Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in the Ganga River Basin: A Future Health Danger
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Reasons behind the Pollution of the Ganga
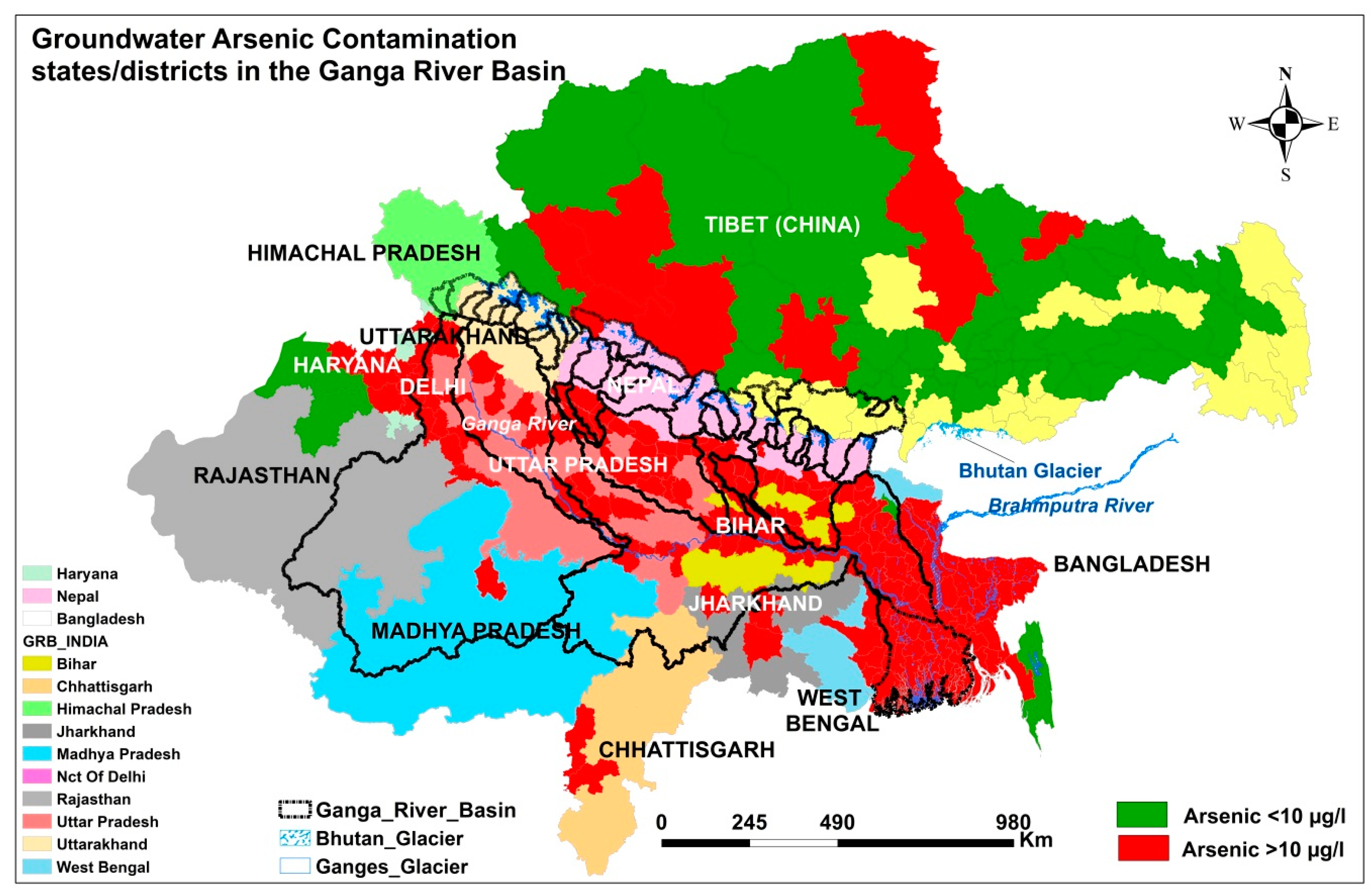
3. Current Magnitude of Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in the GRB
4. Sources and Mechanisms of Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in the GRB
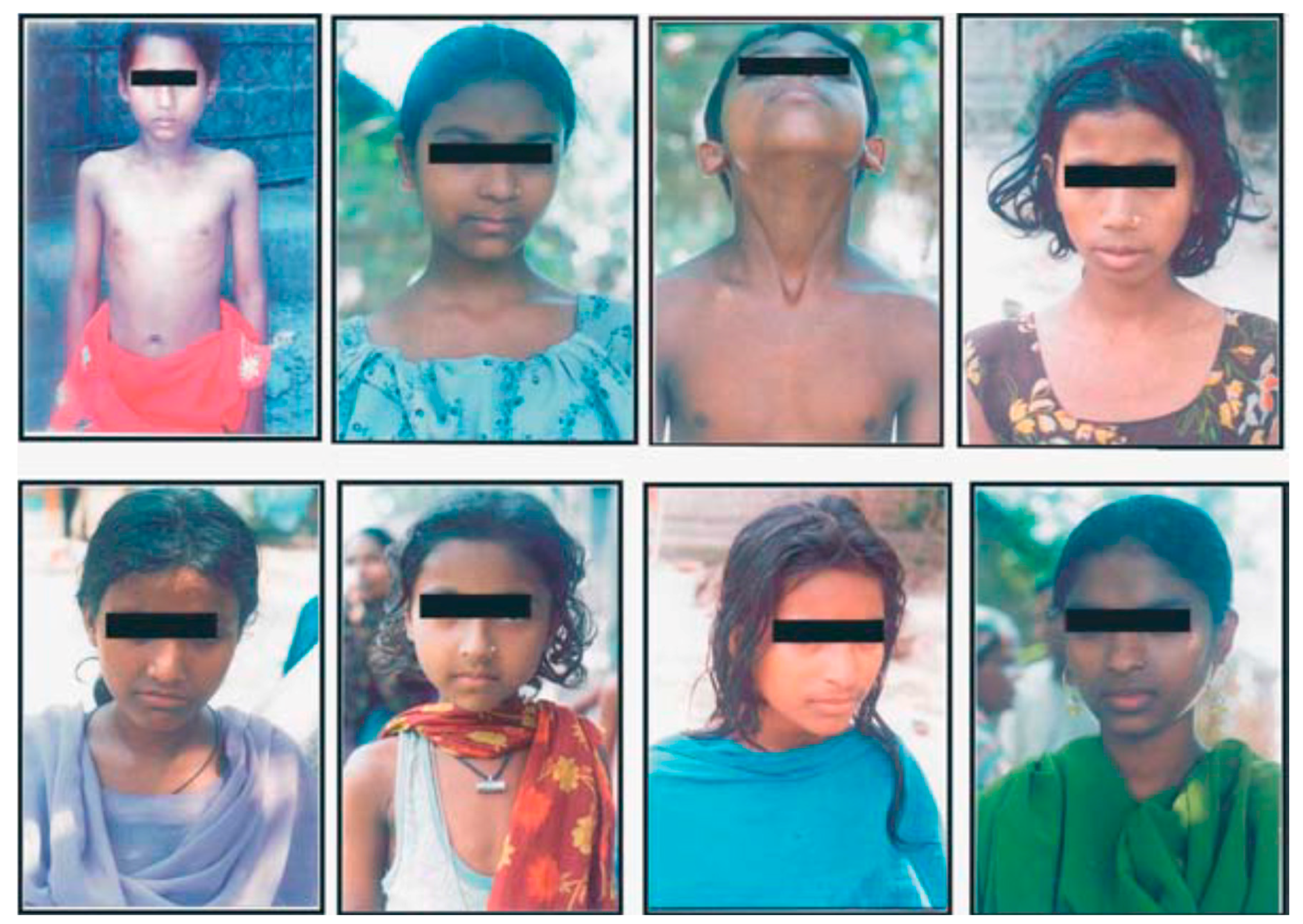
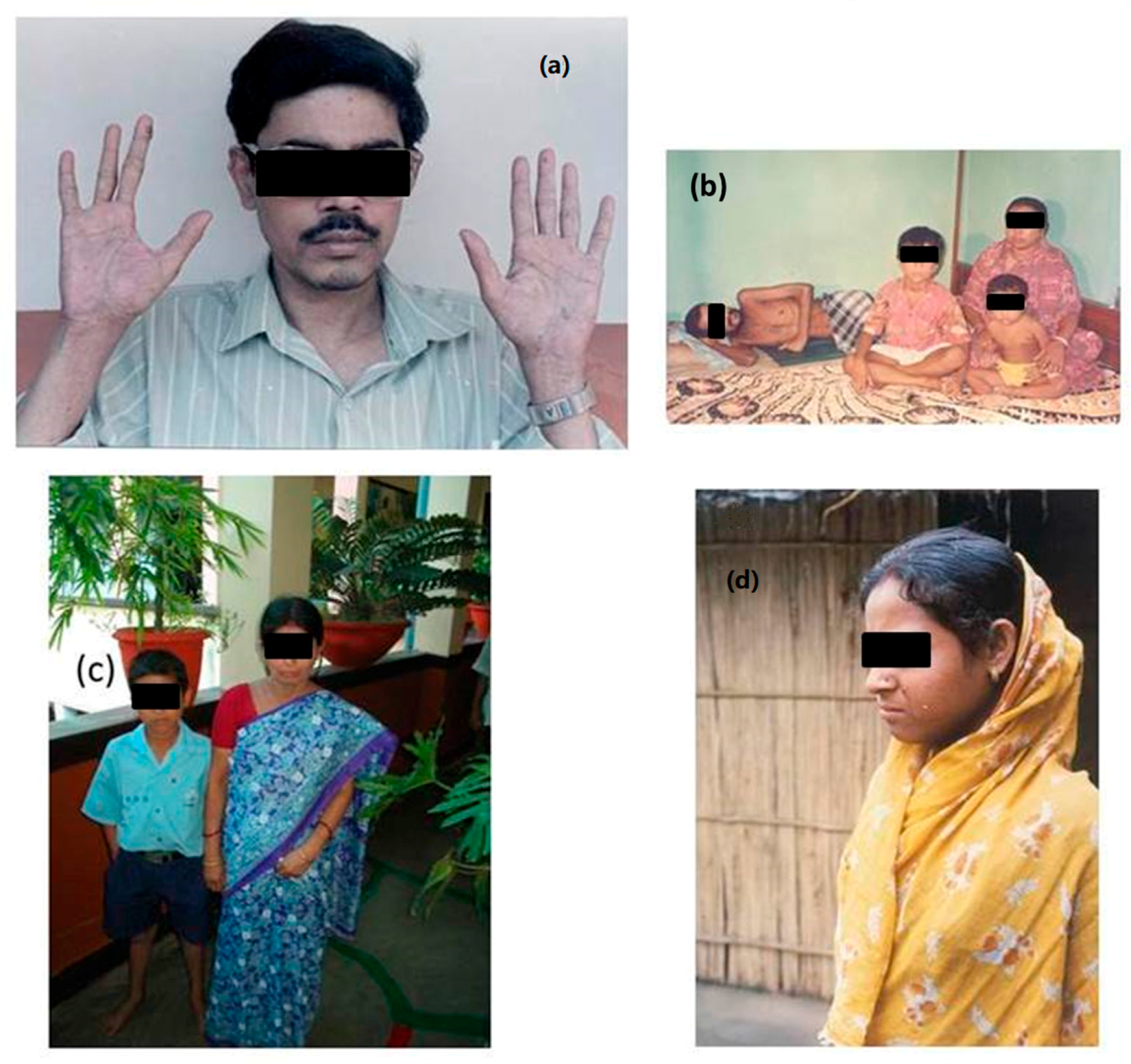
5. Impacts of Arsenic on Human Health in Chronically Exposed Population in the GRB
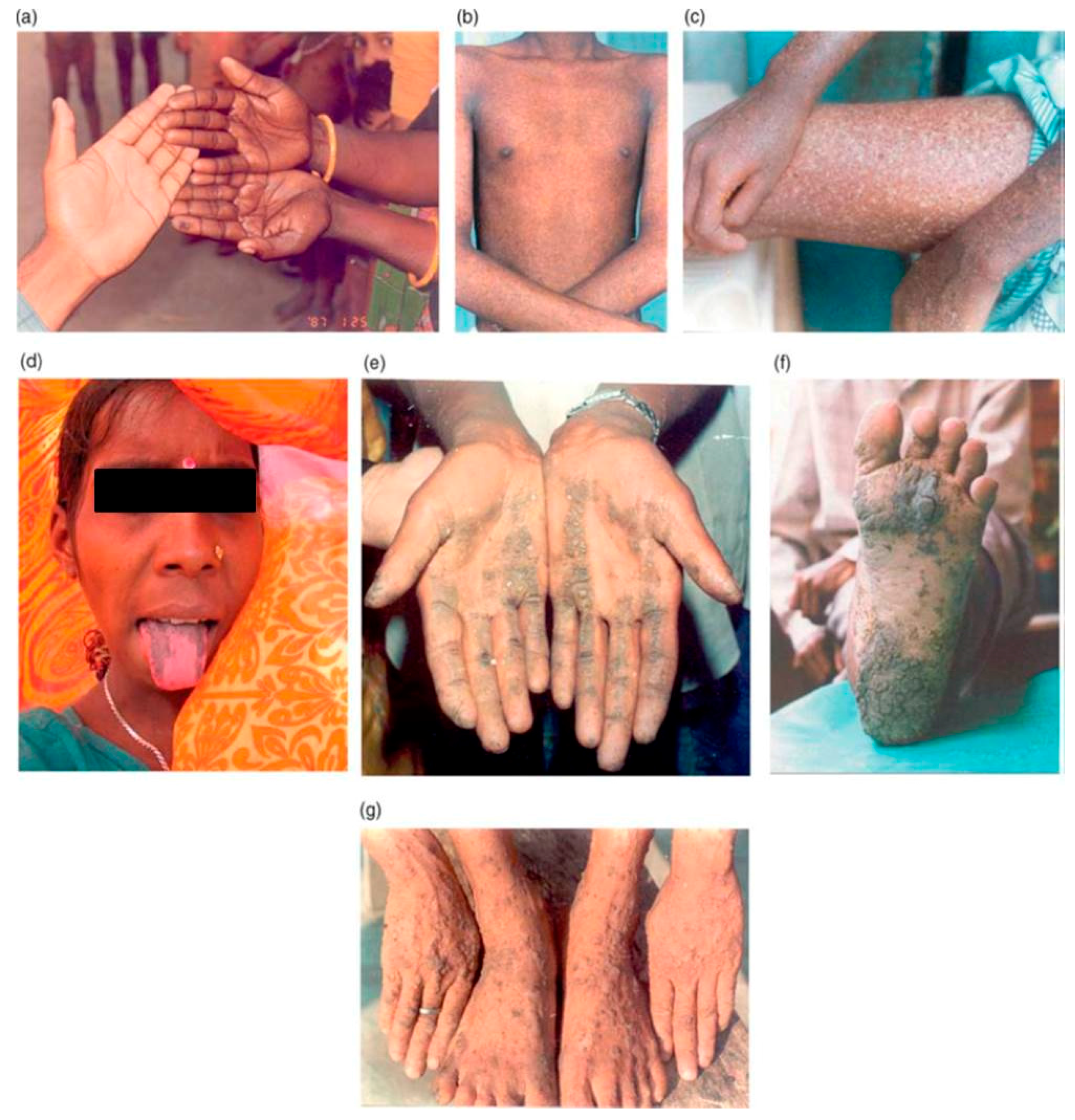
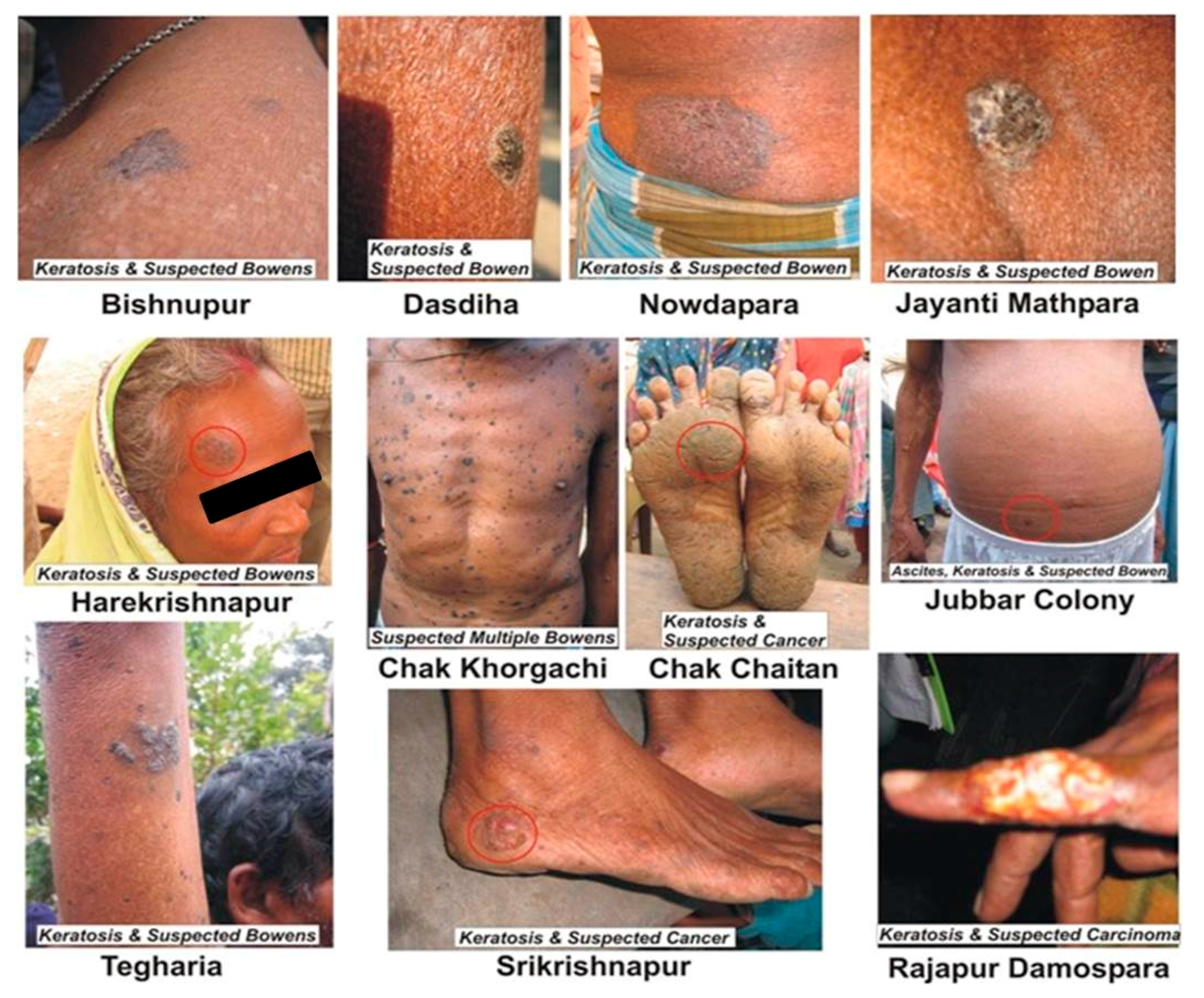
5.1. Dermatological Effects
5.2. Cardiovascular Effects
5.3. Respiratory Effects
5.4. Gastrointestinal Effects
5.5. Hepatological Effects
5.6. Neurological Effects
5.7. Reproduction and Developmental Effects
5.8. Cancerous Effects
5.9. The Other Health Effects and Future Danger
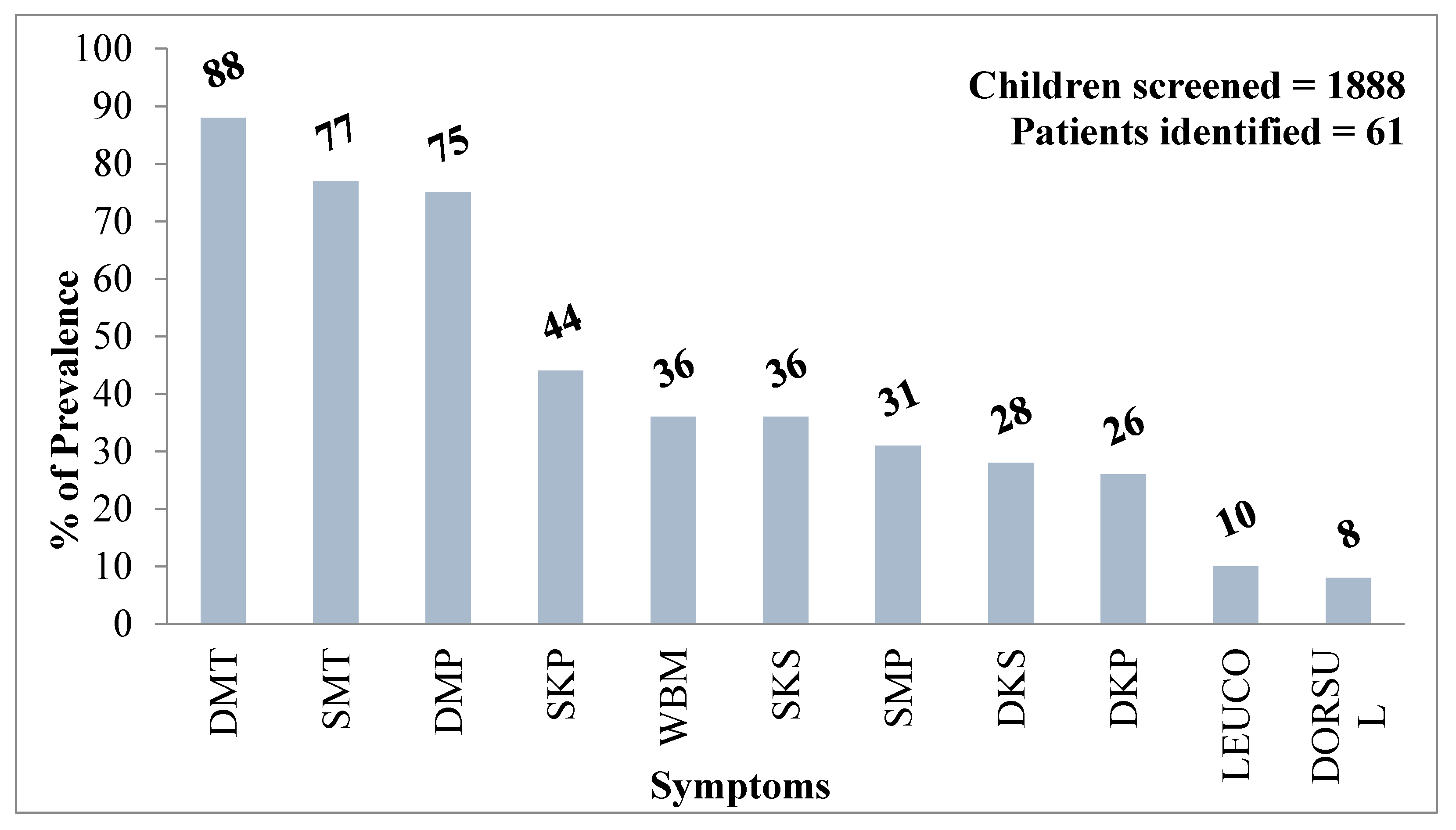
5.10. Health Effects on Children: Our Future Generations at Risk
6. Unsavory Truths: Arsenic in the Food Chain in the GRB
7. Socioeconomic, Psychological, and Cultural Implications of Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in the GRB
8. How to Combat the Present Arsenic Crisis in the GRB
9. Challenges Associated with Arsenic Standards in the GRB
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, L.R.; Sarma, P.B.S.; Syaukat, Y.; Ahmad, S.; Concepcion, R.; Sethaputra, S.; Nguyen, P. Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna 9251072825; Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2012; pp. 1–512. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, D.S. Nature and the Ganga. Environ. Conserv. 1987, 14, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D. Research on heavy metal pollution of river Ganga: A review. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reporter, S. A special report on India: Creaking, groaning: Infrastructure is India’s biggest handicap. Economist, 11 December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, N. Sustainability issues in river tourism: A case study of Ganges in Varanasi. Atn. J. Tour. Stud. 2017, 7, 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tagore, R. Chelebela [My Boyhood Days]. Calcutta: Biśvabhāratī Granthālay. 1940. Available online: http://kolkatasounds.org/old-kolkata-sounds/childhood/ (accessed on 15 August 2017).
- Singh, A. Chemistry of arsenic in groundwater of Ganges–Brahmaputra river basin. Curr. Sci. 2006, 91, 599–606. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, D.; Kaul, M. Arsenic content of drinking water in villages in Northern India: A concept of arsenicosis. J. Assoc. Phys. India 1976, 24, 599–604. [Google Scholar]
