Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Fasting Glucose, Associated with Risk Factors in Rural Kazakh Adults in Xinjiang, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Sampling
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Questionnaire Interviews
2.4. Clinical Measurements
2.5. Blood lipid and Glucose Tests
2.6. Diagnostic Criteria for Diabetes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Subjects
| Characteristics | Total (N = 3919) | Males (N = 1552) | Females (N = 2367) | χ2/t | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 44.18 ± 13.24 | 45.09 ± 13.53 | 43.59 ± 13.02 | 3.460 | <0.01 |
| Weight(kg) | 64.80 ± 12.93 | 70.90 ± 12.72 | 60.79 ± 11.41 | 25.34 | <0.01 |
| Height (cm) | 163.04 ± 8.74 | 169.88 ± 6.95 | 158.55 ± 6.63 | 50.806 | <0.01 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.35 ± 4.61 | 24.56 ± 4.13 | 24.21 ± 4.89 | 2.350 | <0.05 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 85.72 ± 12.30 | 88.425 ± 12.12 | 83.94 ± 12.10 | 11.345 | <0.01 |
| Hip circumference (cm) | 98.10 ± 9.16 | 98.75 ± 8.38 | 97.67 ± 9.62 | 3.728 | <0.01 |
| Systolic blood pressure(mm Hg) | 128.7 ± 23.87 | 131.84 ± 22.95 | 126.64 ± 24.25 | 6.706 | <0.01 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 82.94 ± 14.55 | 84.6 ± 14.15 | 81.85 ± 14.70 | 5.810 | <0.01 |
| Fasting Blood-glucose (m mol/L) | 5.30 ± 1.36 | 5.40 ± 1.57 | 5.24 ± 1.20 | 3.440 | <0.01 |
| Total Cholesterol (m mol/L) | 4.55 ± 1.32 | 4.53 ± 12.23 | 4.56 ± 1.38 | −0.677 | 0.488 |
| Triglycerides (m·mol/l) | 1.25 ± 1.01 | 1.39 ± 1.18 | 1.16 ± 0.87 | 6.700 | <0.01 |
| LDL-Cholesterol (m·mol/L) | 2.40 ± 0.87 | 2.46 ± 0.91 | 2.36 ± 0.84 | 3.568 | <0.01 |
| HDL-Cholesterol (m·mol/L) | 1.41 ± 0.62 | 1.35 ± 0.57 | 1.44 ± 0.65 | −4.987 | <0.01 |
| Overweight (%) | 27.4 | 28.6 | 26.6 | 1.870 | 0.171 |
| Obesity (%) | 18.2 | 18.4 | 18.1 | 0.750 | 0.784 |
| Hypertension (%) | 36.7 | 42.0 | 33.3 | 30.968 | <0.01 |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 49.5 | 53.7 | 46.8 | 18.212 | <0.01 |
