First Evidence of Palytoxin and 42-Hydroxy-palytoxin in the Marine Cyanobacterium Trichodesmium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sampling Sites and Collection of Cyanobacteria
2.3. Taxonomic Identification of Cyanobacterial Samples
2.4. Extraction
2.5. Mouse Bioassay
2.6. Neuroblastoma Cell-Based Assays (CBA)
2.6.1. Evaluation of Cytotoxic Effects of PLTX
2.6.2. Evaluation of Cytotoxic Effects of the Extracts
2.6.3. Evaluation of Cytotoxic Effects of Extracts Spiked with PLTX
2.7. LC-MS/MS Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MBA Toxicity Data
3.2. CBA Cytotoxicity Data
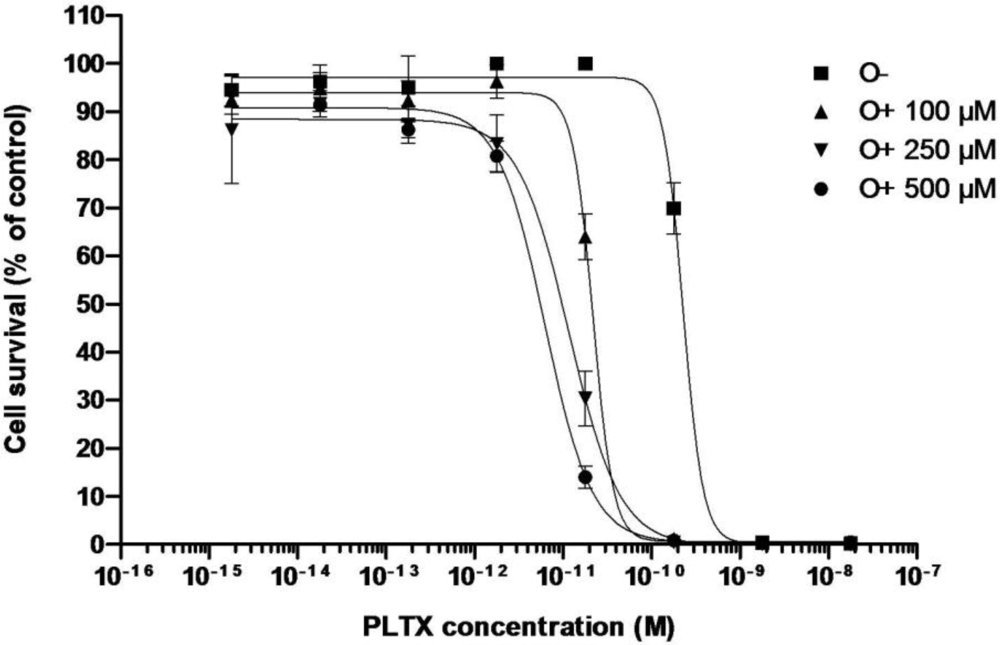
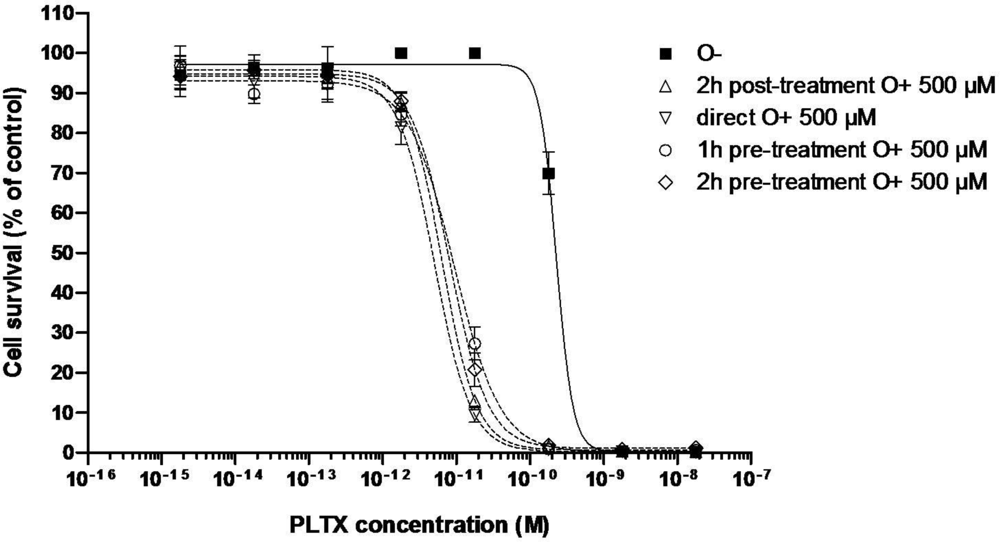
3.2.1. Effect of PLTX
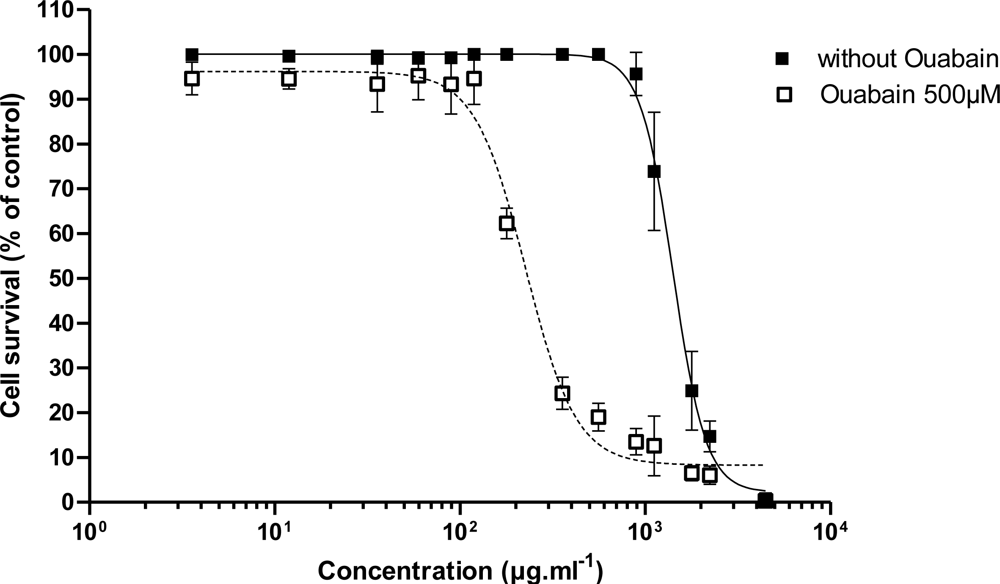
3.2.2. Effect of Trichodesmium Extracts
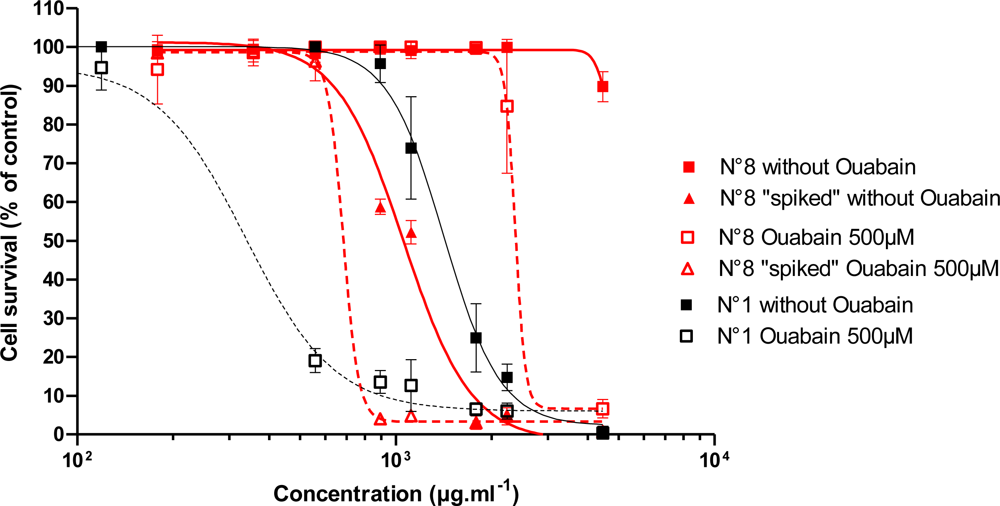
3.2.3. Effect of Trichodesmium Non-Toxic Extracts Spiked with PLTX
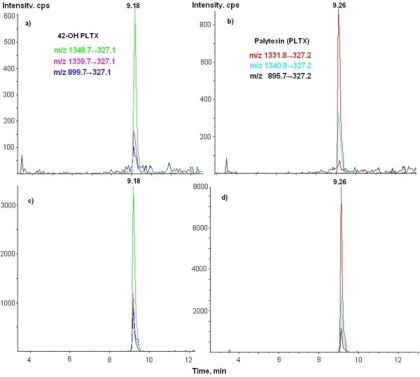
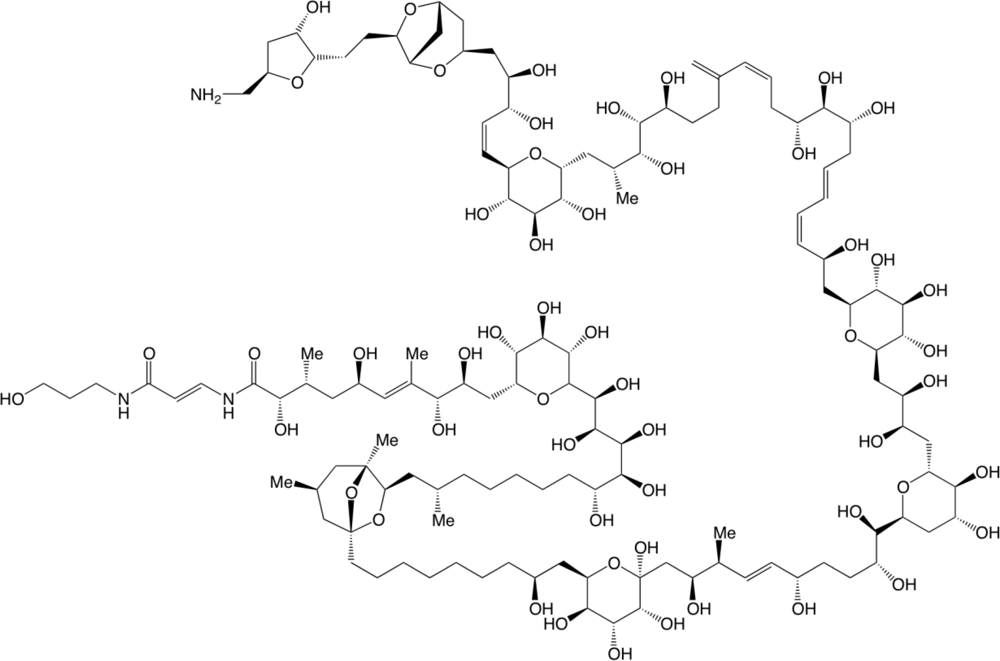
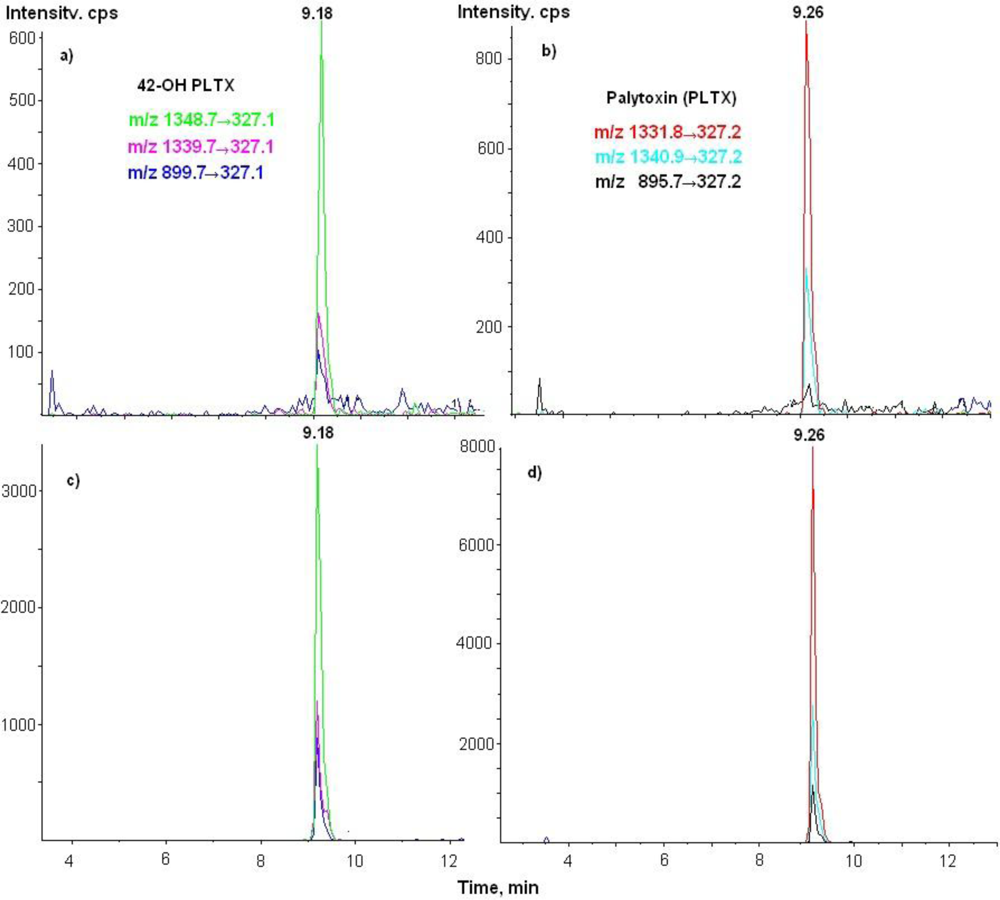
3.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
References
- Capone, DG; Zehr, JP; Paerl, HW; Bergman, B; Carpenter, EJ. Trichodesmium, a globally significant marine cyanobacterium. Science 1997, 276, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Karl, D; Michaels, A; Bergman, B; Capone, D; Carpenter, E; Letelier, R; Lipschultz, F; Paerl, H; Sigman, D; Stal, L. Dinitrogen fixation in the world’s oceans. Biogeochemistry 2002, 57–58, 47–98. [Google Scholar]
- Laroche, J; Breitbarth, E. Importance of the diazotrophs as a source of new nitrogen in the ocean. J Sea Res 2005, 53, 67–91. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, EJ; Subramaniam, A; Capone, DG. Biomass and primary productivity of the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium spp. in the tropical N Atlantic ocean. Deep Sea Res Part I: Oceanogr Res Pap 2004, 51, 173–203. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, C; Qiu, X. Global distribution of summer chlorophyll blooms in the oligotrophic gyres. Prog Oceanogr 2008, 78, 107–134. [Google Scholar]