- Datta, D. Arsenic and non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. Lancet 1976, 307, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, R.; Chakraborty, A.; Dey, S.; Saha, K. Chronic arsenic poisoning from tube-well water. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 1984, 82, 34–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- School of Environmental Studies. International Conference on Arsenic in Groundwater: Cause, Effects and remedy. In School of Environmental Studies (SOES); Jadavpur University: Calcutta, India, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti, D.; Biswas, B.; Chowdhury, T.R.; Basu, G.; Mandal, B.; Chowdhury, U.; Mukherjee, S.; Gupta, J.; Chowdhury, S.; Rathore, K. Arsenic groundwater contamination and sufferings of people in Rajnandgaon district, Madhya Pradesh, India. Curr. Sci. 1999, 77, 502–504. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti, D.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Pati, S.; Sengupta, M.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Chowdhury, U.K.; Lodh, D.; Chanda, C.R.; Chakraborti, A.K.; Basu, G.K. Arsenic groundwater contamination in Middle Ganga Plain, Bihar, India: A future danger? Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamed, S.; Sengupta, M.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Hossain, M.A.; Das, B.; Nayak, B.; Pal, A.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Pati, S.; Dutta, R.N. Arsenic groundwater contamination and its health effects in the state of Uttar Pradesh (UP) in upper and middle Ganga plain, India: A severe danger. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, B.; Das, B.; Chandra Mukherjee, S.; Pal, A.; Ahamed, S.; Amir Hossain, M.; Maity, P.; Dutta, R.N.; Dutta, S.; Chakraborti, D. Groundwater arsenic contamination in the Sahibganj district of Jharkhand state, India in the middle Ganga plain and adverse health effects. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2008, 90, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, D.; Sengupta, M.; Rahman, M.; Ahamed, S.; Chowdhury, U.; Hossain, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Pati, S.; Saha, K.; Dutta, R.; et al. Groundwater arsenic contamination and its health effects in the Ganga-Meghna-Brahmaputra plain. J. Environ. Monit. 2004, 6, 74N–83N. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborti, D.; Ghorai, S.K.; Das, B.; Pal, A.; Nayak, B.; Shah, B.A. Arsenic exposure through groundwater to the rural and urban population in the Allahabad-Kanpur track in the upper Ganga plain. J. Environ. Monit. 2009, 11, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalwani, S.; Dogra, T.; Bhardwaj, D.; Sharma, R.; Murty, O.; Vij, A. Study on arsenic level in ground water of Delhi using hydride generator accessory coupled with atomic absorption spectrophotometer. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 19, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggal, V.; Rani, A.; Mehra, R. Assessment of arsenic content in groundwater samples collected from four districts of Northern Rajasthan, India. Chem. Sin. 2012, 3, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Kumar, A.; Chauhan, R.; Awasthi, S.; Tripathi, R.; Mattusch, J. Current status of ground water arsenic contamination in India and recent advancements in removal techniques from drinking water. Int. J. Plant Environ. 2016, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, R.K.; Biswas, B.K.; Samanta, G.; Mandal, B.K.; Chakraborti, D.; Roy, S.; Jafar, A.; Islam, A.; Ara, G.; Kabir, S.; et al. Groundwater arsenic calamity in Bangladesh. Curr. Sci. 1997, 73, 48–59. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Das, B.; Murrill, M.; Dey, S.; Chandra Mukherjee, S.; Dhar, R.K.; Biswas, B.K.; Chowdhury, U.K.; Roy, S. Status of groundwater arsenic contamination in Bangladesh: A 14-year study report. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5789–5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Arsenic Contamination in Groundwater Affecting Some Countries in the South-East Asia Region; WHO Regional Office for South-East Asia: New Delhi, India, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, R.R.; Shrestha, M.P.; Upadhyay, N.P.; Pradhan, R.; Khadka, R.; Maskey, A.; Maharjan, M.; Tuladhar, S.; Dahal, B.M.; Shrestha, K. Groundwater arsenic contamination, its health impact and mitigation program in Nepal. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2003, 38, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W. B, As, and F contamination of river water due to wastewater discharge of the Yangbajing geothermal power plant, Tibet, China. Environ. Geol. 2008, 56, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, M.; Yang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, B.; Zheng, Y. Enrichment of arsenic in surface water, stream sediments and soils in Tibet. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 135, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Yu, C.; Zha, X.; Wu, J.; Gao, X.; Feng, C.; Luo, K. Distribution and potential health risks of arsenic, Selenium, and Fluorine in natural waters in Tibet, China. Water 2016, 8, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.R.; Basu, G.K.; Mandal, B.K.; Biswas, B.K.; Samanta, G.; Chowdhury, U.K.; Chanda, C.R.; Lodh, D.; Roy, S.L.; Saha, K.C. Arsenic poisoning in the Ganges delta. Nature 1999, 401, 545–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickson, R.; McArthur, J.; Burgess, W.; Ahmed, K.M.; Ravenscroft, P.; Rahmann, M. Arsenic poisoning of Bangladesh groundwater. Nature 1998, 395, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Chatterjee, D.; Jacks, G. Occurrence of Arsenic-contaminated groundwater in alluvial aquifers from Delta Plains, Eastern India: Options for safe drinking water supply. