Characterization of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom Hydrolysate: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
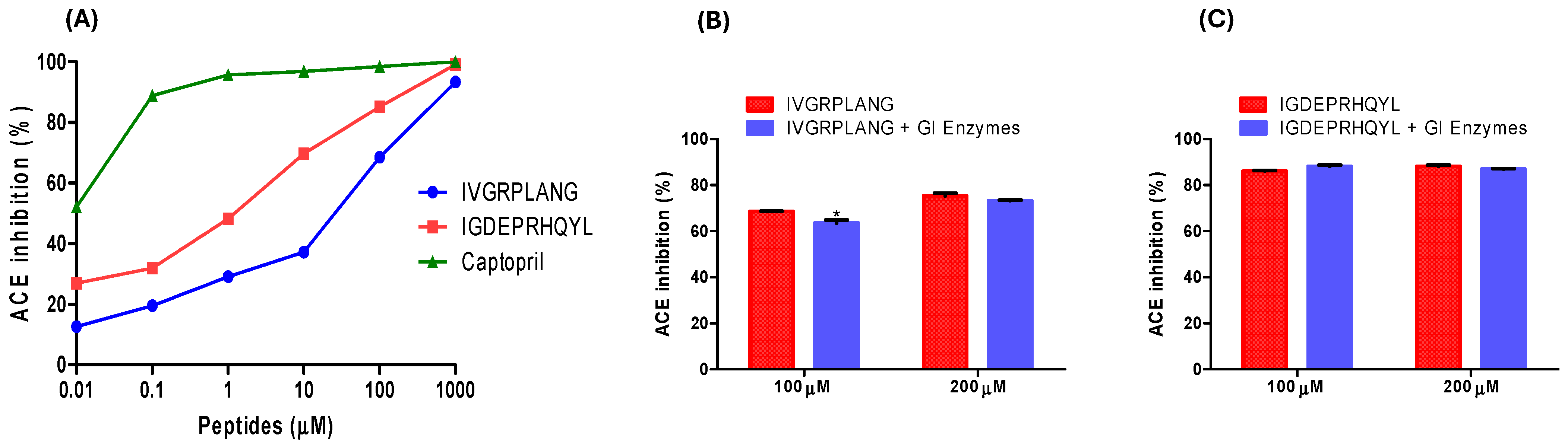
2.1. ACE-Inhibitory Activity and Resistance to Simulated GI Digestion of IVGRPLANG and IGDEPRHQYL Peptides
2.2. Inhibition Pattern of IVGRPLANG and IGDEPRHQYL Peptides
2.3. In Silico Screening of IVGRPLANG and IGDEPRHQYL Peptide with Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme
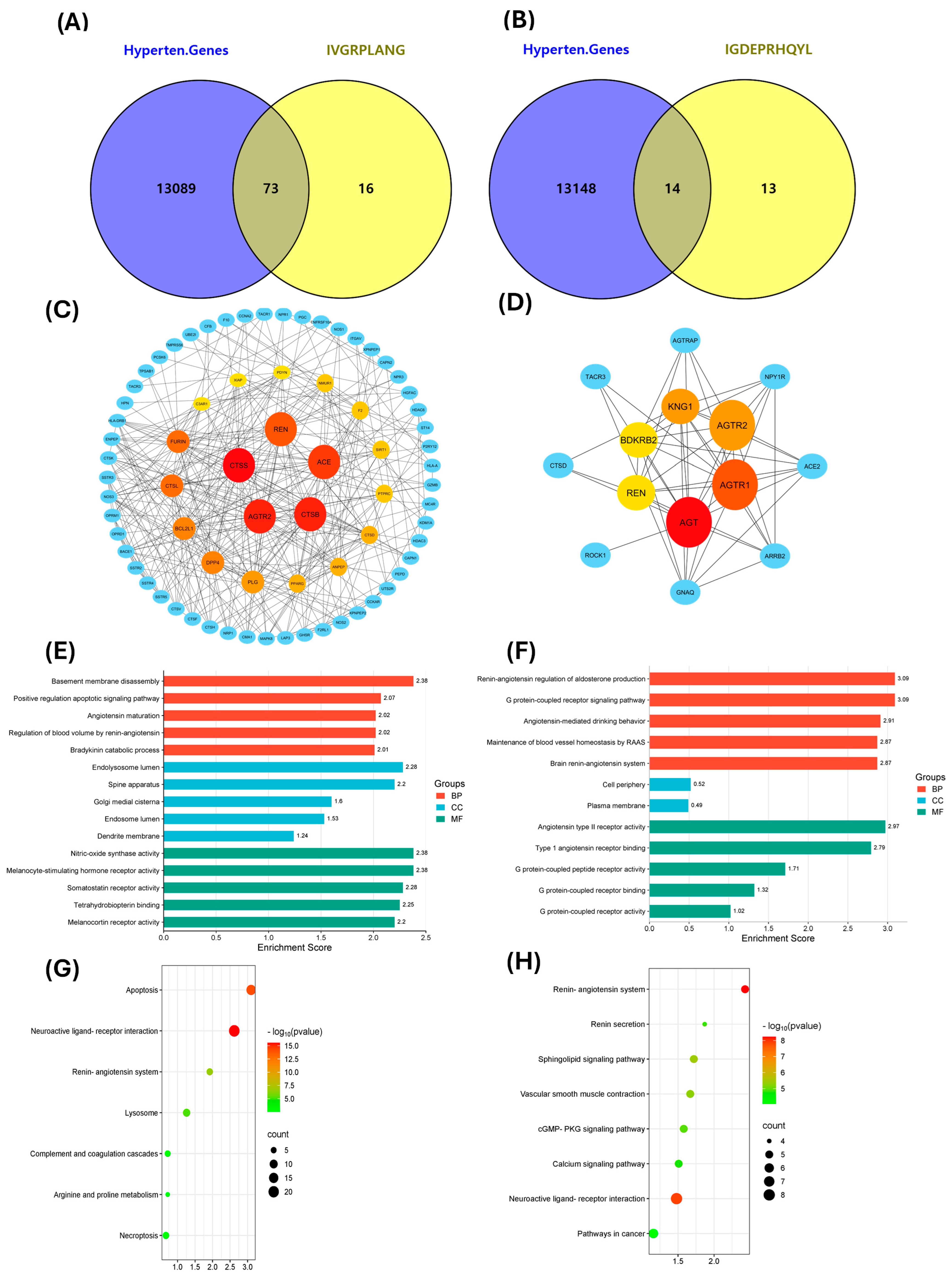