- Rodier, M; Le Borgne, R. Population dynamics and environmental conditions affecting Trichodesmium spp. (filamentous cyanobacteria) blooms in the south-west lagoon of New Caledonia. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 2008, 358, 20–32. [Google Scholar]
- Rodier, M; Le Borgne, R. Population and trophic dynamics of Trichodesmium thiebautii in the SE lagoon of New Caledonia. Comparison with T. erythraeum in the SW lagoon. Mar Pollut Bull 2010, 61, 349–359. [Google Scholar]
- Sellner, KG. Physiology, ecology, and toxic properties of marine cyanobacteria blooms. Limnol Oceanogr 1997, 42, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, YB; Zehr, JP; Mellon, M. Growth and nitrogen fixation of the diazotrophic filamentous nonheterocystous cyanobacterium Trichodesmium sp. IMS 101 in defined media: evidence for a circadian rhythm. J Phycol 1996, 32, 916–923. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, PRF; Uwins, PJR; Elmetri, I; Phillips, JA; Fu, FX; Yago, AJE. Laboratory culture studies of Trichodesmium isolated from the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon, Australia. Hydrobiologia 2005, 532, 9–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hawser, SP; Codd, GA; Capone, DG; Carpenter, EJ. A neurotoxic factor associated with the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Trichodesmium. Toxicon 1991, 29, 227–278. [Google Scholar]
- Hawser, SP; O’Neil, J; Roman, MR; Codd, GA. Toxicity of blooms of the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium to zooplankton. J Appl Phycol 1992, 4, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neil, JM; Roman, MR. Grazers and associated organisms of Trichodesmium. In Marine Pelagic Cyanobacteria: Trichodesmium and Other Diazotrophs; Carpenter, EJ, Capone, DG, Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, ST; Capra, M. The cyanobacterium Oscillatoria erythraea—a potential source of toxin in the ciguatera food-chain. Food Addit Contam 1992, 9, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Lehane, L; Lewis, RJ. Ciguatera: recent advances but the risk remains. Int J Food Microbiol 2000, 61, 91–125. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, MA; Fleming, LE; Fernandez, M; Bienfang, P; Schrank, K; Dickey, R; Bottein, MY; Backer, L; Ayyar, R; Weisman, R; Watkins, S; Granade, R; Reich, A. Ciguatera Fish Poisoning: Treatment, Prevention and Management. Mar Drugs 2008, 6, 456–479. [Google Scholar]
