Diversity and Novelty of Venom Peptides in Vermivorous Cone Snails, Subgenus Rhizoconus (Gastropoda: Mollusca)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Pre-Processing, Assembly, and Annotation Metrics
2.2. Summary of Identified Conopeptides
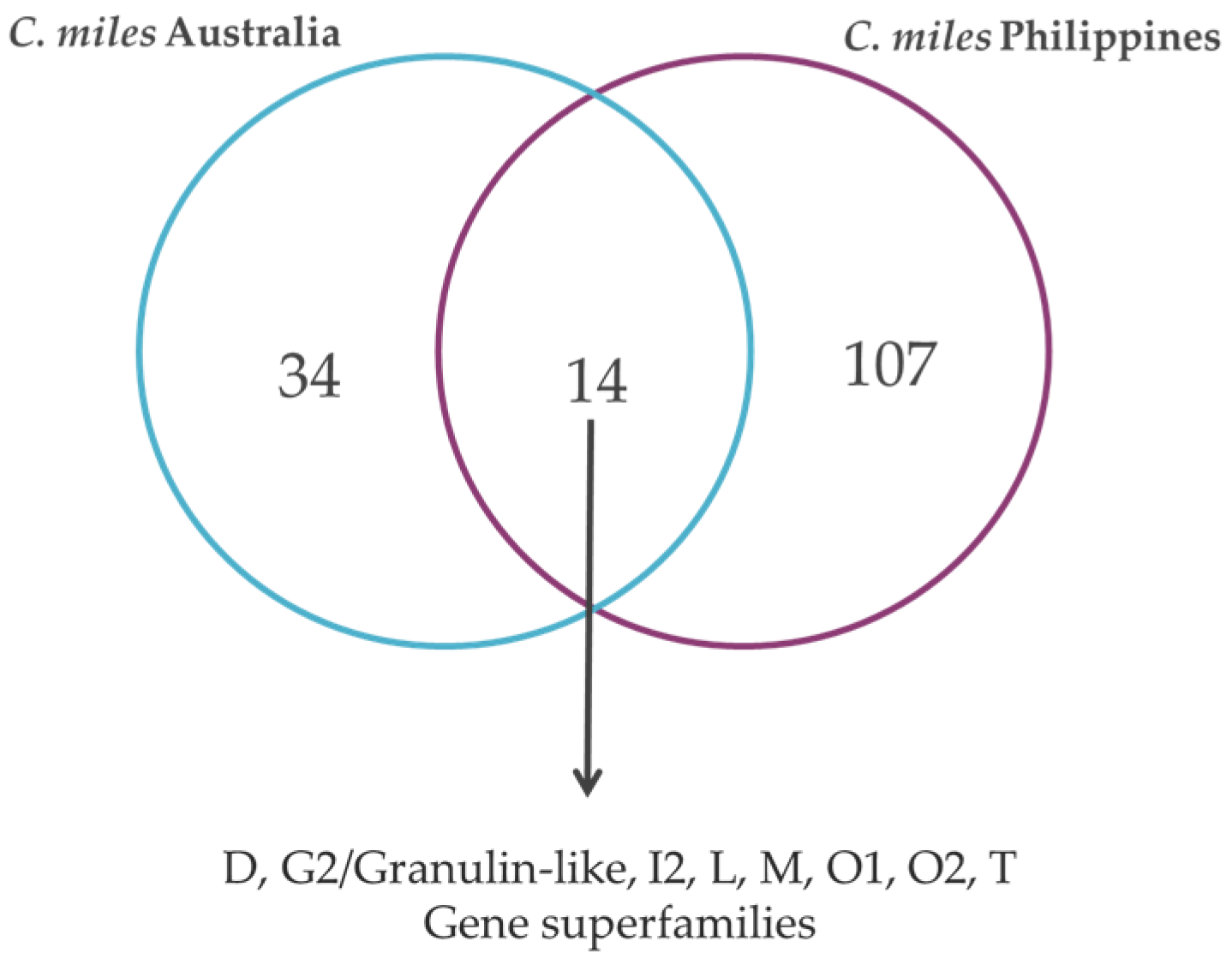
2.3. Conopeptide Diversity
2.4. Relative Gene Expression Profile of Rhizoconus
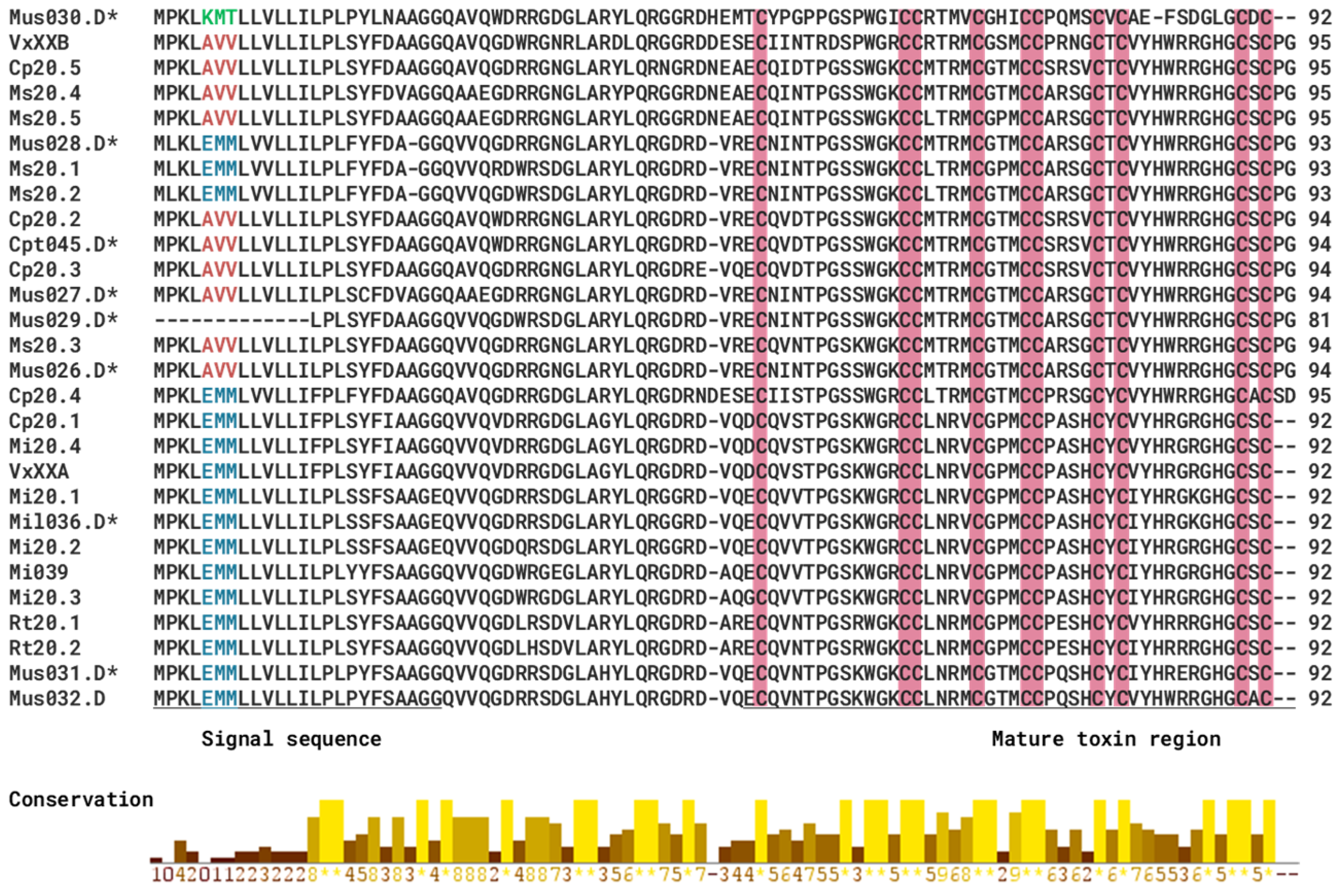
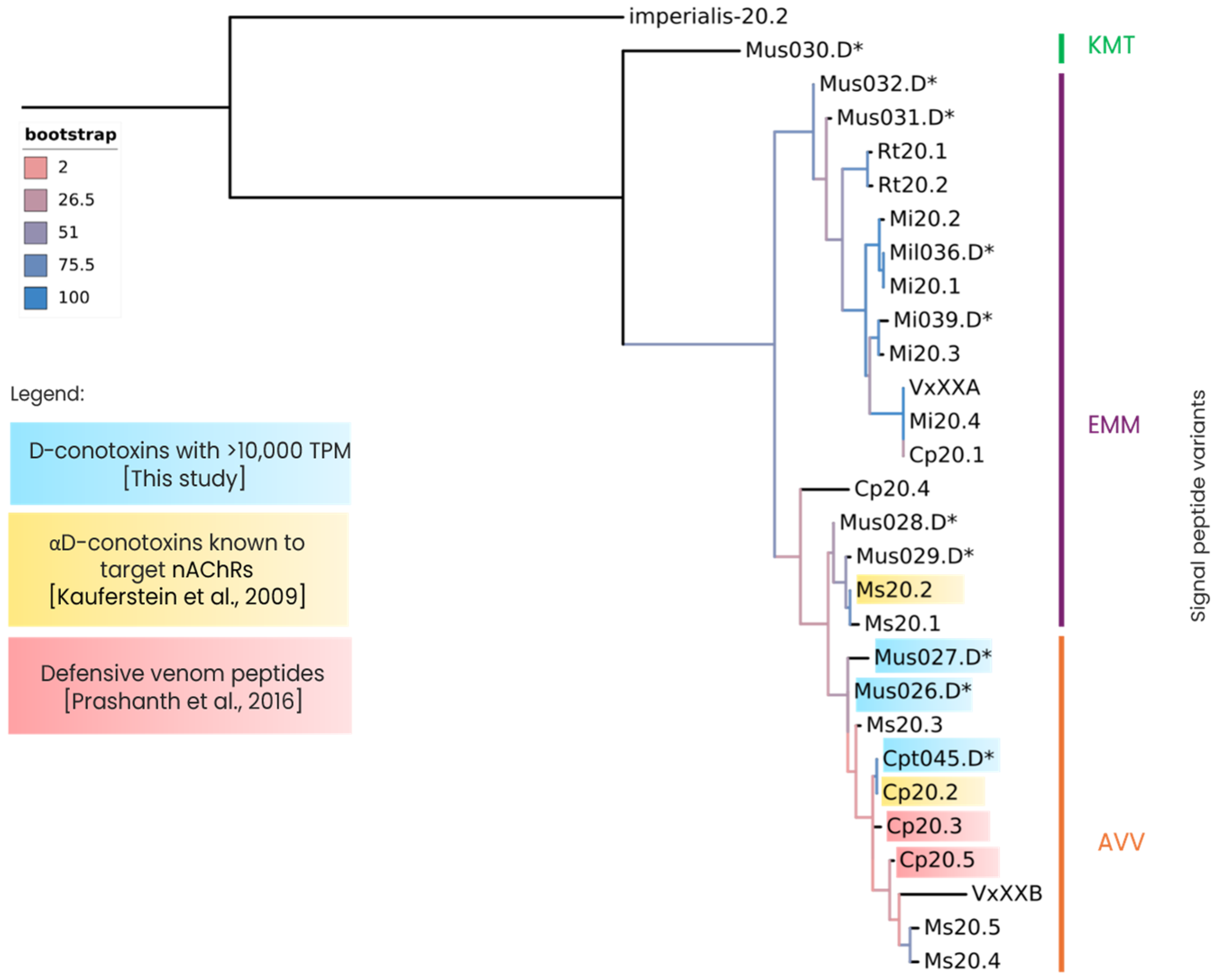
2.5. Gene Superfamilies with Sequence Similarity to Other Previously Studied Rhizoconus Conotoxins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection, Extraction, Sequencing, and Assembly
4.2. Putative Conopeptide Prediction
4.3. Quantification of Transcript Level Expression
4.4. Naming Assignment of Conotoxin Candidates
4.5. Assignment of Cysteine Framework Patterns
4.6. Shannon’s Diversity Index of Venom Conopeptides
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olivera, B.M. Conus Peptides: Biodiversity-based Discovery and Exogenomics. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 31173–31177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Antunes, A. Biomedical Potential of the Neglected Molluscivorous and Vermivorous Conus Species. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aman, J.W.; Imperial, J.S.; Ueberheide, B.; Zhang, M.M.; Aguilar, M.; Taylor, D.; Watkins, M.; Yoshikami, D.; Showers-Corneli, P.; Safavi-Hemami, H.; et al. Insights into the Origins Of Fish Hunting in Venomous Cone Snails from Studies of Conus Tessulatus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5087–5092. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duda, T.F.; Kohn, A.J. Species-Level Phylogeography and Evolutionary History of the Hyperdiverse Marine Gastropod Genus Conus. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2005, 34, 257–272. [Google Scholar]
- Imperial, J.; Silverton, N.; Olivera, B.M.; Bandyopadhay, P.; Sporning, A.; Ferber, M.; Terlau, H. Using Chemistry to Reconstruct Evolution: On the Origins of Fish-Hunting in Venomous Cone Snails. Proc. Am. Philos. Soc. 2017, 151, 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, T.F.; Kohn, A.J.; Palumbi, S.R. Origins of Diverse Feeding Ecologies within Conus, a Genus of Venomous Marine Gastropods. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2001, 73, 391–409. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera, B.M.; Showers-Corneli, P.; Watkins, M.; Fedosov, A. Biodiversity of Cone Snails and Other Venomous Marine Gastropods: Evolutionary Success through Neuropharmacology. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2014, 2, 487–513. [Google Scholar]
- Akondi, K.B.; Muttenthaler, M.; Dutertre, S.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Discovery, Synthesis, and Structure-activity Relationships of Conotoxins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5815–5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavergne, V.; Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.H.; Lewis, R.J.; Taft, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Systematic Interrogation of the Conus marmoreus Venom Duct transcriptome with ConoSorter reveals 158 Novel Conotoxins and 13 New Gene Superfamilies. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 708. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera, B.M.; Watkins, M.; Bandyopadhyay, P.; Imperial, J.S.; de la Cotera, E.P.; Aguilar, M.B.; Vera, E.L.; Concepcion, G.P.; Lluisma, A. Adaptive Radiation of Venomous Marine Snail Lineages and the Accelerated Evolution of Venom Peptide Genes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1267, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Terlau, H.; Olivera, B.M. Conus venoms: A Rich Source of Novel Ion Channel-Targeted Peptides. