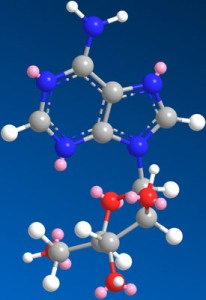
Antiviral Lead Compounds from Marine Sponges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- Samples Availability: Not applicable.
References
- Bergquist, P. Sponges; Univ of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D; Cragg, G. Marine natural products and related compounds in clinical and advanced preclinical trials. J. Nat. Prod 2004, 67, 1216–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, AS; Daum, T; Miiller, WEG. Secondary Metabolites from Marine Sponges; Ullstein-Mosby Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Faulkner, DJ. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep 2002, 19, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
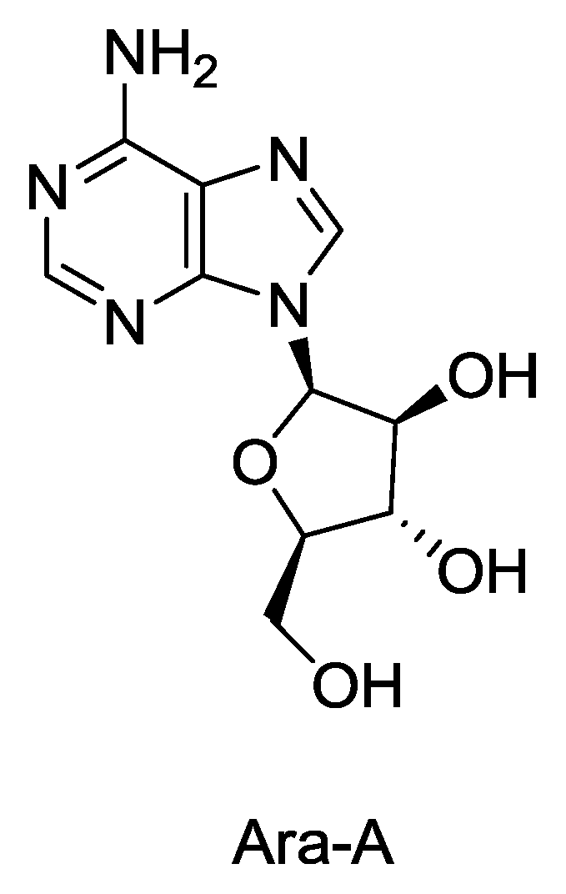
- Bergmann, W; Feeney, RJ. The isolation of a new thymine pentoside from sponges. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1950, 72, 2809–2810. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, W; Feeney, RJ. Contributions to the study of marine products. XXXII. The nucelosides of sponges. I. J. Org. Chem 1951, 16, 981–987. [Google Scholar]
- Shepp, DH; Dandliker, PS; Meyers, JD. Treatment of varicella-zoster virus infection in severely immunocompromised patients. A randomized comparison of acyclovir and vidarabine. N. Engl. J. Med 1986, 314, 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Whitley, RJ; Gnann, JW, Jr; Hinthorn, D; Liu, C; Pollard, RB; Hayden, F; Mertz, GJ; Oxman, M; Soong, SJ. Disseminated herpes zoster in the immunocompromised host: a comparative trial of acyclovir and vidarabine. The NIAID Collaborative Antiviral Study Group. J. Infect. Dis 1992, 165, 450–455. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, JW; Copp, BR; Munro, MH; Northcote, PT; Prinsep, MR. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep 2005, 22, 15–61. [Google Scholar]
- Privat de Garilhe, M; de Rudder, J. Effect of 2 arbinose nucleosides on the multiplication of herpes virus and vaccine in cell culture. C. R. Hebd. Seances Acad. Sci 1964, 259, 2725–2728. [Google Scholar]
- Field, H; De Clercq, E. Antiviral drugs-a short history of their discovery and development. Microbiol. Today 2004, 31, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, AMS; Glaser, KB; Cuevas, C; Jacobs, RS; Kem, W; Little, RD; McIntosh, JM; Newman, DJ; Potts, BC; Shuster, DE. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: a current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci 2010, 31(6), 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Shope, TC; Kauffman, RE; Bowman, D; Marcus, EL. Pharmacokinetics of vidarabine in the treatment of infants and children with infections due to herpesviruses. J. Infect. Dis 1983, 148, 721–725. [Google Scholar]
- Sloan, B; Kielty, J; Miller, F. Effect of a novel adenosine deaminase inhibitor (co-vidarabine, co-V) upon the antiviral activity in vitro and in vivo of vidarabine (Vira-Atm) for DNA virus replication. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci 1977, 284, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Whitley, R; Tucker, B; Kinkel, A; Barton, N; Pass, R; Whelchel, J; Cobbs, C; Diethelm, A; Buchanan, R. Pharmacology, tolerance, and antiviral activity of vidarabine monophosphate in humans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 1980, 18, 709. [Google Scholar]
- Kamiyama, T; Kurokawa, M; Shiraki, K. Characterization of the DNA polymerase gene of varicella-zoster viruses resistant to acyclovir. J. Gen. Virol 2001, 82, 2761–2765. [Google Scholar]
- Shiraki, K; Namazue, J; Okuno, T; Yamanishi, K; Takahashi, M. Novel sensitivity of acyclovir-resistant varicella-zoster virus to anti-herpetic drugs. Antiviral Chem. Chemother 1990, 1, 373–375. [Google Scholar]
- Doering, A; Keller, J; Cohen, S. Some effects of D-arabinosyl nucleosides on polymer syntheses in mouse fibroblasts. Cancer Res 1966, 26, 2444. [Google Scholar]
