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Gu, B.H.; Lin, Q.Q.; Gu, J.G.; Han, B.P. Stable isotope composition of suspended particulate organic matter in twenty reservoirs from guangdong, southern China: Implications for pelagic carbon and nitrogen cycling. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3610–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, A.S.; Manning, A.H.; Verplanck, P.L.; Crouch, C.; McKnight, D.M.; Dunham, R. Climate-change-driven deterioration of water quality in a mineralized watershed. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9324–9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, L.Q.; Deng, L.; Jin, Z.D. Characteristics, sources, water quality and health risk assessment of trace elements in river water and well water in the chinese loess plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, H.; Nasri, O.; Ojaghi, B.; Pasalari, H.; Hosseini, M.; Hashemzadeh, B.; Kavosi, A.; Masoumi, S.; Radfard, M.; Adibzadeh, A.; et al. Data on drinking water quality using water quality index (wqi) and assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes in qorveh&dehgolan, kurdistan, iran. Data Brief 2018, 20, 375–386. [Google Scholar]
- Abbasnia, A.; Radfard, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Yousefi, M.; Soleimani, H.; Alimohammadi, M. Groundwater quality assessment for irrigation purposes based on irrigation water quality index and its zoning with gis in the villages of chabahar, sistan and baluchistan, iran. Data Brief 2018, 19, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Lu, Y.L.; Han, J.Y.; He, G.Z.; Wang, T.Y. Identification of anthropogenic influences on water quality of rivers in taihu watershed. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Zhang, Q.F. Spatial characterization of dissolved trace elements and heavy metals in the upper han river (China) using multivariate statistical techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pertsemli, E.; Voutsa, D. Distribution of heavy metals in lakes doirani and kerkini, northern greece. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, C.; Neal, M.; Hill, L.; Wickham, H. The water quality of the river thame in the thames basin of south/south-eastern england. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 360, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebbi, M.R.; Saeedi, R.; Montazeri, A.; Vaghefi, K.A.; Labbafi, S.; Oktaie, S.; Abtahi, M.; Mohagheghian, A. Assessment of water quality in groundwater resources of iran using a modified drinking water quality index (dwqi). Ecol. Indic. 2013, 30, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovieva, N.; Jones, V.J.; Appleby, P.G.; Kondratenok, B.M. Extent, environmental impact and long-term trends in atmospheric contamination in the usa basin of east-european russian arctic. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2002, 139, 237–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.C.; Poon, B.H.T.; Lan, C.Y.; Wong, M.H. Assessment of metal and nutrient concentrations in river water and sediment collected from the cities in the pearl river delta, south China. Chemosphere 2003, 52, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putro, B.; Kjeldsen, T.R.; Hutchins, M.G.; Miller, J. An empirical investigation of climate and land-use effects on water quantity and quality in two urbanising catchments in the southern united kingdom. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Li, Y.P.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (lake taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (n & p) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar]
- Lumb, A.; Sharma, T.C.; Bibeault, J.F. A review of genesis and evolution of water quality index (wqi) and some future directions. Water Qual. Expos. Health 2011, 3, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Shao, D.G.; Yang, H.D.; Yang, S. Prediction of water quality in south to north water transfer project of China based on ga-optimized general regression neural network. Water Sci. Technol.-Water Supply 2015, 15, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.G.; Wang, Z.M.; Wang, B.; Luo, W.W. A water quality model with three dimensional variational data assimilation for contaminant transport. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 30, 4501–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Tang, X.Y.; Tang, J.L.; Wang, C. Assessing water quality of three gorges reservoir, China, over a five-year period from 2006 to 2011. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4545–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; He, M.; Han, W.; Gu, Y.F. Analysis and assessment on heavy metal sources in the coastal soils developed from alluvial deposits using multivariate statistical methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocer, M.A.T.; Sevgili, H. Parameters selection for water quality index in the assessment of the environmental impacts of land-based trout farms. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 36, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wang, G.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Ko, C.H. Risk assessment of exposure to volatile organic compounds in groundwater in taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2165–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Xia, C.Y.; Xu, M.Y.; Guo, J.; Sun, G.P. Application of modified water quality indices as indicators to assess the spatial and temporal trends of water quality in the dongjiang river. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Arias, H.; Contreras-Caraveo, M.; Manuel Quintana, R.; Alfonso Saucedo-Teran, R.; Pinales-Munguia, A. An overall water quality index (wqi) for a man-made aquatic reservoir in mexico. