Epidemiologic Features of Enterovirus 71-Associated Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease from 2009 to 2013 in Zhejiang, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Case Definitions
2.3. Reported EV71-Associated HFMD
2.4. Data Resources and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Severe and Fatal EV71-associated HFMD Cases
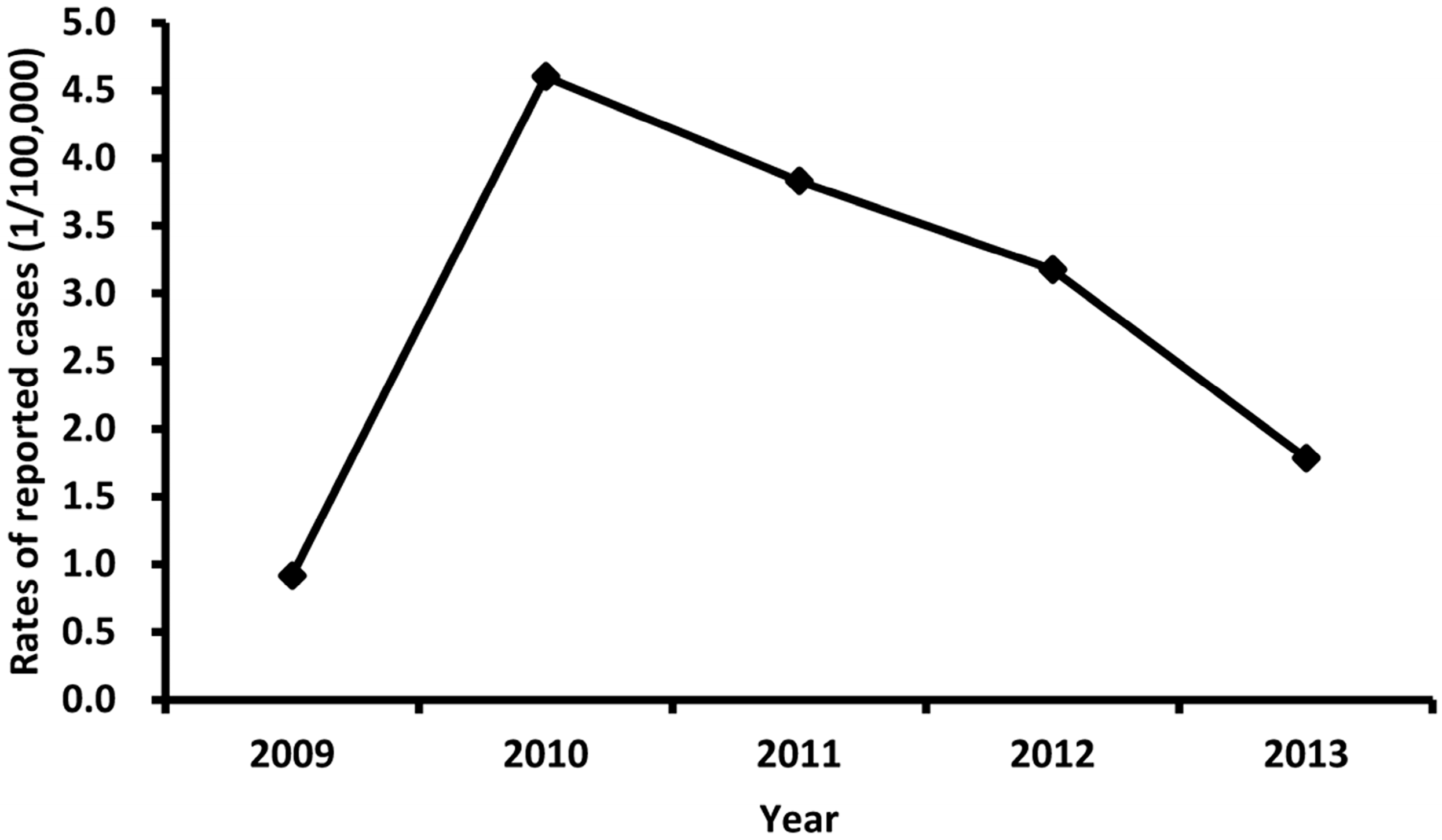
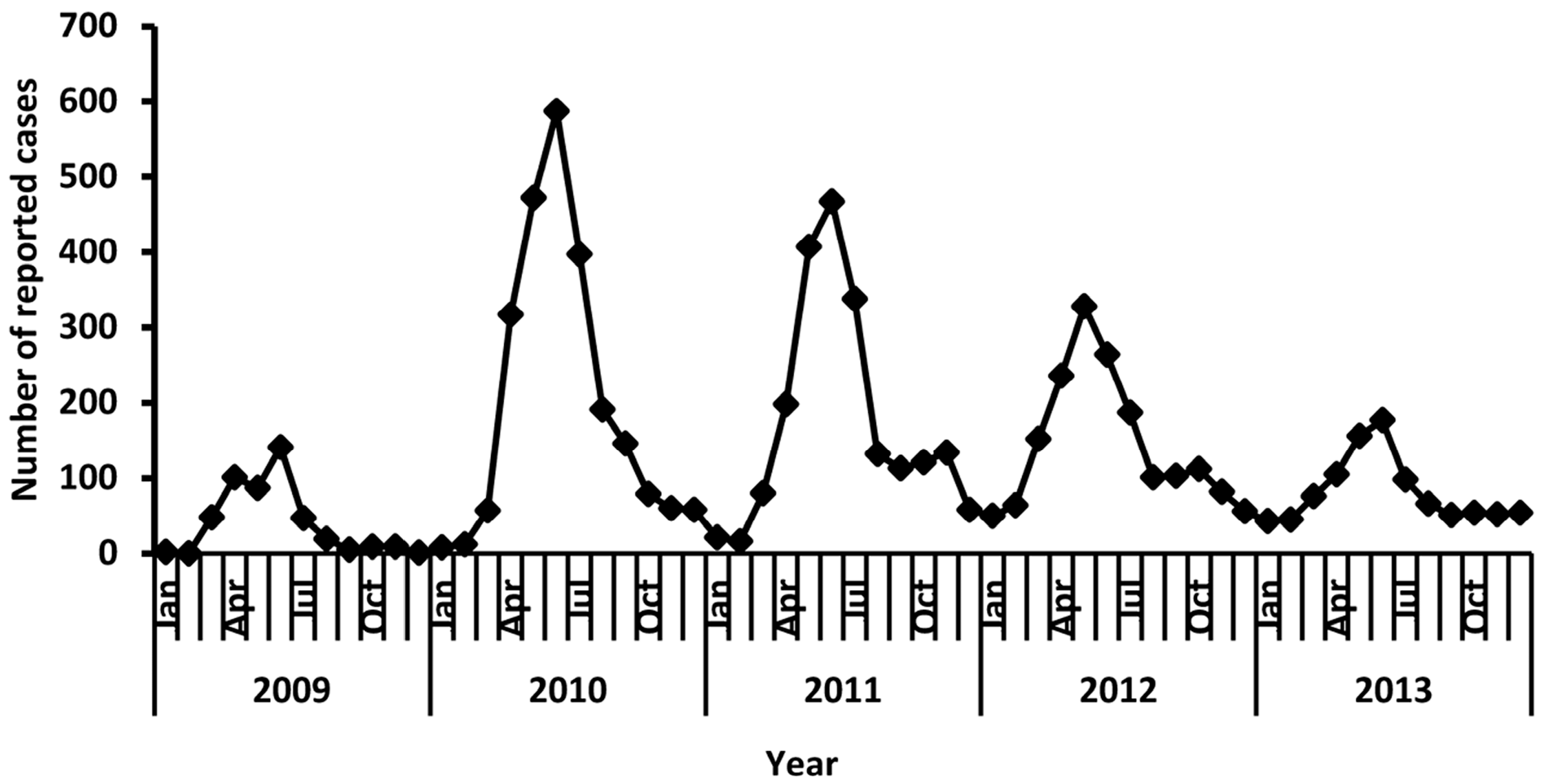
3.2. Description of Overall Trends of EV71-Associated HFMD
3.3. Age Distribution
3.4. Gender Distribution
3.5. Occupational Distribution
3.6. Seasonal Distribution
3.7. Geographic Distribution
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EV71 | enterovirus 71 |
| HFMD | hand-foot-and-mouthdisease |
| NNDRS | national notifiable disease reporting system |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| SPSS | statistical package for the social sciences |
References
- McMinn, P.; Lindsay, K.; Perera, D.; Chan, H.M.; Chan, K.P.; Cardosa, M.J. Phylogenetic analysis of enterovirus 71 strains isolated during linked epidemics in Malaysia, Singapore, and Western Australia. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 7732–7738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.R.; Tuan, Y.C.; Tsai, H.P.; Yan, J.J.; Liu, C.C.; Su, I.J. Change of major genotype of enterovirus 71 in outbreaks of hand-foot-mouth disease in Taiwan between 1998 and 2000. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatproedprai, S.; Theanboonlers, A.; Korkong, S.; Thongmee, C.; Wananukul, S.; Poovorawan, Y. Clinical and molecular characterization of hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Thailand, 2008–2009. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 63, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tu, P.V.; Thao, N.T.; Perera, D.; Huu, T.K.; Tien, N.T.; Thuong, T.C.; How, O.M.; Cardosa, M.J.; McMinn, P.C. Epidemiologic and virologic investigation of hand-foot-and-mouth disease, southern Vietnam, 2005. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.D.; Hu, S.X.; Zhang, H.; Luo, K.W.; Liu, Y.Z.; Xu, Q.H.; Huang, W.; Deng, Z.H.; Zhou, S.F.; Liu, F.Q.; et al. Correlation analysis of EV71 detection and case severity in hand-foot-and-mouth disease in Hunan province of China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease: Signs and Symptoms. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/hand-foot-mouth/about/signs-symptoms.html (accessed on 19 November 2014).
- Xing, W.J.; Liao, Q.H.; Viboud, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.L.; Wu, J.T.; Chang, Z.R.; Liu, F.F.; Fang, V.J.; Zheng, Y.D.; et al. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease in China, 2008–2012: An epidemiological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.K.; Zhou, Z.M.; Zhang, X.P.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, S.B. Analysis on epidemic situation and control of HFMD in childcare settings. Chin. Rural Health Serv. Admin. 2011, 31, 681–689. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.C.; Meng, F.Y.; Li, J.X.; Mao, Q.Y.; Tao, H.; Zhang, Y.T.; Yao, X.; Chu, K.; Chen, Q.H.; Hu, Y.M.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and immunology of an inactivated alum-adjuvant enterovirus 71 in children in China: A multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 2024–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwa, S.H.; Lee, Y.A.; Brewoo, J.N.; Partidos, C.D.; Osorio, J.E. Preclinical evaluation of the immunogenicity and safety of an inactivated enterovirus 71 candidate vaccine. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.C.; Liu, L.D.; Mo, Z.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Xia, J.L.; Liang, Z.L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.P.; Mao, Q.Y.; Wang, J.J.; et al. An inactivated enterovirus 71 vaccine in healthy children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.C.; Xu, W.B.; Xia, J.L.; Liang, Z.L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Tan, X.J.; Wang, L.; Mao, Q.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of an enterovirus 71 vaccine in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistical Review Reports between 2009 and 2013. Available online: http://www.zj.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/tjnj/ (accessed on 16 December 2016).