2.4. Exploring Potential Hypertension-Related Targets for IVGRPLANG and IGDEPRHQYL Peptides and Performing GO and KEGG Analyses
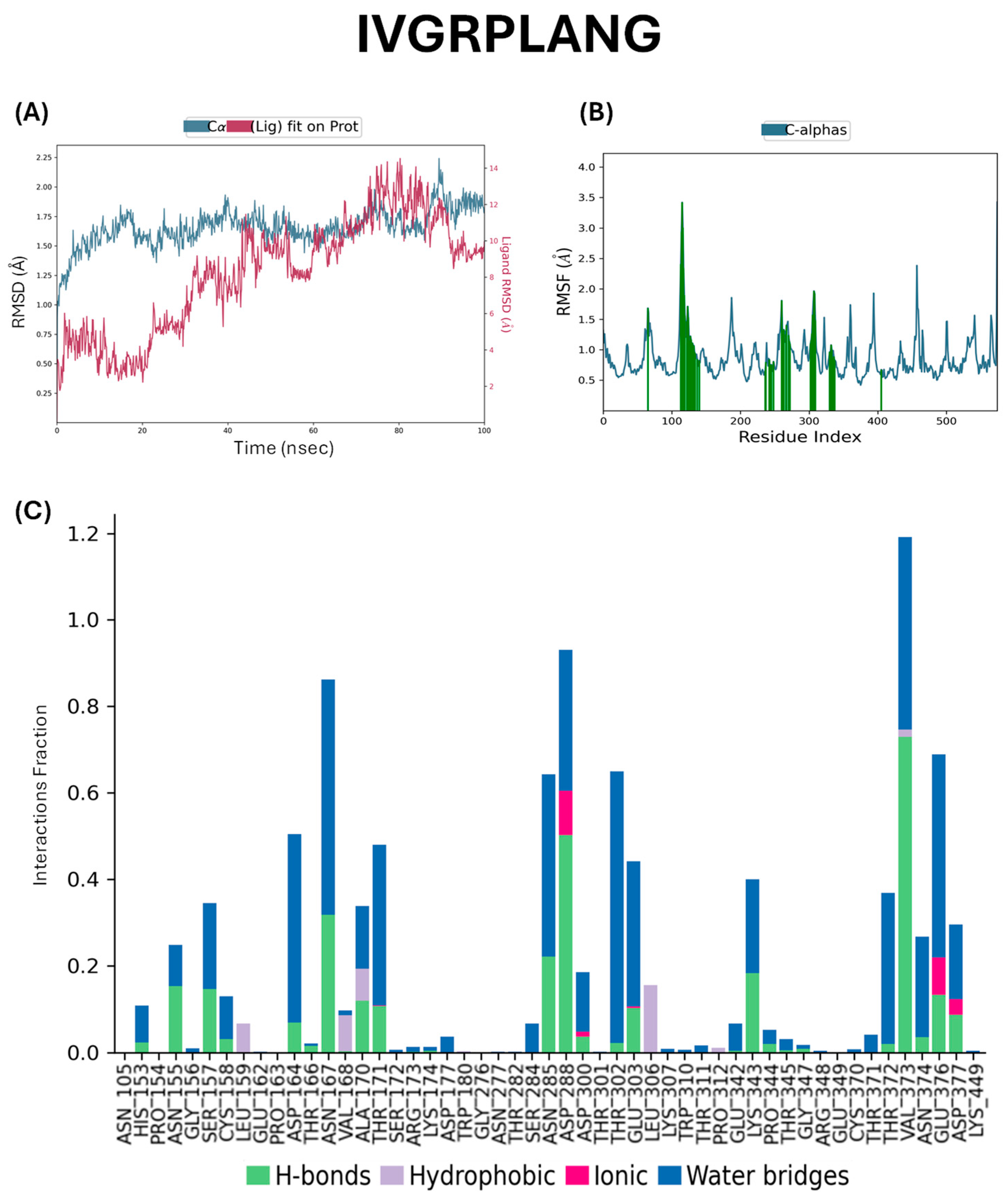
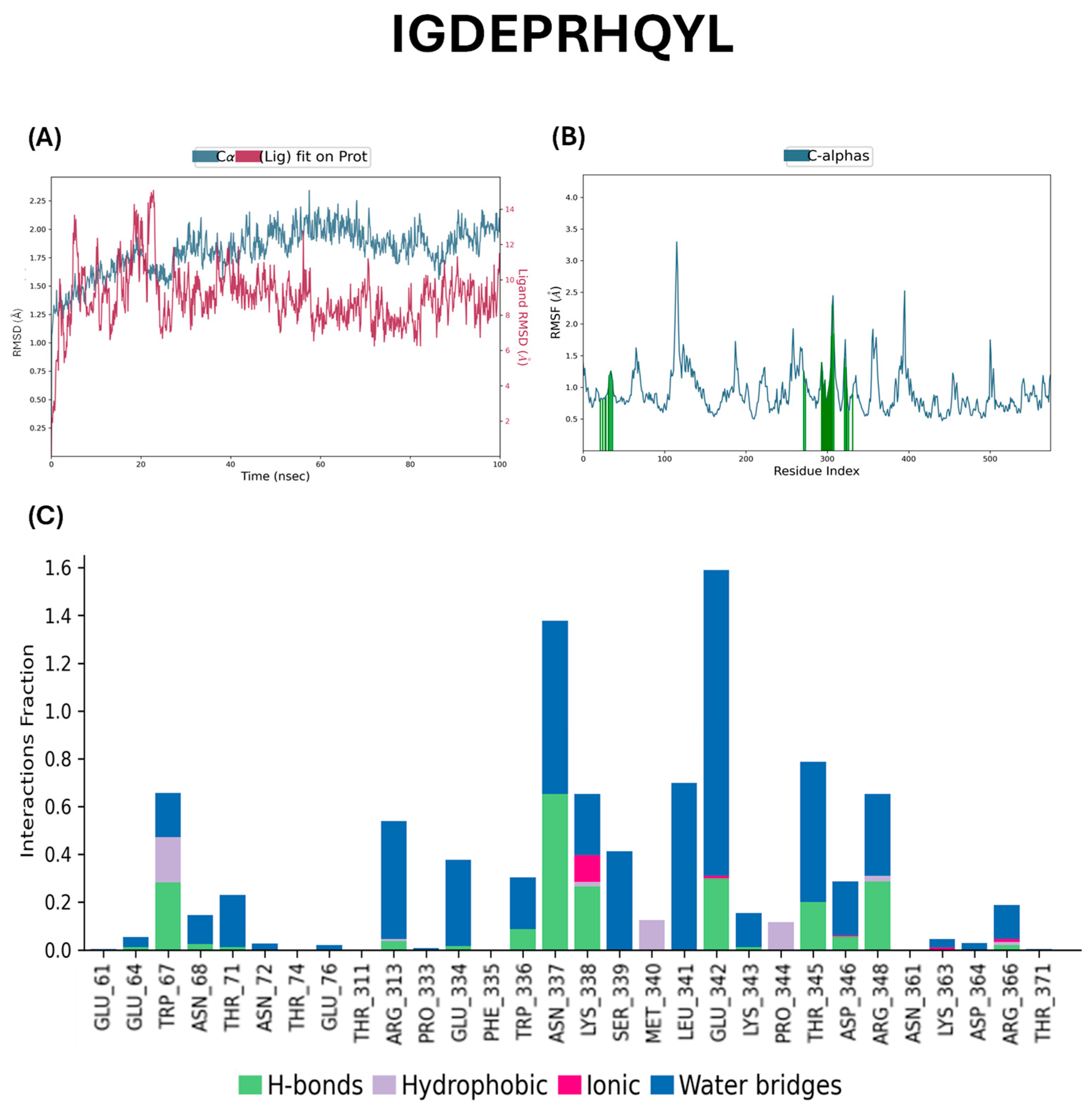
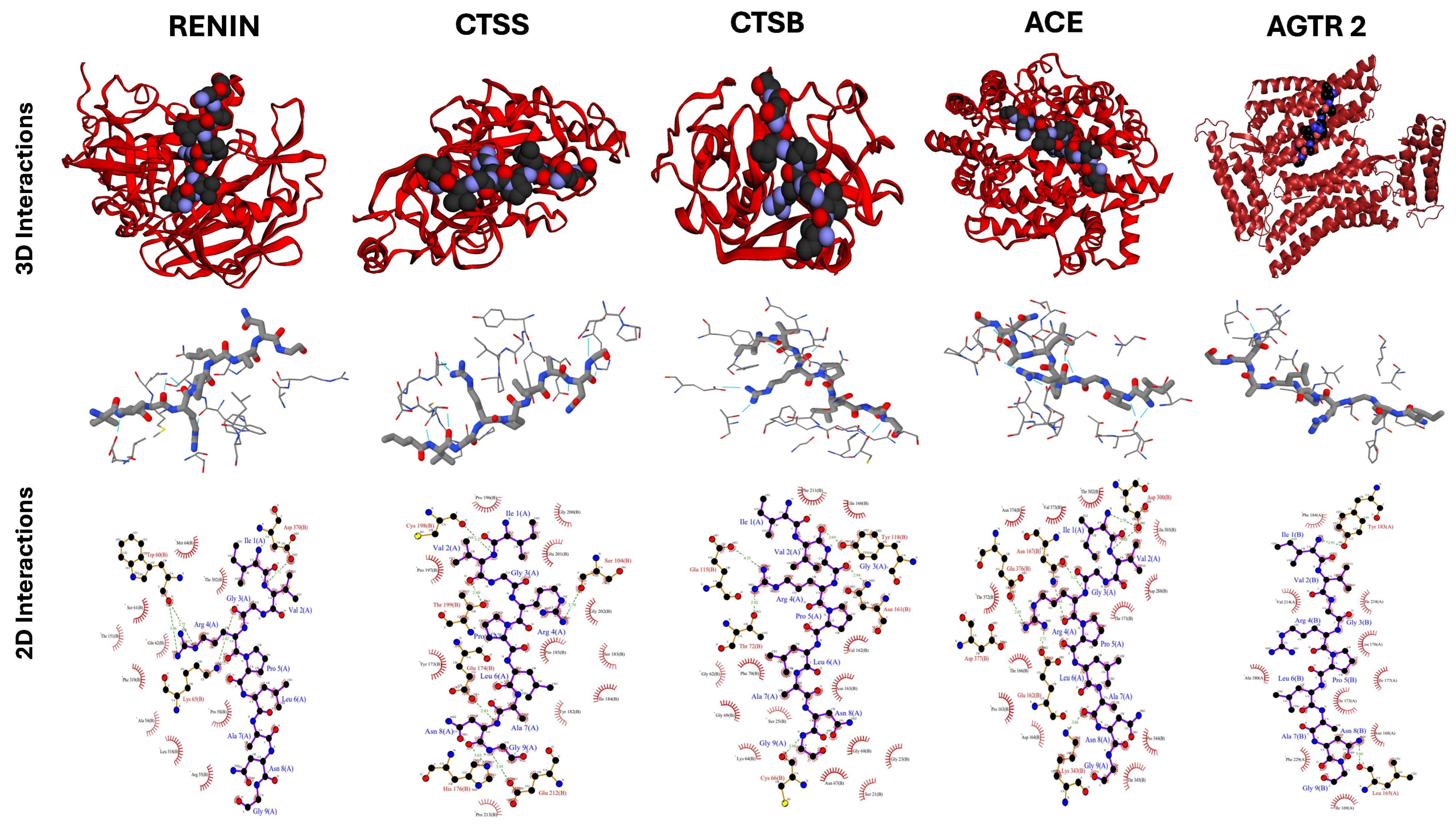
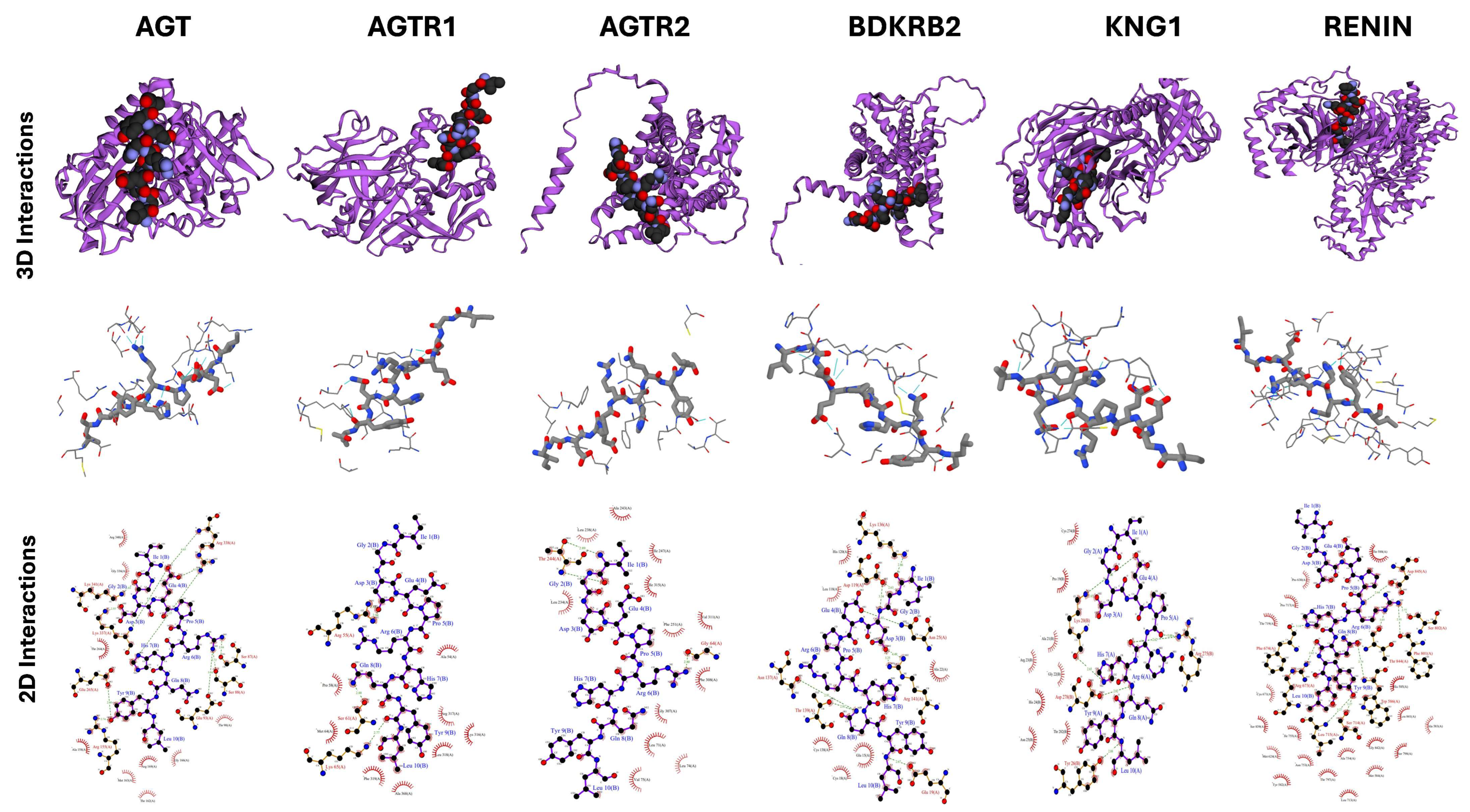
2.5. Docking Studies of Potential Hypertensive Target Proteins with IGDEPRHQYL and IVGRPLANG Peptide
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptide Synthesis
4.2. ACE-Inhibitory Effect