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 1687–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, G.S.; Jardim, W.D.F. A new water quality index for protection of aquatic life appllied to the atibaia river, region of campinas/paulinia cities—Sao paulo state. Quim. Nova 2006, 29, 689–694. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, K.; Wang, J.G.; Wang, J.Q.; Wang, C.X.; Zhang, C.J.; Wang, X.Y. Treatments to control urban river pollution in water source city of south to north water diversion project. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tian, B. Real time temperature simulation on caohe river aqueduct in south to north water transfer project during construction period. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2011, 255–260, 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.W.; Zeng, H.; Guo, J. The mechanism of environmental protection of water resource area of the middle route of chinese south to north water transfer project. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering And Business Management (Ebm2011), Wuhan, China, 22–24 March 2011; Volumes 1–6, pp. 2893–2896. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.C.; Zhang, L.P.; Xia, J.; Gippel, C.J.; Wang, R.C.; Zeng, S.D. Implications of modelled climate and land cover changes on runoff in the middle route of the south to north water transfer project in China. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 2563–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, S.; Sener, E.; Davraz, A. Evaluation of water quality using water quality index (wqi) method and gis in aksu river (sw-turkey). Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengraı̈Ne, K.; Marhaba, T.F. Using principal component analysis to monitor spatial and temporal changes in water quality. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 100, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primpas, I.; Tsirtsis, G.; Karydis, M.; Kokkoris, G.D. Principal component analysis: Development of a multivariate index for assessing eutrophication according to the european water framework directive. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Dwivedi, A.; Kumar, M.S. Use of water quality index and multivariate statistical techniques for the assessment of spatial variations in water quality of a small river. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.H.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.X.; Quan, Q.M. Temporal and spatial variations in water quality of changjiang river basin in luzhou, China based on multivariate statistical techniques. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 145, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Sun, S.H.; Wang, M.Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Xin, X.D.; Sun, L.; Li, W.; Jia, R.B. Assessing water quality of five typical reservoirs in lower reaches of yellow river, China: Using a water quality index method. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.S.; Zhang, D.W.; Cai, Y.J.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.W. Water quality assessment based on the water quality index method in lake poyang: The largest freshwater lake in China. Sci. Rep.-UK 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.S.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Cai, Y.J.; Deng, J.C. Assessing river water quality using water quality index in lake taihu basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesce, S.F.; Wunderlin, D.A. Use of water quality indices to verify the impact of cordoba city (argentina) on suquia river. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2915–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, P.R.; Lee, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Kanel, S.R.; Khan, S.P. Application of water quality indices and dissolved oxygen as indicators for river water classification and urban impact assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 132, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentukeviciene, M.; Bagdziunaite-Litvinaitiene, L.; Chadysas, V.; Litvinaitis, A. Evaluating the impacts of integrated pollution on water quality of the trans-boundary neris (viliya) river. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si yue, L.I.; Zhang, Q.F. Assessing the water quality in the water source area of the middle route of the south to north water transfer project(danjiangkou reservoir) using a water quality index method. Res. Environ. Sci. 2008, 21, 231–246, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, W. Dissolved trace elements and heavy metals from the shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the yangtze river region, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 1503–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun sheng, Q.I.; Chuan, F.U.; Huang, X.S.; Tan, J. Transfer of trace elements in water area ecology systems of the three gorges reservoir. J. Chongqing Univ. 2002, 25, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Huang, J.H.; Zeng, G.M.; Yuan, X.Z.; Li, X.D.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.Y.; Tang, X.J.; Bai, B. Spatial risk assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the dongting lake, middle China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 132, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekey, H.; Karakas, D.; Bakoglu, M. Source apportionment of trace metals in surface waters of a polluted stream using multivariate statistical analyses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 49, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotruvo, J.A. 2017 WHO guidelines for drinking water quality: First addendum to the fourth edition. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2017, 109, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epa sets goal of reducing drinking water systems violating health standards. Groundw. Monit. Remediat. 2019, 39, 8.
- Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Yu, S.; Rhew, D. Relationships between water quality parameters in rivers and lakes: Bod5, cod, nbops, and toc. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kangabam, R.D.; Govindaraju, M. Anthropogenic activity-induced water quality degradation in the loktak lake, a ramsar site in the indo-burma biodiversity hotspot. Environ. Technol. 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, E.; Colmenarejo, M.F.; Vicente, J.; Rubio, A.; García, M.G.; Travieso, L.; Borja, R. Use of the water quality index and dissolved oxygen deficit as simple indicators of watersheds pollution. Ecol. Indic. 2007, 7, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, V.; Shrinithivihahshini, N.D.; Srinivasan, B.; Rengaraj, C.; Mariyaselvam, S. Quality assessment of pollution indicators in marine water at critical locations of the gulf of mannar biosphere reserve, tuticorin. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 126, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Lin, Z.; Song, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation indexes and methods for water quality in ocean dumping areas. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Avigliano, E.; Schenone, N.F. Human health risk assessment and environmental distribution of trace elements, glyphosate, fecal coliform and total coliform in atlantic rainforest mountain rivers (south america). Microchem. J. 2015, 122, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Pei, L.; Wan, S.; Jiang, S.; Liu, S.; Ren, Z.; Yang, Y. Chemical fertilizer pollution control using drip fertigation for conservation of water quality in danjiangkou reservoir. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2014, 98, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Cai, Q.; Min, Z. Spatial gradient and seasonal variation of trophic status in a large water supply reservoir for the south-to-north water diversion project, China. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2015, 30, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Gao, J.F. An improved ensemble kalman filter for optimizing parameters in a coupled phosphorus model for lowland polders in lake taihu basin, China. Ecol. Model. 