- Plunkett, W; Cohen, SS. Two approaches that increase the activity of analogs of adenine nucleosides in animal cells. Cancer Res 1975, 35, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Dicioccio, RA; Srivastava, BI. Kinetics of inhibition of deoxynucleotide-polymerizing enzyme activities from normal and leukemic human cells by 9-beta-d-arabinofuranosyladenine 5′-triphosphate and 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine 5′-triphosphate. Eur. J. Biochem 1977, 79, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, K; Jacob, S. Selective inhibition of RNA polyadenylation by Ara-ATP in vitro: a possible mechanism for antiviral action of Ara-A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1978, 81, 1418–1424. [Google Scholar]
- Hilfinger, JMWZ; Kim, J; Mitchell, S; Breitenbach, J; Amidon, G; Drach, J. Vidarabine Prodrugs as Anti-Pox Virus Agents. Antiviral Res 2006, 70, A14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z; Prudhomme, D; Buck, J; Park, M; Rizzo, C. Stereocontrolled Syntheses of Deoxyribonucleosides via Photoinduced Electron-Transfer Deoxygenation of Benzoyl-Protected Ribo-and Arabinonucleosides. J. Org. Chem 2000, 65, 5969–5985. [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz, E; Kazimierczuk, Z; Shugar, D. Preparation and properties of the O-methyl derivatives of 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. Cancer Biochem. Biophys 1976, 1, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Kotra, L; Manouilov, K; Cretton-Scott, E; Sommadossi, J; Boudinot, F; Schinazi, R; Chu, C. Synthesis, biotransformation, and pharmacokinetic studies of 9-(D-arabinofuranosyl)-6-azidopurine: A prodrug for Ara-A designed to utilize the azide reduction pathway. J. Med. Chem 1996, 39, 5202–5207. [Google Scholar]
- McGuigan, C; Shackleton, J; Tollerfield, S; Riley, P. Synthesis and evaluation of some novel phosphate and phosphinate derivatives of araA. Studies on the mechanism of action of phosphate triesters. Nucleic Acids Res 1989, 17, 10171–10177. [Google Scholar]
- Suhadolnik, R; Pornbanlualap, S; Wu, J; Baker, D; Hebbler, A. Biosynthesis of 9-[beta]-arabinofuranosyladenine: Hydrogen exchange at C-2′and oxygen exchange at C-3′of adenosine* 1. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 1989, 270, 363–373. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, N; Blunt, J; Munro, M; Pannell, L. Mycalamide A, an antiviral compound from a New Zealand sponge of the genus Mycale. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1988, 110, 4850–4851. [Google Scholar]
- Perry, NB; Blunt, JW; Munro, MHG; Thompson, AM. Antiviral and antitumor agents from a New Zealand sponge, Mycale sp. 2. Structures and solution conformations of mycalamides A and B. J. Org. Chem 1990, 55, 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Burres, N; Clement, J. Antitumor activity and mechanism of action of the novel marine natural products mycalamide-A and-B and onnamide. Cancer Res 1989, 49, 2935. [Google Scholar]
- Gurel, G; Blaha, G; Steitz, T; Moore, P. The structures of Triacetyloleandomycin and Mycalamide A bound to the large ribosomal subunit of Haloarcula marismortui. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2009, 53, 5010–5014. [Google Scholar]
- Kagawa, N; Ihara, M; Toyota, M. Total Synthesis of (+)-Mycalamide A. Org. Lett 2006, 8, 875–878. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, J; Waizumi, N; Zhong, H; Rawal, V. Total synthesis of mycalamide A. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2005, 127, 7290–7291. [Google Scholar]
- Toyota, M; Hirota, M; Hirano, H; Ihara, M. A stereoselective synthesis of the C-10 to C-18 (right-half) fragment of mycalamides employing lewis acid promoted intermolecular aldol reaction. Org. Lett 2000, 2, 2031–2034. [Google Scholar]
- Trost, B; Yang, H; Probst, G. A formal synthesis of (−)-mycalamide A. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2004, 126, 48–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara, K; Kondoh, Y; Ueda, A; Yamada, K; Goto, H; Watanabe, T; Nakata, T; Osada, H; Aida, Y. Discovery of novel antiviral agents directed against the influenza A virus nucleoprotein using photo-cross-linked chemical arrays. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2010, 394(3), 721–727. [Google Scholar]
