Trends and Knowledge Gaps in the Study of Nature-Based Participation by Latinos in the United States
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
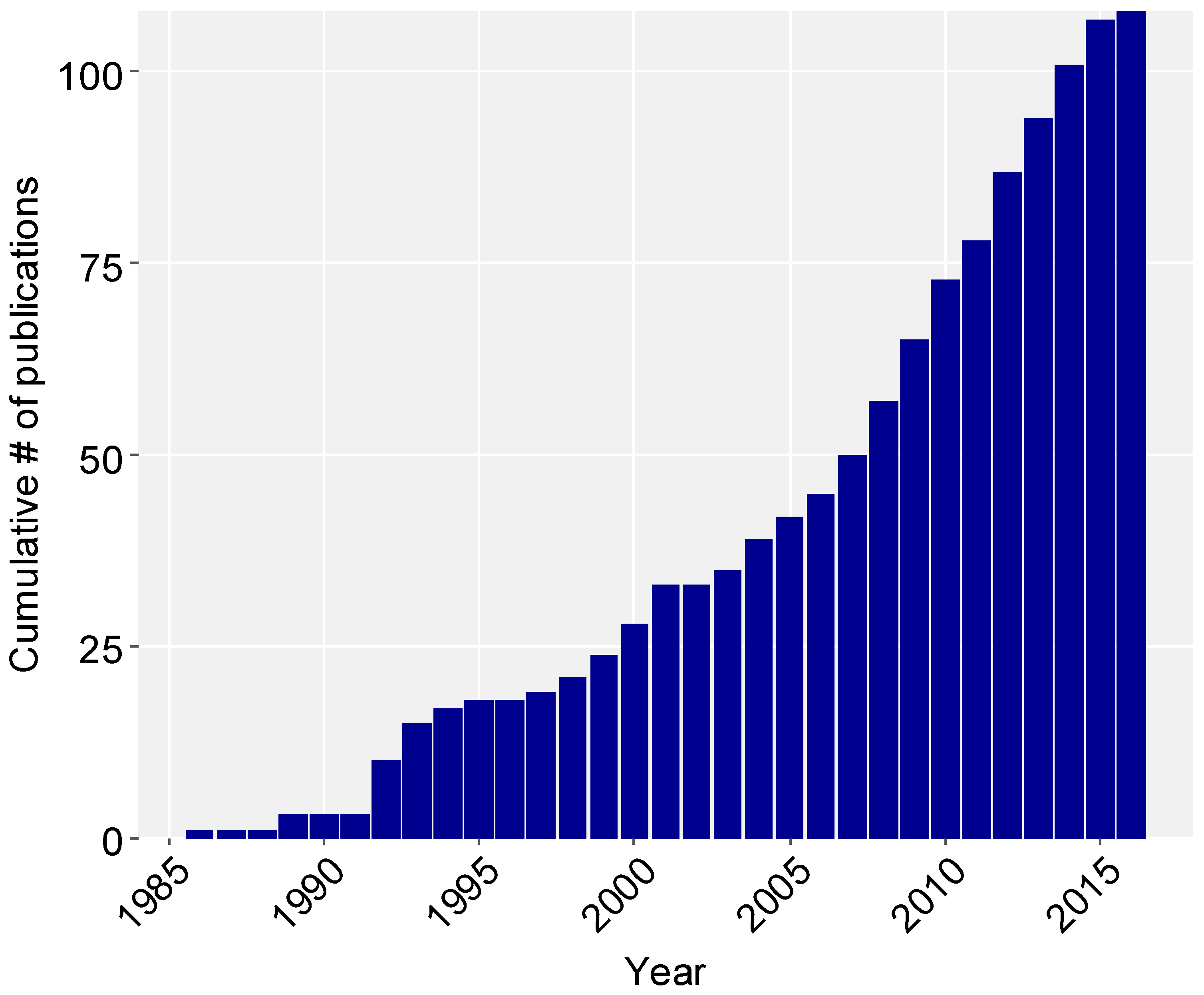
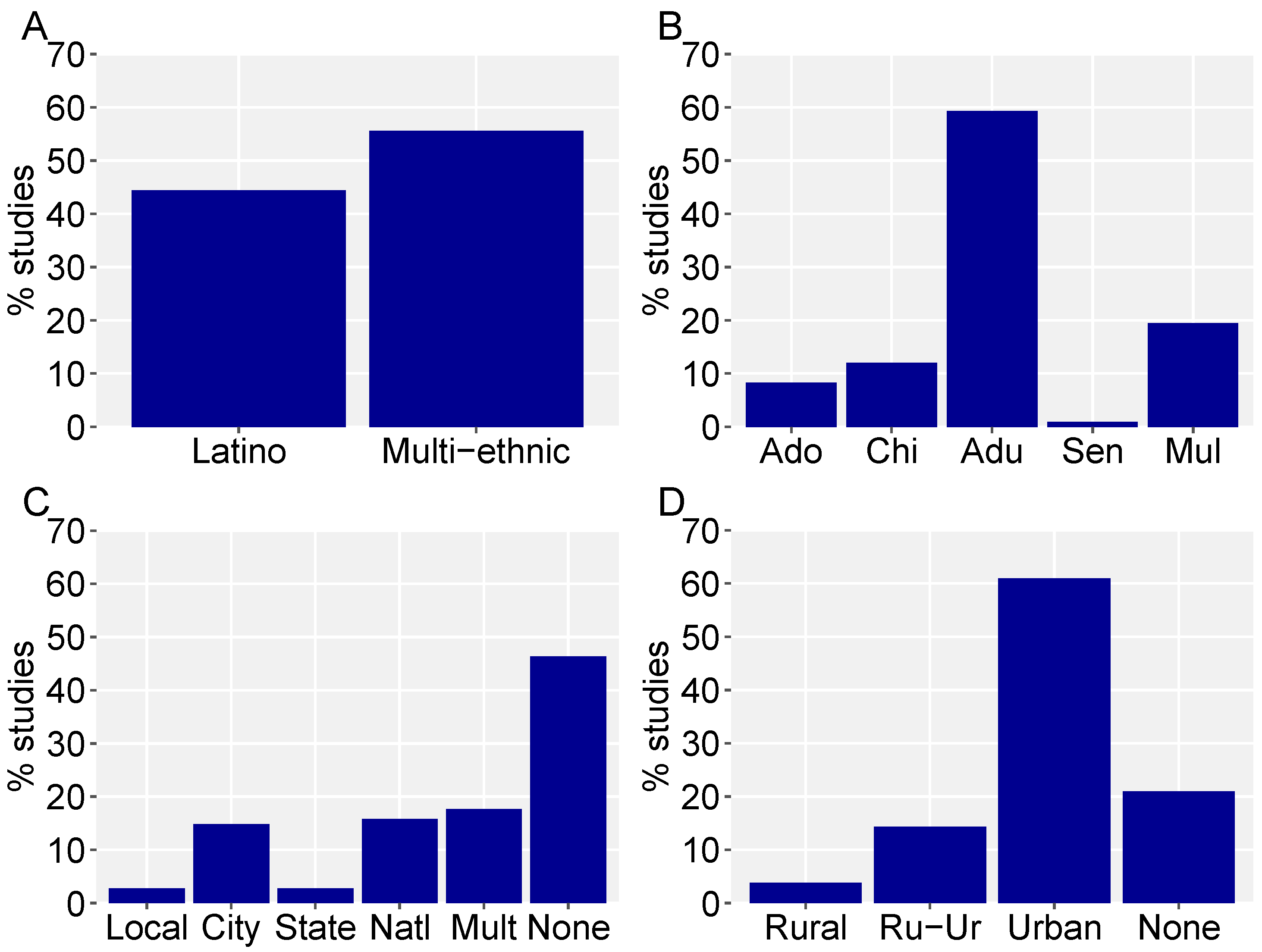
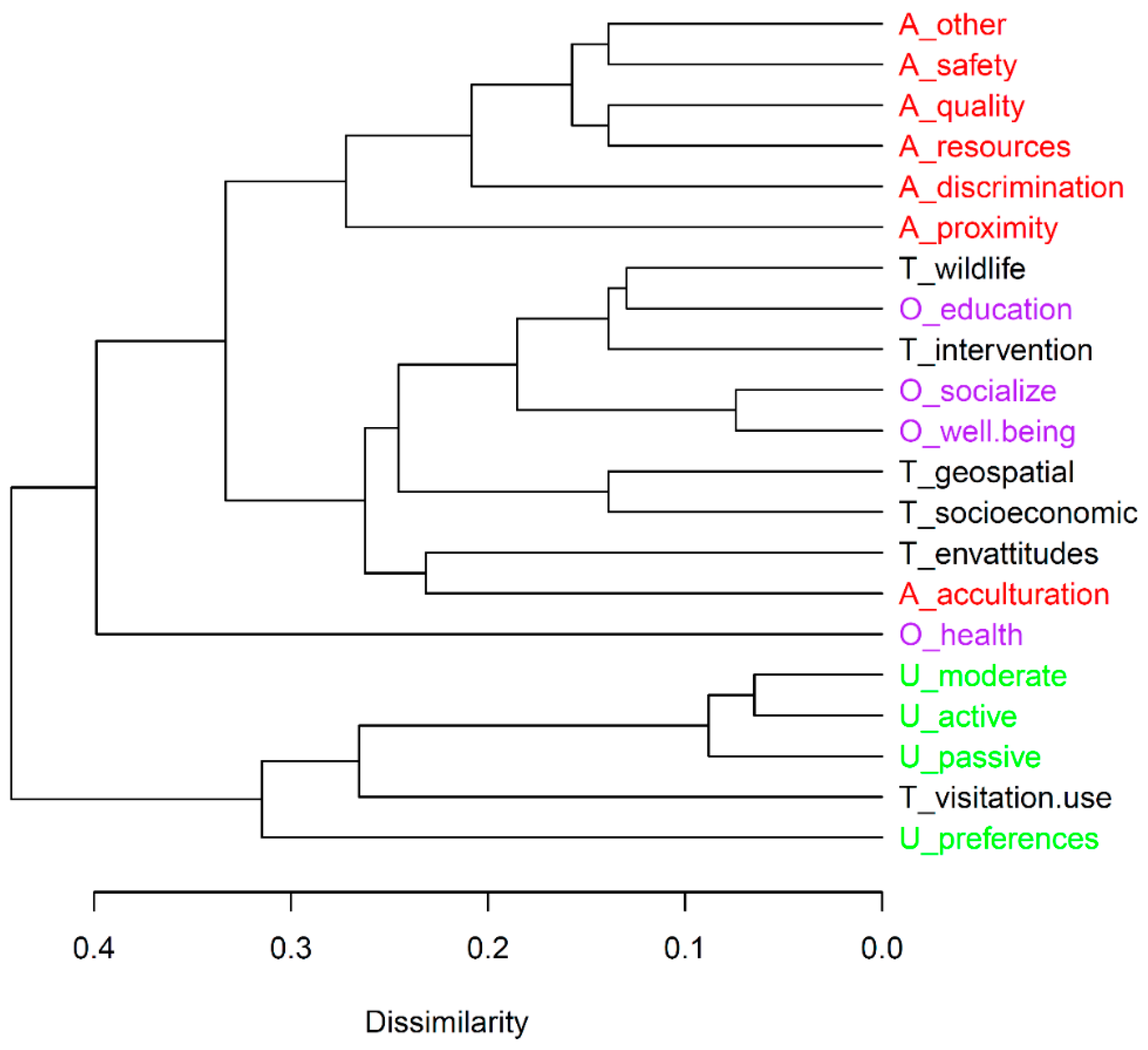
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bratman, G.N.; Hamilton, J.P.; Daily, G.C. The impacts of nature experience on human cognitive function and mental health. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1249, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, P.; Banay, R.F.; Hart, J.E.; Laden, F. A review of the health benefits of greenness. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2015, 2, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, L.; Derr, V. The development of conservation behaviors in childhood and youth. In The Oxford Handbook of Environmental and Conservation Psychology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Frumkin, H.; Bratman, G.N.; Breslow, S.J.; Cochran, B.; Kahn, P.H., Jr.; Lawler, J.J.; Levin, P.S.; Tandon, P.S.; Varanasi, U.; Wolf, K.L. Nature contact and human health: A research agenda. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 075001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.; Popham, F. Effect of exposure to natural environment on health inequalities: An observational population study. Lancet 2008, 372, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRPA (National Recreation and Park Association). Parks & Recreation in Underserved Areas: A Public Health Perspective; National Recreation and Park Association: Ashburn, VA, USA, 2011; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, I.T.; Purner, E.K.; Guzmán, P.D. Socioeconomic disparities in the provision of school gardens in Santa Clara County, California. Child. Youth Environ. 2013, 23, 127–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, W.C.; Floyd, M.F.; Whitt-Glover, M.C.; Brooks, J. Environmental justice: A framework for collaboration between the public health and parks and recreation fields to study disparities in physical activity. J. Phys. Act. Health 2007, 4, S50–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.J.; Richardson, E.A.; Shortt, N.K.; Pearce, J.R. Neighborhood environments and socioeconomic inequalities in mental well-being. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 49, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, B.W.; Sabel, C.E.; Alcock, I.; Husk, K.; White, M.P.; Depledge, M.H.; Osborne, N.J.; Lovell, R.; Higgins, S.L. Beyond greenspace: An ecological study of population general health and indicators of natural environment type and quality. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2015, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- APHA (American Public Health Association). Improving health and Wellness through Access to Nature; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Colby, S.L.; Ortman, J.M. Projections of the Size and Composition of the US Population: 2014 to 2060: Population Estimates and Projections; Current Population Reports; U.S. Census Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Velasco-Mondragon, E.; Jimenez, A.; Palladino-Davis, A.G.; Davis, D.; Escamilla-Cejudo, J.A. Hispanic health in the USA: A scoping review of the literature. Public Health Rev. 2016, 37, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero-Somaini, A. Hidden Danger: Environmental Health Threats in the Latino Community; Natural Resources Defense Council: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, V.; Floyd, M.F.; Shanahan, D.; Coutts, C.; Sinykin, A. Emerging issues in urban ecology: Implications for research, social justice, human health, and well-being. Popul. Environ. 2017, 39, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, D.J. Serving the needs of Latino recreation visitors to urban proximate natural resource recreation areas. In Visitor Research: Studies of Diversity; USDA Forest Service: Riverside, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Stodolska, M.; Shinew, K.J. Leisure among Latino Americans. In Race, Ethnicity and Leisure; Human Kinetics: Champagne, IL, USA, 2014; pp. 75–96. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Watson, M. Guidance on conducting a systematic literature review. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, H.H.; Wagner, H. vegan: Community Ecology Package for the R Programming Language. 2015. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/ (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- Kawachi, I.; Berkman, L.F. Neighborhoods and Health; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Arkin, E.; Braveman, P.; Egerter, S.; Williams, D. Time to Act: Investing in the Health of Our Children and Communities; Robert Wood Johnson Foundation Commission to Build a Healthier America: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, J.; Wolch, J. Nature, race, and parks: Past research and future directions for geographic research. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2009, 33, 743–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D. Race, ethnicity, and leisure services: Can we hope to escape the past. In Race Ethnicity, and Leisure: Perspectives on Research, Theory, and Practice; Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL, USA, 2014; pp. 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, A.; Anderson, D.H. Barriers to participation for Latino people at Dodge Nature Center. J. Environ. Educ. 2006, 37, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, J.; Radel, C.; Endter-Wada, J. Justice and immigrant Latino recreation geography in Cache Valley, Utah. J. Leis. Res. 2014, 46, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, C.; Sohn, W. Urban natural environments, obesity, and health-related quality of life among Hispanic children living in inner-city neighborhoods. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, M.; Maloney, T.N. Latino residential isolation and the risk of obesity in Utah: The role of neighborhood socioeconomic, built-environmental, and subcultural context. J. Immigr. Minority Health 2011, 13, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanahan, D.F.; Lin, B.B.; Bush, R.; Gaston, K.J.; Dean, J.H.; Barber, E.; Fuller, R.A. Toward improved public health outcomes from urban nature. Am. J. Public Health 2015, 105, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heynen, N.; Perkins, H.A.; Roy, P. The political ecology of uneven urban green space the impact of political economy on race and ethnicity in producing environmental inequality in Milwaukee. Urban Aff. Rev. 2006, 42, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolch, J.; Wilson, J.P.; Fehrenbach, J. Parks and park funding in Los Angeles: An equity-mapping analysis. Urban Geogr. 