Comparison of the Cumulative Incidence Rates of Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis between 1970 and 2013 among Four State-Owned Colliery Groups in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Diagnosis of Pneumoconiosis
2.3. Occupational Categories
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Details
| Characteristics | Datong | Kailuan | Fuxin | Tiefa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With CWP | Without CWP | With CWP | Without CWP | With CWP | Without CWP | With CWP | Without CWP | ||
| N | 1847 | 43,742 | 838 | 16,185 | 143 | 10,230 | 45 | 14,874 | |
| Average durations of dust exposure | 19.8 ± 7.2 | 18.9 ± 9.5 | 24.9 ± 7.1 | 23.0 ± 10.4 | 23.5 ± 5.1 | 17.8 ± 10.7 | 20.5 ± 6.2 | 17.5 ± 7.7 | |
| Occupational categories | Tunneling | 735 (21.82) * | 2634 | 248 (17.91) | 1137 | 96 (2.58) | 3630 | 36 (0.67) | 5328 |
| Mining | 619 (5.74) | 10,161 | 245 (8.74) | 2559 | 41 (1.54) | 2613 | 5 (0.17) | 2921 | |
| Combining | 297 (5.92) | 4721 | 259 (11.35) | 2022 | 5 (0.60) | 822 | 2 (0.30) | 654 | |