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Li, C.; Dong, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhangsun, D.; Luo, S. Discovery Methodology of Novel Conotoxins from Conus species. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.D.; Li, Q.; Lu, A.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Yandell, M.; Olivera, B.M.; Safavi-Hemami, H. The Venom Repertoire of Conus gloriamaris (Chemnitz, 1777), the Glory of the Sea. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtigall, P.G.; Rautsaw, R.M.; Ellsworth, S.A.; Mason, A.J.; Rokyta, D.R.; Parkinson, C.L.; Junqueira-De-Azevedo, I.L.M. ToxCodAn: A New Toxin Annotator and Guide to Venom Gland Transcriptomics. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab095. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, A.H.; Dutertre, S.; Kaas, Q.; Lavergne, V.; Kubala, P.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Transcriptomic Messiness in the Venom Duct of Conus miles Contributes to Conotoxin Diversity. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 3824–3833. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, A.; Chen, S.; Xu, A. Identifying Novel Conopepetides from the Venom Ducts of Conus litteratus through Integrating Transcriptomics and Proteomics. J. Proteom. 2019, 192, 346–357. [Google Scholar]
- Abalde, S.; Tenorio, M.J.; Afonso, C.M.L.; Zardoya, R. Comparative Transcriptomics of the Venoms of Continental and Insular Radiations of West African Cones. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20200794. [Google Scholar]
- Dutt, M.; Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.H.; Lavergne, V.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Venomics Reveals Venom Complexity of the Piscivorous Cone Snail, Conus tulipa. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.H.; Dutertre, S.; Dutt, M.; Lavergne, V.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Transcriptomic-Proteomic Correlation in the Predation-Evoked Venom of the Cone Snail, Conus imperialis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Florea, L. Rcorrector: Efficient and Accurate Error Correction for Illumina RNA-seq reads. GigaScience 2015, 4, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Huang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Han, Y.; Xu, M.; Gu, J. AfterQC: Automatic Filtering, Trimming, Error Removing and Quality Control for Fastq Data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-Length Transcriptome Assembly from RNA-Seq Data Without a Reference Genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, C.Z.; Xu, C.Q.; Fan, C.X.; Dai, X.D.; Chen, J.S.; Chi, C.W. A Novel M-superfamily Conotoxin with a Unique Motif from Conus vexillum. Peptides 2006, 27, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.D.; Safavi-Hemami, H.; McIntosh, L.D.; Purcell, A.W.; Norton, R.S.; Papenfuss, A.T. Diversity of Conotoxin Gene Superfamilies in the Venomous Snail, Conus victoriae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, M.A.; Mahardika, G.N.; Alfaro, M.E. Dietary Breadth is Positively Correlated with Venom Complexity in Cone Snails. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 401. [Google Scholar]