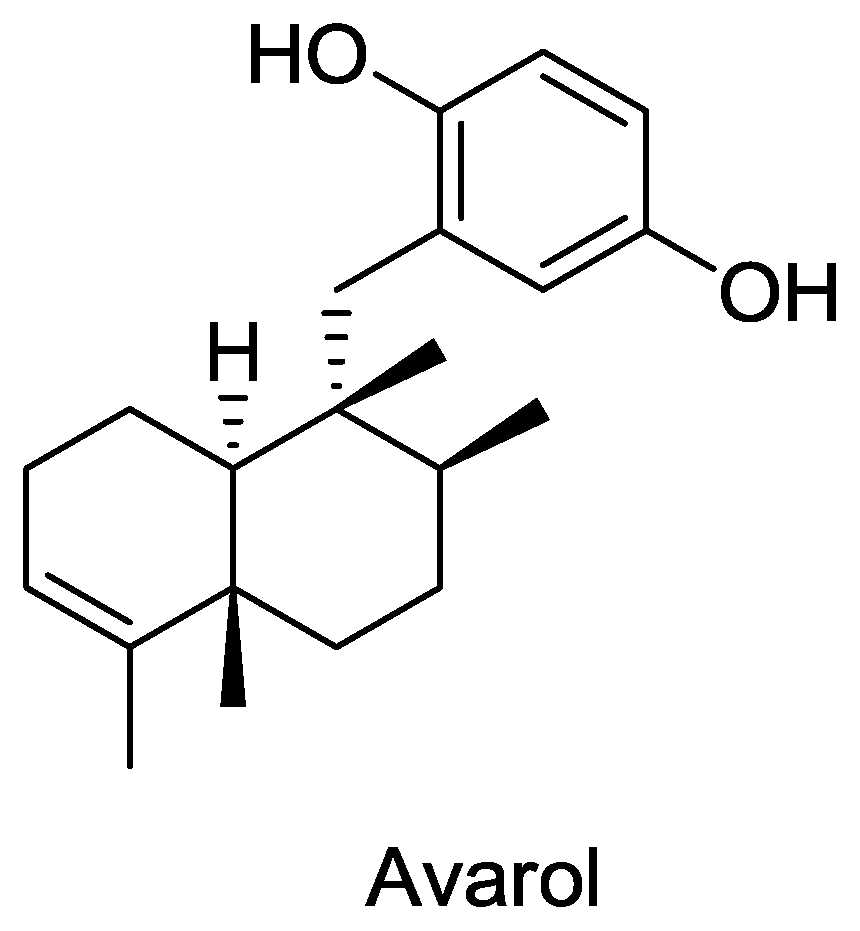
- Minale, L; Riccio, R; Sodano, G. Avarol a novel sesquiterpenoid hydroquinone with a rearranged drimane skeleton from the sponge. Tetrahedron Lett 1974, 15, 3401–3404. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, S; Minale, L; Riccio, R; Sodano, G. The absolute configuration of avarol, a rearranged sesquiterpenoid hydroquinone from a marine sponge. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1976, 1976, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, A; Chattopadhyay, P. Synthetic studies of trans-clerodane diterpenoids and congeners: stereocontrolled total synthesis of (±)-avarol. J. Org. Chem 1982, 47, 1727–1731. [Google Scholar]
- Sarin, P; Sun, D; Thornton, A; Muller, W. Inhibition of replication of the etiologic agent of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (human T-lymphotropic retrovirus/lymphadenopathy-associated virus) by avarol and avarone. J. Natl. Cancer Inst 1987, 78, 663–666. [Google Scholar]
- Batke, E; Ogura, R; Vaupel, P; Hummel, K; Kallinowski, F; Gasić, MJ; Schröder, H; Müllerm, W. Action of the antileukemic and anti-HTLV-III (anti-HIV) agent avarol on the levels of superoxide dismutases and glutathione peroxidase activities in L5178y mouse lymphoma cells. Cell Biochem. Funct 1988, 6, 123–129. [Google Scholar]
- Kuchino, Y; Nishimura, S; Schröder, H; Rottmann, M; Müller, W. Selective inhibition of formation of suppressor glutamine tRNA in Moloney murine leukemia virus-infected NIH-3T3 cells by Avarol. Virology 1988, 165, 518–526. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, W; Schroder, H. Cell biological aspects of HIV-1 infection: effects of the anti-HIV-1 agent avarol. Int. J. Sports Med 1991, 12, S43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, WE; Schroder, HC; Reuter, P; Sarin, PS; Hess, G; Meyer zum Buschenfelde, KH; Kuchino, Y; Nishimura, S. Inhibition of expression of natural UAG suppressor glutamine tRNA in HIV-infected human H9 cells in vitro by Avarol. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1988, 4, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Loya, S; Hizi, A. The inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase by avarol and avarone derivatives. FEBS Lett 1990, 269, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Schröder, H; Bégin, M; Klöcking, R; Matthes, E; Sarma, A; Gašić, M; Müller, W. Avarol restores the altered prostaglandin and leukotriene metabolism in monocytes infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Virus Res 1991, 21, 213–223. [Google Scholar]
- Sarin, P; Sun, D; Thornton, A; Miller, W. Inhibition of replication of the etiologic agent of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (human T-lymphotropic retrovirus/lymphadenopathy-associated virus) by avarol and avarone. J. Natl. Cancer Inst 1987, 78, 663. [Google Scholar]
- De Giulio, A; De Rosa, S; Strazzulo, G; Diliberto, L; Obino, P; Marongiu, ME; Pani, A; La Colla, P. Synthesis and evaluation of cytostatic and antiviral activities of 3′and 4′-avarone derivatives. Antiviral Chem. Chemother 1991, 2, 223–227. [Google Scholar]
- Suhadolnik, R; Pornbanlualap, S; Baker, D; Tiwari, K; Hebbler, A. Stereospecific 2′-amination and 2′-chlorination of adenosine by Actinomadura in the biosynthesis of 2′-amino-2′-deoxyadenosine and 2′-chloro-2′-deoxycoformycin* 1. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 1989, 270, 374–382. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, T; Xiang, A; Theodorakis, E. Enantioselective total synthesis of avarol and avarone. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 1999, 38, 3089–3091. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, W; Bohm, M; Batel, R; De Rosa, S; Tommonaro, G; Muller, I; Schroder, H. Application of cell culture for the production of bioactive compounds from sponges: synthesis of avarol by primmorphs from Dysidea avara. J. Nat. Prod 2000, 63, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, W; Grebenjuk, V; Le Pennec, G; Schröder, H; Brümmer, F; Hentschel, U; Müller, I; Breter, H. Sustainable production of bioactive compounds by sponges—cell culture and gene cluster approach: a review. Mar. Biotechnol 2004, 6, 105–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, P; Gustafson, K; McKee, T; Shigematsu, N; Maurizi, L; Pannell, L; Williams, D; de Silva, E; Lassota, P; Allen, T. Papuamides A–D, HIV-Inhibitory and Cytotoxic Depsipeptides from the Sponges Theonella mirabilis and Theonella swinhoei Collected in Papua New Guinea. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1999, 121, 5899–5909. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W; Ding, D; Zi, W; Li, G; Ma, D. Total Synthesis and Structure Assignment of Papuamide B, A Potent Marine Cyclodepsipeptide with Anti-HIV Properties13. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2008, 47, 2844–2848. [Google Scholar]
- Andjelic, C; Planelles, V; Barrows, L. Characterizing the Anti-HIV Activity of Papuamide A. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 528–549. [Google Scholar]
- Esté, J; Telenti, A. HIV entry inhibitors. Lancet 2007, 370, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Volpon, L; Besson, F; Lancelin, J. NMR structure of active and inactive forms of the sterol-dependent antifungal antibiotic bacillomycin L. Eur. J. Biochem 2001, 264, 200–210. [Google Scholar]
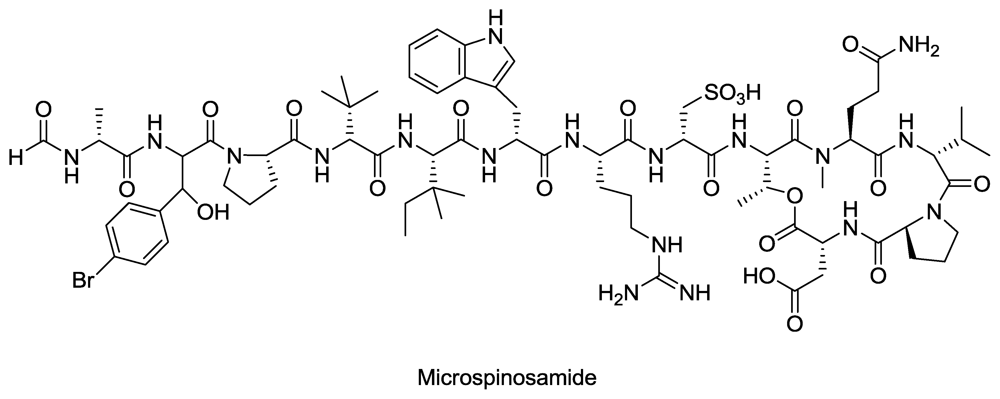
- Rashid, M; Gustafson, K; Cartner, L; Shigematsu, N; Pannell, L; Boyd, M. Microspinosamide, a new HIV-inhibitory cyclic depsipeptide from the marine sponge Sidonops microspinosa1. J. Nat. Prod 2001, 64, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, M. De Vita, VT, Jr, Hellman, S, Rosenberg, SA, Eds.; AIDS Etiology, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1988; pp. 305–319. [Google Scholar]
- Valeria D’Auria, M; Zampella, A; Paloma, LG; Minale, L; Debitus, C; Roussakis, C; Le Bert, V. Callipeltins B and C; bioactive peptides from a marine Lithistida sponge Callipelta sp. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 9589–9596. [Google Scholar]
- Zampella, A; D’Auria, M; Paloma, L; Casapullo, A; Minale, L; Debitus, C; Henin, Y. Callipeltin A, an anti-HIV cyclic depsipeptide from the New Caledonian Lithistida sponge Callipelta sp. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1996, 118, 6202–6209. [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho, AF; Chanas, B; e Souza, TML; Frugrulhetti, ICPP; de A Epifanio, R. Anti HSV-1 alkaloids from a feeding deterrent marine sponge of the genus Aaptos. Heterocycles 2002, 57, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar]
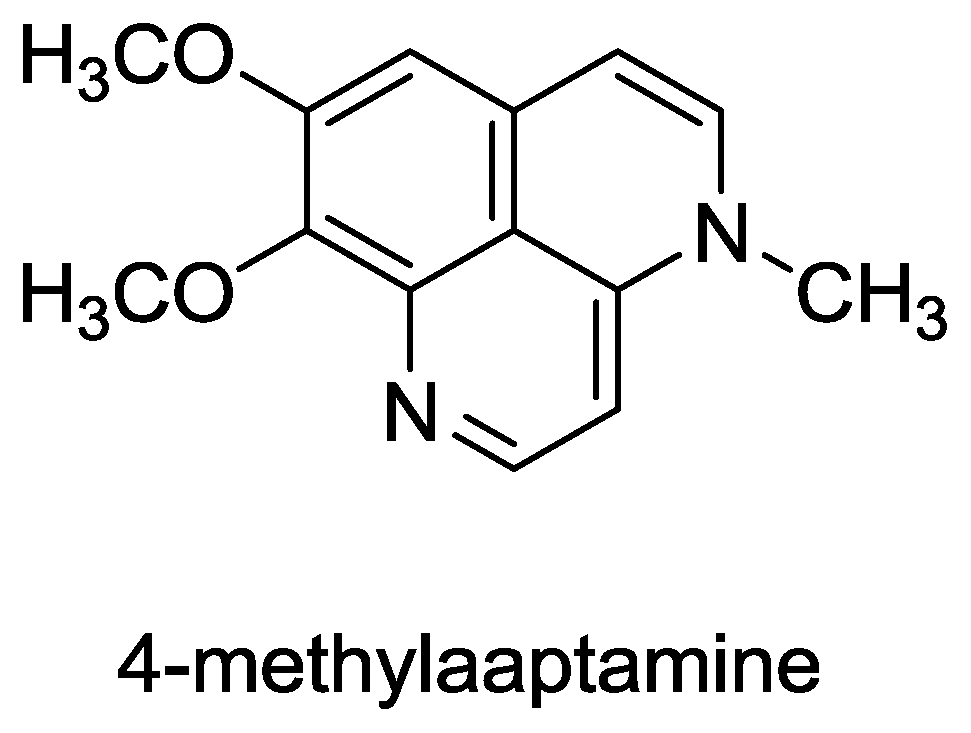
- Souza, T; Abrantes, J; de A Epifanio, R; Fontes, C; Frugulhetti, I. The Alkaloid 4-Methylaaptamine Isolated from the Sponge Aaptos aaptos Impairs Herpes simplex Virus Type 1 Penetration and Immediate-Early Protein Synthesis. Planta Med 2007, 73, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, H; Kobayashi, J; Ohizumi Yoshimasa, Y. Isolation and structure of aaptamine a novel heteroaromatic substance possessing [alpha]-blocking activity from the sea sponge. Tetrahedron Lett 1982, 23, 5555–5558. [Google Scholar]
- Pettit, G; Hoffmann, H; Herald, D; McNulty, J; Murphy, A; Higgs, K; Hamel, E; Lewin, N; Pearce, L; Blumberg, P. Antineoplastic agents 491. Synthetic conversion of aaptamine to isoaaptamine, 9-demethylaaptamine, and 4-methylaaptamine. J. Org. Chem 2004, 69, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, W; Hammond, N; Yousaf, M; Bowling, J; Schinazi, R; Wirtz, S; de Castro Andrews, G; Cuevas, C; Hamann, M. Modification at the C9 position of the marine natural product isoaaptamine and the impact on HIV-1, mycobacterial, and tumor cell activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2006, 14, 8495–8505. [Google Scholar]
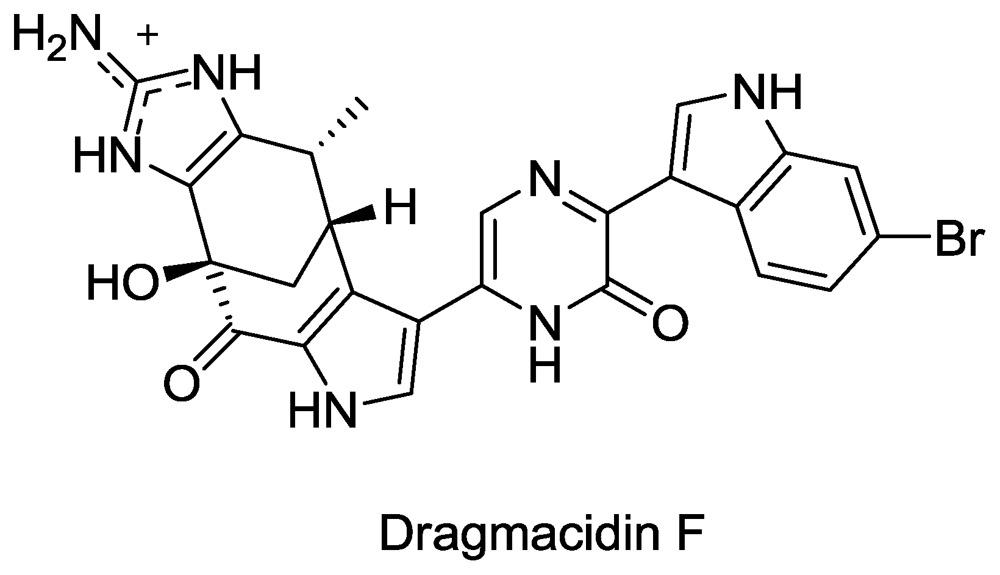