- Dickey, RW; Plakas, SM. Ciguatera: A public health perspective. Toxicon 2010, 56, 123–136. [Google Scholar]
- Endean, R; Monks, SA; Griffith, JK; Llewellyn, LE. Apparent relationships between toxins elaborated by the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium erythraeum and those present in the flesh of the narrow-barred Spanish mackerel Scomberomorus commersoni. Toxicon 1993, 31, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar]
- Kerbrat, AS; Darius, HT; Pauillac, S; Chinain, M; Laurent, D. Detection of ciguatoxin-like and paralysing toxins in Trichodesmium spp. from New Caledonia lagoon. Mar Pollut Bull 2010, 61, 360–366. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, AG; Geoffrey, AM; Codd, A; Soler, E; Coca, J; Redondo, A; Morrison, LF; Metcalf, JS; Ojeda, A; Suárez, S; Petit, M. Bloom of the marine diazotrophic cyanobacterium Trichodesmium erythraeum in the Northwest African Upwelling. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 2005, 30, 303–305. [Google Scholar]
- Proença, LAO; Tamanaha, MS. Screening the toxicity and toxin content of blooms of the cyanobacterium Trichodesmium erythraeum (Ehrenberg) in northeast Brasil. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis 2009, 15, 204–215. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, S; Paranagua, M; Eskinazi, E. On the mechanism of red tide of Trichodesmium in Recife northeastern Brazil, with some considerations of the relation to the human disease, “Tamandare fever”. Trab Inst Oceanogr Univ Recife 1963, 5–6, 7–49. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, D; Kerbrat, AS; Darius, HT; Girard, E; Golubic, S; Benoit, E; Sauviat, MP; Chinain, M; Molgo, J; Pauillac, S. Are cyanobacteria involved in Ciguatera Fish Poisoning-like outbreaks in New Caledonia. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 827–838. [Google Scholar]
