Aqueous and Methanolic Extracts of Caulerpa mexicana Suppress Cell Migration and Ear Edema Induced by Inflammatory Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
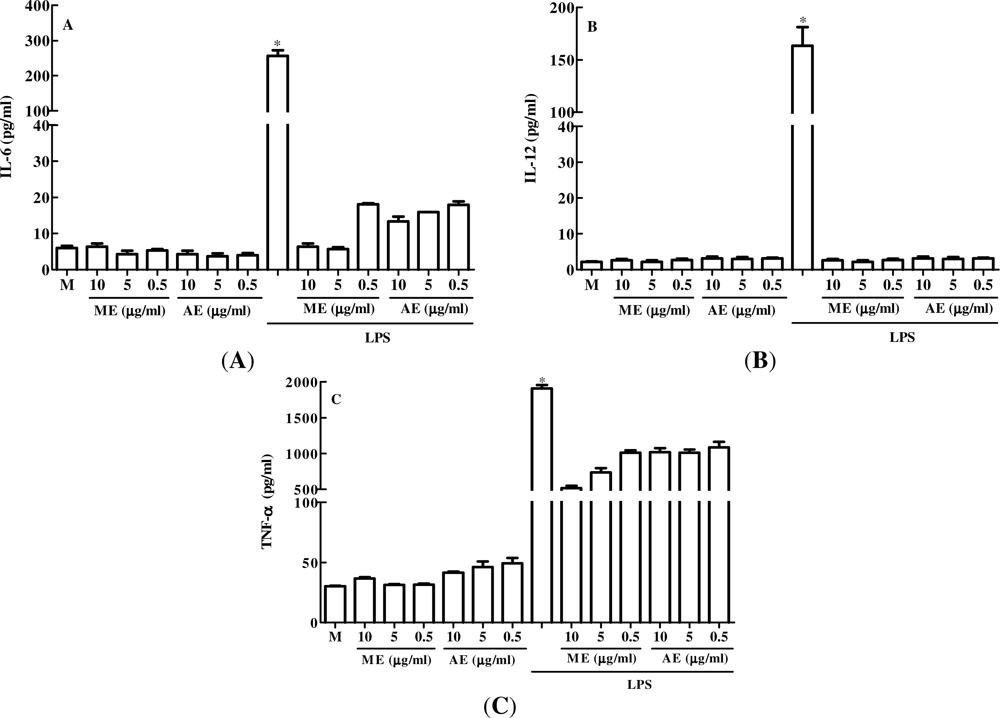
2.1. The Effect of Caulerpa mexicana Extracts in vitro Production of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines by Peritoneal Macrophages
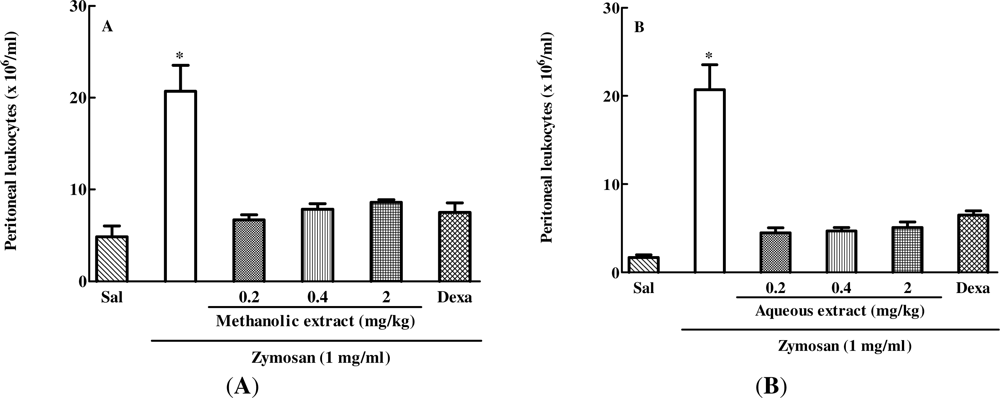
2.2. The Effect of Different Doses of Caulerpa mexicana Extracts on Zymosan-Induced Peritonitis in Mice
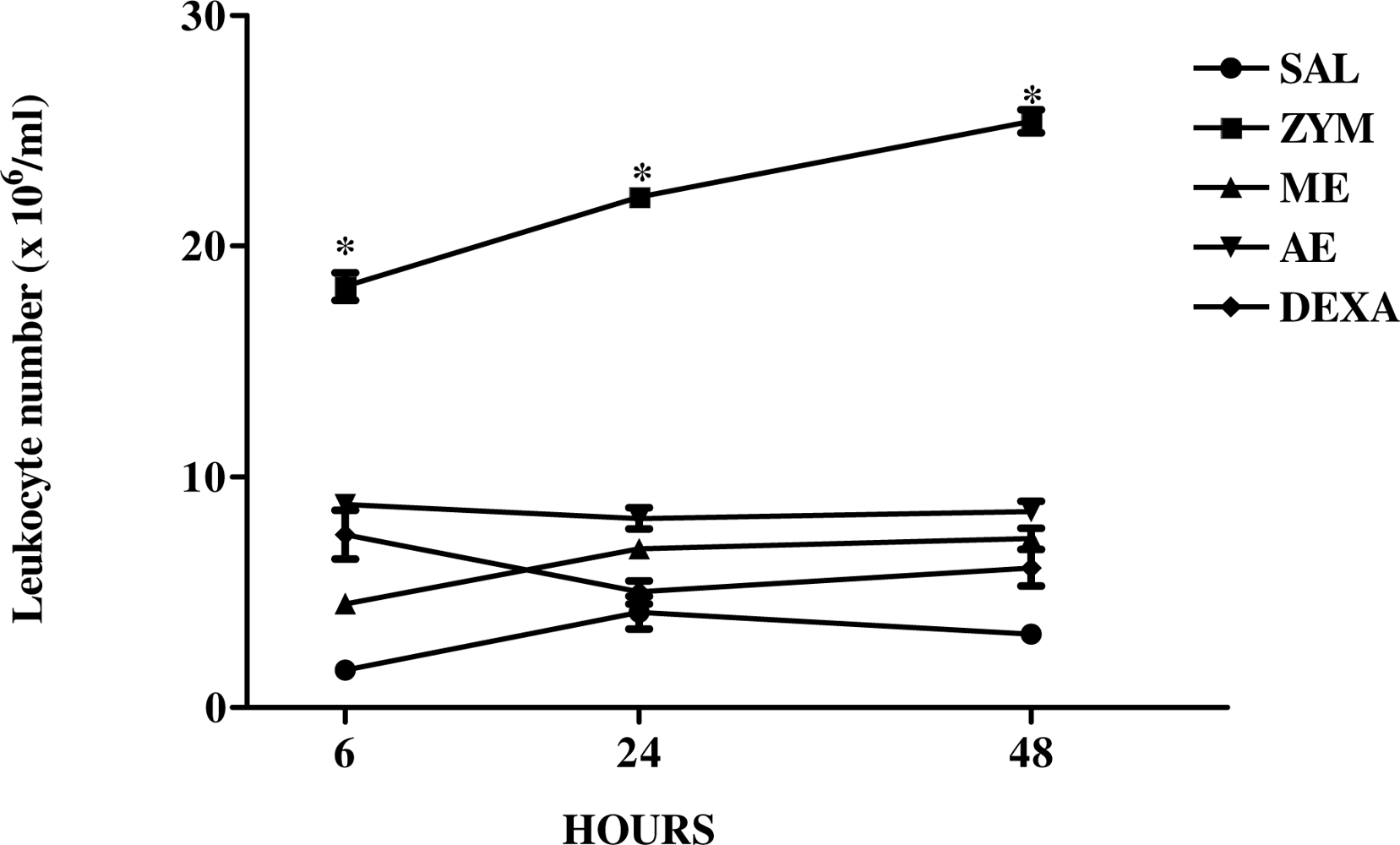
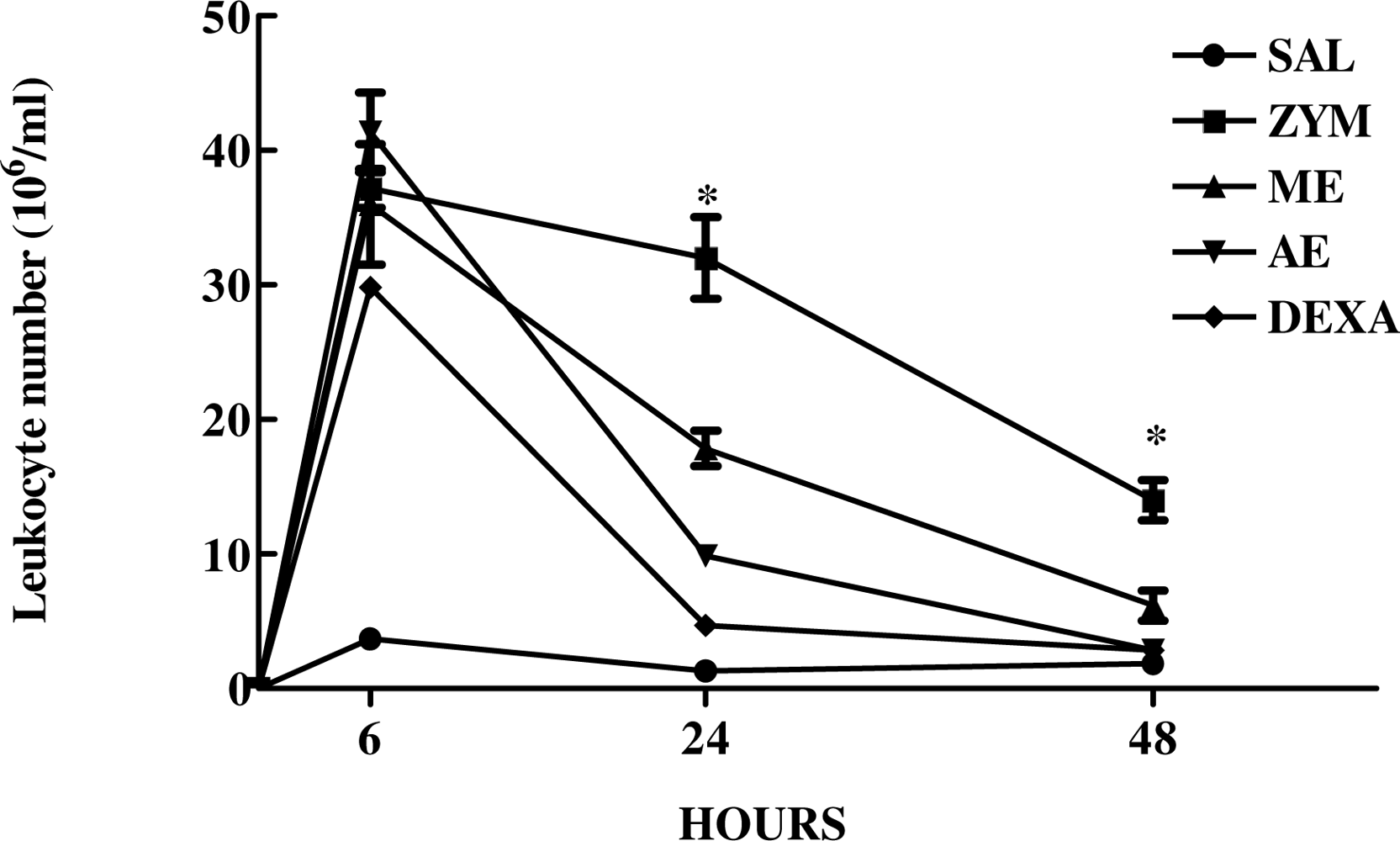
2.3. The Effect of Caulerpa mexicana Extracts on the Kinetics of Zymosan-Induced Peritonitis in Mice
2.4. The Effect of Extracts of Caulerpa mexicana on Xylene-Induced Ear Edema
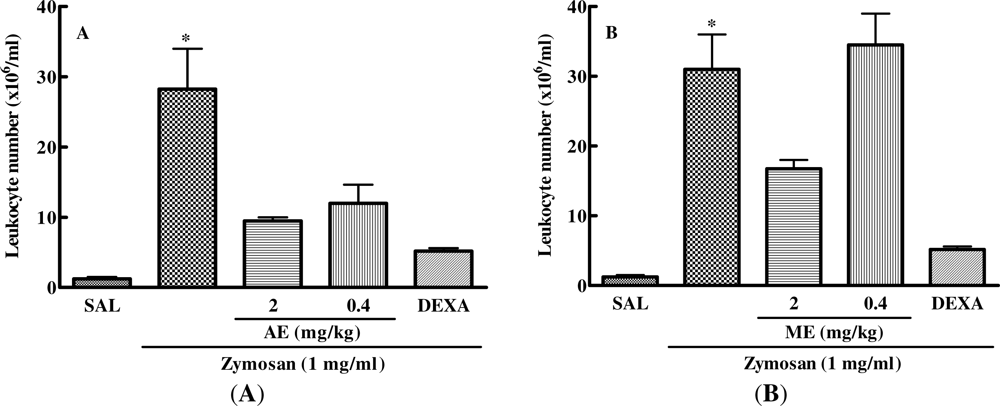
2.5. Effect of Caulerpa mexicana Extracts on the Zymosan-Injected Mouse Air Pouch
3. Discussion
4. Experimental
4.1. Extraction and Isolation
4.2. Animal
4.3. Peritoneal Macrophage Cell Culture
4.4. Induction of Peritonitis
4.5. Xylene-Induced Ear Edema
4.6. Mouse Air Pouch Model
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Vuorella, P; Leinonenb, M; Saikkuc, P; Tammelaa, P; Rauhad, JP; Wenneberge, T; Vuorella, H. Natural products in the process of finding new drug candidates. Curr. Med. Chem 2004, 11, 1375–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Itokawa, H; Morris-Natschke, SL; Akiyama, T; Lee, KH. Plant-derived natural product research aimed at new drug discovery. J. Nat. Med 2008, 62, 263–280. [Google Scholar]
- Falcão, HS; Mariath, IR; Diniz, MFFM; Batista, LM; Barbosa-Filho, JM. Plants of the American continent with antiulcer activity. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 132–146. [Google Scholar]
- Agra, MF; Silva, KN; Basílio, IJLD; França, PF; Barbosa-Filho, JM. Survey of medicinal plants used in the region Northeast of Brazil. Braz. J. Pharmacogn 2008, 18, 472–508. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, FCF; Melo, CTV; Citó, MCO; Félix, FHC; Vasconcelos, SMM; Fonteles, MMF; Barbosa Filho, JM; Viana, GSB. Medicinal plants and their bioactive constituents: A scientific review of bioactivity and potential benefits in the anxiety disorders in animal models. Braz. J. Pharmacogn 2008, 18, 642–654. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa-Filho, JM; Alencar, AA; Nunes, XP; Tomaz, ACA; Sena-Filho, JG; Athayde-Filho, PF; Silva, MS; Souza, MFV; Cunha, EVL. Sources of alpha-, beta-, gamma-, delta- and epsilon-carotenes: a twentieth century review. Braz. J. Pharmacogn 2008, 18, 135–154. [Google Scholar]
