Harmful Cyanobacterial Material Production in the North Han River (South Korea): Genetic Potential and Temperature-Dependent Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
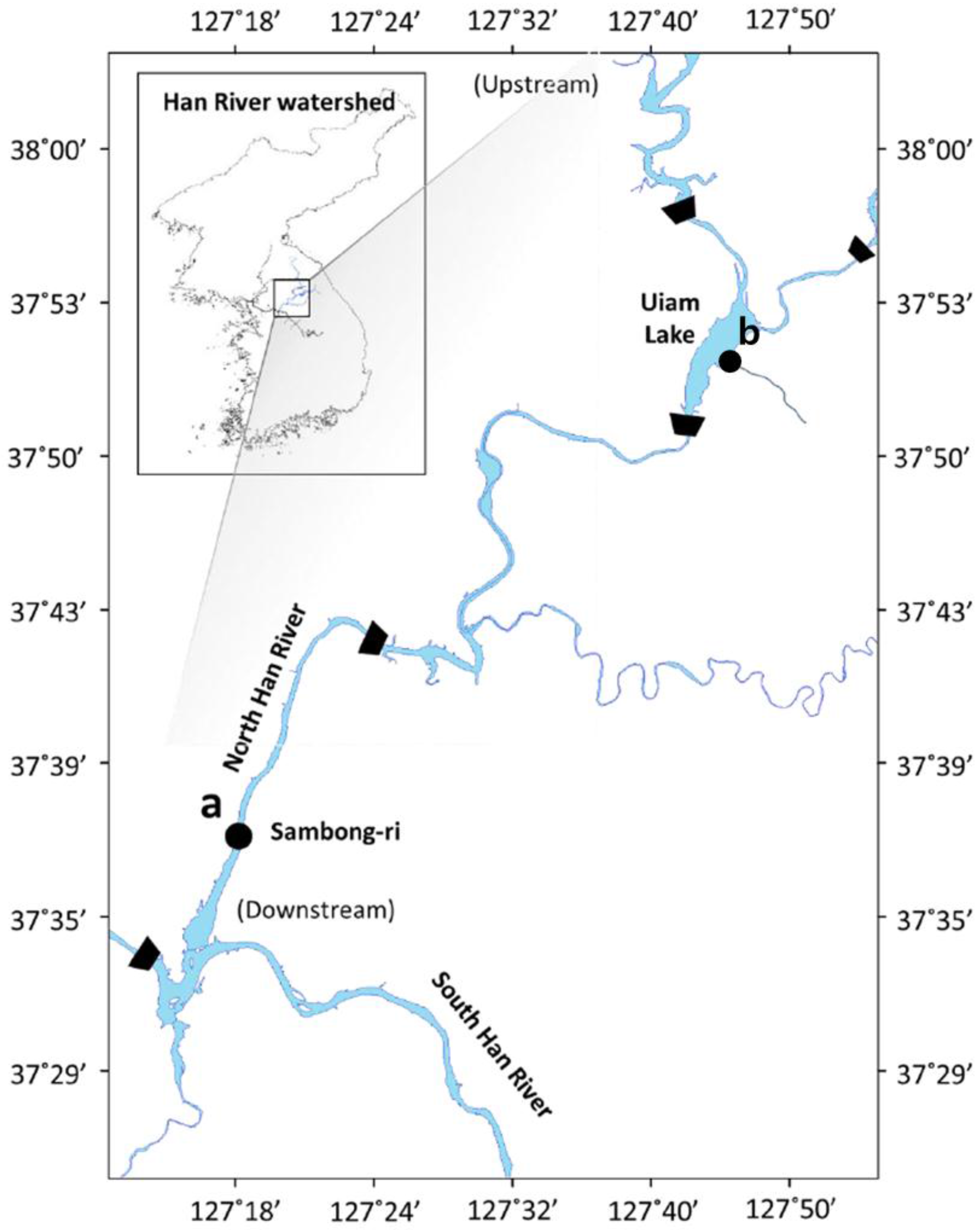
2.1. Sampling, Isolation, and Cultivation of Cyanobacterial Strains
2.2. Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of the 16S rDNA of Isolated Cyanobacterial Strains
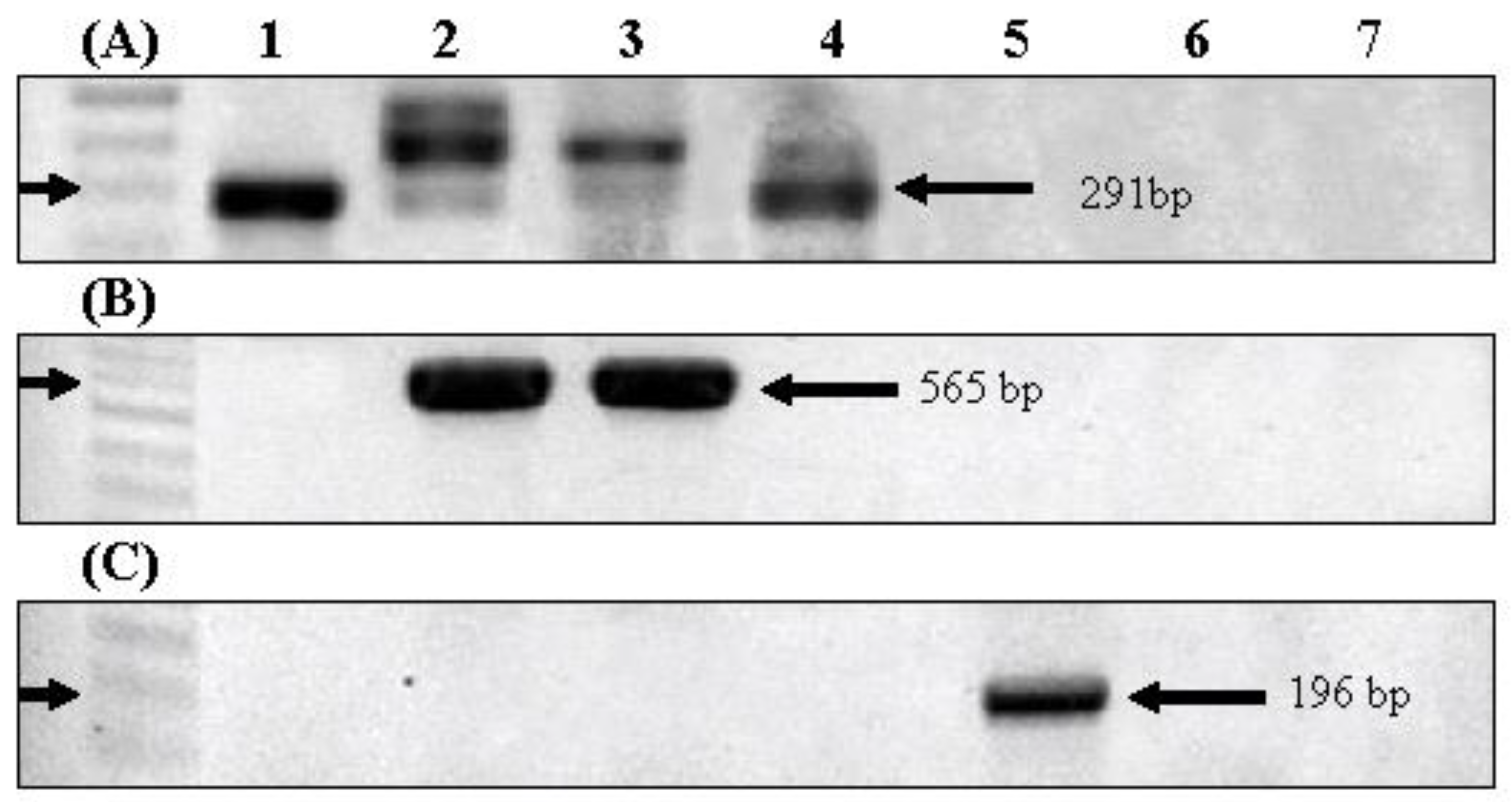
2.3. Evaluation of Harmful Material Production Potentials
2.4. Analysis of Harmful Materials Produced by the Isolated Cyanobacterial Strains
2.5. Analysis of Temperature Effects on Harmful Material Production
2.6. Registration of Isolated Cyanobacterial Strains (Accession Numbers)
3. Results
3.1. Phylogeny of the Isolated Cyanobacterial Strains
3.2. Harmful Material Production Potentials
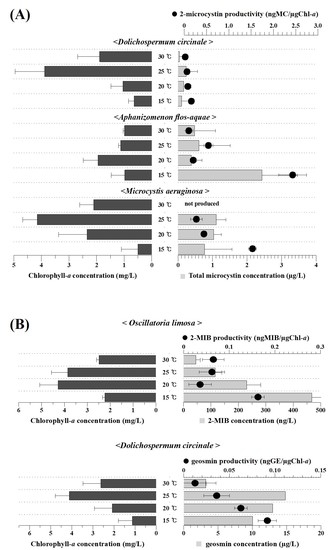
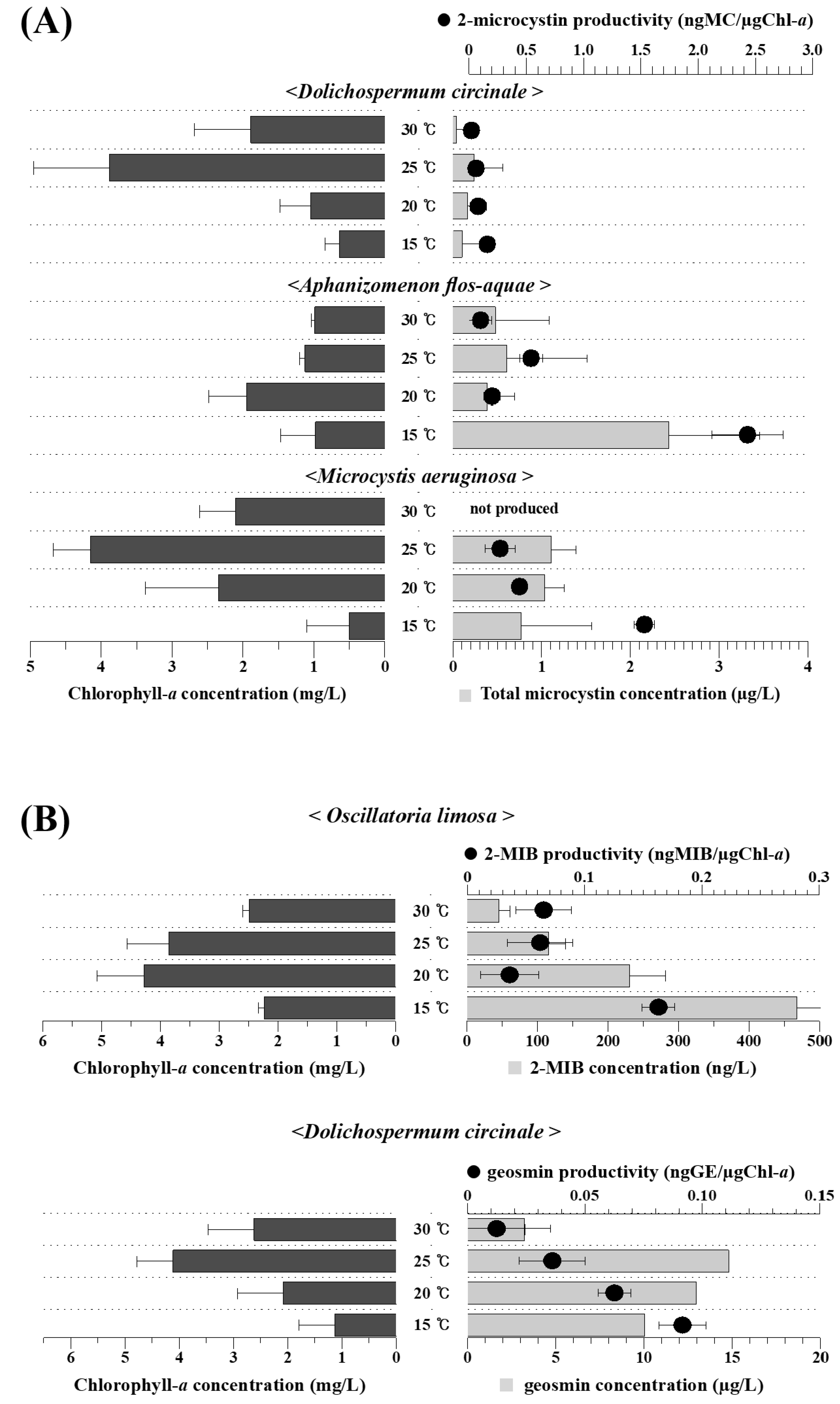
3.3. Temperature Dependency of Harmful Material Production by the Isolated Cyanobacteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olsen, B.K.; Chislock, M.F.; Wilson, A.E. Eutrophication mediates a common off-flavor compound, 2-methylisoborneol, in a drinking water reservoir. Water Res. 2016, 92, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, E.I.; Bartram, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; WHO: London, UK, 1999; p. 416. [Google Scholar]
- Tabachek, J.-A.L.; Yurkowski, M. Isolation and identification of blue-green algae producing muddy odor metabolites, geosmin, and 2-methylisoborneol, in saline lakes in manitoba. J. Fish. Board Can. 1976, 33, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, G.; Taylor, W. Geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol production in a major aqueduct system. Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 31, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto, A.; Tsuchiya, Y. Earthy-musty odor-producing cyanophytes isolated from five water areas in Tokyo. Water Sci. Technol. 1988, 20, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Henley, D.E. Odorous Metabolite and Other Selected Studies of Cyanophyta; North Texas State University: Denton, TX, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Glaze, W.H.; Schep, R.; Chauncey, W.; Ruth, E.C.; Zarnoch, J.J.; Aieta, E.M.; Tate, C.H.; McGuire, M.J. Evaluating oxidants for the removal of model taste and odor compounds from a municipal water supply. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1990, 82, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, A.; Podkościelny, P.; Hubicki, Z.; Barczak, M. Adsorption of phenolic compounds by activated carbon—A critical review. