Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Epiphytic and Endophytic Fungi from Marine Organisms: Isolation, Bioassay and Taxonomy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Sample Collection and Strains Isolation
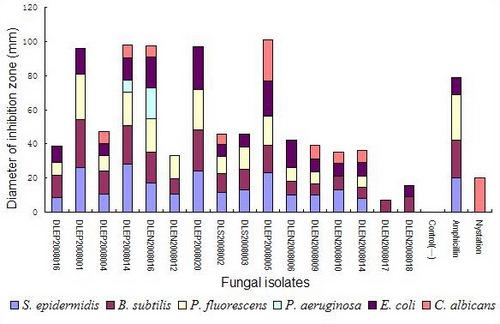
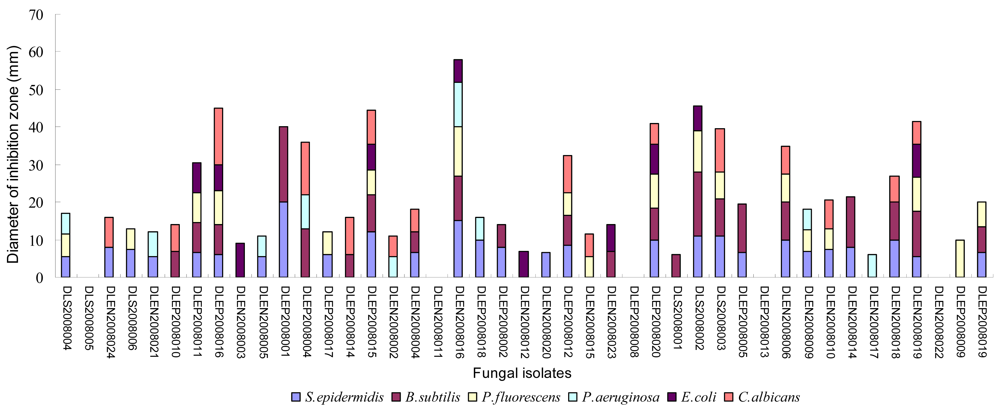
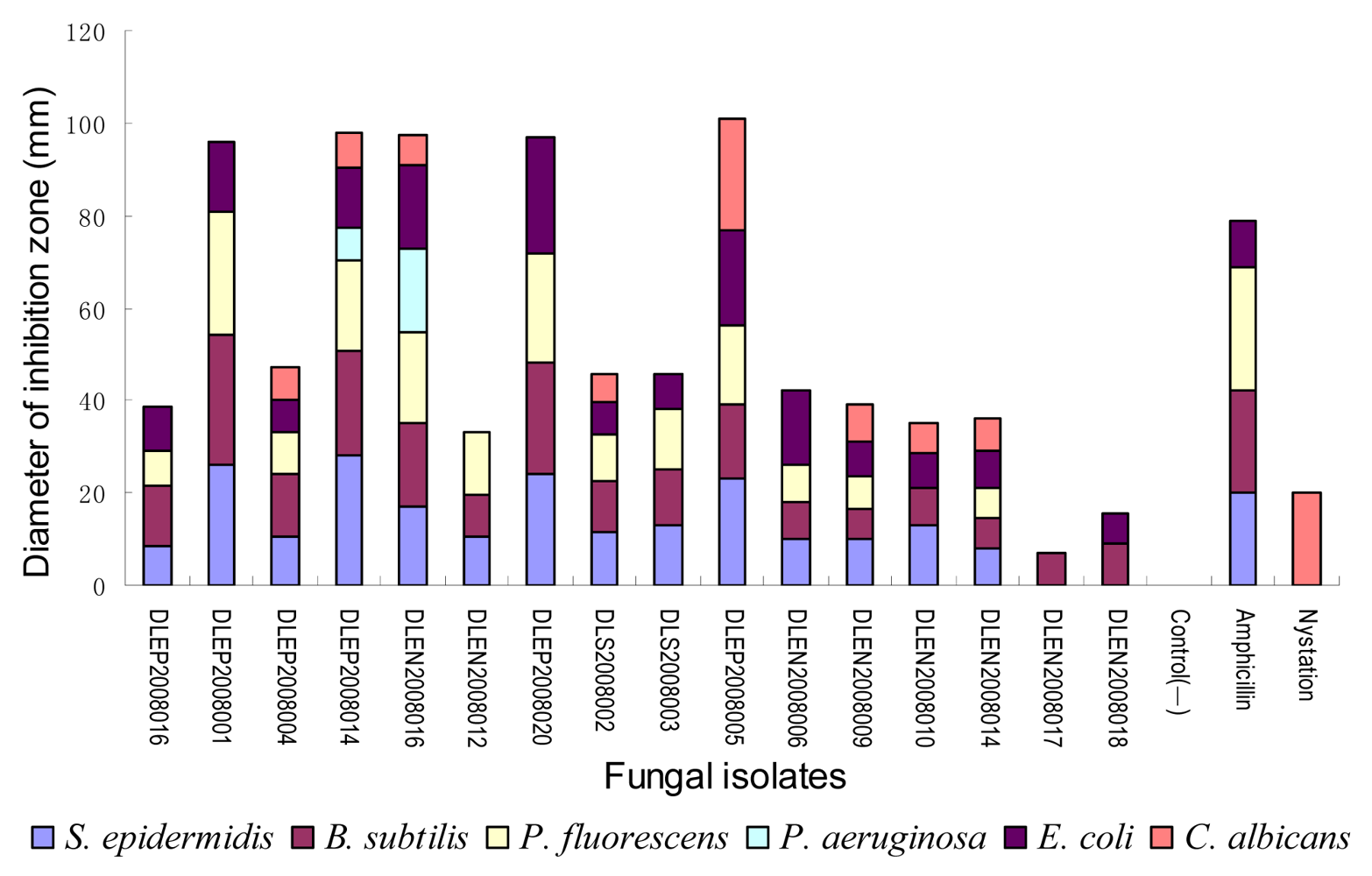
2.2. Preliminary antimicrobial assay
2.3. Secondary antimicrobial assay
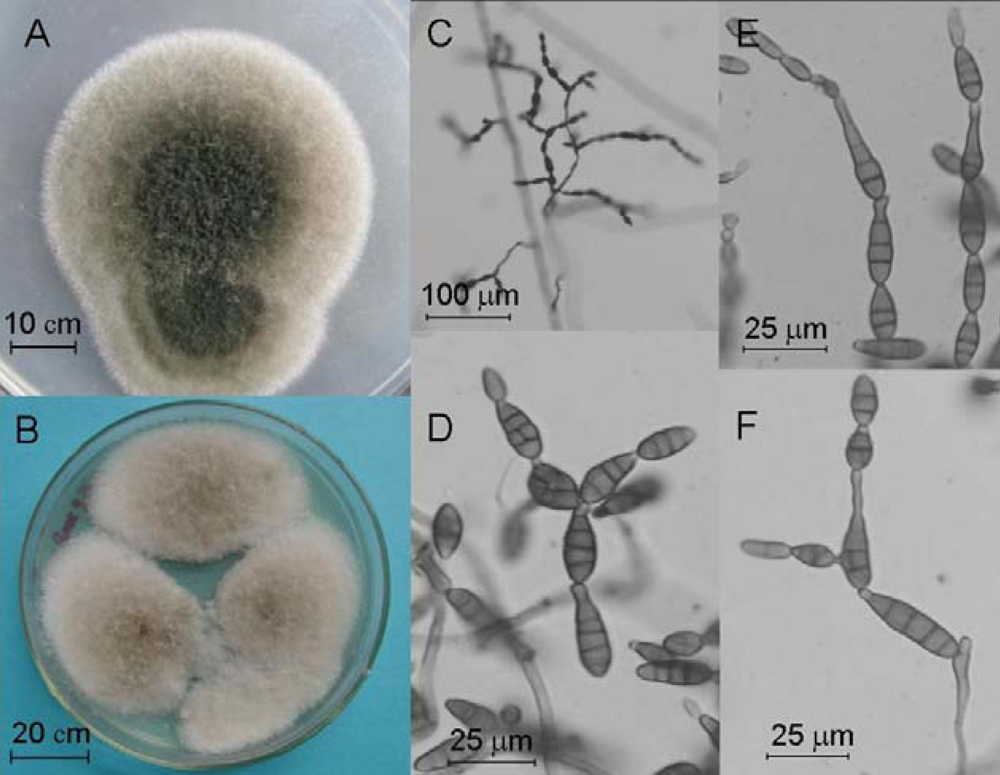
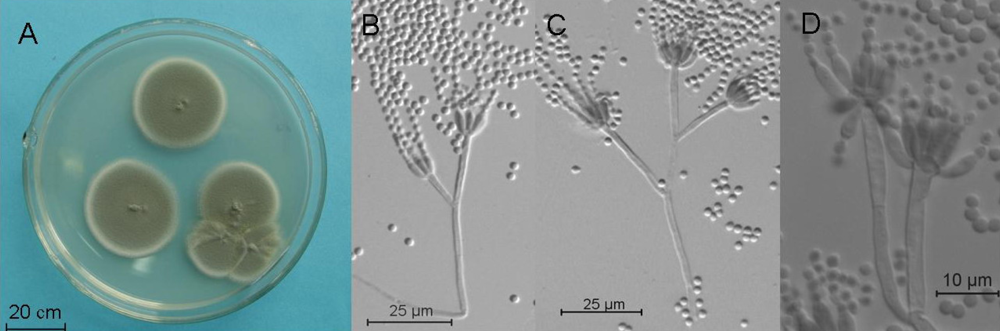
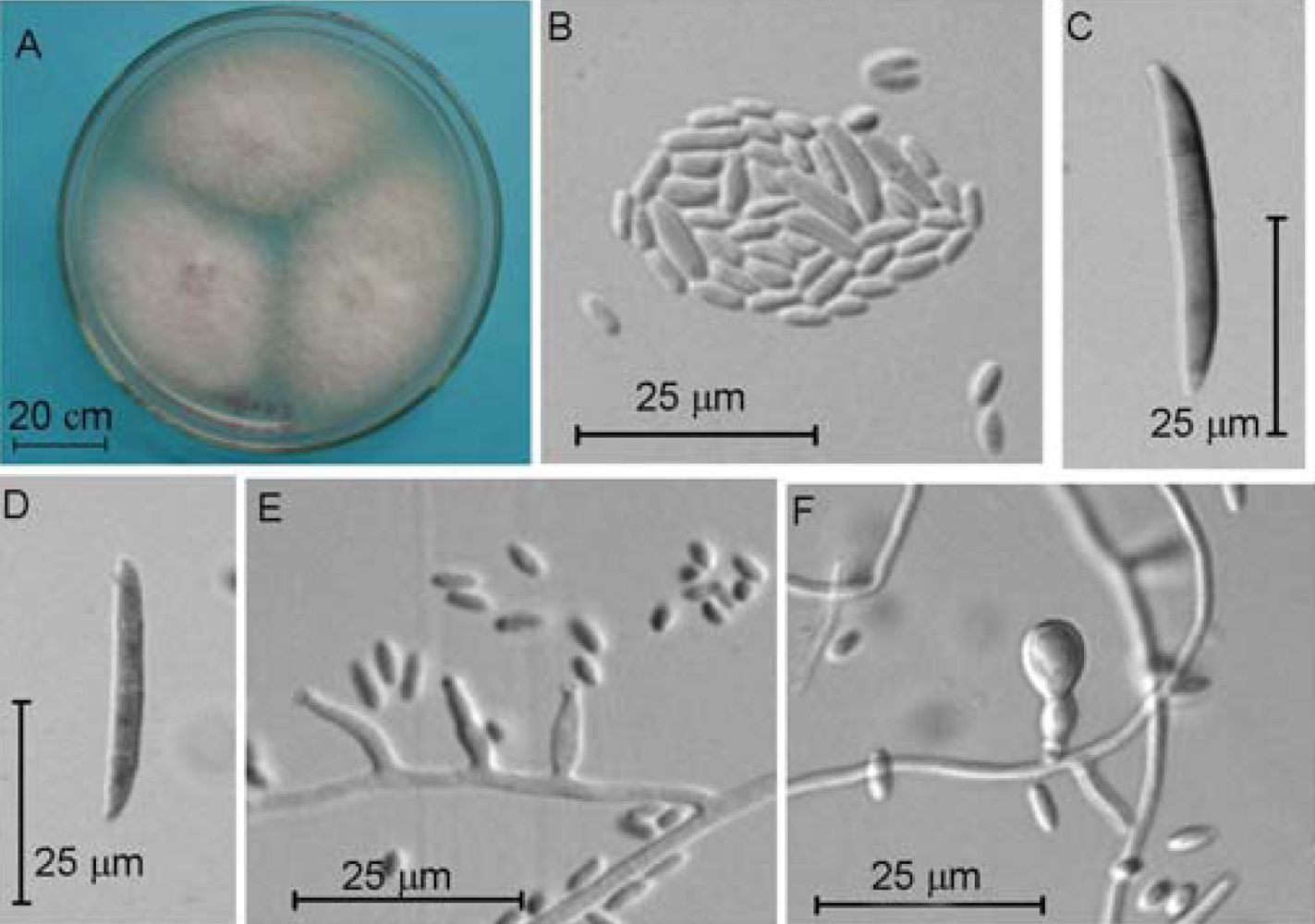
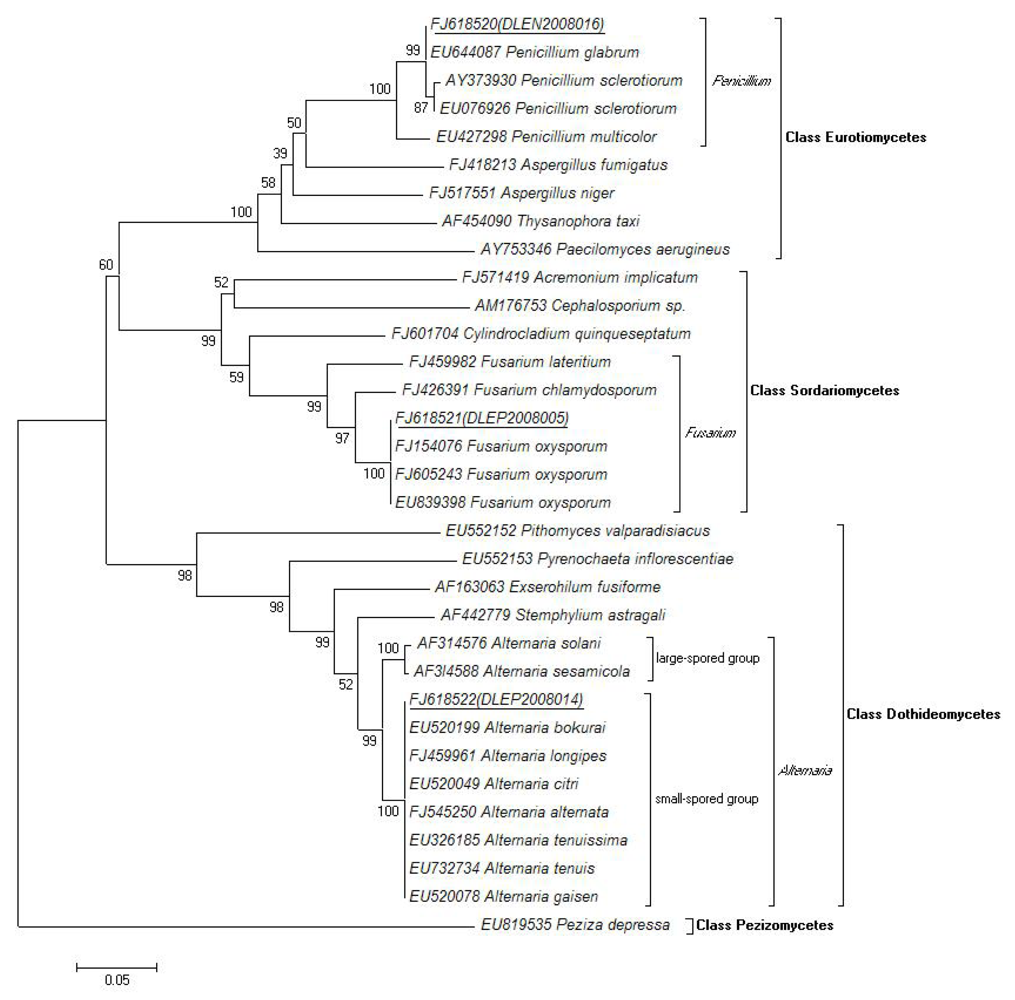
2.4. Molecular and Morphological Taxonomy
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Sample Collection and Strains Isolation
4.2. Preliminary antimicrobial assay
4.3. Secondary antimicrobial assay
4.4. Morphological Taxonomy
4.5. Molecular Taxonomy
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Cassell, GH; Mekalanos, J. Development of antimicrobial agents in the era of new and reemerging infectious diseases and increasing antibiotic resistance. J Am Med Assoc 2001, 285, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszak, P; Cunningham, AA; Hyatt, AD. Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife--threats to biodiversity and human health. Science 2000, 287, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, DJ. Highlights of marine natural products chemistry (1972–1999). Nat Prod Rep 2000, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, P; Edrada, RA; Ebel, R. Drugs from the seas--current status and microbiological implications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2002, 59, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marris, E. Marine natural products: Drugs from the deep. Nature 2006, 443, 