3.2. Prevalence of DM and IFG in Different Ages and Sex
| Age Group (Years) | Total Group | Male | Female | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | IFG | Diabetes | IFG | Diabetes | IFG | ||||||||
| N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | N | % | ||
| 18–24 | 10 | 2.9 | 20 | 5.9 | 4 | 3.2 | 9 | 7.2 | 6 | 2.8 | 11 | 5.1 | |
| 25–34 | 19 | 2.5 | 57 | 7.5 | 11 | 3.7 | 29 | 9.7 | 8 | 1.7 | 28 | 6.0 | |
| 35–44 | 36 | 3.6 | 78 | 7.8 | 19 | 5.3 | 32 | 8.8 | 17 | 2.5 * | 46 | 7.2 | |
| 45–54 | 72 | 7.3 | 118 | 12.0 | 32 | 8.5 | 58 | 15.4 | 40 | 6.6 | 60 | 9.9 * | |
| 55–64 | 72 | 11.6 | 93 | 15.0 | 39 | 13.1 | 47 | 15.8 | 33 | 10.3 | 46 | 14.3 | |
| ≥65 | 22 | 10.5 | 27 | 12.9 | 10 | 11.0 | 14 | 15.4 | 12 | 10.2 | 13 | 11.0 | |
| Total prevalence | 231 | 5.9 | 393 | 10.0 | 115 | 7.4 | 189 | 12.2 | 116 | 4.9 * | 204 | 8.6 * | |
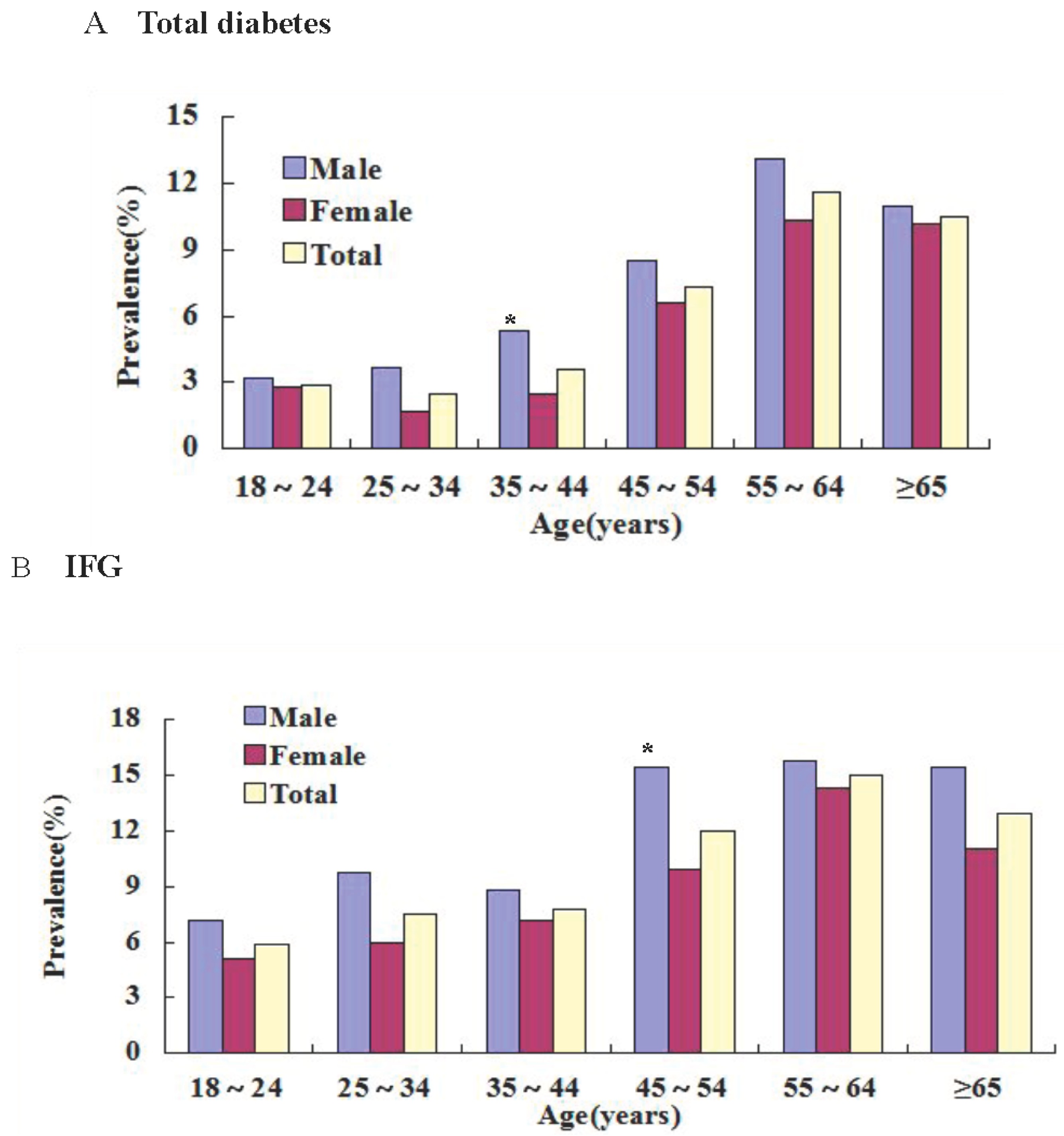
3.3. Prevalence of DM and IFG in Different BMI
| BMI | Total Group | Male | Female | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetes | IFG | Diabetes | IFG | Diabetes | IFG | |||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | |
| Normal | 73 | 3.4 | 172 | 8.1 | 41 | 5.0 | 85 | 10.3 | 32 | 2.4 * | 87 | 6.7 * |
| Overweight | 72 | 6.7 | 128 | 11.9 | 36 | 8.1 | 56 | 12.6 | 36 | 5.7 | 72 | 11.4 |
| Obesity | 86 | 12.0 | 93 | 13.0 | 38 | 13.3 | 48 | 16.8 | 48 | 11.2 | 45 | 10.5 * |
| Total | 231 | 5.9 | 393 | 10.0 | 115 | 7.4 | 189 | 12.2 | 116 | 4.9 * | 204 | 8.6 * |
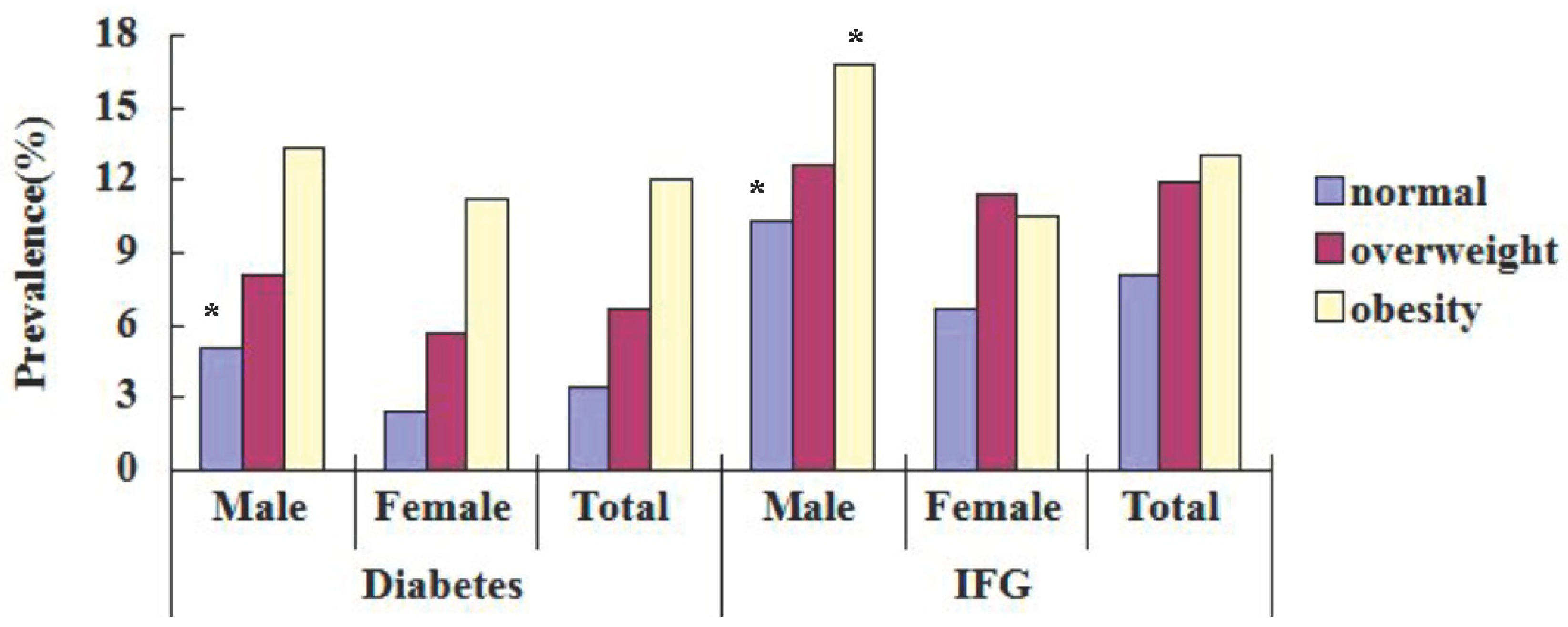
3.4. Adjusted ORs of Associated Factors for Diabetes
| Explanatory Variables | β | Odds Ratio | OR 95%CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Females sex (vs. males) | −0.355 | 0.702 | 0.52–0.946 | 0.020 |
| Age(control:18–24 year) | ||||
| 25–34 | 0.286 | 1.332 | 0.592–2.994 | 0.488 |
| 35–44 | 0.47 | 1.600 | 0.744–3.437 | 0.229 |
| 45–54 | 1.088 | 2.969 | 1.441–6.119 | 0.003 |
| 55–64 | 1.422 | 4.144 | 1.995–8.610 | <0.01 |