| Helping | 196 (0.74) | 26,226 | 86 (0.81) | 10,467 | 1 (0.03) | 3165 | 2 (0.03) | 5971 | |
| Years of first dust exposure | 1970s | 1217 (17.21) | 5854 | 710 (10.81) | 5855 | 103 (5.56) | 1750 | 36 (4.31) | 800 |
| 1980s | 630 (1.64) | 37,888 | 128 (1.22) | 10,330 | 40 (0.47) | 8480 | 9 (0.06) | 14,074 | |
3.2. Cumulative Incidence Rates of CWP
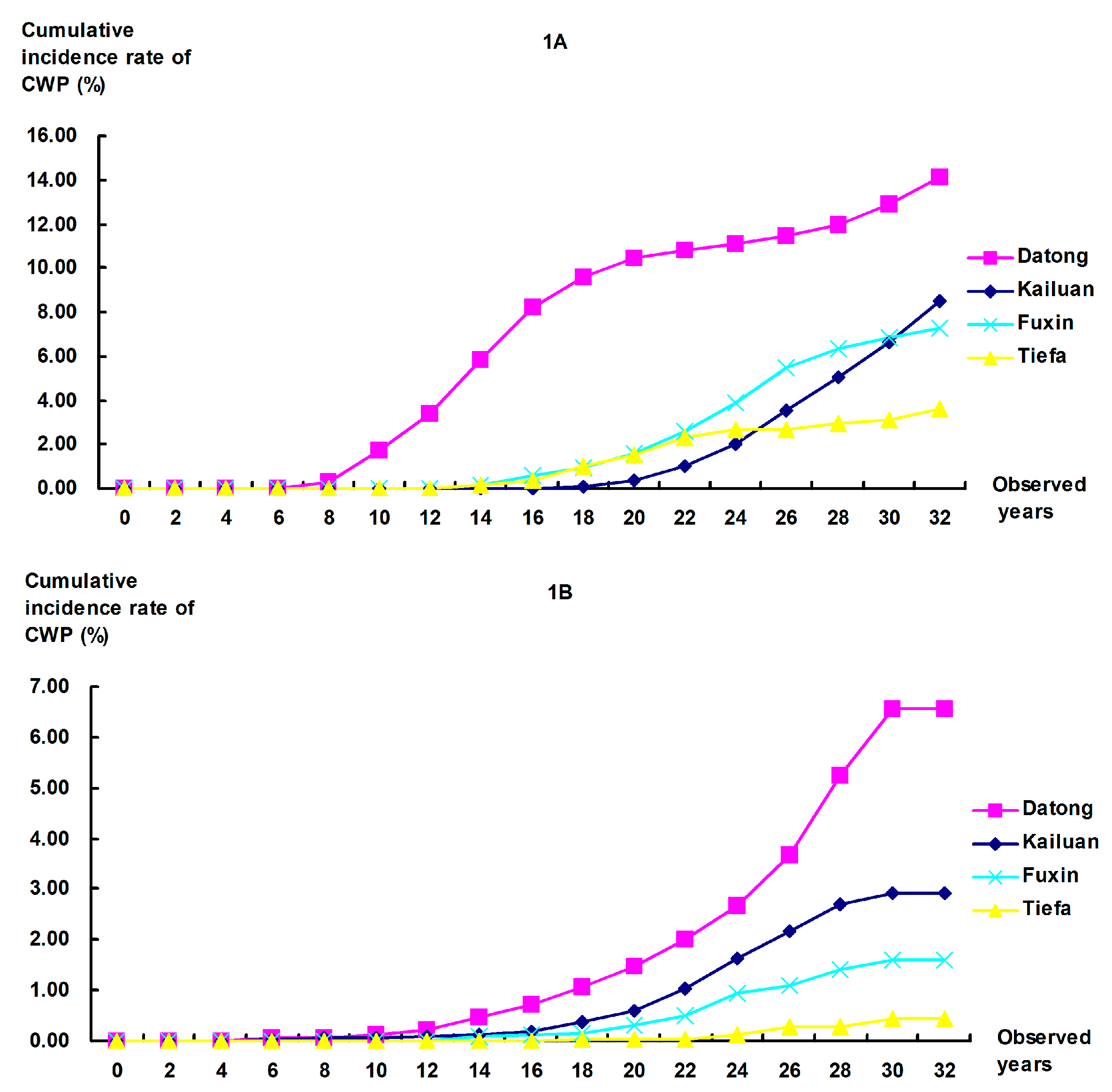
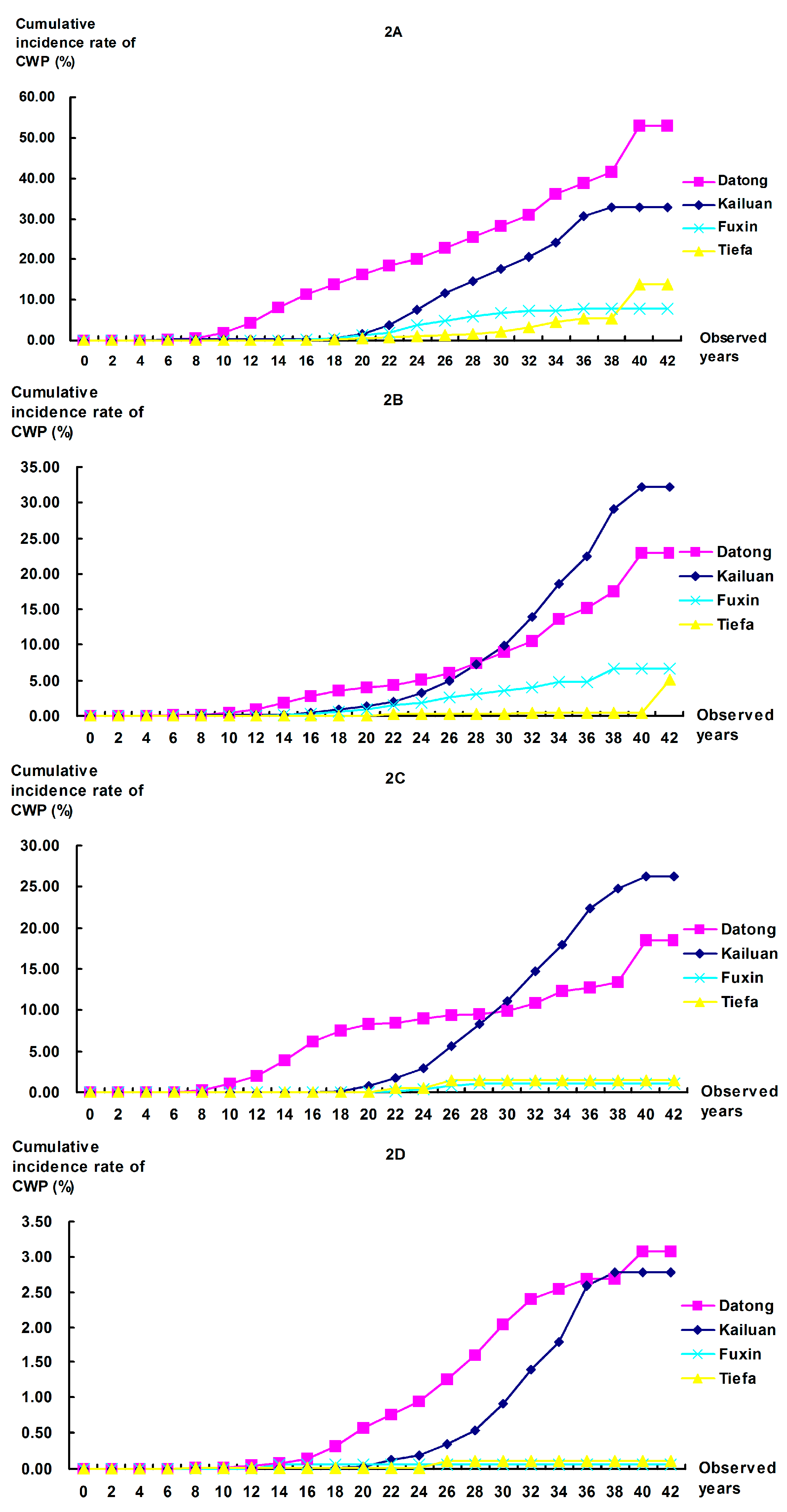

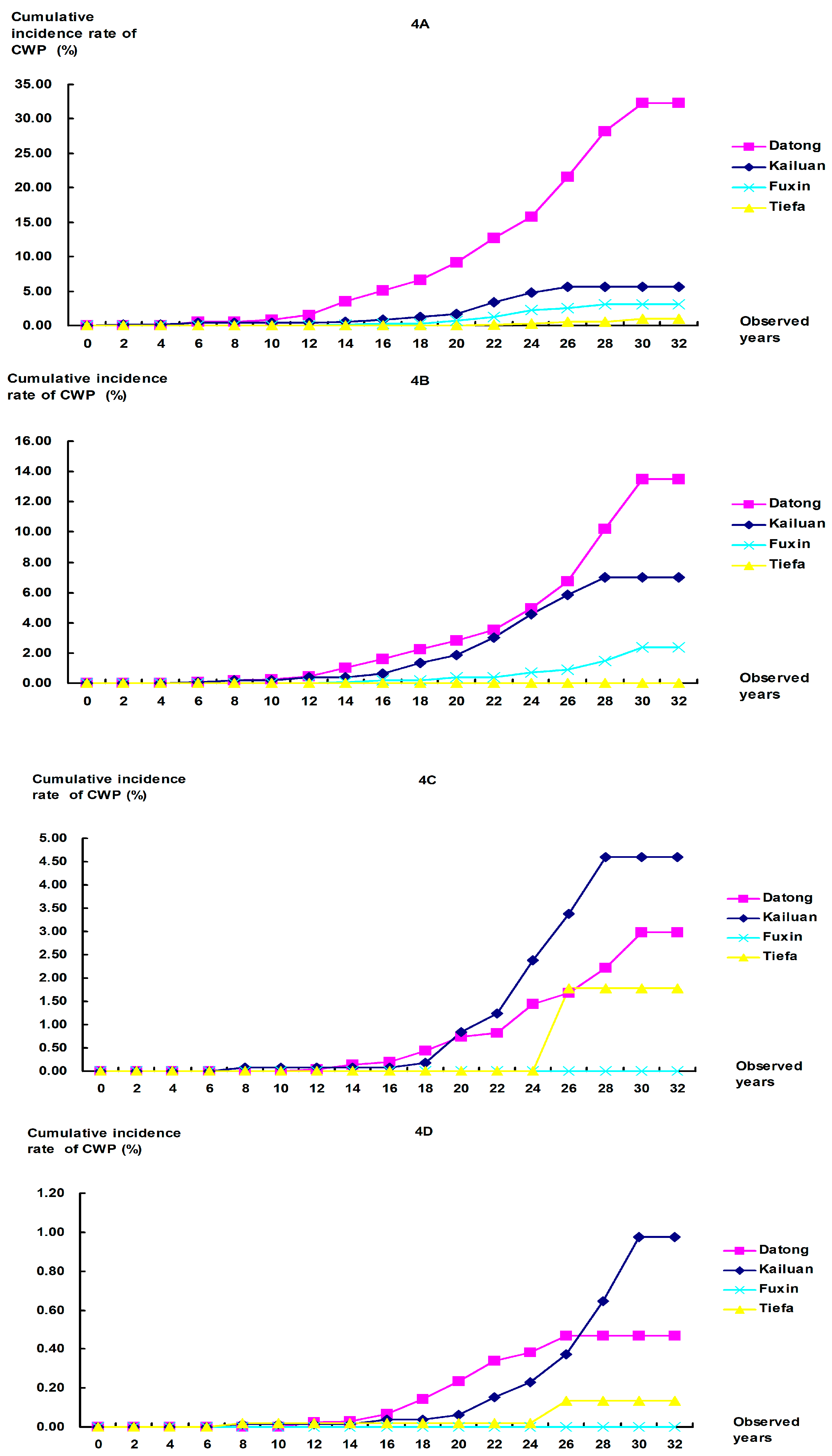
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santo Tomas, L.H. Emphysema and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in coal miners. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2011, 17, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Coal workers’ pneumoconiosis-related years of potential life lost before age 65 years-United States, 1968–2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009, 58, 1412–1416. [Google Scholar]