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 1049–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KEITI. Cyanobacterial Bloom Water Management and Respons Technique; Korea Environment Industry and Technology Institute: Seoul, Korea, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Recommendations for Public Water Systems to Manage Cyanotoxins in Drinking Water; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Metcalf, J.S.; Godd, G.A. Cyanobacterial Toxins (Cyanotoxins) in Water; Foundation for Water Research: Bucks, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zamyadi, A.; MacLeod, S.L.; Fan, Y.; McQuaid, N.; Dorner, S.; Sauvé, S.; Prévost, M. Toxic cyanobacterial breakthrough and accumulation in a drinking water plant: A monitoring and treatment challenge. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lim, B.-J.; You, K.-A.; Park, M.-H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, B.-H.; Hwang, S.J. Identification and analysis of geosmin production potential of anabaena stain isolated from north Han river using genetic methods. Korean J. Environ. Ecol. 2014, 47, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, A.; Loram, J.E.; Hackett, J.D.; Anderson, D.M.; Plumley, F.G.; Bhattacharya, D. Origin of saxitoxin biosynthetic genes in cyanobacteria. PLoS ONE 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsao, H.-W.; Michinaka, A.; Yen, H.-K.; Giglio, S.; Hobson, P.; Monis, P.; Lin, T.-F. Monitoring of geosmin producing anabaena circinalis using quantitative PCR. Water Res. 2014, 49, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, Y.; Nagata, S.; Tsutsumi, T.; Hasegawa, A.; Watanabe, M.F.; Park, H.-D.; Chen, G.-C.; Chen, G.; Yu, S.-Z. Detection of microcystins, a blue-green algal hepatotoxin, in drinking water sampled in haimen and fusui, endemic areas of primary liver cancer in China, by highly sensitive immunoassay. Carcinogenesis 1996, 17, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaitomaa, J.; Rantala, A.; Halinen, K.; Rouhiainen, L.; Tallberg, P.; Mokelke, L.; Sivonen, K. Quantitative real-time pcr for determination of microcystin synthetase e copy numbers for microcystis and anabaena in lakes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 7289–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, J.R.; Sato, T.; Weightman, A.J.; Martin, T.A.; Fry, J.C.; Hiom, S.J.; Wade, W.G. Design and evaluation of useful bacterium-specific pcr primers that amplify genes coding for bacterial 16s RRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lyra, C.; Suomalainen, S.; Gugger, M.; Vezie, C.; Sundman, P.; Paulin, L.; Sivonen, K. Molecular characterization of planktic cyanobacteria of anabaena, aphanizomenon, microcystis and planktothrix genera. Int. J. Syst. Evolut. Microbiol. 