- Quintans-Júnior, LJ; Almeida, JRGS; Lima, JT; Nunes, XP; Siqueira, JS; Oliveira, LEG; Almeida, RN; Athayde-Filho, PF; Barbosa-Filho, JM. Plants with anticonvulsant properties—a review. Braz. J. Pharmacogn 2008, 18, 798–819. [Google Scholar]
- Falcão, HS; Leite, JA; Barbosa-Filho, JM; Athayde-Filho, PF; Chaves, MCO; Moura, MD; Ferreira, AL; Almeida, ABA; Souza-Brito, ARM; Diniz, MFFM; et al. Gastric and duodenal antiulcer activity of alkaloids: A review. Molecules 2008, 13, 3198–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, KSL; Dias, GEN; Pinto, MEF; Luiz-Ferreira, A; Souza-Brito, ARM; Hiruma-Lima, CA; Barbosa-Filho, JM; Batista, LM. Flavonoids with gastroprotective activity. Molecules 2009, 14, 979–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Mariath, IR; Falcão, HS; Barbosa-Filho, JM; Sousa, LCF; Tomaz, ACA; Batista, LM; Diniz, MFFM; Athayde-Filho, PF; Tavares, JF; Silva, MS; et al. Plants of the American continent with antimalarial activity. Braz. J. Pharmacogn 2009, 19, 158–192. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Filho, J; Falcão, HS; Batista, LM; Barbosa-Filho, JM; Piuvezam, MR. Effects of plant extracts on HIV-1 protease. Curr. HIV Res 2010, 8, 531–544. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, FL; Fischer, DCH; Tavares, JF; Silva, MS; Athayde-Filho, PF; Barbosa-Filho, JM. Compilation of Secondary Metabolites from Bidens pilosa L. Molecules 2011, 16, 1070–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, AMS; Rodriguez, AD; Berlinck, D; Fusetani, N. Marine pharmacology in 2007–2008: Marine compounds with antibacterial, anticoagulant, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis and antiviral activities; affecting the immune and nervous system, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2011, 153, 191–222. [Google Scholar]
