Time-Dependent Toxic and Genotoxic Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles after Long-Term and Repetitive Exposure to Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Isolation and Culture of Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
2.3. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of ZnO-NP
2.4. Genotoxicity Evaluation
2.5. Repetitive Exposure to ZnO-NP
2.6. Dependency of ZnO-NP-Induced Cytotoxicity on Early Differentiation of hMSC
2.7. Long-Term Exposure and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Particle Characterization
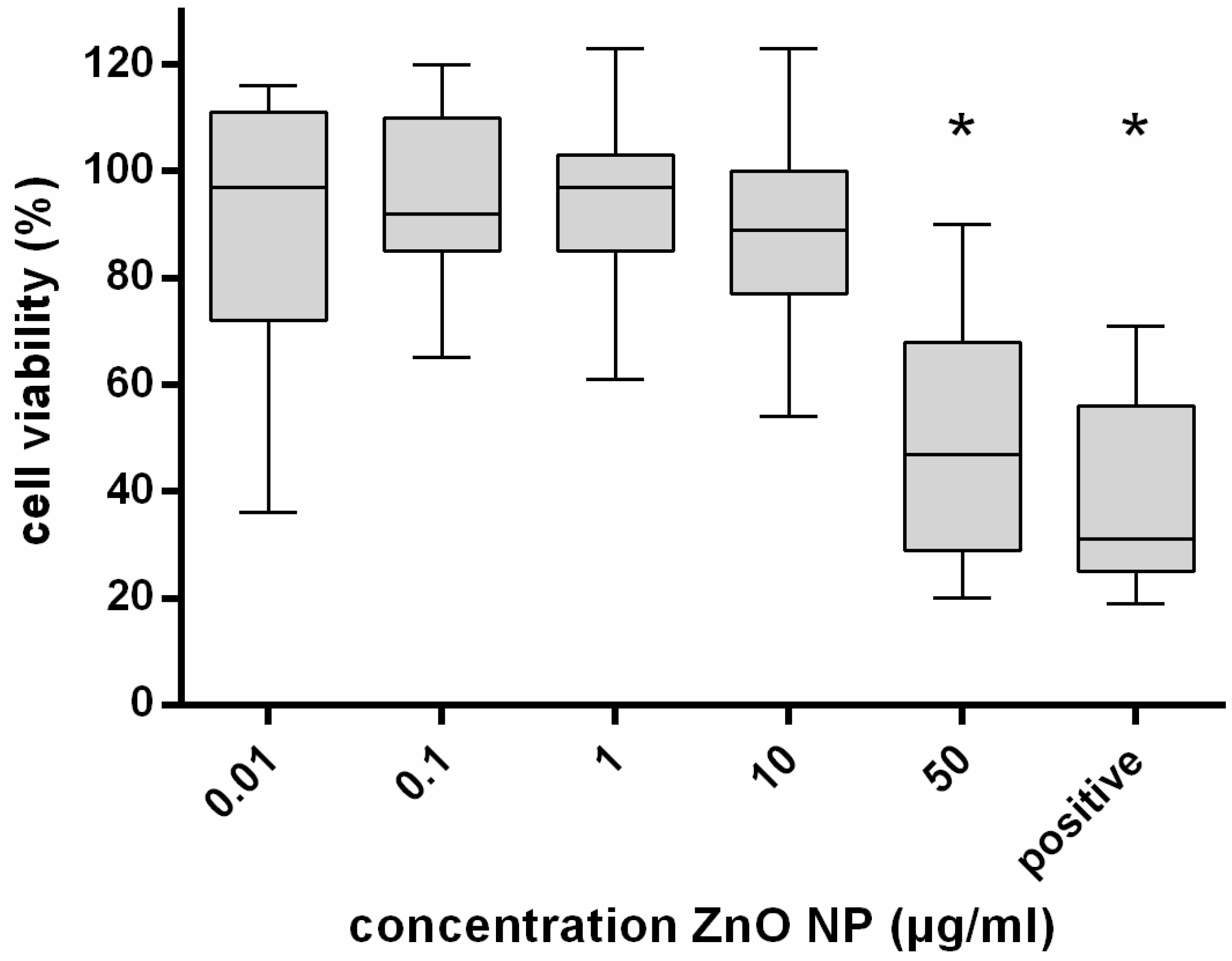
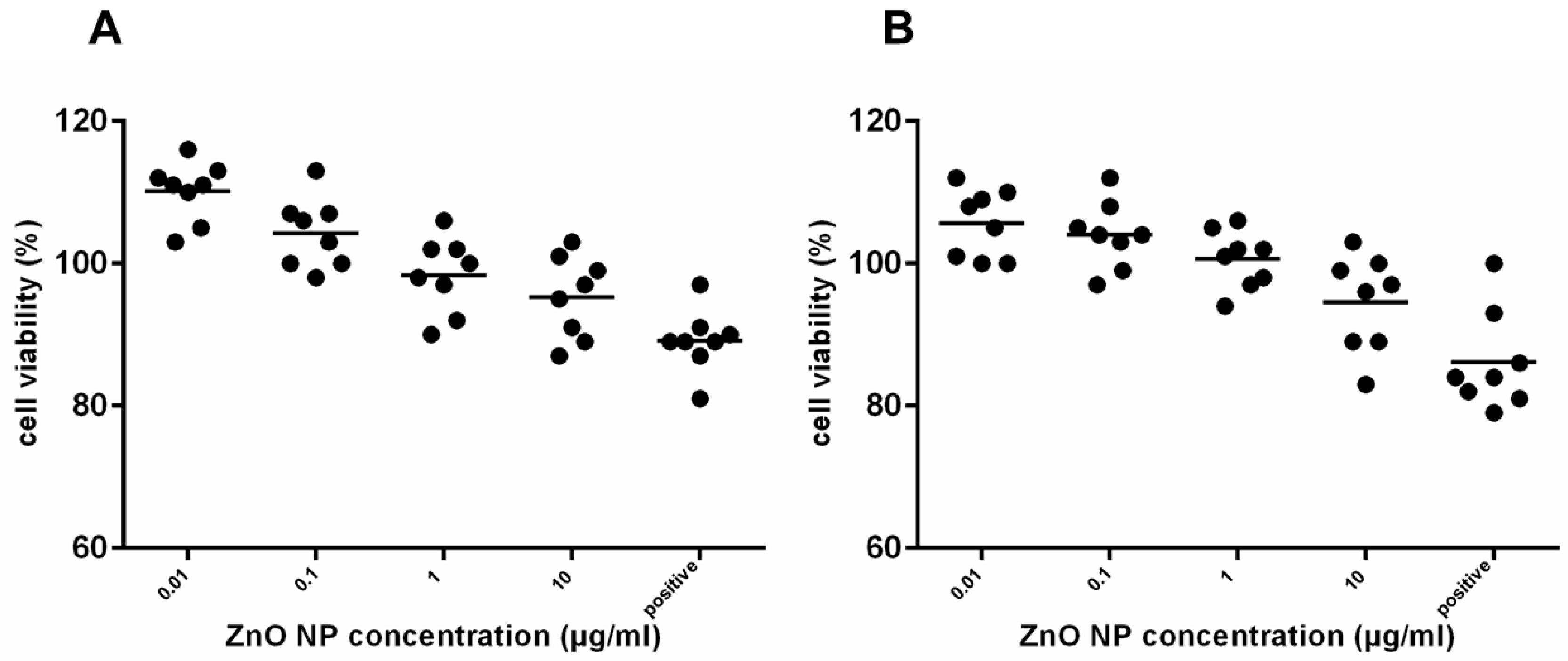
3.2. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of ZnO-NP after 24 h and Repetitive Exposure
3.3. Cytotoxicity in Partially Differentiated hMSC
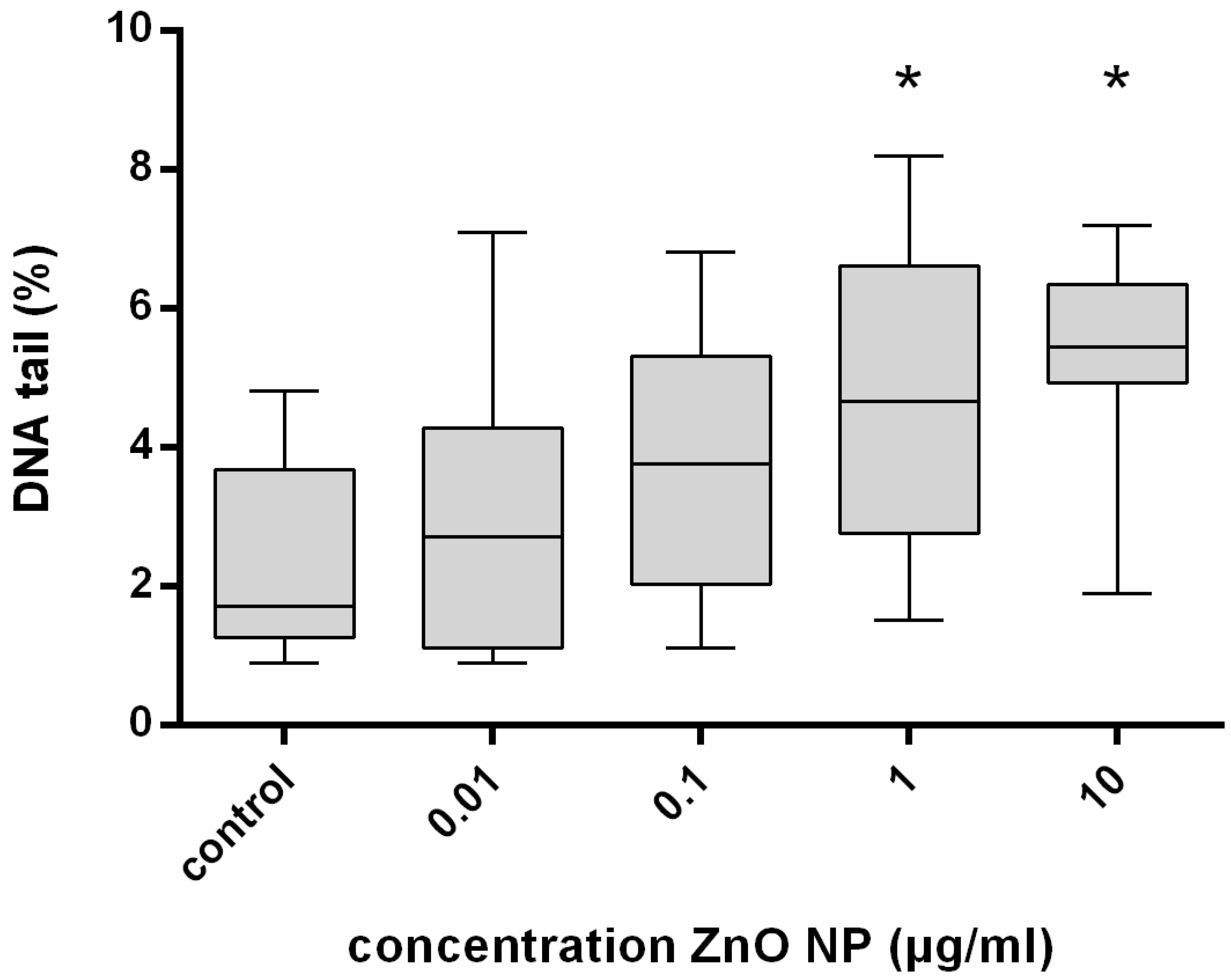
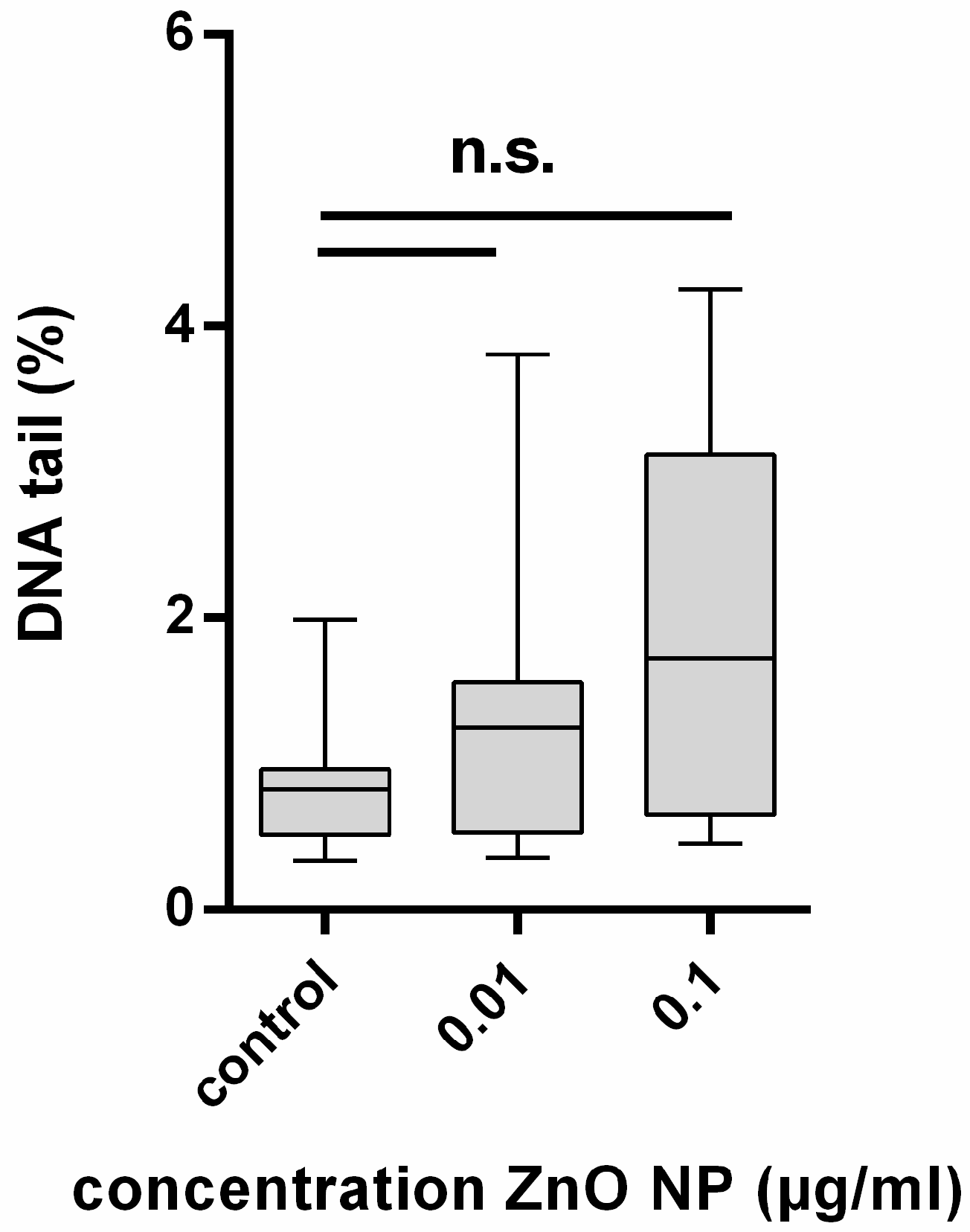
3.4. Genotoxicity Evaluation of ZnO-NP after 24 h and Repetitive Exposure
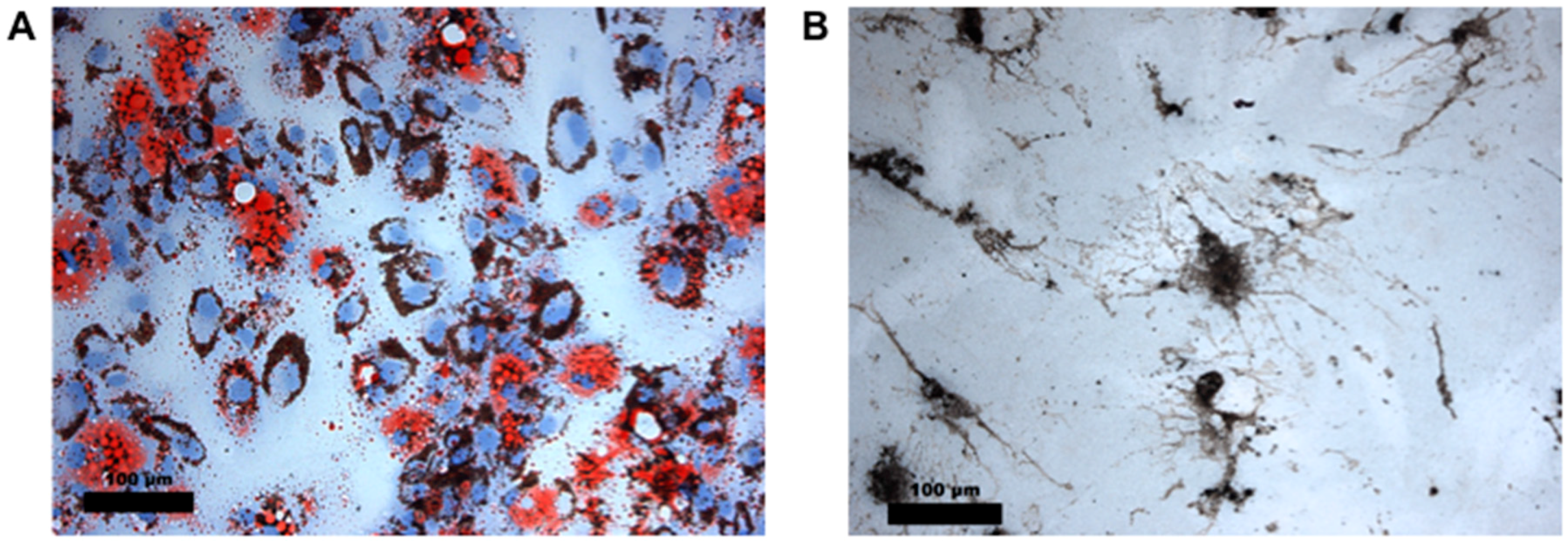
3.5. Time-Dependent Cellular Uptake and Accumulation of ZnO-NP in hMSC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasmussen, J.W.; Martinez, E.; Louka, P.; Wingett, D.G. Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.B.; Kim, Y.W.; Lim, S.K.; Roh, T.H.; Bang, D.Y.; Choi, S.M.; Lim, D.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, M.K.; et al. Risk Assessment of Zinc Oxide, a Cosmetic Ingredient Used as a Uv Filter of Sunscreens. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2017, 20, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.P.; Cruz, M.A.E.; Tovani, C.B.; Ciancaglini, P. Biomedical Applications of Nanotechnology. