Combined Effects of Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A on the Human Prostate Epithelial Cell Line RWPE-1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Concentration-response Analysis of Nonylphenol (NP) and Bisphenol A (BPA) Alone or in Combination in the Cell Viability Assay
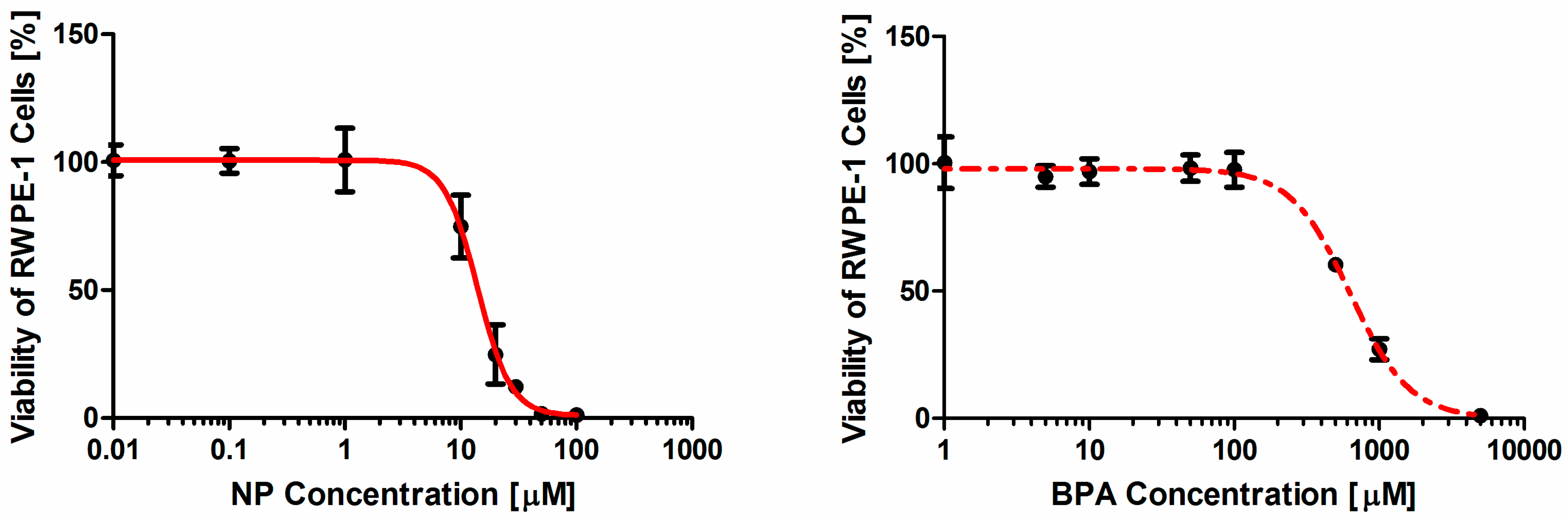
| Hill-Function Parameters (α ± 95CI) | Viability Assay | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| NP | BPA | Combined | |
| Slope (p) a | −2.68 ± 0.24 | −2.10 ± 0.23 | −3.217 ± 0.2161 |
| EC50 (μM) b | 15.00 | 610.27 | 7.44 (NP); 297.68 (BPA) |
| Vmax (%) c | 1.008 ± 0.018 | 0.981 ± 0.01 | 0.9956 ± 0.014 |
| R2 d | 0.9726 | 0.9796 | 0.9781 |
| Chi2/DoF e | 0.2543 | 0.1309 | 0.3384 |
2.2. Concentration-response Analysis of Nonylphenol (NP) and Bisphenol A (BPA) alone or in Combination in the Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Leakage Rate Assay
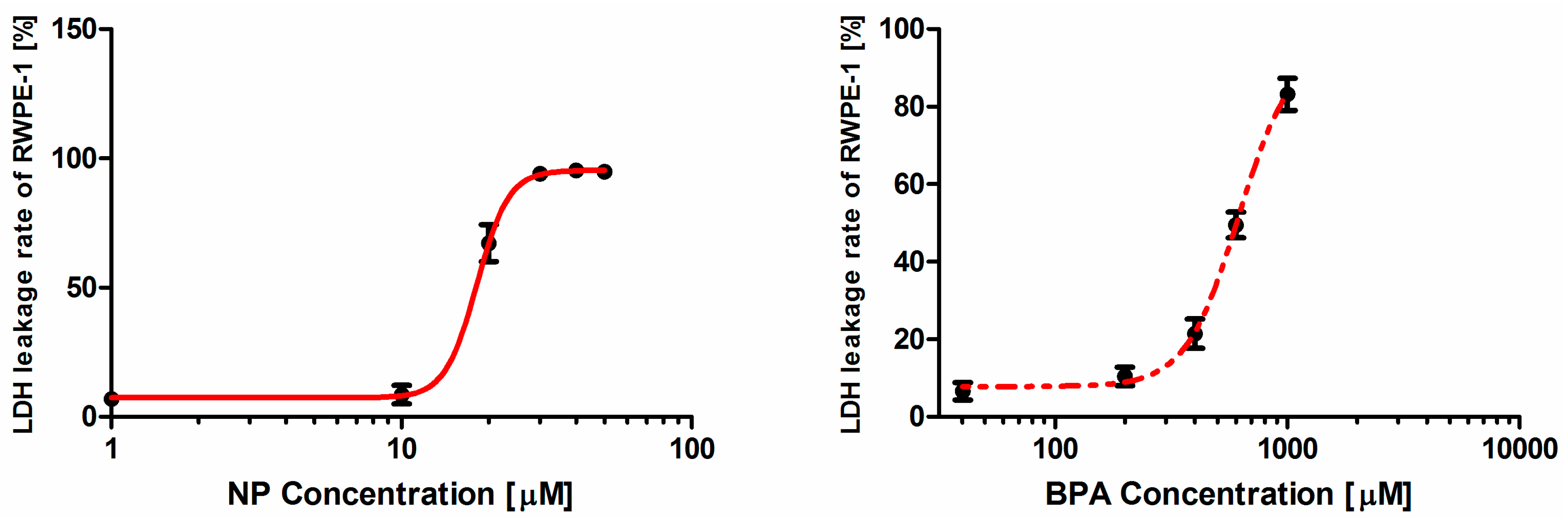
| Hill-Function Parameters (α ± 95%CI) | LDH leakage Assay | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| NP | BPA | Combined | |
| Slope (p) a | 7.92 ± 2.13 | 4.69 ± 0.48 | 2.94 ± 0.2129 |
| EC50 (μM) b | 18.18 | 616.3 | 22.18 (NP); 776.3 (BPA) |
| Vmax (%) c | 0.9535 ± 0.010 | 1.01 ± 0.04 | 0.9956 ± 0.024 |
| R2 d | 0.9940 | 0.9874 | 0.9907 |
| Chi2/DoF e | 0.3306 | 0.4522 | 0.6615 |
2.3. The Analysis by the Two Models for Determining the Combined Effects of Nonylphenol (NP) and Bisphenol A (BPA) on Cell Viability
| Dose (μM) | Series of Viability Effects (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E90 | E80 | E70 | E60 | E50 | E40 | E30 | E10 | E5 | |
| DNP a | 6.8 | 9.07 | 11.04 | 12.99 | 15.09 | 17.54 | 20.67 | 34.17 | 45.1492 |
| DBPA b | 193.66 | 300.58 | 395.02 | 491.47 | 599 00 | 728.87 | 901.56 | 1719.74 | 2456.00 |
| dNP c | 3.71 | 4.81 | 5.69 | 6.54 | 7.42 | 8.42 | 9.67 | 14.71 | 18.56 |
| dBPA d | 148.27 | 192.13 | 227.70 | 261.53 | 296.86 | 336.89 | 386.62 | 588.45 | 742.37 |
| LCI e | 1.31 | 1.17 | 1.09 | 1.04 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.77 | 0.71 |
| ±95% Confidence interval | 1.18~1.34 | 1.11~1.18 | 1.06~1.1 | 1.01~1.07 | 0.97~0.99 | 0.93~0.95. | 0.84~0.94 | 0.66~0.88 | 0.58~0.85 |