- Cen-Pacheco, F; Nordstrom, L; Souto, ML; Martin, MN; Fernandez, JJ; Daranas, AH. Studies on polyethers produced by red algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Guven, KC; Percot, A; Sezik, E. Alkaloids in marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrita, MT; Vale, C; Rauter, AP. Halogenated compounds from marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2301–2317. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, G; Tedone, L; Hamann, MT; Morabito, M. The mediterranean red alga Asparagopsis: A source of compounds against Leishmania. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 361–366. [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan, L; Murphy, B; McLoughlin, P; Duggan, P; Lawlor, PG; Hughes, H; Gardiner, GE. Prebiotics from marine macroalgae for human and animal health applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2038–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Pallela, R; Na-Young, Y; Kim, SK. Anti-photoaging and photoprotective compounds derived from marine organisms. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, VJ; Desbois, AP; Dyrynda, EA. Conventional and unconventional antimicrobials from fish, marine invertebrates and micro-algae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1213–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Cantillo-Ciau, Z; Moo-Puc, R; Quijano, L; Freile-Pelegrin, Y. The tropical brown alga Lobophora variegata: A source of antiprotozoal compounds. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1292–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Iannitti, T; Palmieri, B. An update on the therapeutic role of alkylglycerols. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2267–2300. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, JL; Xia, WS; Liu, P; Cheng, QY; Tahirou, T; Gu, WX; Li, B. Chitosan modification and pharmaceutical/biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1962–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Neto, JTBB; Rodrigues, JAG; Pontes, GC; Farias, WRL. Sulfated polysaccharides of the alga Caulerpa sertularioides (GMEL.) Howe: Analysis of methods of precipitation. Rev. Bras. Eng. Pesca 2008, 3, 50–62. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, WZ; Wang, H; Guo, GQ; Tuo, JJ. Immunomodulatory effects of Caulerpa racemosa var peltata polysaccharide and its selenizing product on T lymphocytes and NK cells in mice. Sci. China Ser. C 2008, 51, 795–801. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, MR; Sousa, APA; Silva Filho, EAT; Pessoa, CO; Moraes, MEA; Moraes, MO; Lotufo, LVC. Biological activity of aqueous and organic extracts of seaweeds from Ceará state, Brazil. Arq. Cien. Mar. 2005, 38, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, FD; Pereira, RC; Kaplan, MAC; Teixeira, VL. Produtos naturais de algas marinhas e seu potencial antioxidante. Braz. J. Pharmacogn 2007, 17, 631–639. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros, E; Martins, D; Uriz, MJ. Biological activity of extracts from some Mediterranean Macrophytes. Bot. Mar 1992, 35, 481–485. [Google Scholar]
- Cumashi, A; Ushakova, NA; Preobrazhenskaya, ME; D’Incecco, A; Piccoli, A; Totani, L; Tinari, N; Morozevich, GE; Berman, AE; Bilan, MI; et al. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar]
- Luster, AD. Chemokines-chemotactic cytokines that mediate inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med 1998, 338, 436–445. [Google Scholar]
- Castellheim, A; Brekke, OL; Espevik, T; Harboe, M; Mollnes, TE. Innate immune responses to danger signals in systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis. Scand. J. Immunol 2009, 69, 479–491. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, DQ; Targan, SR. Immmunopathogeneses of inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastroenterol 2008, 21, 390–400. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, AMS; Glaser, KB; Cuevas, C; Jacobs, RS; Kem, W; Little, RD; McIntosh, JM; Newman, DJ; Potts, BC; Shuster, DE. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: A current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, O; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, EJ; Moon, JY; Kim, MJ; Kim, DS; Kim, CS; Lee, WJ; Hyun, CG. Inhibition effect of Jeju endemic seaweeds on the production of pro-inflammatory mediators in mouse macrophage cell line Raw 264.7. J. Zhejiang. Univ. Sci. B 2010, 11, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Mollnes, TE; Christiansen, D; Brekke, OL; Espevik, T. Hypothesis: Combined inhibition of complement and CD14 as treatment regimen to attenuate the inflammatory response. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 2008, 632, 253–263. [Google Scholar]
