Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of the Lihe River Watershed, East China: Spatial Distribution, Ecological Risk, and Pollution Source
Abstract
1. Introduction
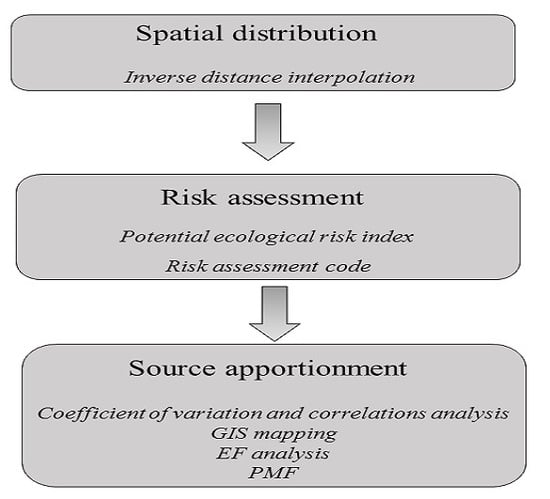
2. Materials and Methods
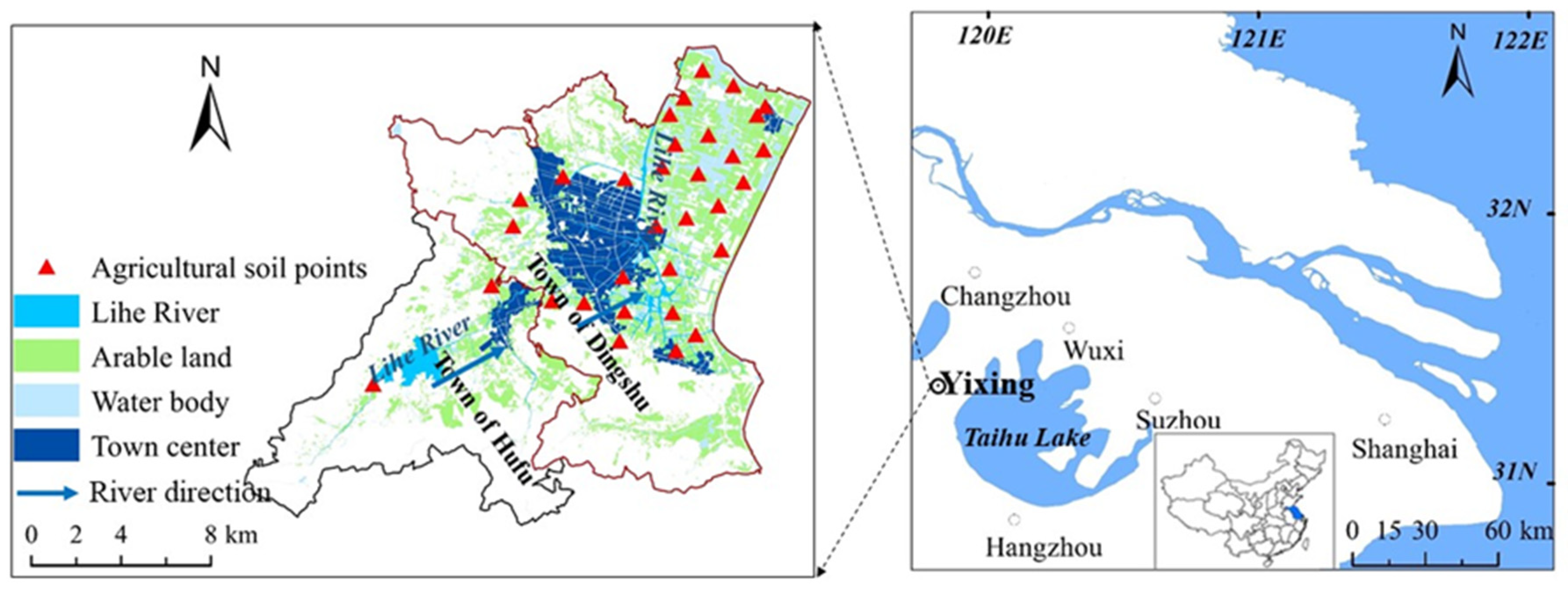
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.3.1. Soil Properties
2.3.2. Total Heavy Metal Concentrations
2.3.3. Acid-Soluble Heavy Metal Fractions
2.3.4. Quality Assurance and Control
2.4. Assessment of Soil Contamination
2.4.1. Potential Ecological Risk Index
2.4.2. Risk Assessment Code
2.5. Source Identification and Apportionment
2.5.1. Source Identification
GIS Mapping
Coefficient of Variation (CV)
Correlation Analysis of Heavy Metals
Enrichment Factors (EF)
2.5.2. Source Apportionment by Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF)
3. Results and Discussion
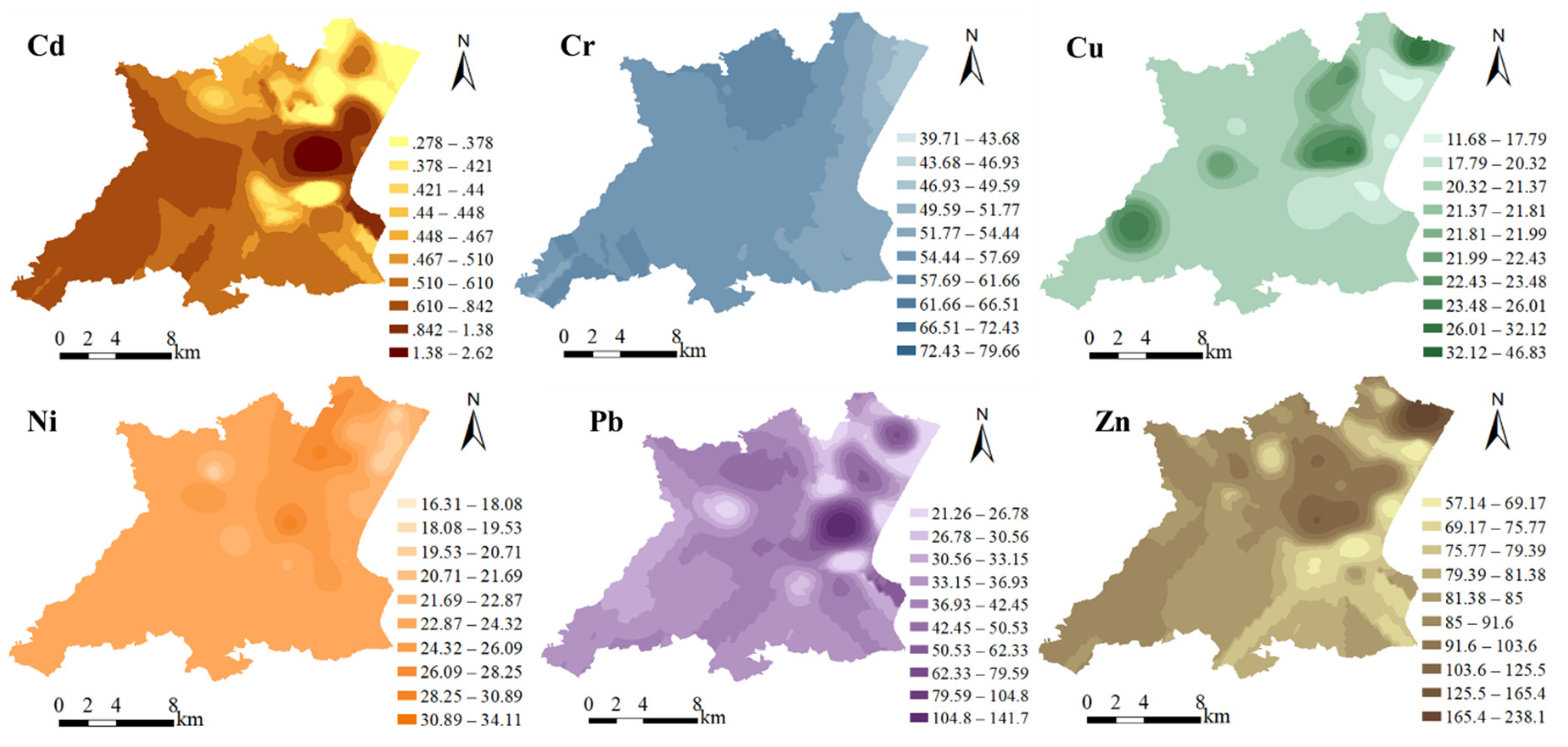
3.1. Concentrations of Heavy Metals in Soils
3.1.1. Descriptive Statistics of Soil Properties
3.1.2. Descriptive Statistics of Total Heavy Metal Concentrations
3.1.3. Acid-Soluble Heavy Metal Concentration
3.1.4. Correlation between Heavy Metal Concentration and Soil Properties
3.2. Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Soil
3.2.1. Potential Ecological Risk Indices
3.2.2. Risk Assessment Code
3.3. Identification and Apportionment of Pollution Sources
3.3.1. Identification of Pollution Sources
GIS Mapping of Heavy Metals
Coefficient of Variation of Metal Concentrations
Correlations between Metals
Enrichment Factors
3.3.2. Source Apportionment by PMF
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, T.; Liu, X.M.; Li, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, J.B.; Xu, J.M.; Shi, J.C.; Dahlgren, R.A. Heavy metal sources identification and sampling uncertainty analysis in a field-scale vegetable soil of Hangzhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Hu, B.; Fu, Z.; Wang, J.; Lou, G.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, B.; Li, Y.; Shi, Z. Source Identification and Apportionment of Trace Elements in Soils in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamuyarira, K.K.; Gumbo, J.R. Assessment of heavy metals in municipal sewage sludge: A case study of Limpopo province, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2569–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Heavy metals in food crops, soil, and water in the Lihe River Watershed of the Taihu Region and their potential health risks when ingested. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 615, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laidlaw, M.A.S.; Filippelli, G.M.; Brown, S.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Reichman, S.M.; Netherway, P.; Truskewycz, A.; Ball, A.S.; Mielke, H.W. Case studies and evidence-based approaches to addressing urban soil lead contamination. Appl. Geochem. 2017, 83, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Wang, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, K.; Han, P.; Zhang, S. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and origin of heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunyi, Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 425, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, F.; Cao, W.; Pan, J.; Lv, J.; Wu, Q. Source analysis, spatial distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in sewage irrigation area farmland soils of Longkou city. Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, X.; Gui, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, W. Ecological risk assessment and source identification for heavy metals in surface sediment from the Liaohe River protected area, China. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Yu, W.; Shen, Z. Spatial variation, environmental risk and biological hazard assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the Yangtze River estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 93, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Liang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z. Chemical speciation, pollution and ecological risk of toxic metals in readily washed off road dust in a megacity (Nanjing) China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maanan, M.; Saddik, M.; Maanan, M.; Chaibi, M.; Assobhei, O.; Zourarah, B. Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perin, G.; Fabris, R.; Manente, S.; Wagener, A.R.; Hamacher, C.; Scotto, S. A five-year study on the heavy-metal pollution of Guanabara Bay sediments (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil) and evaluation of the metal bioavailability by means of geochemical speciation. Water Res. 1997, 31, 3017–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, G.O.; Goonetilleke, A.; Ayoko, G.A. Potential bioavailability assessment, source apportionment and ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediment of Brisbane River estuary, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Z.B.; Wang, X.M.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.J. Fractionation and mobility risks of heavy metals and metalloids in wastewater-irrigated agricultural soils from greenhouses and fields in Gansu, China. Geoderma 2018, 328, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachenko, A.G.; Singh, B. Heavy Metals Contamination in Vegetables Grown in Urban and Metal Smelter Contaminated Sites in Australia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2006, 169, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Uría, A.; López-Mateo, C.; Roca, E.; Fernández-Marcos, M.L. Source identification of heavy metals in pastureland by multivariate analysis in NW Spain. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Li, G.; Ren, H.; Yang, F.; Cao, Q. Content analysis and risk evaluation of heavy metal elements in soil and ginseng root from nonforested land base with cultivated ginseng in Jilin Province. J. Plant Res. Environ. 2015, 24, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, J.P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Martens, W.N.; Goonetilleke, A. Enrichment, distribution and sources of heavy metals in the sediments of Deception Bay, Queensland, Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 81, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.B.; Gaillardet, J.; Bouchez, J.; Louvat, P.; Wang, Y.N. Anthropophile elements in river sediments: Overview from the Seine River, France. Geochem.Geophys. Geosyst. 