4.3. Resistance to Simulated GI Digestion Assay
4.4. Lineweaver–Burk Plot and Secondary Plot
4.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
- Software: Desmond (Schrödinger suite).
- Force field: OPLS-AA.
- Protein preparation: Protein–ligand complexes were optimized and refined using the Protein Preparation Wizard.
- System setup: All systems were solvated in an orthorhombic water box (125 Å × 125 Å × 125 Å) using the SPC water model. Systems were neutralized with appropriate counterions.
- Energy minimization: Performed using a combination of steepest descent (SD) and conjugate-gradient (CG) algorithms until convergence.
- Equilibration: Conducted using Desmond’s default relaxation protocol.
- Production MD:
- -
- Duration: 100 ns;
- -
- Ensemble: NPT (constant number of particles, pressure, temperature);
- -
- Temperature: 300 K;
- -
- Pressure: 1 atm;
- -
- Periodic boundary conditions applied in all directions;
- -
- Electrostatics calculated via Particle Mesh Ewald (PME);
- -
- Bond constraints: SHAKE algorithm used for hydrogen-containing bonds.
- Trajectory sampling: Saved at 10 ps intervals (0.01 ns).
- Analyses performed: RMSD, RMSF, Radius of Gyration (Rg), SASA, total energy (kcal/mol), and simulation event analysis.
- Initial structures: Obtained from top-ranked HADDOCK protein–peptide complexes based on docking score and cluster statistics. All trajectory analyses were carried out using the Desmond simulation package within the Schrödinger environment.