2005, 26, 4–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, L. Where do we belong? Urban adolescents’ struggle for place and voice. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2006, 37, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, P.W.; Unipan, J.B.; Gamba, R.J. Acculturation and ecological worldview among Latino Americans. J. Environ. Educ. 2000, 31, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, L. Benefits of nature contact for children. J. Plan. Lit. 2015, 30, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babey, S.H.; Hastert, T.A.; Yu, H.; Brown, E.R. Physical activity among adolescents: When do parks matter? Am. J. Prev. Med. 2008, 34, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronan, M.K.; Shinew, K.J.; Schneider, I.; Wilhelm Stanis, S.A.; Chavez, D. Physical activity patterns and preferences among Latinos in different types of public parks. J. Phys. Act. Health 2008, 5, 894–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J. Does Living in Latino Neighborhoods Affect Risk for Obesity? Findings from a Study of Social Capital and Park Availability in Los Angeles Neighborhoods; University of California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, C.; Olvera, N.E.; Ellis, C.D. The role of landscape spatial patterns on obesity in Hispanic children residing in inner-city neighborhoods. J. Phys. Act. Health 2014, 11, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, T.M.; Cerin, E.; Lee, R.E.; Parker, N.; Chen, T.-A.; Hughes, S.O.; Mendoza, J.A.; Baranowski, T. Environmental and cultural correlates of physical activity parenting practices among Latino parents with preschool-aged children: Niños Activos. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, L.G.; Slymen, D.J.; Sallis, J.F.; Ayala, G.X.; Elder, J.P.; Arredondo, E.M. Interactions between individual and perceived environmental factors on Latinas’ physical activity. J. Public Health 2016, 39, e10–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallis, J.F.; Zakarian, J.M.; Hovell, M.F.; Hofstetter, C.R. Ethnic, socioeconomic, and sex differences in physical activity among adolescents. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanis, S.A.W.; Schneider, I.E.; Chavez, D.J.; Shinew, K.J. Visitor constraints to physical activity in park and recreation areas: Differences by race and ethnicity. J. Park Recreat. Adm. 2009, 27, 78–95. [Google Scholar]
- Flegal, K.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Ogden, C.L.; Curtin, L.R. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999–2008. JAMA 2010, 303, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartig, T.; Mitchell, R.; De Vries, S.; Frumkin, H. Nature and health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2014, 35, 207–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatto, N.M.; Ventura, E.E.; Cook, L.T.; Gyllenhammer, L.E.; Davis, J.N. LA Sprouts: A garden-based nutrition intervention pilot program influences motivation and preferences for fruits and vegetables in Latino youth. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawthorne, A.; Shaibi, G.; Gance-Cleveland, B.; McFall, S. Grand Canyon Trekkers: School-based lunchtime walking program. J. Sch. Nurs. 2011, 27, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
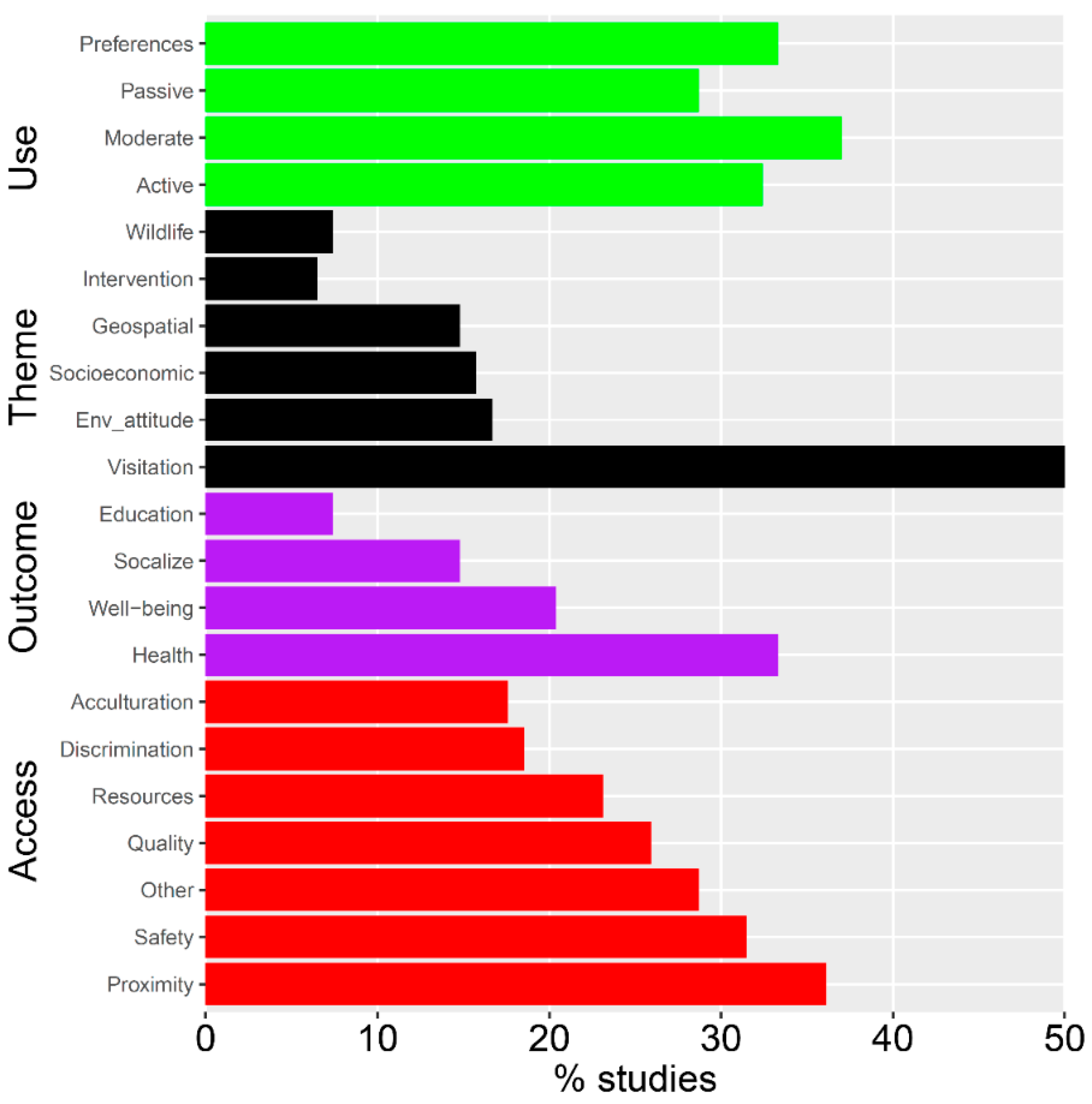
| Category | Topic | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Theme | ||
| Socioeconomic | Examines the importance of socio-economic factors? | |
| Geospatial | Uses spatial or remotely-sensed data? | |
| Environmental attitudes | Environmental attitudes assessed? | |
| Visitation | Explores recreational visitation and use? | |
| Wildlife | Relates to interactions with fishing, hunting, or wildlife? | |
| Intervention | Recounts results from an intervention program? | |
| Use and Activities | ||
| Activities: Active | Involves hiking, climbing, or horseback riding? | |
| Activities: Moderate | Involves walking, swimming, or fishing? | |
