Abstract
Highly selective N-type voltage-gated calcium (CaV) channel inhibitors from cone snail venom (the ω-conotoxins) have emerged as a new class of therapeutics for the treatment of chronic and neuropathic pain. Earlier in 2005, Prialt (Elan) or synthetic ω-conotoxin MVIIA, was the first ω-conotoxin to be approved by Food and Drug Administration for human use. This review compares the action of three ω-conotoxins, GVIA, MVIIA and CVID, describing their structure-activity relationships and potential as leads for the design of improved N-type therapeutics that are more useful in the treatment of chronic pain.
Introduction
There are approximately 500 different species of the genus Conus. Cone snails, found on the Great Barrier Reef in Australia and most other tropical waters around the world, are predatory marine gastropods they prey on fish, worms or molluscs [1]. They capture their prey by injecting lethal or paralysing venom, comprising more than a hundred different polypeptides [1]. These polypeptides known as conopeptides or conotoxins act selectively at a wide variety of ion channels and receptors in their prey, as well as in mammals. Channels targeted include the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR), the voltage-gated sodium (NaV) channel, the voltage-gated potassium (KV) channel, the voltage-gated calcium (CaV) channel, and the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor [2, 3]. Many of these conotoxins have been used to gain further information about their target, either at the pharmacological, physiological or structural level. They are typically 8–30 amino acid residues in length and have been divided into both structural and pharmacological classes. The structural classes are based on the nature of the peptide’s secondary structure, which is generally defined by a characteristic pattern of Cys-residues [2, 3]. Table 1 illustrates the structural and pharmacological diversity within conopeptides. Importantly, several of these pharmacological classes have therapeutic potential in the treatment of pain, including the noradrenaline transporter inhibitor χ-MrIA (Xen2174), the neurotensin receptor agonist (contulakin-G), the AChR antagonist (α-Vc1.1), and the N-type CaV channel blockers. This review describes the structure-activity relationship (SAR) and therapeutic potential of ω-conotoxin N-type CaV channel blockers form cone snails, the first of the conotoxin classes to be approved as a therapeutic.

Table 1.
Conotoxin nomenclature and pharmacology.
ω-Conotoxins
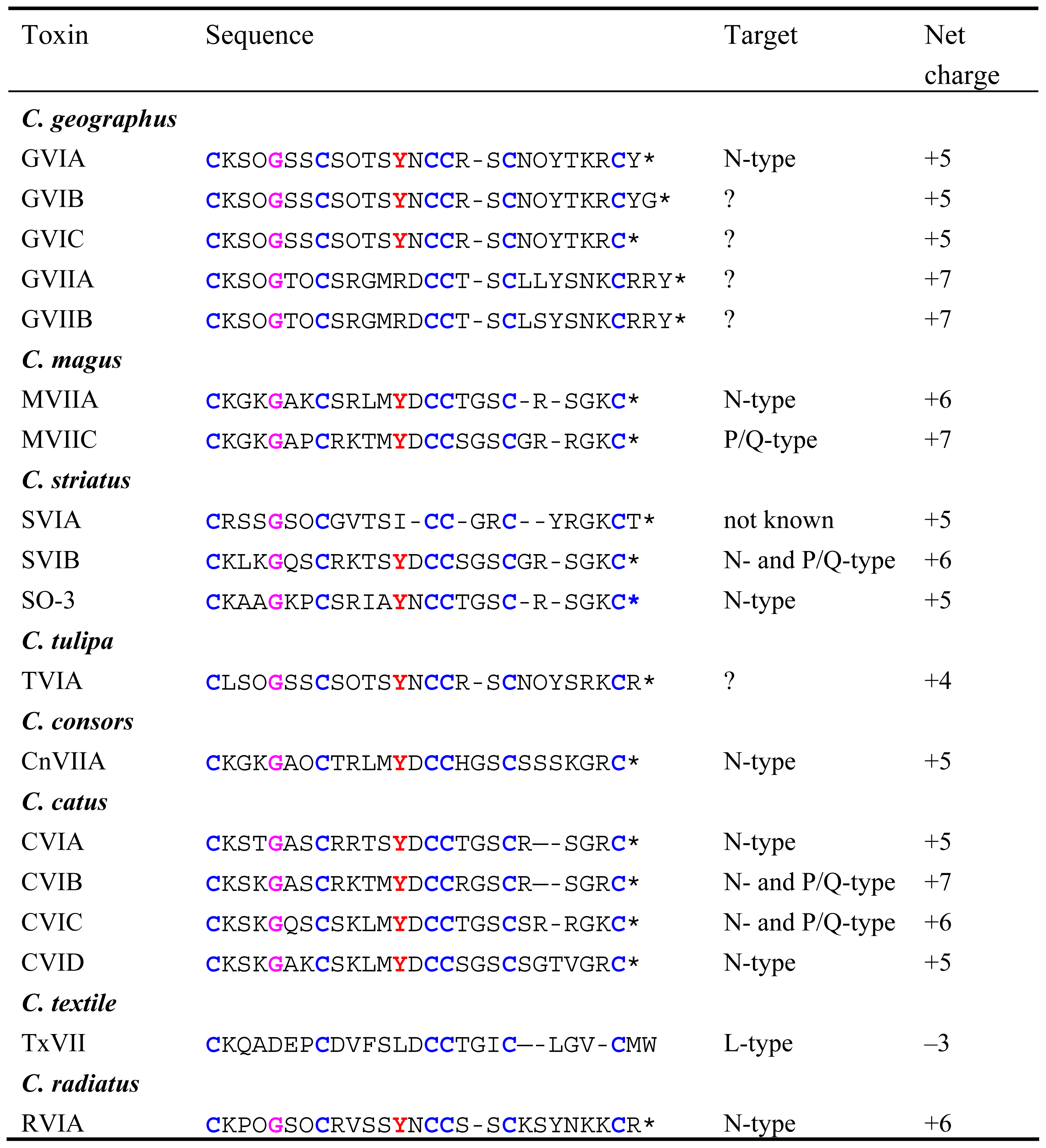
All ω-conotoxins identified to date have been found in piscivorous cone snails ranging from the small Conus catus to the large Conus geographus (Figure 1). The ω-conotoxins are basic peptides of 24–29 residues with an amidated C-terminus [5] and with six Cys-residues arranged to give a fourloop Cys framework (C-C-CC-C-C). ω-Conotoxins target the CaV channel with most of the ω-conotoxins discovered to date being selective for the N-type CaV channel (Table 2) while a few target the P/Q-type CaV channel. In addition, the recently isolated ω-conotoxin TxVII, from Conus textile was found to target the L-type CaV channel [6]. The most studied ω-conotoxins are the selective N-type CaV channel blockers GVIA and MVIIA [7, 8], and the modestly selective P/Q-type CaV channel blocker, MVIIC [9]. In 2000, four novel ω-conotoxins CVIA-D were identified from Conus catus[10]. The most interesting of the four being CVID, which displayed high potency at the N-type CaV channel and low potency at the P/Q-type CaV channel, making it the most selective ω-conotoxin for the N-type CaV channel found to date [10].

Figure 1.
The shells of three piscivorous cone snails. A, Conus catus (2–3 cm); B, C. magus (3–4 cm); and C, C. geographus (~6 cm).

Table 2.
The known native ω-conotoxin sequences from different Conus species. Conserved Cys residues (blue) and the conserved Gly (purple) are indicated. The critical binding residue Tyr13 is highlighted in red.
Sequence hypervariability has been observed between functionally homologous ω-conotoxins, with the six Cys-residues and one Gly being the only residues conserved throughout this set of peptides (Table 2). Comparison of the sequences of two ω-conotoxins, MVIIA and GVIA, reveals that they share less than one-third of the non-Cys residues [11]. The amino acid composition in each of the corresponding four loops is strikingly different, with GVIA containing three hydroxyprolines and
MVIIA containing none. Despite the low sequence identity, they both selectively target the N-subtype of CaV channels and elicit similar biological effects in animals [3]. Conversely, MVIIC has high sequence identity to MVIIA (Table 2), but quite different selectivity.
Because of their high selectivity and affinity for neuronal CaV channels found in mammals, the ω-conotoxins have become standard pharmacological reagents to investigate the role of CaV channels in neurotransmitter release [5, 8, 20–23]. In addition to their use as research tools, animal studies have revealed that ω-conotoxins targeting N-type CaV channels have clinical potential in ischaemic brain injury [24, 25] and pain [26–35].
Voltage-gated calcium channels
CaV channels are included in the same transmembrane gene superfamily as the NaV and KV channels [36]. The influx of calcium ions through CaV channels is involved in a wide range of essential cellular responses including activation of calcium-dependent enzymes, gene transcription, muscle contraction and neurotransmitter release [37]. CaV channels are part of a suite of ion channels the cell uses to couple electrical signalling at the plasma membrane to a physiological response in the cell. Neuronal CaV channels are composed of pore forming α1 subunit that co-assembles with different β and α2δ subunits (Figure 2). While the α1 subunit is largely responsible for determining the electrophysiological characteristics of the channel, these characteristics are modified by associated β and α2δ subunits [38]. To date, six different α1 channel types named L-, T-, R-, P/Q-and N-type have been identified (Table 3).
