κ/ι-Carrageenan Blends in Plant Capsules: Achieving Harmony Between Mechanical and Disintegration Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
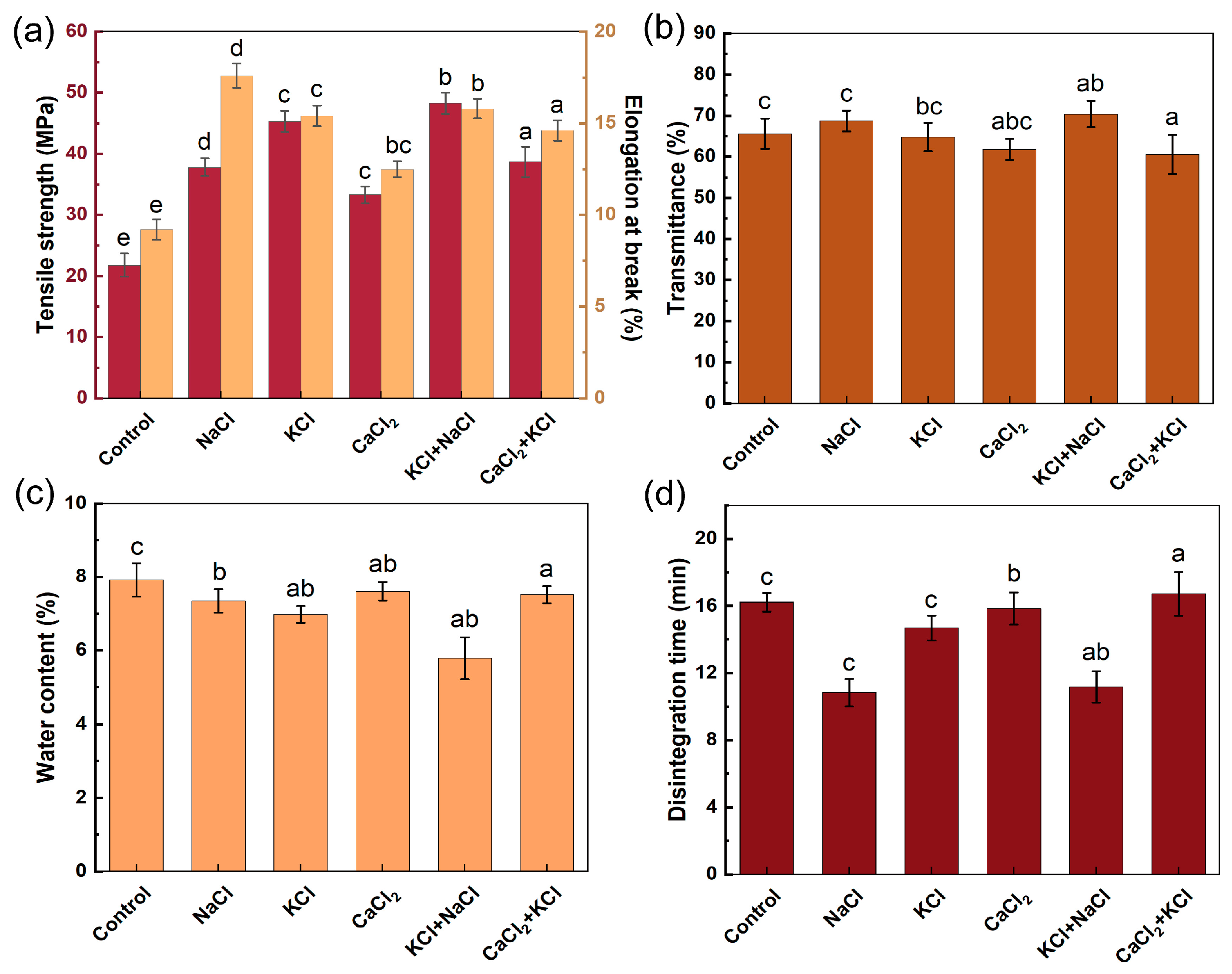
2.1. Effect of Coagulant on Capsule Properties
2.2. Rheological Properties of Gel Solution
2.3. Mechanical and Transmittance Properties of κ-C/ι-C Membranes at Different Ratios
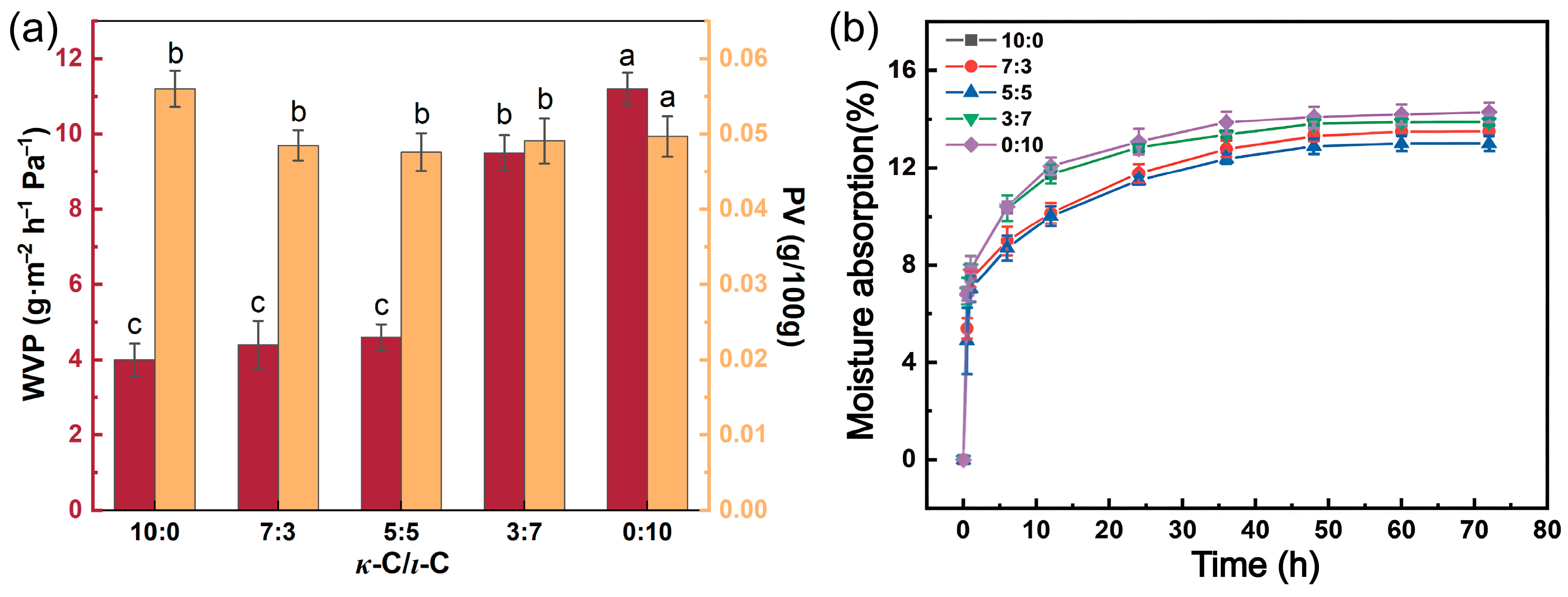
2.4. Barrier Properties and Hygroscopicity Properties of κ-C/ι-C Membranes
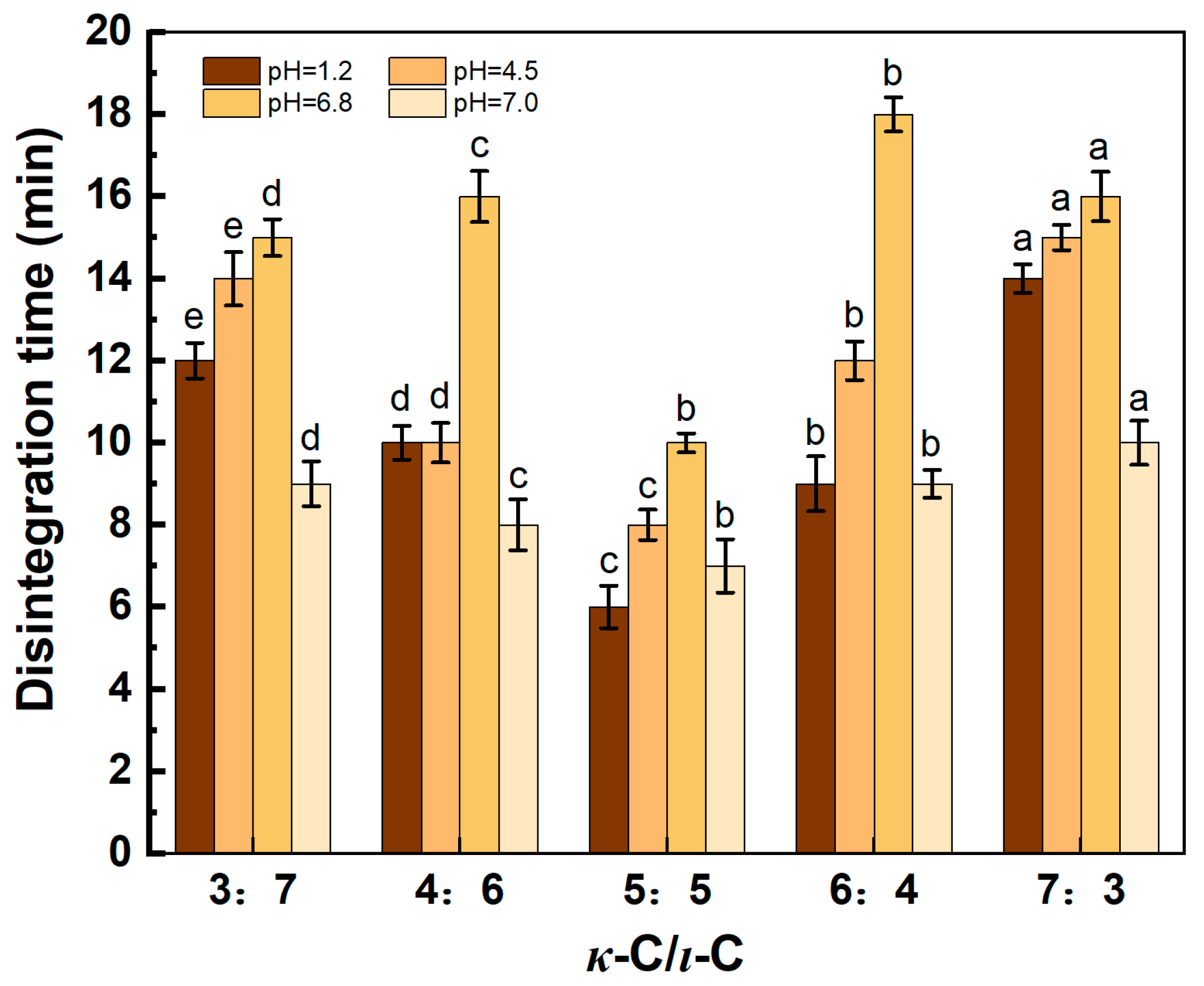
2.5. Disintegration Time
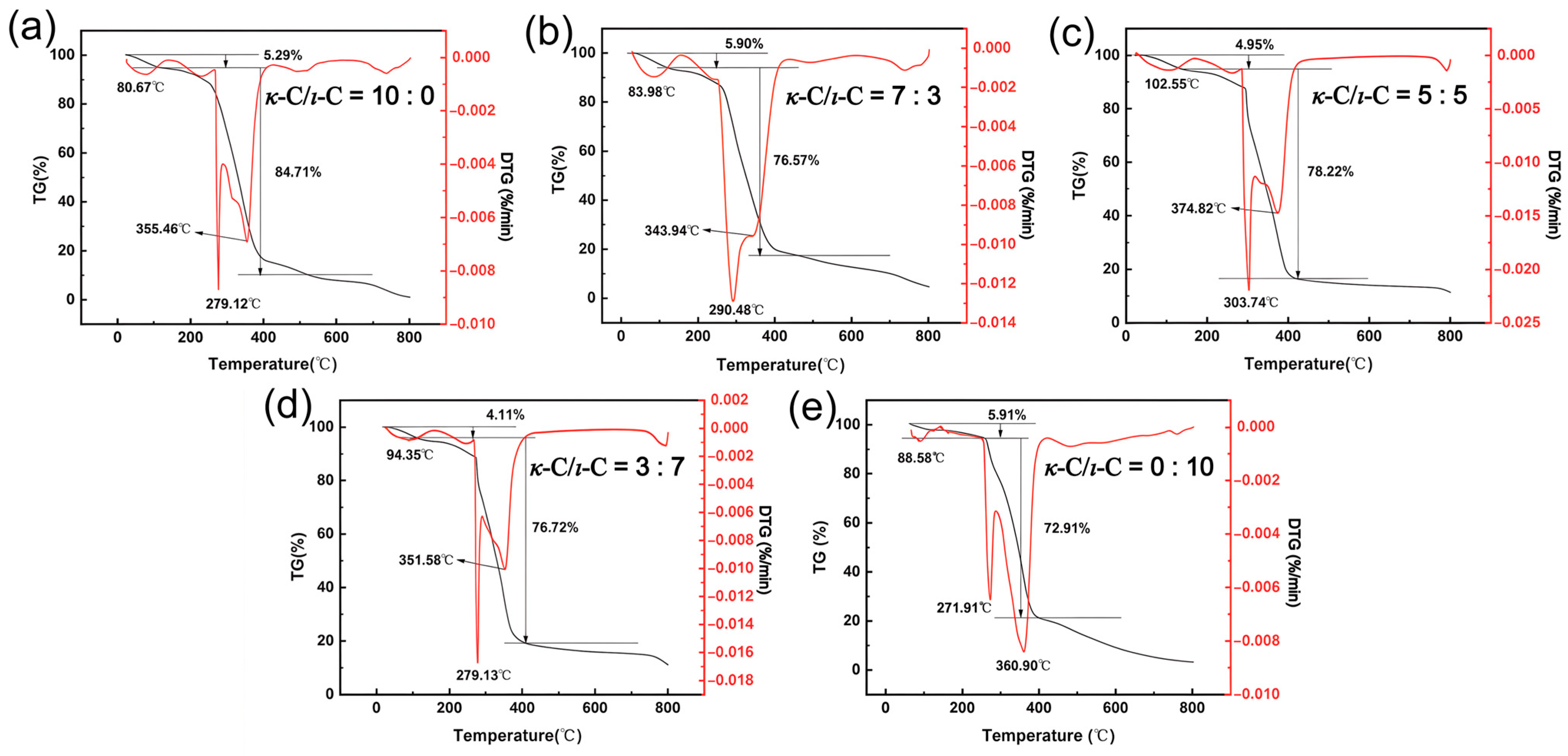
2.6. Thermal Stability of κ-C/ι-C Membranes
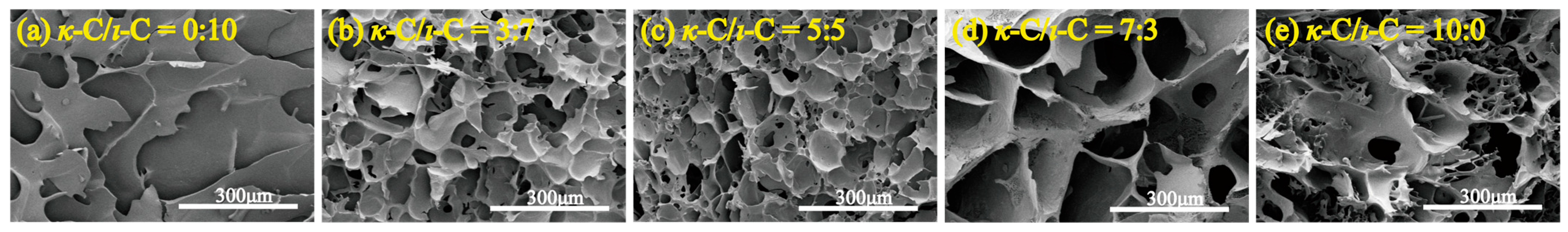
2.7. Microstructure of κ-C/ι-C Freeze-Dried Membranes
2.8. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
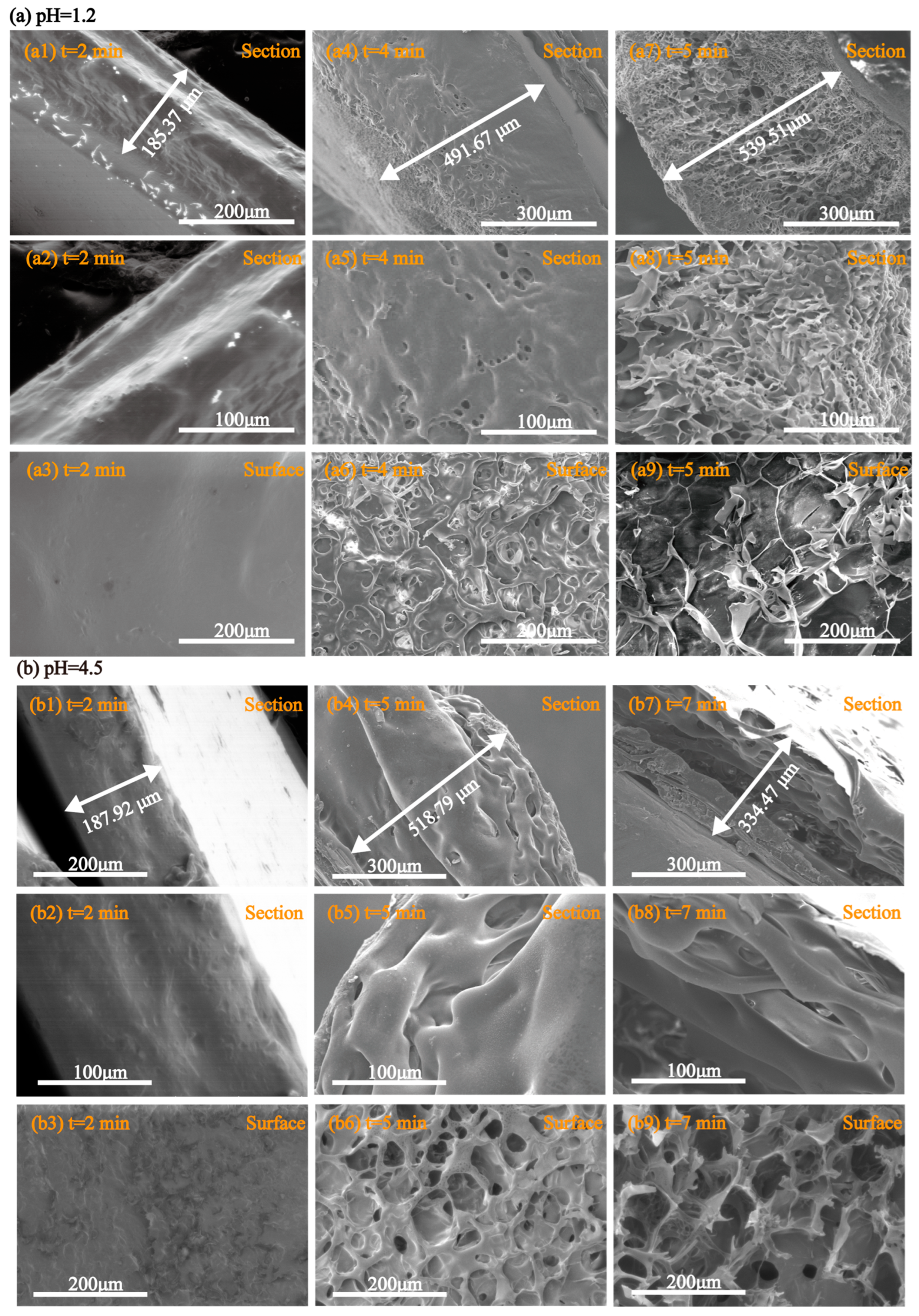
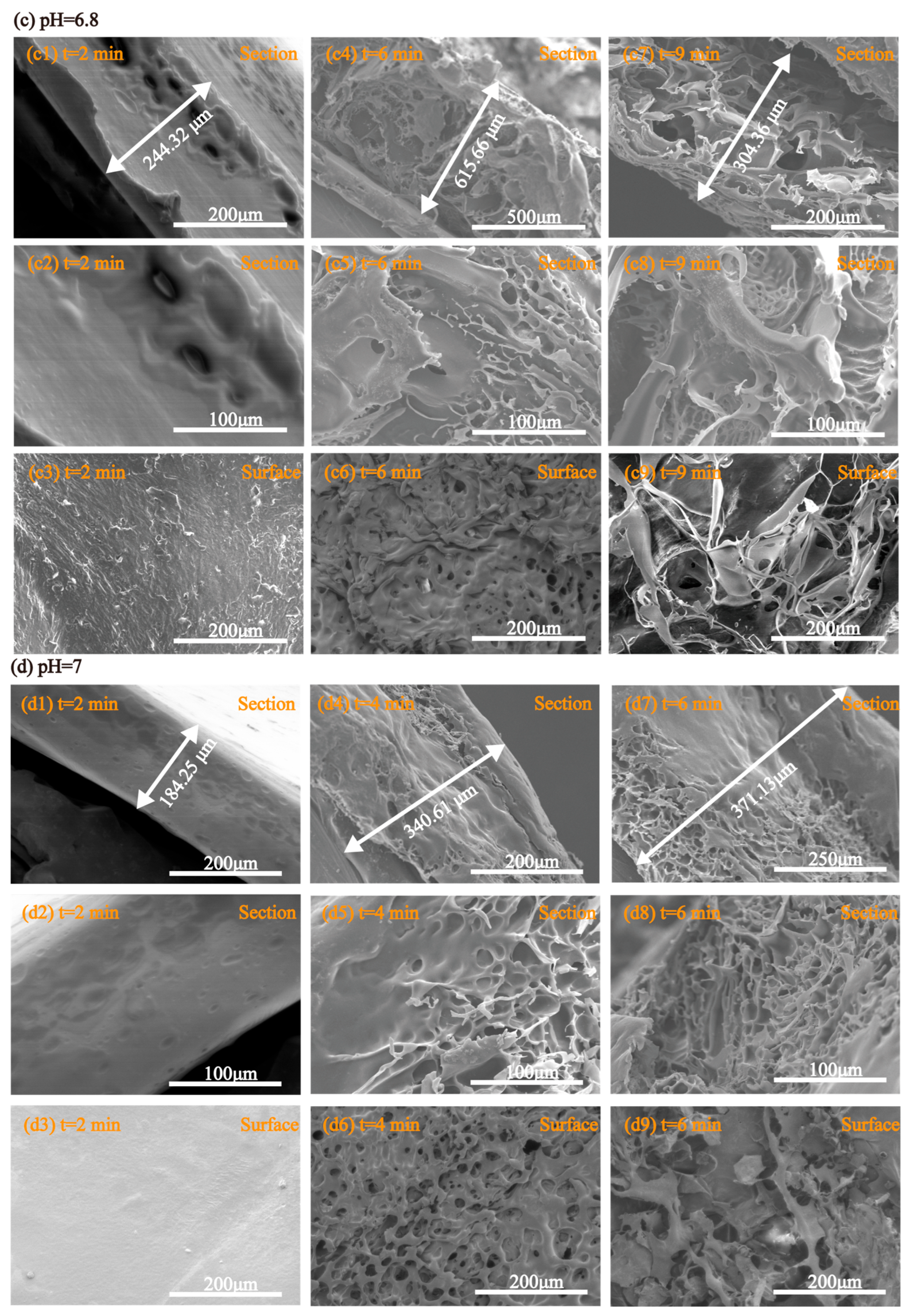
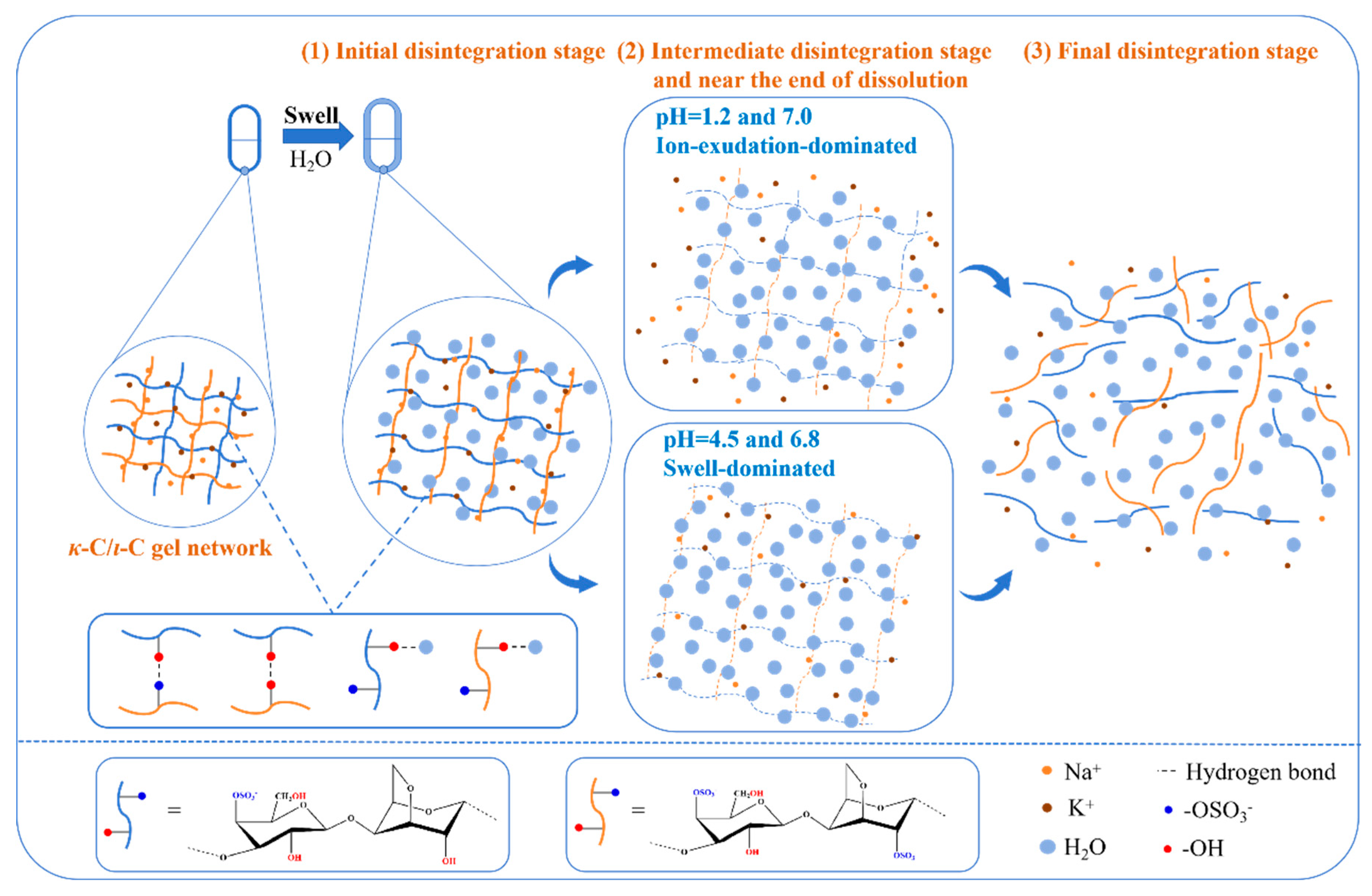
2.9. Morphological Behavior During Disintegration
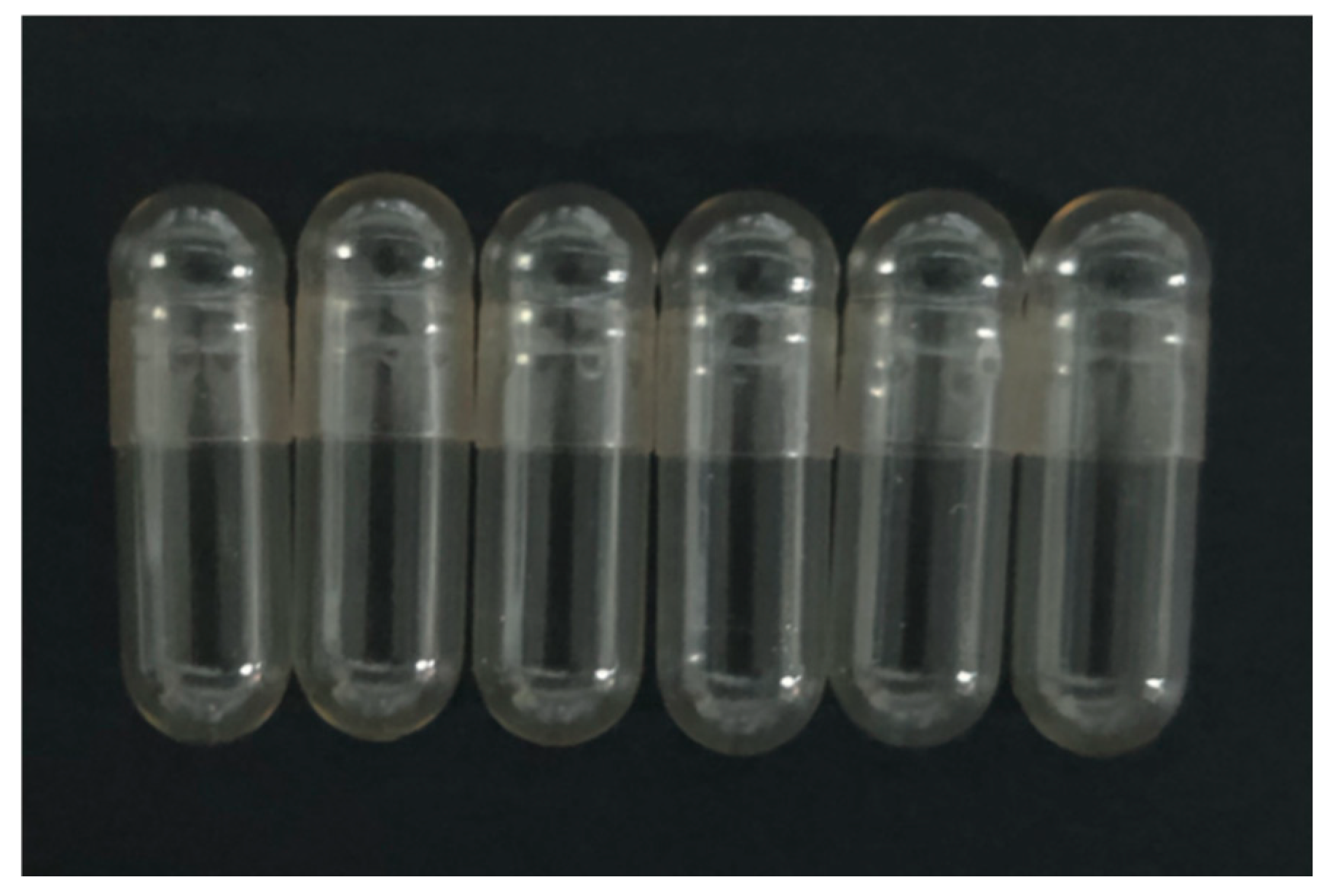
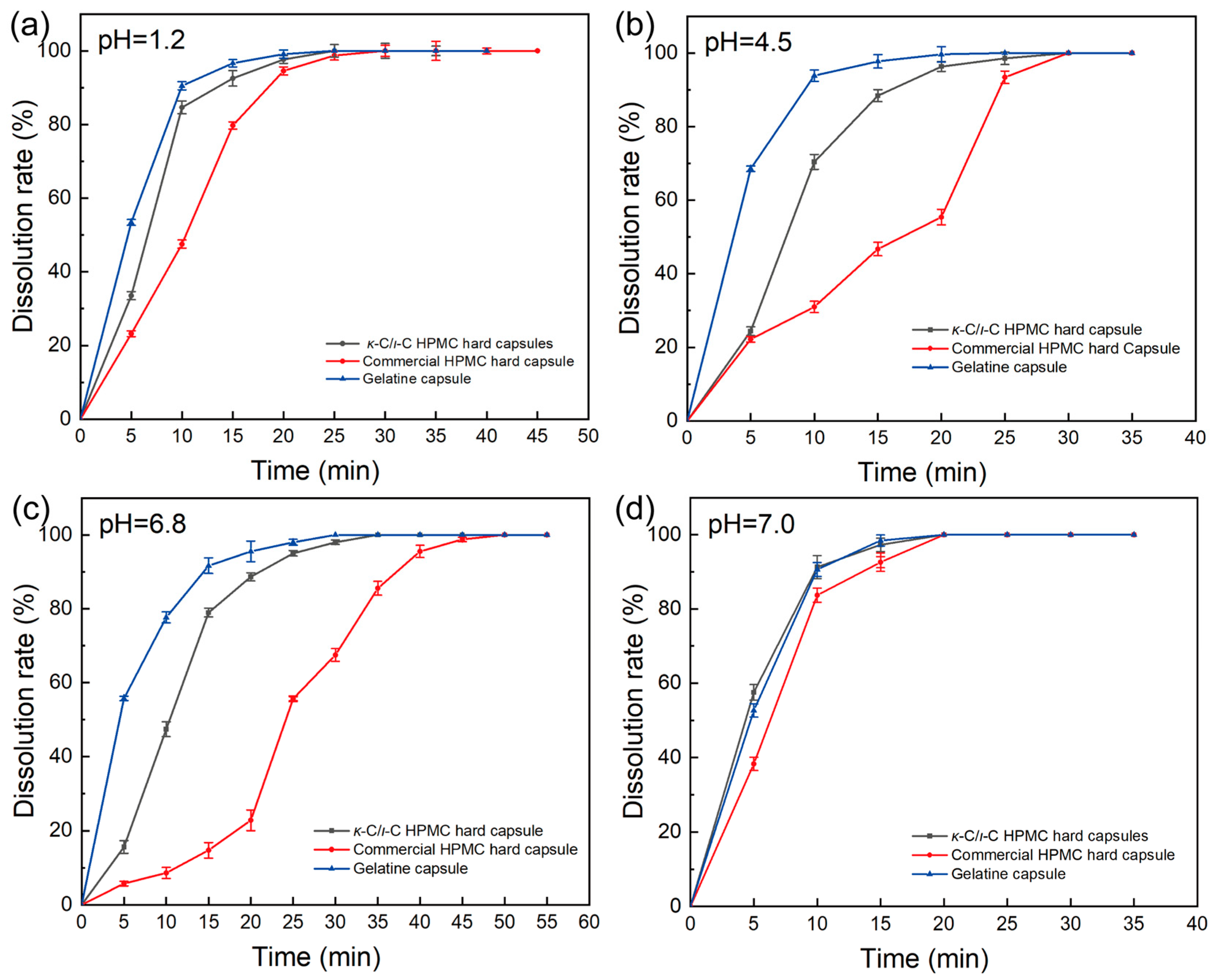
2.10. Properties of κ-C/ι-C Capsules
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Gel Solution Preparation
3.3. Preparation of HPMC-Based Hard Capsules
3.4. Preparation of Membranes
3.5. Preparation of Different pH Media
3.6. Capsule Properties
3.6.1. Mechanical Properties
3.6.2. UV-vis Measurements
3.6.3. Water Content
3.6.4. Disintegration Time
3.6.5. Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
3.6.6. Peroxide Value (PV)
3.6.7. Hygroscopicity Properties
3.6.8. Dissolution Rate
3.6.9. Capsule Friability
3.6.10. Capsule Formation Rate
3.7. Characterization
3.7.1. Rheology
3.7.2. FTIR
3.7.3. SEM
3.7.4. TG-DTG
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| κ-C | Kappa-Carrageenan |
| ι-C | Iota-Carrageenan |
| HPMC | Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose |
| WPV | Water vapor permeability |
| PV | Peroxide value |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| TG-DTG | Thermogravimetric analysis–derivative thermogravimetry |
References
- Damian, F.; Harati, M.; Schwartzenhauer, J.; Van Cauwenberghe, O.; Wettig, S.D. Challenges of Dissolution Methods Development for Soft Gelatin Capsules. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelini, L.; Probo, L.; Farè, S.; Contessi Negrini, N. Characterization of gelatin hydrogels derived from different animal sources. Mater. Lett. 2020, 272, 127865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, R.K.; Arntzen, C.J. On risk and plant-based biopharmaceuticals. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Chen, H.F.; Jin, Z.; Hou, J.W.; Zhang, Y.H.; Han, H.J.; Shen, Y.Y.; Guo, S.R. Moisture sorption and desorption properties of gelatin, HPMC and pullulan hard capsules. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanzholkyzy, A.; Zhumagaliyeva, S.; Sultanova, N.; Abilov, Z.; Ongalbek, D.; Donbayeva, E.; Niyazbekova, A.; Mukazhanova, Z. Hydrogel Delivery Systems for Biological Active Substances: Properties and the Role of HPMC as a Carrier. Molecules 2025, 30, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdock, G.A. Safety assessment of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose as a food ingredient. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, M.S.; Lu, Q.H.; Li, W.Y.; Chen, Y.S. Performance qualification of a new hypromellose capsule: Part II. Disintegration and dissolution comparison between two types of hypromellose capsules. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 416, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Arowo, M.; Ye, J.; Zhang, N.; Xiao, M. Drying Behavior and Kinetics of Drying Process of Plant-Based Enteric Hard Capsules. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciper, M.; Bodmeier, R. Modified conventional hard gelatin capsules as fast disintegrating dosage form in the oral cavity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 62, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukami, J.; Yonemochi, E.; Yoshihashi, Y.; Terada, K. Evaluation of rapidly disintegrating tablets containing glycine and carboxymethylcellulose. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 310, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yao, W.; Rao, Y.; Lu, X.; Gao, J. pH-Responsive carriers for oral drug delivery: Challenges and opportunities of current platforms. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duconseille, A.; Astruc, T.; Quintana, N.; Meersman, F.; Sante-Lhoutellier, V. Gelatin structure and composition linked to hard capsule dissolution: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazial, F.F.; Ahmad, A.; Hani, N.M. Comprehensive characterisation of tilapia fish gelatine under varied extraction conditions for the advancement of hard capsule production. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.L.; Dai, F.Y.; Chen, Y.M.; Gu, Z.H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, W.J.; Liu, P.Y.; He, Y.Y.; Gu, Z.W.; et al. Engineering innovative Pullulan-Hyaluronan water-soluble packaging films for fast-disintegrating hard capsules. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.-C.; Liu, P.-Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, B.-D.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Ye, J.; Xiao, M.-T. Heterogeneous hydroxypropylation for the preparation of hydroxypropyl carrageenan and its application in Plant-Based hard capsules. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2025, 10, 100792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.J.; Zong, Z.Y.; Gao, X.; Zhao, Y.L.; Wang, J.H. Preparation and characterization of nanostarch-based green hard capsules reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauzi, M.A.D.; Pudjiastuti, P.; Wibowo, A.C.; Hendradi, E. Preparation, Properties and Potential of Carrageenan-Based Hard Capsules for Replacing Gelatine: A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.F.; Yu, M.Q.; Wang, Z.Z.; Luo, K.Y.; Adhikari, B.; Miao, S.; Liu, S.T. Modulation of soy protein isolate gel properties by a novel "two-step" gelation process: Effects of pre-aggregation with different divalent sulfates. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udo, T.; Mummaleti, G.; Mohan, A.; Singh, R.K.; Kong, F.B. Current and emerging applications of carrageenan in the food industry. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L. Carrageenan: A review. Vet. Med. 2013, 58, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Quito, E.-M.; Ruiz-Caro, R.; Veiga, M.-D. Carrageenan: Drug Delivery Systems and Other Biomedical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Viñas, M.; Souto, S.; Flórez-Fernández, N.; Torres, M.D.; Bandín, I.; Domínguez, H. Antiviral Activity of Carrageenans and Processing Implications. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomartire, S.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Algal Phycocolloids: Bioactivities and Pharmaceutical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, R.M.; Alnaief, M.; Mashaqbeh, H. Investigation of Carrageenan Aerogel Microparticles as a Potential Drug Carrier. AAPS Pharmscitech 2018, 19, 2226–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.H.; Liang, T.Q.; Tan, W.Y.; Wang, L.J. Rheological behaviors and physical properties of plasticized hydrogel films developed from κ-carrageenan incorporating hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 85, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ni, R.; Shao, Y.; Mao, S.R. Carrageenan and its applications