Length of Stay for Mental and Behavioural Disorders Postpartum in Primiparous Mothers: A Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Definitions
2.4. Diagnosis of Mental and Behavioral Disorders
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethics Approval
3. Results
| Measurement | Diagnosis | N a | Patient Days | Mean ALOS | Median ALOS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days | 95% CI | Days | 95% CI | ||||||
| Entire length in the first year after birth | Principal | 2,479 | 28,212 | 11.38 | 10.70 | 12.06 | 6 | 5.87 | 6.13 |
| Non-principal | 3,679b | 23,286 | 6.33 | 6.14 | 6.52 | 6 | 5.92 | 6.08 | |
| Total | 5,861 | 51,498 | 8.79 | 8.45 | 9.12 | 6 | 5.93 | 6.07 | |
| Length per admission | Principal | 3,332 | 28,212 | 8.47 | 8.03 | 8.90 | 5 | 4.90 | 5.10 |
| Non-principal | 4,062 | 23,286 | 5.73 | 5.57 | 5.89 | 5 | 4.92 | 5.08 | |
| Overall | 7,394 | 51,498 | 6.96 | 6.75 | 7.18 | 5 | 4.93 | 5.07 | |
| Admissions | Sum | Mean ALOS | Median ALOS | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis | n | % | (Patient days) | % | Days | 95% CI | Days | 95% CI | ||
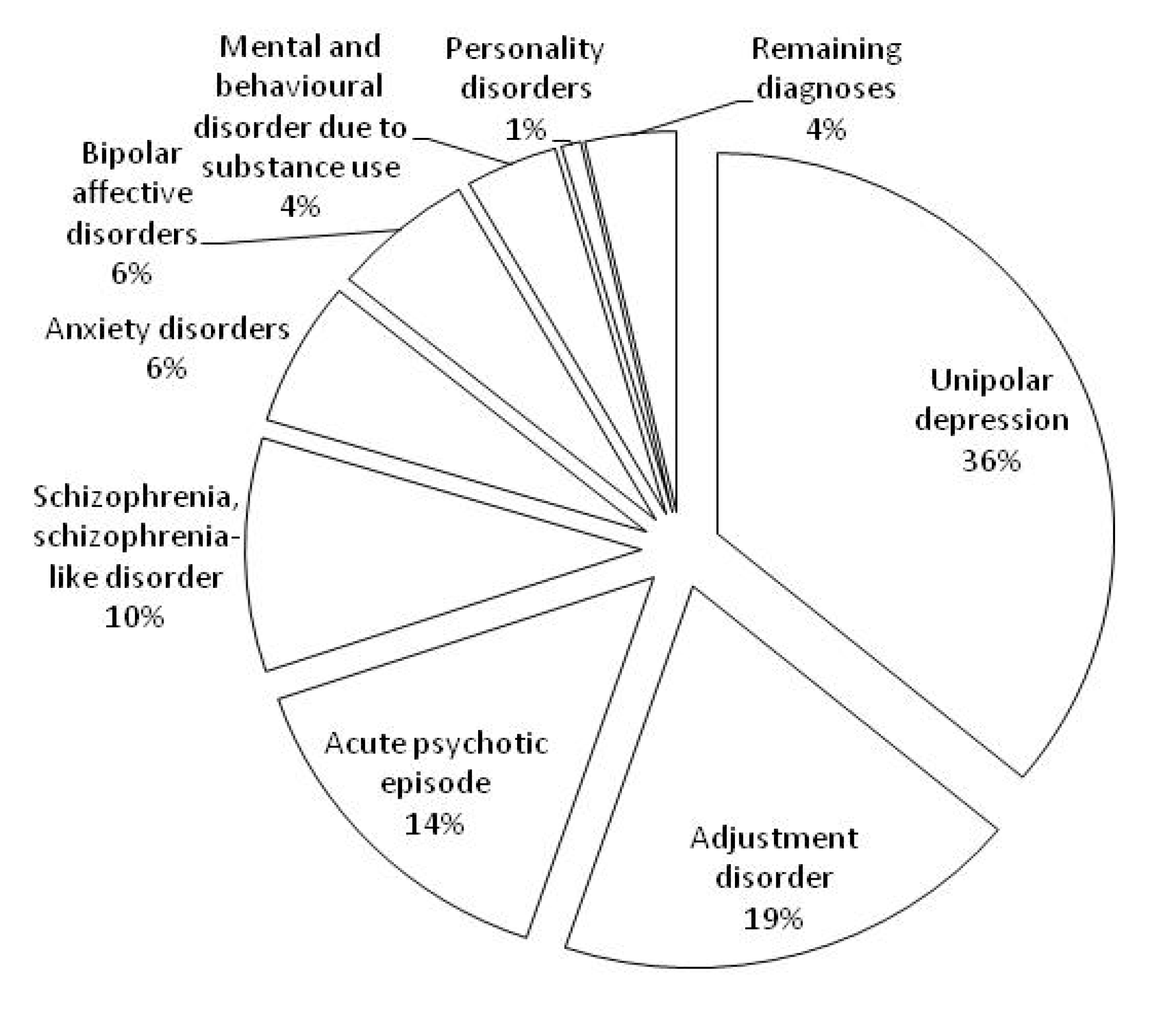
| Unipolar depression | 1,251 | 37.55 | 10,166 | 36.03 | 8.13 | 7.55 | 8.71 | 5 | 4.83 | 5.17 |
| Adjustment disorder | 905 | 27.16 | 5,410 | 19.18 | 5.98 | 5.78 | 6.17 | 6 | 5.87 | 6.13 |
| Acute psychotic episode | 220 | 6.60 | 4,121 | 14.61 | 18.73 | 16.06 | 21.40 | 12 | 9.31 | 14.69 |
| Schizophrenia, schizophrenia-like disorder | 125 | 3.75 | 2,800 | 9.92 | 22.40 | 15.91 | 28.89 | 9 | 4.30 | 13.70 |
| Anxiety disorders | 303 | 9.09 | 1,736 | 6.15 | 5.73 | 5.08 | 6.38 | 5 | 4.84 | 5.16 |
| Bipolar affective disorders | 105 | 3.15 | 1,642 | 5.82 | 15.64 | 12.79 | 18.49 | 11 | 7.87 | 14.14 |
| Mental and behavior disorder due to substance use | 273 | 8.19 | 1,062 | 3.76 | 3.89 | 3.20 | 4.59 | 1 | - | - |
| Personality disorders | 61 | 1.83 | 225 | 0.80 | 3.69 | 2.11 | 5.27 | 1 | - | - |
| Remaining diagnoses | 89 | 2.67 | 1,050 | 3.72 | 11.80 | 7.83 | 15.76 | 5 | 3.15 | 6.85 |