| Combined effect | antagonism | antagonism | antagonism | antagonism | synergism | synergism | synergism | synergism | synergism |
| dNP (μM) a | 5.00 | 10.00 | 15.00 | 20.00 | 25.00 | 30.00 | 50.00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dBPA (μM) b | 200.00 | 400.00 | 600.00 | 800.00 | 1100.00 | 1200.00 | 2000.00 |
| ENP c | 0.97 | 0.74 | 0.45 | 0.25 | 0.97 | 0.74 | 0.45 |
| EBPA d | 0.90 | 0.71 | 0.52 | 0.37 | 0.90 | 0.71 | 0.52 |
| Predicted effect e | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.75 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 0.30 | 0.11 |
| Observed effect f | 0.78 | 0.28 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.09 |
| q value | 0.78 | 0.30 | 0.13 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| Combined effect | synergism | synergism | synergism | synergism | synergism | synergism | synergism |
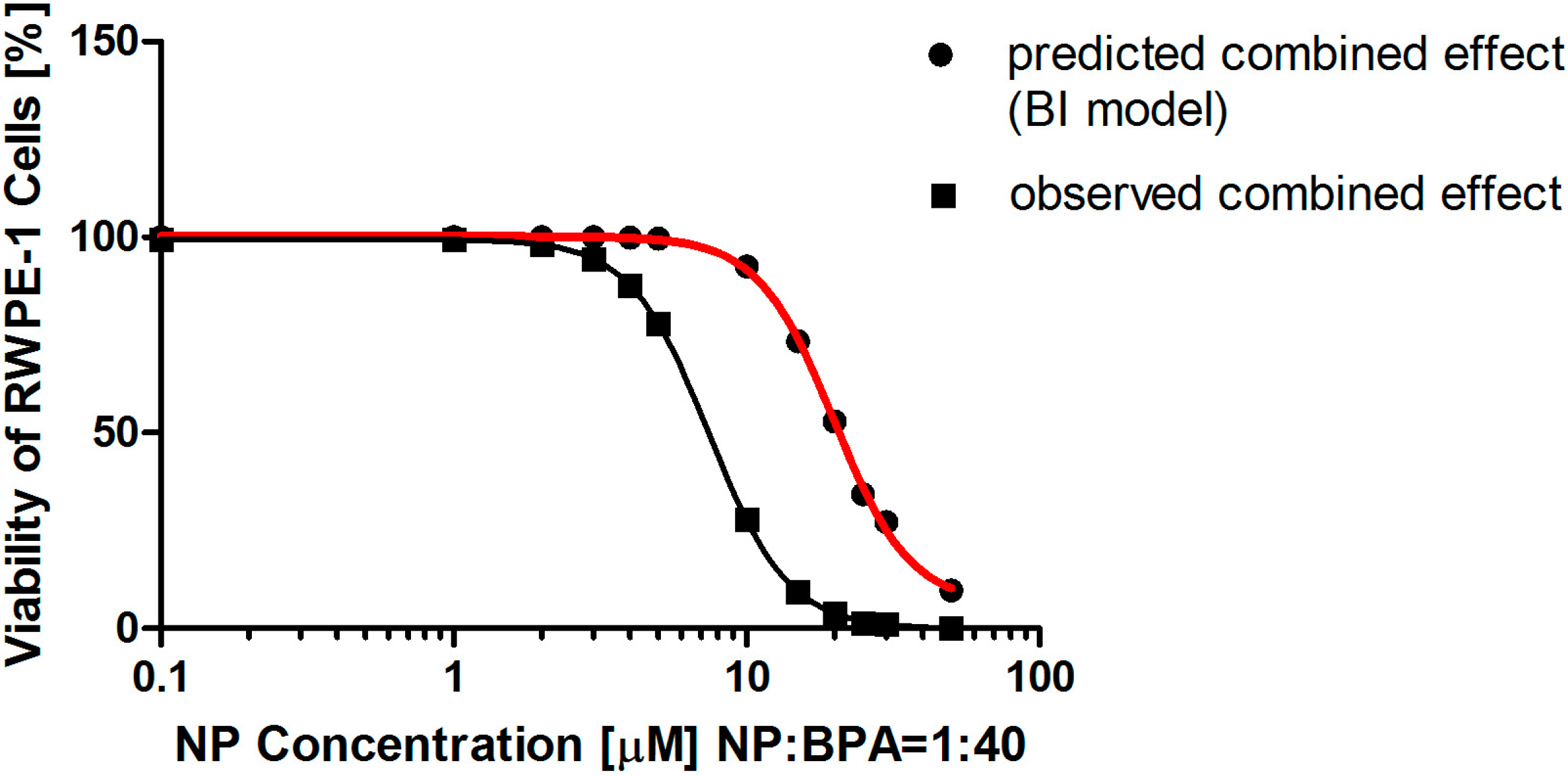
2.4. The Analysis by the Two Models for Determining the Combined Effects of Nonylphenol (NP) and Bisphenol A (BPA) on Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Leakage Rate
| Dose (μM) | Series of LDH Leakage Rate (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | E10 | E40 | E50 | E60 | E70 | E80 | E90 | |
| DNP a | 10.24 | 13.87 | 17.45 | 18.41 | 19.44 | 20.67 | 22.39 | 25.96 |
| DBPA b | 230.77 | 384.79 | 563.25 | 613.70 | 668.45 | 733.24 | 819.78 | 964.97 |
| dNP c | 4.65 | 10.52 | 19.37 | 22.25 | 25.56 | 29.74 | 35.81 | 47.55 |
| dBPA d | 162.89 | 368.28 | 677.99 | 778.64 | 894.45 | 1040.82 | 1253.42 | 1664.37 |
| CI | 1.48 | 2.44 | 3.65 | 4.01 | 4.41 | 4.90 | 5.57 | 6.72 |
| Combined effect | antaonism | antagonism | antagonism | antagonism | antagonism | antagonism | antagonism | antagonism |
| dNP (μM) a | 1.00 | 5.00 | 10.00 | 15.00 | 20.00 | 30.00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dBPA (μM) b | 35.00 | 175.00 | 350.00 | 525.00 | 700.00 | 1050.00 |
| ENP c | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 0.65 | 0.94 |
| EBPA d | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.32 | 0.65 | 0.93 |
| Predicted effect e | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.44 | 0.88 | 1.00 |