in drug delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 103, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangione, M.R.; Giacomazza, D.; Bulone, D.; Martorana, V.; Cavallaro, G.; San Biagio, P.L. K(+) and Na(+) effects on the gelation properties of kappa-Carrageenan. Biophys. Chem. 2005, 113, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangione, M.R.; Giacomazza, D.; Bulone, D.; Martorana, V.; San Biagio, P.L. Thermoreversible gelation of kappa-carrageenan: Relation between conformational transition and aggregation. Biophys. Chem. 2003, 104, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilliou, L. Structure–Elastic Properties Relationships in Gelling Carrageenans. Polymers 2021, 13, 4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, T.; Tuvikene, R.; Fang, Y.P.; Matsukawa, S.; Nishinari, K. Rheology of highly elastic iota-carrageenan/kappa-carrageenan/xanthan/konjac glucomannan gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, T.; Tuvikene, R.; Parker, A.; Matsukawa, S.; Nishinari, K. Rheology and structure of mixed kappa-carrageenan/iota-carrageenan gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.H.; Ye, J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Huang, Y.Y.; Li, X.H.; Xiao, M.T. K-Carrageenan/locust bean gum as hard capsule gelling agents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, F.; Jamaludin, J.; Abu Bakar, S.H.; Abdul Rasid, R.; Hassan, Z. Evaluation of hard capsule application from seaweed: Gum Arabic-Kappa carrageenan biocomposite films. Cogent Eng. 2020, 7, 1765682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudjiastuti, P.; Wafiroh, S.; Hendradi, E.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Harsini, M.; Fauzi, M.A.D.; Nahar, L.; Sarker, S.D. Disintegration, In vitro Dissolution, and Drug Release Kinetics Profiles of κ-Carrageenan-based Nutraceutical Hard-shell Capsules Containing Salicylamide. Open Chem. 2020, 18, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.; Nguyen, B.T.; Nicolai, T.; Renou, F. Mixed iota and kappa carrageenan gels in the presence of both calcium and potassium ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfaruk, M.S.; Wen, C.; Chi, C.; Li, X.; Janaswamy, S. Effect of salt addition on iota-carrageenan solution properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Running, C. Structural and Functional Changes in Iota-Carrageenan upon Addition of Salts and Sweeteners. Master’s Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Pan, Y.D.; Zhou, Z.R.; Gao, Y.; Li, A.J.; Shi, B.K.