Disparities in Unintentional Occupational Injury Mortality between High-Income Countries and Low- and Middle-Income Countries: 1990–2016
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Data Analysis
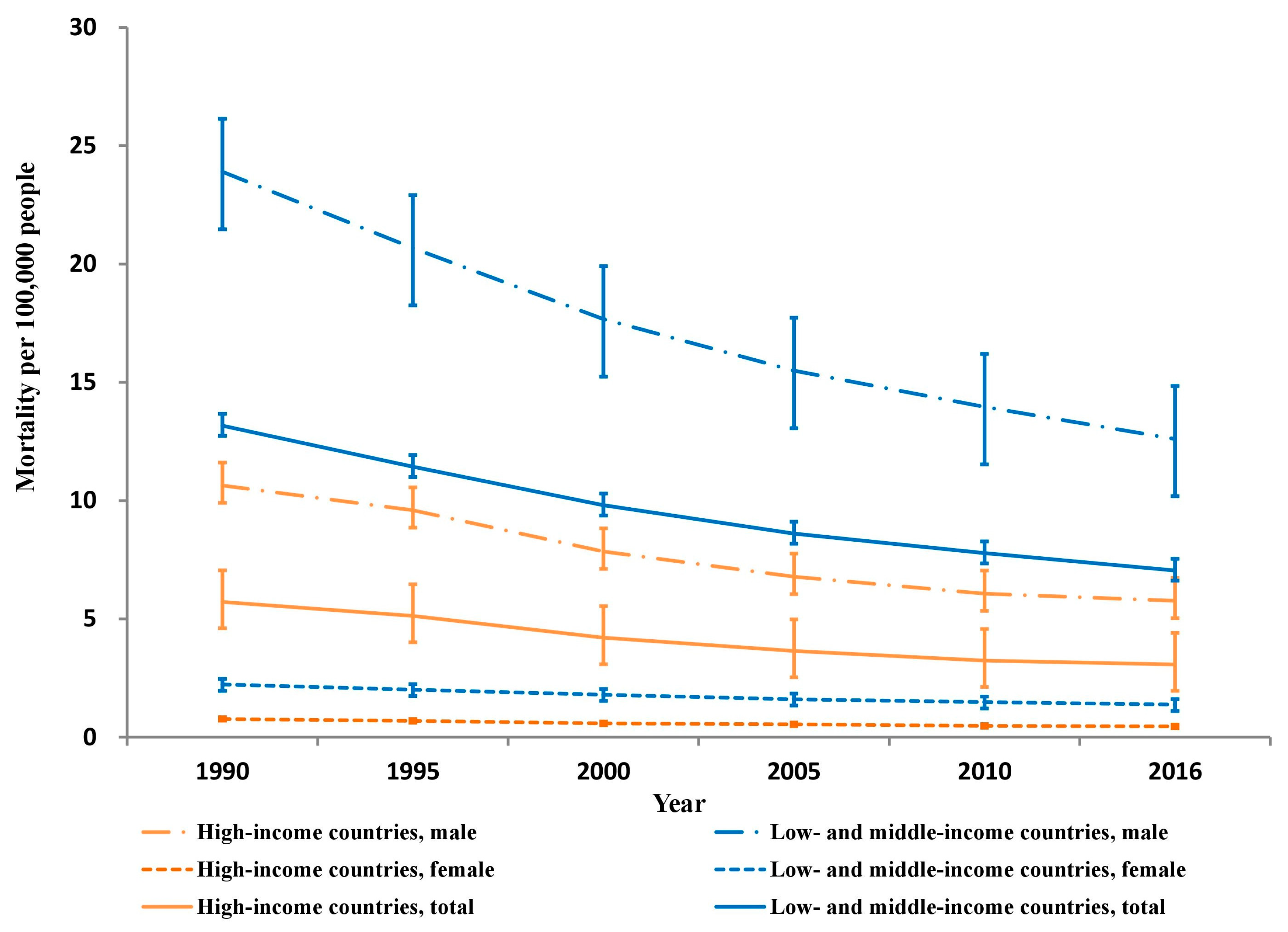
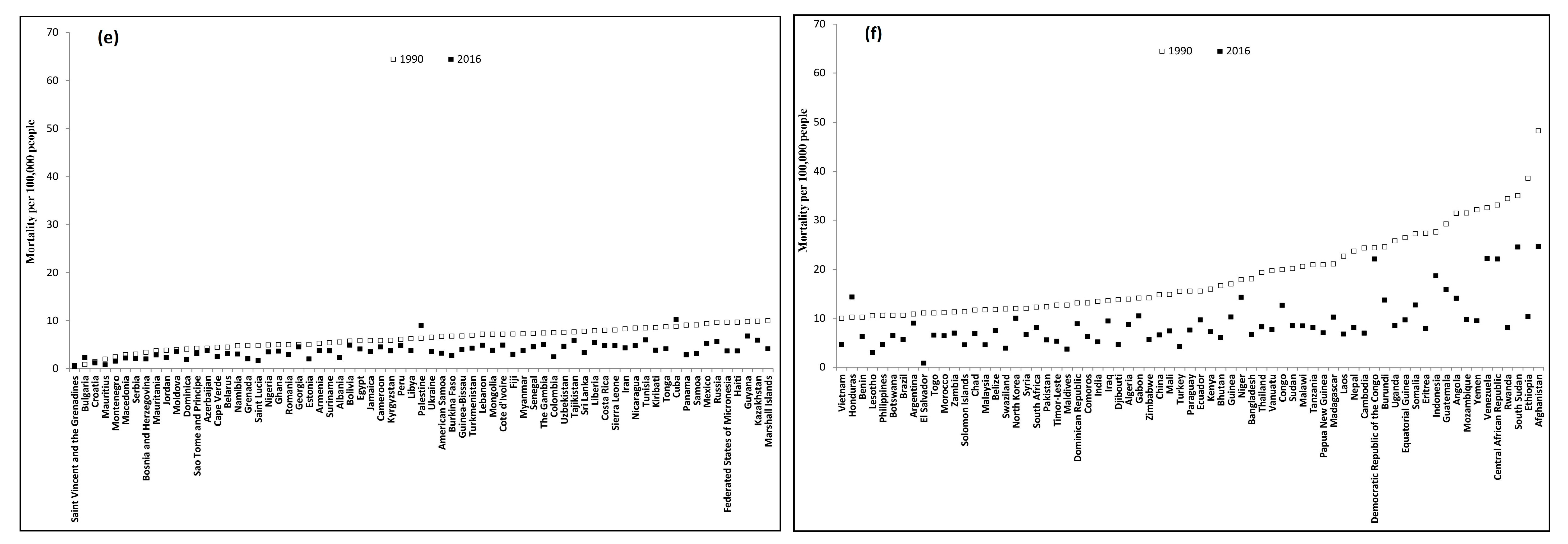
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributors
Funding
Ethics Approval
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/post2015/transformingourworld (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- International Labour Office (ILO). Independent Evaluation of the Ilo’s Strategy on Occupational Safety and Health: Workers and Enterprises Benefit from Improved Safety and Health Conditions at Work; International Labour Office: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Census of Fatal Occupational Injuries Charts, 1992–2016. Washington, DC: USDOL Bureau of Labor Statistics (Bls). Available online: https://www.bls.gov/iif/oshwc/cfoi/cfch0015.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- ’t Mannetje, A.; Pearce, N. Quantitative estimates of work-related death, disease and injury in New Zealand. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 2005, 31, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Employment and Labor. Major Statistics. Available online: http://www.moel.go.kr/english/pas/pasMajor.jsp (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Harris, E.C.; Palme, K.T.; Cox, V.; Darnton, A.; Osman, J.; Coggon, D. Trends in mortality from occupational hazards among men in England and Wales during 1979–2010. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 73, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, K.; Courtney, T.K. Work-related fatalities in the People’s Republic of China. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2009, 6, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abas, A.B.; Mohd Said, D.A.; Aziz Mohammed, M.A.; Sathiakumar, N. Fatal occupational injuries among non-governmental employees in Malaysia. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2013, 56, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eurostat European Commission. Accidents at Work Statistics. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/pdfscache/11539.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Giuffrida, A.; Iunes, R.F.; Savedoff, W.D. Occupational risks in Latin America and the Caribbean: Economic and health dimensions. Health Policy Plan 2002, 17, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takala, J. Global estimates of fatal occupational accidents. Epidemiology 1999, 10, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hämäläinen, P.; Takala, J.; Leena Saarela, K. Global estimates of occupational accidents. Saf. Sci. 2006, 44, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takala, J. ILO Introductory Report: Decent Work-Safework. In Proceedings of the XVII World Congress on Safety and Health at Work, Orlando, FL, USA, 18–22 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hämäläinen, P.; Leena Saarela, K.; Takala, J. Global trend according to estimated number of occupational accidents and fatal work-related diseases at region and country level. J. Saf. Res. 2009, 40, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Labour Office (ILO). ILO Introductory Report: Global Trends and Challenges on Occupational Safety and Health. In Proceedings of the XIX World Congress on Safety and Health at Work, Istanbul, Turkey, 11–15 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Takala, J.; Hämäläinen, P.; Saarela, K.L.; Yun, L.Y.; Manickam, K.; Jin, T.W.; Heng, P.; Tjong, C.; Kheng, L.G.; Lim, S.; et al. Global estimates of the burden of injury and illness at work in 2012. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2014, 11, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Labour Office (ILO). Safety and Health at Work, A Vision for Sustainable Prevention. In Proceedings of the XX World Congress for Safety and Health at Work, Frankfurt, Germany, 24–27 August 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hämäläinen, P.; Takala, J.; Tan, B.K. Global Estimates of Occupational Accidents and Work-Related Illnesses 2017; Hämäläinen, P., Takala, J., Tan, B.K., Eds.; Workplace Safety and Health: Singapore, 2017; ISBN 9789811148446.