| Overall | 3,332 | 100.00 | 28,212 | 100.00 | 8.47 | 8.03 | 8.90 | 5 | 4.90 | 5.10 |
| Sum | Mean ALOS | Median ALOS | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Admissions | (Patient day) | Days | 95% CI | Days | 95% CI | ||
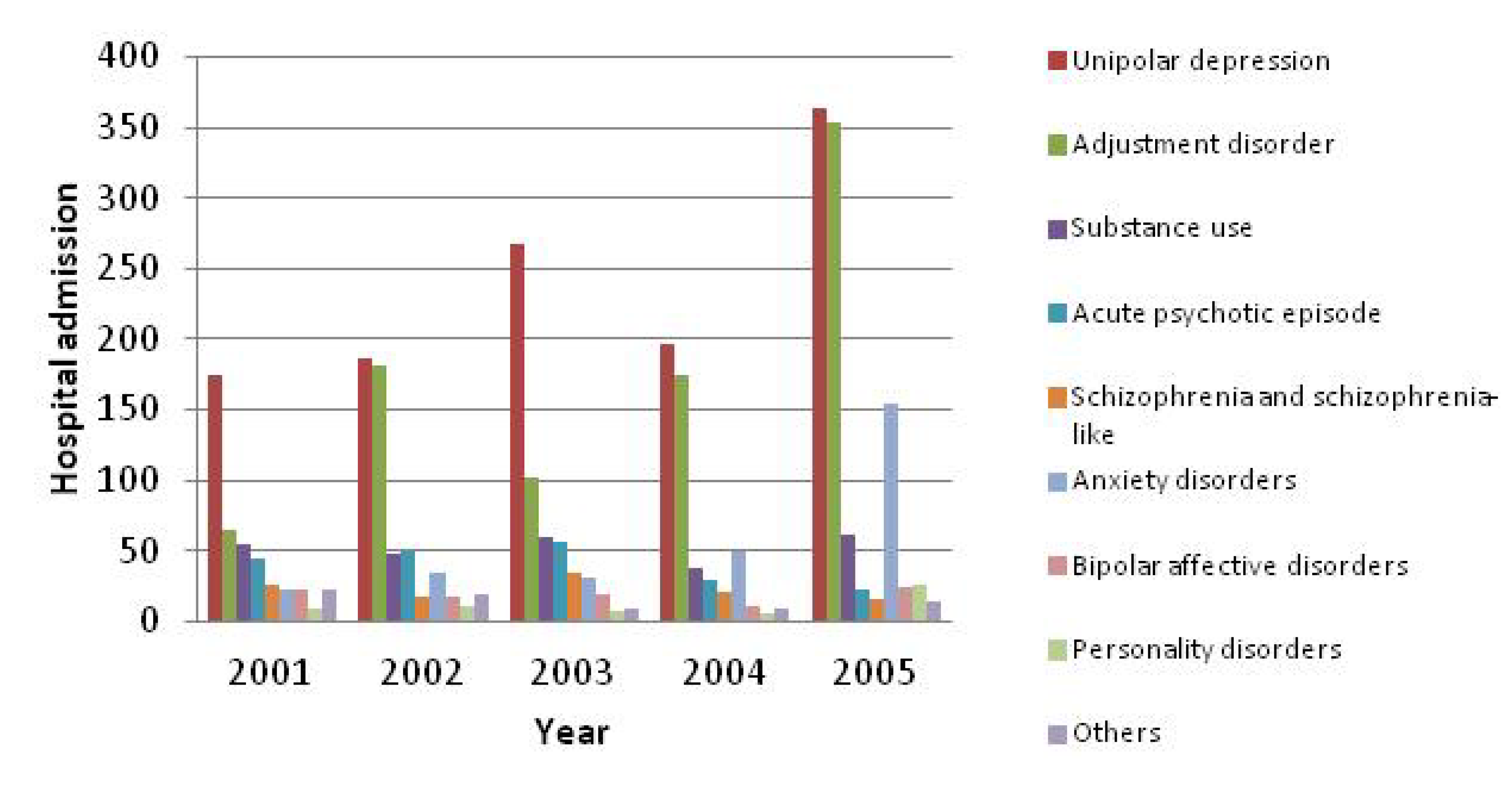
| 2000 a | 169 | 1,940 | 11.48 | 9.38 | 13.57 | 6 | 4.79 | 7.21 |
| 2001 | 441 | 4,353 | 9.87 | 8.46 | 11.28 | 5 | 4.56 | 5.44 |
| 2002 | 565 | 5,064 | 8.96 | 7.94 | 9.99 | 6 | 5.75 | 6.25 |
| 2003 | 587 | 4,788 | 8.16 | 6.77 | 9.55 | 5 | 4.75 | 5.25 |
| 2004 | 532 | 4,371 | 8.22 | 7.32 | 9.11 | 5 | 4.88 | 5.12 |
| 2005 | 1,038 | 7,696 | 7.41 | 6.83 | 7.99 | 6 | 5.85 | 6.15 |
| Overall | 3,332 | 28,212 | 8.47 | 8.03 | 8.90 | 5 | 4.90 | 5.10 |
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
List of Abbreviations
| ALOS | Average Length of Stay |
| APDC | Admitted Patients Data Collection |
| CHeReL | Centre for Health Record Linkage |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| MBD | Mental and Behavioural Disorders |
| MDC | Midwives Data Collection |
| NHMRC | The National Health and Medical Research Council |
| NSW | New South Wales |
| US | United States |
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Mental Health Aspects of Women’s Reproductive Health: A Global Review of the Literature; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. Available online: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2009/9789241563567_eng.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- O’Hara, M.W.; Swain, A.M. Rates and risk of postpartum depression—A meta-analysis. Int. Rev. Psychiatr. 1996, 8, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, N.; Gaynes, B.; Lohr, K.; Meltzer-Brody, S.; Gartlehner, G.; Swinson, T. Perinatal depression: A systematic review of prevalence and incidence. Obstet. Gynecol. 