Rosmarinic Acid Protects Against Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Suppressing Ferroptosis and Oxidative Stress Through Nrf2/HO-1 Activation in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
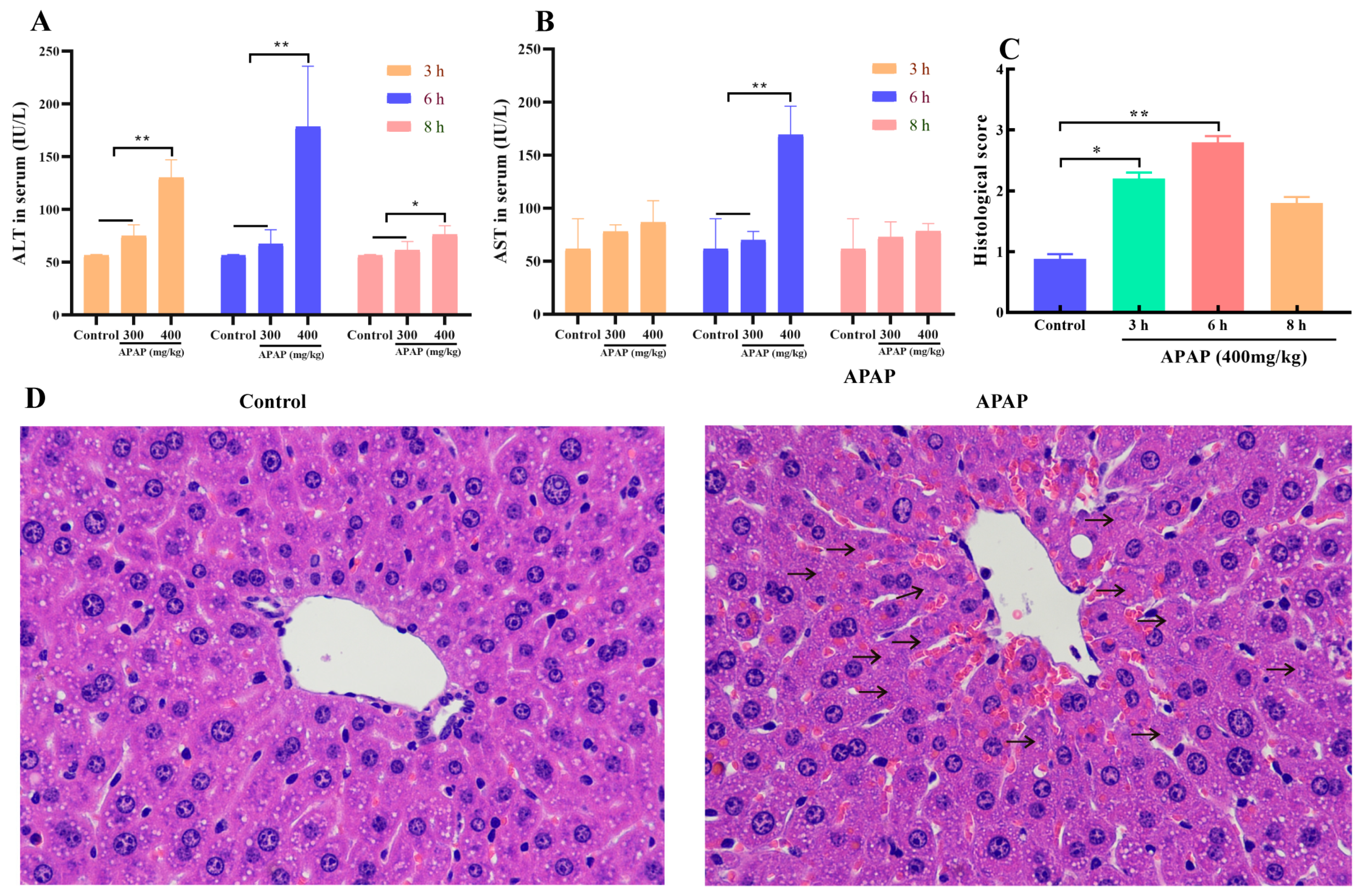
2.1. APAP Caused Liver Injury
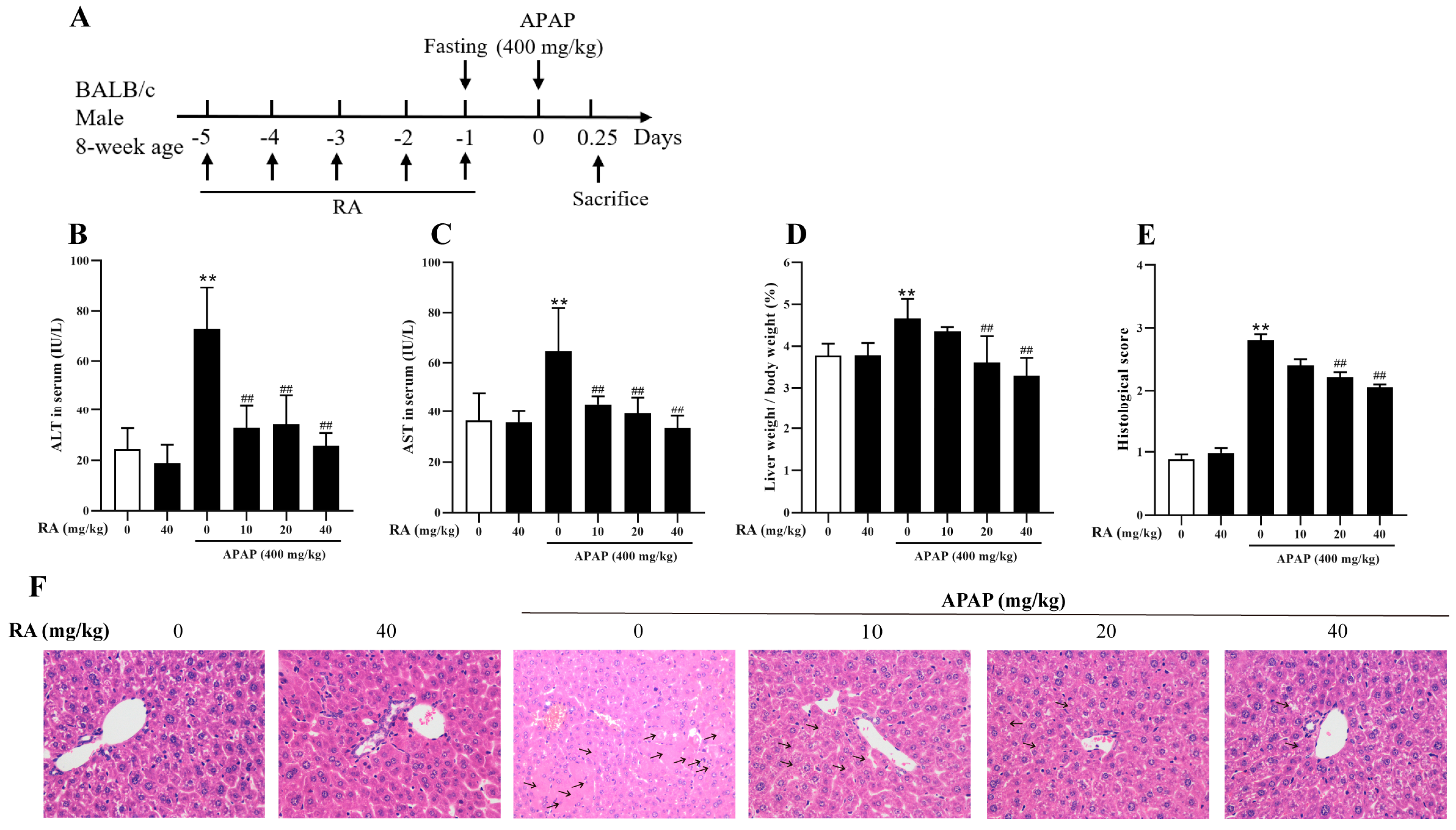
2.2. RA Mitigated APAP-Induced Hepatic Injury
2.3. RA Regulated the APAP-Induced Inflammatory Response
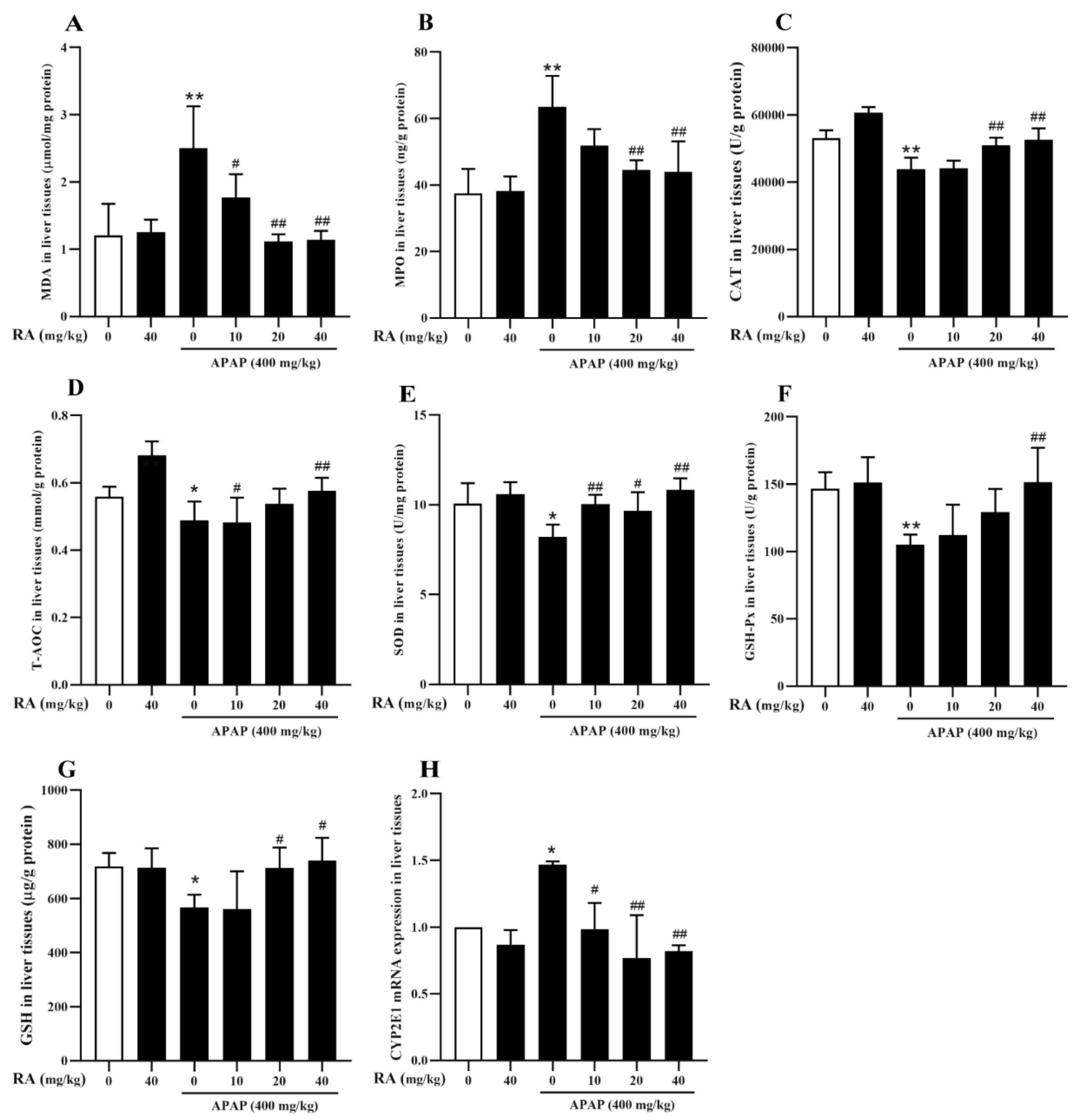
2.4. RA Alleviated APAP-Triggered Oxidative Damage
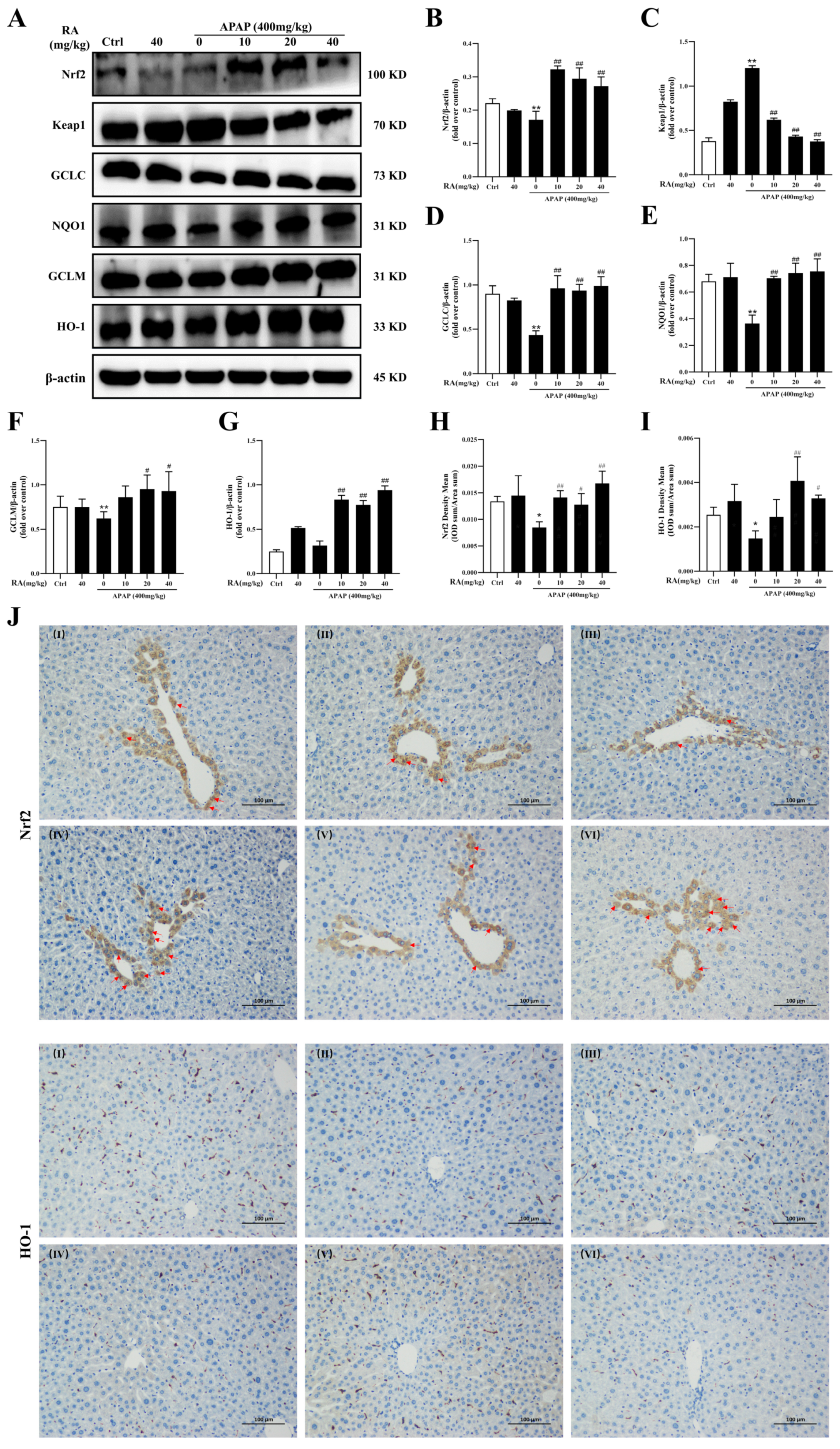
2.5. RA Ameliorates APAP-Mediated Oxidative Damage by Regulating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway
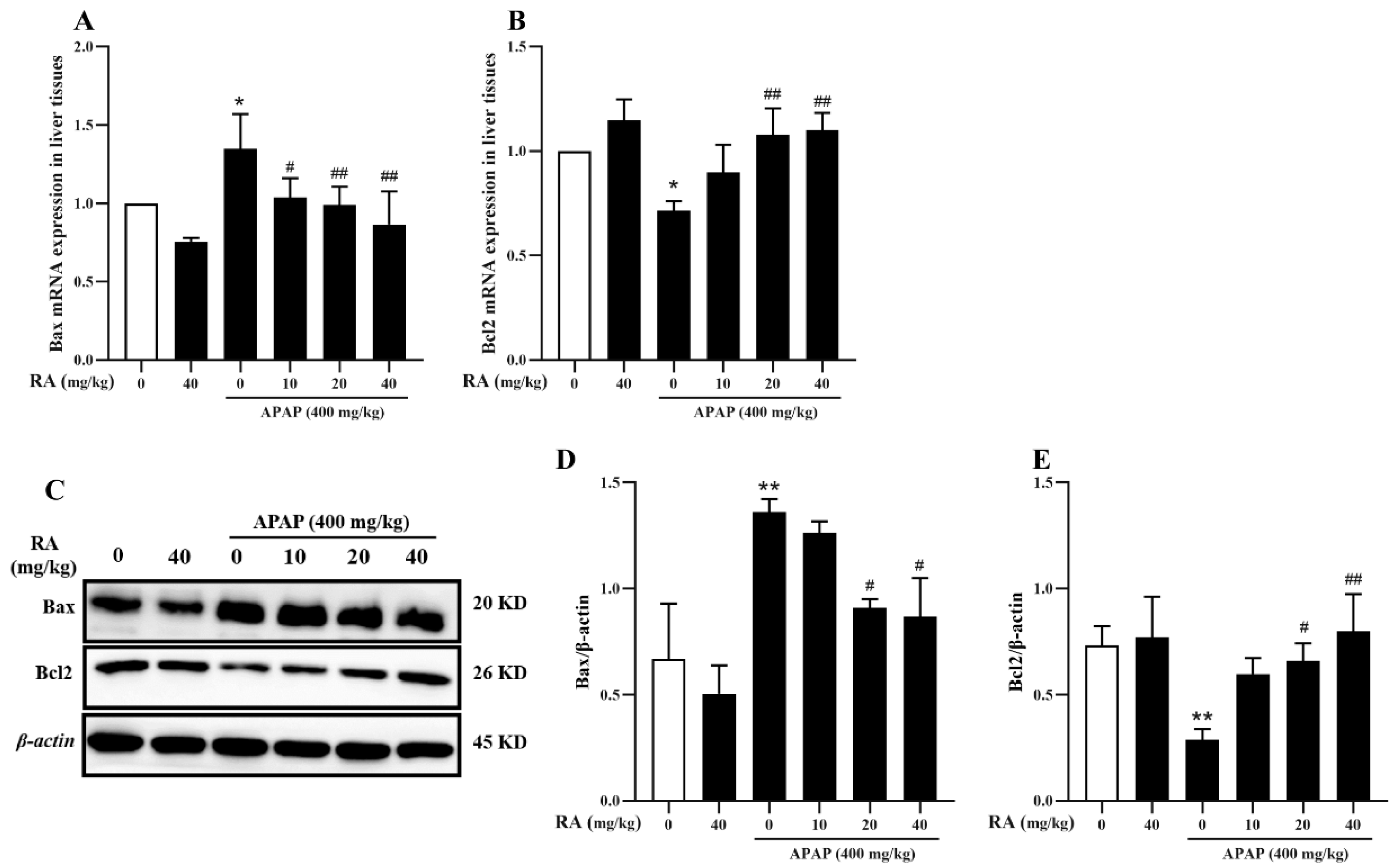
2.6. RA Inhibits APAP-Induced Hepatocyte Apoptosis
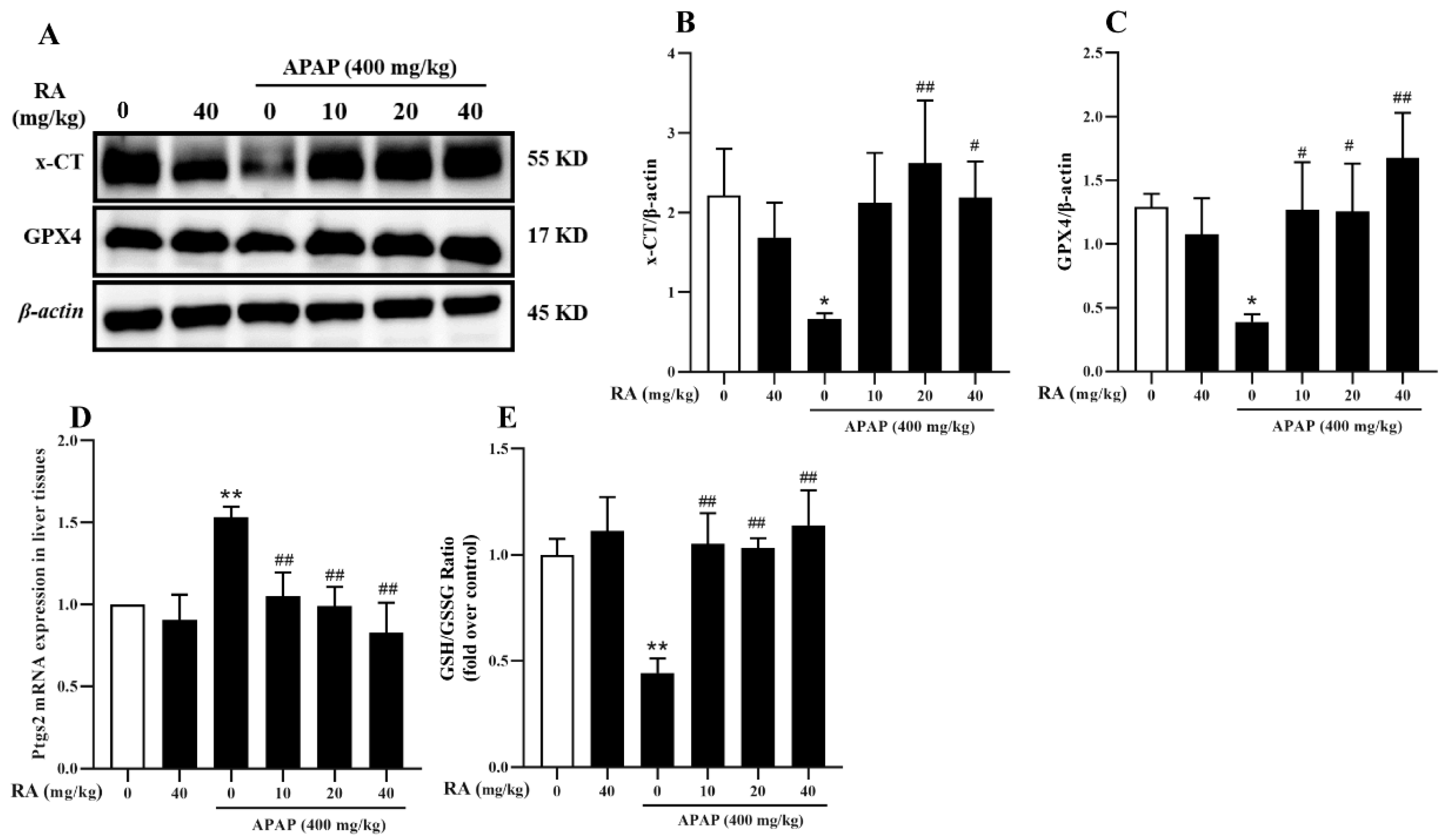
2.7. RA Alleviates APAP-Induced Ferroptosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Chemicals
4.2. Animal Experiment Setup
4.3. Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Examination
4.4. Measurement of Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress
4.5. ELISA
4.6. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR Analysis
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AILI | Acute liver injury caused by acetaminophen |
| APAP | Acetaminophen |
| DILI | Drug-induced liver injury |
| RA | Rosmarinic acid |
References
- Chen, S.; Lu, Z.; Jia, H.; Yang, B.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, S.