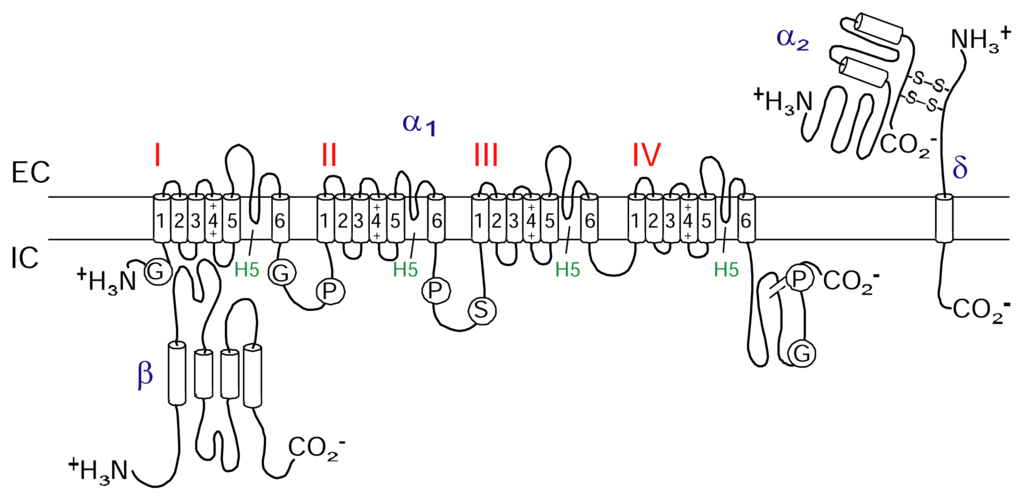
Figure 2.
Schematic figure of a neuronal calcium channel. The cartoon shows four domains with six transmembrane helices in each making up the pore-forming α-subunit. Also shown are the intracellular auxiliary β-subunit and the transmembrane δ-subunit disulfide bonded with the extracellular auxiliary α2-subunit forming the α2/δ-subunit.
CaV Channel as a therapeutic target
Because CaV channels are involved in a multitude of cellular responses, including muscle contraction and neurotransmitter release [39, 40], different CaV channel subtypes have been found to be interesting therapeutical targets. Of the six pharmacologically distinct CaV channel subtypes (Table 2), the N-type, T-type, and P/Q-type calcium channels are the best validated targets for the treatment of pain [41, 42] although dose-limiting side-effects may limit their clinical application. The N-type CaV channel has been found to be concentrated in the spinal dorsal horn region [43–47] and helps convey the nociceptive message from the peripheral nervous system (PNS) into the central nervous system (CNS) [48]. Being able to inhibit the nociceptive message has been shown to lead to the interception of the pain signal in animals and will hopefully result in pain relief when used in a clinical setting [49–52]. The therapeutic potential of MVIIA in pain management has now been identified confirming the role of N-type CaV channel in pain transmission [53–55].
ω-Conotoxins as therapeutics
Pain management is currently one of the most actively researched areas in medicine and there has never been a more critical need for novel therapeutics with a number of Cox-2 inhibitors withdrawn from the market [56]. However, despite advances in a number of areas, opioids still play a key part in often inadequate pain management strategies. Since opioids only target certain types of pain and develop tolerance, novel non-opioid analgesic therapies for more severe chronic pain states are desirable. The ω-conotoxins are of fundamental interest as they represent a group of structurally related peptides with a wide range of CaV channel subtype specificities [57] that are believed to act at or near the outer vestibule of the CaV2.2 ion conducting pore [58]. They are now emerging as a new therapeutic class for intrathecal (IT) pain management [26, 28–31, 33, 35] as well as having the potential to treat ischaemic brain injury [24, 25, 59]. However, all ω-conotoxins evaluated produce dose-limiting side-effects in animal models which may be associated with effects on inhibitory or supraspinal pathways. Peptides are readily targeted by proteases and tend not to display satisfactory bio-availability unless administered directly to the target, hence the need for IT delivery. ω-Conotoxins such as GVIA, MVIIA and CVID, selective towards N-type CaV channels have been shown to possess neuroprotective and analgesic properties [5, 10, 60, 61] and are therefore interesting in drug development, whereas ω-conotoxins selective to the P/Q-subtypes (i.e., MVIIC and SVIB) are not considered useful leads as they are likely to be lethal to mammals and there have been several reports raising concerns about side effects if these peptides are used as drugs in a clinical setting [62]. It is therefore important to define those structural and functional factors that contribute to N-type as opposed to P/Q-type selectivity so that side-effects associated with P/Q-type current inhibition might be avoided. Several groups have provided insight into the domains and specific residues of the ω-conotoxins that are responsible for this selectivity [63–70].
GVIA
GVIA is a selective inhibitor of the N-type CaV channel [5, 71–73] with greater potency in vivo than MVIIA [74] and CVID [32]. Intrathecal administration of morphine, GVIA, MVIIA and CVID is effective in attenuating neuropathic pain in rats [32], with GVIA being about three to four times more potent than MVIIA and CVID and approximately 40-fold more potent than morphine [32]. Due to its slow onset and recovery kinetics [75–78], GVIA is an almost irreversible inhibitor of the N-type CaV channel [79] complicating dose control in a clinical setting.
MVIIC and SVIB
CaV channel blockers, such as MVIIC and SVIB target the P/Q-type CaV channel [9, 15]. Since the P/Q-type current plays an important physiological role including the regulation of transmitter release at neuromuscular junctions [80], the ω-conotoxins are less interesting drug leads for pain management and can be lethal even at low doses [62]. In addition, MVIIC did not provide neuroprotection when tested on a rat model of global ischaemia [81].
MVIIA (Ziconotide or Prialt)
MVIIA is the first ω-conotoxin to enter into clinical trials. Intrathecal MVIIA has recently been approved by the FDA for the management of chronic pain in the USA and Europe [82, 83]. MVIIA is a selective, reversible and potent blocker of the N-type CaV channel [76, 84] which shows analgesic and neuroprotective effects in humans [85]. MVIIA has been found to be effective in preventing neuronal cell death following cerebral ischaemia. A single bolus injection provided protection even when administered 24 h after an ischaemic injury [81, 86, 87]. MVIIA has been reported to inhibit both neuronal excitability and neurotransmission [84, 88]. In animal models, IT administered MVIIA reverses acute [26, 48, 89], persistent [26, 48, 89] and neuropathic pain [26, 90, 91], and in humans IT administration of MVIIA provides relief from chronic pain [83, 92]. However, it has some undesired side effects such as dizziness, blurred vision, nystagmus, sedation [93] and orthostatic hypotension in humans [78, 94, 95]. Adverse side effects such as intractable delirium after being treated with MVIIA were reversed with electroconvulsive therapy [96]. Intrathecal MVIIA causes a variety of neurological side effects of unknown origin [97] despite N-type CaV channels being predominant at synapses carrying nociceptive information to the spinal cord [46]. Importantly, inhibition of N-type CaV channels with MVIIA produces substantial pain relief in otherwise treatment-refractory patients, and unlike opioid pain management, MVIIA does not develop tolerance or produce addiction [32, 85, 98].
CVID (AM336)
Another ω-conotoxin isolated from the fish-hunting C. catus, CVID [10] has also entered clinical trials with AMRAD [99]. CVID is the most selective inhibitor of N-type over P/Q-type CaV channels showing 6-orders of magnitude selectivity in binding studies [10]. Amongst the ω-conotoxins CVID, GVIA and MVIIA, CVID had the largest ratio of ED50 (dose causing 50% effect) to TD50 (dose causing toxicity in 50% of animals) when administered IT in a rat model of neuropathic pain [32]. Due to greater therapeutic margin for CVID seen in animals [34], it is anticipated that AM336 will produce less side effects than MVIIA in the clinic. CVID has undergone a Phase I/IIa assessment for treatment of severe morphine-resistant pain after it was given approval for human trials by the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration [34, 99].
Opioids and ω-conotoxins
Morphine is a spinal analgesic agent [100] that exerts its effect by binding mainly to μ-opioid receptors. Activating the μ-opioid receptor has been shown to inhibit the N-type CaV channel current by interacting with the pore-forming α1 subunit via the G-protein (Figure 3) [101–105]. This inhibition of the N-type CaV channel contributes to morphine analgesia and uncoupling of the opioid receptor and G-protein [106–109] may underlie morphine tolerance development.