2017, 357, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, B.; Hao, H.; Zhou, H.; Lu, J. Nitrogen and phosphorus in sediments in China: A national-scale assessment and review. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Xu, C.; Ridoutt, B.G.; Wang, X.; Ren, P. Nitrogen and phosphorus losses and eutrophication potential associated with fertilizer application to cropland in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 171–179. [Google Scholar]
- Filstrup, C.T.; Downing, J.A. Relationship of chlorophyll to phosphorus and nitrogen in nutrient-rich lakes. Inland Waters 2017, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karastoyanov, V.; Bojinov, M. Mechanism of anodic oxidation of tungsten in neutral sulphate-fluoride solutions. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Xiang, X.; Lu, Y.; Yan, X.; Xiao, L.; Liu, S. The temporal-spatial distribution and changes of dissolved oxygen in the changjiang estuary and its adjacent waters for the last 50 a. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2017, 36, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, D.J.; Karpe, A.V.; Ahmed, W.; Cook, S.; Morrison, P.D.; Staley, C.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Palombo, E.A. A community multi-omics approach towards the assessment of surface water quality in an urban river system. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.C.; Schmalz, B.; Fohrer, N. Development and testing of a phytoplankton index of biotic integrity (p-ibi) for a german lowland river. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 13, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdighi, A.; Arabi, M.; Osmond, D.L. The relationship between land use and vulnerability to nitrogen and phosphorus pollution in an urban watershed. J. Environ. Qual. 2017, 46, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutel, M.W.; Cox, S.E.; Gebremariam, S. Effects of chironomid density and dissolved oxygen on mercury efflux from profundal lake sediment. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2016, 32, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