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific Mas activation enhances lipophagy and fatty acid oxidation to protect against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, J.; Dhull, S.B.; Rose, P.K.; MK, K. Drug-induced liver injury and anti-hepatotoxic effect of herbal compounds: A metabolic mechanism perspective. Phytomedicine 2024, 122, 155142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Chen, M. Epidemiology and Risk Determinants of Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Current Knowledge and Future Research Needs. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e16146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, B.; Pandey, A.K.; Dubey, S.K. Integrated omics analyses elucidate acetaminophen biodegradation by Enterobacter sp. APAP_BS8. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wu, H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, H.; Lv, X.; Liao, C.; Ye, J.; Li, H. Underlying mechanisms and treatment of acetaminophen-induced liver injury (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2025, 34, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Wan, M.; Mei, F.; Wang, F. Oral magnesium prevents acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by modulating microbial metabolism. Cell Host Microbe 2024, 32, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Huo, Y.; Yin, S.; Hu, H. Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its implications for therapeutic interventions. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yin, X.; Fu, H.; Liu, J.; Weng, Z.; Mao, Q.; Zhu, L.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, B.; et al. Ethanol extract of Eclipta prostrata induces multiple myeloma ferroptosis via Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 axis. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-X.; Li, M.; Xu, X.-W.; Zhao, W.-B.; Jin, Y.-M.; Li, L.