Influence of Surfactant and Lipid Type on the Physicochemical Properties and Biocompatibility of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Cell Line
2.2. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) Preparation
2.3. Dynamic light scattering and zeta potential
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. Cell Viability Assay
2.7. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.8. Morphological Identification for Cell Death
2.9. Erythrocyte Hemolysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) Preparation and Characterization
| SLN * | Tripalmitin (%) | Glycerol Monostearate (%) | Stearic Acid (%) | Polysorbate 80 (%) | Lecithin S75 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 2 | - | - | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| F2 | 2 | - | - | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| F3 | 2 | - | - | 1.2 | 0.3 |
| F4 | - | 2 | - | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| F5 | - | 2 | - | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| F6 | - | 2 | - | 1.2 | 0.3 |
| F7 | - | - | 2 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| F8 | - | - | 2 | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| F9 | - | - | 2 | 1.2 | 0.3 |
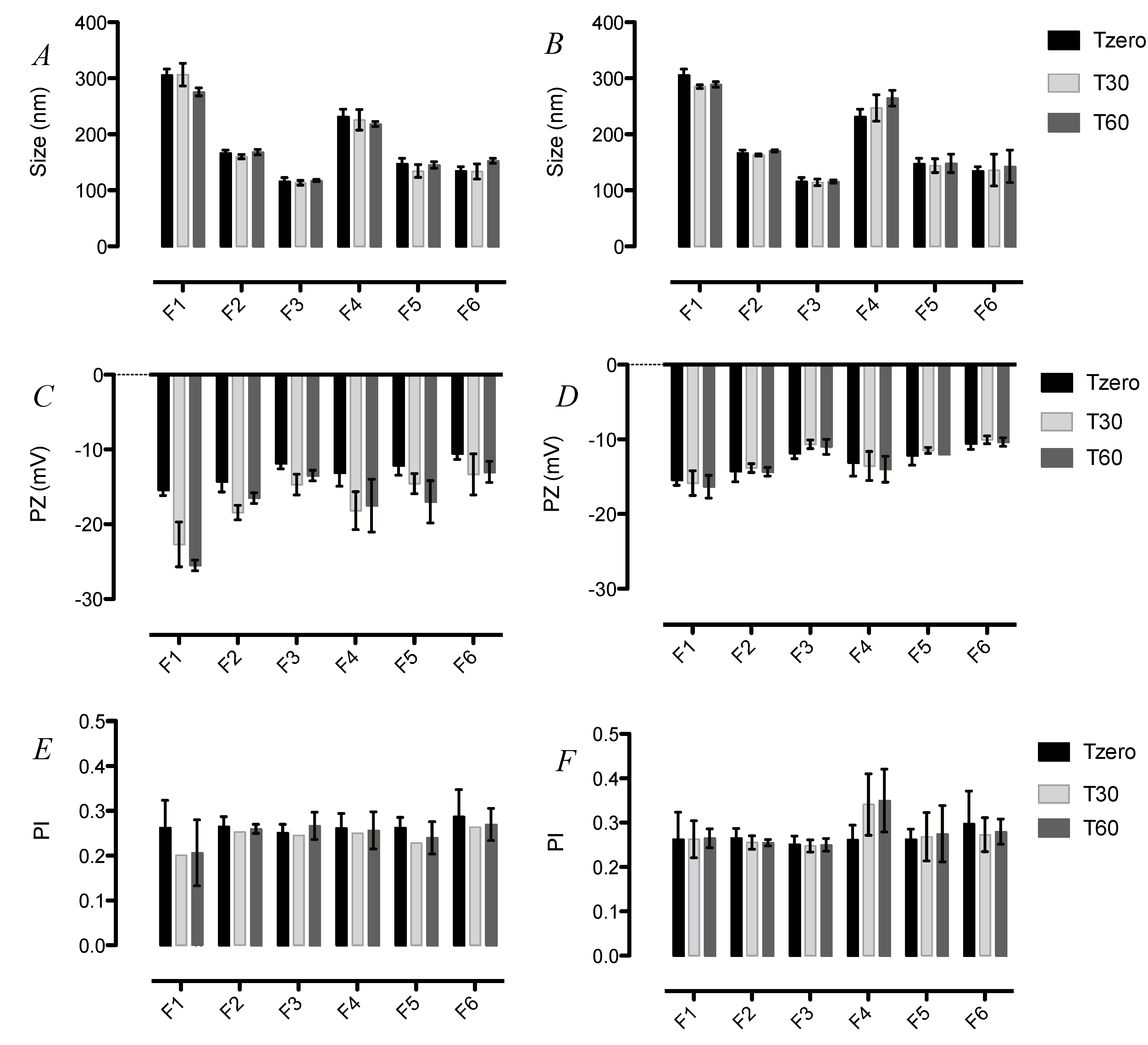
| SLN | z-Average Diameter (nm) * | PI * | Zeta Potential (mV) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 306 ± 9.9 | 0.26 ± 0.06 | −15 ± 0.7 |
| F2 | 167 ± 5.3 | 0.27 ± 0.02 | −14 ± 1.4 |
| F3 | 116 ± 6.9 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | −12 ± 0.7 |
