Investigation of E. coli and Virus Reductions Using Replicate, Bench-Scale Biosand Filter Columns and Two Filter Media
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Column Design, Preparation and Operation
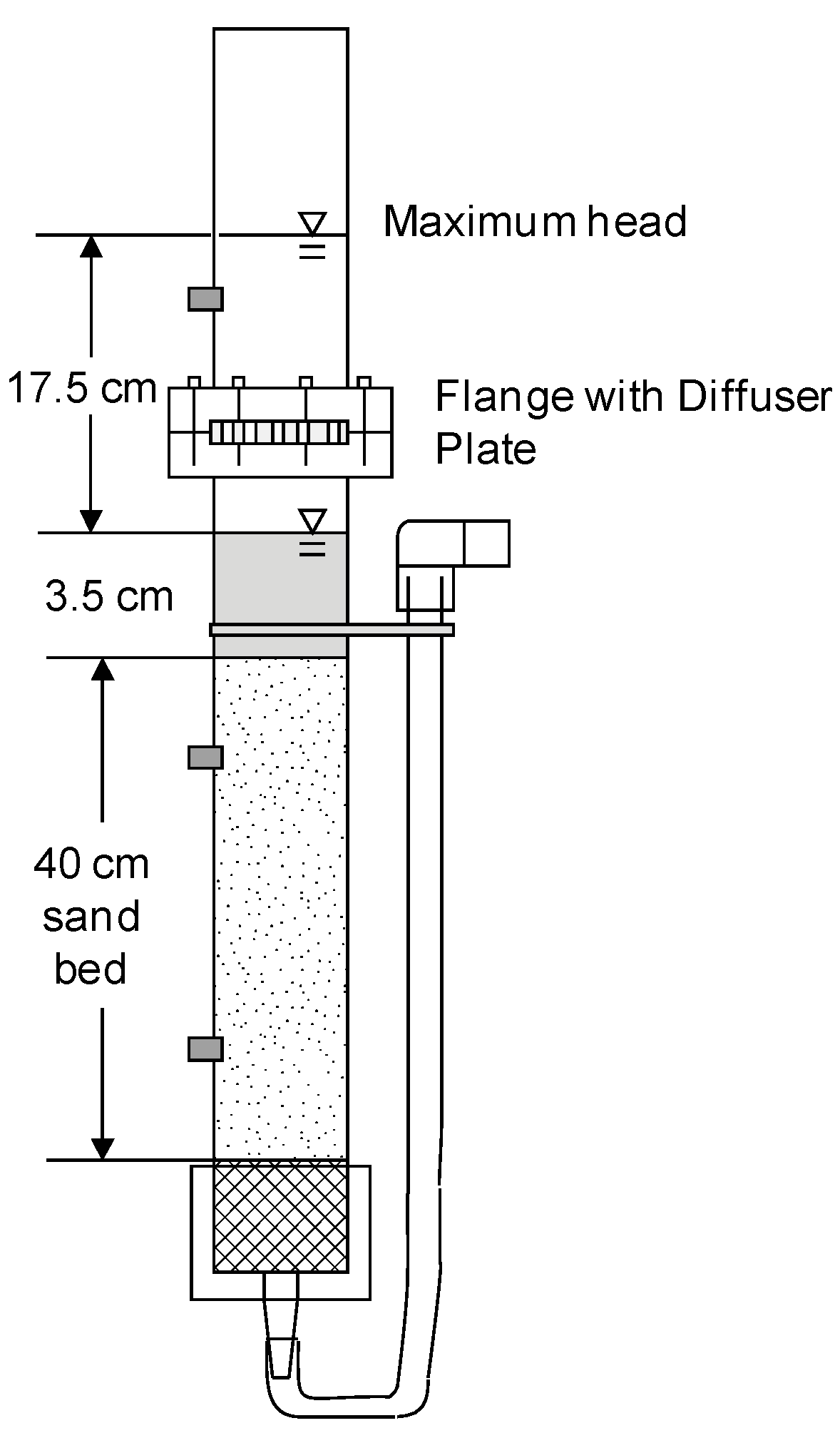
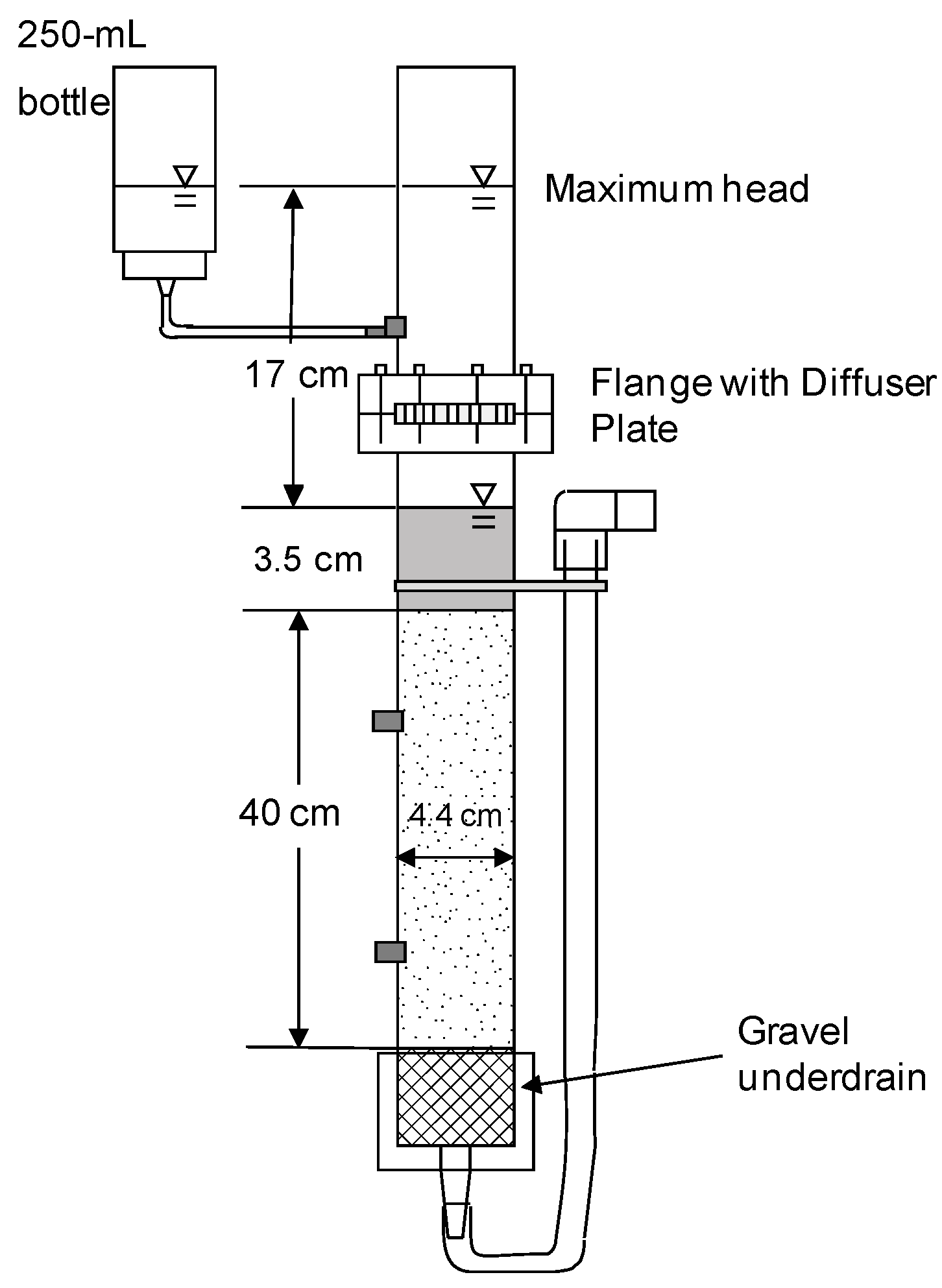
| Experiment Coding | Columns Backwashed | External Reservoir | Daily Charge Volume (mL) | Charge-to-Pore Volume Ratio | Daily Charge Aliquots | Maximum Head (cm) | Media Depth (cm) | Diffuser to Standing Water (cm) | Standing Water (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column Test No. 1 | No | No | 430 | 1.3:1 | 2 | 17 | 40 | 2 | 3.5 |
| Column Test No. 2 | Yes | Yes | 450 | 1.3:1 | 1 | 17.5 | 40 | 2 | 3.5 |
2.2. Tracer Tests
2.3. Feed Water for Microbial Challenge Studies
| Experiment Coding | Length (Days) | Source Water* | Pasteurized PE ** | E. coli B log10 | MS2 log10 | PRD-1 log10 | Echovirus 12 log10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column Test No. 1 | 54 | Cane Creek | 1.0% | 2.9 ± 1.1 | 3.5 ± 0.9 | - | 3.6 ± 1.1 |
| Column Test No. 2 | 56 | Cane Creek | 2.5% | 2.8 ± 1.3 | 2.8 ± 0.3 | 3.1 ± 0.7 | - |
2.4. Microbial Methods and Virus Characteristics
| Virus/Phage | Size (nm) | Isoelectric Point | Genetic Material |
|---|---|---|---|
| MS2 | 26 | 3.5–3.9 | ss-RNA |
| PRD-1 | 62 | 4.2 | ds-DNA |
| Echovirus 12 | 28–30 | 5.0–6.4 * | ss-RNA |