- Kazlowska, K; Hsu, T; Hou, CC; Yang, WC; Tsai, GJ. Anti-inflammatory properties of phenolic compounds and crude extract from Porphyra dentata. J. Ethanophamacol 2010, 128, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Kolaczkowska, E; Seljelid, R; Plytycz, B. Role of mast cells in zymosan-induced peritoneal inflammation in Balb/c and mast cell-deficient WBB6F1 mice. J. Leukoc. Biol 2001, 69, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kolaczkowska, E; Koziol, A; Plytycz, B; Arnold, B. Inflammatory macrophages, and not only neutrophils, die by apoptosis during acute peritonitis. Immunobiology 2010, 215, 492–504. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, ET; Lira, DP; Queiroz, AC; Silva, DJC; Aquino, AB; Mella, EA; Lorenzo, VP; Miranda, GEC; Araújo-Júnior, JX; Chaves, MCO; et al. The antinoceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of caulerpin, a bisindole alkaloid, isolated from seaweeds of the genus Caulerpa. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 689–704. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, ET; Queiroz, AC; Miranda, GEC; Lorenzo, VP; Silva, EF; Freire-Dias, TLM; Cupertino-Silva, YK; Melo, GMA; Santos, BVO; Chaves, MCO; et al. Antinociceptive activities of crude methanolic extract and phases, n-butanolic, chloroformic and ethyl acetate from Caulerpa racemosa (Caulerpaceae). Braz. J. Pharmacogn 2009, 19, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, MM; Mcnagny, K; Williams, DL; Van Rooijen, N; Maxwell, L; Gwozd, C; Mody, CH; Kubes, P. The lung responds to zymosan in a unique manner independent of toll-like receptors. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol 2008, 38, 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ushakova, NA; Preobrazhenskaya, ME; Nifantiev, NE; Usov, AI; Pochechueva, TV; Galanina, OE; Bovin, NV. Inhibitory activity of monomeric and polymeric selectin ligands. Vopr. Med. Khim 1999, 45, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Krieger, M; Herz, J. Structures and functions of multiligand lipoprotein receptors: Macrophage scavenger receptors and LDL receptor-related protein (LRP). Annu. Rev. Biochem 1994, 63, 601–637. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z; Luo, P; Li, J; Yi, T; Wang, J; An, J; Zhang, H. Comparison of the anti-inflammatory activities of three medicinal plants known as “Meiduoluomi” in Tibetan folk medicine. Yakugaku Zassi 2008, 128, 805–810. [Google Scholar]