2005, 106, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munk-Olsen, T.; Laursen, T.M.; Pedersen, C.B.; Mors, O.; Mortensen, P.B. New parents and mental disorders: A population-based register study. JAMA 2006, 296, 2582–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws, P.; Abeywardana, S.; Walker, J.; Sullivan, E. Australia’s Mothers and Babies 2005; Perinatal Statistics Series No. 20; AIHW National Perinatal Statistics Unit: Sydney, Australia, 2007. Available online: http://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442458959 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Mental Health Services in Australia 2004–05; Mental Health Series No. 9; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2007. Available online: http://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442456853 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Australian Hospital Statistics 2000–01; Health Services Series No. 19; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2002. Available online: http://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442456508 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Australian Hospital Statistics 2001–02; Health Services Series No. 20; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2003. Available online: http://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442456589 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Australian Hospital Statistics 2002–03; Health Services Series No. 22; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2004. Available online: https://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442456688 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Australian Hospital Statistics 2003–04; Health Services Series No. 23; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2005. Available online: https://aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442456747 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Australian Hospital Statistics 2004–05; Health Services Series No. 26; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2006. Available online: http://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442456820 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Australian Hospital Statistics 2005–06; Health Services Series No. 30; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2007. Available online: http://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442456888 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Kendell, R.E.; Chalmers, J.C.; Platz, C. Epidemiology of puerperal psychoses. Brit. J. Psychiat. 1987, 150, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrou, S.; Cooper, P.; Murray, L.; Davidson, L.L. Economic costs of post-natal depression in a high-risk British cohort. Brit. J. Psychiat. 2002, 181, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.; Cramer-Benjamin, D.; Anastas, J. Predicting length of stay of substance-using pregnant and postpartum women in day treatment. J. Subst. Abuse Treat. 1997, 14, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Centre for Classification in Health (NCCH). The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision, Australian Modification Source Information; ICD-10-AM; NCCH: Sydney, Australia, 1999. Available online: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/sourcereleasedocs/current/ICD10AM/ (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- How Health Record Linkage Works. Available online: http://www.cherel.org.au/how-record-linkage-works/technical-details (accessed on 12 March 2014).
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (AIHW). Australian Hospital Statistics 2008–09; Health Services Series No. 17; AIHW: Canberra, Australia, 2010. Available online: http://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442457186 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Xu, F.; Hilder, L.; Austin, M.P.; Sullivan, E.A. Data preparation techniques for a perinatal psychiatric study based on linked data. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM SPSS Software. Available online: http://www-01.ibm.com/software/analytics/spss (accessed on 12 March 2014).