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 1997, 13, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akai, J.; Izumi, K.; Fukuhara, H.; Masuda, H.; Nakano, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Ohfuji, H.; Anawar, H.M.; Akai, K. Mineralogical and geomicrobiological investigations on groundwater arsenic enrichment in Bangladesh. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.S.; Gault, A.G.; Boothman, C.; Polya, D.A.; Charnock, J.M.; Chatterjee, D.; Lloyd, J.R. Role of metal-reducing bacteria in arsenic release from Bengal delta sediments. Nature 2004, 430, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, C.F.; Swartz, C.H.; Badruzzaman, A.; Keon-Blute, N.; Yu, W.; Ali, M.A.; Jay, J.; Beckie, R.; Niedan, V.; Brabander, D. Arsenic mobility and groundwater extraction in Bangladesh. Science 2002, 298, 1602–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Samanta, G.; Mandal, B.K.; Chowdhury, T.R.; Chanda, C.R.; Chowdhury, P.P.; Basu, G.K.; Chakraborti, D. Arsenic in groundwater in six districts of West Bengal, India. Environ. Geochem. Health 1996, 18, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuckey, J.W.; Schaefer, M.V.; Kocar, B.D.; Benner, S.G.; Fendorf, S. Arsenic release metabolically limited to permanently water-saturated soil in Mekong Delta. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharyya, S.; Shah, B.; Ashyiya, I.; Pandey, Y. Arsenic contamination in groundwater from parts of Ambagarh-Chowki block, Chhattisgarh, India: Source and release mechanism. Environ. Geol. 2005, 49, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.M.; Bhattacharya, P.; Hasan, M.A.; Akhter, S.H.; Alam, S.M.; Bhuyian, M.H.; Imam, M.B.; Khan, A.A.; Sracek, O. Arsenic enrichment in groundwater of the alluvial aquifers in Bangladesh: An overview. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, J.K.; Thakur, R.K.; Ramanathan, A.; Kumar, M.; Singh, S.K. Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Nepal—An overview. Water 2010, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendorf, S.; Michael, H.A.; van Geen, A. Spatial and temporal variations of groundwater arsenic in South and Southeast Asia. Science 2010, 328, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Brachfeld, S.A.; Taylor, R.W. Evaluating Hydrogeological and Topographic Controls on Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in the Mid-Gangetic Plain in India: Towards Developing Sustainable Arsenic Mitigation Models. In Emerging Issues in Groundwater Resources, Advances in Water Security; Fares, A., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 263–287. [Google Scholar]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer-World Health Organization. IARC Monograph on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Man; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), World Health Organization (WHO): Lyon, France, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer-World Health Organization. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), World Health Organization (WHO): Lyon, France, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Das, B.; Chatterjee, A.; Das, D.; Nayak, B.; Pal, A.; Chowdhury, U.K.; Ahmed, S.; Biswas, B.K.; et al. Groundwater arsenic contamination and its health effects in India. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, D. Arsenic: Occurrence in Groundwater. Encyclopedia of Environmental Health. 2011, pp. 165–180. Available online: https://books.google.co.uk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=2RiNtZt5BlgC&oi=fnd&pg=PT199&dq=Encyclopedia+of+Environmental+Health&ots=9DB0wuIRjY&sig=KkxadWHczH3pKdz_TzjKjSlcgbM#v=snippet&q=Occurrence%20in%20groundwater&f=false (accessed on 21 January 2018).
- Mazumder, D.G.; Chakraborty, A.; Ghose, A.; Gupta, J.D.; Chakraborty, D.; Dey, S.; Chattopadhyay, N. Chronic arsenic toxicity from drinking tubewell water in rural West Bengal. Bull. World Health Organ. 1988, 66, 499. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ng, J.C.; Naidu, R. Chronic exposure of arsenic via drinking water and its adverse health impacts on humans. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, D.N.G.; Haque, R.; Ghosh, N.; De, B.K.; Santra, A.; Chakraborti, D.; Smith, A.H. Arsenic in drinking water and the prevalence of respiratory effects in West Bengal, India. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2000, 29, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milton, A.H.; Hasan, Z.; Rahman, A.; Rahman, M. Chronic arsenic poisoning and respiratory effects in Bangladesh. J. Occup. Health 2001, 43, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, A.H.; Hasan, Z.; Rahman, A.; Rahman, M. Non-cancer effects of chronic arsenicosis in Bangladesh: Preliminary results. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2003, 38, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, D.; Das, G.J.; Santra, A.; Pal, A.; Ghose, A.; Sarkar, S. Chronic arsenic toxicity in west Bengal—The worst calamity in the world. J. Indian Med. Assoc. 1998, 96, 18. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Ahamed, S.; Dutta, R.N.; Pati, S.; Mukherjee, S.C. Arsenic contamination of groundwater and its induced health effects in Shahpur block, Bhojpur district, Bihar state, India: Risk evaluation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 9492–9504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborti, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Ahamed, S.; Dutta, R.N.; Pati, S.; Mukherjee, S.C. Arsenic groundwater contamination and its health effects in Patna district (capital of Bihar) in the middle Ganga plain, India. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.H.; Hopenhayn-Rich, C.; Bates, M.N.; Goeden, H.M.