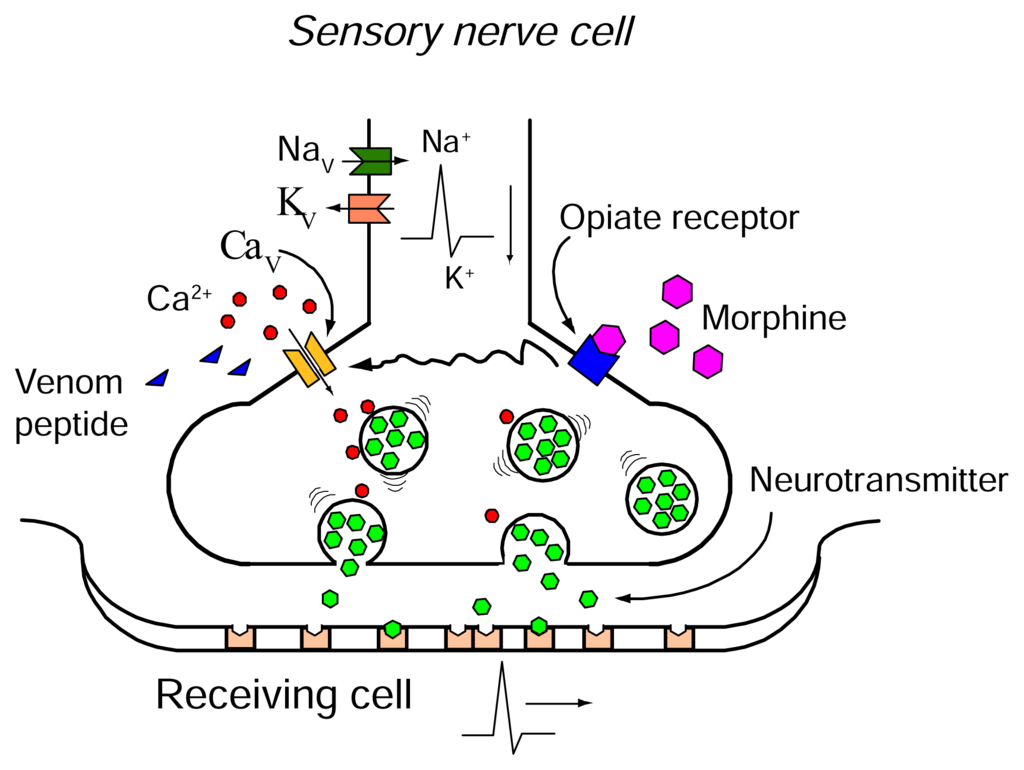
Figure 3.
Schematic figure of the presynaptic nerve terminal. Calcium influx through a N-type CaV channel causes neurotransmitter release and propagation of the pain message. The propagation of the action potential and thereby the influx of calcium can be blocked by venom (e.g., Ziconotide or AM336). Activation of the opioid receptor leads to inhibition of the N-type CaV channel via G-protein coupled receptor by changing channel gating and by altering ion permeation.
N-type CaV channel antagonists show analgesic effect alone [97, 110] and in combination with μ-opioids [111, 112]. Interestingly, several studies have reported synergistic effects between ω-conotoxins (Zicontide or AM336) and morphine when administered IT [32, 98, 112]. However, simultaneous administration of morphine and ω-conotoxin did not prevent the development of morphine tolerance [98]. Importantly, this tolerance development did not result in cross-tolerance to MVIIA [98] and instead there was an upregulation of ω-conotoxin binding sites (N-type CaV channel) in the brain after chronic morphine exposure [113]. Further investigation into the extent of this synergistic effect in the clinic would enable the use of lower doses of N-type antagonists and potentially limit toxic side effects associated with IT administration of ω-conotoxins [32].
Structural studies of ω-conotoxins
To date, all structural information available on the ω-conotoxins has been obtained from 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopic studies. Although the three dimensional (3D) structures of GVIA [114–118], MVIIA [119–121] and MVIIC [57, 122, 123] have been determined several times, there is scope for improvement as developments in NMR technology and structure calculation methods overcome current limitations. Overall, ω-conotoxins have remarkably similar structures, despite considerable variance in primary sequences within the intercysteine loops [57]. It is possible to identify structural similarities amongst the ω-conotoxins to gain a generalised picture of the features that contribute to their potencies in blocking CaV channels. However, the identical disulfide arrangement and a conserved Gly in loop 1 are insufficient to define CaV channel selectivity, but instead provide a structural framework that allows the four hypervariable loops to display key functional groups required for receptor interaction [57]. Therefore, knowledge of the 3D structure of the ω-conotoxins together with an understanding of the critical differences amongst them, are important steps towards understanding the relationship between structure and activity for these peptides.
Structurally the ω-conotoxins are characterised by the common cysteine scaffold that stabilizes the 4-loop framework. This configuration defines the canonical ω-conotoxin fold [57], which comprises a triple-stranded β-sheet/cysteine knot motif [124]. This configuration has been observed in aqueous solution for N-type CaV channel blockers GVIA [114–118], MVIIA [119–121] and CVID [10]. Recent studies have revealed a β-bridge formed by residues 1–2 and 14–16 [10, 65]. It is possible that a salt-bridge between the side chains of Lys2 and Asp14 in MVIIA, MVIIC and CVID stabilises the β-bridge [10, 65]. This may perhaps be replaced by a hydrogen bond between Lys2 and Asn14 in GVIA, although this has not been explicitly defined. The network of β-sheet and β-bridge provides a stable base from which critical side chains are anchored. The intervening regions are composed of β-turns. These structural regions are shown schematically for MVIIA [125] in Figure 4A and B.
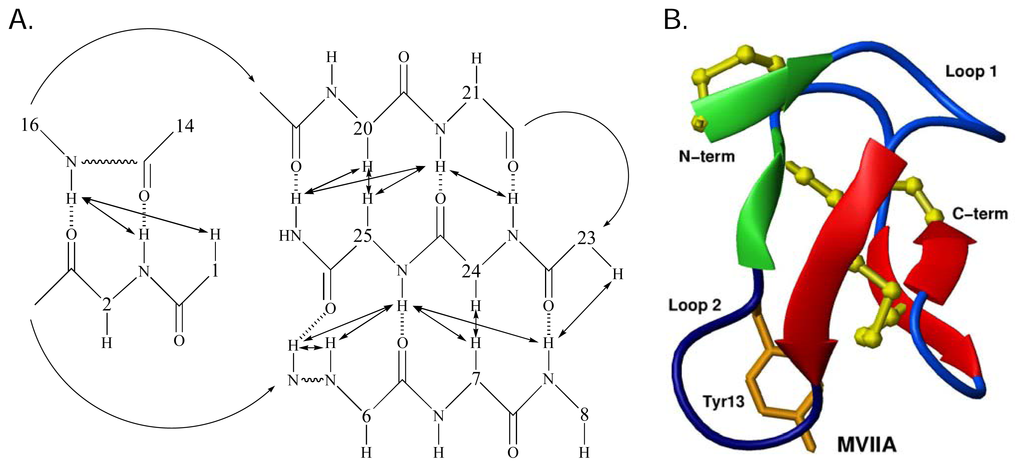
Figure 4.
A. The β-sheet network of MVIIA. Double-headed arrows indicate observed NOEs and dashed lines represent putative H-bonds. B. Three dimensional solution structure of MVIIA. The three disulfide bridges (yellow ball and stick), the β-bridge region (green arrows), β-sheet region (red arrows) and the orientation of Tyr13 (orange) can be seen. Adapted from Nielsen et al. [126].
Structures of ω-conotoxins targeting different types of calcium channels including TxVII (L-type), MVIIC (P/Q-type), and GVIA, MVIIA and CVID (N-type) are compared in Figure 5, highlighting the common fold adopted by these five peptides. There are structural similarities amongst the N-and the P/Q-type ω-conotoxins, despite their selectivity differences, supporting the notion that the ω-conotoxin macrosites on the N-and P/Q-type CaV channels are related. The L-type CaV channel blocker TxVII (Figure 5A) shares the overall canonical fold but has some significant differences, most notably in loop 4. TxVII has the shortest loop 4, containing only three residues compared to MVIIA (Figure 5D) with four residues, to MVIIC (Figure 5B) with five residues, and to CVID (Figure 5E) and GVIA (Figure 5C) both with six residues in loop 4. The most notable structural difference between TxVII, MVIIA and MVIIC compared to GVIA is that the loop is oriented outwards in GVIA and downwards in the other peptides. In CVID, loop 4 is significantly different in that it curves towards loop 2, thus presenting a more globular surface. The presence of a H-bond between Gly22 in loop 4 and Lys10 in loop 2 in CVID is likely to brace loop 4 in this different orientation and is also likely to account for the enhanced stabilisation of loop 2 in CVID [10]. Such a H-bond between loops 2 and 4 has not been reported for ω-conotoxins GVIA, MVIIA, MVIIC or TxVII. The structural uniqueness of CVID may have a significant effect in determining its improved selectivity for the N-type CaV channel over MVIIA and GVIA, since loops 2 and 4 have been shown to act in combination to influence ω-conotoxin selectivity [65].