2015, 15, 4526–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lee, S.L.; Wong, S.C.; Shi, W.; Thornton, I. The study of metal contamination in urban soils of Hong Kong using a GIS-based approach. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 129, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Lin, F.F.; Wong, M.T.F.; Feng, X.L.; Wang, K. Identification of soil heavy metal sources from anthropogenic activities and pollution assessment of Fuyang County, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 154, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, S.; Scheifler, R.; Benslama, M.; Crini, N.; Lucot, E.; Brahmia, Z.; Benyacoub, S.; Giraudoux, P. Spatial distribution of heavy metal concentrations in urban, suburban and agricultural soils in a Mediterranean city of Algeria. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2294–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tume, P.; Roca, N.; Rubio, R.; King, R.; Bech, J. An assessment of the potentially hazardous element contamination in urban soils of Arica, Chile. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 184, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, T.B.; Lei, M.; Yang, J.; Guo, Q.J.; Song, B.; Zhou, X.Y. Spatial distribution of soil heavy metal pollution estimated by different interpolation methods: Accuracy and uncertainty analysis. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; Szatmári, G.; Pásztor, L. Maps of heavy metals in the soils of the European Union and proposed priority areas for detailed assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.L.; Zhi, Y.Y.; Yang, L.P.; Shi, J.C.; Zeng, L.Z.; Wu, L.S. Positive matrix factorization as source apportionment of soil lead and cadmium around a battery plant (Changxing County, China). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7698–7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.P.; Huang, W.Y.; Yang, G.S.; Liu, X.M. Non-point pollutant concentrations for different land uses in Lihe River watershed of Taihu Region China. Environ. Sci. 2006, 26, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Fu, H.; Cui, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z. Health risk of heavy metals in food crops grown on reclaimed tidal flat soil in the Pearl River Estuary, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 227, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Du, Y.; Wang, D.; Gao, S. Distribution Patterns of Heavy Metal in Sediment and Their Influence on the Environment Quality of the Intertidal Flat of Luoyuan, Bay, Fujian Coast. Environ. Sci. 2012, 33, 3097–3103. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.; Gao, S.; Bokuniewicz, H. Net sediment transport patterns over the Bohai Strait based on grain size trend analysis. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhou, S.; Sun, B.; Zhao, Q. Heavy metals in wheat grain: Assessment of potential health risk for inhabitants in Kunshan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 405, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.I.; Nam, S.-H.; Kim, S.W.; Bajagain, R.; Jeong, S.-W.; An, Y.