904–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugni, TS; Ireland, CM. Marine-derived fungi: a chemically and biologically diverse group of microorganisms. Nat Prod Rep 2004, 21, 143–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadury, P; Mohammad, BT; Wright, PC. The current status of natural products from marine fungi and their potential as anti-infective agents. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 2006, 33, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M; Ali, MS; Hussain, S; Jabbar, A; Ashraf, M; Lee, YS. Marine natural products of fungal origin. Nat Prod Rep 2007, 24, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cueto, M; Jensen, PR; Kauffman, C; Fenical, W; Lobkovsky, E; Clardy, J. Pestalone, a new antibiotic produced by a marine fungus in response to bacterial challenge. J Nat Prod 2001, 64, 1444–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, RX; Zou, WX. Endophytes: a rich source of functional metabolites. Nat Prod Rep 2001, 18, 448–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, R; Fish, DN; Obritsch, MD; Maclaren, R. Surveillance of multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an urban tertiary-care teaching hospital. Pharmacotherapy 2005, 25, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, HA; Marcinak, JF. Candidiasis in the breastfeeding mother and infant. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 1990, 19, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egusa, H; Soysa, NS; Ellepola, AN; Yatani, H; Samaranayake, LP. Oral candidosis in HIV-infected patients. Curr HIV Res 2008, 6, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, K. Hospital infections by specific organisms and their management. 