Assessment of Ecological and Human Health Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in Agriculture Soils Disturbed by Pipeline Construction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Pipeline Introduction
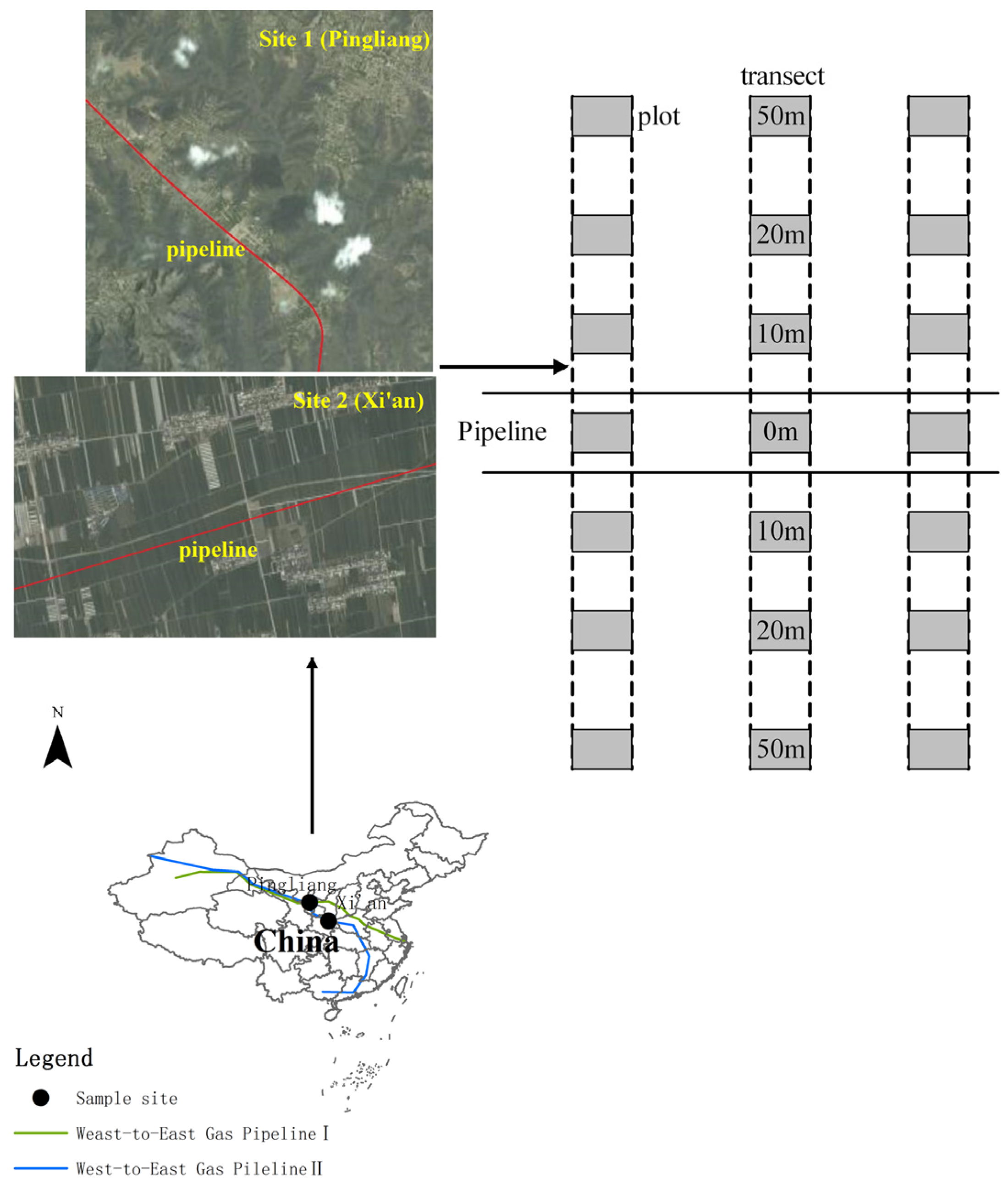
2.2. The Study Area
2.3. Sample Methods and Laboratory Analysis
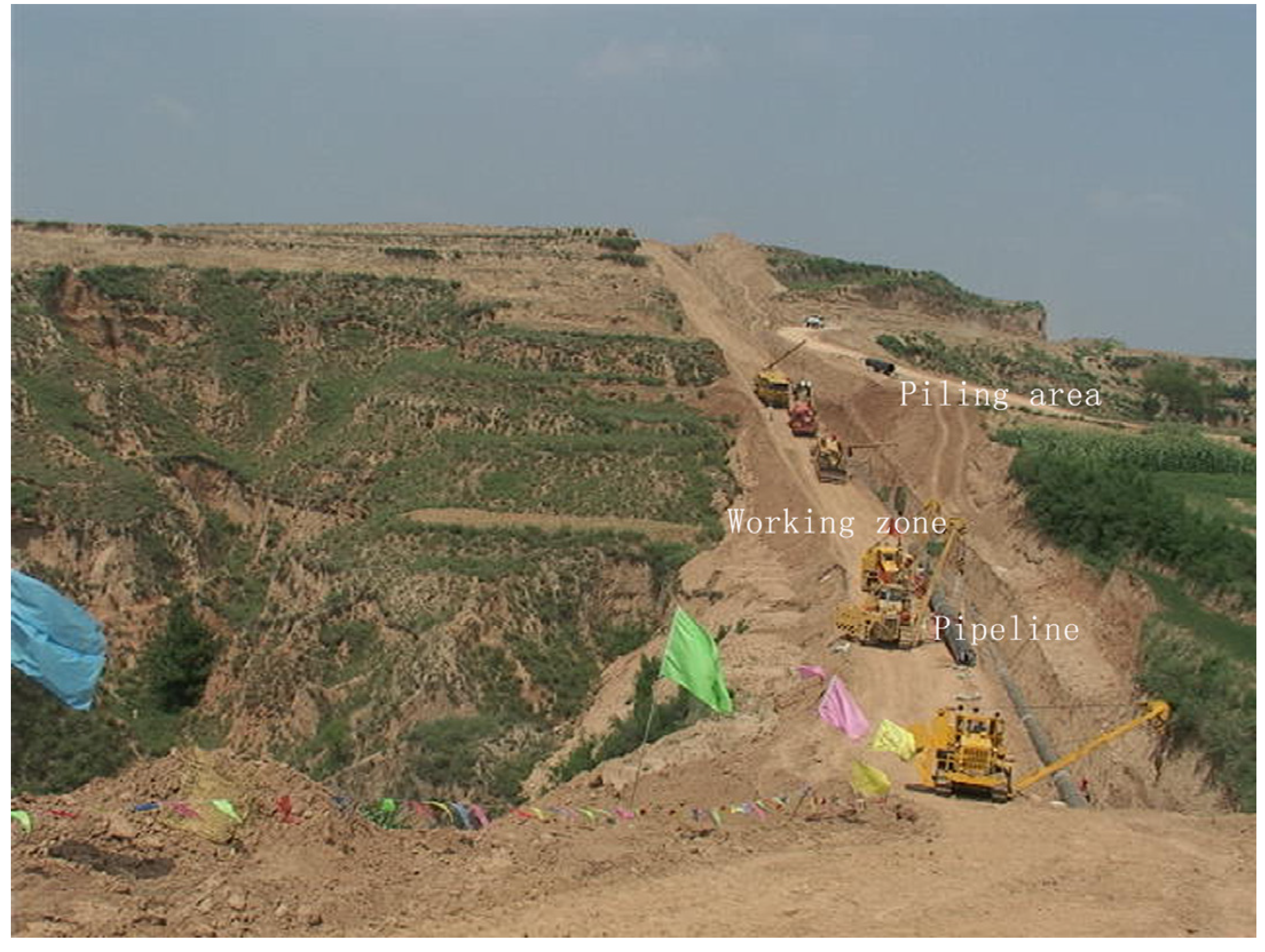

2.4. Data Analysis and Evaluation Methods
2.4.1. Index of Geo-accumulation (Igeo)
2.4.2. The Potential Ecological Risk Index (RI)
2.4.3. Human Health Risk Assessment










| Parameters | Unit | Definition | Value | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Child | Adult | ||||
| C | mg/kg | heavy metal concentration | |||
| ABSd | -- | dermal absorption factor | 0.03 | 0.001 | [16] |
| AF | mg/cm2 | soil to skin adherence factor | 0.2 | 0.07 | [15] |
| BW | kg | average body weight | 16.2 | 61.8 | [17] |
| ED | year | exposure duration | 6 | 30 | [15] |
| EF | d/year | exposure frequency | 350 | 350 | [15] |