-J. Changes in soil properties after remediation influence the performance and survival of soil algae and earthworm. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Pu, L.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Ge, Y.; Sun, L. Effects of soil reclamation on the oat cultivation in the newly reclaimed coastal land, eastern China. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 129, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, T.; Lian, H.; Ding, Z. Bioaccessibility and health risk of arsenic, mercury and other metals in urban street dusts from a mega-city, Nanjing, China. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.G.; Bai, S.Q. Contamination and potential mobility assessment of heavy metals in urban soils of Hangzhou, China: Relationship with different land uses. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 60, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P.; Krishnakumar, S.; Pradhap, D.; Silva, J.D.; Arumugam, K.; Magesh, N.S.; Srinivasalu, S. Elemental concentration based potential ecological risk (PER) status of the surface sediments, Pulicat lagoon, Southeast coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, G.; Liu, W.; Qiu, Y.; Li, K.; Hou, H.; Peng, P.; Liao, B. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of the paddy soils in a smelting area in Central Hunan. Environ. Chem. 2013, 32, 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, T.; Wu, C.; He, Z.; Japenga, J.; Deng, M.; Yang, X. An integrated approach to assess heavy metal source apportionment in peri-urban agricultural soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, J. Factorial kriging and stepwise regression approach to identify environmental factors influencing spatial multi-scale variability of heavy metals in soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 261, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cai, L.; Wen, H.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naifar, I.; Pereira, F.; Zmemla, R.; Bouaziz, M.; Elleuch, B.; Garcia, D. Spatial distribution and contamination assessment of heavy metals in marine sediments of the southern coast of Sfax, Gabes Gulf, Tunisia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Fabian, K.; Hron, K.; Birke, M.; Demetriades, A.; Dinelli, E.; Ladenberger, A. The concept of compositional data analysis in practice:Total major element concentrations in agricultural and grazing land soils of Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Li, T.G.; Li, A.C.; Yu, X.K.; Hu, N.J. Distribution, enrichment and sources of heavy metals in surface sediments of the North Yellow Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 73, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X. Size Distribution and Source Apportionment of Airborne Metallic Elements in Nanjing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 1796–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Dong, L.; Huang, B.; Borggaard, O.K.; Bruun Hansen, H.C.; He, Y.; Holm, P.E. Source identification of heavy metals in peri-urban agricultural soils of southeast China: An integrated approach. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, C.L. Riverine Composition and Estuarine Geochemistry of Particulate Metals in China—Weathering Features, Anthropogenic Impact and Chemical Fluxes. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2002, 54, 1051–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive matrix factorization: A non-negative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatero, P. Least squares formulation of robust non-negative factor analysis. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1997, 37, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, S.; Zhou, S.L.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Chen, H.; Yu, Y.; Shi, Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils from urban to rural areas in Nanjing: Concentration, source, spatial distribution, and potential human health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 375, 527–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.; Shi, F.; Li, R.; Shen, X. Heavy metal contamination and ecological risk in Spartina alterniflora marsh in intertidal sediments of Bohai Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 84, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giuseppe, D.; Vittori Antisari, L.; Ferronato, C.; Bianchini, G. New insights on mobility and bioavailability of heavy metals in soils of the Padanian alluvial plain (Ferrara Province, northern Italy). Geochemistry 2014, 74, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Shan, B.; Zhang, H.; Mao, Z. Heavy metal sources and associated risk in response to agricultural intensification in the estuarine sediments of Chaohu Lake Valley, East China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 176, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Xu, Z.; Ren, M.; Guo, Q.; Hu, X.; Hu, G.; Wan, H.; Peng, P. Source identification of eight hazardous heavy metals in agricultural soils of Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperato, M.; Adamo, P.; Naimo, D.; Arienzo, M.; Stanzione, D.; Violante, P. Spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils of Naples city (Italy). Environ. Pollut. 2003, 124, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duzgoren-Aydin, N.S.; Weiss, A.L. Use and abuse of Pb-isotope fingerprinting technique and GIS mapping data to assess lead in environmental studies. Environ. Geochem. Health 2008, 30, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, B.; Shu, L.J.; Cheng, Z.J.; Lu, Z.Z.; Yang, L.; Jia, Z.R. Assessment of Sources, Spatial Distribution and Ecological Risk of Heavy Metals in Soils in a Typical Industry-based City of Shandong Province, Eastern China. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 507. [Google Scholar]
- Peris, M.; Recatalá, L.; Micó, C.; Sánchez, R.; Sánchez, J. Increasing the Knowledge of Heavy Metal Contents and Sources in Agricultural Soils of the European Mediterranean Region. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2008, 192, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Assessment Criterion | PERI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Moderate | Considerable | High | Very High | |
| Ei | <40 | 40–80 | 80–160 | 160–320 | ≥320 |
| RI | <150 | 150–300 | 300–600 | ≥600 | |
| Risk | Acid Soluble Fraction (%) |