2. Staphylococcus epidermidis. Nippon Naika Gakkai Zasshi 2008, 97, 2673–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCann, MT; Gilmore, BF; Gorman, SP. Staphylococcus epidermidis device-related infections: pathogenesis and clinical management. J Pharm Pharmacol 2008, 60, 1551–1571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pappas, G; Karavasilis, V; Christou, L; Tsianos, EV. Pseudomonas fluorescens infections in clinical practice. Scand J Infect Dis 2006, 38, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, TY. Flora Fungorum Sinicorum: Genus of Alternaria; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2003; Volume 16, pp. 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kusaba, M; Tsuge, T. Nuclear ribosomal DNA variation and pathogenic specialization in Alternaria fungi known to produce host-specific toxins. Appl Environ Microbiol 1994, 60, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, HK; Zhang, TY; Zhang, M. Junwu Xitong (Mycosystema) 2001, 20, 168–173.
- Pitt, JI. The Genus Penicillium and its teleomorphic states Eupenicillium and Talaromyces. Academic Press: London, U.K, 1979; pp. 170–172. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, PE; Toussoun, TA; Marasas, W. Fusarium species – An Illustrated Manual for Identification; The Pennsylvania State University Press: London, U.K, 1983; pp. 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Raviraja, NS; Maria, GL; Sridhar, KR. Antimicrobial Evaluation of Endophytic Fungi Inhabiting Medicinal Plants of the Western Ghats of India. Eng Life Sci 2006, 6, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musetti, R; Polizzotto, R; Vecchione, A; Borselli, S; Zulini, L; D’Ambrosio, M; di Toppi, LS; Pertot, I. Antifungal activity of diketopiperazines extracted from Alternaria alternata against Plasmopara viticola: an ultrastructural study. Micron 2007, 38, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maria, GL; Sridhar, KR; Raviraja, NS. Antimicrobial and enzyme activity of mangrove endophytic fungi of southwest coast of India. J Agri Tech 2005, 1, 67–80. [Google Scholar]