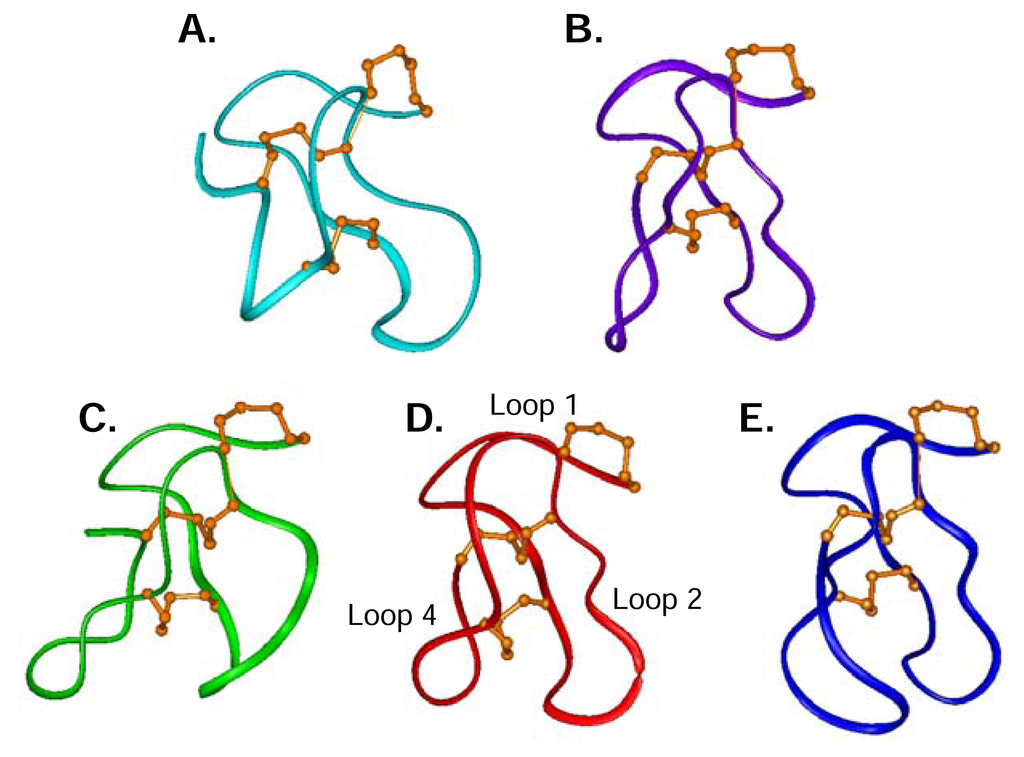
Figure 5.
Representative ribbon structures of five ω-conotoxins. (A) L-type CaV channel blocker TxVII [127]. (B) P/Q-type CaV channel blocker MVIIC [122]. N-type CaV channel blockers GVIA (C)[116], MVIIA (D) (Schroeder et al. unpublished results), and CVID (E)[10]. Disulfide connectivity (orange) and Loop 1, Loop 2 and Loop 4 are indicated. Peptides were superimposed across the backbone atoms C, Cα, and N for residue 1–14.
Prior to the determination of the 3D structure of CVID [10], the conformation of loop 2 of ω-conotoxins was poorly defined. In MVIIA for example, the ensemble of structures contained two backbone conformations for Tyr13, where this residue was found to lie in different regions of the Ramachandran plot. Other residues in this loop had broadened NH resonances suggesting that conformational averaging was indeed occurring. In GVIA, a similar situation was encountered, although it was believed that a single conformation of the Tyr13 sidechain predominated [116]. A similar situation was reported for MVIIC, based on structure calculations, despite the fact that this was not clear from the raw data, and again, linewidths in loop 2 were broadened with respect to the remainder of the peptide [57]. In contrast, examination of the CVID NMR data provided convincing evidence that the Tyr13 sidechain adopted a single conformation, unusual for such a bulky residue, on the Ramachandran plot. In addition, broadening of NH resonances in loop 2 were reduced or not apparent [10].
The role of structure in structure-activity relationships
Many ω-conotoxin SAR studies have neglected the structural component, instead assuming that this is unaffected by residue replacement. This assumption may represent a serious drawback to these studies, as it is not possible to distinguish between structural change and removal of a binding interaction for large ΔpIC50 values. As enthalpic and entropic terms contribute equally to the free energy of binding (i.e., ΔG = ΔH – TΔS), omission of effects of entropy may lead to misinterpretation of binding results. Regrettably, most of the studies on MVIIA have not been accompanied by structural data [64, 84, 128, 129] and many of these analogues may need to be re-examined before any specific sidechain effects can be fully interpreted. The first attempt to introduce structural studies in ω-conotoxin SAR was by Kim et al. [130], where circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy was used to examine the structures of the analogues. A significant improvement on this is the treatment of Lew et al. [131], where NMR spectroscopy has been used to determine the Hα and NH chemical shifts for the series of GVIA analogues. Unfortunately, the structural affects of several Ala-replacements were not further investigated. Due to the accessibility of high-field NMR equipment these days, the structural component of SAR is becoming more and more carefully evaluated. This approach will help improve the accuracy of the analysis of residues important for binding to a target, since residues important for structural stabilisation of a molecule will be omitted from the pharmacophore.
ω-Conotoxin residues important for binding to the N-type CaV channel
To determine which residues were important for the binding and activity of ω-conotoxins to the N-type CaV channel, Ala-replacement studies have been widely used [64, 129–132]. These studies have unequivocally shown Tyr13 to be the single most important residue, with the hydroxyl moiety being the key binding determinant. In addition, several other residues, not always conserved across the ω-conotoxins, also have an effect on potency when replaced by alanine. In MVIIA, these include Lys2, Arg10, Leu11 and Arg21 [64], while in GVIA these residues are Lys2, Arg17, Tyr22 and Lys24 (functional assays only) [133]. Smaller effects are observed for Hyp10, Hyp21 and Arg25 in GVIA [133]. In both peptides, N-acetylation of the N-terminus results in a significant drop in potency [64, 133]. Deamidation of the C-terminus in GVIA and MVIIA also reduces potency [133].
In Figure 6A,B, the structure of GVIA is shown with particular reference to the side chains that are reputedly important for function. For comparison, the structure of MVIIA is shown below (Figure 6C,D), with residues important for binding highlighted. Unfortunately, any structural effects of replacing these residues are not known for MVIIA, and are not fully analysed for GVIA.
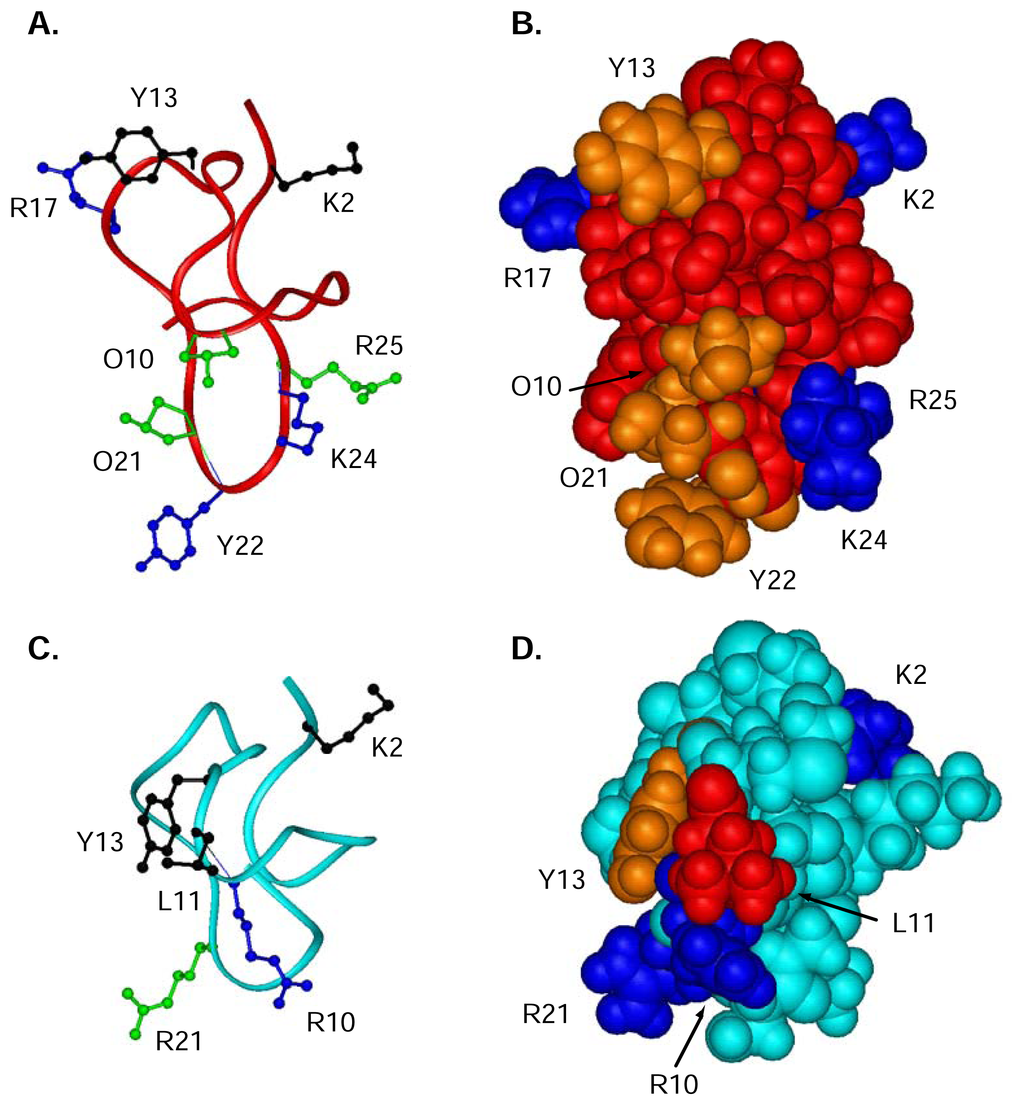
Figure 6.