- Abed, RMM; Palinska, KA; Camoin, G; Golubic, S. Common evolutionary origin of planktonic and benthic nitrogen-fixing oscillatoriacean cyanobacteria from tropical oceans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2006, 260, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Charpy, L; Palinska, K; Casareto, B; Langlade, M; Suzuki, Y; Abed, R; Golubic, S. Dinitrogen-Fixing Cyanobacteria in Microbial Mats of Two Shallow Coral Reef Ecosystems. Microb Ecol 2010, 59, 174–186. [Google Scholar]
- Méjean, A; Peyraud-Thomas, C; Kerbrat, AS; Golubic, S; Pauillac, S; Chinain, M; Laurent, D. First identification of the neurotoxin homoanatoxin-a from mats of Hydrocoleum lyngbyaceum (marine cyanobacterium) possibly linked to giant clam poisoning in New Caledonia. Toxicon 2010, 56, 829–835. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, C; Beattie, KA; Scrimgeour, CM; Codd, GA. Identification of anatoxin-a in benthic cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) and in associated dog poisonings at Loch Insh, Scotland. Toxicon 1992, 30, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Gugger, M; Lenoir, S; Berger, C; Ledreux, A; Druart, J-C; Humbert, JF; Guette, C; Bernard, C. First report in a river in France of the benthic cyanobacterium Phormidium favosum producing anatoxin-a associated with dog neurotoxicosis. Toxicon 2005, 45, 919–928. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, RE; Scheuer, PJ. Palytoxin: A new marine toxin from a coelenterate. Science 1971, 172, 495–498. [Google Scholar]
- Ciminiello, P; Dell’Aversano, C; Dello Iacovo, E; Fattorusso, E; Forino, M; Grauso, L; Tartaglione, L; Florio, C; Lorenzon, P; De Bortoli, M; Tubaro, A; Poli, M; Bignami, G. Stereostructure and biological activity of 42-hydroxy-palytoxin: A new palytoxin analogue from hawaiian palythoa subspecies. Chem Res Toxicol 2009, 22, 1851–1859. [Google Scholar]
- Katikou, P. Palytoxins and analogues: Ecobiology and origin, chemistry, metabolism and chemical analysis. In Phycotoxins: Chemistry and Biochemistry, 2nd ed; Botana, LM, Ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 631–663. [Google Scholar]