- Broadbent, D. Antibiotics produced by fungi. Bot Rev 1966, 32, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demain, AL. Pharmaceutically active secondary metabolites of microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 1999, 52, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajori, FA; Otani, TT; Hamilton, MA. The isolation and some properties of an antibiotic from Fusarium bostrycoides. J Biol Chem 1954, 208, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burmeister, HR; Bennett, GA; Vesonder, RF; Hesseltine, CW. Antibiotic Produced by Fusarium equiseti NRRL 5537. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 1974, 5, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesonder, RF; Tjarks, LW; Rohwedder, WK; Burmeister, HR; Laugal, JA. Equisetin, an antibiotic from Fusarium equisetiNRRL 5537 identified as a derivative of N-methyl-2,4-pyrollidone. J. Antibiot 1979, 32, 759–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, NN; Ammar, MS. New antibiotic pigments related to fusarubin from Fusarium solani (Mart.) Sacc. II. Structure elucidations. J Antibiot 1979, 32, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurobane, I; Vining, LC; McInnes, AG; Gerber, NN. Metabolites of Fusarium solani related to dihydrofusarubin. J Antibiot 1980, 33, 1376–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golinski, P; Wnuk, S; Che kowski, J; Visconti, A; Schollenberger, M. Antibiotic Y: biosynthesis by Fusarium avenaceum (Corda ex Fries) Sacc., isolation, and some physicochemical and