4.6. Peptide Mining Antihypertensive Targets
4.7. GO and KEGG Analysis
4.8. Molecular Docking
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Hypertension: The Race Against a Silent Killer; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Danaei, G.; Ding, E.L.; Mozaffarian, D.; Taylor, B.; Rehm, J.; Murray, C.J.; Ezzati, M. The Preventable Causes of Death in the United States: Comparative Risk Assessment of Dietary, Lifestyle, and Metabolic Risk Factors. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, A.D.; Mathers, C.D.; Ezzati, M.; Jamison, D.T.; Murray, C.J. Global and Regional Burden of Disease and Risk Factors, 2001: Systematic Analysis of Population Health Data. Lancet 2006, 367, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Risks-Mortality and Burden of Disease Attributable to Selected Major Risks; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.; Boddula, R.; Genitta, G.; Bhatia, V.; Bansal, B.; Kongara, S.; Ramesh, V. Prevalence & Risk Factors of Pre-Hypertension & Hypertension in an Affluent North Indian Population. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, A.; Lawes, C.; MacMahon, S. Reducing the Global Burden of Blood Pressure-Related Cardiovascular Disease. J. Hypertens. Suppl. 2000, 18, S3–S6. [Google Scholar]
- Carey, R.M.; Moran, A.E.; Whelton, P.K. Treatment of Hypertension: A Review. JAMA 2022, 72, 1278–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Te Riet, L.; van Esch, J.H.; Roks, A.J.; van den Meiracker, A.H.; Danser, A.H. Hypertension: Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Alterations. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 960–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffer, R.L. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme and the Regulation of Vasoactive Peptides. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1976, 45, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, D.T.; Kuo, W.W.; Ho, T.J.; Chang, R.L.; Lin, W.T.; Day, C.H.; Viswanadha, V.V.P.; Liao, P.H.; Huang, C.Y. Bioactive Peptide VHVV Upregulates the Long-Term Memory-Related Biomarkers in Adult Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Eight Antihypertensive Peptides from the Protein Hydrolysate of Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba): Isolation, Identification, and Activity Evaluation on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs). Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phase, P. Low-Dose Captopril for the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Hypertension. Arch. Intern. Med. 1984, 144, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar]
- Zusman, R.M. Renin- and Non-Renin-Mediated Antihypertensive Actions of Converting-Enzyme Inhibitors. Kidney Int. 1984, 25, 969–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimsheena, V.K.; Gowda, L.R. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Arachin by Simulated Gastric Digestion. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Zeng, M. A Novel ACE Inhibitory Peptide Isolated from Acaudina Molpadioidea Hydrolysate. Peptides 2009, 30, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Shen, H.X.; Xiao, Y.; Luo, Y.K. Preparation of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from Pearl Mussel Meat. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 23, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, R.Z.; Li, C.Y.; Liu, W.Y.; Yi, W.X.; Cai, M.Y. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Activity of Low-Molecular-Weight Peptides from Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) Skin. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lv, S.; Li, B. Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory and Antihypertensive Properties of Squid Skin Gelatin Hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.L.; Chen, X.L.; Sun, C.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhou, B.C. Analysis of Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from Protease-Hydrolyzed Marine Shrimp Acetes Chinensis. J. Pept. Sci. 2006, 12, 726–733. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Jia, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Z.; Liu, C. Purification and Characterization of Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from Jellyfish Rhopilema Esculentum. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, S.A.; Vinu, D.; Krupakar, P.; Govindaraju, K.; Sharma, D.; Vivek, R. Jellyfish Venom Proteins and Their Pharmacological Potentials: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 176, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Bae, S.; Hwang, D.H.; Prakash, R.L.M.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, I.H.; Kim, W.H.; Rho, I.R.; Kim, E.; Kang, C. Nemopilema Nomurai Jellyfish Venom Attenuates Phenotypic Modulation of PDGF BB Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Kappa-Carrageenan-Induced Rat Tail Thrombosis. Toxicon 2023, 233, 107266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, I.; Lee, H.; Pyo, M.J.; Heo, Y.; Chae, J.; Yum, S.S.