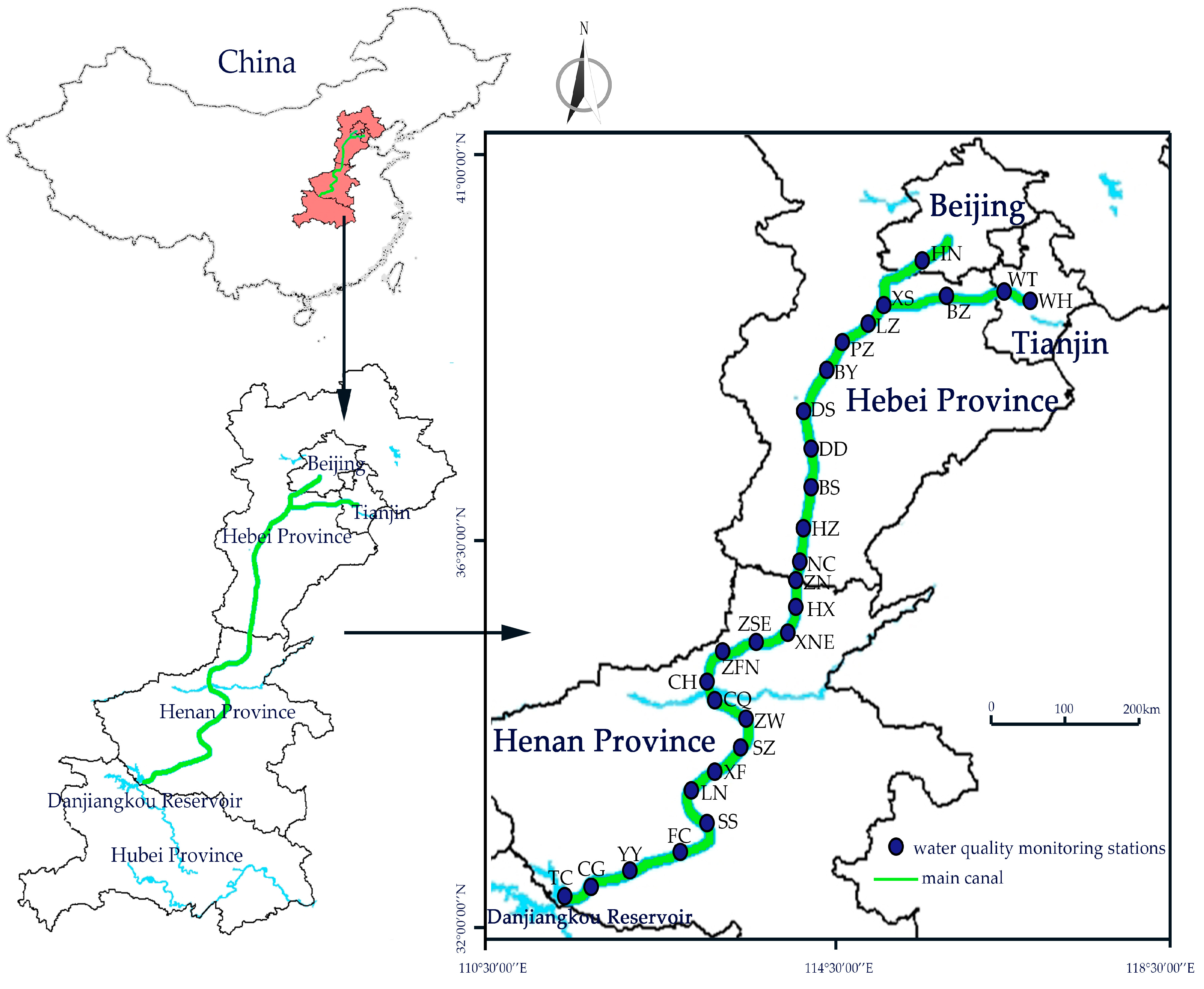
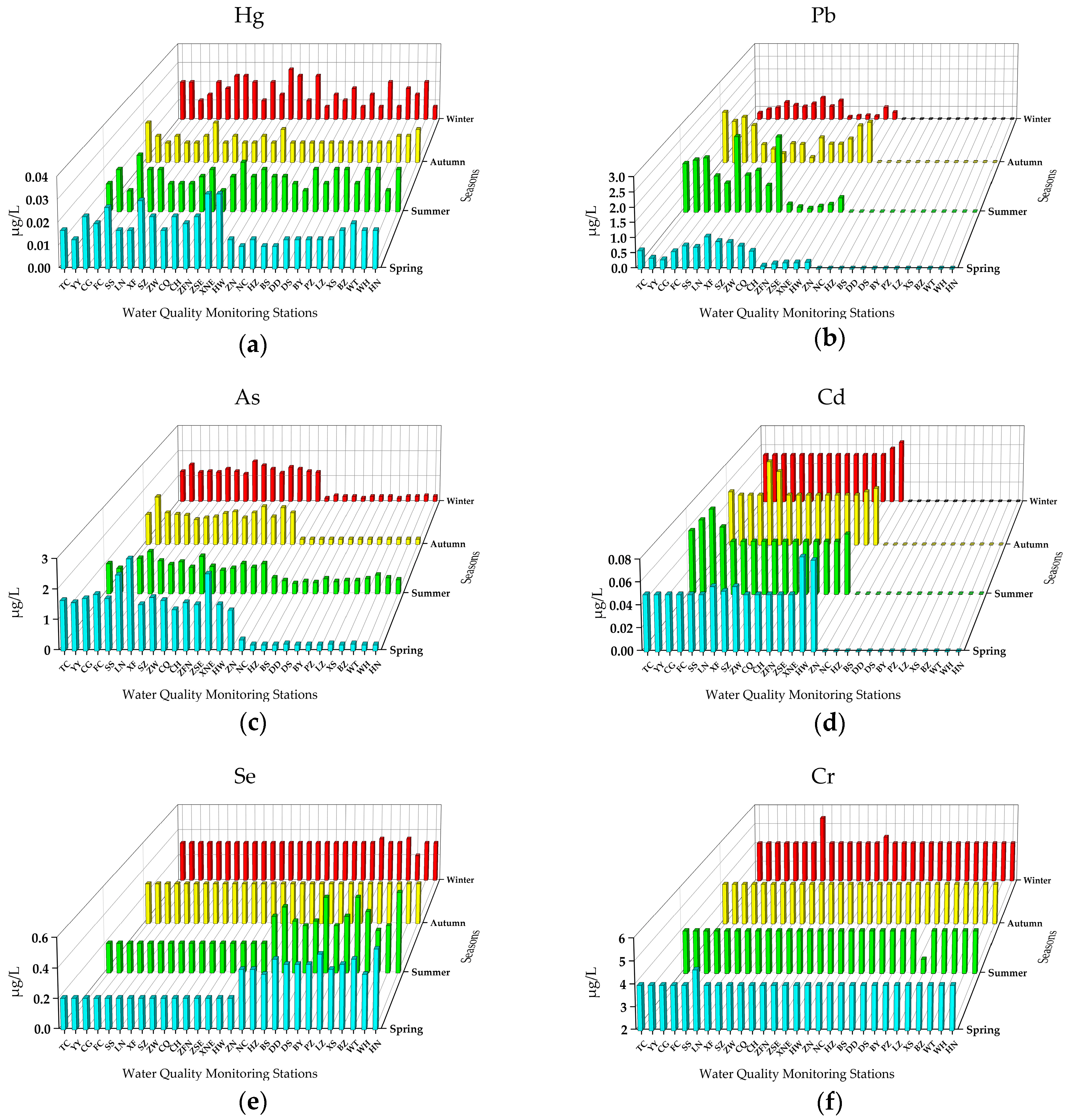
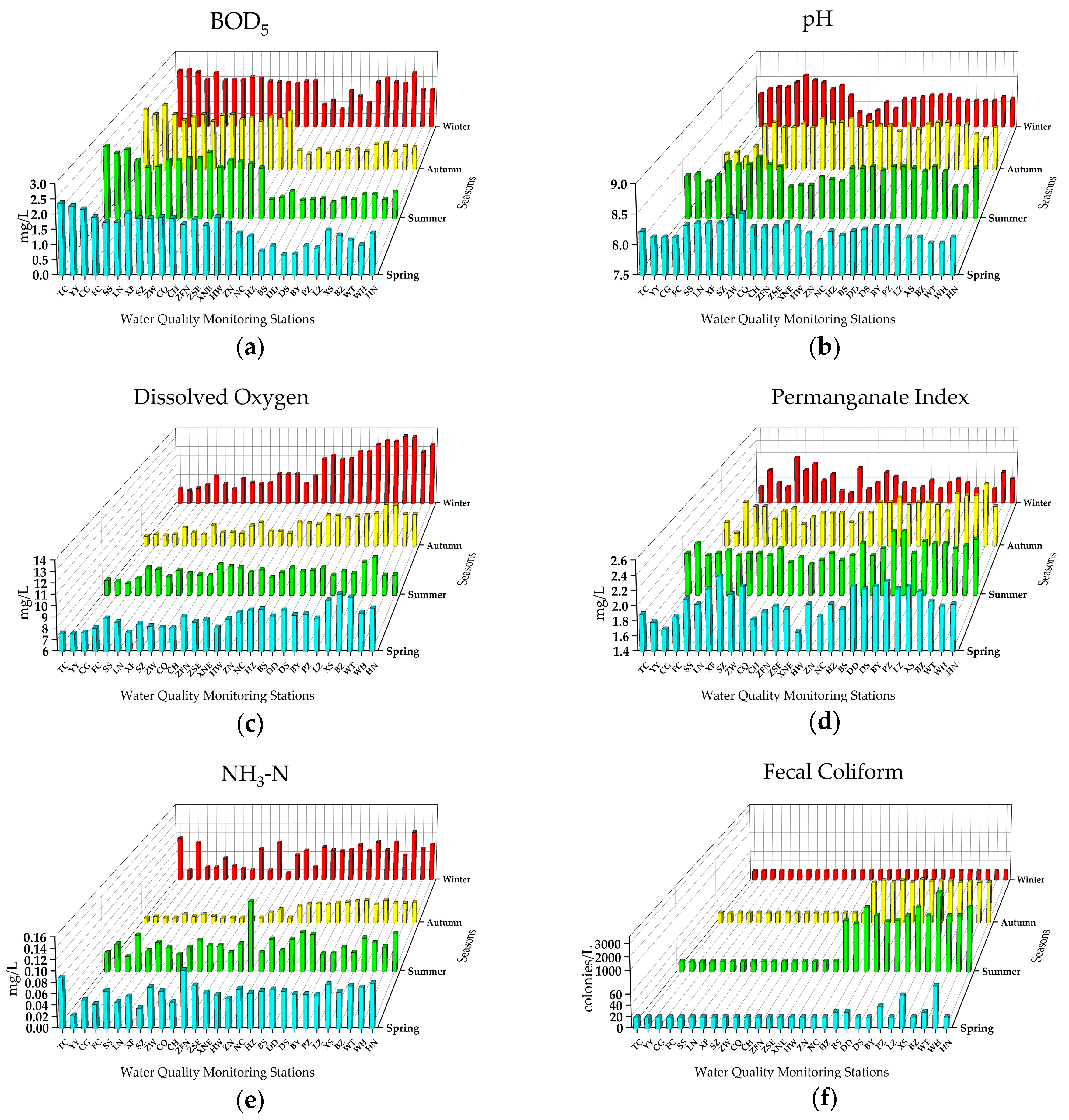
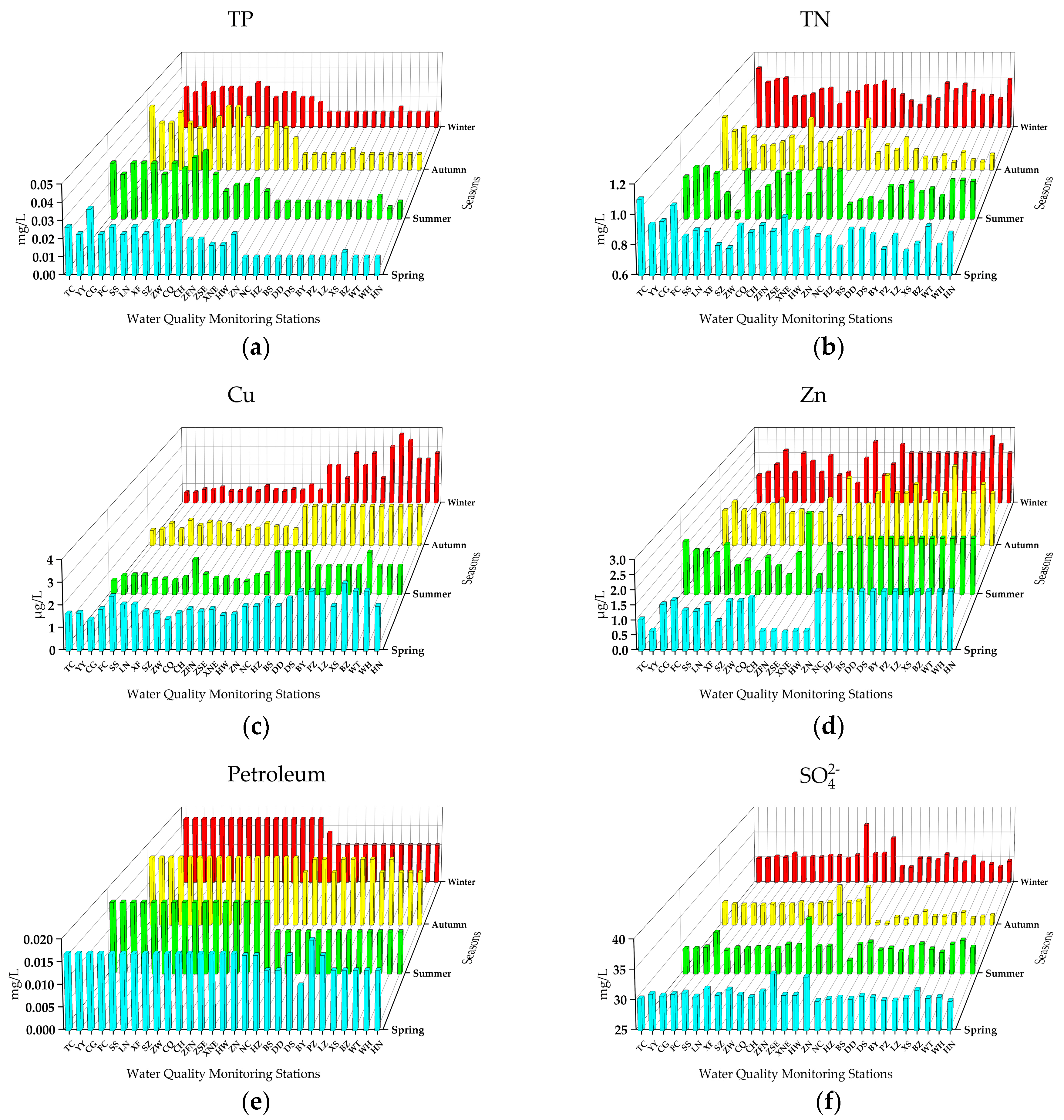


| Province/Municipality | City/County | Population (×104) | Stations | Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henan | Xichuan County | 68.56 | Taocha | TC |
| Dengzhou City | 178.6 | Yaoying | YY | |
| Nanyang City | 863.4 | Chenggou | CG | |
| Fangcheng County | 102.8 | Fangcheng | FC | |
| Lushan County | 78.16 | Shahe South | SS | |
| Shan County | 35.01 | Lanhe North | LN | |
| Yuzhou City | 114.87 | Xinfeng | XF | |
| Xizheng County | 63.58 | Suzhang | SZ | |
| Zhengzhou City | 988.1 | Zhengwan | ZW | |
| Xingyang County | 61.58 | Chuanhuangqian | CQ | |
| Zhengzhou City | 988.1 | Chuanhuanghou | CH | |
| Hui County | 75.13 | Zhifanghe North | ZFN | |
| Hui County | 75.13 | Zhaozhuang Southeast | ZSE | |
| Weihui County | 48.59 | Xisimen Northeast | XNE | |
| Anyang City | 512.85 | Houxiaotun West | HW | |
| Anyang County | 85.42 | Zhanghe North | ZN | |
| Hebei | Ci County | 65 | Nanyingcun | NC |
| Shahe City | 44.52 | Houzhuang | HZ | |
| Lincheng County | 20.41 | Beipanshi | BS | |
| Lincheng County | 20.41 | Dongdu | DD | |
| Shijiazhuang City | 1,078.46 | Daanshe | DS | |
| Xinle City | 48.8 | Beidayue | BY | |
| Shunping County | 32.1 | Puwangzhuang | PZ | |
| Mancheng County | 42.2 | Liujiazuo | LZ | |
| Xushui County | 61.01 | Xiheishan | XS | |
| Bazhou City | 56.62 | Bazhou | BZ | |
| Tianjin Municipality | Wuqing District | 119.96 | Wangqingtuo | WT |
| Xiqing District | 85.37 | Waihuanhe | WH | |
| Beijing Capital | Fangshan District | 109.6 | Huinanzhuang | HN |
| Classification | Weight (Pi) | Indicators | Surface Water Environmental Quality Standards | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | IV | V | |||
| = 20 | = 40 | = 60 | = 80 | = 100 | |||
| Toxic metals | - | As/μg L−1 ≤ | 50 | 50 | 50 | 100 | 100 |
| - | Hg/μg L−1 ≤ | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 1 | 1 | |
| - | Cd/μg L−1 ≤ | 1 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10 | |