- Naing, N.N. Easy way to learn standardization: Direct and indirect methods. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2000, 7, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ho, M. Enterovirus 71: The virus, its infections and outbreaks. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2000, 33, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sadeharju, K.; Knip, M.; Virtanen, S.M.; Savilahti, E.; Tauriainen, S.; Koskela, P.; Akerblom, H.K.; Hyoty, H.; Finnish TRIGR Study Group. Maternal antibodies in breast milk protect the child from enterovirus infections. Pediatrics 2007, 119, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witso, E.; Cinek, O.; Aldrin, M.; Grinde, B.; Rasmussen, T.; Wetlesen, T.; Ronningen, K.S. Predictors of sub-clinical enterovirus infections in infants: A prospective cohort study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.C.; Liang, Z.L.; Meng, F.Y.; Zeng, Y.; Mao, Q.Y.; Chu, K.; Song, X.F.; Yao, X.; Li, J.X.; Ji, H.; et al. Retrospective study of the incidence of HFMD and seroepidemiology of antibodies against EV71 and CoxA16 in prenatal women and their infants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, M.Y.; Chiang, P.S.; Chung, W.Y.; Luo, S.T.; Lee, M.S. Epidemiology of enterovirus 71 infections in Taiwan. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2014, 55, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.G.; Yang, Z.C.; Liu, X.Y.; Kang, Y.; Wang, M. Hand-food-and-mouth disease epidemiological status and relationship with meteorological variables in Guangzhou, southern China, 2008–2012. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2014, 56, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.X.; Wang, H.C.; Wang, Q.Z.; Xin, Q.H.; Lin, H.L. The effect of meteorological factors on adolescent hand-foot-and-mouth disease and associated effect modifiers. Glob. Health Act. 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yan, Y.S.; Hong, R.T.; Wang, L.L. Preliminary study on reccurance with viruses causing hand foot and mouth disease. Dis. Surveill. 2013, 28, 735–739. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.D.; Zeng, D.J.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zheng, X.L.; Wang, F.Y. An epidemiological analysis of the Beijing 2008 Hand-Foot-Mouth epidemic. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.B.; Kasri, A.R. Hand foot and mouth disease due to enterovirus 71 in Malaysia. Virol. Sin. 2011, 26, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.W.; Hus, Y.W.; Smith, D.J.; Kiang, D.; Tsai, H.P.; Lin, K.H.; Wang, S.M.; Liu, C.C.; Su, I.J. Reemergence of Enterovirus 71 in 2008 in Taiwan: Dynamics of genetic and antigenic evolution from 1998 to 2008. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 3653–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.J. Epidemiology of hand-foot-and-mouth disease in China, 2008. Dis. Surveill. 2010, 25, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.L.; Zou, H.; Wang, Q.Z.; Liu, C.X.; Lang, L.L.; Hou, X.X.; Li, Z.J. Short-term effect of EI Nino-southern oscillation on pediatric hand, foot and mouth disease in Shenzhen, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 65585. [Google Scholar]
- Hii, Y.L.; Rocklov, J.; Ng, N. Short term effects of weather on hand, foot and mouth disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 16796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ooi, M.H.; Wong, S.C.; Podin, Y.; Akin, W.; Sel, S.; Mohan, A.; Chieng, C.H.; Perera, D.; Clear, D.; Wong, D.; et al. Human enterovirus 71 disease in Sarawak, Malaysia: A prospective clinical, virological, and molecular epidemiological study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Age Group | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2009–2013 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Months) | N | R | N | R | N | R | N | R | N | R | N | R |