- Parveen, Z; Deng, Y; Saeed, MK; Dai, R; Ahamad, W; Yu, YH. Antiiflammatory and analgesic activities of Theseus chinese Turcz extracts and its major flavonoids, kaempferol and kaempferol-3-O-glucoside. Pharm. Soc. Jpn 2007, 127, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, JD; Vasko, MR. Cellular mechanisms of neurogenic inflammation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 2002, 302, 839–845. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, MN; Choi, JS; Lee, MC; Kim, E; Nam, TJ; Hong, YK. Anti-inflammatory activities of methanol extracts from various seaweed species. J. Environ. Biol 2008, 29, 465–469. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, SY; Kwon, YB; Kim, HW; Roh, DH; Kang, SY; Kim, CY; Han, HJ; Kim, KW; Yang, IS; Beitz, AJ; Lee, JH. Intrathecal neostigmine reduces the zymosan-induced inflammatory response in a mouse air pouch model via adrenomedullary activity: Involvement of spinal muscarinic type 2 receptors. Neuropharmacology 2005, 49, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera, PV; Blanco, G; Gravisaco, MJ; Alvarez, E; Hajos, S. Zymosan modulates CD44 isoform expression in a murine model of inflammation resembling rheumatoid arthritis synovitis. J. Rheumatol 2001, 28, 5943–5949. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, EH; Shim, B; Kang, S; Jeong, G; Lee, LS; Yu, YB; Chun, M. Anti-inflammatory effects of Scutellaria baicalensis extract via suppression of immune modulators and MAP kinase signaling molecules. J. Ethanopharmacol 2009, 126, 320–331. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, SY; Yoon, SY; Roh, DH; Jeon, MJ; Seo, HS; Uh, DR; Kwon, YB; Kim, HW; Han, HJ; Lee, HJ; et al. The anti-arthritic effect of ursolic acid on zimosan-induced acute inflammation and adjuvant-induced chronic arthritis models. J. Pharm. Pharmacol 2008, 60, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar]