2001, 51, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillard, R.R. Methods for microflagellates and nannoplankton. In Handbook of Phycological Methods: Culture Methods and Growth Measurements; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1973; pp. 69–85. [Google Scholar]
- Stanier, R.; Kunisawa, R.; Mandel, M.; Cohen-Bazire, G. Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order chroococcales). Bacteriol. Rev. 1971, 35, 171–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nübel, U.; Garcia-Pichel, F.; Muyzer, G. Pcr primers to amplify 16s RRNA genes from cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Yoon, Y.D.; Hwang, S.-J. Development of molecular probes for evaluating 2-methylisoborneol (2-MIB) production potential in cyanobacterial communities. J. Microbiol. 2018. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, K.-H.; Han, A.-W.; Cho, Y.-C. Analysis of sequence diversity of mcya gene involved in microcystin synthesis in Korean reservoirs. Korean J. Microbiol. 2010, 46, 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Hisbergues, M.; Christiansen, G.; Rouhiainen, L.; Sivonen, K.; Börner, T. PCR-based identification of microcystin-producing genotypes of different cyanobacterial genera. Arch. Microbiol. 2003, 180, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MOE. Standard Methods of Environmental Examination and Inspection Act; Ministry of Environment: Sejong, Korea, 2013.
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 1504. [Google Scholar]
- Vezie, C.; Brient, L.; Sivonen, K.; Bertru, G.; Lefeuvre, J.-C.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M. Variation of microcystin content of cyanobacterial blooms and isolated strains in lake grand-lieu (France). Microb. Ecol. 1998, 35, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihali, T.K.; Kellmann, R.; Neilan, B.A. Characterisation of the paralytic shellfish toxin biosynthesis gene clusters in anabaena circinalis awqc131c and aphanizomenon sp. Nh-5. BMC Biochem. 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivonen, K.; Niemelä, S.; Niemi, R.; Lepistö, L.; Luoma, T.; Räsänen, L. Toxic cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) in Finnish fresh and coastal waters. Hydrobiologia 1990, 190, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saker, M.L.; Jungblut, A.-D.; Neilan, B.A.; Rawn, D.F.