Ribbon (A, C) and CPK (B, D) representation of 3D solution structures of GVIA (red) [116], and MVIIA (cyan) (Schroeder et al. unpublished results). (A, C) Ribbon of GVIA and MVIIA, respectively, showing residues important for binding in ball and stick. The most important residues are shown in black, secondary important residues are indicated in blue and residues contributing slightly shown in green. (B, D) CPK representation of GVIA and MVIIA, respectively are shown. Charged residues are coloured in dark blue, hydrophobic residues in red and hydroxyl-containing residues are coloured orange.
For CVID, a specific alanine scan has not been conducted, but instead several residues have systematically been replaced with residues of either similar character, such as a Lys to Arg replacement or with a residue believed to cause a clash, such as a Gly to Tyr replacement (Lewis et al., unpublished results). As reported for GVIA and MVIIA, residues located in loop 2, such as Lys10, Leu11 and most importantly Tyr13 of CVID are crucial for binding. The other loops are more resistant to changes in activity following residue replacement.
Analysis of SAR of ω-conotoxin GVIA, MVIIA and CVID at the N-type CaV channel has lead to the development of a couple of ω-conotoxin pharmacophores that can help guide the rational development of N-type CaV channel inhibitors [126, 131]. Initial ω-conotoxin pharmacophores included Lys2 as a major binding determinant. Lys2 is located in loop 1 on the opposite side of the peptide compared to the other important residues located in loop 2. However, recent evidence in our laboratory suggest that Lys2 is not directly involved in binding to the receptor but instead is involved in an important stabilising interaction between Lys2 and residue 14 (see above) (Schroeder et al., unpublished results). A novel minimal pharmacophore was subsequently proposed based on CVID including only residues in loop 2; Lys10, Leu11 and Tyr13 [134]. When designing a pharmacophore it is important to pinpoint which residues that are involved in a direct interaction with the receptor and which are structurally important to facilitate the design and maximise the chance of novel inhibitor being active. These pharmacophores have been utilised in the search for the development of small molecule to block the N-type CaV channel [134, 135]. Whilst these small molecules still only display modest activity, they were found to retain selectivity for the N-type CaV channel over the undesired P/Q-type CaV channel and are consequently promising candidates for further development in the search for novel therapies for the treatment of pain.
There has never been a more critical need for novel therapeutics for pain management with a number of Cox-2 inhibitors withdrawn from the market [56]. While Prialt, the first FDA approved conotoxin, displays some undesired side effects, the next generation ω-conotoxin AM336 with a larger therapeutic window shows that N-type calcium channel inhibitors can be developed with fewer side effects. Furthermore, the behavioural studies and extensive SAR conducted on the ω-conotoxins over the last two decades now places the medicinal chemists in a strong position to design novel small molecules for the treatment of intractable pain.
Abbreviations
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| AChR | nicotinic acetylcholine receptor |
| NaV | voltage-gated sodium channel |
| KV | voltage-gated potassium channel |
| CaV | voltage-gated calcium channel |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| PNS | peripheral nervous system |
| IT | intrathecal |
| ED50 | dose causing 50% effect |
| TD50 | dose causing toxicity in 50% of animals |
| IC50 | dose causing 50% inhibition |
| NMR | nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| 3D | three dimensional |
| SAR | structure-activity relationships |
| CD | circular dichroism |
- Samples Availability: Not available.
References
- Olivera, B. M.; Gray, W. R.; Zeikus, R.; McIntosh, J. M.; Varga, J.; Rivier, J.; de Santos, V.; Cruz, L. J. Peptide neurotoxins from fish-hunting cone snails. Science 1985, 230, 1338–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera, B. M.; Rivier, J.; Clark, C.; Ramilo, C. A.; Corpuz, G. P.; Abogadie, F. C.; Mena, E. E.; Woodward, S. R.; Hillyard, D. R.; Cruz, L. J. Diversity of Conus neuropeptides. Science 1990, 249, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera, B. M.; Rivier, J.; Scott, J. K.; Hillyard, D. R.; Cruz, L. J. Conotoxins. J. Biol. Chem 1991, 266, 22067–22070. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, J. M.; Jones, R. M. Cone venom-from accidental stings to deliberate injection. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1447–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Miljanich, G. P.; Ramachandran, J. Antagonists of neuronal calcium channels: structure, function, and therapeutic implications. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol 1995, 35, 707–734. [Google Scholar]
- Fainzilber, M.; Lodder, J. C.; van der Schors, R. C.; Li, K. W.; Yu, Z.; Burlingame, A. L.; Geraerts, W. P.; Kits, K. S. A novel hydrophobic omega-conotoxin blocks molluscan dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 8748–8752. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, L. J.; Gray, W. R.; Olivera, B. M.; Zeikus, R. D.; Kerr, L.; Yoshikami, D.; Moczydlowski, E. Conus geographus toxins that discriminate between neuronal and muscle sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem 1985, 260, 9280–9288. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, T.; Momiyama, A. Different types of calcium channels mediate central synaptic transmission. Nature 1993, 366, 156–158. [Google Scholar]
- Hillyard, D. R.; Monje, V. D.; Mintz, I. M.; Bean, B. P.; Nadasdi, L.; Ramachandran, J.; Miljanich, G.; Azimi-Zoonooz, A.; McIntosh, J. M.; Cruz, L. J.; Imperial, J. S.; Olivera, B. M. A new Conus peptide ligand for mammalian presynaptic Ca2+ channels. Neuron 1992, 9, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Nielsen, K. J.; Craik, D. J.; Loughnan, M. L.; Adams, D. A.; Sharpe, I. A.; Luchian, T.; Adams, D. J.; Bond, T.; Thomas, L.; Jones, A.; Matheson, J. L.; Drinkwater, R.; Andrews, P. R.; Alewood, P. F. Novel omega-conotoxins from Conus catus discriminate among neuronal calcium channel subtypes. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 35335–35344. [Google Scholar]
- Myers, R. A.; Cruz, L. J.; Rivier, J. E.; Olivera, B. M. Conus Peptides as Chemical Probes for Receptors and Ion Channels. Chem. Rev 1993, 93, 1923–1936. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera, B. M.; McIntosh, J. M.; Cruz, L. J.; Luque, F. A.; Gray, W. R. Purification and sequence of a presynaptic peptide toxin from Conus geographus venom. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 5087–5090. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, T.; Saisu, H. Identification of the receptor for omega-conotoxin in brain. Probable components of the calcium channel. J. Biol. Chem 1987, 262, 9877–9882. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera, B. M.; Cruz, L. J.; de Santos, V.; LeCheminant, G. W.; Griffin, D.; Zeikus, R.; McIntosh, J. M.; Galyean, R.; Varga, J.; Gray, W. R.; Rivier, J. Neuronal calcium channel antagonists. Discrimination between calcium channel subtypes using omega-conotoxin from Conus magus venom. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 2086–2090. [Google Scholar]
- Ramilo, C. A.; Zafaralla, G. C.; Nadasdi, L.; Hammerland, L. G.; Yoshikami, D.; Gray, W. R.; Kristipati, R.; Ramachandran, J.; Miljanich, G.; Olivera, B. M.; Cruz, L. J. Novel alpha- and omega-conotoxins from Conus striatus venom. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 9919–9926. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Yang, S.; Qiao, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, P. SO-3, a new O-superfamily conopeptide derived from Conus striatus, selectively inhibits N-type calcium currents in cultutured hipppcampal neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol 2005, 145, 728–739. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J. A. Novel omega-conopeptides reduced field potential amplitudes in the rat hippocampal slice. Neurosci. Lett 1994, 165, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Favreau, P.; Gilles, N.; Lamthanh, H.; Bournaud, R.; Shimahara, T.; Bouet, F.; Laboute, P.; Letourneux, Y.; Menez, A.; Molgo, J.; Le Gall, F. A new omega-conotoxin that targets N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels with unusual specificity. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 14567–14575. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, J. R.; Litzinger, M. J. Different omega-conotoxins mark the development of Swiss Webster mouse cortex suggesting N-type voltage sensitive calcium channel subtypes. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci 1994, 12, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Currie, K. P.; Fox, A. P. Comparison of N- and P/Q-type voltage-gated calcium channel current inhibition. J. Neurosci 1997, 17, 4570–4579. [Google Scholar]