| - | Cr/μg L−1 ≤ | 10 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 100 | |
| - | Pb/μg L−1 ≤ | 10 | 10 | 50 | 50 | 100 | |
| - | Se/μg L−1 ≤ | 10 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 20 | |
| Easily treated parameters | 1 | pH | 6~9 | ||||
| 4 | DO/mg L−1 ≥ | 7.5 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| 3 | PI/mg L−1 ≤ | 2 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 15 | |
| 3 | BOD5/mg L−1 ≤ | 3 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 10 | |
| 3 | NH3– N /mg L−1 ≤ | 0.15 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | |
| 3 | FC/colonies L−1 ≤ | 200 | 2,000 | 10,000 | 20,000 | 40,000 | |
| Other parameters | 4 | TP/mg L−1 ≤ | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| - | TN*/mg L−1 ≤ | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | |
| 2 | Cu/μg L−1 ≤ | 10 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | 1000 | |
| 2 | Zn/μg L−1 ≤ | 50 | 1000 | 1000 | 2000 | 2000 | |
| 2 | F-/mg L−1 ≤ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| 2 | Petroleum/ mg L−1 ≤ | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 1 | |
| - | WT/°C | Maximum weekly average rise ≤ 1, drop ≤ 2. | |||||
| 2 | SO42−/mg L−1 ≤ | 250 | |||||
| WQI Value | ≤20 | 21–40 | 41–60 | 61–80 | 81–100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Quality | Excellent | Good | Medium | Poor | Very Poor |
| As | Hg | Pb | Cd | Se | Cr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | 3.033 | 0.033 | 2.660 | 0.083 | 0.567 | 2.667 |
| Min | 0.133 | 0.007 | nd | nd | 0.200 | 5.333 |
| Mean | 0.860 | 0.016 | 0.430 | 0.030 | 0.302 | 4.009 |
| SD | 0.612 | 0.006 | 0.593 | 0.028 | 0.083 | 0.189 |
| Danjiangkou Reservoir, China [46] | 0.86 | nd | 0.76 | 0.015 | 0.13 | 0.26 |
| Han Jiang River, China [12] | 14.42 | nd | nd | 2.31 | nd | 8.14 |
| Three Gorges Reservoir, China [47] | nd | 0.018 | 3.244 | 1.125 | nd | 10.12 |
| Background, Dongting lake, China [48] | 0.9 | 0.025 | 1 | 0.06 | nd | 0.89 |
| Dil Deresi, Turkey [49] | 50 | nd | 120 | 8 | nd | 42 |
| WHO a | 10 | 1 | 10 | 3 | 10 | 50 |
| US EPA MCL b | 10 | 2 | 15 | 5 | 50 | 100 |