-L.; Qin, Z.-H.; Sheng, R.; Ni, H. BNIP3-mediated mitophagy attenuates hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats by inhibiting ferroptosis through P62-KEAP1-NRF2 pathway activation to maintain iron and redox homeostasis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2025, 46, 33–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Shen, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, R.; Meng, X.; Xu, P.; Liu, X.; Bian, D.; Wang, J.; Shi, J. ELANE enhances KEAP1 protein stability and reduces NRF2-mediated ferroptosis inhibition in metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourakbar, L.; Moghaddam, S.; Enshasy, H.; Sayyed, R. Antifungal Activity of the Extract of a Macroalgae, Gracilariopsis persica, against Four Plant Pathogenic Fungi. Plants 2021, 10, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, S.A.; Hira, K.; Pal, P.P.; Nessa, S.; Kulkarni, O.P.; Danaraj, J.; Shaik, A.B.; Araya, H.; Fujimoto, Y. Halodule pinifolia (Seagrass) attenuated lipopolysaccharide-, carrageenan-, and crystal-induced secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines: Mechanism and chemistry. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Hernández, D.; Sandoval-Gil, J.M.; Enerstvedt, K.H.; Gonzalez, S.V.; Ferreira-Arrieta, A.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Jordheim, M. Sulfated Flavonoids from Phyllospadix (Zosteraceae) Taxa from Baja California, Mexico. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 6079–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Ji, M.; Wu, L.; Lv, L.; Liang, Q.; Deng, R.; Deng, Z.; Liu, X.; Ren, L.; Feng, X.; et al. Rosmarinic Acid Prevents Cisplatin-Induced Liver and