| ET | h/d | exposure time | 24 | 24 | [15] |
| IngR | mg/d | soil ingestion rate for receptor | 200 | 100 | [15] |
| SA | cm2/event | Skin surface area available for exposure | 2,800 | 5,700 | [15] |
| ATnc | d | averaging time for non-carcinogenic | ED × 365 | [15] | |
| ATca | d | averaging time for carcinogenic | LT × 365 | [15] | |
| DFSadj | mg × year/kg/d | soil dermal contact factor-age-adjusted | 362.4 | [18] | |
| IR | mg × year/kg/d | Soil ingestion rate-age adjusted | 113 | [18] | |
| LT | year | lifetime | 72 | [19] | |
| PEF | m3/kg | Soil-to-air particulate emission factor | 1.36 × 109 | [15] | |
| Elements | RfDing (mg/kg/d) | RfCinh (mg/m3) | ABSGI | CSFing (mg/kg/d) | IUR (μg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1.0 × 10−3 | 1.0 × 10−5 | 0.025 | -- | 1.8 × 10−3 |
| Cr | 3.0 × 10−3 | -- | 0.013 | -- | 1.2 × 10−2 |
| Cu | 4.0 × 10−2 | -- | 1 | -- | -- |
| Ni | 2.0 × 10−2 | 9.0 × 10−5 | 0.04 | -- | 2.6 × 10−4 |
| Pb | 3.5 × 10−3 | -- | 1 | 8.5 × 10−3 | 1.2 × 10−5 |