- Cutignano, A; Bifulco, G; Bruno, I; Casapullo, A; Gomez-Paloma, L; Riccio, R. Dragmacidin F: A New Antiviral Bromoindole Alkaloid from the Mediterranean Sponge Halicortex sp. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 3743–3748. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, N; Caspi, D; Stoltz, B. The total synthesis of (+)-dragmacidin F. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2004, 126, 9552–9553. [Google Scholar]
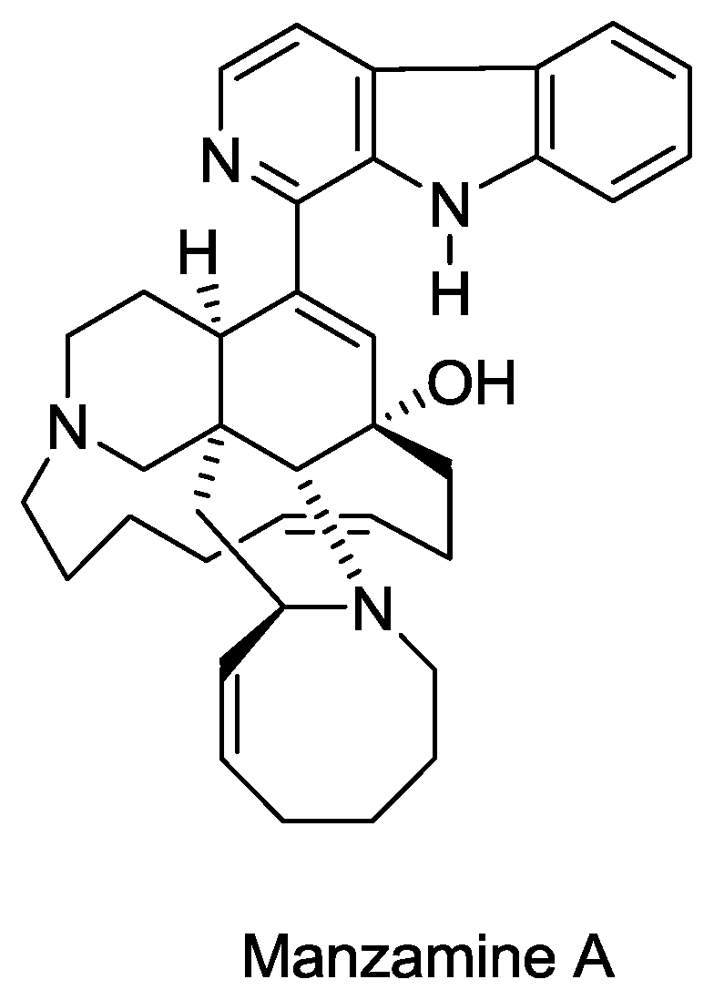
- Sakai, R; Higa, T; Jefford, CW; Bernardinelli, G. Manzamine A, a novel antitumor alkaloid from a sponge. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1986, 108, 6404–6405. [Google Scholar]
- El Sayed, KA; Kelly, M; Kara, UAK; Ang, KKH; Katsuyama, I; Dunbar, DC; Khan, AA; Hamann, MT. New Manzamine Alkaloids with Potent Activity against Infectious Diseases. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2001, 123, 1804–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, KV; Santarsiero, BD; Mesecar, AD; Schinazi, RF; Tekwani, BL; Hamann, MT. New Manzamine Alkaloids with Activity against Infectious and Tropical Parasitic Diseases from an Indonesian Sponge. J. Nat. Prod 2003, 66, 823–828. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, K; Holmes, M; Higa, T; Hamann, M; Kara, U. In vivo antimalarial activity of the betacarboline alkaloid manzamine A. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2000, 44, 1645. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J; Shen, X; El Sayed, K; Dunbar, D; Perry, T; Wilkins, S; Hamann, M; Bobzin, S; Huesing, J; Camp, R. Marine natural products as prototype agrochemical agents. J. Agric. Food Chem 2003, 51, 2246–2252. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J; Rao, K; Choo, Y; Hamann, M. Fattorusso, E, Taglialatela-Scafati, O, Eds.; Manzamine Alkaloids. In Modern Alkaloids: Structure, Isolation, Synthesis and Biology; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; pp. 189–231. [Google Scholar]
- Ichiba, T; Corgiat, J; Scheuer, P; Kelly-Borges, M. 8-Hydroxymanzamine A, a beta-carboline alkaloid from a sponge, Pachypellina sp. J. Nat. Prod 1994, 57, 168–170. [Google Scholar]
- Edrada, R; Proksch, P; Wray, V; Witte, L; Muller, W; van Soest, R. Four new bioactive manzamine-type alkaloids from the Philippine marine sponge Xestospongia ashmorica. J. Nat. Prod 1996, 59, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, K; Santarsiero, B; Mesecar, A; Schinazi, R; Tekwani, B; Hamann, M. New manzamine alkaloids with activity against infectious and tropical parasitic diseases from an Indonesian sponge. J. Nat. Prod 2003, 66, 823–828. [Google Scholar]
- Samoylenko, V; Khan, S; Jacob, M; Tekwani, B; Walker, L; Hufford, C; Muhammad, I. Bioactive (+)-Manzamine A and (+)-Hydroxymanzamine A Tertiary Bases and Salts from Acanthostrongylophora ingens and Their Preparations. Nat. Prod. Commun 2009, 4, 185–192. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, J; Liao, Y; Ali, A; Rein, T; Wong, Y; Chen, H; Courtney, A; Martin, S. Enantioselective total syntheses of manzamine A and related alkaloids. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2002, 124, 8584–8592. [Google Scholar]
- Yousaf, M; Hammond, N; Peng, J; Wahyuono, S; McIntosh, K; Charman, W; Mayer, A; Hamann, M. New manzamine alkaloids from an Indo-Pacific sponge. Pharmacokinetics, oral availability, and the significant activity of several manzamines against HIV-I, AIDS opportunistic infections, and inflammatory diseases. J. Med. Chem 2004, 47, 3512–3517. [Google Scholar]
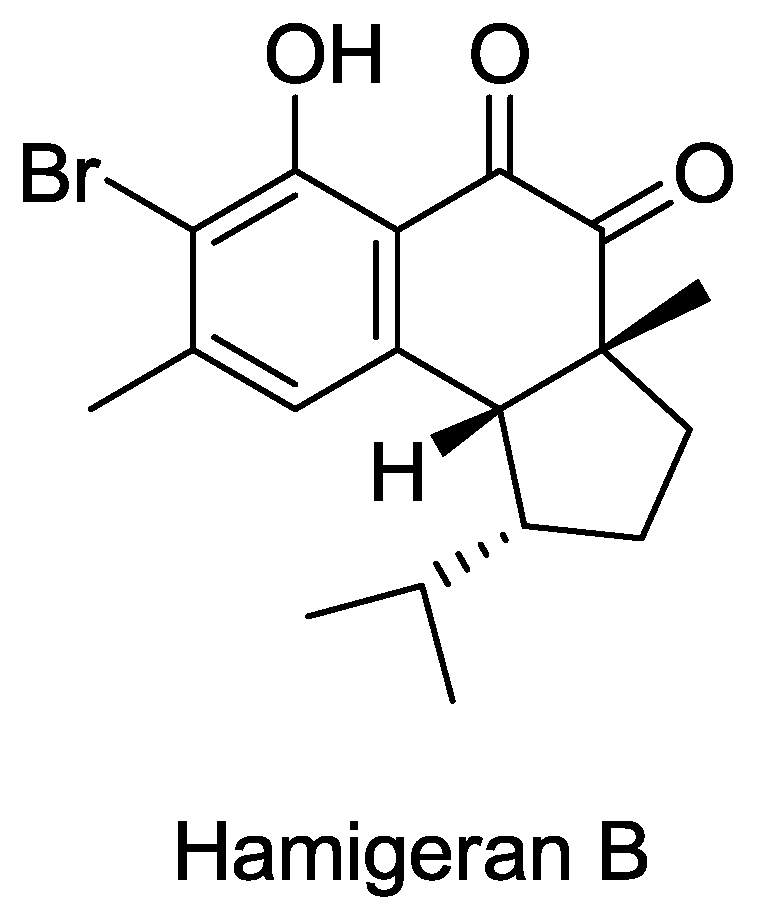
- Clive, DLJ; Wang, J. Stereospecific Total Synthesis of the Antiviral Agent Hamigeran B - Use of Large Silyl Groups to Enforce Facial Selectivity and to Suppress Hydrogenolysis13. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2003, 42, 3406–3409. [Google Scholar]
- Trost, B; Pissot-Soldermann, C; Chen, I; Schroeder, G. An asymmetric synthesis of hamigeran B via a Pd asymmetric allylic alkylation for enantiodiscrimination. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2004, 126, 4480–4481. [Google Scholar]