- Fedosov, A.; Tucci, C.F.; Kantor, Y.; Farhat, S.; Puillandre, N. Collaborative Expression: Transcriptomics of Conus virgo Suggests Contribution of Multiple Secretory Glands to Venom Production. J. Mol. Evol. 2023, 91, 837–853. [Google Scholar]
- Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.H.; Kaas, Q.; Jones, A.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Deep Venomics Reveals the Mechanism for Expanded Peptide Diversity in Cone Snail Venom. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 312–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauferstein, S.; Kendel, Y.; Nicke, A.; Coronas, F.I.V.; Possani, L.D.; Favreau, P.; Križaj, I.; Wunder, C.; Kauert, G.; Mebs, D. New Conopeptides of the D-Superfamily Selectively Inhibiting Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxicon 2009, 54, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughnan, M.L.; Nicke, A.; Lawrence, N.; Lewis, R.J. Novel Alpha D-Conopeptides and their Precursors Identified By cDNA Cloning Define the D-Conotoxin Superfamily. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 3717–3729. [Google Scholar]
- Prashanth, J.R.; Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.H.; Lavergne, V.; Hamilton, B.; Cardoso, F.C.; Griffin, J.; Venter, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. The Role of Defensive Ecological Interactions in the Evolution of Conotoxins. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 598–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhangsun, D.; Feng, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y. Diversity of the O-superfamily conotoxins from Conus miles. J. Pept. Sci. 2007, 13, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramiro, I.B.L.; Bjørn-Yoshimoto, W.E.; Imperial, J.S.; Gajewiak, J.; Florez Salcedo, P.; Watkins, M.; Taylor, D.; Resager, W.; Ueberheide, B.; Brauner-Osborne, H.; et al. Somatostatin Venom Analogs Evolved by Fish-Hunting Cone Snails: From Prey Capture Behavior to Identifying Drug Leads. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, 1410. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, A.H.; Dekan, Z.; Smout, M.J.; Wilson, D.; Dutertre, S.; Vetter, I.; Lewis, R.J.; Loukas, A.; Daly, N.L.; Alewood, P.F. Conotoxin Φ-MiXXVIIA from the Superfamily G2 Employs a Novel Cysteine Framework that Mimics Granulin and Displays Anti-Apoptotic Activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14973–14976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, B.M. Conus Venom Peptides: Reflections from the Biology of Clades and Species. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2002, 33, 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, A.J. Maximal Species Richness in Conus: Diversity, Diet and Habitat on Reefs of Northeast Papua New Guinea. Coral Reefs 2001, 20, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Elliger, C.A.; Richmond, T.A.; Lebaric, Z.N.; Pierce, N.T.; Sweedler, J.V.; Gilly, W.F. Diversity of Conotoxin Types from Conus californicus Reflects a Diversity of Prey Types and a Novel Evolutionary History. Toxicon 2011, 57, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remigio, E.A.; Duda, T.F. Evolution of Ecological Specialization and Venom of a Predatory Marine Gastropod. Mol. Ecol. 2008, 17, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himaya, S.W.A.; Arkhipov, A.; Yum, W.Y.; Lewis, R.J. Comparative Venomics of C. flavidus and C. frigidus and Closely Related Vermivorous Cone Snails. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Dutertre, S.; Vetter, I.; Christie, M.J. Conus Venom Peptide Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 259–298. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J. Hormone-Like Conopeptides—New Tools for Pharmaceutical Design. RSC Med. Chem. 2020, 11, 1235–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Olivera, B.M.; Seger, J.; Horvath, M.P.; Fedosov, A.E. Prey-capture Strategies of Fish-hunting Cone Snails: Behavior, neurobiology and evolution. Brain Behav. Evol. 2015, 86, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Safavi-Hemami, H.; Hu, H.; Gorasia, D.G.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Veith, P.D.; Young, N.D.; Reynolds, E.C.; Yandell, M.; Olivera, B.M.; Purcell, A.W. Combined Proteomic and Transcriptomic Interrogation of the Venom Gland of Conus geographus Uncovers Novel Components and Functional Compartmentalization. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 938–953. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, S.; Norton, R. Conotoxin gene superfamilies. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 6058–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barghi, N.; Concepcion, G.P.; Olivera, B.M.; Lluisma, A.O. Comparison of the Venom Peptides and Their Expression in Closely Related Conus Species: Insights into Adaptive Post-Speciation Evolution of Conus Exogenomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2015, 7, 1797–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, G.; Peng, C.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, C.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J.; Cao, Y.; Shi, Q. High-Throughput Identification and Analysis of Novel Conotoxins from Three Vermivorous Cone Snails by Transcriptome Sequencing. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughnan, M.; Nicke, A.; Jones, A.; Schroeder, C.I.; Nevin, S.T.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Identification of a Novel Class of Nicotinic Receptor Antagonists: Dimeric Conotoxins VxXIIA, VxXIIB, and VxXIIC from Conus vexillum. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 24745–24755. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, T.; Kompella, S.N.; Yan, M.; Lu, A.; Wang, Y.; Shao, X.; Chi, C.; Adams, D.J.; Ding, J.; et al. Conotoxin αD-GeXXA Utilizes a Novel Strategy to Antagonize Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14261. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Sámano, A.C.; Falcón, A.; Zamudio, F.; Batista, C.V.; Michel-Morfín, J.E.; Landa-Jaime, V.; López-Vera, E.; Jeziorski, M.C.; Aguilar, M.B. αD-Conotoxins in Species of the Eastern Pacific: The Case of Conus princeps from Mexico. Toxins 2019, 11, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ruiz, X.C.; Aguilar, M.B.; Ortíz-Arellano, M.A.; Safavi-Hemami, H.; López-Vera, E. A Novel Dimeric Conotoxin, FrXXA, from the Vermivorous Cone Snail Conus fergusoni, of the Eastern Pacific, Inhibits Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Toxins 2022, 14, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, M.W.; Rueter, L.E.; Bitner, R.S. Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonists: A Potential New Class of Analgesics. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2004, 4, 369–384. [Google Scholar]
- Giribaldi, J.; Dutertre, S. α-Conotoxins to Explore the Molecular, Physiological and Pathophysiological Functions of Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 679, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.G. The Characterization of Conotoxins. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 2000, 19, 53–93. [Google Scholar]