- Onder, M.; Onder, S. Evaluation of occupational exposures to respirable dust in underground coal mines. Ind. Health 2009, 47, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Advanced pneumoconiosis among working underground coal miners-eastern Kentucky and southwestern Virginia, 2006. JAMA 2007, 298, 734–736. [Google Scholar]
- Laney, A.S.; Weissman, D.N. The classic pneumoconioses: New epidemiological and laboratory observations. Clin. Chest Med. 2012, 33, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petsonk, E.L.; Rose, C.; Cohen, R. Coal mine dust lung disease. New lessons from old exposure. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarthana, E.; Laney, A.S.; Storey, E.; Hale, J.M.; Attfield, M.D. Coal workers’ pneumoconiosis in the United States: Regional differences 40 years after implementation of the 1969 federal coal mine health and safety act. Occu. Environ. Med. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Pneumoconiosis prevalence among working coal miners examined in federal chest radiograph surveillance programs-United States, 1996–2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2003, 52, 336–340. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health Division of Respiratory Disease Studies. Work-Related Lung Disease Surveillance Report, 2007; National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2008.
- Laney, A.S.; Petsonk, E.L.; Attfield, M.D. Pneumoconiosis among underground bituminous coal miners in the United States: Is silicosis becoming more frequent? Occup. Environ. Med. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Schenk, L.; Hansson, S.O. Occupational diseases in the People’s Republic of China between 2000 and 2010. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2013, 56, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. The Bulletin of Prevention and Control Work of Occupational Disease in 2009 and the Key Work of 2010 were Issued by Ministry of Health of China. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2010-04/28/content_1594571.htm (accessed on 28 April 2010).
- Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Du, X.; Chen, S. Analyses on the characteristics and the trends of pneumoconiosis notified between 1997 and 2009, in China. Chinese J. Ind. Hyg. Occup. Dis. 2013, 31, 321–334. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. National Occupational Diseases Report for 2013. Available online: http://www.nhfpc.gov.cn/jkj/s5899t/201406/ed8ed220d0b74010bcb6dcd8e340f4fb.shtml (accessed on 30 June 2014).
- Liang, Y.X.; Wong, O.; Fu, H.; Hu, T.X.; Xue, S.Z. The economic burden of pneumoconiosis in china. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 60, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Pan, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Ma, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, N. The estimation of the number of underground coal miners and the annual dose to coal miners in China. Health Physics. 2007, 93, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, J.; Wang, L.; Au, W.; Su, M. Prevalence of coal workers’ pneumoconiosis in China: A systematic analysis of 2001–2011 studies. Int. J. Hyg. Environ Health 2014, 217, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Chinese Diagnostic Criteria of Pneumoconiosis (GBZ 70-2009). Available online: http://www.nhfpc.gov.cn/zwgkzt/s9489/200907/41986.shtml (accessed on 29 July 2009).
- Liu, H.; Yan, B.; Han, B.; Sun, J.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J. Assessment of respiration-related quality of life of Chinese patients with silicosis and its influencing factors using the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ). J. Clin. Nurs. 2011, 21, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Tang, Z.; Weng, D.; Yang, Y.; Tian, L.; Duan, Z.; Chen, J. Prevalence characteristics and prediction of coal workers’ pneumoconiosis in the Tiefa colliery in China. Ind. Health 2009, 47, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Yuan, J.; Sun, Z.; Hua, Z.; Qin, T.; Yao, S.; Fan, X.; Chen, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, J. Risk identification and prediction of coal workers’ pneumoconiosis in Kailuan colliery group in China: A historical cohort study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, J.; Zhou, C. The prevention of silicosis and prediction of its future prevalence in China. Am. J. Public Health 1989, 79, 1613–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China National Coal Association. Top 100 List of Chinese Coal Enterprise in 2013. Available online: http://www.coalchina.org.cn/detail/13/09/13/00000025/content.html (accesed on 13 September 2013).
- Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Qu, J.; Sun, L.; Sun, J. Investigation on coal workers’ pneumoconiosis among underground mining and tunneling workers. Chinese J. Health Stat. 1995, 12, 37–38. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- McCunney, R.J.; Morfeld, P.; Payne, S. What component of coal causes coal workers’ pneumoconiosis? J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2009, 51, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attfield, M.D.; Morring, K. An investigation into the relationship between coal workers’ pneumoconiosis and dust exposure in U.S. Coal miners. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1992, 53, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, K.; Shen, F.; Han, B.; Yuan, J.; Suo, X.; Qin, T.; Liu, H.; Chen, J. Comparison of the Cumulative Incidence Rates of Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis between 1970 and 2013 among Four State-Owned Colliery Groups in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7444-7456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120707444
Cui K, Shen F, Han B, Yuan J, Suo X, Qin T, Liu H, Chen J. Comparison of the Cumulative Incidence Rates of Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis between 1970 and 2013 among Four State-Owned Colliery Groups in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2015; 12(7):7444-7456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120707444
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Kai, Fuhai Shen, Bing Han, Juxiang Yuan, Xia Suo, Tianbang Qin, Hongbo Liu, and Jie Chen. 2015. "Comparison of the Cumulative Incidence Rates of Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis between 1970 and 2013 among Four State-Owned Colliery Groups in China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 12, no. 7: 7444-7456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120707444
APA StyleCui, K., Shen, F., Han, B., Yuan, J., Suo, X., Qin, T., Liu, H., & Chen, J. (2015). Comparison of the Cumulative Incidence Rates of Coal Workers’ Pneumoconiosis between 1970 and 2013 among Four State-Owned Colliery Groups in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(7), 7444-7456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120707444