- Trost, BM; Pissot-Soldermann, C; Chen, I. A short and concise asymmetric synthesis of hamigeran B. Chemistry 2005, 11, 951–959. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, A; Kratz, J; Farias, F; Henriques, A; dos SANTOS, J; Leonel, R; Lerner, C; Mothes, B; Barardi, C; Simões, C. In vitro antiviral activity of marine sponges collected off Brazilian coast. Biol. Pharm. Bull 2006, 29, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Proksch, P; Edrada, R; Ebel, R. Drugs from the seas-current status and microbiological implications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2002, 59, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, J; Lill, R; Hickford, S; Blunt, J; Munro, M. The halichondrins: chemistry, biology, supply and delivery. Drugs Sea 2000, 134–153. [Google Scholar]
- Wall, M; Wani, M. Camptothecin and taxol: discovery to clinic—thirteenth Bruce F. Cain Memorial Award Lecture. Cancer Res 1995, 55, 753–760. [Google Scholar]
- Belarbi, E; Gómez, C. Producing drugs from marine sponges. Biotechnol. Adv 2003, 21, 585–598. [Google Scholar]
- Flowers, A; Garson, M; Webb, R; Dumdei, E; Charan, R. Cellular origin of chlorinated diketopiperazines in the dictyoceratid sponge Dysidea herbacea (Keller). Cell Tissue Res 1998, 292, 597–607. [Google Scholar]
- Ridley, C; Bergquist, P; Harper, M; Faulkner, D; Hooper, J; Haygood, M. Speciation and biosynthetic variation in four dictyoceratid sponges and their cyanobacterial symbiont, Oscillatoria spongeliae. Chem. Biol 2005, 12, 397–406. [Google Scholar]
- Unson, M; Holland, N; Faulkner, D. A brominated secondary metabolite synthesized by the cyanobacterial symbiont of a marine sponge and accumulation of the crystalline metabolite in the sponge tissue. Mar. Biol 1994, 119, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M; Radax, R; Steger, D; Wagner, M. Sponge-associated microorganisms: evolution, ecology, and biotechnological potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev 2007, 71, 295. [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann, R; Graeber, I; Kaesler, I; Szewzyk, U; von Doehren, H. Rapid screening and dereplication of bacterial isolates from marine sponges of the Sula Ridge by intact-cell-MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry (ICM-MS). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2005, 67, 539–548. [Google Scholar]
- Gunasekera, A; Sfanos, K; Harmody, D; Pomponi, S; McCarthy, P; Lopez, J. HBMMD: an enhanced database of the microorganisms associated with deeper water marine invertebrates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2005, 66, 373–376. [Google Scholar]
- Staley, J; Konopka, A. Measurement of in situ activities of nonphotosynthetic microorganisms in aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Annu. Rev. Microbiol 1985, 39, 321–346. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, N; Hill, R. The culturable microbial community of the Great Barrier Reef sponge Rhopaloeides odorabile is dominated by an -Proteobacterium. Mar. Biol 2001, 138, 843–851. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, N; Wilson, K; Blackall, L; Hill, R. Phylogenetic diversity of bacteria associated with the marine sponge Rhopaloeides odorabile. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2001, 67, 434. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, J; Lord, C; McCarthy, P. Improved recoverability of microbial colonies from marine sponge samples. Microb. Ecol 2000, 40, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Burja, A; Webster, N; Murphy, P; Hill, R. Microbial symbionts of Great Barrier Reef sponges. Mem. Queensl. Mus 1999, 44, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, M; Radax, R; Steger, D; Wagner, M. Sponge-associated microorganisms: evolution, ecology, and biotechnological potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev 2007, 71, 295–307. [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth, A. Farming Sponges to Supply Bioactive Metabolites and Bath Sponges: A Review. Mar. Biotechnol 2009, 11, 669–679. [Google Scholar]