- Vale, C; Ares, IR. Biochemistry of palytoxins and ostreocins. In Phycotoxins: Chemistry and Biochemistry; Botana, LM, Ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 95–118. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, CH. Palytoxin: Membrane mechanisms of action. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, V; Vasconcelos, V. Palytoxin and analogs: Biological and ecological effects. Mar Drugs 2010, 8, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar]
- Aligizaki, K; Katikou, P; Milandri, A; Diogene, J. Occurrence of palytoxin-group toxins in seafood and future strategies to complement the present state of the art. Toxicon 2011, 57, 390–399. [Google Scholar]
- Kodama, AM; Hokama, Y; Yasumoto, T; Fukui, M; Manea, SJ; Sutherland, N. Clinical and laboratory findings implicating palytoxin as cause of ciguatera poisoning due to Decapterus macrosoma (mackerel). Toxicon 1989, 27, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Deeds, JR; Schwartz, MD. Human risk associated with palytoxin exposure. Toxicon 2010, 56, 150–162. [Google Scholar]
- Riobó, P; Franco, JM. Palytoxins: Biological and chemical determination. Toxicon 2011, 57, 368–375. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, JE. Review of clupeotoxism, an often fatal illness from the consumption of clupeoid fishes. Pac Sci 2005, 59, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Onuma, Y; Satake, M; Ukena, T; Roux, J; Chanteau, S; Rasolofonirina, N. Identification of putative palytoxin as the cause of clupeotoxism. Toxicon 1999, 37, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Taniyama, S; Arakawa, O; Terada, M; Nishio, S; Takatani, T; Mahmud, Y; Noguchi, T. Ostreopsis sp., a possible origin of palytoxin (PLTX) in parrotfish Scarus ovifrons. Toxicon 2003, 42, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Tubaro, A; Durando, P; Del Favero, G; Ansaldi, F; Icardi, G; Deeds, JR; Soda, S. Case definitions for human poisonings postulated to palytoxine exposure. Toxicon 2011, 57, 478–495. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, L; Towers, N; Briggs, L; Munday, R; Adamson, J. Uptake of palytoxin-like compounds by shellfish fed Ostreopsis siamensis (Dinophyceae). N Z J Mar Freshw Res 2002, 36, 631–636. [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir, S; Ten-Hage, L; Turquet, J; Quod, JP; Bernard, C; Hennion, MC. First evidence of palytoxin analogues from an Ostreopsis