- McDonough, S. I.; Swartz, K. J.; Mintz, I. M.; Boland, L. M.; Bean, B. P. Inhibition of calcium channels in rat central and peripheral neurons by omega-conotoxin MVIIC. J. Neurosci 1996, 16, 2612–2623. [Google Scholar]
- Seabrook, G. R.; Adams, D. J. Inhibition of neurally-evoked transmitter release by calcium channel antagonists in rat parasympathetic ganglia. Br. J. Pharmacol 1989, 97, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L. G.; Saggau, P. Presynaptic inhibition of elicited neurotransmitter release. Trends. Neurosci 1997, 20, 204–212. [Google Scholar]
- Fern, R.; Ransom, B. R.; Waxman, S. G. Voltage-gated calcium channels in CNS white matter: role in anoxic injury. J. Neurophysiol 1995, 74, 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, K.; Teraoka, T.; Morita, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Nabeshima, T. Omega-conotoxin GVIA protects against ischemia-induced neuronal death. Neuropharmacology 1994, 33, 251–254. [Google Scholar]
- Bowersox, S. S.; Gadbois, T.; Singh, T.; Pettus, M.; Wang, Y. X.; Luther, R. R. Selective N-type neuronal voltage-sensitive calcium channel blocker, SNX-111, produces spinal antinociception in rat models of acute, persistent and neuropathic pain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 1996, 279, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie, K. S. Calcium channel blockers in the treatment of disease. J. Neurosci. Res 2004, 75, 733–741. [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg, A. B.; Yaksh, T. L. Effect of continuous intrathecal infusion of omega-conopeptides, N-type calcium-channel blockers, on behavior and antinociception in the formalin and hot-plate tests in rats. Pain 1995, 60, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Nebe, J.; Vanegas, H.; Schaible, H. G. Spinal application of omega-conotoxin GVIA, an N-type calcium channel antagonist, attenuates enhancement of dorsal spinal neuronal responses caused by intra-articular injection of mustard oil in the rat. Exp. Brain. Res 1998, 120, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Neugebauer, V.; Vanegas, H.; Nebe, J.; Rumenapp, P.; Schaible, H. G. Effects of N- and L-type calcium channel antagonists on the responses of nociceptive spinal cord neurons to mechanical stimulation of the normal and the inflamed knee joint. J. Neurophysiol 1996, 76, 3740–3749. [Google Scholar]
- Omote, K.; Kawamata, M.; Satoh, O.; Iwasaki, H.; Namiki, A. Spinal antinociceptive action of an N-Type voltage-dependent calcium channel blocker and the synergistic interaction with morphine. Anesthesiology 1996, 84, 636–643. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, D.; Wright, C.; Angus, J. Actions of intrathecal omega-conotoxins CVID, GVIA, MVIIA, and morphine in acute and neuropathic pain in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2002, 451, 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Sluka, K. A. Blockade of calcium channels can prevent the onset of secondary hyperalgesia and allodynia induced by intradermal injection of capsaicin in rats. Pain 1997, 71, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M. T.; Cabot, P. J.; Ross, F. B.; Robertson, A. D.; Lewis, R. J. The novel N-type calcium channel blocker, AM336, produces potent dose-dependent antinociception after intrathecal dosing in rats and inhibits substance P release in rat spinal cord slices. Pain 2002, 96, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- White, D. M.; Cousins, M. J. Effect of subcutaneous administration of calcium channel blockers on nerve injury-induced hyperalgesia. Brain Res 1998, 801, 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Catterall, W. A. Structure and function of voltage-gated ion channels. Annu. Rev. Biochem 1995, 64, 493–531. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, D. B.; Randall, A.; Tsien, R. W. Roles of N-type and Q-type Ca2+ channels in supporting hippocampal synaptic transmission. Science 1994, 264, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Arikkath, J.; Cambell, K. P. Auxiliary subunits: essential components of the voltage-gated calcium channel complex. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol 2003, 13, 298–307. [Google Scholar]
- Augustine, G. J.; Charlton, M. P.; Smith, S. J. Calcium action in synaptic transmitter release. Annu. Rev. Neurosci 1987, 10, 633–693. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R. J. Multiple calcium channels and neuronal function. Science 1987, 235, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Altier, C.; Zamponi, G. W. Targeting Ca2+ channels to treat pain: T-type versus N-type. Trends. Pharmacol. Sci 2004, 25, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- McGivern, J. G.; McDonough, S. I. Voltage-gated calcium channels as targets for the treatment of chronic pain. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord 2004, 3, 457–478. [Google Scholar]
- Gohil, K.; Bell, J. R.; Ramachandran, J.; Miljanich, G. P. Neuroanatomical distribution of receptors for a novel voltage-sensitive calcium-channel antagonist, SNX-230 (omega-conopeptide MVIIC). Brain Res 1994, 653, 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, S. B. H. Chemical synthesis of peptides and proteins. Ann. Rev. Biochem 1988, 57, 957–989. [Google Scholar]
- Takemura, M.; Kiyama, H.; Fukui, H.; Tohyama, M.; Wada, H. Autoradiographic visualization in rat brain of receptors for omega-conotoxin GVIA, a newly discovered calcium antagonist. Brain Res 1988, 451, 386–389. [Google Scholar]
- Westenbroek, R. E.; Hell, J. W.; Warner, C.; Dubel, S. J.; Snutch, T. P.; Catterall, W. A. Biochemical properties and subcellular distribution of an N-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunit. Neuron 1992, 9, 1099–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Westenbroek, R. E.; Hoskins, L.; Catterall, W. A. Localization of Ca2+ channel subtypes on rat spinal motor neurons, interneurons, and nerve terminals. J. Neurosci 1998, 18, 6319–6330. [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg, A. B.; Yaksh, T. L. Voltage-sensitive calcium channels in spinal nociceptive processing: blockade of N- and P-type channels inhibits formalin-induced nociception. J. Neurosci 1994, 14, 4882–4890. [Google Scholar]
- Chaplan, S. R.; Pogrel, J. W.; Yaksh, T. L. Role of voltage-dependent calcium channel subtypes in experimental tactile allodynia. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 1994, 269, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, B. N-type Ca2+ channel blockers in pain and stroke. Exp. Opin. Ther. Patents 1998, 8, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, M.; Kowaluk, E. A.; Arneric, S. P. Emerging molecular approaches to pain therapy. J. Med. Chem 1999, 42, 1481–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Winquist, R. J.; Qian Pan, J.; Gribkoff, V. K. Use-dependent blockade of Cav2.2 voltage-gated calcium channels for neuopathic pain. Biochem. J 2005, 70, 489–499. [Google Scholar]
- Bridges, D.; Thompson, S. W. N.; Rice, A. S. C. Mechanisms of neuropathic pain. Br. J. Anaesth 2001, 87, 12–26. [Google Scholar]
- Prado, W. A. Involvement of calcium in pain and nociception. J. Med. Biol. Res 2001, 34, 449–461. [Google Scholar]
- Vanegas, H.; Schaible, H. Effects of antagonists to high-threshold calcium channels upon spinal mechanisms of pain, hyperalgesia and allodynia. Pain 2000, 85, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Stix, G. A toxin against pain. Sci. Am 2005, 292, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, K. J.; Thomas, L.; Lewis, R. J.; Alewood, P. F.; Craik, D. J. A consensus structure for omega-conotoxins with different selectivities for voltage-sensitive calcium channel subtypes: comparison of MVIIA, SVIB and SNX-202. J. Mol. Biol 1996, 263, 297–310. [Google Scholar]
- Ellinor, P. T.; Zhang, J. F.; Horne, W. A.; Tsien, R. W. Structural determinants of the blockade of N-type calcium channels by a peptide neurotoxin. Nature 1994, 372, 272–275. [Google Scholar]
- Small, D. L.; Monette, R.; Buchan, A. M.; Morley, P. Identification of calcium channels involved in neuronal injury in rat hippocampal slices subjected to oxygen and glucose deprivation. Brain Res 1997, 753, 209–218. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, D. J.; Smith, A. B.; Schroeder, C. I.; Yasuda, T.; Lewis, R. J. ω-Conotoxin CVID inhibit a pharmacologically distinct voltage-sensitive calcium channel associated with transmitter release from preganglionic nerve terminals. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R. J.; Garcia, M. G. Therapeutic potential of venom peptides. Nat. Rev. Drug Disc 2003, 2, 790–802. [Google Scholar]
- Bowersox, S. S.; Valentino, K. L.; Luther, R. R. Neuronal voltage-sensitive calcium channels. Drugs News Perspect 1994, 7, 261–268. [Google Scholar]