| Zn | 3.0 × 10−1 | -- | 1 | -- | -- |
| References | [15] | [15] | [16] | [15] | [15] |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentrations of Soil Heavy Metals
| Sites | Elements (mg/kg) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | |
| Site 1 | 0.107 | 57.5 | 23 | 29.3 | 16.8 | 67.9 |
| Site 2 | 0.092 | 64.5 | 22.4 | 26.5 | 25.1 | 71.1 |
| Standard a | 0.2 | 90 | 35 | 40 | 35 | 100 |

3.2. Index of Geo-accumulation (Igeo)
3.2.1. Cadmium
| Pipeline zones | Cr | Cd | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E50 | −0.466 | −0.608 | −0.068 | −0.646 | −1.119 | −0.864 |
| E20 | −0.282 | −0.784 | −0.020 | −0.660 | −1.371 | −0.915 |
| Piling | −0.006 * | −0.170 | 0.098 | −0.488 | −0.133 | −0.852 |
| Trench | −0.004 * | 0.245 | 0.272 | −0.123 | 0.291 * | −0.690 |
| Working | −0.091 * | 0.057 | 0.032 | −0.639 | 0.235 * | −0.765 |
| W20 | −0.192 | −0.263 | −0.003 | −0.695 | −0.487 | −0.835 |
| W50 | −0.365 | −0.870 | 0.146 | −0.678 | −0.801 | −0.732 |