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, M.E.; Wang, S.Q. Current Sunscreen Controversies: A Critical Review. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2011, 27, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohynek, G.J.; Lademann, J.; Ribaud, C.; Roberts, M.S. Grey Goo on the Skin? Nanotechnology, Cosmetic and Sunscreen Safety. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2007, 37, 251–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Manshian, B.; Jenkins, G.J.; Griffiths, S.M.; Williams, P.M.; Maffeis, T.G.; Wright, C.J.; Doak, S.H. Nanogenotoxicology: The DNA Damaging Potential of Engineered Nanomaterials. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3891–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackenberg, S.; Zimmermann, F.-Z.; Scherzed, A.; Friehs, G.; Froelich, K.; Ginzkey, C.; Koehler, C.; Burghartz, M.; Hagen, R.; Kleinsasser, N. Repetitive exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles induces dna damage in human nasal mucosa mini organ cultures. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2011, 52, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froelich, K.; Mickler, J.; Steusloff, G.; Technau, A.; Ramos Tirado, M.; Scherzed, A.; Hackenberg, S.; Radeloff, A.; Hagen, R.; Kleinsasser, N. Chromosomal aberrations and deoxyribonucleic acid single-strand breaks in adipose-derived stem cells during long-term expansion in vitro. Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 767–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sadik, A.O.; El-Ansary, A.; Sabry, S.M. Nanoparticle-Labeled Stem Cells: A Novel Therapeutic Vehicle. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 2, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackenberg, S.; Scherzed, A.; Technau, A.; Froelich, K.; Hagen, R.; Kleinsasser, N. Functional Responses of Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Metal Oxide Nanoparticles In Vitro. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bihari, P.; Vippola, M.; Schultes, S.; Praetner, M.; Khandoga, A.G.; Reichel, C.A.; Coester, C.; Tuomi, T.; Rehberg, M.; Krombach, F. Optimized Dispersion of Nanoparticles for Biological In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2008, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, S.; Kessler, M.; Mandel, K.; Dembski, S.; Heuzé, K.; Hackenberg, S. Polycarboxylate ethers: The key towards non-toxic TiO2 nanoparticle stabilisation in physiological solutions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moratin, H.; Scherzad, A.; Gehrke, T.; Ickrath, P.; Radeloff, K.; Kleinsasser, N.; Hackenberg, S. Toxicological Characterization of Zno Nanoparticles in Malignant and Non-Malignant Cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.H.; Kim, B.; Choi, I.; Kim, H.; Choi, H.S.; Suh, K.; Bae, Y.C.; Jung, J.S. Characterization and Expression Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Bone Marrow and Adipose Tissue. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 14, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherzed, A.; Hackenberg, S.; Froelich, K.; Radeloff, A.; Technau, A.; Kessler, M.; Hagen, R.; Rak, K.; Koehler, C.; Kleinsasser, N. The Effect of Wound Fluid on Adipose-Derived Stem Cells In Vitro: A Study in Human Cell Materials. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2011, 17, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackenberg, S.; Scherzed, A.; Gohla, A.; Technau, A.; Froelich, K.; Ginzkey, C.; Koehler, C.; Burghartz, M.; Hagen, R.; Kleinsasser, N. Nanoparticle-induced photocatalytic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell death is associated with autophagy. Nanomedicine 2014, 9, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naha, P.C.; Davoren, M.; Lyng, F.M.; Byrne, H.J. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced cytokine production and cytotoxicity of PAMAM dendrimers in J774A.1 cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 246, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tice, R.R.; Agurell, E.; Anderson, D.; Burlinson, B.; Hartmann, A.; Kobayashi, H.; Miyamae, Y.; Rojas, E.; Ryu, J.C.; Sasaki, Y.F. Single Cell Gel/Comet Assay: Guidelines for In Vitro and In Vivo Genetic Toxicology Testing. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2000, 35, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naha, P.C.; Bhattacharya, K.; Tenuta, T.; Dawson, K.A.; Lynch, I.; Gracia, A.; Lyng, F.M.; Byrne, H.J. Intracellular localisation, geno- and cytotoxic response of polyN-isopropylacrylamide (PNIPAM) nanoparticles to human keratinocyte (HaCaT) and colon cells (SW 480). Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 198, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginzkey, C.; Stueber, T.; Friehs, G.; Koehler, C.; Hackenberg, S.; Richter, E.; Hagen, R.; Kleinsasser, N.H. Analysis of nicotine-induced DNA damage in cells of the human respiratory tract. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 208, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olive, P.L.; Durand, R.E.; le Riche, J.; Olivotto, I.A.; Jackson, S.M. Gel Electrophoresis of Individual Cells to Quantify Hypoxic Fraction in Human Breast Cancers. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pittenger, M.F.; Mackay, A.M.; Beck, S.C.; Jaiswal, R.K.; Douglas, R.; Mosca, J.D.; Moorman, M.A.; Simonetti, D.W.; Craig, S.; Marshak, D.R. Multilineage Potential of Adult Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Science 1999, 284, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Berardis, B.; Civitelli, G.; Condello, M.; Lista, P.; Pozzi, R.; Arancia, G.; Meschini, S. Exposure to ZnO nanoparticles induces oxidative stress and cytotoxicity in human colon carcinoma cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 246, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Lu, J.G. Zinc Oxide Nanostructures: Synthesis and Properties. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2005, 5, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmond, M.J.; Mccall, M.J. Zinc oxide nanoparticles in modern sunscreens: An analysis of potential exposure and hazard. Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 15–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, S.E.; Innes, B.; Roberts, M.S.; Tsuzuki, T.; Robertson, T.A.; McCormick, P. Human Skin Penetration of Sunscreen Nanoparticles: In-Vitro Assessment of a Novel Micronized Zinc Oxide Formulation. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2007, 20, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, E.; Akca, H.; Kaya, B.; Burgucu, D.; Tokgun, O.; Turna, F.; Aksakal, S.; Vales, G.; Creus, A.; Marcos, R. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Genotoxicity, Interactions with Uv-Light and Cell-Transforming Potential. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.J.; Choy, J.H. Biokinetics of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Toxicokinetics, Biological Fates, and Protein Interaction. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9 (Suppl. 2), 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Hackenberg, S.; Scherzed, A.; Technau, A.; Kessler, M.; Froelich, K.; Ginzkey, C.; Koehler, C.; Burghartz, M.; Hagen, R.; Kleinsasser, N. Cytotoxic, genotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles in human nasal mucosa cells in vitro. Toxicol. In Vitro. 2011, 25, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackenberg, S.; Scherzed, A.; Zapp, A.; Radeloff, K.; Ginzkey, C.; Gehrke, T.; Ickrath, P.; Kleinsasser, N. Genotoxic Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles in Nasal Mucosa Cells Are Antagonized by Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Mutat. Res. 2017, 816–817, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lai, F.N.; Liu, J.C.; Sun, Y.C.; Wang, J.J.; Cheng, S.F.; Zhang, X.F.; Sun, L.L.; Li, L.; et al. Cutaneous Applied Nano-Zno Reduce the Ability of Hair Follicle Stem Cells to Differentiate. Nanotoxicology 2017, 11, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orazizadeh, M.; Khodadadi, A.; Bayati, V.; Saremy, S.; Farasat, M.; Khorsandi, L. In Vitro Toxic Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Rat Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell J. 2015, 17, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Auffan, M.; Rose, J.; Wiesner, M.R.; Bottero, J.-Y. Chemical stability of metallic nanoparticles: A parameter controlling their potential cellular toxicity in vitro. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandebriel, R.J.; de Jong, W.H. A Review of Mammalian Toxicity of Zno Nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2012, 5, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ickrath, P.; Wagner, M.; Scherzad, A.; Gehrke, T.; Burghartz, M.; Hagen, R.; Radeloff, K.; Kleinsasser, N.; Hackenberg, S. Time-Dependent Toxic and Genotoxic Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles after Long-Term and Repetitive Exposure to Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121590
Ickrath P, Wagner M, Scherzad A, Gehrke T, Burghartz M, Hagen R, Radeloff K, Kleinsasser N, Hackenberg S. Time-Dependent Toxic and Genotoxic Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles after Long-Term and Repetitive Exposure to Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(12):1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121590
Chicago/Turabian StyleIckrath, Pascal, Martin Wagner, Agmal Scherzad, Thomas Gehrke, Marc Burghartz, Rudolf Hagen, Katrin Radeloff, Norbert Kleinsasser, and Stephan Hackenberg. 2017. "Time-Dependent Toxic and Genotoxic Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles after Long-Term and Repetitive Exposure to Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 12: 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121590
APA StyleIckrath, P., Wagner, M., Scherzad, A., Gehrke, T., Burghartz, M., Hagen, R., Radeloff, K., Kleinsasser, N., & Hackenberg, S. (2017). Time-Dependent Toxic and Genotoxic Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles after Long-Term and Repetitive Exposure to Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(12), 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14121590