| Activities: Passive | Involves picnicking or socializing? | |
| Preferences | Explores types of amenities and modes of communication? | |
| Outcomes | ||
| Health | Examines physical activity or physiological metrics? | |
| Well-being | Examines relaxation, travel, or solitude? | |
| Socialization | Examines family bonding or sense of community? | |
| Education | Examines nature, culture, or learning? | |
| Barriers and Access | ||
| Acculturation | Is acculturation considered as a barrier to access? | |
| Quality | Is the quality of available resources (e.g., facility type, maintenance) considered as a barrier? | |
| Safety | Is safety (perceived or realized) considered as a barrier? | |
| Discrimination | Is discrimination (i.e., unequal attention from police, racist incidents) considered as a barrier? | |
| Resources | Is lack of resources (e.g., money, equipment, or transportation) considered as a barrier? | |
| Proximity | Are distance and/or proximity considered as a barrier? | |
| Other | Are additional factors (e.g., cultural relevance, language barriers) considered as a barrier? | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tandon, P.S.; Kuehne, L.M.; Olden, J.D. Trends and Knowledge Gaps in the Study of Nature-Based Participation by Latinos in the United States. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061287
Tandon PS, Kuehne LM, Olden JD. Trends and Knowledge Gaps in the Study of Nature-Based Participation by Latinos in the United States. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(6):1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061287
Chicago/Turabian StyleTandon, Pooja S., Lauren M. Kuehne, and Julian D. Olden. 2018. "Trends and Knowledge Gaps in the Study of Nature-Based Participation by Latinos in the United States" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 6: 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061287
APA StyleTandon, P. S., Kuehne, L. M., & Olden, J. D. (2018). Trends and Knowledge Gaps in the Study of Nature-Based Participation by Latinos in the United States. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(6), 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15061287