| 0–11 | 62 | 10 | 388 | 62.5 | 219 | 46.4 | 158 | 35.9 | 94 | 21.7 | 921 | 35.6 |
| 12–23 | 123 | 20 | 642 | 104.0 | 625 | 133.2 | 521 | 105.2 | 304 | 62.2 | 2215 | 82.5 |
| 24–35 | 111 | 17.9 | 547 | 88.3 | 493 | 104.8 | 401 | 80.9 | 215 | 44.1 | 1767 | 65.6 |
| 36–47 | 88 | 14.2 | 375 | 60.9 | 398 | 85.1 | 320 | 65.5 | 183 | 38.1 | 1364 | 51.1 |
| 48–59 | 47 | 7.5 | 236 | 38.1 | 168 | 35.7 | 170 | 34.8 | 106 | 22.1 | 727 | 27.1 |
| 60–71 | 16 | 2.5 | 114 | 18.1 | 92 | 19.3 | 92 | 20.4 | 37 | 8.4 | 351 | 13.3 |
| ≥72 | 22 | 0.1 | 82 | 0.2 | 90 | 0.2 | 73 | 0.1 | 38 | 0.1 | 305 | 0.1 |
| Year | Male | Female | Ratio (Male/Female) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | R | N | R | ||
| 2009 | 297 | 1.1 | 172 | 0.7 | 1.7 |
| 2010 | 1497 | 5.7 | 887 | 3.5 | 1.6 |
| 2011 | 1318 | 4.7 | 767 | 2.9 | 1.6 |
| 2012 | 1098 | 3.9 | 637 | 2.4 | 1.6 |
| 2013 | 584 | 2.1 | 393 | 1.5 | 1.4 |
| Total | 4794 | 3.5 | 2856 | 2.2 | 1.6 |
| Occupation | 2009 (%) | 2010 (%) | 2011 (%) | 2012 (%) | 2013 (%) | 2009–2013 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scattered children | 286 (61.0) | 1617 (67.8) | 1451 (69.6) | 1195 (68.9) | 675 (69.10) | 5224 (68.3) |
| Preschool children | 166 (35.4) | 724 (30.4) | 584 (28.0) | 504 (29.0) | 278 (28.5) | 2256 (29.5) |
| School children | 16 (3.4) | 40 (1.7) | 42 (2.0) | 33 (1.9) | 24 (2.5) | 155 (2.0) |
| Others | 1 (0.2) | 3 (0.1) | 8 (0.4) | 3 (0.2) | 0 (0) | 15 (0.2) |
| Total | 469 (100) | 2384 (100) | 2085 (100) | 1735 (100) | 977 (100) | 7650 (100) |
| City | Population/km2 | Reported Cases/km2 * |
|---|---|---|
| Wenzhou | 773.98 | 0.17 |
| Ningbo | 774.83 | 0.16 |
| Jiaxing | 1149.85 | 0.14 |
| Zhoushan | 778.65 | 0.11 |
| Shaoxing | 594.99 | 0.06 |
| Huzhou | 497.17 | 0.06 |
| Taizhou | 634.24 | 0.05 |
| Quzhou | 239.98 | 0.04 |
| Jinhua | 4900 | 0.04 |
| Hangzhou | 524.25 | 0.04 |
| Lishui | 122.38 | 0.03 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Lv, H.; Zhu, W.; Mo, Z.; Mao, G.; Wang, X.; Lou, X.; Chen, Y. Epidemiologic Features of Enterovirus 71-Associated Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease from 2009 to 2013 in Zhejiang, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010033
Wang Z, Lv H, Zhu W, Mo Z, Mao G, Wang X, Lou X, Chen Y. Epidemiologic Features of Enterovirus 71-Associated Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease from 2009 to 2013 in Zhejiang, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2017; 14(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010033
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhifang, Huakun Lv, Wenming Zhu, Zhe Mo, Guangming Mao, Xiaofeng Wang, Xiaoming Lou, and Yongdi Chen. 2017. "Epidemiologic Features of Enterovirus 71-Associated Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease from 2009 to 2013 in Zhejiang, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 14, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010033
APA StyleWang, Z., Lv, H., Zhu, W., Mo, Z., Mao, G., Wang, X., Lou, X., & Chen, Y. (2017). Epidemiologic Features of Enterovirus 71-Associated Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease from 2009 to 2013 in Zhejiang, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010033