| Observed effect f | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.42 | 0.71 |
| q value | 75.25 | 4.42 | 1.18 | 0.55 | 0.48 | 0.71 |
| Combined effect | synergism | synergism | synergism | antagonism | antagonism | antagonism |
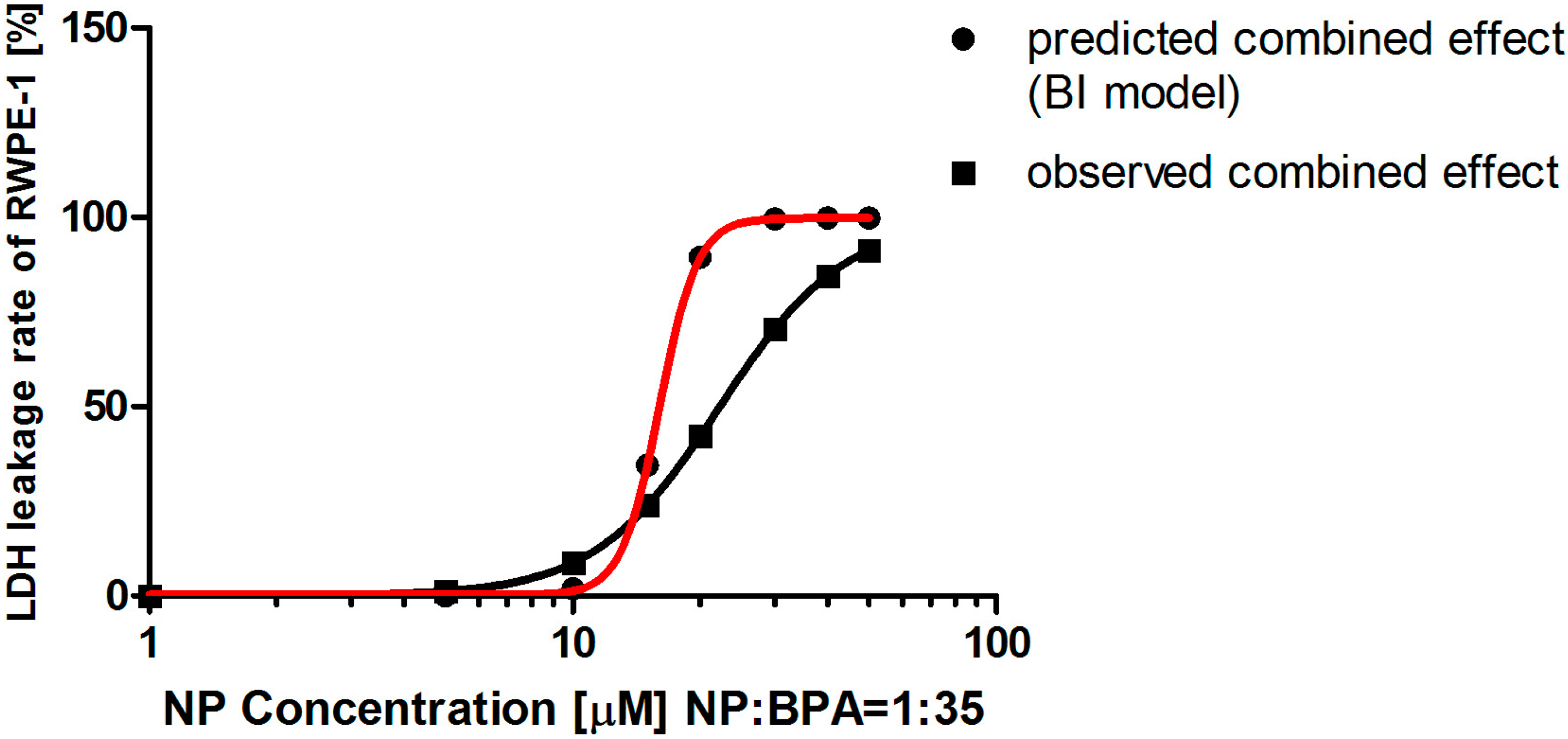
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Culture of the Human Prostate Epithelial Cell Line RWPE-1
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Leakage Rate Assay
4.5. Chemical Combination and Data Analysis
4.5.1. The Modeling for the Single Effect
4.5.2. Dose Selection of the Mixture of Nonylphenol (NP) and Bisphenol A (BPA)
4.6. The Modelling for the Mixture Effect
4.6.1. The Loewe Additivity (LA) Models
4.6.2. The Bliss Independence (BI) Model
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The EU Water Framework Directive—An Introduction. Available online: http://www.iwaponline.com/wio/2007/04/wio200704RF1900222124.htm (accessed on 10 April 2015).
- Welshons, W.V.; Thayer, K.A.; Judy, B.M.; Taylor, J.A.; Curran, E.M.; vom Saal, F.S. Large effects from small exposures. I. Mechanisms for endocrine-disrupting chemicals with estrogenic activity. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calafat, A.M.; Kuklenyik, Z.; Reidy, J.A.; Caudill, S.P.; Ekong, J.; Needham, L.L. Urinary concentrations of bisphenol A and 4-nonylphenol in a human reference population. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Wong, L.Y.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L. Exposure of the U.S. population to bisphenol A and 4-tertiary-octylphenol: 2003–2004. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, K.; Heinke, V.; Thiele, B.; Kleist, E.; Prast, H.; Raecker, T. Endocrine disrupting nonylphenols are ubiquitous in food. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1676–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochester, J.R. Bisphenol A and Human Health: A review of the literature. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.; Guieysse, B.; Jefferson, B.; Cartmell, E.; Lester, J.N. Nonylphenol in the environment: A critical review on occurrence, fate, toxicity and treatment in wastewaters. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 1033–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.D.; Tu, Z.G.; Gong, Y.; Shen, S.N.; Wang, X.Y.; Kang, L.N.; Hou, Y.Y.; Chen, J.X. The toxic effects of nonylphenol on the reproductive system of male rats. Reprod. Toxicol. 2004, 19, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Wu, J.; Huang, Y.F.; Shen, S.N.; Han, X.D. Nonylphenol induces apoptosis in rat testicular Sertoli cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 186, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, K.P.; Tanphaichitr, N. Human exposure to endocrine disrupters and semen quality. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2008, 11, 188–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, J.R.; Chakraborty, S.; Chakraborty, T.R. Estrogen-like endocrine disrupting chemicals affecting puberty in humans—A review. Med. Sci. Monit. 2009, 15, RA137–RA145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huggins, C.; Scott, W.W.; Heinen, J.H. Chemical composition of human semen and of the secretions of the prostate and seminal vesicles. Am. J. Physiol. Leg. Content 1942, 136, 467–473. [Google Scholar]
- Cormio, P.G.; Christmann, M.; Rastall, A.; Grund, S.; Hollert, H.; Schuphan, I.; Schmidt, B. Chlorinated isomers of nonylphenol differ in estrogenic and androgenic activity. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard Subst. Environ. Eng. 2011, 46, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Gong, E.Y.; Ahn, R.S.; Lee, K. Antiandrogenic effects of bisphenol A and nonylphenol on the function of androgen receptor. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 75, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, C.A.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Farabollini, F.; Newbold, R.R.; Rubin, B.S.; Talsness, C.E.; Vandenbergh, J.G.; Walser-Kuntz, D.R.; Saal, F.S.V. In vivo effects of bisphenol A in laboratory rodent studies. Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 199–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Koupparis, M.A. Recent trends in biomonitoring of bisphenol A, 4-t-octylphenol, and 4-nonylphenol. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 210, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, W.R.; Bravo, G.; Parsons, J.C. The search for synergy: A critical review from a response surface perspective. Pharmacol. Rev. 1995, 47, 331–385. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Faust, M.; Altenburger, R.; Backhaus, T.; Blanck, H.; Boedeker, W.; Gramatica, P.; Hamer, V.; Scholze, M.; Vighi, M.; Grimme, L.H. Predicting the joint algal toxicity of multi-component s-triazine mixtures at low-effect concentrations of individual toxicants. Aquat. Toxicol. 2001, 56, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konemann, W.H.; Pieters, M.N. Confusion of concepts in mixture toxicology. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1996, 34, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, P.R.; Christiansen, S.; Boberg, J.; Nellemann, C.; Hass, U. Combined exposure to endocrine disrupting pesticides impairs parturition, causes pup mortality and affects sexual differentiation in rats. Int. J. Androl. 2010, 33, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zha, J.; Wang, Z. Interactions between estrogenic chemicals in binary mixtures investigated using vitellogenin induction and factorial analysis. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonefeld-Jorgensen, E.C.; Long, M.; Hofmeister, M.V.; Vinggaard, A.M. Endocrine-disrupting potential of bisphenol A, bisphenol A dimethacryla te, 4-n-nonylphenol, and 4-n-octylphenol in vitro: New data and a brief review. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115 (Suppl. 1), 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaro, A.A.; Esposito, A.I.; Mirisola, V.; Mehilli, A.; Rosano, C.; Noonan, D.M.; Albini, A.; Pfeffer, U.; Angelini, G. Endocrine disruptor agent Nonyl phenol exerts an estrogen-like transcriptional activity on estrogen receptor positive breast cancer cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfosse, V.; Grimaldi, M.; Pons, J.L.; Boulahtouf, A.; le Maire, A.; Cavailles, V.; Labesse, G.; Bourguet, W.; Balaguer, P. Structural and mechanistic insights into bisphenols action provide guidelines for risk assessment and discovery of bisphenol A substitutes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14930–14935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöpel, M.; Jockers, K.F.; Düppe, P.M.; Autzen, J.; Potheraveedu, V.N.; Ince, S.; Yip, K.T.; Heumann, R.; Herrmann, C.; Scherkenbeck, J.; et