- Concha-Barrientos, M.; Nelson, D.I.; Fingerhut, M.; Driscoll, T.; Leigh, J. The global burden due to occupational injury. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2005, 48, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO methods and data sources for country-level causes of death 2000–2016. In Global Health Estimates Technical Paper WHO/HIS/IER/GHE/2018.3; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation, University of Washington. GBD Compare Viz Hub. Available online: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare/ (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Murray, C.J.L.; Lopez, A.D. Measuring global health: Motivation and evolution of the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2017, 390, 1460–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1345–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommel, A.; Varnaccia, G.; Lahmann, N.; Kottner, J.; Kroll, L.E. Occupational injuries in Germany: Population-wide national survey data emphasize the importance of work-related factors. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The World Bank. World Bank List of Economies. Available online: https:// databank.worldbank.org/data/download/site-content/CLASS.xls (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- NiakanKalhori, S.R.; Behzadi, A.; Maharlou, H.; Rahimzadeh, S.; Khajavi, A.; Pouryaghoub, G.; Mehrdad, R.; Aminian, O.; Jeddian, A.; Naderimagham, S. A burden assessment of occupational exposures in Iran, 1990–2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 26, 9–56. [Google Scholar]
- Rantanen, J.; Lehtinen, S.; Valenti, A.; Iavicoli, S. A global survey on occupational health services in selected international commission on occupational health (ICOH) member countries. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takala, J.; Hämäläinen, P.; Nenonen, N.; Takahashi, K.; Chimed-Ochir, O.; Rantanen, J. Comparative analysis of the burden of injury and illness at work in selected countries and regions. Central Eur. J. Occ. Env. Med. 2017, 23, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Hämäläinen, P. The effect of globalization on occupational accidents. Saf. Sci. 2009, 47, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, A.; Winker, R.; Ponocny-Seliger, E.; Sögner, L. Economic growth and the incidence of occupational injuries in Austria. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr 2007, 119, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koradecka, D. Poland in transition to the European union (in the context of meeting standards in occupational safety and health). Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2001, 7, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Improvements in workplace safety—United States, 1900–1999. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 1999, 48, 461–469. [Google Scholar]
- International Labour Office (ILO). Where Are the Jobs? Available online: http://ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---dgreports/---stat/documents/publication/wcms_629568.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- International Social Security Association (ISSA). Survey on Social Security in Times of Crisis: Final Report on Findings and Conclusions. Available online: https://www.issa.int/en/details?uuid=2aed5a32-2b0c-44f4-ae68-52de38cd7405 (accessed on 1 March 2018).