- Koopmans, M; Martens, D; Wijffels, R. Towards Commercial Production of Sponge Medicines. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 787–802. [Google Scholar]
- Wijffels, R. Potential of sponges and microalgae for marine biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 2008, 26, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, J; Marchesi, J; Dobson, A. Metagenomic approaches to exploit the biotechnological potential of the microbial consortia of marine sponges. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2007, 75, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Handelsman, J. Metagenomics: Application of Genomics to Uncultured Microorganisms. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev 2004, 68, 669–685. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, TK; Fuerst, JA. Diversity of polyketide synthase genes from bacteria associated with the marine sponge Pseudoceratina clavata: culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches. Environ. Microbiol 2006, 8, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer, A; Gadkari, R; Reeves, CD; Ibrahim, F; DeLong, EF; Hutchinson, CR. Metagenomic Analysis Reveals Diverse Polyketide Synthase Gene Clusters in Microorganisms Associated with the Marine Sponge Discodermia dissoluta. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2005, 71, 4840–4849. [Google Scholar]
- Rachid, S; Krug, D; Kunze, B; Kochems, I; Scharfe, M; Zabriskie, TM; Blöcker, H; Müller, R. Molecular and Biochemical Studies of Chondramide Formation--Highly Cytotoxic Natural Products from Chondromyces crocatus Cm c5. Chem. Biol 2006, 13, 667–681. [Google Scholar]
- Fieseler, L; Horn, M; Wagner, M; Hentschel, U. Discovery of the Novel Candidate Phylum “Poribacteria” in Marine Sponges. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2004, 70, 3724–3732. [Google Scholar]
- Fieseler, L; Quaiser, A; Schleper, C; Hentschel, U. Analysis of the first genome fragment from the marine sponge-associated, novel candidate phylum Poribacteria by environmental genomics. Environ. Microbiol 2006, 8, 612–624. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, F; Ring, M; Perlova, O; Fu, J; Schneider, S; Gerth, K; Kuhlmann, S; Stewart, A; Zhang, Y; Müller, R. Metabolic engineering of Pseudomonas putida for methylmalonyl-CoA biosynthesis to enable complex heterologous secondary metabolite formation. Chem. Biol 2006, 13, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, S; Gross, F; Zhang, Y; Fu, J; Stewart, A; Müller, R. Heterologous expression of a myxobacterial natural products assembly line in pseudomonads via red/ET recombineering. Chem. Biol 2005, 12, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Khosla, C; Keasling, J. Metabolic engineering for drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2003, 2, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Mutka, S; Carney, J; Liu, Y; Kennedy, J. Heterologous Production of Epothilone C and D in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, J; Marshall, J; Chang, M; Nowroozi, F; Paradise, E; Pitera, D; Newman, K; Keasling, J. High-level production of amorpha-4, 11-diene in a two-phase partitioning bioreactor of metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng 2006, 95, 684–691. [Google Scholar]