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Detection of microcystin synthetase genes in health food supplements containing the freshwater cyanobacterium aphanizomenon flos-aquae. Toxicon 2005, 46, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, S.A.; Rasmussen, J.P.; Holland, P.T.; Campbell, R.; Crowe, A.L. First report of the cyanotoxin anatoxin-a from aphanizomenon issatschenkoi (cyanobacteria). J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jüttner, F.; Höflacher, B.; Wurster, K. Seasonal analysis of volatile organic biogenic substances (VOBS) in freshwater phytoplankton populations dominated by dinobryon, microcystis and aphanizomenon. J. Phycol. 1986, 22, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotak, B.G.; Kenefick, S.L.; Fritz, D.L.; Rousseaux, C.G.; Prepas, E.E.; Hrudey, S.E. Occurrence and toxicological evaluation of cyanobacterial toxins in alberta lakes and farm dugouts. Water Res. 1993, 27, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotak, B.G.; Lam, A.K.Y.; Prepas, E.E.; Kenefick, S.L.; Hrudey, S.E. Variability of the hepatotoxin microcystin-lr in hypereutrophic drinking water lakes. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.D.; Watanabe, M.F.; Harada, K.I.; Suzuki, M.; Hayashi, H.; Okino, T. Seasonal variations of microcystis species and toxic heptapeptide microcystins in lake suwa. Environ. Toxicol. 1993, 8, 425–435. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, A.-R.; Oh, H.-M.; Lee, J. Ecological study on the toxic microcystis in the lower nakdong river. Algae 2002, 17, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownell, A.C. The Roles of Microcystin and Sulfide in Physiology and Tactic Responses of Pathogenic and Non-Pathogenic Mat-Forming Cyanobacteria. Master’s Thesis, Florida International University, Miami, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; An, W.; Vogt, R.D.; Andersen, T.; Jia, D.; Wang, J.; Yang, M. Mib-producing cyanobacteria (planktothrix sp.) in a drinking water reservoir: Distribution and odor producing potential. Water Res. 2015, 68, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mez, K.; Hanselmann, K.; Naegeli, H.; Preisig, H.R. Protein phosphatase-inhibiting activity in cyanobacteria from alpine lakes in Switzerland. Phycologia 1996, 35, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater, S.; Vilalta, E.; Gaudes, A.; Guasch, H.; Munoz, I.; Romani, A. Ecological implications of mass growth of benthic cyanobacteria in rivers. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 32, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, G.; Taylor, W. A guide to geosmin-and mib-producing cyanobacteria in the United States. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oudra, B.; Loudiki, M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Sabour, B.; Sbiyyaa, B.; Oufdou, K.; Mezrioui, N. Detection and quantification of microcystins from cyanobacteria strains isolated from reservoirs and ponds in morocco. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.D.; Watanabe, M.F.; Harada, K.I.; Nagai, H.; Suzuki, M.; Watanabe, M.; Hayashi, H. Hepatotoxin (microcystin) and neurotoxin (anatoxin-a) contained in natural blooms and strains of cyanobacteria from Japanese freshwaters. Nat. Toxins 1993, 1, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halinen, K.; Jokela, J.; Fewer, D.P.; Wahlsten, M.; Sivonen, K. Direct evidence for production of microcystins by anabaena strains from the baltic sea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 6543–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbedi, S.; Welker, M.; Fastner, J.; Wiedner, C. Variability of the microcystin synthetase gene cluster in the genus planktothrix (oscillatoriales, cyanobacteria). FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 245, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jüttner, F.; Watson, S.B. Biochemical and ecological control of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in source waters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4395–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almanza, V.; Parra, O.; Carlos, E.D.M.; Baeza, C.; Beltran, J.; Figueroa, R.; Urrutia, R. Occurrence of toxic blooms of microcystis aeruginosa in a central chilean (36° lat. S) urban lake. Rev. Chil. Hist. Nat. 2016, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Kong, F.; Zhang, M. Groundwater contamination by microcystin from toxic cyanobacteria blooms in lake chaohu, china. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, S.-C.; Lin, T.-F.; Liu, C.-L.; Lai, S.-D. The effect of oxidants on 2-mib concentration with the presence of cyanobacteria. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Komárek, J.; Zapomělová, E. Planktic morphospecies of the cyanobacterial genus anabaena = subg. Dolichospermum—1. Part: Coiled types. Fottea 2007, 7, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komárek, J.; Zapomělová, E. Planktic morphospecies of the cyanobacterial genus anabaena = subg. Dolichospermum–2. Part: Straight types. Fottea 2008, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGregor, G. Freshwater cyanobacteria of north-eastern Australia: 2. Chroococcales. Phytotaxa 2013, 133, 1–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, S.; Suda, S.; Li, R.; Watanabe, M.; Oyaizu, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Watanabe, M.M. 16s RDNA sequences and phylogenetic analyses of microcystis strains with and without phycoerythrin. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 164, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, E.C.; Neilan, B.A. Geographical segregation of the neurotoxin-producing cyanobacterium anabaena circinalis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 4468–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, F.; Erata, M.; Watanabe, M.M. Cryopreservation of cyanobacteria and green algae in the nies-collection. Microbiol. Cult. Collect. 2002, 18, 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, L.; Mihali, T.; Moffitt, M.; Kellmann, R.; Neilan, B. On the chemistry, toxicology and genetics of the cyanobacterial toxins, microcystin, nodularin, saxitoxin and cylindrospermopsin. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1650–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, Y.; Sano, T.; Kasai, F.; Watanabe, M.M. Recombination, cryptic clades and neutral molecular divergence of the microcystin synthetase (MCY) genes of toxic cyanobacterium microcystis aeruginosa. BMC Evolut. Biol. 2009, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.-T.; Yen, H.-K.; Lin, T.-F. An alternative method to quantify 2-mib producing cyanobacteria in drinking water reservoirs: Method development and field applications. Environ. Res. 2016, 151, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngwa, F.F.; Madramootoo, C.A.; Jabaji, S. Comparison of cyanobacterial microcystin synthetase (MCY) e gene transcript levels, mcy e gene copies, and biomass as indicators of microcystin risk under laboratory and field conditions. MicrobiologyOpen 2014, 3, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, B.-F.; Wu, J.-H.; Dang, C.-Y.; Lv, Y.-T.; Fan, J.-Z.; Yan, X.-J. Sensitive and rapid detection of microcystin synthetase e gene (mcyE) by loop-mediated isothermal amplification: A new assay for detecting the potential microcystin-producing microcystis in the aquatic ecosystem. Harmful Algae 2014, 37, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathi, T.; Ki, J.-S. Impact of environmental factors on the regulation of cyanotoxin production. Toxins 2014, 6, 1951–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmann, E.; Neilan, B.A.; Erhard, M.; Von Döhren, H.; Börner, T. Insertional mutagenesis of a peptide synthetase gene that is responsible for hepatotoxin production in the cyanobacterium microcystis aeruginosa PCC 7806. Mol. Microbiol. 1997, 26, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blevins, W.; Schrader, K.; Saadoun, I. Comparative physiology of geosmin production by streptomyces halstedii and anabaena sp. Water Sci. Technol. 