- Minami, K.; Raymond, C.; Martin-Moutot, N.; Ohtake, A.; Van Renterghem, C.; Takahashi, M; Seagar, M. J.; Mori, Y.; Sato, K. Role of Thr11 in the binding of ω-conotoxin MVIIC to the N-type Ca2+ channels. FEBS Lett. 2001, 491, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Nadasdi, L.; Yamashiro, D.; Chung, D.; Tarczy-Hornoch, K.; Adriaenssens, P.; Ramachandran, J. Structure-activity analysis of a Conus peptide blocker of N-type neuronal calcium channels. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 8076–8081. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, K. J.; Adams, D.; Thomas, L.; Bond, T.; Alewood, P. F.; Craik, D. J.; Lewis, R. J. Structure-activity relationships of omega-conotoxins MVIIA, MVIIC and 14 loop splice hybrids at N and P/Q-type calcium channels. J. Mol. Biol 1999, 289, 1405–1421. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Kohno, T.; Sato, K. Combinatorial synthesis of ω-conotoxin MVIIC analogues and their binding with N- and P/Q-type calcium channels. FEBS Lett 2000, 466, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Park, N.-G.; Kohno, T.; Maeda, T.; Kim, J.-I.; Kato, R.; Takahashi, M. Role of basic residues for the binding of ω-conotoxin GVIA to N-type calcium channels. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1993, 194, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Raymond, C.; Martin-Moutot, N.; Sasaki, T.; Omori, A.; Ohtake, A.; Kim, J. I.; Kohno, T.; Takahashi, M.; Seagar, M. Binding of chimeric analogs of omega-conotoxin MVIIA and MVIIC to the N- and P/Q-type calcium channels. FEBS Lett 1997, 414, 480–484. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Raymond, C.; Martin-Moutot, N.; Sasaki, T.; Ohtake, A.; Minami, K.; van Renterghem, C.; Kim, J. I.; Takahashi, M.; Seagar, M. J. Binding of Ala-scanning analogs of ω-conotoxin MVIIC to N- and P/Q-type calcium channels. FEBS Lett 2000, 469, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, K.; Raymond, C.; Martin-Moutot, N.; Sasaki, T.; Ohtake, A.; Minami, K.; van Renterghem, C.; Takahasi, M.; Seager, M. J. Binding of six chimeric analogs of ω-conotoxin MVIIA and MVIIC to N- and P/Q-type calcium channels. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2000, 269, 254–256. [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap, K.; Luebke, J. I.; Turner, T. J. Exocytotic Ca2+ channels in mammalian central neurons. Trends Neurosci 1995, 18, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera, B. M.; Miljanich, G. P.; Ramachandran, J.; Adams, M. E. Calcium Channel Diversity and Neurotransmitter Release: The ω–Conotoxins and the ω-Agatoxins. Ann. Rev. Biochem 1994, 63, 823–867. [Google Scholar]
- Tsien, R. W.; Lipscombe, D.; Madison, D. V.; Bley, K. R.; Fox, A. P. Multiple types of neuronal calcium channels and their selective modulation. Trends Neurosci 1988, 11, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Vega, T.; De Pascual, R.; Bulbena, O.; Garcia, A. G. Effects of omega-toxins on noradrenergic neurotransmission in beating guinea pig atria. Eur. J. Pharmacol 1995, 276, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, H.; Albillos, A.; Fernandez, F.; Medrano, J.; Jurkiewicz, A.; Garcia, A. G. Omega- Conotoxins block neurotransmission in the rat vas deferens by binding to different presynaptic sites on the N-type Ca2+ channel. Eur. J. Pharmacol 1997, 321, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kristipati, R.; Nadasdi, L.; Tarczy-Hornoch, K.; Lau, K.; Miljanich, G. P.; Ramachandran, J.; Bell, J. R. Characterization of the binding of omega-conopeptides to different classes of non-L-type neuronal calcium channels. Mol. Cell. Neurosci 1994, 5, 219–228. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Haus, S.; Edgerton, J.; Lipscombe, D. Identification of functionally distinct isoforms of the N-type Ca2+ channel in rat sympathetic ganglia and brain. Neuron 1997, 18, 153–166. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, C. E.; Robertson, A. D.; Whorlow, S. L.; Angus, J. A. Cardiovascular and autonomic effects of omega-conotoxins MVIIA and CVID in conscious rabbits and isolated tissue assays. Br. J. Pharmacol 2000, 131, 1325–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Pin, J. P.; Bockaert, J. Omega-conotoxin GVIA and dihydropyridines discriminate two types of Ca2+ channels involved in GABA release from striatal neurons in culture. Eur. J. Pharmacol 1990, 188, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Llinas, R.; Sugimori, M.; Hillman, D. E.; Cherksey, B. Distribution and functional significance of the P-type, voltage- dependent Ca2+ channels in the mammalian central nervous system. Trends Neurosci 1992, 15, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Valentino, K.; Newcomb, R.; Gadbois, T.; Singh, T.; Bowersox, S.; Bitner, S.; Justice, A.; Yamashiro, D.; Hoffman, B. B.; Ciaranello, R.; Miljanich, G.; Ramachandran, J. A selctive N-type calcium channel antagonist protects against neuronal loss after global cerebral ischemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7894–7897. [Google Scholar]
- Miljanich, G. P.; Approved!!!, Prialt. Ziconotide intrathecal infusion), a conopeptide for treating severe chronic pain. In Venoms to Drugs 2005; 2005; Heron Island, Australia. [Google Scholar]
- Wermeling, D. P. Ziconotide, an intrathecally administered N-type calcium channle antagonsit for the treatment of chronic pain. Pharmacotherapy 2005, 25, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. X.; Bezprozvannaya, S.; Bowersox, S. S.; Nadasdi, L.; Miljanich, G.; Mezo, G.; Silva, D.; Tarczy-Hornoch, K.; Luther, R. R. Peripheral versus central potencies of N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channel blockers. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol 1998, 357, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, K. K. An evaluation of intrathecal ziconotide for the treatment of chronic pain. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2000, 9, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M. L.; Siesjo, B. K. Postischemic treatment of omega-conopeptide SNX-111 protects the rat brain against ischemic damage. In Pharmacology of Cerebral Ischemia; Krieglstein, J., Ed.; 1992; pp. 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Smith, M. L.; Siesjo, B. K. The omega-conopeptide SNX-111, an N-type calcium-channel blocker, dramatically ameliorates brain damage due to transient focal ischemia. Acta. Physiol. Scand 1994, 150, 459–461. [Google Scholar]
- Gaur, S.; Newcomb, R.; Rivnay, B.; Bell, J. R.; Yamashiro, D.; Ramachandran, J.; Miljanich, G. P. Calcium channel antagonist peptides define several components of transmitter release in the hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 1994, 33, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar]
- MacPherson, R. D. The pharmacologcial basis of contemporary pain management. Pharmacol. Ther 2000, 88, 163–185. [Google Scholar]
- Chaplan, S. R.; Bach, F. W.; Pogrel, J. W.; Chung, J. M.; Yaksh, T. L. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J. Neurosci. Methods 1994, 53, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T.; Sakashita, Y. Differential effects of intrathecally administered N- and P-type voltage-sensitive calcium channel blockers upon two models of experimental mononeuropathy in the rat. Brain Res 1998, 794, 329–232. [Google Scholar]
- Miljanich, G. P. Ziconotide: neuronal calcium channel blocker for the treating severe chronic pain. Curr. Med. Chem 2004, 11, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Atanassoff, P. G.; Hartmannsgruber, M. W. B.; Thrasher, J.; Wermeling, D.; Longton, W.; Gaete, R.; Singh, R.; Mayo, M.; McGuire, D.; Luther, R. R. Ziconotide, a new N-type calcium channel blocker, administrered intracthecally for acute postoperative pain. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med 2000, 25, 274–8. [Google Scholar]
- McGuire, D.; Bowersox, S.; Fellmann, J. D.; Luther, R. R. Sympatholysis after neuron-specific, N-type, voltage-sensitive calcium channel blockade: first demonstration of N-channel function in humans. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol 1997, 30, 400–403. [Google Scholar]
- Penn, R. D.; Paice, J. A. Adverse effects associated with the intrathecal administration of ziconotide. Pain 2000, 85, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, T.; Petrides, G.; Weiner, J.; Saravay, S. Intractable delerium associated with ziconotide succesfully treated with electoconvulsive therapy. Psychosomatics 2002, 43, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- Brose, W. G.; Gutlove, D. P.; Luther, R. R.; Bowersox, S. S.; McGuire, D. Use of intrathecal SNX-111, a novel, N-type, voltage-sensitive, calcium channel blocker, in the management of intractable brachial plexus avulsion pain. Clin. J. Pain 1997, 13, 256–259. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Gao, D.; Pettus, M.; Phillips, C.; Bowersox, S. S. Interactions of intrathecally administrated ziconotide, a selective blocker of neuronal N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels, with morphine on nociception in rats. Pain 2000, 84. [Google Scholar]
- Cousins, M. J.; Cjoucke, R. C.; Cher, C. M.; Brooker, C. D.; Amor, P. E.; Crump, D. E. A phase I clinical trial of AM336, a novel N-type calcium channel blocker. 10th World Congress of Pain, IASP Press.