Kidney Injury by Inhibiting Inflammatory Responses and Enhancing Total Antioxidant Capacity, Thereby Activating the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2022, 27, 7815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, S.; Xue, Y.; Li, F.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Wang, Y. Improving the stability of myofibrillar proteins undergoing hemoglobin-mediated oxidation by rosmarinic acid or chlorogenic acid: Insights into the underlying mechanisms. Food Chem. 2025, 483, 144259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, L.; Deng, X.; Liang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Deng, R.; Lv, L.; Ji, M.; Hao, Z.; He, J. The Antioxidant Rosmarinic Acid Ameliorates Oxidative Lung Damage in Experimental Allergic Asthma via Modulation of NADPH Oxidases and Antioxidant Enzymes. Inflammation 2020, 43, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Nie, H.; Xu, Y.; Peng, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wen, X.; Qiu, J.; Zhong, W.; Deng, X. Therapeutic effects of rosmarinic acid on airway responses in a murine model of asthma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 12, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, D.; Long, L.; He, N. Rosmarinic acid alleviates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by targeting Nrf2 and NEK7-NLRP3 signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.H.; Song, C.C.; Pantopoulos, K.; Wei, X.L.; Zheng, H.; Luo, Z. Mitochondrial oxidative stress mediated Fe-induced ferroptosis via the NRF2-ARE pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 180, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Liu, M.; Xu, K.; Pu, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. Ferroptosis is involved in the benzene-induced hematotoxicity in mice via iron metabolism, oxidative stress and NRF2 signaling pathway. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 362, 110004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Lu, X.; Zeng, J.; Ma, X.; Efferth, T. Paeoniflorin protects hepatocytes from APAP-induced damage through launching autophagy via the MAPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2024, 29, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luedde, T.; Kaplowitz, N.; Schwabe, R.F. Cell Death and Cell Death Responses in Liver Disease: Mechanisms and Clinical Relevance—ScienceDirect. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: When metabolism meets cell death. Physiol. Rev. 2025, 105, 651–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chu, X.; Li, Q.; Zhu, G.; Hu, J.; Sun, J.; Zeng, H.; Huang, J.; Ge, G. Xanthohumol ameliorates drug-induced hepatic ferroptosis via activating Nrf2/xCT/GPX4 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2024, 126, 155458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Xu, N.; Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Fu, X.; Shang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Yao, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, H. Mifepristone protects acetaminophen induced liver injury through NRF2/GSH/GST mediated ferroptosis suppression. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 222, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.-X.; Zhu, J.-H.; Cao, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.-W.; Sun, S.-J.; Fu, J.-T.; Chen, Y.-T.; et al. Gasdermin-E-Dependent Non-Canonical Pyroptosis Promotes Drug-Induced Liver Failure by Promoting CPS1 deISGylation and Degradation. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2305715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Supuran, C.T.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Godfrey, K. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Lu, W.; Xin, Y.; Ma, H.; Sheng, X.; Gao, G.; Kang, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, Y. Liver-specific Bcl3 knockout alleviates acetaminophen-induced liver injury by activating Nrf2 pathway in male mice. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 19, 101483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Ma, H.; Peng, J.; Shen, X.; Zhen, X.; Yu, C.; Zhang, P.; Ji, F.; Wang, J.X. USP25 regulates KEAP1-NRF2 anti-oxidation axis and its inactivation protects acetaminophen-induced liver injury in male mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Chen, A.; Li, L.; Liang, Q.; Wang, S.; Dong, Q.; Fu, M.; Lan, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Repression of the antiporter SLC7A11/glutathione/glutathione peroxidase 4 axis drives ferroptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells to facilitate vascular calcification. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 1259–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Weng, Q.; Gong, S.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, J.; Lan, T. Kaempferol prevents acetaminophen-induced liver injury by suppressing hepatocyte ferroptosis via Nrf2 pathway activation. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.; Karasawa, T.; Kimura, H.; Watanabe, S.; Takahashi, M. Ferroptosis driven by radical oxidation of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids mediates acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, N.; Karasawa, T.; Takahashi, M. Role of ferroptosis in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 1769–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.W.; Ji, J.; Hu, L.; Wanh, H. Dihydromyricetin alleviates acetaminophen-induced liver injury via the regulation of transformation, lipid homeostasis, cell death and regeneration. Life Sci. 2019, 227, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, D.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Miyata, K.; Tomishima, Y.; Kondo, Y.; Irikura, M.; Iwawaki, T.; Oike, Y.; Irie, T. Protection afforded by pre- or post-treatment with 4-phenylbutyrate against liver injury induced by acetaminophen overdose in mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 87, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dönmez, M.; Uysal, B.; Poyrazoğlu, Y.; Öztas, Y.; Türker, T.; Kaldirim, ü.; Korkmaz, A. PARP inhibition prevents acetaminophen-induced liver injury and increases survival rate in rats. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 45, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Targets | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | AAAAAAGCCTCGTGCTGTCG | GTCGTTGCTTGGTTCTCCTTG |
| IL-6 | CTAGTGCGTTATGCCTAAGC | ATAGTGTCCCAACATTCATATTGTC |
| IL-10 | CAAGGCCATGAATGAATTTGACATC | TTCGGAGAGAGGTACAAACGAGGTT |
| TNF-α | CGCTGAGGTCAATCTGC | GGCTGGGTAGAGAATGGA |
| CYP2E1 | GACGTGCGGAGGTTTTC | GCTGGCCTTTGGTCTTTT |
| Ptgs2 | AAATGCTGGTGTGGAAGGT | TTGTTGCTCTAGGCTTTGCT |
| Bax | CTGGATCCAAGACCAGGGTG | GTGAGGACTCCAGCCACAAA |