1995, 31, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Saadoun, I.M.; Schrader, K.K.; Blevins, W.T. Environmental and nutritional factors affecting geosmin synthesis by anabaena sp. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Song, L.; Chen, W. Effects of temperature and light on the growth and geosmin production of lyngbya kuetzingii (cyanophyta). J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, K.R.; Paytan, A.; Caldeira, K.; Grossman, A.R.; Moran, D.; McIlvin, M.; Saito, M.A. Effect of temperature on photosynthesis and growth in marine synechococcus spp. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, K.; Byeon, M.; Youn, S.; Hwang, S.; Rhew, D. Growth characteristics of blue-green algae (Anabaena spiroides) causing tastes and odors in the north-Han river, Korea. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 46, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziallas, C.; Grossart, H.-P. Increasing oxygen radicals and water temperature select for toxic microcystis sp. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapala, J.; Sivonen, K.; Luukkainen, R.; Niemelä, S.I. Anatoxin-a concentration inanabaena andaphanizomenon under different environmental conditions and comparison of growth by toxic and non-toxicanabaena-strains—A laboratory study. J. Appl. Phycol. 1993, 5, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jähnichen, S.; Long, B.M.; Petzoldt, T. Microcystin production by microcystis aeruginosa: Direct regulation by multiple environmental factors. Harmful Algae 2011, 12, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Park, J.; Seo, J.; Youn, S.; Moon, J. Investigation of criterion on harmful algae alert system using correlation between cell numbers and cellular microcystins content of Korean toxic cyanobacteria. J. Korean Soc. Water Qual. 2011, 27, 491–498. [Google Scholar]

| Primer | Direction | Sequence (5′→ 3′) | Expected Size | Melting Temp | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16S rDNA | Forward | GGGGAATTTTCCGCAATGGG | 1284 bp | 60 ℃ | [23] |
| Reverse | ACCTTGTTACGACTT | ||||
| geosmin (gys1) | Forward | CTA GAC CMA TGC GGG TTT TA | 569 bp | 56 ℃ | [16] |
| Reverse | CCA TTC TTT RGA ATG MTT | ||||
| 2-MIB (mibC) | Forward | ACG ACA GCT TCT ACA CCT CCA TGA | 196 bp | 62 ℃ | [24] |
| Reverse | AAT CTG TAGCAC CAT GTT GAC WGG TG | ||||
| microcystin (mcyA) | Forward | AAA AGT GTT TTA GCG GCT CAT | 291 bp | 54 ℃ | [25] |
| Reverse | AAA ATT AAA AGC CGT ATC AAA |
| Cyanobacteria Species | Cyanotoxin | Location | Reference | Off-Flavor Compound | Location | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dolichospermum circinale (Anabaena circinalis) | microcystin, anatoxin-a saxitoxin | France Finland USA S. Korea | [29,30,31] and This study | geosmin | Australia S. Korea | [6,13,16] and This study |