| Pipeline Zones | Cr | Cd | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N50 | −0.562 | −0.631 | 0.260 | −0.604 | −1.218 | −0.462 |
| N20 | −0.351 | 0.350 | 0.220 | −0.349 | −0.533 | −0.544 |
| Piling | −0.006 * | 0.460 | 0.384 | 0.150 | −0.262 | −0.839 |
| Trench | 0.004 * | 1.312 * | 0.304 | −0.096 | −0.343 | −0.716 |
| Working | −0.110 * | 0.544 | 0.334 | −0.035 | 0.048 | −0.634 |
| S20 | −0.054 * | 0.025 | 0.262 | −0.115 | −0.493 | −0.704 |
| S50 | −0.390 | −0.594 | 0.193 | −0.341 | −1.083 | −0.733 |
3.2.2. Chromium
3.2.3. Copper
3.2.4. Nickel
3.2.5. Lead
3.2.6. Zinc
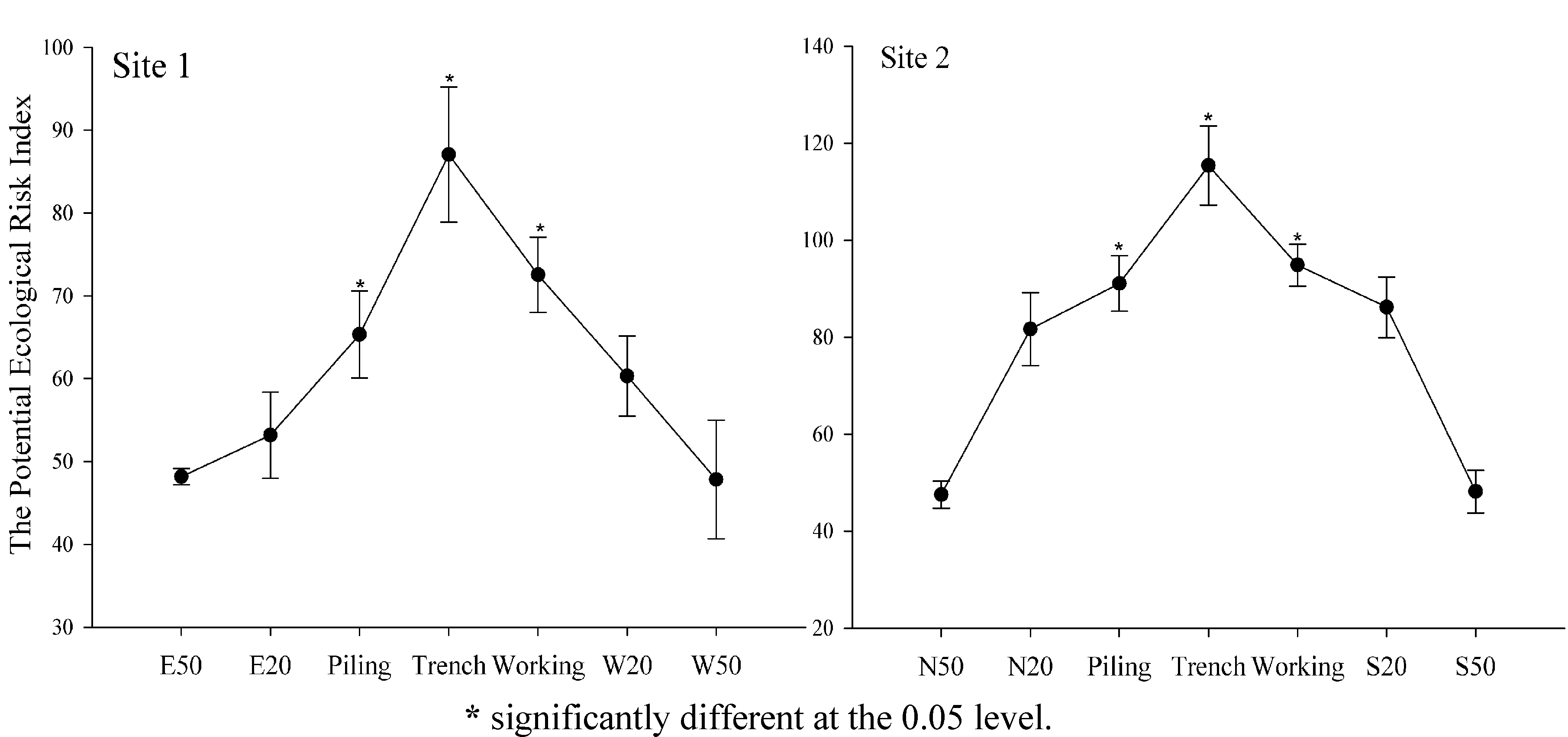
3.3. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment
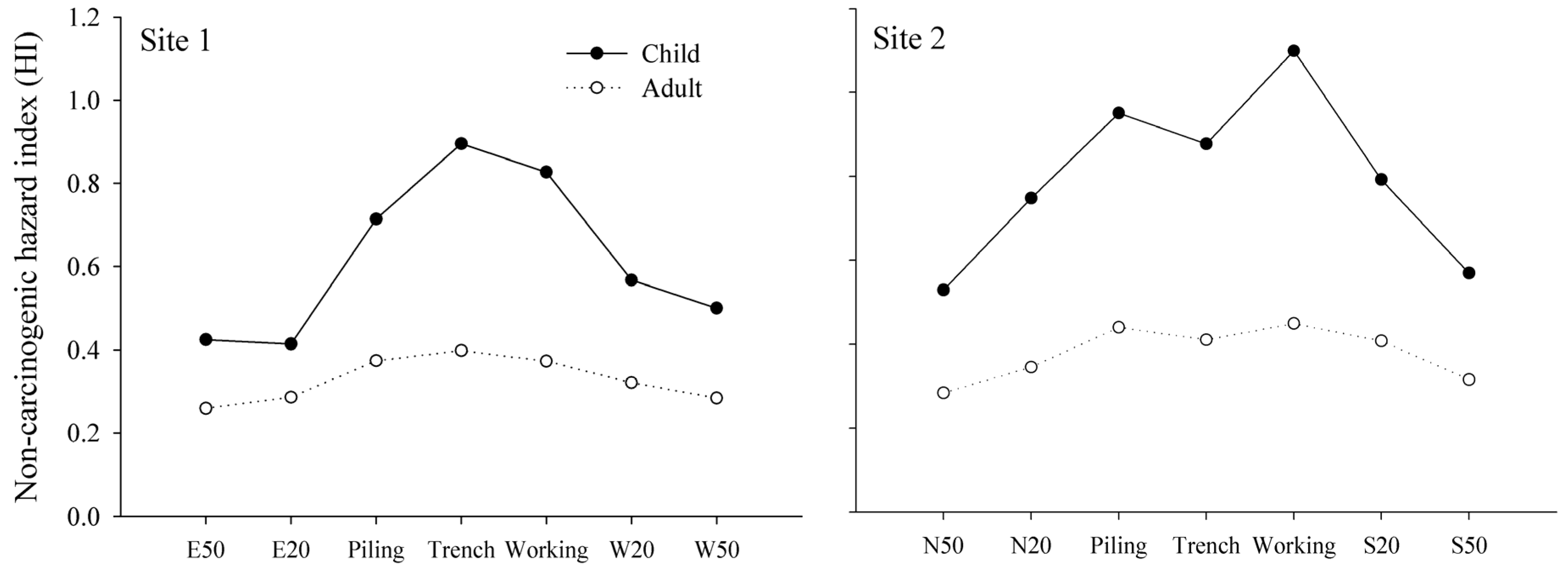
3.4. Human Health Risk Assessment
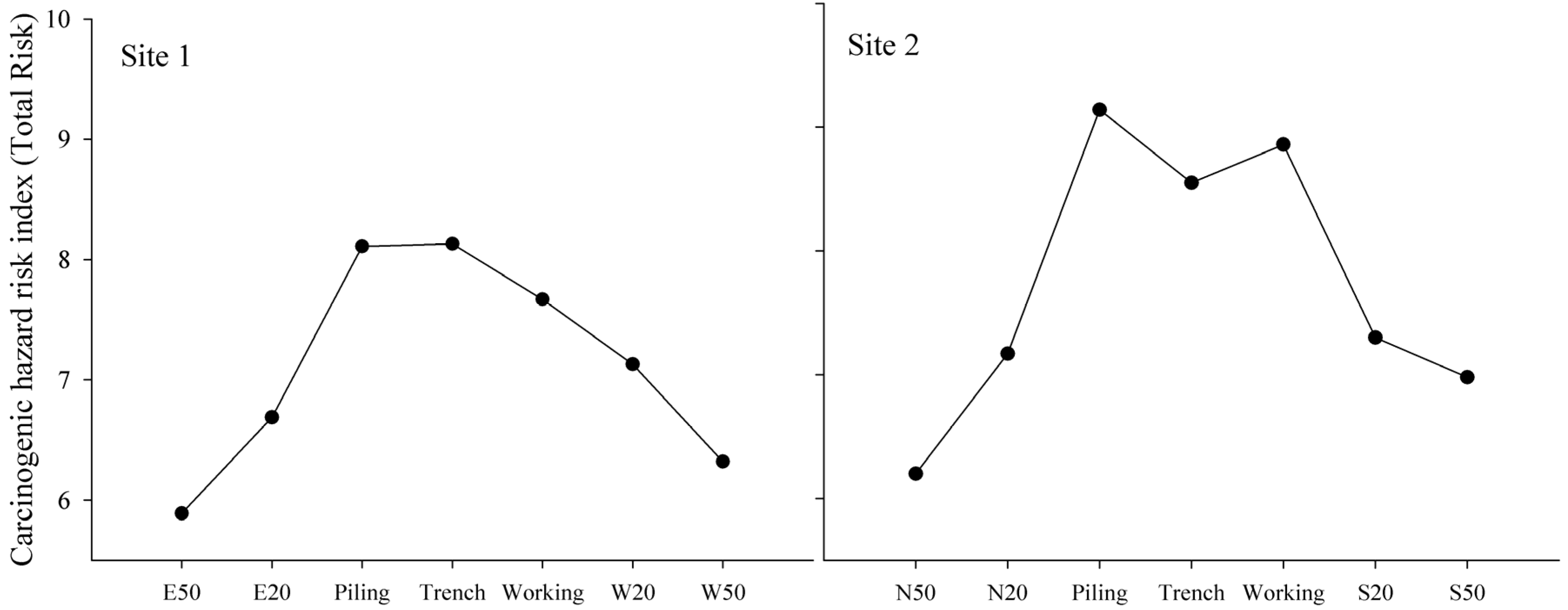
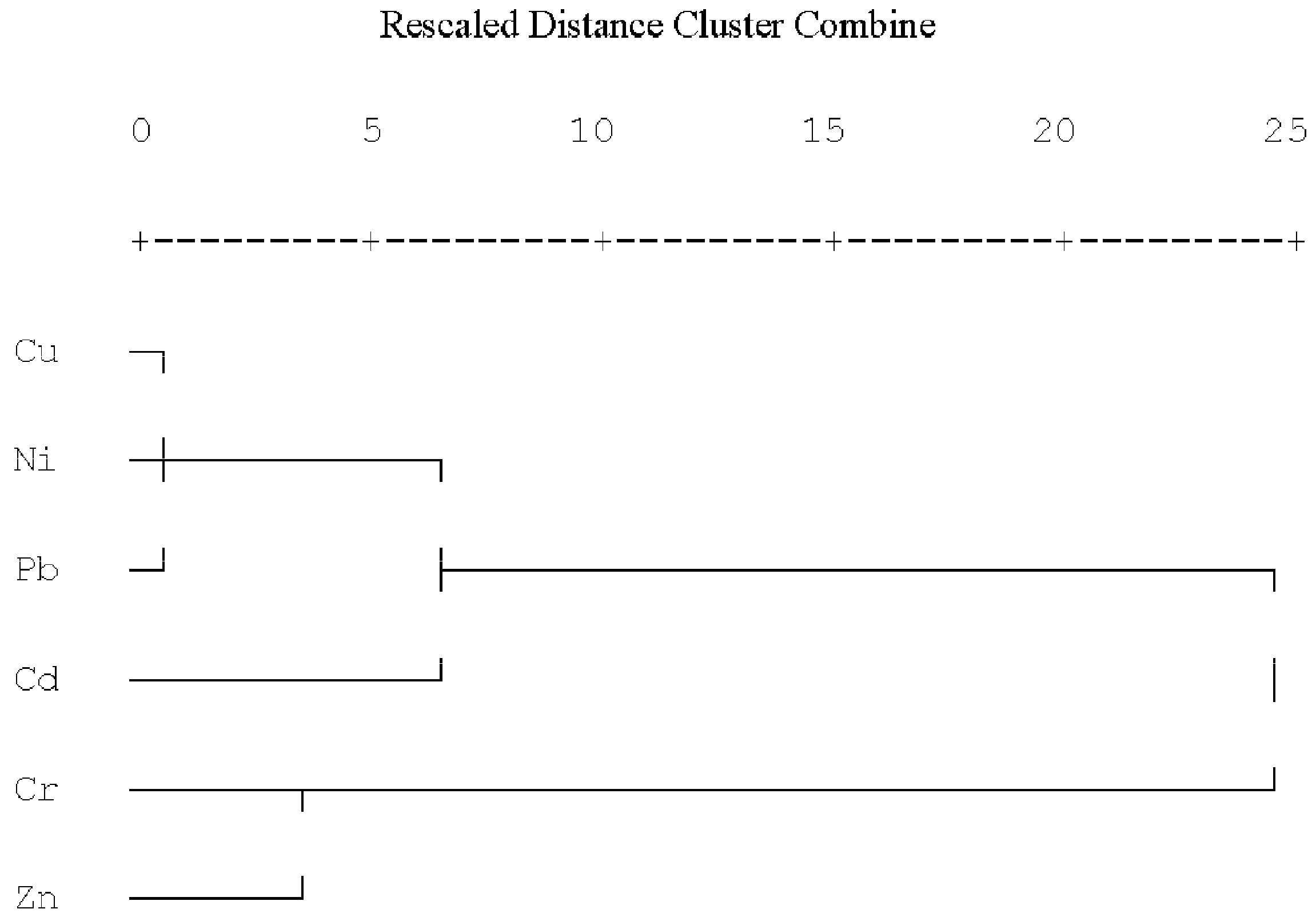
3.5. Relationships of Heavy Metals and Sources Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Authors Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.-D.; Gao, Q.