| F4 | 232 ± 13 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | −13 ± 1.8 |
| F5 | 148 ± 9.3 | 0.26 ± 0.02 | −12 ± 1.3 |
| F6 | 135 ± 7.5 | 0.30 ± 0.07 | −11 ± 0.8 |
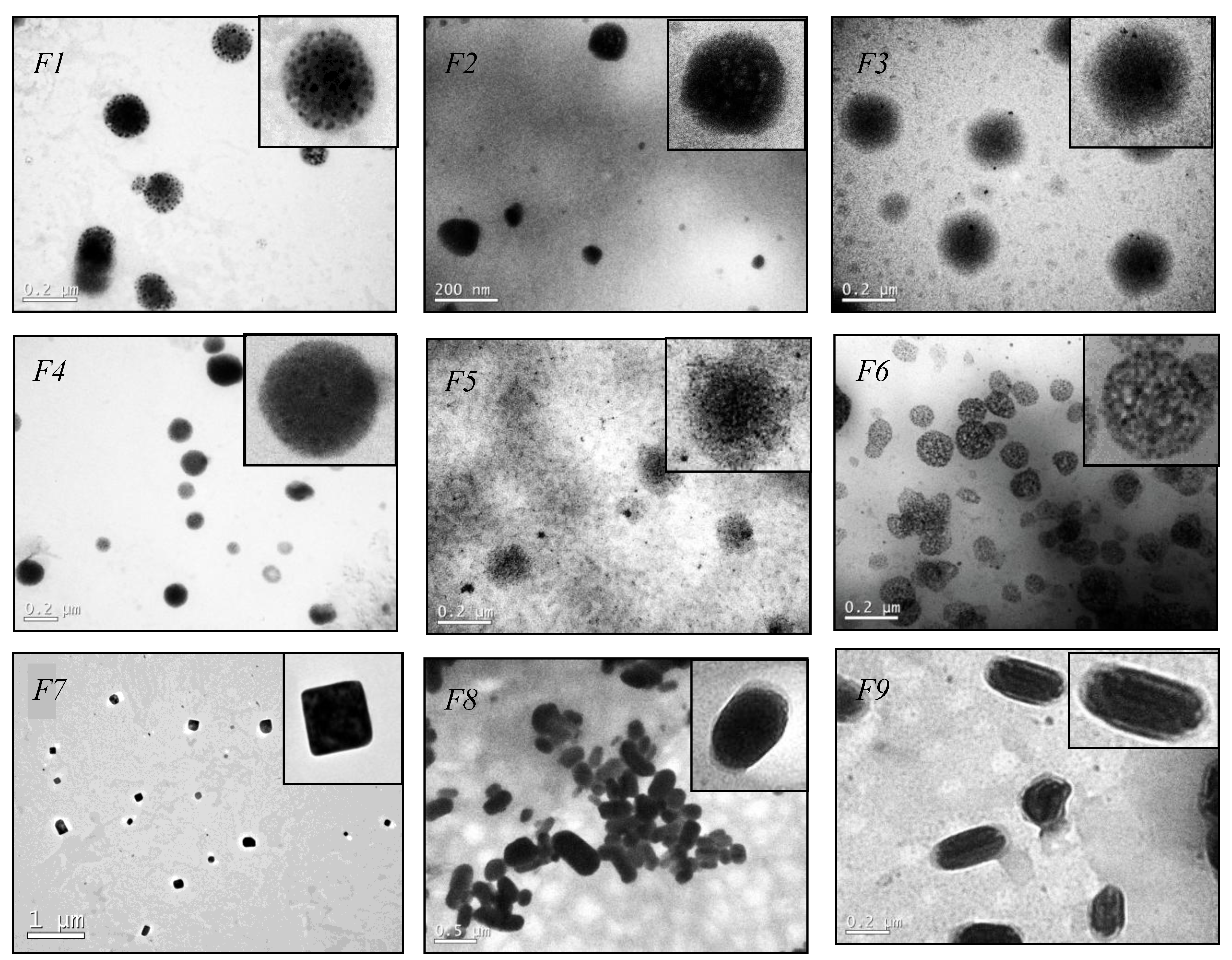
3.2. Stability of SLN upon Storage
3.3. Cell Viability Assay
| SLN | CC50 (μg·mL−1) * |
|---|---|
| F1 | 1420 ± 20 |
| F2 | 730 ± 12 |
| F3 | 602 ± 39 |
| F4 | 410 ± 27 |
| F5 | 480 ± 32 |
| F6 | 260 ± 15 |
| F7 | 330 ± 19 |
| F8 | 210 ± 38 |
| F9 | 310 ± 25 |
3.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
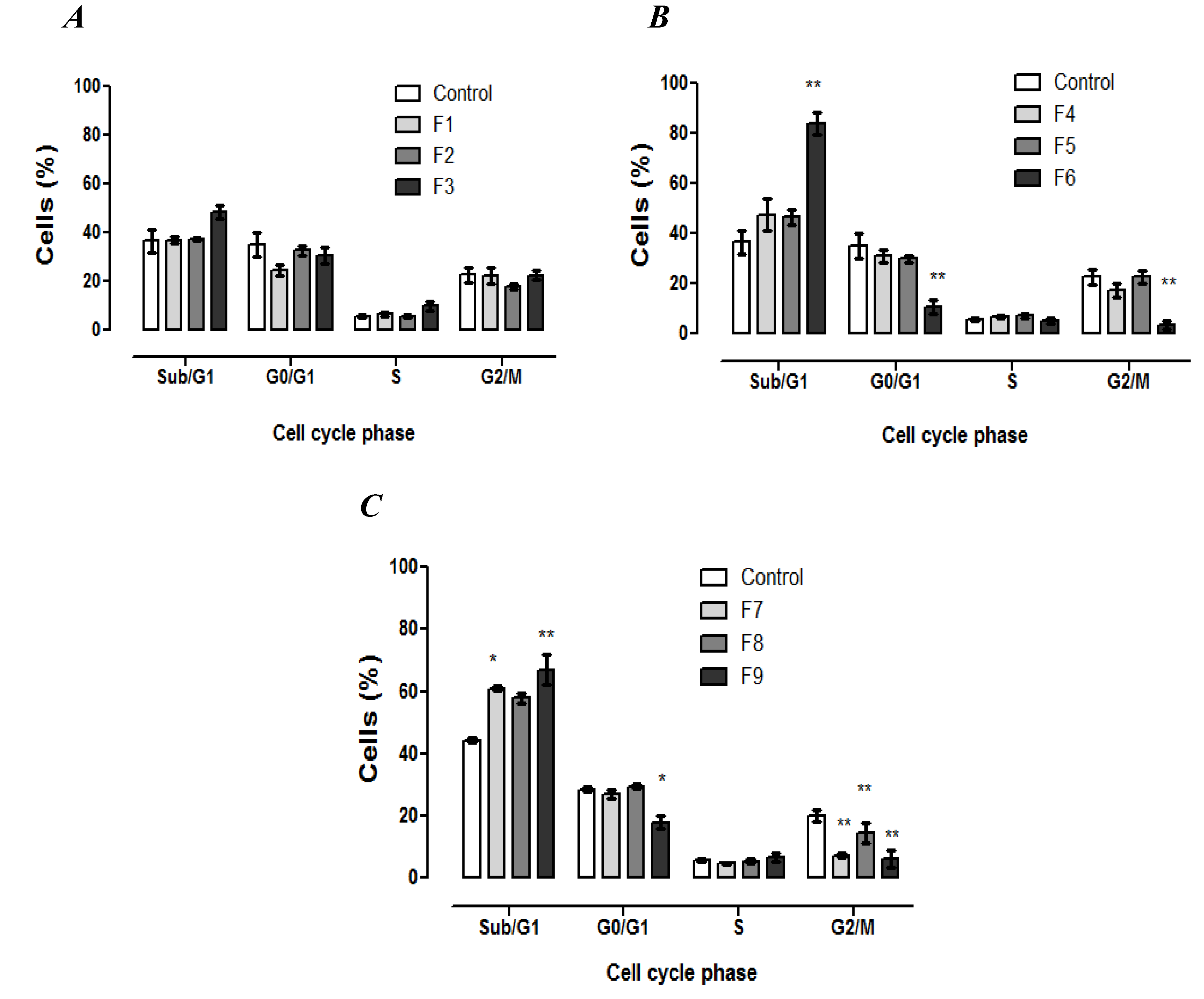
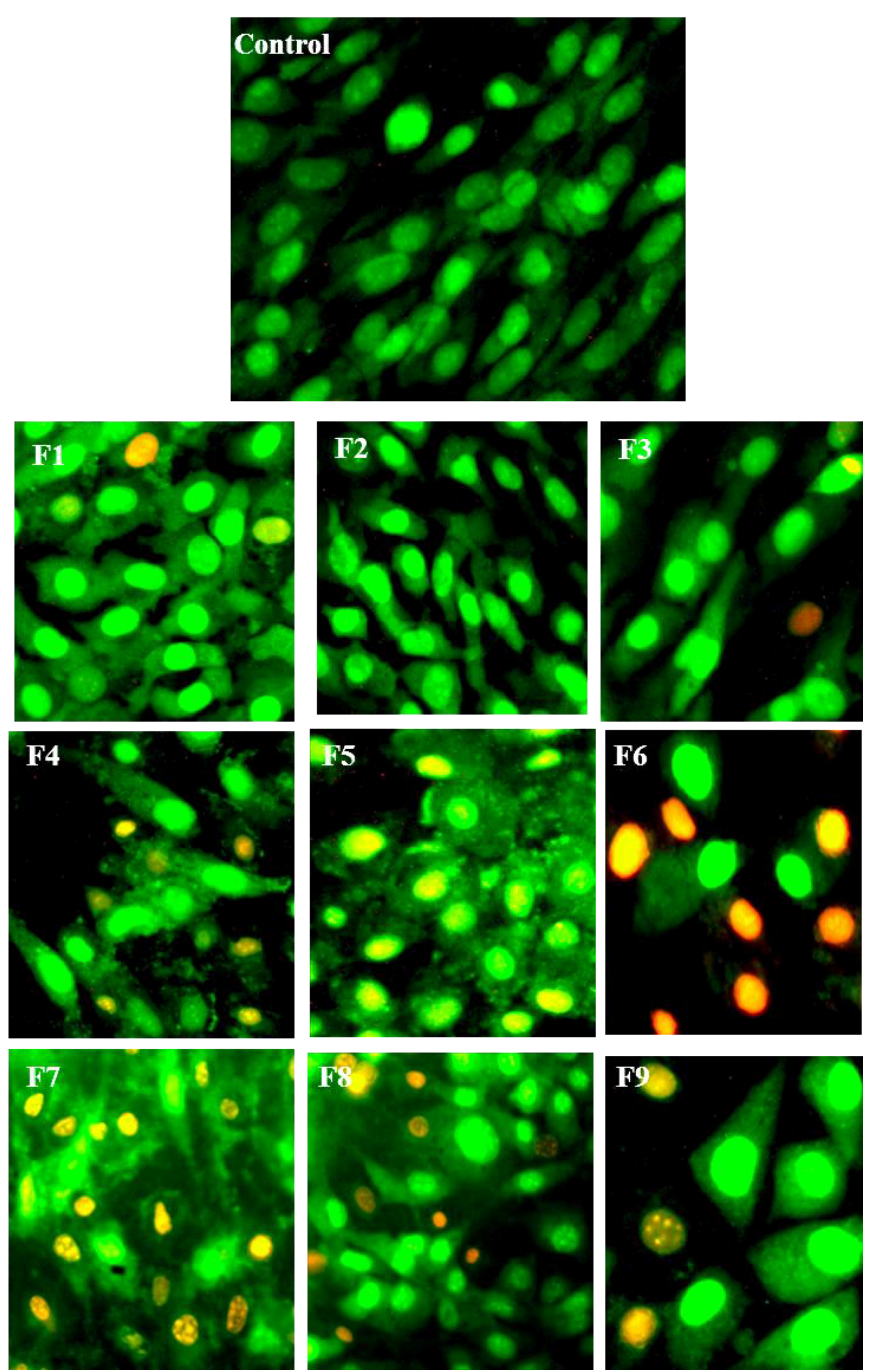
3.5. Morphological Identification of Cell Death
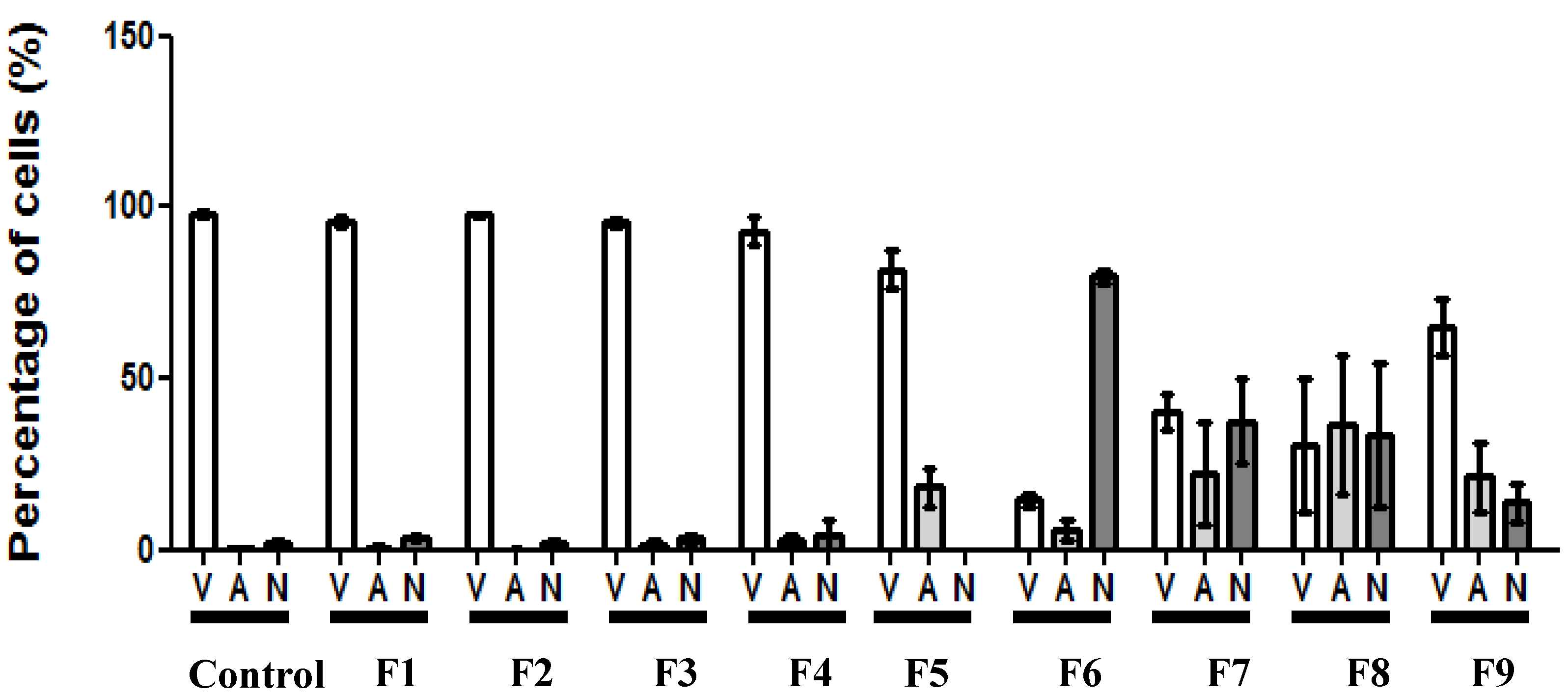
3.6. Erythrocyte Hemolysis
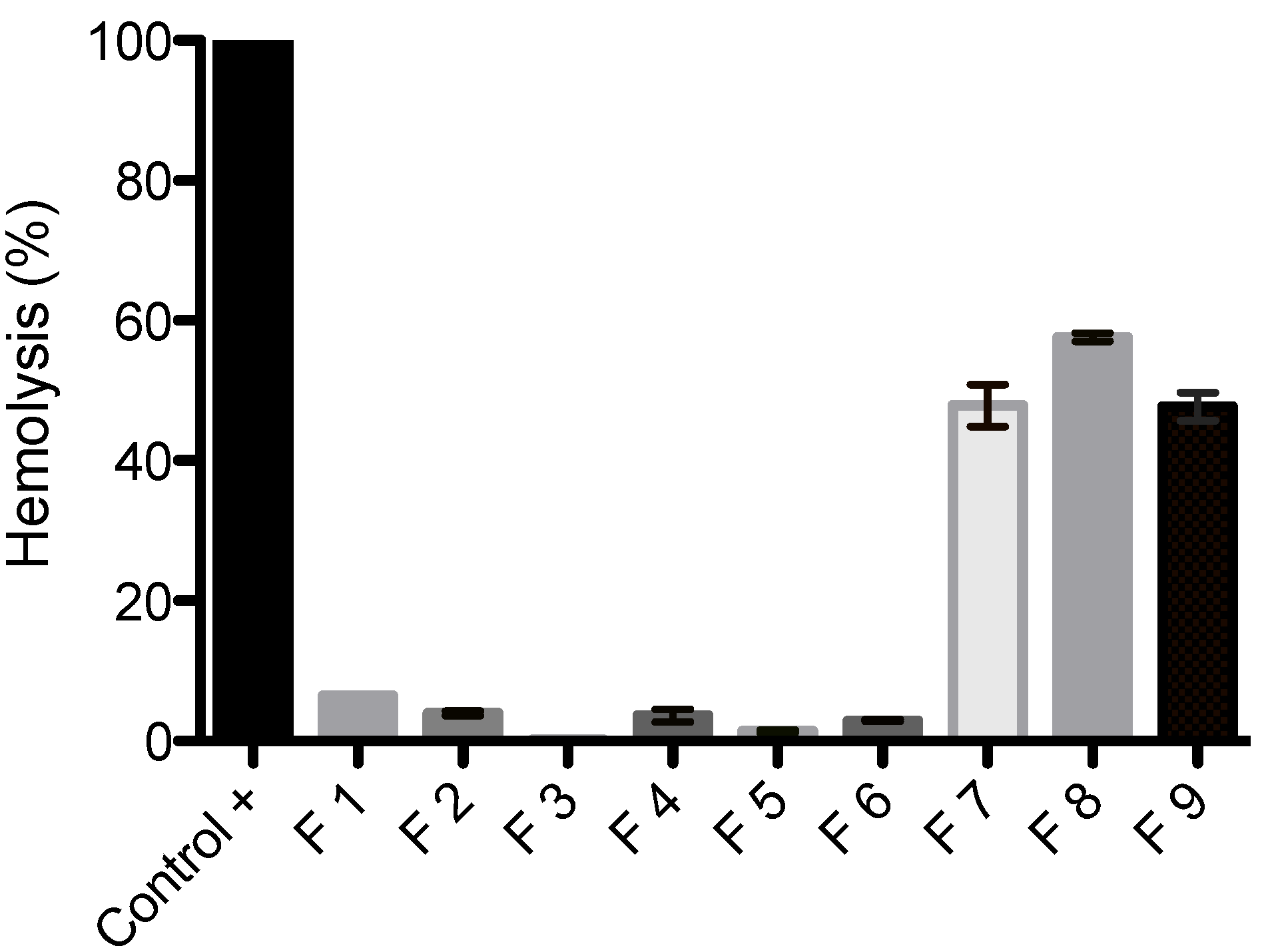
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.J.; Liu, K.S.; Sung, K.C.; Tsai, C.Y.; Fang, J.Y. Lipid nanoparticles with different oil/fatty ester ratios as carriers of buprenorphine and its prodrugs for injection. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 38, 138–146. [Google Scholar]
- Mitri, K.; Shegokar, R.; Gohla, S.; Anselmi, C.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanocarriers for dermal delivery of lutein: Preparation, characterization, stability and performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 414, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswarlu, V.; Manjunath, K. Preparation, characterization and in vitro release kinetics of clozapine solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Control Release 2004, 95, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Mader, K.; Gohla, S. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—A review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar]