biological properties. Appl Environ Microbiol 1986, 51, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, RA; Tatum, JH; Nemec, SJ. Antimicrobial activity of naphthoquinones from. Fusaria Mycopathologia 1990, 111, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H; Sunaga, R; Furihata, K; Morisaki, N; Iwasaki, S. Isolation and structures of an antifungal antibiotic, fusarielin A, and related compounds produced by a Fusarium sp. J Antibiot 1995, 48, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saepudin, E; Harrison, P. The biosynthesis of antibiotic F-244 in Fusarium sp. ATCC 20788: origin of the carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. Can J Chem 1995, 73, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z; Barret, MO; Boyd, KG; Adams, DR; Boyd, ASF; Burgess, JG. JM47, a cyclic tetrapeptide HC-toxin analogue from a marine Fusarium species. Phytochemistry 2002, 60, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, MK; Jensen, PR; Fenical, W. Neomangicols: structures and absolute stereochemistries of unprecedented halogenated sesterterpenes from a marine fungus of the genus Fusarium. J Org Chem 1998, 63, 8346–8354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Y; Zhao, LL; Hu, CQ; Zhang, HP. Fusarielin E, a new antifungal antibiotic from Fusarium sp. Chin Chem Lett 2007, 18, 954–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S; Li, XM; Teuscher, F; Li, DL; Diesel, A; Ebel, R; Proksch, P; Wang, BG. Chaetopyranin, a benzaldehyde derivative, and other related metabolites from Chaetomium globosum, an endophytic fungus derived from the marine red alga Polysiphonia urceolata. J Nat Prod 2006, 69, 1622–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malibari, AA. Isolation and screening of antibiotics producing streptomycetes from western region soils of Saudi Arabia. J King Abdulaziz Univ: Sci 1991, 3, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleeyinmi, AF. Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of gongronema latifolium. J. Zhejiang univ 2007, 8, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, TJ; Bruns, T; Lee, S; Taylor, J. Innis, MA, Gelfand, DH, Sninsky, JJ, White, TJ, Eds.; PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, U.S.A, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
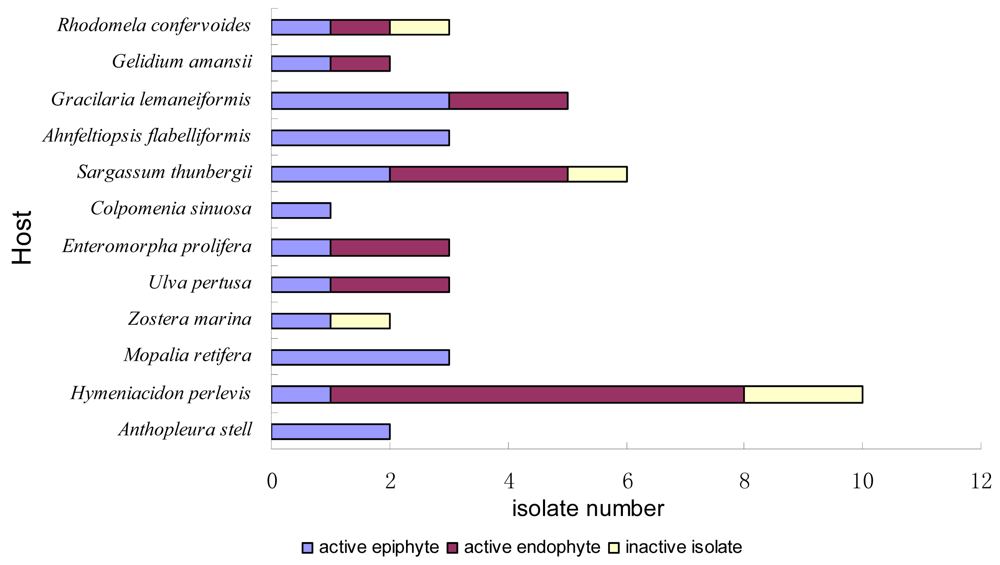
| origin | type | Strain number | origin | type | Strain number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seaweeds | Ulva pertusa | epi- | DLEP2008012 | ||
| Rhodophyta | endo- | DLEN2008015 | |||
| Rhodomela confervoides | epi- | DLS2008004 | endo- | DLEN2008023 | |
| epi- | DLS2008005 | Higher plants | |||
| endo- | DLEN2008024 | Magnoliophyta | |||
| Gelidium amansii | epi- | DLS2008006 | Zostera marina | epi- | DLEP2008008 |
| endo- | DLEN2008021 | epi- | DLEP2008020 | ||
| Gracilaria lemaneiformis | epi- | DLEP2008010 | Invertebrates | ||
| epi- | DLEP2008011 | Mollusca | |||
| epi- | DLEP2008016 | Mopalia retifera | epi- | DLS2008001 | |
| endo- | DLEN2008003 | epi- | DLS2008002 | ||
| endo- | DLEN2008005 | epi- | DLS2008003 | ||
| Ahnfeltiopsis flabelliformis | epi- | DLEP2008001 | Spongia | ||
| epi- | DLEP2008004 | Hymeniacidon perlevis | epi- | DLEP2008005 | |
| epi- | DLEP2008017 | epi- | DLEP2008013 | ||
| Phaeophyta | endo- | DLEN2008006 | |||
| Sargassum thunbergii | epi- | DLEP2008014 | endo- | DLEN2008009 | |
| epi- | DLEP2008015 | endo- | DLEN2008010 | ||
| endo- | DLEN2008002 | endo- | DLEN2008014 | ||
| endo- | DLEN2008004 | endo- | DLEN2008017 | ||
| endo- | DLEN2008011 | endo- | DLEN2008018 | ||