| ≥65 | 1.421 | 4.140 | 1.746–9.816 | 0.001 |
| unmarried (vs. married) | 1.552 | 4.723 | 3.382–6.596 | <0.01 |
| Overweight | 1.153 | 3.166 | 1.119–8.958 | 0.030 |
| Obesity | 0.375 | 1.454 | 1.04–2.035 | 0.029 |
| Hypertension | 0.481 | 1.618 | 1.183–2.213 | 0.003 |
| Triglycerides | 0.773 | 2.167 | 1.574–2.983 | <0.01 |
| Smoking (vs. no smoking) | 0.521 | 1.684 | 1.199–2.366 | 0.003 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interests
References
- Shaw, J.E.; Sicree, R.A.; Zimmet, P.Z. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 87, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guariguata, L.; Whiting, D.R.; Hambleton, I.; Beagle, J.; Linnenkamp, U.; Shaw, J.E. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035 for the IDF Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, D.; Reynolds, K.; Duan, X.; Xin, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Mo, J.; Whelton, P.K.; He, J.; InterASIA Collaborative Group. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in the Chinese adult population: International Collaborative Study of Cardiovascular Disease in Asia (InterASIA). Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lu, J.; Weng, J.; Jia, W.; Ji, L.; Xiao, J.; Shan, Z.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Ji, Q.; et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X. China’s demographic history and future challenges. Science 2011, 333, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. WHO Tech. Rep. Ser. 2000, 894, 1–253. [Google Scholar]
- Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications, Part 1: Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- Li, R.; Lu, W.; Jiang, Q.W.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhao, G.M.; Shi, L.; Yang, Q.D.; Ruan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, S.N.; et al. Increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes in Chinese adults in Shanghai. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1028–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Gao, W.; Nan, H.; Yu, H.; Li, F.; Duan, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Qian, R.; Tuomilehto, J.; Qiao, Q. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes in urban and rural Chinese populations in Qingdao. China Diabetes Med. 2005, 22, 1427–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.H.; Yang, Y.C.; Wu, J.S.; Wu, C.H.; Chang, C.J. A population-based study of the prevalence and associated factors of diabetes mellitus in southern Taiwan. Diabetes Med. 1998, 15, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Zhai, F. The Tenth Report on the China National Nutrition and Health Survey—The 2002 Dataset; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Song, Y.; Yi, G.; Xu, S.; Guo, B. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose in urban and rural residents of Hubei Province. Hua Zhong Ke Ji Da Xue Xue Bao 2010, 39, 572–576. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.N.; Xie, X.; Ma, Y.T.; Li, X.M.; Fu, Z.Y.; Ma, X.; Huang, D.; Chen, B.-D.; Liu, F.; Huang, Y.; et al. Type 2 diabetes in Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region, China. PLoS One 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, G.; Lai, X.; Huang, B.; Chen, Z.; Yao, L.; Zhu, S.; Yao, J.; Wen, J.; Huang, H.; Lin, C. Diabetes and its chronic complications in the she ethnic minority group of China. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2012, 14, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, K.; Wu, N.; Wang, D.; Li, P.; Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J. Prevalence of diabetes among Han, Manchu and Korean ethnicities in the Mudanjiang area of China: A cross-sectional survey. BMC Public Health 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Health Statistics National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005–2006. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/about/major/nhanes2005–2006/nhanes05_06.htm (accessed on 31 March 2014).