- Pardeike, J.; Hommoss, A.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles (SLN, NLC) in cosmetic and pharmaceutical dermal products. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 366, 170–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kheradmandnia, S.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E.; Nosrati, M.; Atyabi, F. Preparation and characterization of ketoprofen-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles made from beeswax and carnauba wax. Nanomed. Nanotech. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uner, M. Preparation, characterization and physico-chemical properties of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN) and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC): Their benefits as colloidal drug carrier systems. Pharmazie 2006, 61, 375–386. [Google Scholar]
- Mehnert, W.; Máder, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles: Production, characterization and applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.R.; Mehnert, W.; Lucks, J.S.; Schwarz, C.; Zur Mühlen, A.; Weyhers, H.; Freitas, C.; Rühl, D. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN): An alternative colloidal carrier system for controlled drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1995, 41, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Anna, R.S. Stability of lipid excipients in solid lipid nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Meth. 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, S.; Steiniger, F.; Fischer, D.; Fahr, A.; Bunjes, H. The physical state of lipid nanoparticles influences their effect on in vitro cell viability. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 150–161. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, M.D.; Müller, R.H. Lipid nanoparticles for parenteral delivery of actives. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 61–172. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Gong, T.; Fu, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; He, Q.; Zhang, Z. Solid lipid nanoparticles for pulmonary delivery of insulin. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 356, 333–344. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.H.; Runge, S.; Ravelli, V.; Mehnert, W.; Thünemann, A.F.; Souto, E.B. Oral bioavailability of cyclosporine: Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) versus drug nanocrystals. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 317, 82–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Zhang, W.; Du, Y.Z.; Hu, F.Q. Ternary nanoparticles of anionic lipid nanoparticles/protamine/DNA for gene delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 392, 224–231. [Google Scholar]
- Weyenberg, W.; Filev, P.; Van den Plas, D.; Vandervoort, J.; de Smet, K.; Sollie, P.; Ludwig, A. Cytotoxicity of submicron emulsions and solid lipid nanoparticles for dermal application. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 337, 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.H.; Filippin-Monteiro, F.B.; Mattei, B.; Zanetti-Ramos, B.G.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B. In vitro biocompatibility of solid lipid nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 432, 382–388. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, M.N.; Pandit, A.B. Cavitation—A novel technique for making stable nano-suspensions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, F.; Wu, P. 23,24-Dihydrocucurbitacin B induces G2/M cell-cycle arrest and mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human breast cancer cells (Bcap37). Cancer Lett. 2007, 256, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.J. Apoptosis. Immunol. Today 1993, 14, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garti, N.; Wellner, E.; Sarig, S. Effect of surfactants on crystal structure modification of stearic acid. J. Cryst. Growth 1982, 57, 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- Zetzl, A.; Ollivon, M.; Marangon, A. A coupled differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray study of the mesomorphic phases of monostearin and stearic acid in water. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 3928–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, G.; Larsson, K.; Johansson, L.; Fontell, K.; Forsén, S. The cubic phase of monoglyceride-water systems. Arguments for a structure based upon Lamellar Bilayer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979, 101, 5465–5470. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, R.H.; Lucks, J.S. Azneistoffträger Aus Festen Lipidteilchen—Feste Lipid Nanosphären (SLN). European Patent 0605497, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Heurtault, B.; Saulnier, P.; Pech, B.; Proust, J.E.; Benoit, J.P. Physico-chemical stability of colloidal lipid particles. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4283–4300. [Google Scholar]
- Pouton, C.W.; Porter, C.J.H. Formulation of lipid-based delivery systems for oral administration: Materials, methods and strategies. Adv. Drug Del. Rev. 2008, 60, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Gong, C.; Wang, Y.; Guo, G.; Luo, F.; Qian, Z. Polysorbate 80 coated poly (ɛ-caprolactone)–poly (ethylene glycol)–poly (ɛ-caprolactone) micelles for paclitaxel delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 434, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pereverzeva, E.; Treschalin, I.; Bodyagin, D.; Maksimenko, O.; Langer, K.; Dreis, S.; Asmussen, B.; Kreuter, J.; Gelperina, S. Influence of the formulation on the tolerance profile of nanoparticle-bound doxorubicin in healthy rats: Focus on cardio- and testicular toxicity. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 337, 346–356. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, D.H.; Shin, J.S.; Jin, F.L.; Shin, G.S.; Park, S.J. Effect of hydrogenated lecithin on cytotoxicity of liposome. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2009, 30, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, A.; Lovrié, J.; Voinovich, D.; Filipovié-Gréié, J. Melatonin-loaded lecithin/chitosan nanoparticles: Physicochemical characterisation and permeability through Caco-2 cell monolayers. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 381, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, R.; Eleutério, C.V.; Gonçalves, L.M.D.; Cruz, M.E.M.; Almeida, A.J. Lipid nanoparticles containing oryzalin for the treatment of leishmaniasis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckman, M.A.; Randolph, L.N.; VanMeter, A.; Hern, S.; Shoffstall, A.J.; Taurog, R.E.; Steinmetz, N.F. Biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, and blood compatibility of native and PEGylated tobacco mosaic virus nano-rods and -spheres in mice. Virol. J. 2014, 449, 163–173. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.C.; Kamal, M.; Nasreen, N.; Baumuratov, A.; Sharma, P.; Antony, V.B.; Moudgil, B.M. Influence of shape, adhension and simulated lung mechanics on amorphous silica nanoparticle toxicity. Adv. Powder Technol. 2007, 18, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnida; Janát-Amsbury, M.M.; Ray, A.; Peterson, C.M.; Ghandehari, H. Geometry and surface characteristics of gold nanoparticles influence their biodistribution and uptake by macrophages. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 77, 417–423. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, M.; Pathak, S.; Sharma, S.; Patravale, V. Design and in vivo pharmacodynamic evaluation of nanostructured lipid carriers for parenteral delivery of artemether: Nanoject. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Pizzol, C.D.; Filippin-Monteiro, F.B.; Restrepo, J.A.S.; Pittella, F.; Silva, A.H.; Alves de Souza, P.; Machado de Campos, A.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B. Influence of Surfactant and Lipid Type on the Physicochemical Properties and Biocompatibility of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8581-8596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110808581
Pizzol CD, Filippin-Monteiro FB, Restrepo JAS, Pittella F, Silva AH, Alves de Souza P, Machado de Campos A, Creczynski-Pasa TB. Influence of Surfactant and Lipid Type on the Physicochemical Properties and Biocompatibility of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11(8):8581-8596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110808581
Chicago/Turabian StylePizzol, Carine Dal, Fabíola Branco Filippin-Monteiro, Jelver Alexander Sierra Restrepo, Frederico Pittella, Adny Henrique Silva, Paula Alves de Souza, Angela Machado de Campos, and Tânia Beatriz Creczynski-Pasa. 2014. "Influence of Surfactant and Lipid Type on the Physicochemical Properties and Biocompatibility of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11, no. 8: 8581-8596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110808581
APA StylePizzol, C. D., Filippin-Monteiro, F. B., Restrepo, J. A. S., Pittella, F., Silva, A. H., Alves de Souza, P., Machado de Campos, A., & Creczynski-Pasa, T. B. (2014). Influence of Surfactant and Lipid Type on the Physicochemical Properties and Biocompatibility of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(8), 8581-8596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110808581