- Abram, S. E.; Yaksh, T. L. Morphine, but not inhalation anesthesia, blocks post-injury facilitation. The role of preemptive suppression of afferent transmission. Anesthesiology 1993, 78, 713–721. [Google Scholar]
- Bourinet, E.; Soong, T. W.; Stea, A.; Snutch, T. P. Determinants of the G-protein dependent opioid modulation of neuronal calcium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 1996, 93, 1486–1491. [Google Scholar]
- De Waard, M.; Liu, H.; Walker, D.; Scott, V. E.; Gurnett, C. A.; Campbell, K. P. Direct binding of G-protein betagamma complex to voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature 1997, 385, 446–450. [Google Scholar]
- Seward, E.; Hammond, C.; Henderson, G. Mu-opioid-receptor-mediated inhibition of the N-type calcium-channel current. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci 1991, 244, 129–135. [Google Scholar]
- Toth, P. T.; Shekter, L. R.; Ma, G. H.; Philipson, L. H.; Miller, R. J. Selective G-protein regulation of neuronal calcium channels. J. Neurosci 1996, 16, 4617–4624. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J. F.; Ellinor, P. T.; Aldrich, R. W.; Tsien, R. W. Multiple structural elements in voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels support their inhibition by G proteins. Neuron 1996, 17, 991–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Basbaum, A. I. Insights into the development of opioid tolerance. Pain 1995, 61, 349–352. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, C.; Henderson, G. Mu-opioid receptor inhibition of calcium current: development of homologous tolerance in single SH-SY5Y cells after chronic exposure to morphine in vitro. Mol. Pharmacol 1991, 40, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, C.; Henderson, G. Chronic exposure to morphine does not induce dependence at the level of the calcium channel current in human SH-SY5Y cells. Neuroscience 1992, 49, 937–944. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, P. L.; Lee, C. R.; Law, P. Y.; Loh, H. H. The interaction of the mu-opioid receptor and G protein is altered after chronic morphine treatment in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol 1993, 348, 504–508. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, H. W.; Song, D. K.; Choi, S. R.; Huh, S. O.; Kim, Y. H. Effects of intrathecal injection of nimodipine, omega-conotoxin GVIA, calmidazolium, and KN-62 on the antinociception induced by cold water swimming stress in the mouse. Brain Res 1997, 767, 144–147. [Google Scholar]
- Basilico, L.; Parolaro, D.; Rubino, T.; Gori, E.; Giagnoni, G. Influence of omega-conotoxin on morphine analgesia and withdrawal syndrome in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol 1992, 218, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Pirec, V.; Laurito, C. E.; Lu, Y.; Yeomans, D. C. The combined effects of N-type calcium channel blockers and morphine on A delta versus C fiber mediated nociception. Anesth. Analg 2001, 92, 239–243. [Google Scholar]
- Suematsu, M.; Ohnishi, T.; Shinno, E.; Maeda, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Sakuda, M.; Saito, K. Effect of prolonged administration of clonidine on [3H]PN 200-110 and [125I]omega-conotoxin binding in mouse brain. Neurosci. Lett 1993, 163, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J. H.; Bradley, E. K.; Miljanich, G. P.; Nadasdi, L.; Ramachandran, J.; Basus, V. J. Solution structure of omega-conotoxin GVIA using 2-D NMR spectroscopy and relaxation matrix analysis. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 7396–7405. [Google Scholar]
- Pallaghy, P. K.; Duggan, B. M.; Pennington, M. W.; Norton, R. S. Three-dimensional structure in solution of the calcium channel blocker omega-conotoxin. J. Mol. Biol 1993, 234, 405–420. [Google Scholar]
- Pallaghy, P. K.; Norton, R. S. Refined solution structure of omega-conotoxin GVIA: implications for calcium channel binding. J. Pept. Res 1999, 53, 343–351. [Google Scholar]
- Sevilla, P.; Bruix, M.; Santoro, J.; Gago, F.; Garcia, A. G.; Rico, M. Three-dimensional structure of omega-conotoxin GVIA determined by 1H NMR. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1993, 192, 1238–1244. [Google Scholar]
- Skalicky, J. J.; Metzler, W. J.; Ciesla, D. J.; Galdes, A.; Pardi, A. Solution structure of the calcium channel antagonist omega-conotoxin GVIA. Protein Sci 1993, 2, 1591–1603. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, R. A.; Kieffer, B.; Dejaegere, A.; Sirockin, F.; Lefevre, J. F. Structural and dynamic characterization of omega-conotoxin MVIIA: the binding loop exhibits slow conformational exchange. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 3908–3919. [Google Scholar]
- Basus, V. J.; Nadasdi, L.; Ramachandran, J.; Miljanich, G. P. Solution structure of omega-conotoxin MVIIA using 2D NMR spectroscopy. FEBS Lett 1995, 370, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Kohno, T.; Kim, J. I.; Kobayashi, K.; Kodera, Y.; Maeda, T.; Sato, K. Three-dimensional structure in solution of the calcium channel blocker omega-conotoxin MVIIA. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 10256–10265. [Google Scholar]
- Farr-Jones, S.; Miljanich, G. P.; Nadasdi, L.; Ramachandran, J.; Basus, V. J. Solution structure of omega-conotoxin MVIIC, a high affinity ligand of P-type calcium channels, using 1H NMR spectroscopy and complete relaxation matrix analysis. J. Mol. Biol 1995, 248, 106–124. [Google Scholar]
- Nemoto, N.; Kubo, S.; Yoshida, T.; Chino, N.; Kimura, T.; Sakakibara, S.; Kyogoku, Y.; Kobayashi, Y. Solution structure of omega-conotoxin MVIIC determined by NMR. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1995, 207, 695–700. [Google Scholar]
- Pallaghy, P. K.; Nielsen, K. J.; Craik, D. J.; Norton, R. S. A common structural motif incorporating a cystine knot and a triple- stranded beta-sheet in toxic and inhibitory polypeptides. Prot. Sci 1994, 3, 1833–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, K. J.; Adams, D. A.; Alewood, P. F.; Lewis, R. J.; Thomas, L.; Schroeder, T.; Craik, D. J. Effects of chirality at Tyr13 on the structure-activity relationships of omega-conotoxins from Conus magus. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 6741–6751. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, K. J.; Schroeder, T.; Lewis, R. J. Structure-activity relationship of ω-conotoxins at the N-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels. J. Mol. Recogn 2000, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, K.; Sasaki, T.; Sato, K.; Kohno, T. Three-dimensional solution structure of omega-conotoxin TxVII, an L- type calcium channel blocker. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 14761–14767. [Google Scholar]
- Author Methods for producing analgesia. International Patent Classification, A61K 038/00, C07K 005/00, C07K 007/00 United States Patent 5, 859, 186, 1999.
- Author Compositions for delayed treatement of ischemia-related neuronal damage. International patent application no PCT/US96 09766; Classification, C07K 7/10, A61K 37/02, 1993.
- Kim, J. I.; Takahashi, M.; Ogura, A.; Kohno, T.; Kudo, Y.; Sato, K. Hydroxyl group of Tyr13 is essential for the activity of omega- conotoxin GVIA, a peptide toxin for N-type calcium channel. J. Biol. Chem 1994, 269, 23876–23978. [Google Scholar]
- Lew, M. J.; Flinn, J. P.; Pallaghy, P. K.; Murphy, R.; Whorlow, S. L.; Wright, C. E.; Norton, R. S.; Angus, J. A. Structure-function relationships of omega-conotoxin GVIA. Synthesis, structure, calcium channel binding, and functional assay of alanine- substituted analogues. J. Biol. Chem 1997, 272, 12014–12023. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J. I.; Takahashi, M.; Martin-Moutot, N.; Seagar, M. J.; Ohtake, A.; Sato, K. Tyr13 is essential for the binding of omega-conotoxin MVIIC to the P/Q- type calcium channel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1995, 214, 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Flinn, J. P.; Pallaghy, P. K.; Lew, M. J.; Murphy, R.; Angus, J. A.; Norton, R. S. Roles of key functional groups in omega-conotoxin GVIA synthesis, structure and functional assay of selected peptide analogues. Eur. J. Biochem 1999, 262, 447–455. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, C. I.; Smythe, M. L.; Lewis, R. J. Development of small molecules that mimic the binding of ω-conotoxin at the N-type voltage-gated calcium channel. Molec. Diversity 2004, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Baell, J. B.; Duggan, P. J.; Forsyth, S. A.; Lewis, R. J.; Lok, Y. P.; Schroeder, C. I. Synthesis and biological evaluation of non-peptidic mimetics of ω-conotoxin GVIA. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2004, 12, 4025–4037. [Google Scholar]