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
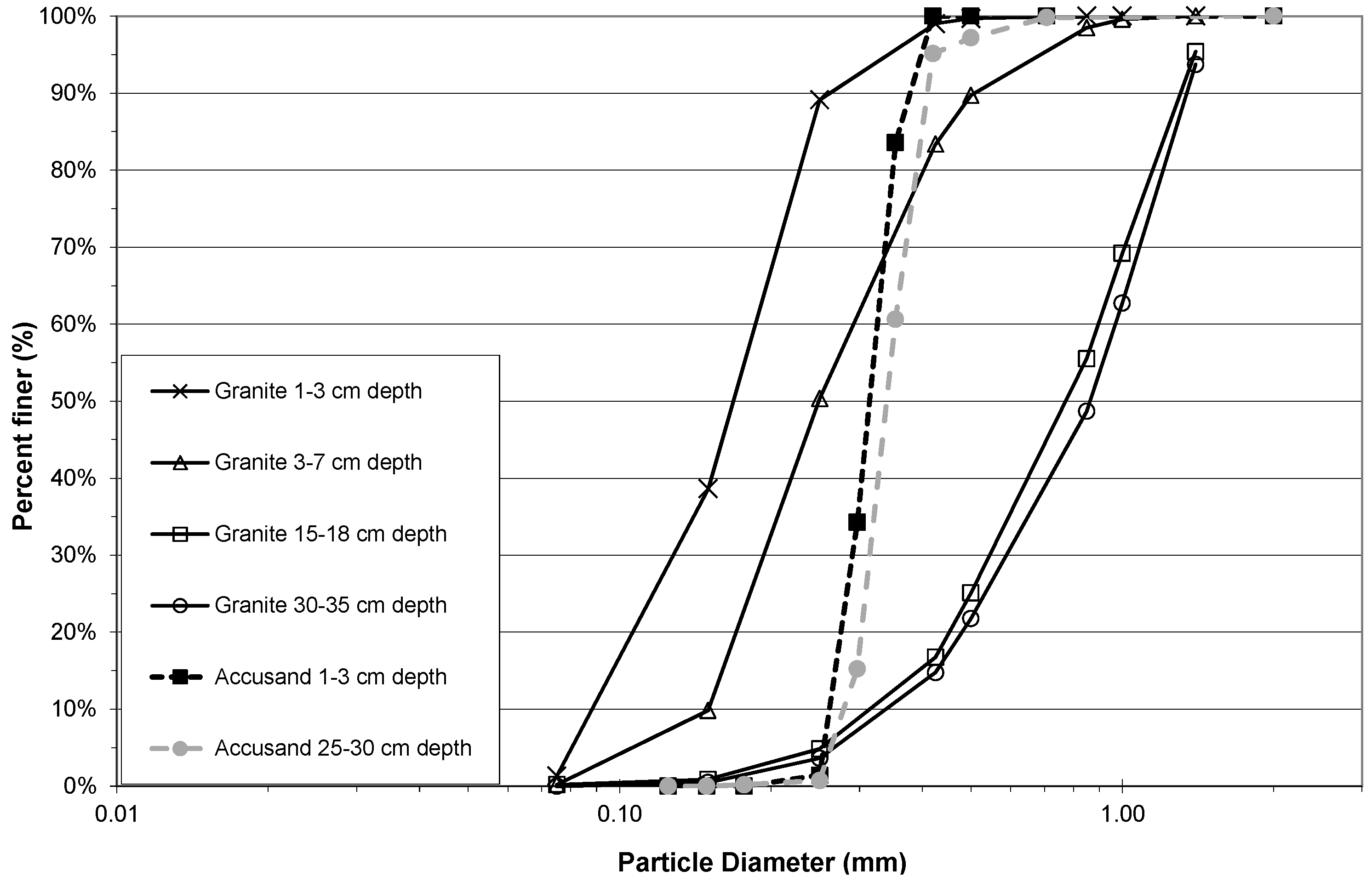
3.1. Comparison of Filter Media Characteristics
| Granite (mg/kg) | Accusand (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium (Ca) | 12,270 | 90 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 14,875 | 60 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 920 | 0 |
| Iron (Fe) | 23,250 | 55 |
| Aluminum (Al) | 17.03 | 90 |
3.2. Effects of Backwashing on Grain Size Distribution and Hydraulic Characteristics
| Replicate | ||
|---|---|---|
| Columns in | Column | Column |
| Each Test | Test No. 1 | Test No. 2 |
| Granite #1 | 1.31 | 2.24 |
| Granite #2 | 1.31 | 2.66 |
| Granite #3 | 1.29 | 3.10 |
| Accusand #1 | 1.16 | 1.19 |
| Accusand #2 | 1.22 | 1.36 |
| Accusand #3 | 1.16 | 1.25 |
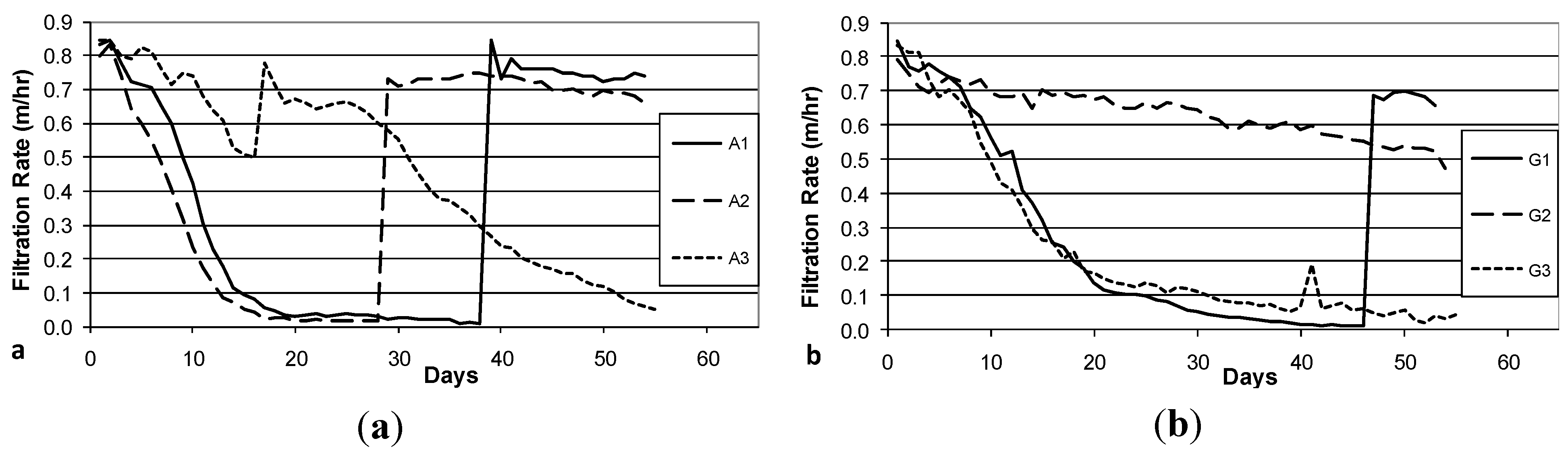
3.3. Decline in Filtration Rate with Filter Operation
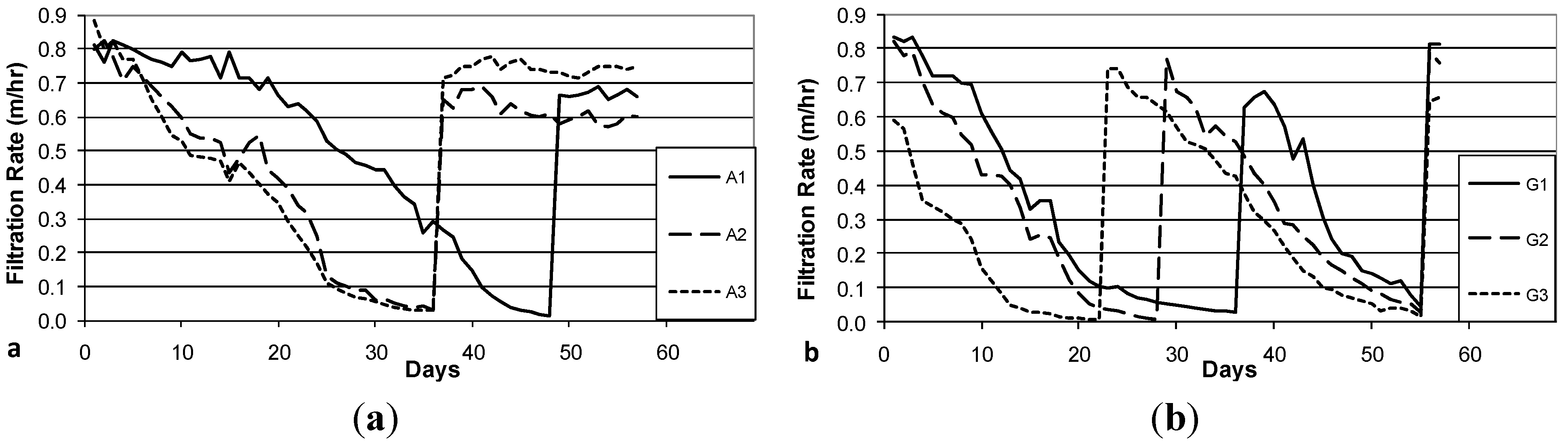
3.4. Reductions in Challenge E. coli
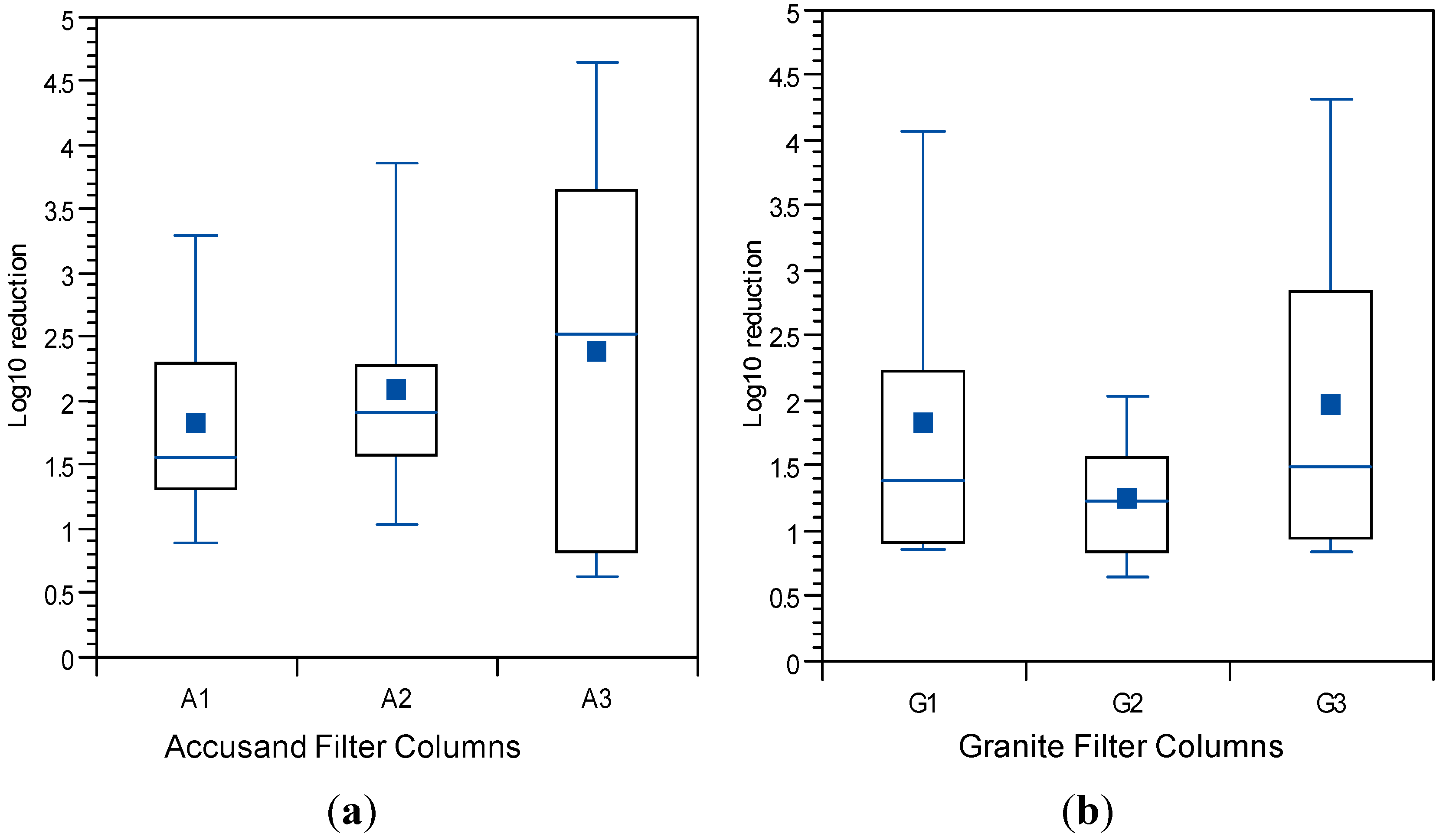
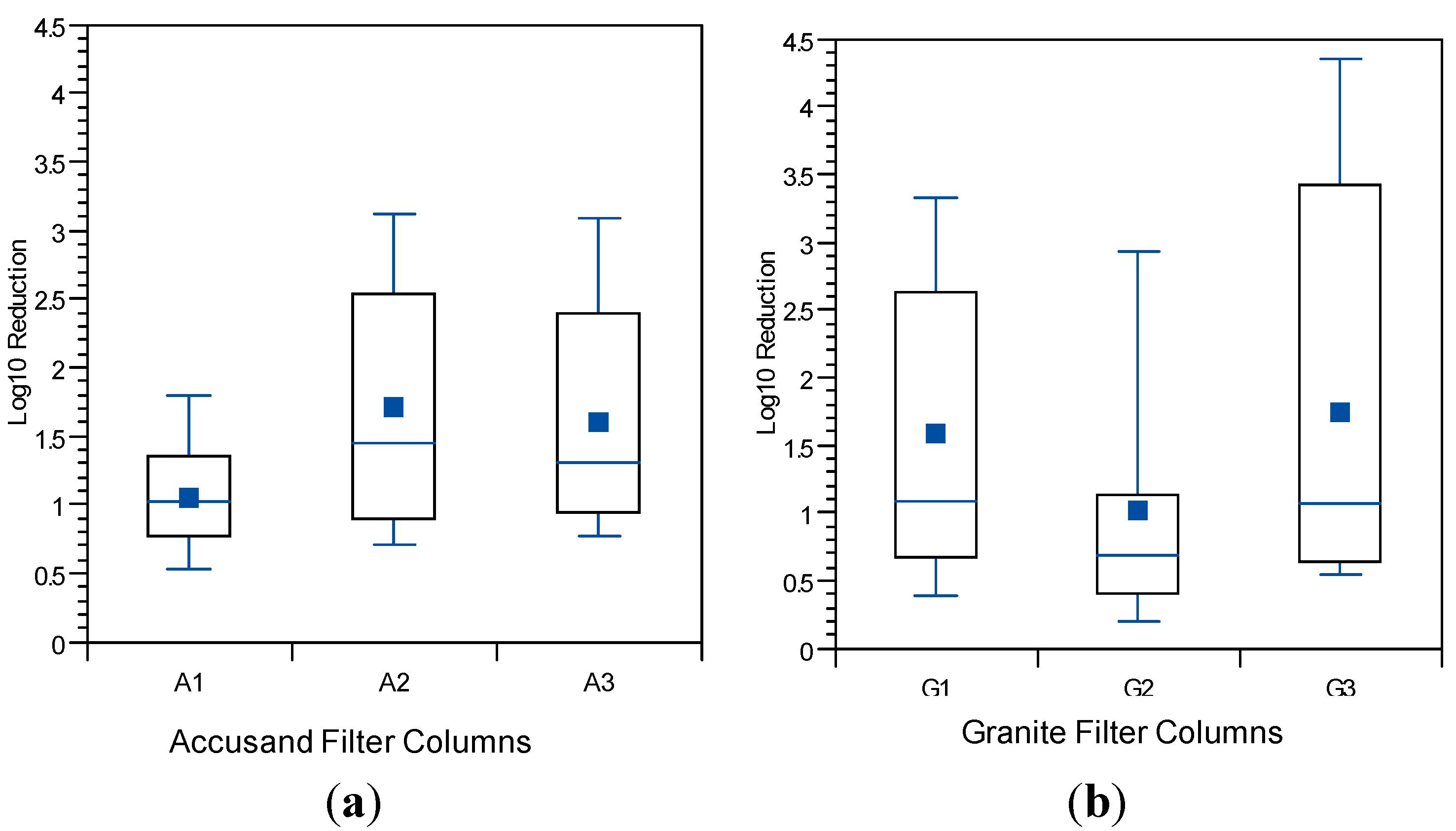
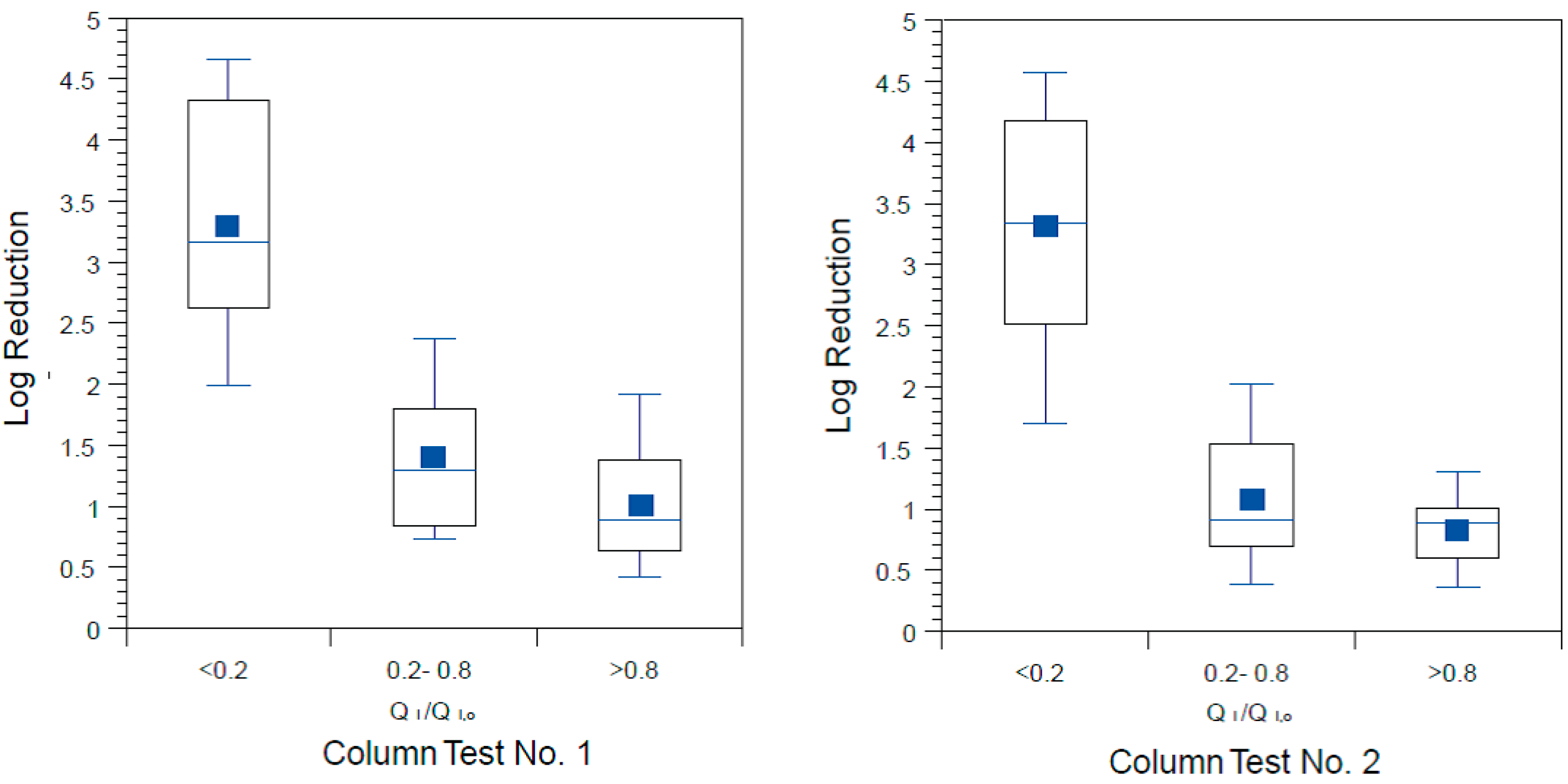
3.5. Reductions in Challenge Viruses

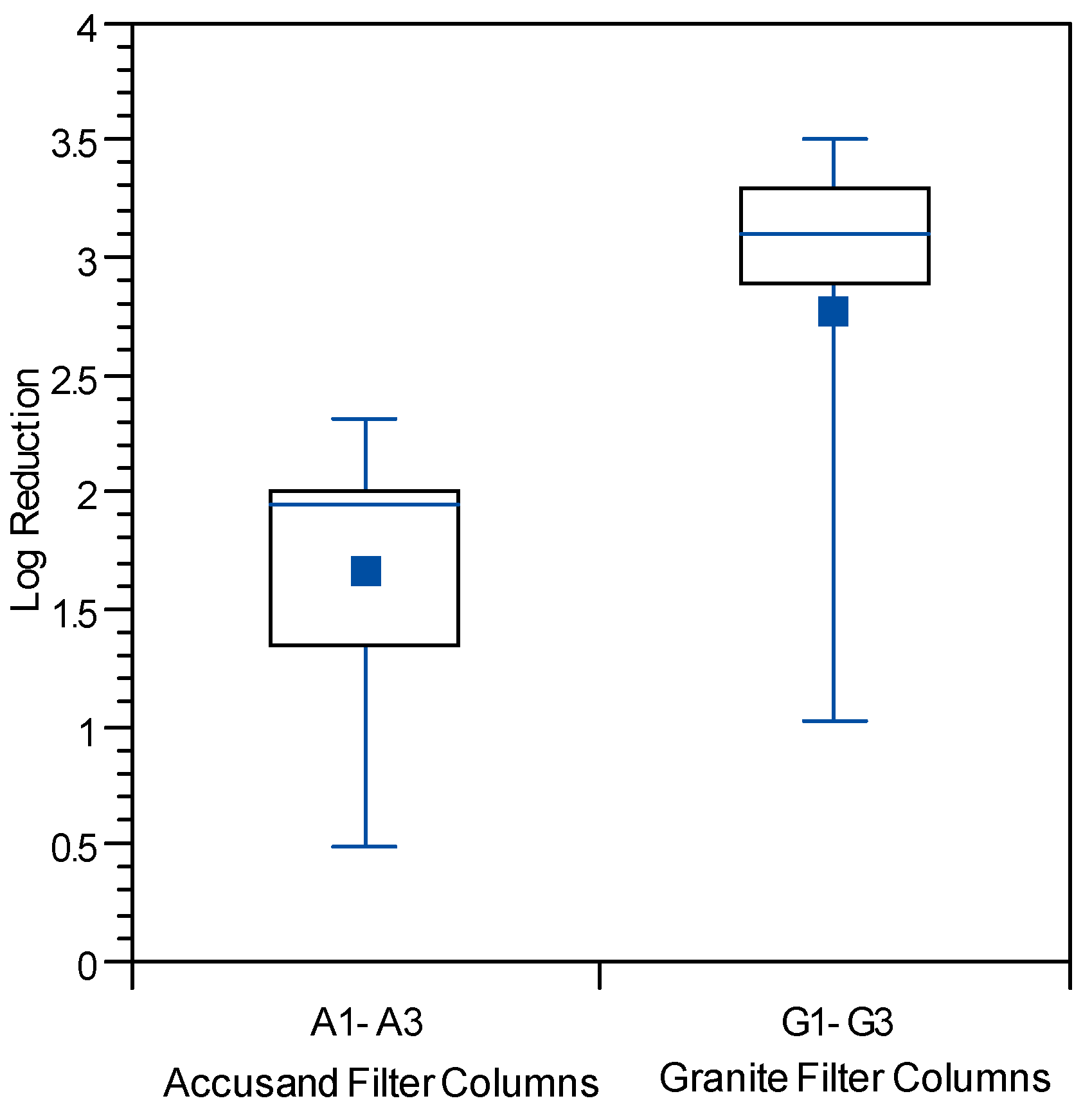
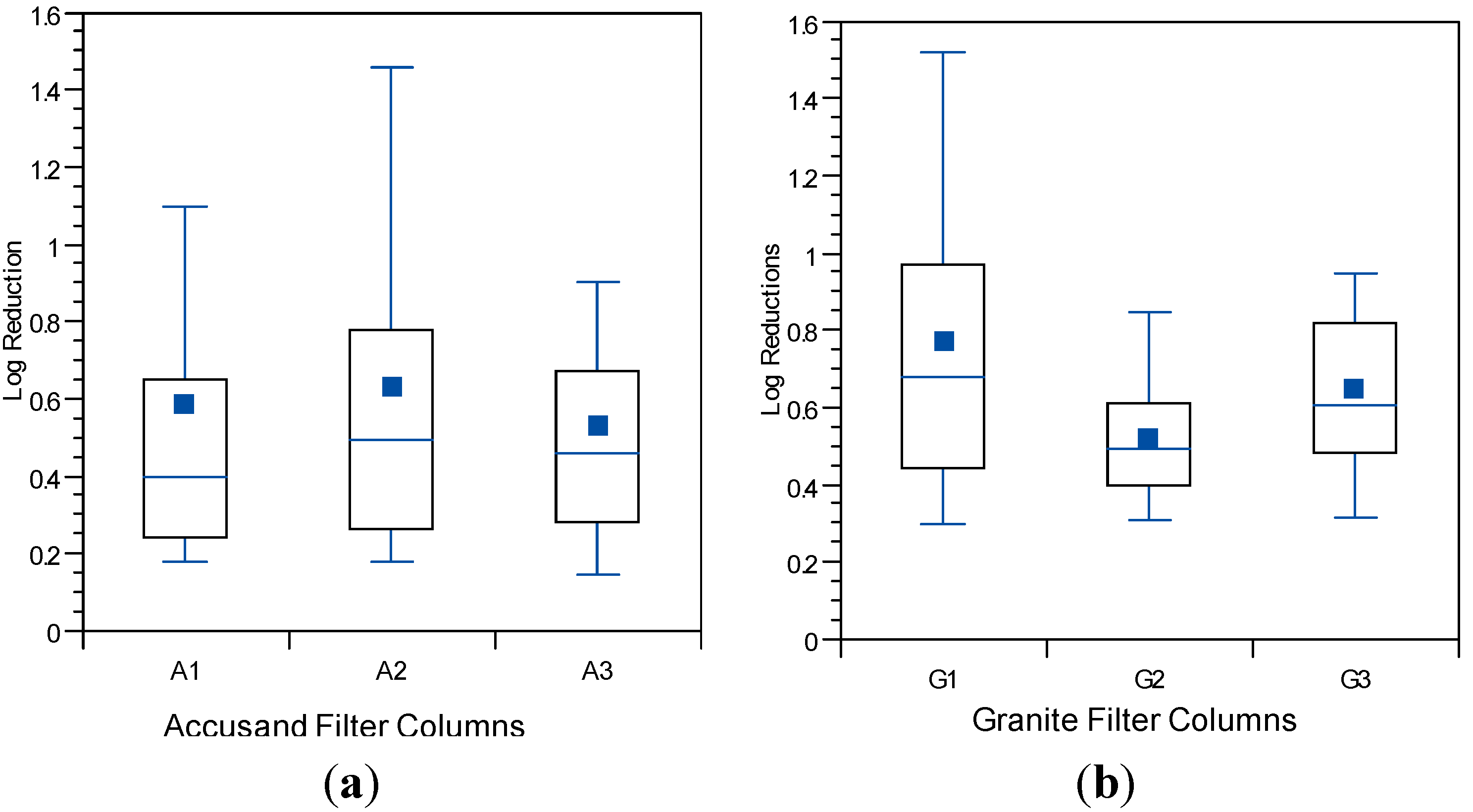
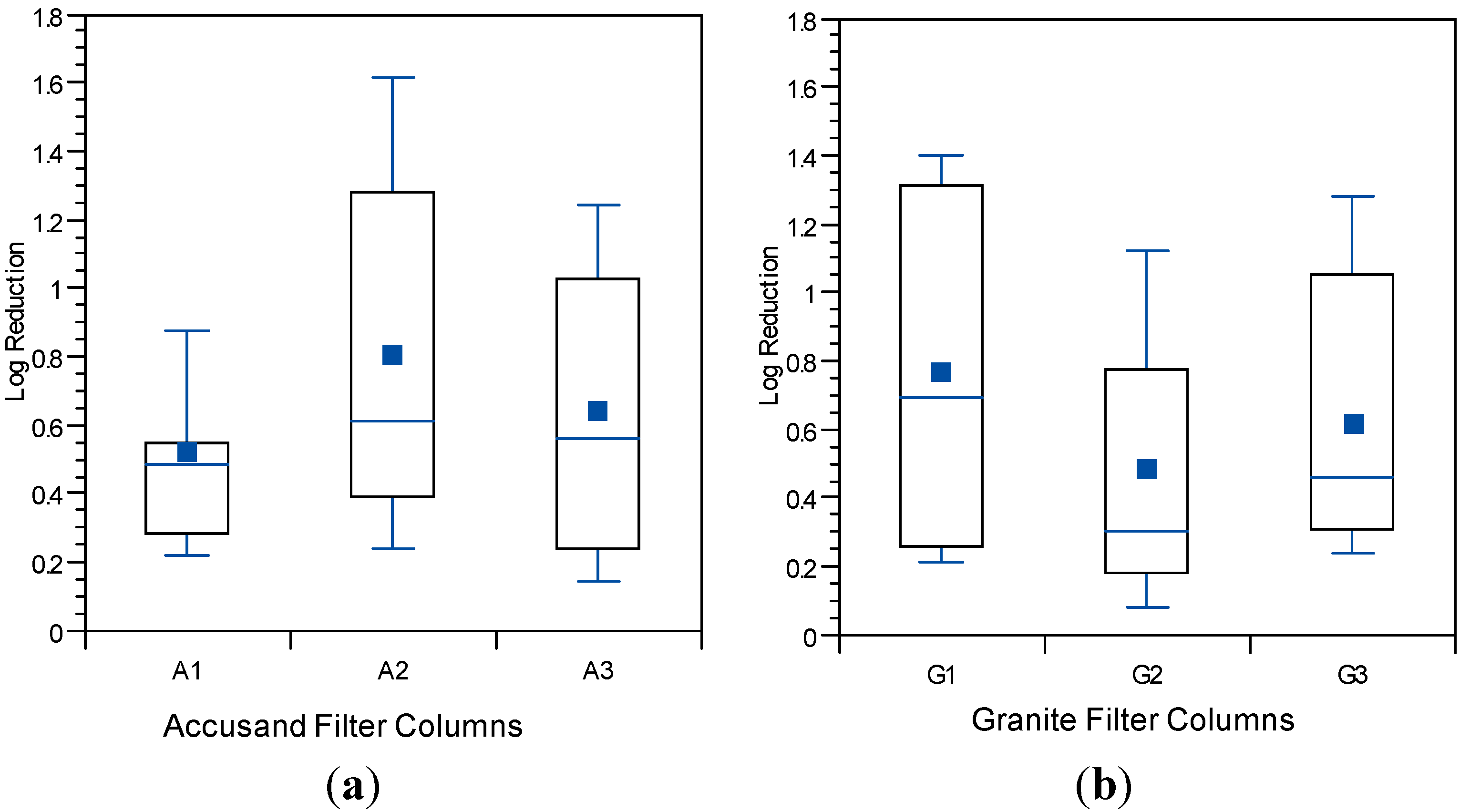
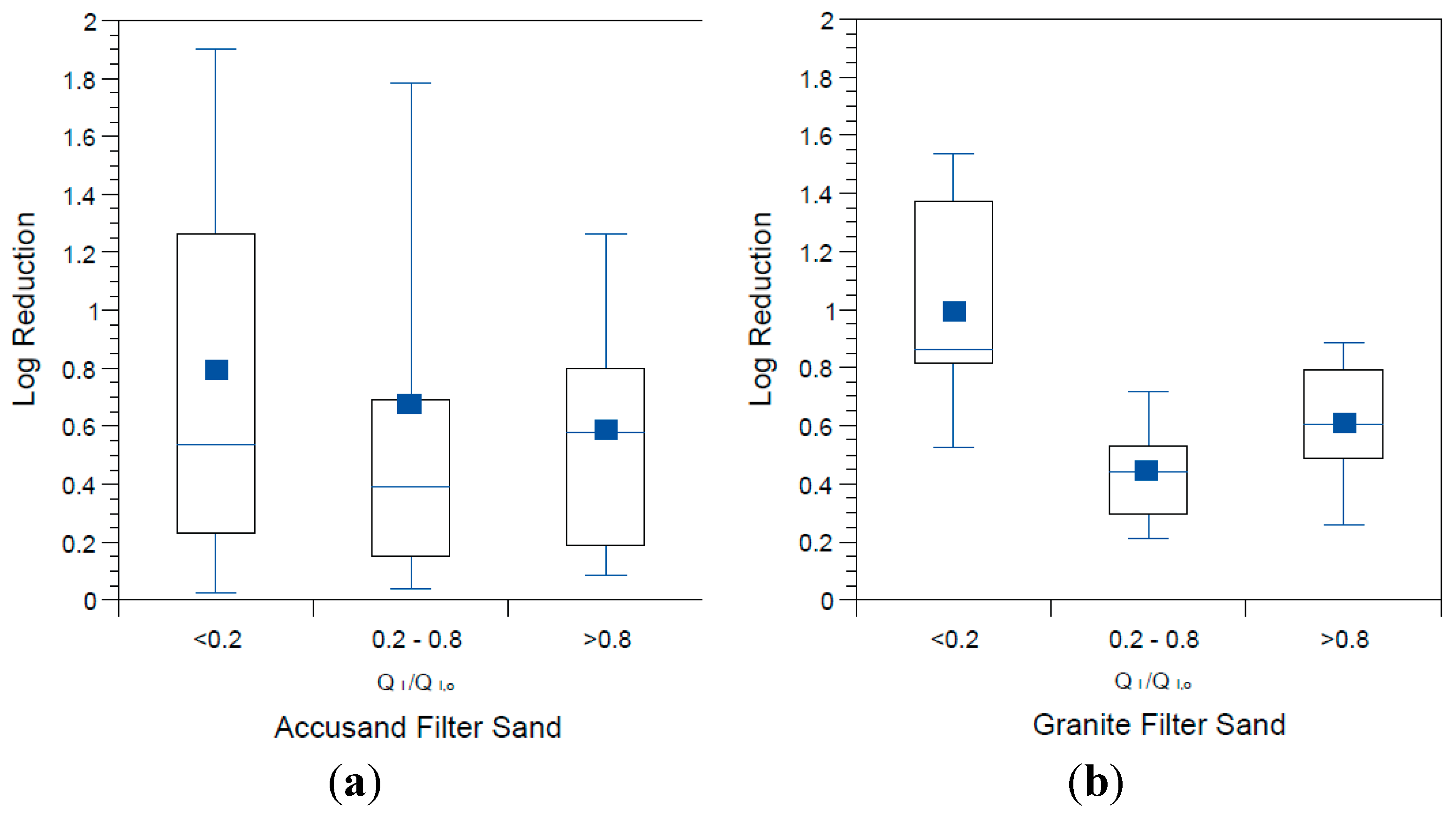
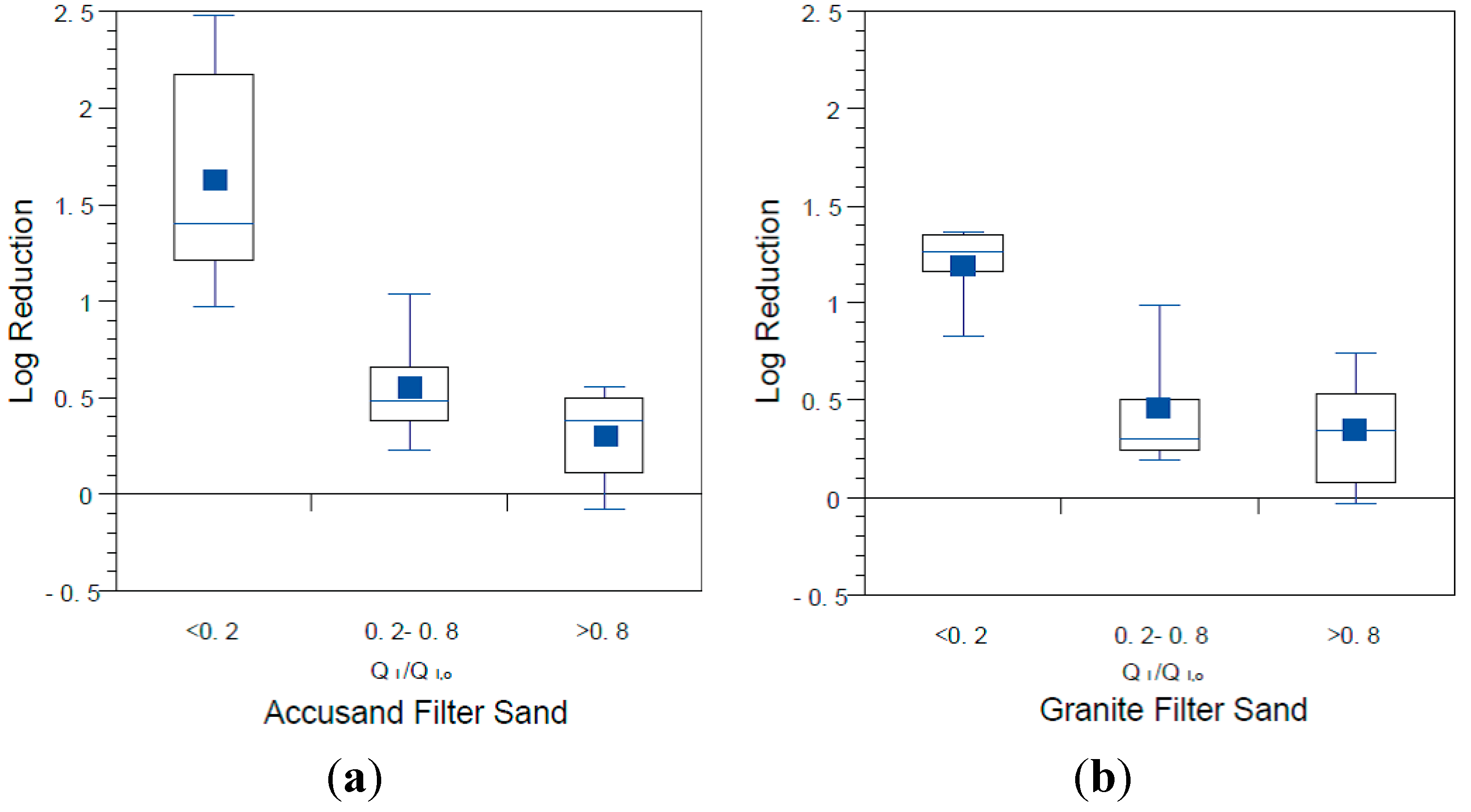
3.6. Microbial Reductions in Context