- Mebs, D.; Kordiš, D.; Kendel, Y.; Kauferstein, S. The Evolution of αD-Conopeptides Targeting Neuronal Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Acta Chim. Slov. 2011, 58, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ratibou, Z.; Inguimbert, N.; Dutertre, S. Predatory and Defensive Strategies in Cone Snails. Toxins 2024, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluisma, A.O.; Milash, B.A.; Moore, B.; Olivera, B.M.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K. Novel Venom Peptides from the Cone Snail Conus Pulicarius Discovered Through Next-Generation Sequencing of its Venom Duct Transcriptome. Mar. Genom. 2012, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Barghi, N.; Lu, A.; Fedosov, A.E.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Lluisma, A.O.; Concepcion, G.P.; Yandell, M.; Olivera, B.M.; Safavi-Hemami, H. Divergence of the Venom Exogene Repertoire in Two Sister Species of Turriconus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 2211–2225. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.D.; Han, Y.H.; Wang, C.G.; Chi, C.W. From the Identification of Gene Organization of Alpha Conotoxins to the Cloning of Novel Toxins. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1135–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Puillandre, N.; Bouchet, P.; Duda, T.; Kauferstein, S.; Kohn, A.; Olivera, B.; Watkins, M.; Meyer, C. Molecular phylogeny and evolution of the cone snails (Gastropoda, Conoidea). Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2014, 78, 290–303. [Google Scholar]
- Whiteaker, P.; Christensen, S.; Yoshikami, D.; Dowell, C.; Watkins, M.; Gulyas, J.; Rivier, J.; Olivera, B.M.; McIntosh, J.M. Discovery, Synthesis, and Structure Activity of a Highly Selective α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonist. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 6628–6638. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; You, Y.; Zhu, X.; Qiang, Y.; Qin, M.; Luo, S.; Ren, Z.; Xu, A. Molecular Evolution and Diversity of Conus Peptide Toxins, as Revealed by Gene Structure and Intron Sequence Analyses. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82495. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, A.; Kompella, S.N.; Akondi, K.B.; Melaun, C.; Daly, N.L.; Luetje, C.W.; Alewood, P.F.; Craik, D.J.; Adams, D.J.; Marí, F. RegIIA: An α4/7-Conotoxin from the Venom of Conus regius that Potently Blocks α3β4 nAChRs. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaas, Q.; Westermann, J.; Craik, D.J. Conopeptide characterization and classifications: An analysis using ConoServer. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1491–1509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, A.; Watkins, M.; Li, Q.; Robinson, S.D.; Concepcion, G.P.; Yandell, M.; Weng, Z.; Olivera, B.M.; Safavi-Hemami, H.; Fedosov, A.E. Transcriptomic Profiling Reveals Extraordinary Diversity of Venom Peptides in Unexplored Predatory Gastropods of the Genus Clavus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2020, 12, 684. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, T.L.; Ramiro, I.B.L.; Salcedo, P.F.; Engholm, E.; Jensen, K.J.; Chase, K.; Olivera, B.M.; Bjørn-Yoshimoto, W.E.; Safavi-Hemami, H. Reconstructing the Origins of the Somatostatin and Allatostatin-C signaling Systems Using the Accelerated Evolution of Biodiverse Cone Snail Toxins. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2022, 39, msac075. [Google Scholar]