al. Bisphenol A binds to Ras proteins and competes with guanine nucleotide exchange: Implications for GTPase-selective antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9664–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohmé, M.; Prud’homme, S.M.; Boulahtouf, A.; Samarut, E.; Brunet, F.; Bernard, L.; Bourguet, W.; Gibert, Y.; Balaguer, P.; Laudet, V. Estrogen-related receptor γ is an in vivo receptor of bisphenol A. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 3124–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, X.; Ya, W.; Jie, Y.; Hashim, J.H.; Liu, X.Y.; Fan, Q.Y.; Yan, L. Toxic effect of gestational exposure to nonylphenol on F1 male rats. Birth Defects Res. B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2010, 89, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, W.; Zhou, M.; Xiang, Z.; Han, X.; Li, D. Combined Effects of Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A on the Human Prostate Epithelial Cell Line RWPE-1. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 4141-4155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120404141
Gan W, Zhou M, Xiang Z, Han X, Li D. Combined Effects of Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A on the Human Prostate Epithelial Cell Line RWPE-1. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2015; 12(4):4141-4155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120404141
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Weidong, Ming Zhou, Zou Xiang, Xiaodong Han, and Dongmei Li. 2015. "Combined Effects of Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A on the Human Prostate Epithelial Cell Line RWPE-1" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 12, no. 4: 4141-4155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120404141
APA StyleGan, W., Zhou, M., Xiang, Z., Han, X., & Li, D. (2015). Combined Effects of Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A on the Human Prostate Epithelial Cell Line RWPE-1. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(4), 4141-4155. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120404141