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. Proteomic Investigation to Identify Anticancer Targets of Nemopilema Nomurai Jellyfish Venom in Human Hepatocarcinoma HepG2 Cells. Toxins 2018, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Bae, S.K.; Kim, M.; Pyo, M.J.; Kim, M.; Yang, S.; Won, C.K.; Yoon, W.D.; Han, C.H.; Kang, C.; et al. Anticancer Effect of Nemopilema Nomurai Jellyfish Venom on HepG2 Cells and a Tumor Xenograft Animal Model. Evid. Based Complemen. Alter. Med. 2017, 2017, 2752716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamela Berilyn, T. In Vitro Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Inhibition by a Peptide Isolated from Chiropsalmus quadrigatus Haeckel (Box jellyfish) Venom Hydrolysate. Toxicon 2016, 119, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan Prakash, R.L.; Ravi, D.A.; Hwang, D.H.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. Identification of New Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Isolated from the Hydrolysate of the Venom of Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish. Toxins 2024, 16, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordon, K.d.C.F. From Animal Poisons and Venoms to Medicines: Achievements, Challenges and Perspectives in Drug Discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Cai, S.; Liu, S.; Pan, N.; Su, J.; Qiao, K.; Xu, M.; Chen, B.; Yang, S.; et al. A Novel Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide from Takifugu flavidus. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, H.; Yokoyama, K.; Yoshikawa, M. Classification and Antihypertensive Activity of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Food Proteins. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 564–569. [Google Scholar]
- Priyanto, A.D.; Doerksen, R.J.; Chang, C.I.; Sung, W.C.; Widjanarko, S.B.; Kusnadi, J. Screening, Discovery, and Characterization of Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Proteolytic Hydrolysate of Bitter Melon Seed Proteins. J. Proteomics 2015, 128, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ding, X. Characterization of Inhibition and Stability of Soy-Protein-Derived Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yan, W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Dai, Z.Y. A Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide from Tilapia Skin: Preparation, Identification and Its Potential Antihypertensive Mechanism. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 137074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bincy Bhaskar, B.B.; Laxmi Ananthanarayan, L.A.; Sahayog Jamdar, S.J. Purification, Identification, and Characterization of Novel Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Alcalase Digested Horse Gram Flour. LWT 2019, 103, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, B.; Zarei, M.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Philip, R.; Bakar, J.; Hamid, A.A.; Saari, N. Purification and Characterization of Angiotensin Converting Enzymeinhibitory Peptides Derived from Stichopus horrens: Sta- Bility Study against the ACE and Inhibition Kinetics. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setayesh-Mehr, Z.; Asoodeh, A. The Inhibitory Activity of HL-7 and HL-10 Peptide from Scorpion Venom (Hemiscorpius lepturus) on Angiotensin Converting Enzyme: Kinetic and Docking Study. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 75, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, J.S.; Chen, J.L.; Pan, B.S. ACE-Inhibitory Peptides Identified from the Muscle Protein Hydrolysate of Hard Clam (Meretrix lusoria). Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Xia, W. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide Derived from Enzymatic Hydrolysate of Grass Carp Protein. Peptides 2012, 33, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Alabdullah, N.H.; Ehmedat, H.M.; Abulifa, A.R.; Taban, I.; Upadhyayula, S. NSAIDs as Potential Treatment Option for Preventing Amyloid β Toxicity in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Investigation by Docking, Molecular Dynamics, and DFT Studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 2099–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Abodabos, H.S.; Taban, I.M.; Rfieda, A.R.; Mahmood, D.; Anwar, M.J.; Khan, S.; Sizochenko, N.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T. Rutin as Promising Drug for the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease: An Assessment of MAO-B Inhibitory Potential by Docking, Molecular Dynamics and DFT Studies. Mol. Simul. 