- Gifford, E.; Foster, E.M. Provider-level effects on psychiatric inpatient length of stay for youth with mental health and substance abuse disorders. Med. Care 2008, 46, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, L.; Mattick, R.P.; Cooke, M. The use of record linkage to examine illicit drug use in pregnancy. Addiction 2006, 101, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mental Health Services in Australia 2007–08. Available online: https://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442457209 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Yelland, J.; Sutherland, G.; Brown, S.J. Postpartum anxiety, depression and social health: Findings from a population-based survey of Australian women. BMC Public Health 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almond, P. Postnatal depression: A global public health perspective. Persp. Public Health 2009, 129, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New South Wales Mothers and Babies 2005. Available online: http://www.publish.csiro.au/?act=view_file&file_id=NB07S01.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- National Centre for Classification in Health (NCCH). The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Revision, Australian Modification Source Information; ICD-10-AM; NCCH: Sydney, Australia, 1999. Available online: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/research/umls/sourcereleasedocs/current/ICD10AM/ (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- National Center for Classification in Health. ICD-10-AM Early Parenting Manual: Guidelines for Use of the Early Parenting Manual in Early Parenting Centres, 2nd ed.; National Centre for Classification in Health: Sydney, NSW, Australia.
- Mai, Q.; Holman, C.D.J.; Sanfilippo, F.; Emery, J.; Preen, D. Mental illness related disparities in diabetes prevalence, quality of care and outcomes: A population-based longitudinal study. BMC Med. 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Hospital Statistics 2009–10. Available online: https://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=10737418865 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Mental Health Services in Australia 2001–02. Available online: http://www.aihw.gov.au/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=6442456665 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- National Mental Health Report 2010: Summary of 15 Years of Reform in Australia’s Mental Health Services under the National Mental Health Strategy 1993–2008. Available online: http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/58B9C24B0D74E79ACA257BF0001FEADF/$File/report10v3.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- The Beyondblue National Postnatal Depression Program : Prevention and Early Intervention 2001–2005. Available online: http://www.beyondblue.org.au/docs/default-source/8.-perinatal-documents/bw0075-report-beyondblue-national-research-program-vol2.pdf?sfvrsn=2 (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Framework for the National Perinatal Depression Initiative 2008–09 to 2012–13. Available online: http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/content/D617C5D13F84437BCA257BF0001ACD7D/$File/perinat.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Supporting Families Early SAFE START Strategic Policy. Available online: http://www0.health.nsw.gov.au/policies/pd/2010/pdf/PD2010_016.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2013).
- Yelland, J.S.; Sutherland, G.A.; Wiebe, J.L.; Brown, S.J. A national approach to perinatal mental health in Australia: Exercising caution in the roll-out of a public health initiative. Med. J. Aust. 2009, 191, 276–279. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Sullivan, E.A.; Black, D.A.; Pulver, L.R.; Madden, R.C. Under-reporting of birth registrations in New South Wales, Australia. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.K. How good is New South Wales admitted patient data collection in recording births? HIMJ 2011, 40, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, F.; Austin, M.-P.; Reilly, N.; Hilder, L.; Sullivan, E.A. Length of Stay for Mental and Behavioural Disorders Postpartum in Primiparous Mothers: A Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3540-3552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110403540
Xu F, Austin M-P, Reilly N, Hilder L, Sullivan EA. Length of Stay for Mental and Behavioural Disorders Postpartum in Primiparous Mothers: A Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11(4):3540-3552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110403540
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Fenglian, Marie-Paule Austin, Nicole Reilly, Lisa Hilder, and Elizabeth A Sullivan. 2014. "Length of Stay for Mental and Behavioural Disorders Postpartum in Primiparous Mothers: A Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11, no. 4: 3540-3552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110403540
APA StyleXu, F., Austin, M.-P., Reilly, N., Hilder, L., & Sullivan, E. A. (2014). Length of Stay for Mental and Behavioural Disorders Postpartum in Primiparous Mothers: A Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(4), 3540-3552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110403540