mascarenensis (Dinophyceae) benthic bloom in southwestern Indian Ocean. J Phycol 2004, 40, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Ciminiello, P; Dell’Aversano, C; Fattorusso, E; Forino, M; Magno, GS; Tartaglione, L; Grillo, C; Melchiorre, N. The Genoa 2005 outbreak. Determination of putative Palytoxin in Mediterranean Ostreopsis ovata by a new Liquid Chromatography tandem Mass Spectrometry Method. Anal Chem 2006, 78, 6153–6159. [Google Scholar]
- Ciminiello, P; Dell’Aversano, C; Dello Iacovo, E; Fattorusso, E; Forino, M; Tartaglione, L. LC-MS of palytoxin and its analogues: State of the art and future perspectives. Toxicon 2011, 57, 376–389. [Google Scholar]
- Janson, S; Siddiqui, PJA; Walsby, AE; Romans, KM; Carpenter, EJ; Bergman, B. Cytomorphological characterization of the planktonic diazotrophic cyanobacteria Trichodesmium spp. from the Indian Ocean and Caribbean and Sargasso seas. J Phycol 1995, 31, 463–477. [Google Scholar]
- Ledreux, A; Krys, S; Bernard, C. Suitability of the Neuro-2a cell line for the detection of palytoxin and analogues (neurotoxic phycotoxins). Toxicon 2009, 53, 300–308. [Google Scholar]
- Mossman, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Espiña, B; Cagide, E; Louzao, MC; Fernandez, MM; Vieytes, MR; Katikou, P; Villar, A; Jaen, D; Maman, L; Botana, L. Specific and dynamic detection of palytoxins by in vitro microplate assay with Neuroblastoma cells. Biosci Rep 2009, 29, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wachi, KM; Hokama, Y; Haga, LS; Shiraka, A; Takenaka, WE; Bignami, GS; Levine, L. Evidence for palytoxin as one of the sheep erythrocyte lytic factors in crude extracts of ciguateric and non-ciguateric reef fish tissue. J Nat Toxins 2000, 9, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Cañete, E; Diogene, J. Comparative study of the use of Neuroblastoma cells (Neuro-2a) and Neuroblastoma x glioma hybrids cells (NG108-15) for the toxic effect quantification of marine toxins. Toxicon 2008, 52, 541–550. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Scientific Opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish—Palytoxin group. EFSA Panel on Contamination in the Food Chain (CONTAM). EFSA J 2009, 7, 1393.