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Duggan, H.M.; Wood, R.; Kosnett, M.J.; Smith, M.T. Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 1992, 97, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.H.; Lopipero, P.A.; Bates, M.N.; Steinmaus, C.M. Arsenic epidemiology and drinking water standards. Science 2002, 296, 2145–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.H.; Marshall, G.; Yuan, Y.; Ferreccio, C.; Liaw, J.; von Ehrenstein, O.; Steinmaus, C.; Bates, M.N.; Selvin, S. Increased mortality from lung cancer and bronchiectasis in young adults after exposure to arsenic in utero and in early childhood. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1293–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Murrill, M.; Das, B.; Roy, B.; Dey, S.; Maity, D.; Chakraborti, D. Water consumption patterns and factors contributing to water consumption in arsenic affected population of rural West Bengal, India. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Ghosh, A.K. Health risk assessment due to groundwater arsenic contamination: Children are at high risk. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2012, 18, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Ghosh, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Kislay, K.; Kumar, C.; Tiwari, R.R.; Parwez, R.; Kumar, N.; Imam, M. Groundwater Arsenic contamination and associated health risks in Bihar, India. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, K.; Prasad, P.; Sinha, D. Chronic low level arsenic exposure evokes inflammatory responses and DNA damage. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2015, 218, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Vedwan, N. Mapping composite vulnerability to groundwater Arsenic contamination: An analytical framework and a case study in India. Nat. Hazard. 2015, 75, 1883–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Mukherjee, A.; Alauddin, M.; Hassan, M.; Dutta, R.N.; Pati, S.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Roy, S.; Quamruzzman, Q. Groundwater arsenic contamination in Bangladesh—21 years of research. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 31, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamed, S.; Chakraborti, D. Groundwater Arsenic Contamination and Health Effects in Bihar and Up; LAP Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2012; p. 384. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Ahsan, H.; Factor-Litvak, P.; Kline, J.; Van Geen, A.; Slavkovich, V.; Lolacono, N.J.; Levy, D. Water arsenic exposure and intellectual function in 6-year-old children in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserman, G.A.; Liu, X.; Parvez, F.; Ahsan, H.; Factor-Litvak, P.; van Geen, A.; Slavkovich, V.; Lolacono, N.J.; Cheng, Z.; Hussain, I. Water arsenic exposure and children’s intellectual function in Araihazar, Bangladesh. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 1329–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, U.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Mandal, B.; Paul, K.; Lodh, D.; Biswas, B.K.; Basu, G.K.; Chanda, C.R.; Saha, K.C.; Mukherjee, S.C. Groundwater arsenic contamination and human suffering in West Bengal, India and Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. 2001, 8, 393–415. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborti, D.; Rahman, M.M.; Chatterjee, A.; Das, D.; Das, B.; Nayak, B.; Pal, A.; Chowdhury, U.K.; Ahmed, S.; Biswas, B.K. Fate of over 480 million inhabitants living in arsenic and fluoride endemic Indian districts: Magnitude, health, socio-economic effects and mitigation approaches. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2016, 38, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Chowdhury, U.K.; Mondal, D.; Das, B.; Nayak, B.; Ghosh, A.; Maity, S.; Chakraborti, D. Arsenic burden from cooked rice in the populations of arsenic affected and nonaffected areas and Kolkata City in West-Bengal, India. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3349–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meharg, A.A. Arsenic in rice-understanding a new disaster for South-East Asia. Trend. Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Rahman, M.M.; Ramanathan, A.; Naidu, R. Arsenic and other elements in drinking water and dietary components from the middle Gangetic plain of Bihar, India: Health risk index. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Ghosh, A.K. Entry of arsenic into food material—A case study. World Appl. Sci. J. 2011, 13, 385–390. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Naidu, R. Consumption of arsenic and other elements from vegetables and drinking water from an arsenic-contaminated area of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 262, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, M.K.; Mukherjee, A.; Ahamed, S.; Hossain, M.A.; Das, B.; Nayak, B.; Goswami, A.B.; Chakraborti, D. Comment on “Limited temporal variability of arsenic concentrations in 20 wells monitored for 3 Years in Araihazar, Bangladesh”. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 1714–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Taylor, R.W.; Su, H. Developing sustainable models of Arsenic-mitigation technologies in the Middle-Ganga Plain in India. Curr. Sci. 2017, 113, 80–93. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.K. An analysis of the Cost-effectiveness of Arsenic mitigation technologies: Implications for public policy. Int. J. Sustain. Built Environ. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborn, K. Shout it out loud: Arsenic. Water Technology, 7 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dartmouth-College in Small Doses: Arsenic. Available online: http://www.dartmouth.edu/~toxmetal/InSmallDoses/ (accessed on 7 June 2017).