-C. Chance and challenge for China on ecosystem management: Lessons from the West-to-East pipeline project construction. J. Hum. Environ. 2006, 35, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-X.; Shen, L.-F.; Liu, J.-W.; Wang, Y.-W.; Li, S.-R. Uptake of toxic heavy metals by rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivated in the agricultural soil near Zhengzhou city, People’s Republic of China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 79, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, L. Heavy metals in soil and crops of an intensively farmed area: A case study in Yucheng city, Shandong province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.-N.; Zhang, W.-W.; Sun, D.-F.; Li, H.; Zhou, L.-D.; Li, B.-G. Spatial pattern analysis of heavy metals in Beijing agricultural soils based on spatial autocorrelation statistics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2074–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yan, X.-D.; Zeng, C.; Zhang, M.; Shrestha, S.; Devkota, L.P.; Yao, T.-D. Influence of traffic activity on heavy metal concentrations of roadside farmland soil in mountainous Areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 1715–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.H.; Khanam, D.; Adyel, T.M.; Islam, M.S.; Ahsan, M.A.; Akbor, M.A. Assessment of heavy metal contamination of agricultural soil around Dhaka Export Processing Zone (DEPZ), Bangladesh: Implication of seasonal variation and indices. Appl. Sci. 2012, 2, 584–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.R.; Haby, V.A. Simplified colorimetric determination of soil organic matter. Soil. Sci. 1971, 112, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal. 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasa, G.S.; Ramakrishna, R.M.; Govil, P.K. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils at Jajmau (Kanpur) and Unnao industrial areas of the Ganga Plain, Uttar Pradesh, India. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaylali-Abanuz, G. Heavy metal contamination of surface soil around Gebze industrial area, Turkey. Microchem. J. 2011, 99, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loska, K.; Wiechuła, D.; Korus, I. Metal contamination of farming soils affected by industry. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.R.; Mclennan, S.M. The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev. Geophys. 1995, 33, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water. Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.-Y.; Hseu, Z.-Y.; Chen, T.-C.; Chen, B.-C.; Guo, H.-Y.; Chen, Z.-S. Health risk-based assessment and management of heavy metals-contaminated soil sites in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health. 2010, 7, 3595–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Energy. The Risk Assessment Information System (RAIS); U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge Operations Office (ORO): Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2011.