| As | Hg | Cd | Pb | Se | pH | DO | PI | BOD5 | NH3– N | FC | TP | TN | Cu | Zn | F- | SO42− | WT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| Hg | 0.639a | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cd | 0.977a | 0.624a | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Pb | 0.881a | 0.465a | 0.875a | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| Se | −0.930a | −0.598a | −0.934a | −0.818a | 1 | |||||||||||||
| pH | 0.165 | 0.056 | 0.100 | 0.208 | −0.033 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| DO | −0.860a | −0.373b | −0.858a | −0.869a | 0.812a | −0.120 | 1 | |||||||||||
| PI | −0.566a | −0.354 | −0.593a | −0.446b | 0.598a | 0.369a | 0.602a | 1 | ||||||||||
| BOD5 | 0.942a | 0.606a | 0.946a | 0.901a | −0.881a | −0.006 | −0.829a | −0.613a | 1 | |||||||||
| NH3–N | −0.644a | −0.498a | −0.635a | −0.619a | 0.603a | −0.249 | 0.591a | 0.275 | −0.599a | 1 | ||||||||
| FC | −0.875a | −0.479a | −0.880a | −0.771a | 0.874a | −0.115 | 0.858a | 0.542a | −0.794a | 0.578a | 1 | |||||||
| TP | 0.929a | 0.524a | 0.904a | 0.928a | −0.863a | 0.228 | −0.870a | −0.503a | 0.936a | −0.633a | −0.812a | 1 | ||||||
| TN | 0.655a | 0.445b | 0.683a | 0.641a | −0.596a | −0.362 | −0.688a | −0.626a | 0.741a | −0.239 | −0.609a | 0.623a | 1 | |||||
| Cu | −0.942a | −0.561a | −0.954a | −0.840a | 0.927a | −0.047 | 0.893a | 0.666a | −0.902a | 0.588a | 0.930a | −0.869a | −0.724a | 1 | ||||
| Zn | −0.875a | −0.570a | −0.917a | −0.807a | 0.848a | −0.180 | 0.789a | 0.521a | −0.859a | 0.577a | 0.788a | −0.819a | −0.630a | 0.896a | 1 | |||
| F- | −0.418b | −0.331 | −0.388b | −0.509a | 0.342 | −0.472a | 0.433b | 0.234 | −0.406b | 0.351 | 0.319 | −0.491a | −0.243 | 0.434b | 0.479a | 1 | ||
| SO42 | 0.558a | 0.478a | 0.617a | 0.339 | −0.556a | −0.152 | −0.363 | −0.397b | 0.511a | −0.525a | −0.490a | 0.405a | 0.406b | −0.575a | −0.499a | 0.01 | 1 | |
| WT | 0.875a | 0.486a | 0.833a | 0.777a | −0.859a | 0.328 | −0.798a | −0.402b | 0.751a | −0.621a | −0.828a | 0.841a | 0.460b | −0.855a | −0.780a | −0.457b | 0.442a | 1 |
| Component | Initial Eigen Values | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||
| Total | % of variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 11.872 | 65.958 | 65.958 | 8.759 | 48.664 | 48.664 |