- Ujcic-Voortman, J.K.; Schram, M.T.; van der Bruggen, M.A.J.; Verhoeff, A.P.; Baan, C.A. Diabetes prevalence and risk factors among ethnic minorities. Eur. J. Public Health 2009, 19, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, F.; Yuan, S.; Pan, S.; Peng, X.; Sun, M. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired fasting glucose among Kazaks population study in Fuhai County of Xingu, China. China Diabet Med. 2010, 2, 424–427. [Google Scholar]
- Anniwaer, A.; Wang, L.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Liu, F. Prevalence of diabetes among Uyghurs populations in Hetian region of Xinjiang, China. Chin. J. Gen. Pract. 2011, 9, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Qiu, Q.; Tan, L.L.; Liu, T.; Deng, X.Q.; Chen, Y.M.; Chen, W.; Yu, X.Q.; Hu, B.J.; Chen, W.Q. Prevalence and determinants of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose among urban community-dwelling adults in Guangzhou, China. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 35, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, H.; Shi, Z.; Hussain, A. Prevalence, trends and risk factors for the diabetes epidemic in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 104, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Rimm, E.B.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Comparison of abdominal adiposity and overall obesity in predicting risk of type 2 diabetes among men. Amer. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Shuxia, G.; Rulin, M.; Heng, G.; Jingyu, Z.; Shangzhi, X.; Dongsheng, R.; Yusong, D.; Jieting, C. Prevalence of dyslipidemia among Kazakh and Han adult populations in Xinjiang area. China J. Public Health 2012, 28, 435–438. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaojia, M.; Mei, Z.; Shuxia, G.; Rulin, M.; Yusong, D. Prevalence of hypertension in Uyghur, Kazakhs and Han people in rural areas of Xinjiang. China J. Hypertens. 2013, 21, 1164–1168. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Guo, S.; He, F.; Zhang, M.; He, J.; Yan, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Guo, H.; et al. Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Fasting Glucose, Associated with Risk Factors in Rural Kazakh Adults in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 554-565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120100554
Li S, Guo S, He F, Zhang M, He J, Yan Y, Ding Y, Zhang J, Liu J, Guo H, et al. Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Fasting Glucose, Associated with Risk Factors in Rural Kazakh Adults in Xinjiang, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2015; 12(1):554-565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120100554
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shugang, Shuxia Guo, Fei He, Mei Zhang, Jia He, Yizhong Yan, Yusong Ding, Jingyu Zhang, Jiaming Liu, Heng Guo, and et al. 2015. "Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Fasting Glucose, Associated with Risk Factors in Rural Kazakh Adults in Xinjiang, China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 12, no. 1: 554-565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120100554
APA StyleLi, S., Guo, S., He, F., Zhang, M., He, J., Yan, Y., Ding, Y., Zhang, J., Liu, J., Guo, H., Xu, S., & Ma, R. (2015). Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Fasting Glucose, Associated with Risk Factors in Rural Kazakh Adults in Xinjiang, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 12(1), 554-565. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120100554