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sobsey, M.D. Managing Water in the Home: Accelerated Health Gains from Improved Water Supply; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ngai, T.; Coff, B.; Baker, D.; Lentz, R. Global review of the adoption, use and performance of biosand filter. In Progess in Slow Sand and Alternative Biofiltration Processes; Nakamoto, N., Graham, N., Collins, M., Gimbel, R., Eds.; International Water Association: London, UK, 2014; pp. 309–317. [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey, M.; Stauber, C.; Casanova, L.; Brown, J.; Elliott, M. Point of use household drinking water filtration: A practical, effective solution for providing sustained access to safe drinking water in the developing world. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4261–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiken, B.; Stauber, C.; Ortiz, G.; Sobsey, M. An assessment of continued use and health impact of the concrete biosand filter in Bonao, Dominican Republic. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 85, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.R.; Stauber, C.E.; Sobsey, M.D. Independent Evaluation of the Biosand Water Filter in Rural Cambodia: Sustainability, Health Impact and Water Quality Improvement; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, J.; Clasen, T. High adherence is necessary to realize health gains from water quality interventions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enger, K.; Nelson, K.; Rose, J.; Eisenberg, J. The joint effects of efficacy and compliance: A study of household water treatment effectiveness against childhood diarrhea. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CAWST. Biosand Filter Literature Summary; CAWST: Calgary, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Stauber, C.E.; Elliot, M.A.; Koksal, F.; Ortiz, G.M.; DiGiano, F.A.; Sobsey, M.D. Characterisation of the biosand filter for E. coli reductions from household drinking water under controlled laboratory and field use conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, M.; Stauber, C.; Koksal, F.; DiGiano, F.; Sobsey, M. Reductions of E. coli, echovirus type 12 and bacteriophages in an intermittently operated household-scale slow sand filter. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2662–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young-Rojanschi, C.; Madramootoo, C. Intermittent versus continuous operation of biosand filters. Water Res. 2014, 49, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, M.W.; Tiwari, S.K.; Darby, J. Bacterial, viral and turbidity removal by intermittent slow sand filtration for household use in developing countries: Experimental investigation and modeling. Water Res. 2011, 45, 6227–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, T.J.; Wanjugi, P.; Harwood, V.J.; Ergas, S.J. Dynamic Performance of Biosand Filters. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2013, 105, E587–E595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, T.J.; Hernandez, E.A.; Morse, A.N.; Anderson, T.A. Hydraulic Loading Rate Effect on Removal Rates in a BioSand Filter: A Pilot Study of Three Conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4527–4537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napotnik, J.; Jellison, K. Transport effects on hydraulic loading rate and microbial removal performance in biosand filters. J. Water Health 2014, 12, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahaffy, N.C.; Dickson, S.; Cantwell, R.E.; Lucier, K.; Schuster-Wallace, C.J. Effects of physical disturbances on media and performance of household-scale slow sand (BioSand) filters. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2015, 64, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, T.K.K.; Shrestha, R.R.; Dangol, B.; Maharjan, M.; Murcott, S.E. Design for sustainable development—Household drinking water filter for arsenic and pathogen treatment in Nepal. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2007, 42, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellen, V.; Nkeng, G.; Dentel, S. Improved filtration technology for pathogen reduction in rural water supplies. Water 2010, 2, 285–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebremichael, K.; Wasala, L.D.; Kennedy, M.; Graham, N.J.D. Comparative treatment performance and hydraulic characteristics of pumice and sand biofilters for point-of-use water treatment. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2012, 61, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, I.; Straub, A.; Maraccini, P.; Markazi, S.; Nguyen, T.H. Iron oxide amended biosand filters for virus removal. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4501–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Narihiro, T.; Straub, A.P.; Pugh, C.R.; Tamaki, H.; Moor, J.F.; Bradley, I.M.; Kamagata, Y.; Liu, W.-T.; Nguyen, T.H. MS2 Bacteriophage Reduction and Microbial Communities in Biosand Filters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6702–6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, M.A.; Stauber, C.E.; Koksal, F.; Liang, K.R.; Huslage, D.K.; DiGiano, F.A.; Sobsey, M.D. The operation, flow conditions and microbial reductions of an intermittently operated, household scale slow sand filter. In Recent Progress in Slow Sand and Alternative Biofiltration Processes; Gimbel, R., Graham, N.J.D., Collins, M.R., Eds.; International Water Association: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, M.A.; Digiano, F.A.; Sobsey, M.D. Virus attenuation by microbial mechanisms during the idle time of a household slow sand filter. Water Res. 2011, 45, 4092–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CAWST. Biosand Filter Construction Manual (CAWST); CAWST: Calgary, Canada, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Manz, D.H. Preparation of Media for the Biosand Water Filter; Manz Water Info: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Manz, D.H. BioSand Water Filter Technology; Manz Water Info: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Schroth, M.; Istok, J.; Ahearn, S.; Selker, J. Characterization of Miller-similar silica sands for laboratory hydrologic studies. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 60, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litton, G.M.; Olson, T.M. Colloid deposition rates on silica bed media and artifacts related to collector surface preparation methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US EPA. Method 3051: Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges, Soils, and Oils; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Burton, F.L.; Stensel, H.D. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- US EPA. Design Manual, Municipal Wastewater Disinfection. EPA/625/1-86/021; US Environmental Protection Agency: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1986.