- O’Neil, JM. The colonial cyanobacterium Trichodesmium as a physical and nutritional substrate for the harpacticoid copepod Macrosetella gracilis. J Plankton Res 1998, 20, 43–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan, C; Steinberg, D; Kling, G. The microbial and metazoan community associated with colonies of Trichodesmium spp.: A quantitative survey. J Plankton Res 2002, 24, 913–922. [Google Scholar]
- Wachi, KM; Hokama, Y. Diversity of marine biotoxins in the near-shore ocean area: Presence of a palytoxin-like entity at Barbers Point Harbor, Oahu. J Nat Toxins 2001, 10, 317–333. [Google Scholar]
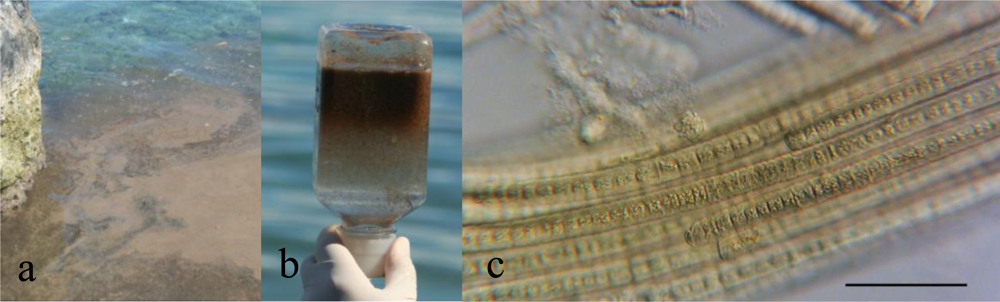
| No. | Date | Reference | Location | Latitude | Longitude | Water-soluble fraction % of dried material |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2007-03-01 | Tricho 5îles | 5îles | −22.771900 | 166.800995 | 64.3 |
| 2 | 2007-09-24 | Tricho BD 2007 | Baie des citrons | −22.297600 | 166.438004 | 51.6 |
| 3 | 2008-02-08 | Tricho BD 2008 | Baie des citrons | −22.295700 | 166.436005 | 68.8 |
| 4 | 2008-02-18 | Tricho Dumbéa | Passe de Dumbéa | −22.349501 | 166.274994 | 26.2 |
| 5 | 2008-02-18 | Tricho Ricaudy | Récif Ricaudy | −22.306900 | 166.460210 | 21.5 |
| 6 | 2008-11-04 | Tricho Lifou C01 | Lifou–Hunëtë | −20.767310 | 167.093006 | 52.5 |
| 7 | 2009-02-01 | Tricho Nouméa 3 | Passe de Dumbéa | −22.349501 | 166.274994 | 49.7 |
| 8 | 2009-11-18 | Tricho Lifou C02 | Lifou–Hunëtë | −20.767310 | 167.093006 | 55.4 |
| Toxins | Transitions m/z | Declustering potential (V) | Cell exit potential (V) | Dwell time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLTX | 1340→327 | 26 | 18 | 250 |
| 1332→327 | 26 | 18 | 250 | |
| 896→327 | 61 | 8 | 250 | |
| Ovatoxin-a | 1324→327 | 26 | 18 | 250 |
| 1315→327 | 26 | 18 | 250 | |
| 889→327 | 61 | 8 | 250 | |
| 42-OH-PLTX | 1348.7→327 | 26 | 18 | 250 |
| 1339.7→327 | 26 | 18 | 250 | |
| 899.7→327 | 61 | 8 | 250 |
| Conditions | Without O | Pre PLTX | O | Pre O | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O (μM) Pre-incubation time (h) | 0 | 500 2 | 500 0 | 500 1 | 500 2 | 250 2 | 100 2 |
| C50 (pM) | 170 ± 60 (n = 3) | 6.37 | 5.08 | 9.41 | 6.0 ± 2.2 (n = 3) | 11.65 | 21.74 |