|---|---|
| No risk | <1 |
| Low risk | 1–10 |
| Medium risk | 11–30 |
| High risk | 31–50 |
| Very high risk | 51–75 |
| Soil Properties | Range | Mean Value | Standard Deviation | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 4.85–7.45 | 5.81 | 0.69 | 0.12 |
| CEC (cmol·kg−1) | 11.76–22.99 | 18.41 | 2.60 | 0.14 |
| EC (ms·cm−1) | 0.67–3.05 | 1.59 | 0.65 | 0.41 |
| OM (%) | 1.84–5.35 | 3.58 | 0.94 | 0.26 |
| Average particle size (Φ) | 8.45–52.06 | 24.37 | 8.37 | 0.34 |
| Heavy Metals | The Lihe River Watershed | Background Values of Soil in Jiangsu Province | SEQ-II | The Yangtze River Estuary, China | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean ± SD | Median | First Quartile | Third Quartile | CV | Mean | |||
| Cd | 0.28–2.62 | 0.57 ± 0.41 | 0.45 | 0.40 | 0.59 | 0.72 | 0.13 | 0.3 | 0.19 |
| Cr | 39.71–79.66 | 54.60 ± 9.04 | 53.95 | 47.64 | 59.61 | 0.17 | 77.8 | 200 | 79.1 |
| Cu | 11.68–46.83 | 22.71 ± 9.44 | 21.17 | 16.09 | 22.96 | 0.42 | 22.3 | 100 | 24.7 |
| Ni | 16.31–34.11 | 24.35 ± 4.88 | 24.05 | 21.10 | 27.17 | 0.20 | 26.7 | 50 | 31.9 |
| Pb | 21.26–141.72 | 39.78 ± 20.61 | 36.75 | 29.10 | 43.13 | 0.52 | 26.2 | 300 | 23.8 |
| Zn | 57.14–238.06 | 93.29 ± 38.50 | 82.61 | 76.08 | 93.45 | 0.39 | 62.6 | 250 | 82.9 |
| References | Present study | Chen et al. [4] | Chen et al. [4] | Wang et al. [9] | |||||
| Heavy Metals | Range | Mean Value ± Standard Deviation | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.11–1.54 | 0.25 ± 0.25 | 98.16 |
| Cr | 0.60–1.85 | 1.27 ± 0.26 | 20.01 |
| Cu | 7.45–34.00 | 14.85 ± 7.09 | 47.76 |
| Ni | 1.16–4.18 | 2.64 ± 0.77 | 29.29 |
| Pb | 12.51–91.84 | 26.84 ± 13.61 | 50.73 |
| Zn | 9.32–59.10 | 18.92 ± 11.44 | 60.46 |
| Heavy Metals | pH | CEC | EC | OM | Average Particle Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd-s | 0.222 | 0.123 | 0.287 | 0.132 | 0.033 |
| Cr-s | 0.444 * | 0.449 ** | 0.316 | 0.266 | −0.223 |
| Cu-s | 0.229 | 0.075 | 0.146 | 0.076 | 0.103 |
| Ni-s | 0.041 | 0.040 | 0.024 | −0.098 | −0.131 |
| Pb-s | 0.098 | 0.115 | 0.255 | 0.182 | −0.038 |
| Zn-s | −0.008 | −0.117 | −0.086 | −0.226 | −0.113 |
| Cd-sa | 0.199 | 0.081 | 0.216 | 0.122 | 0.072 |
| Cr-sa | 0.215 | 0.627 ** | 0.301 | 0.285 | −0.334 |
| Cu-sa | 0.123 | 0.049 | 0.075 | 0.067 | 0.184 |
| Ni-sa | −0.120 | 0.457 ** | 0.130 | 0.032 | −0.154 |
| Pb-sa | 0.044 | 0.124 | 0.247 | 0.194 | −0.062 |
| Zn-sa | −0.062 | −0.242 | −0.111 | −0.309 | −0.104 |
| Parameter | Heavy Metal | Mean | Max | Min | SD | CV | Risk Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ei | Cd | 131.9 | 604.4 | 64.16 | 95.26 | 0.722 | Considerable risk |
| Cr | 1.403 | 2.048 | 1.021 | 0.232 | 0.166 | Low risk | |
| Cu | 5.093 | 10.50 | 2.619 | 2.117 | 0.416 | Low risk | |
| Ni | 4.560 | 6.388 | 3.054 | 0.914 | 0.200 | Low risk | |
| Pb | 7.592 | 27.04 | 4.057 | 3.933 | 0.518 | Low risk | |
| Zn | 1.490 | 3.803 | 0.913 | 0.615 | 0.413 | Low risk | |
| RI | (Multi-metal) | 152.0 | 649.5 | 300-600 | 99.79 | 0.656 | Moderate risk |
| Heavy Metals | Acid Soluble Fraction (%) | Risk Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Cd | 43.02 ± 10.35 | High risk |
| Cr | 2.36 ± 0.46 | Low risk |
| Cu | 65.19 ± 10.29 | Very high risk |