2019, 45, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospital, A.; Goñi, J.R.; Orozco, M.; Gelpí, J.L. Molecular Dynamics Simulations: Advances and Applications. Adv. Appl. Bioinform. Chem. 2015, 27, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D. Construction of Fucoxanthin Vector Based on Binding of Whey Protein Isolate and Its Subsequent Complex Coacervation with Lysozyme. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 2980–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, D.B.; McGuffin, L.J. In Silico Identification and Characterization of Protein-Ligand Binding Sites. Comput. Des. Ligand Bind. Proteins 2016, 1414, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Rauf, A.; Khan, H.; Abu-Izneid, T. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone (RAAS): The Ubiquitous System for Homeostasis and Pathologies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, J.N.; Uma, K.; Noor, A.R.; Rahman, A.R.A. Blood Pressure Regulation by the Kallikrein-Kinin System. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1996, 27, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, S.; Patel, B.M. Unravelling the Role of Cathepsins in Cardiovascular Diseases. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Cao, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, B. Studies on Purification and the Molecular Mechanism of a Novel ACE Inhibitory Peptide from Whey Protein Hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACE Kit-WST. Technical Manual; Dojindo Molecular Technologies: Kumamoto, Japan, 2013; Available online: https://www.dojindo.com/manual/A502/ (accessed on 23 February 2025).
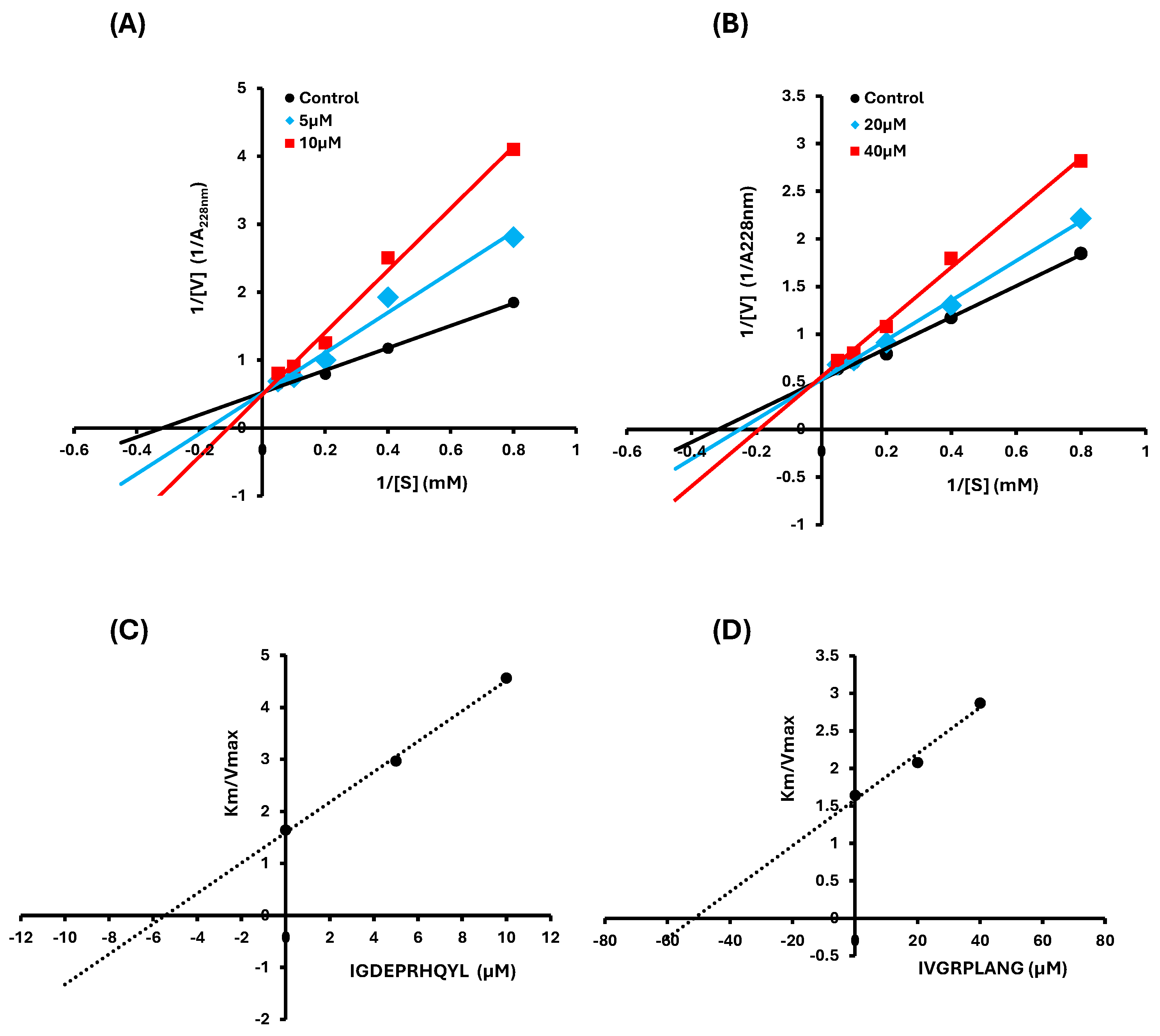
| Peptide | Concentration (µM) | Vmax | Km | Ki (µM) | Mode of Inhibition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVGRPLANG | 0 | 1.919 ± 0.00019 | 3.145 ± 0.0196 | 51.389 | - |
| 20 | 1.918 ± 0.00021 | 3.982 ± 0.00383 | Competitive | ||
| 40 | 1.811 ± 0.00076 | 5.175 ± 0.02686 | Competitive | ||
| IGDEPRHQYL | 0 | 1.919 ± 0.00019 | 3.147 ± 0.0196 | 5.457 | - |
| 5 | 1.953 ± 0.00613 | 5.801 ± 0.10923 | Competitive | ||
| 10 | 2.015 ± 0.05609 | 9.198 ± 0.39909 | Competitive |
| Targets for IVGRPLANG | Cluster Number | Cluster Size a | HADDOCK Score b | Overall RMSD c | Z-Score d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renin | 4 | 15 | −65.4 ± 2.5 | 2.3 ± 0.0 | −1.2 |
| Cathepsin S | 1 | 42 | −54.5 ± 4.1 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | −1.9 |
| Cathepsin B | 8 | 7 | −27.8 ± 6.2 | 2.8 ± 0.0 | −2.2 |
| Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme | 1 | 20 | −17.2 ± 5.1 | 1.5 ± 0.0 | −2.1 |
| Angiotensin II Receptor type 2 | 3 | 18 | −29.5 ± 5.3 | 0.4 ± 0.3 | −2.5 |
| Targets for IGDEPRHQYL | |||||
| Angiotensin | 3 | 18 | −72.2 ± 1.8 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | −1.3 |
| Angiotensin II Receptor type 1 | 3 | 12 | −60.3 ± 3.2 | 3.0 ± 0.0 | −1.7 |
| Angiotensin II Receptor type 2 | 3 | 12 | −36.3 ± 4.0 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | −2.9 |
| Renin | 2 | 42 | −67.3 ± 3.5 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | −1 |
| Bradykinin receptor 2 | 1 | 36 | −87.4 ± 2.8 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | −1.9 |
| Kininogen I | 2 | 44 | −115.3 ± 8.3 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | −1.7 |
| Protein Name | Gene Symbol | PDB ID |
|---|---|---|
| Angiotensinogen | AGT | 2WXW |
| Angiotensin Receptor 1 | AGTR1 | 4YAY |
| Angiotensin Receptor 2 | AGTR2 | 5UNF |
| Kininogen 1 | KNG1 | 1NY2 |
| Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme | ACE | 1O8A |
| Cathepsin S | CTSS | 4P6G |
| Cathepsin B | CTSB | 1GMY |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prakash, R.L.M.; Ravi, D.A.; Hwang, D.H.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. Characterization of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom Hydrolysate: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070267
Prakash RLM, Ravi DA, Hwang DH, Kang C, Kim E. Characterization of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom Hydrolysate: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(7):267. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070267
Chicago/Turabian StylePrakash, Ramachandran Loganathan Mohan, Deva Asirvatham Ravi, Du Hyeon Hwang, Changkeun Kang, and Euikyung Kim. 2025. "Characterization of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom Hydrolysate: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches" Marine Drugs 23, no. 7: 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070267
APA StylePrakash, R. L. M., Ravi, D. A., Hwang, D. H., Kang, C., & Kim, E. (2025). Characterization of Novel ACE-Inhibitory Peptides from Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom Hydrolysate: In Vitro and In Silico Approaches. Marine Drugs, 23(7), 267. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070267