- Bateman, A.; Bennett, H.P. The Granulin Gene Family: From Cancer to Dementia. BioEssays News Rev. Mol. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2009, 31, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, R.B.; Jimenez, E.C.; De la Cruz, R.G.C.; Gray, W.R.; Cruz, L.J.; Olivera, B.M. A Novel D-Leucine-Containing Conus Peptide: Diverse Conformational Dynamics in the Contryphan Family. J. Pept. Res. 1999, 54, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, A.M.; Dutertre, S.; Lewis, R.J.; Marí, F. Intraspecific Variations in Conus purpurascens Injected Venom Using LC/MALDI-TOF-MS and LC-ESI-TripleTOF-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6105–6116. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.B.S.; Baker, M.R.; Kim, D.H.; LeRoy, M.; Toribo, P.; Bingham, J.P. Cone Snail Milked Venom Dynamics—A Quantitative Study of Conus purpurascens. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinology 2012, 60, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Möller, C.; Marí, F. 9.3 kDa Components of the Injected Venom of Conus purpurascens Define a New 5-disulfide Conotoxin Framework. Biopolymers 2011, 96, 158. [Google Scholar]
- Grandal, M.; Hoggard, M.; Neely, B.; Davis, W.C.; Marí, F. Proteogenomic Assessment of Intraspecific Venom Variability: Molecular Adaptations in the Venom Arsenal of Conus purpurascens. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100100. [Google Scholar]
- Safavi-Hemami, H.; Siero, W.A.; Gorasia, D.G.; Young, N.D.; MacMillan, D.; Williamson, N.A.; Purcell, A.W. Specialisation of the Venom Gland Proteome in Predatory Cone Snails Reveals Functional Diversification of the Conotoxin Biosynthetic Pathway. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3904–3919. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Olenzek, A.M.; Duda, T.F., Jr. Effects of Geographical Heterogeneity in Species Interactions on the Evolution of Venom Genes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20141984. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Peng, C.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, T.; Huang, Y.; Shi, Q. High Throughput Identification of Novel Conotoxins from the Vermivorous Oak Cone Snail (Conus quercinus) by Transcriptome Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.; Vetter, I.; Hamilton, B.; Sunagar, K.; Lavergne, V.; Dutertre, V.; Fry, B.G.; Antunes, A.; Venter, D.J.; et al. Evolution of Separate Predation- and Defence-Evoked Venoms in Carnivorous Cone Snails. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Abdel-Nabi, I.M.; El-Naggar, M.S.; Abbas, O.A.; Strong, P.N. Intraspecific Variation in the Venom of the Vermivorous Cone Snail Conus vexillum. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 154, 318–325. [Google Scholar]
- Prator, C.A.; Murayama, K.M.; Schulz, J.R. Venom Variation during Prey Capture by the Cone Snail, Conus textile. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98991. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Remarkable Inter- and Intraspecies Complexity of Conotoxins Revealed by LC/MS. Peptides 2009, 30, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Dutertre, S.; Biass, D.; Stocklin, R.; Favreau, P. Dramatic Intraspecimen Variations Within the Injected Venom of Conus consors: An Unsuspected Contribution to Venom Diversity. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski, J.A.; Kelley, W.P.; Sweedler, J.V.; Gilly, W.F.; Schulz, J.R. Intraspecific Variation of Venom Injected by Fish-hunting Conus snails. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 2873–2883. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 8 March 2022).