| Ni | 11.25 ± 4.05 | Medium risk |
| Pb | 67.72 ± 6.97 | Very high risk |
| Zn | 19.79 ± 4.72 | Medium risk |
| Heavy Metals | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1 | −0.012 | 0.450 a | 0.121 | 0.841 a | 0.079 |
| Cr | 1 | 0.053 | 0.677 a | −0.194 | −0.045 | |
| Cu | 1 | 0.040 | 0.617 a | 0.763 a | ||
| Ni | 1 | −0.013 | −0.103 | |||
| Pb | 1 | 0.345 | ||||
| Zn | 1 |
| Heavy Metal | Mean ± SD | Range | CV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 15.56 ± 11.68 | 7.92–74.03 | 0.75 |
| Cr | 1.19 ± 0.12 | 0.95–1.45 | 0.10 |
| Cu | 1.75 ± 0.80 | 0.88–3.88 | 0.45 |
| Ni | 1.53 ± 0.18 | 1.29–2.16 | 0.12 |
| Pb | 2.63 ± 1.46 | 1.22–9.63 | 0.56 |
| Zn | 2.58 ± 1.28 | 1.51–7.84 | 0.50 |
| Elements | Profile Contribution (mg/kg) | Percentage Contribution (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | |
| Ca | 196.84 | 2.9 × 10−15 | 5.9 × 10−6 | 2220.70 | 8.14 | 1.2 × 10−16 | 2.4 × 10−7 | 91. 86 |
| Cd | 0.30 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 2.0 × 10−13 | 52.11 | 21.62 | 26.27 | 3.5 × 10−11 |
| Co | 0.92 | 4.71 | 7.24 | 8.17 | 4.38 | 22.37 | 34.43 | 38.82 |
| Cr | 0.21 | 11.23 | 19.52 | 22.82 | 0.40 | 20.88 | 36.30 | 42.43 |
| Cu | 1.51 | 14.03 | 1.48 | 4.75 | 6.92 | 64.44 | 6.81 | 21.82 |
| Fe | 254.28 | 3477.7 | 6417.3 | 7712.2 | 1.42 | 19.47 | 35.93 | 43.18 |
| K | 69.38 | 2557.1 | 3587.2 | 5308.9 | 0.60 | 22.19 | 31.13 | 46.07 |
| Mg | 5.3 × 10−5 | 491.51 | 982.34 | 1624.2 | 1.7 × 10−6 | 15.87 | 31.71 | 52.43 |
| Mn | 19.46 | 52.68 | 45.14 | 140.26 | 7.55 | 20.46 | 17.53 | 54.46 |
| Ni | 0.50 | 4.33 | 9.27 | 9.70 | 2.10 | 18.19 | 38.94 | 40.77 |
| Pb | 9.74 | 18.90 | 6.01 | 3.53 | 25.51 | 49.50 | 15.74 | 9.25 |
| Zn | 0 | 56.52 | 6.24 | 28.10 | 0 | 62.21 | 6.87 | 30.93 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Wu, S.; Xia, Z.; Cui, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhou, S. Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of the Lihe River Watershed, East China: Spatial Distribution, Ecological Risk, and Pollution Source. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122094
Chen L, Wang G, Wu S, Xia Z, Cui Z, Wang C, Zhou S. Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of the Lihe River Watershed, East China: Spatial Distribution, Ecological Risk, and Pollution Source. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(12):2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122094
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lian, Genmei Wang, Shaohua Wu, Zhen Xia, Zhenang Cui, Chunhui Wang, and Shenglu Zhou. 2019. "Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of the Lihe River Watershed, East China: Spatial Distribution, Ecological Risk, and Pollution Source" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 12: 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122094
APA StyleChen, L., Wang, G., Wu, S., Xia, Z., Cui, Z., Wang, C., & Zhou, S. (2019). Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils of the Lihe River Watershed, East China: Spatial Distribution, Ecological Risk, and Pollution Source. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(12), 2094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122094