| Aphanizomenon flos-aquae | microcystin, anatoxin-a saxitoxin | USA Canada New- Zealand S. Korea | [30,32,33] and This study | geosmin | USA | [34] |
| Microcystis aeruginosa | microcystin | Canada Japan S. Korea | [35,36,37,38] and This study | Not reported | - | Not reported |
| Planktothricoides raciborskii | microcystin | USA | [39] | 2-MIB | China | [40] |
| Oscillatoria limosa | microcystin | Switzerland | [41] | geosmin, 2-MIB | USA Spain S. Korea | [4,42,43] and This study |
| Pseudanabaena mucicola | microcystin | Morocco | [44] | Not reported | - | Not reported |
| Microcystin and Off-Flavor Materials | Microcystis | Dolichospermum (Anabaena) | Aphanizomenon | Oscillatoria | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microcystin | 0.12 (±0.08) ngMC/μgChl-a | 0.26 (±0.11) ngMC/μgChl-a | 0.68 (±0.54) ngMC/μgChl-a | 0.02 (±0.01) ngMC/μgChl-a | Shown underneath each material value |
| [36,37,45] | [29,35,46] | [46] | [47] | ||
| 0.37 (±0.15) ngMC/μgChl-a | 0.02 (±0.01) ngMC/μgChl-a | 0.38 (±0.26) ngMC/μgChl-a | - | This study | |
| Odorous materials | - | 0.05 (±0.05) × 103 ngGE/μgChl-a | - | 0.03 (±0.01) ngMIB/μgChl-a | Shown underneath each material value |
| [48] | [40,48] | ||||
| - | 0.06 (±0.02) × 103 ngGE/μgChl-a | - | 0.04 (±0.02) ngMIB/μgChl-a | This study |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.; Park, C.; Yoon, Y.; Hwang, S.-J. Harmful Cyanobacterial Material Production in the North Han River (South Korea): Genetic Potential and Temperature-Dependent Properties. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15030444
Kim K, Park C, Yoon Y, Hwang S-J. Harmful Cyanobacterial Material Production in the North Han River (South Korea): Genetic Potential and Temperature-Dependent Properties. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(3):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15030444
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Keonhee, Chaehong Park, Youngdae Yoon, and Soon-Jin Hwang. 2018. "Harmful Cyanobacterial Material Production in the North Han River (South Korea): Genetic Potential and Temperature-Dependent Properties" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 3: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15030444
APA StyleKim, K., Park, C., Yoon, Y., & Hwang, S.-J. (2018). Harmful Cyanobacterial Material Production in the North Han River (South Korea): Genetic Potential and Temperature-Dependent Properties. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(3), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15030444