- Signorelli, C.; Riccò, M.; Odone, A. The Italian National Health Service expenditure on workplace prevention and safety (2006–2013): A national-level analysis. Ann. Ig. 2016, 28, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Otte im Kampe, E.; Kovats, S.; Hajat, S. Impact of high ambient temperature on unintentional injuries in high-incomecountries: A narrative systematic literature review. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Solanas, È.; López-Ruiz, M.; Wellenius, G.A.; Gasparrini, A.; Sunyer, J.; Benavides, F.G.; Basagaña, X. Evaluation of the impact of ambient temperatures on occupational injuries in Spain. Environ. Health Perspect 2018, 126, 067002. [Google Scholar]
- Riccò, M. Air temperature exposure and agricultural occupational injuries in the Autonomous Province of Trento (2000-2013, North-Eastern Italy). Int. J. Occup. Med. Environ. Health 2018, 31, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Country Income/Age Group/Cause | 1990 | 2016 | Percent Change in Rate (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deaths | Rate | Deaths | Rate | ||
| HICs, 15–49 years | |||||
| All injury | 29,113 | 6.0 | 17,462 | 3.4 | −44 (−45, −43) |
| Road injury | 18,859 | 3.9 | 10,959 | 2.1 | −46 (−47, −44) |
| Other transport injury | 1227 | 0.3 | 894 | 0.2 | −32 (−37, −26) |
| Falls | 2343 | 0.5 | 1794 | 0.3 | −28 (−33, −24) |
| Drowning | 1774 | 0.4 | 1089 | 0.2 | −43 (−47, −38) |
| Poisonings | 703 | 0.1 | 331 | 0.1 | −56 (−61, −50) |
| Exposure to mechanical forces | 1881 | 0.4 | 979 | 0.2 | −51 (−55, −47) |
| Foreign body | 638 | 0.1 | 606 | 0.1 | −11 (−20, −1) |
| Other injuries | 1688 | 0.3 | 810 | 0.2 | −55 (−59, −51) |
| LMICs, 15–49 years | |||||
| All injury | 288,906 | 13.1 | 237,333 | 7.2 | −45 (−45, −45) |
| Road injury | 151,573 | 6.9 | 139,998 | 4.2 | −38 (−39, −38) |
| Other transport injury | 11,286 | 0.5 | 9720 | 0.3 | −43 (−44, −41) |
| Falls | 25,668 | 1.2 | 21,716 | 0.7 | −44 (−45, −43) |
| Drowning | 32,173 | 1.5 | 20,129 | 0.6 | −58 (−59, −58) |
| Poisonings | 7906 | 0.4 | 4353 | 0.1 | −63 (−65, −62) |
| Exposure to mechanical forces | 19,697 | 0.9 | 14,607 | 0.4 | −51 (−52, −49) |
| Foreign body | 4141 | 0.2 | 4177 | 0.1 | −33 (−36, −30) |
| Other injuries | 36,462 | 1.7 | 22,633 | 0.7 | −59 (−59, −58) |
| HICs, 50–69 years | |||||
| All injury | 8468 | 4.8 | 6934 | 2.5 | −47 (−49, −46) |
| Road injury | 4155 | 2.4 | 3074 | 1.1 | −52 (−55, −50) |
| Other transport injury | 342 | 0.2 | 345 | 0.1 | −35 (−44, −25) |
| Falls | 1608 | 0.9 | 1631 | 0.6 | −35 (−39, −30) |
| Drowning | 500 | 0.3 | 470 | 0.2 | −40 (−47, −32) |
| Poisonings | 197 | 0.1 | 109 | 0.0 | −65 (−72, −55) |
| Exposure to mechanical forces | 669 | 0.4 | 431 | 0.2 | −59 (−63, −53) |
| Foreign body | 428 | 0.2 | 455 | 0.2 | −32 (−40, −22) |
| Other injuries | 569 | 0.3 | 419 | 0.2 | −53 (−58, −46) |
| LMICs, 50–69 years | |||||
| All injury | 67,203 | 13.4 | 66,666 | 6.6 | −51 (−51, −50) |
| Road injury | 30,299 | 6.0 | 34,553 | 3.4 | −43 (−44, −42) |
| Other transport injury | 2561 | 0.5 | 2496 | 0.2 | −51 (−54, −49) |
| Falls | 11,770 | 2.3 | 12,300 | 1.2 | −48 (−49, −47) |
| Drowning | 5715 | 1.1 | 4467 | 0.4 | −61 (−63, −60) |
| Poisonings | 2117 | 0.4 | 1261 | 0.1 | −70 (−72, −68) |
| Exposure to mechanical forces | 4280 | 0.9 | 3586 | 0.4 | −58 (−60, −56) |
| Foreign body | 1671 | 0.3 | 1629 | 0.2 | −51 (−55, −48) |
| Other injuries | 8790 | 1.7 | 6374 | 0.6 | −64 (−65, −63) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Schwebel, D.C.; Hu, G. Disparities in Unintentional Occupational Injury Mortality between High-Income Countries and Low- and Middle-Income Countries: 1990–2016. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102296
Wu Y, Schwebel DC, Hu G. Disparities in Unintentional Occupational Injury Mortality between High-Income Countries and Low- and Middle-Income Countries: 1990–2016. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2018; 15(10):2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102296
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yue, David C. Schwebel, and Guoqing Hu. 2018. "Disparities in Unintentional Occupational Injury Mortality between High-Income Countries and Low- and Middle-Income Countries: 1990–2016" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15, no. 10: 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102296
APA StyleWu, Y., Schwebel, D. C., & Hu, G. (2018). Disparities in Unintentional Occupational Injury Mortality between High-Income Countries and Low- and Middle-Income Countries: 1990–2016. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(10), 2296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102296