- US EPA. Method 1604: Total Coliforms and Escherichia coli in Water by Membrane Filtration Using Simultaneous Detection Technique (MI Medium); US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- US EPA. Method 1602: Male-specific (F +) and Somatic Coliphage in Water by Single Agar Layer (SAL) Procedure April 2001. EPA Document 821-R-01-029; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- Cromeans, T.; Sobsey, M.D.; Fields, H.A. Development of a plaque assay for a cytopathic, rapidly replicating isolate of hepatitis A virus. J. Med. Virol. 1987, 22, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowd, S.E.; Pillai, S.D.; Wang, S.; Corapcioglu, M.Y. Delineating the specific influence of virus isoelectric point and size on virus adsorption and transport through sandy soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collins, K.; Cronin, A.; Rueedi, J.; Pedley, S.; Joyce, E.; Humble, P.; Tellam, J. Fate and transport of bacteriophage in UK aquifers as surrogates for pathogenic viruses. Eng. Geol. 2006, 85, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, M.M.F.; Stimson, J.; Chae, G.-T.; Tufenkji, N.; Ptacek, C.J.; Blowes, D.W.; Emelko, M.B. Optimal preparation and purification of PRD1-like bacteriophages for use in environmental fate and transport studies. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, S. Mechanisms Involved in Sorption of Microorganisms to Solid Surfaces. In Adsorption of Microorganisms to Surfaces; Bitton, G., Marshall, K., Eds.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Glassman, H.N. Surface Active Agents and their Application in Bacteriology. Bacteriol. Rev. 1948, 12, 105–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blatt, H.; Tracy, R.J. Petrology Igneous, Sedimentary, and Magmatic, 2nd ed.; Prentice-Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Stumm, W.; Morgan, J.J. Aquatic Chemistry: Chemical Equilibria and Rates in Natural Waters; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Knappett, P.S.K.; Emelko, M.B.; Zhuang, J.; McKay, L.D. Transport and retention of a bacteriophage and microspheres in saturated, angular porous media: Effects of ionic strength and grain size. Water Res. 2008, 42, 4368–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukasik, J.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Lu, F.; Tamplin, M.; Farrah, S.R. Removal of microorganisms from water by columns containing sand coated with ferric and aluminum hydroxides. Water Res. 1999, 33, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truesdail, S.; Lukasik, J.; Farrah, S.; Shah, D.; Dickinson, R. Analysis of Bacterial Deposition on Metal (Hydr)oxide-Coated Sand Filter Media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 203, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foppen, J.W.; Liem, Y.; Schijven, J. Effect of humic acid on the attachment of Escherichia coli in columns of goethite-coated sand. Water Res. 2008, 42, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijnen, W.A.M.; Schijven, J.F.; Bonné, P.; Visser, A.; Medema, G.J. Elimination of viruses, bacteria and protozoan oocysts by slow sand filtration. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Unger, M.; Collins, M.R. Assessing Escherichia coli Removal in the Schmutzdecke of Slow-Rate Biofilters. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2008, 100, 60–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, J.N.; Harvey, R.W.; Metge, D.; Elimelech, M.; Navigato, T.; Pieper, A.P. Field and Laboratory Investigations of Inactivation of Viruses (PRD1 and MS2) Attached to Iron Oxide-Coated Quartz Sand. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2403–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Jin, Y. Virus retention and transport through Al-oxide coated sand columns: Effects of ionic strength and composition. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2003, 60, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullemont, Y.; Schijven, J.; Hijnen, W.; Colin, M.; Magic-Knezev, A. Removal of microorganisms by slow sand filtration. In Recent Progress in Slow Sand and Alternative Biofiltration Processes; Gimbel, R., Graham, N., Collins, M., Eds.; International Water Association: London, UK, 2006; pp. 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Poynter, S.; Slade, J. The removal of viruses by slow sand filtration. Prog. Water Technol. 1977, 9, 75–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, D.; Bartram, J.; Lloyd, B.; Graham, N. Removal of viruses by filtration through sand. In Slow Sand Filtration: Recent Developments in Water Treatment Technology; Graham, N., Ed.; Ellis Horwood Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1988; pp. 207–229. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elliott, M.; Stauber, C.E.; DiGiano, F.A.; De Aceituno, A.F.; Sobsey, M.D. Investigation of E. coli and Virus Reductions Using Replicate, Bench-Scale Biosand Filter Columns and Two Filter Media. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 10276-10299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120910276
Elliott M, Stauber CE, DiGiano FA, De Aceituno AF, Sobsey MD. Investigation of E. coli and Virus Reductions Using Replicate, Bench-Scale Biosand Filter Columns and Two Filter Media. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2015; 12(9):10276-10299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120910276
Chicago/Turabian StyleElliott, Mark, Christine E. Stauber, Francis A. DiGiano, Anna Fabiszewski De Aceituno, and Mark D. Sobsey. 2015. "Investigation of E. coli and Virus Reductions Using Replicate, Bench-Scale Biosand Filter Columns and Two Filter Media" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 12, no. 9: 10276-10299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120910276
APA StyleElliott, M., Stauber, C. E., DiGiano, F. A., De Aceituno, A. F., & Sobsey, M. D. (2015). Investigation of E. coli and Virus Reductions Using Replicate, Bench-Scale Biosand Filter Columns and Two Filter Media. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(9), 10276-10299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120910276