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.Y. Effect of Potassium-Ion-Triggered Double Helix Aggregation on Shakedown Behavior of κ-Carrageenan/Polyacrylamide Hydrogel. Gels 2025, 11, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrimawithana, T.R.; Young, S.; Dunstan, D.E.; Alany, R.G. Texture and rheological characterization of kappa and iota carrageenan in the presence of counter ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Yuan, C.; Cui, B.; Liu, Y.W. Influence of cations on texture, compressive elastic modulus, sol-gel transition and freeze-thaw properties of kappa-carrageenan gel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 202, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Wei, X.H.; Liu, A.D.; Wang, S.J.; Chen, B.Q.; Chen, Z.M.; Lyu, M.; Guo, W.X.; Cao, X.Z.; Ye, M.D. Tough Hydro-Aerogels with Cation Specificity Enabled Ultra-High Stability for Multifunctional Sensing and Quasi-Solid-State Electrolyte Applications. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2313088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, T.; Palla, C.S.; Dethe, D.H.; Joshi, Y.M. Rheological investigation of the network structure in mixed gels of Kappa and Iota Carrageenan. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, D.W.; Shen, A.Q.; Haward, S.J. Microtomographic particle image velocimetry measurements of viscoelastic instabilities in a three-dimensional microcontraction. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 923, R6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro-Córdova, C.; Royall, C.P.; van Duijneveldt, J.S. Anisotropic viscoelastic phase separation in polydisperse hard rods leads to nonsticky gelation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3415–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, K.; Banerjee, R. Effect of density ratios on droplet breakup for newtonian and power-law fluids. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2023, 167, 104561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Ma, M.T.; Huang, W.Y.; Sui, Z.Q.; Corke, H. Removing internal lipids influences the interactions between blueberry anthocyanins and maize starch: Thermal and rheological properties, and digestibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 305, 141232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabarkhyl, S.; Barigou, M.; Badve, M.; Zhu, S.P. Rheological properties of wet foams generated from viscous pseudoplastic fluids. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 64, 102304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Gardner, D.J.; Stark, N.M.; Bousfield, D.W.; Tajvidi, M.; Cai, Z.Y. Moisture and Oxygen Barrier Properties of Cellulose Nanomaterial-Based Films. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, V.L.; Kawano, D.F.; da Silva, D.B.; Carvalho, I. Carrageenans: Biological properties, chemical modifications and structural analysis—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 77, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.Y.; Ju, Q.; Zhao, D.; Shen, Y.C.; Wang, T.W. Enhanced oxygen barrier properties of poly(lactic acid) via oxygen scavenging strategy combining with uniaxial stretching. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilliou, L. Hybrid carrageenans: Isolation, chemical structure, and gel properties. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 72, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, X.; Lin, C.; Qian, C.; He, G.J.; Feng, Y.H.; Yin, X.C. Preparation and properties of thermoplastic starch under the synergism of ultrasonic and elongational rheology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.H.; Chen, K.F.; Zeng, J.S.; Xu, J.; Wang, B. Thermal pyrolysis characteristics of macroalgae Cladophora glomerata. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.A.; Xu, Z.G.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Q.P. Bioinspired strategy for tuning thermal stability of PVA via hydrogen-bond crosslink. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 118, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tyrikos-Ergas, T.; Zhu, Y.T.; Fittolani, G.; Bordoni, V.; Singhal, A.; Fair, R.J.; Grafmüller, A.; Seeberger, P.H.; Delbianco, M. Systematic Hydrogen-Bond Manipulations To Establish Polysaccharide Structure-Property Correlations. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 13127–13132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanpour, M.; Tamaddon, A.M.; Kadivar, M.; Abolmaali, S.S.; Shekarchizadeh, H. Fabrication of nanostructured mesoporous starch encapsulating soy-derived phytoestrogen (genistein) by well-tuned solvent exchange method. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 1031–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, R.G.; Zhang, W.S.; Kang, H.L.; Che, N.; Li, P.P.; Huang, Y. Effects of additives on dissolution of cellobiose in aqueous solvents. Cellulose 2015, 22, 1641–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanaki, S.; Karavas, E.; Kalantzi, L.; Bikiaris, D. Miscibility study of carrageenan blends and evaluation of their effectiveness as sustained release carriers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volod’ko, A.V.; Davydova, V.N.; Petrova, V.A.; Romanov, D.P.; Pimenova, E.A.; Yermak, I.M. Comparative Analysis of the Functional Properties of Films Based on Carrageenans, Chitosan, and Their Polyelectrolyte Complexes. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.W.; Zhuang, Q.Y.; Huang, G.; Deng, H.Z.; Zhang, X. Infrared Spectrum Characteristics and Quantification of OH Groups in Coal. Acs Omega 2023, 8, 17064–17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Sun, W.; Zhan, S.; Jia, R.; Lou, Q.; Huang, T. Glycosylation with different saccharides on the gelling, rheological and structural properties of fish gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-F.; Ejeta, D.D.; Wu, J.-Y.; Kuo, S.-W.; Lin, C.-H.; Lai, J.-Y. Tuning the Wettability and Surface Free Energy of Poly(vinylphenol) Thin Films by Modulating Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions. Polymers 2020, 12, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyas, A.M.; Shah, U.U. Encyclopedia of Pharmaceutical Technology; Informa Healthcare USA, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kortejärvi, H.; Yliperttula, M.; Dressman, J.B.; Junginger, H.E.; Midha, K.K.; Shah, V.P.; Barends, D.M. Biowaiver monographs for immediate release solid oral dosage forms:: Ranitidine hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meitian, X.; He, C.; Chaoxing, C.; Ye, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, N. Plant-Based Hard Capsule for Rapid Disintegration and Method Thereof. U.S. Patent 18,131,908, 10 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, A.; Elder, T.J.; Ragauskas, A.J. Moisture barrier properties of xylan composite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Tong, Q.Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Deng, F.M. Rheological properties of pullulan-sodium alginate based solutions during film formation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudoin, N.A.; Chirdon, W.M. Nanocomposite formulations of titanium dioxide and algal biomass: A rheological characterization for topical cosmetics and dermal applications. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 703, 135401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
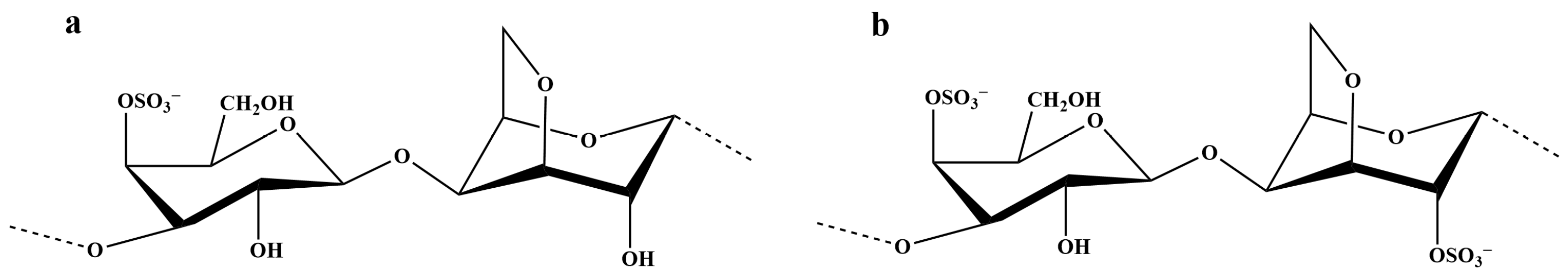