| 2 | 1.925 | 10.697 | 76.655 | 4.006 | 22.258 | 70.922 |
| 3 | 1.083 | 6.018 | 82.673 | 2.115 | 11.752 | 82.673 |
| 4 | 0.768 | 4.268 | 86.941 | |||
| 5 | 0.521 | 2.895 | 89.836 | |||
| Variables | Component | Communalities | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| As | 0.793 | 0.550 | 0.167 | 0.959 | ||
| Hg | 0.347 | 0.639 | 0.040 | 0.530 | ||
| Cd | 0.796 | 0.568 | 0.094 | 0.966 | ||
| Pb | 0.832 | 0.313 | 0.289 | 0.873 | ||
| Se | −0.763 | −0.553 | −0.066 | 0.892 | ||
| pH | −0.077 | 0.094 | 0.939 | 0.897 | ||
| DO | −0.880 | −0.267 | −0.160 | 0.871 | ||
| PI | −0.720 | −0.142 | 0.395 | 0.695 | ||
| BOD5 | 0.845 | 0.446 | 0.039 | 0.915 | ||
| NH3– N | −0.318 | −0.706 | −0.312 | 0.698 | ||
| FC | −0.761 | −0.466 | −0.112 | 0.809 | ||
| TP | 0.822 | 0.394 | 0.278 | 0.908 | ||
| TN | 0.819 | 0.131 | −0.348 | 0.809 | ||
| Cu | −0.855 | −0.471 | −0.057 | 0.956 | ||
| Zn | −0.764 | −0.461 | −0.190 | 0.832 | ||
| F- | −0.501 | 0.061 | −0.608 | 0.625 | ||
| SO42− | 0.202 | 0.839 | −0.275 | 0.820 | ||
| WT | 0.674 | 0.491 | 0.362 | 0.827 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nong, X.; Shao, D.; Xiao, Y.; Zhong, H. Spatio-Temporal Characterization Analysis and Water Quality Assessment of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122227
Nong X, Shao D, Xiao Y, Zhong H. Spatio-Temporal Characterization Analysis and Water Quality Assessment of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(12):2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122227
Chicago/Turabian StyleNong, Xizhi, Dongguo Shao, Yi Xiao, and Hua Zhong. 2019. "Spatio-Temporal Characterization Analysis and Water Quality Assessment of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 12: 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122227
APA StyleNong, X., Shao, D., Xiao, Y., & Zhong, H. (2019). Spatio-Temporal Characterization Analysis and Water Quality Assessment of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project of China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(12), 2227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122227