| No. | Reference | CBA | LC-MS/MS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| preO− | preO+ | PLTX | 42-OH-PLTX | Total PLTX eqv. | |||
| EC50 μg/mL | μg/g extract | μg/g extract | μg/g eqv. dried material | ||||
| 1 | Tricho 5îles | 1337 ± 126 | 113.8 ± 110.8 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 1.70 | 1.10 |
| 2 | Tricho BD 2007 | >LOQ | 2261 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| 3 | Tricho BD 2008 | >LOQ | 1138 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| 4 | Tricho Dumbéa | 1324/1066 | 494/158 | 0.57 | 0.52 | 1.08 | 0.28 |
| 5 | Tricho Ricaudy | 927 | NA | 0.89 | 0.64 | 1.53 | 0.33 |
| 6 | Tricho Lifou C01 | 1214 | 397 | 0.86 | 0.59 | 1.45 | 0.76 |
| 7 | Tricho Nouméa 3 | 1212 | 91 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
| 8 | Tricho Lifou C02 | >LOQ | 2054 ± 277 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Kerbrat, A.S.; Amzil, Z.; Pawlowiez, R.; Golubic, S.; Sibat, M.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Laurent, D. First Evidence of Palytoxin and 42-Hydroxy-palytoxin in the Marine Cyanobacterium Trichodesmium. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 543-560. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9040543
Kerbrat AS, Amzil Z, Pawlowiez R, Golubic S, Sibat M, Darius HT, Chinain M, Laurent D. First Evidence of Palytoxin and 42-Hydroxy-palytoxin in the Marine Cyanobacterium Trichodesmium. Marine Drugs. 2011; 9(4):543-560. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9040543
Chicago/Turabian StyleKerbrat, Anne Sophie, Zouher Amzil, Ralph Pawlowiez, Stjepko Golubic, Manoella Sibat, Helene Taiana Darius, Mireille Chinain, and Dominique Laurent. 2011. "First Evidence of Palytoxin and 42-Hydroxy-palytoxin in the Marine Cyanobacterium Trichodesmium" Marine Drugs 9, no. 4: 543-560. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9040543
APA StyleKerbrat, A. S., Amzil, Z., Pawlowiez, R., Golubic, S., Sibat, M., Darius, H. T., Chinain, M., & Laurent, D. (2011). First Evidence of Palytoxin and 42-Hydroxy-palytoxin in the Marine Cyanobacterium Trichodesmium. Marine Drugs, 9(4), 543-560. https://doi.org/10.3390/md9040543