| κ-C/ι-C | K/Pa·sn | n | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0:10 | 0.4218 ± 0.0348 | 0.7615 ± 0.0137 | 0.9905 |
| 3:7 | 0.4989 ± 0.0062 | 0.7884 ± 0.0021 | 0.9998 |
| 5:5 | 1.7440 ± 0.0600 | 0.6576 ± 0.0057 | 0.9978 |
| 7:3 | 1.9108 ± 0.0833 | 0.6547 ± 0.0073 | 0.9965 |
| 10:0 | 5.0277 ± 0.2037 | 0.5473 ±0.0068 | 0.9954 |
| Samples | This Work | Purchased Gelatine Capsules | Purchased HPMC-Based Hard Capsules | The Pharmacopoeia Requirements for HPMC-Based Hard Capsules |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness/N | 30.44 ± 1.01 | 39.54 ± 3.12 | 29.37 ± 0.32 | - |
| Resilient/Pa | 0.831 ± 0.017 | 0.815 ± 0.020 | 0.816 ± 0.024 | - |
| Disintegration time (pH = 1.2)/min | <7 | <6 | <15 | <15 |
| Disintegration time (pH = 4.5)/min | <9 | <9 | <17 | <15 |
| Disintegration time (pH = 6.8)/min | <11 | <7 | <16 | <15 |
| Disintegration time (pH = 7.0)/min | <8 | <8 | <12 | <15 |
| Elasticity | 0/10 | 0/10 | 0/10 | ≤1/10 |
| Brittleness | 0/50 | 0/50 | 0/50 | ≤2/50 |
| Loss on drying/% | 5.84 ± 0.30 | 13~17 | <8 | <8 |
| Scorching residue/% | 1.17 | <1.50 | <3 | <3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; He, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Dong, Y.; Ye, J.; Zheng, B.; Kankala, R.K.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, M. κ/ι-Carrageenan Blends in Plant Capsules: Achieving Harmony Between Mechanical and Disintegration Properties. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070284
Liu Z, He C, Yang Z, Zhao Q, Dong Y, Ye J, Zheng B, Kankala RK, Zhang X, Xiao M. κ/ι-Carrageenan Blends in Plant Capsules: Achieving Harmony Between Mechanical and Disintegration Properties. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(7):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070284
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhenyu, Chuqi He, Zhibin Yang, Qing Zhao, Yuting Dong, Jing Ye, Bingde Zheng, Ranjith Kumar Kankala, Xueqin Zhang, and Meitian Xiao. 2025. "κ/ι-Carrageenan Blends in Plant Capsules: Achieving Harmony Between Mechanical and Disintegration Properties" Marine Drugs 23, no. 7: 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070284
APA StyleLiu, Z., He, C., Yang, Z., Zhao, Q., Dong, Y., Ye, J., Zheng, B., Kankala, R. K., Zhang, X., & Xiao, M. (2025). κ/ι-Carrageenan Blends in Plant Capsules: Achieving Harmony Between Mechanical and Disintegration Properties. Marine Drugs, 23(7), 284. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070284