- Julien, B; Shah, S. Heterologous expression of epothilone biosynthetic genes in Myxococcus xanthus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2002, 46, 2772. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer, B; Khosla, C. Biosynthesis of polyketides in heterologous hosts. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev 2001, 65, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Long, P; Dunlap, W; Battershill, C; Jaspars, M. Shotgun cloning and heterologous expression of the patellamide gene cluster as a strategy to achieving sustained metabolite production. ChemBioChem 2005, 6, 1760–1765. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, S; Chao, C; Clardy, J. New natural product families from an environmental DNA (eDNA) gene cluster. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2002, 124, 9968–9969. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, S; Chao, C; Handelsman, J; Clardy, J. Cloning and heterologous expression of a natural product biosynthetic gene cluster from eDNA. Org. Lett 2001, 3, 1981–1984. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, D; Brady, S; Bettermann, A; Cianciotto, N; Liles, M; Rondon, M; Clardy, J; Goodman, R; Handelsman, J. Isolation of antibiotics turbomycin A and B from a metagenomic library of soil microbial DNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2002, 68, 4301. [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil, I; Tiong, C; Minor, C; August, P; Grossman, T; Loiacono, K; Lynch, B; Phillips, T; Narula, S; Sundaramoorthi, R. Expression and isolation of antimicrobial small molecules from soil DNA libraries. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2001, 3, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Sipkema, D; Franssen, M; Osinga, R; Tramper, J; Wijffels, R. Marine sponges as pharmacy. Mar. Biotechnol 2005, 7, 142–162. [Google Scholar]
- Piel, J; Hui, D; Wen, G; Butzke, D; Platzer, M; Fusetani, N; Matsunaga, S. Antitumor polyketide biosynthesis by an uncultivated bacterial symbiont of the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16222. [Google Scholar]
- Sudek, S; Lopanik, N; Waggoner, L; Hildebrand, M; Anderson, C; Liu, H; Patel, A; Sherman, D; Haygood, M. Identification of the putative bryostatin polyketide synthase gene cluster from “Candidatus Endobugula sertula”, the uncultivated microbial symbiont of the marine bryozoan Bugula neritina. J. Nat. Prod 2007, 70, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Fortman, JL; Sherman, DH. Utilizing the Power of Microbial Genetics to Bridge the Gap Between the Promise and the Application of Marine Natural Products. ChemBioChem 2005, 6, 960–978. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, MW; Radax, R; Steger, D; Wagner, M. Sponge-Associated Microorganisms: Evolution, Ecology, and Biotechnological Potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev 2007, 71, 295–347. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G. Diversity and biotechnological potential of the sponge-associated microbial consortia. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2006, 33, 545–551. [Google Scholar]
- Fisch, K; Gurgui, C; Heycke, N; van der Sar, S; Anderson, S; Webb, V; Taudien, S; Platzer, M; Rubio, B; Robinson, S. Polyketide assembly lines of uncultivated sponge symbionts from structure-based gene targeting. Nat. Chem. Biol 2009, 5, 494–501. [Google Scholar]
- Hochmuth, T; Piel, J. Polyketide synthases of bacterial symbionts in sponges-Evolution-based applications in natural products research. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L; An, R; Wang, J; Sun, N; Zhang, S; Hu, J; Kuai, J. Exploring novel bioactive compounds from marine microbes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol 2005, 8, 276–281. [Google Scholar]


© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sagar, S.; Kaur, M.; Minneman, K.P. Antiviral Lead Compounds from Marine Sponges. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2619-2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8102619
Sagar S, Kaur M, Minneman KP. Antiviral Lead Compounds from Marine Sponges. Marine Drugs. 2010; 8(10):2619-2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8102619
Chicago/Turabian StyleSagar, Sunil, Mandeep Kaur, and Kenneth P. Minneman. 2010. "Antiviral Lead Compounds from Marine Sponges" Marine Drugs 8, no. 10: 2619-2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8102619
APA StyleSagar, S., Kaur, M., & Minneman, K. P. (2010). Antiviral Lead Compounds from Marine Sponges. Marine Drugs, 8(10), 2619-2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/md8102619