| Bcl-2 | AAACCCTCCATCCTGTCC | TCCTAAACCCTGCTTCCC |
| β-actin | ATCACTATTGGCAACGAGCG | TCAGCAATGCCTGGGTACAT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, L.; Lv, L.; Xiang, Y.; Yi, D.; Liang, Q.; Ji, M.; Deng, Z.; Qin, L.; Ren, L.; Liang, Z.; et al. Rosmarinic Acid Protects Against Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Suppressing Ferroptosis and Oxidative Stress Through Nrf2/HO-1 Activation in Mice. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070287
Wu L, Lv L, Xiang Y, Yi D, Liang Q, Ji M, Deng Z, Qin L, Ren L, Liang Z, et al. Rosmarinic Acid Protects Against Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Suppressing Ferroptosis and Oxidative Stress Through Nrf2/HO-1 Activation in Mice. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(7):287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070287
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Liqin, Li Lv, Yifei Xiang, Dandan Yi, Qiuling Liang, Min Ji, Zhaoyou Deng, Lanqian Qin, Lingyi Ren, Zhengmin Liang, and et al. 2025. "Rosmarinic Acid Protects Against Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Suppressing Ferroptosis and Oxidative Stress Through Nrf2/HO-1 Activation in Mice" Marine Drugs 23, no. 7: 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070287
APA StyleWu, L., Lv, L., Xiang, Y., Yi, D., Liang, Q., Ji, M., Deng, Z., Qin, L., Ren, L., Liang, Z., & He, J. (2025). Rosmarinic Acid Protects Against Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Suppressing Ferroptosis and Oxidative Stress Through Nrf2/HO-1 Activation in Mice. Marine Drugs, 23(7), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070287