- USEPA. Regional Screening Level Table (RSL) for Chemical Contaminants at Superfund Sites; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Health Statistical Yearbook of China; Peking Union Medical College Press: Beijing, China, 2008; p. 191.
- Luo, X.S.; Ding, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, H.B.; Yu, S. Incorporating bioaccessibility into human health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban park soils. Sci. Total. Environ. 2012, 424, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. World Health Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Environmental Quality Standard for Soils. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Rout, G.R.; Samantaray, S.; Das, P. Effects of chromium and nickel on germination and growth in tolerant and non-tolerant populations of Echinochloa colona (L). Chemosphere 2000, 40, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.C.; Malick, F.K.; Endreszl, C.; Davies, E.C.; Murray, K.S. Distinct responses to copper stress in the halophyte Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Physiolo. Plantarum 1998, 102, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagajyoti, P.C.; Lee, K.D.; Sreekanth, T.V.M. Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ven der Gon, D.H.A.C.; Hulskotte, J.H.J.; Visschedijk, A.J.H.; Schaap, M. A revised estimate of copper emissions from road transport in UNECE-Europe and its impact on predicted copper concentrations. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 8697–8710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.P.G.C.; Moreira, H.; Rangel, A.O.S.S.; Castro, P.M.L. Arsenic, lead and nickel accumulation in Rubus ulmifolius growing in contaminated soil in Portugal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.-Y.; Mo, C.-H.; Li, H.-Q.; Lü, H.-X.; Zeng, Q.-Y.; Li, Y.-W.; Wu, X.-L. Heavy metal contamination of urban soils and dusts in Guangzhou, South China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, M. Trend and concentrations of legacy lead (Pb) in highway runoff. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 160, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Yun, Z.-J.; Shi, J.-B.; Jiang, G.-B. Research progress of heavy metal pollution in China: Sources, analytical methods, status, and toxicity. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, I.; Al-Oudat, M.; Al-Masri, M.S. Lead levels in roadside soils and vegetation of Damascus city. Sci. Total. Environ. 1997, 207, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.-Q.; Li, C.-L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.-X.; Liu, S.-T.; Ye, B. A novel approach for soil contamination assessment from heavy metal pollution: A linkage between discharge and adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.N.; Wasim, A.A.; Sarwar, A.; Rasheed, M.F. Assessment of heavy metal toxicants in the roadside soil along the N-5, National Highway, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 182, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, R.; Oh, S.; Shin, W.S.; Hwang, I. Human health risk assessment of soils contaminated with metal(loid)s by using DGT uptake: A case study of a former Korean metal refinery site. Hum. Ecol. Risk. Assess. 2013, 19, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, Z.; Qureshi, B.A. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in urban soil of Karachi, Pakistan. Hum. Ecol. Risk. Assess. 2013, 20, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Martonez, M.C.; Forja, J.M.; DelValls, T.A. A multivariate assessment of sediment contamination in dredged materials from Spanish ports. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xia, X.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, P. Heavy metal concentrations in roadside soils and correlation with urban traffic in Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 181, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, P.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Assessment of Ecological and Human Health Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in Agriculture Soils Disturbed by Pipeline Construction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2504-2520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110302504
Shi P, Xiao J, Wang Y, Chen L. Assessment of Ecological and Human Health Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in Agriculture Soils Disturbed by Pipeline Construction. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2014; 11(3):2504-2520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110302504
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Peng, Jun Xiao, Yafeng Wang, and Liding Chen. 2014. "Assessment of Ecological and Human Health Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in Agriculture Soils Disturbed by Pipeline Construction" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11, no. 3: 2504-2520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110302504
APA StyleShi, P., Xiao, J., Wang, Y., & Chen, L. (2014). Assessment of Ecological and Human Health Risks of Heavy Metal Contamination in Agriculture Soils Disturbed by Pipeline Construction. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 11(3), 2504-2520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph110302504