| endo- | DLEN2008016 | endo- | DLEN2008019 | ||
| Colpomenia sinuosa | epi- | DLEP2008018 | endo- | DLEN2008022 | |
| Chlorophyta | Coelenterata | ||||
| Enteromorpha prolifera | epi- | DLEP2008002 | Anthopleura stell | epi- | DLEP2008009 |
| endo- | DLEN2008012 | epi- | DLEP2008019 | ||
| endo- | DLEN2008020 |
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Mu, J.; Feng, Y.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gu, P.-J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.-F.; Zhu, Y.-H. Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Epiphytic and Endophytic Fungi from Marine Organisms: Isolation, Bioassay and Taxonomy. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 97-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7020097
Zhang Y, Mu J, Feng Y, Kang Y, Zhang J, Gu P-J, Wang Y, Ma L-F, Zhu Y-H. Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Epiphytic and Endophytic Fungi from Marine Organisms: Isolation, Bioassay and Taxonomy. Marine Drugs. 2009; 7(2):97-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7020097
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yi, Jun Mu, Yan Feng, Yue Kang, Jia Zhang, Peng-Juan Gu, Yu Wang, Li-Fang Ma, and Yan-Hua Zhu. 2009. "Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Epiphytic and Endophytic Fungi from Marine Organisms: Isolation, Bioassay and Taxonomy" Marine Drugs 7, no. 2: 97-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7020097
APA StyleZhang, Y., Mu, J., Feng, Y., Kang, Y., Zhang, J., Gu, P.-J., Wang, Y., Ma, L.-F., & Zhu, Y.-H. (2009). Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Epiphytic and Endophytic Fungi from Marine Organisms: Isolation, Bioassay and Taxonomy. Marine Drugs, 7(2), 97-112. https://doi.org/10.3390/md7020097