- Grush, L. Arsenic in Drinking Water Deemed ‘Safe’ Could Harm Mothers and Children, Study Finds. Fox News. 2012. Available online: http://www.foxnews.com/health/2012/06/01/arsenic-in-drinking-water-deemed- afe-could-harm-mothers-and-children-study.html (accessed on 15 August 2017).
- Bureau of Indian Standards. Drinking Water Specification (First Revision Incorporating Amendments 1 and 2); Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2003.
- Smith, A.H.; Smith, M.M.H. Arsenic drinking water regulations in developing countries with extensive exposure. Toxicology 2004, 198, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Sengupta, M.K.; Hossain, M.A.; Ahamed, S.; Lodh, D.; Das, B.; Nayak, B.; Saha, K.C.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Pati, S. Are some animals more equal than others. Toxicology 2005, 208, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bureau of Indian Standards. Drinking Water Specification (Second Revision of IS 10500). Doc: FAD 25(2047) C. Last Date for Comments: 24/12/2009; Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2009.



| Total No. of Irrigated Tube Wells | Total No. of Irrigated Tube Wells Analyzed | No. of Water Samples Having Arsenic (μg/L) | Distribution of No. of Samples in Different Concentration Range (μg/L) of Arsenic | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| >10 | >50 | <10 | 10–50 | 51–99 | 100–299 | 300–499 | 500–699 | 700–1000 | >1000 | ||
| 3200 | 597 | 574 | 234 | 23 | 339 | 118 | 98 | 11 | 5 | 2 | -- |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chakraborti, D.; Singh, S.K.; Rahman, M.M.; Dutta, R.N.; Mukherjee, S.C.; Pati, S.; Kar, P.B. Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in the Ganga River Basin: A Future Health Danger. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020180
Chakraborti D, Singh SK, Rahman MM, Dutta RN, Mukherjee SC, Pati S, Kar PB. Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in the Ganga River Basin: A Future Health Danger. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(2):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020180
Chicago/Turabian StyleChakraborti, Dipankar, Sushant K. Singh, Mohammad Mahmudur Rahman, Rathindra Nath Dutta, Subhas Chandra Mukherjee, Shyamapada Pati, and Probir Bijoy Kar. 2018. "Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in the Ganga River Basin: A Future Health Danger" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 2: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020180
APA StyleChakraborti, D., Singh, S. K., Rahman, M. M., Dutta, R. N., Mukherjee, S. C., Pati, S., & Kar, P. B. (2018). Groundwater Arsenic Contamination in the Ganga River Basin: A Future Health Danger. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(2), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15020180