- Vigil, SVG; Liz, R; Medeiros, YS; Fröde, TS. Efficacy of tacrolimus in inhibiting inflammation caused by carrageenan in a murine model of air pouch. Transpl. Immunol 2008, 19, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
| Groups | 15 min | 1 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose (mg/kg) | Difference (mg) | Inhibition (%) | Difference (mg) | Inhibition (%) | |
| Saline (i.v.) | – | 32.45 ± 2.603 | – | 31.80 ± 5.289 | – |
| Methanolic | 0.4 | 7.475 ± 2.809 | 77.07% ** | 4.567 ± 2.668 | 85.63% ** |
| Extract (s.c.) | 2 | 8.453 ± 3.500 | 73.55% ** | 5.167 ± 2.580 | 83.75% ** |
| Aqueous | 0.4 | 4.933 ± 4.916 | 84.86% *** | 2.167 ± 3.316 | 93.18% ** |
| Extract (s.c.) | 2 | 24.45 ± 5.212 | 25% | 20.07 ± 5.029 | 36.88% |
| Dexa (i.p.) | 0.5 | 9.600 ± 2.419 | 70.60% ** | 8.467 ± 2.850 | 73.37% ** |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bitencourt, M.A.O.; Dantas, G.R.; Lira, D.P.; Barbosa-Filho, J.M.; Miranda, G.E.C.d.; Santos, B.V.d.O.; Souto, J.T. Aqueous and Methanolic Extracts of Caulerpa mexicana Suppress Cell Migration and Ear Edema Induced by Inflammatory Agents. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1332-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9081332
Bitencourt MAO, Dantas GR, Lira DP, Barbosa-Filho JM, Miranda GECd, Santos BVdO, Souto JT. Aqueous and Methanolic Extracts of Caulerpa mexicana Suppress Cell Migration and Ear Edema Induced by Inflammatory Agents. Marine Drugs. 2011; 9(8):1332-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9081332
Chicago/Turabian StyleBitencourt, Mariana Angelica Oliveira, Gracielle Rodrigues Dantas, Daysianne Pereira Lira, Jose Maria Barbosa-Filho, George Emmanuel Cavalcanti de Miranda, Barbara Viviana de Oliveira Santos, and Janeusa Trindade Souto. 2011. "Aqueous and Methanolic Extracts of Caulerpa mexicana Suppress Cell Migration and Ear Edema Induced by Inflammatory Agents" Marine Drugs 9, no. 8: 1332-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9081332
APA StyleBitencourt, M. A. O., Dantas, G. R., Lira, D. P., Barbosa-Filho, J. M., Miranda, G. E. C. d., Santos, B. V. d. O., & Souto, J. T. (2011). Aqueous and Methanolic Extracts of Caulerpa mexicana Suppress Cell Migration and Ear Edema Induced by Inflammatory Agents. Marine Drugs, 9(8), 1332-1345. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9081332