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar]
- Pardos-Blas, J.R.; Irisarri, I.; Abalde, S.; Tenorio, M.J.; Zardoya, R. Conotoxin Diversity in the Venom Gland Transcriptome of the Magician’s Cone, Pionoconus magus. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashanth, J.R.; Lewis, R.J. An Efficient Transcriptome Analysis Pipeline to Accelerate Venom Peptide Discovery and Characterisation. Toxicon 2015, 107 Pt B, 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and Sensitive Protein Alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2014, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koua, D.; Ebou, A.; Dutertre, S. Improved Prediction of Conopeptide Superfamilies with ConoDictor 2.0. Bioinform. Adv. 2021, 1, vbab011. [Google Scholar]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and Sequence Analysis Tools Services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, Q.; Yu, R.; Jin, A.H.; Dutertre, S.; Craik, D.J. ConoServer: Updated Content, Knowledge, and Discovery Tools in the Conopeptide Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D325–D330. [Google Scholar]
- Teufel, F.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 Predicts All Five Types of Signal Peptides using Protein Language Models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Abalde, S.; Tenorio, M.J.; Afonso, C.M.L.; Zardoya, R. Conotoxin Diversity in Chelyconus ermineus (Born, 1778) and the Convergent Origin of Piscivory in the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific Cones. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate Transcript Quantification from RNA-Seq data With or Without A Reference Genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, T.L.; Robinson, S.D.; Salcedo, P.F.; Chase, K.; Biggs, J.; Fedosov, A.E.; Yandell, M.; Olivera, B.M.; Safavi-Hemami, H. Prey Shifts Drive Venom Evolution in Cone Snails. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae120. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, R.; Masacupan, D.J.; Lluisma, A. Diversity and Novelty of Venom Peptides from Conus (Asprella) rolani Revealed by Analysis of its Venom Duct Transcriptome. SciEnggJ 2024, 17, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørn-Yoshimoto, W.E.; Ramiro, I.B.L.; Yandell, M.; McIntosh, J.M.; Olivera, B.M.; Ellgaard, L.; Safavi-Hemami, H. Curses or Cures: A Review of the Numerous Benefits Versus the Biosecurity Concerns of Conotoxin Research. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.S.; Steel, D.; Jacobsen, R.B.; Lirazan, M.B.; Cruz, L.J.; Hooper, D.; Shetty, R.; DelaCruz, R.C.; Nielsen, J.S.; Zhou, L.M.; et al. The T-superfamily of Conotoxins. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30664–30671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Zhangsun, D.; Luo, S. Diversity of Conopeptides and Their Precursor Genes of Conus litteratus. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassio, G.; Modica, M.V.; Mary, L.; Zaharias, P.; Fedosov, A.E.; Gorson, J.; Kantor, Y.I.; Holford, M.; Puillandre, N. Venom Diversity and Evolution in the Most Divergent Cone Snail Genus Profundiconus. Toxins 2019, 11, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.; Blanchet, F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 24 August 2024).
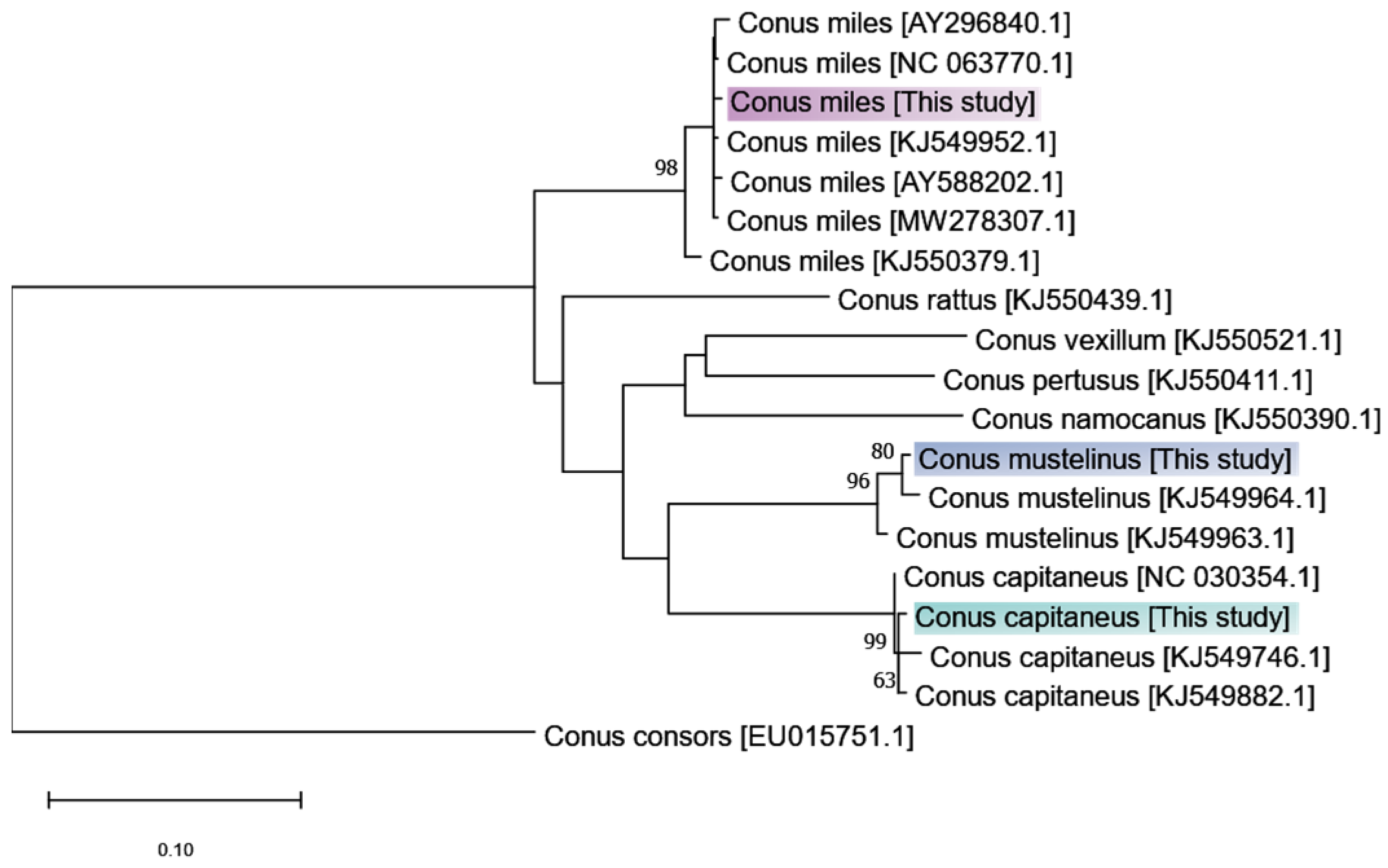
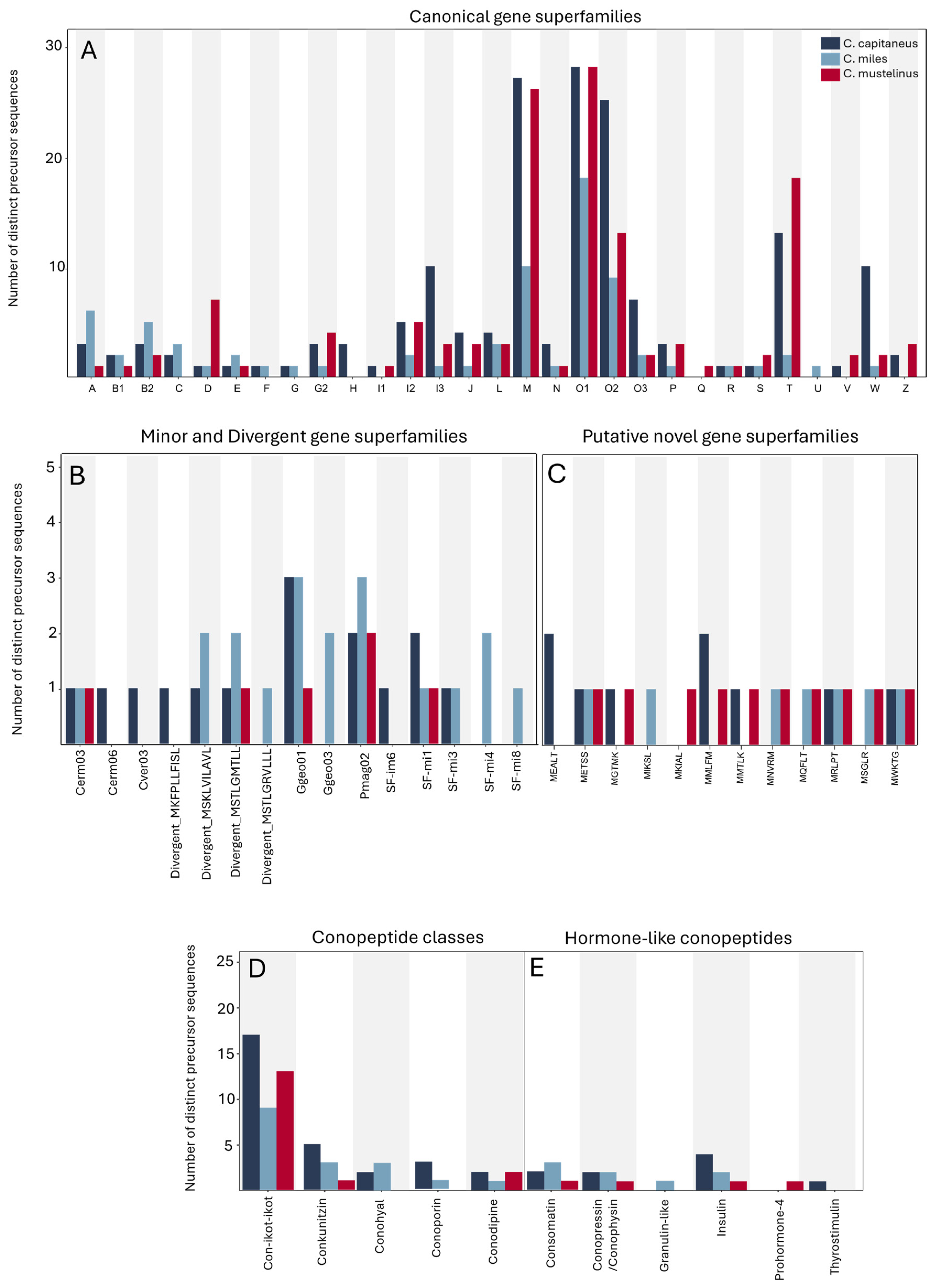
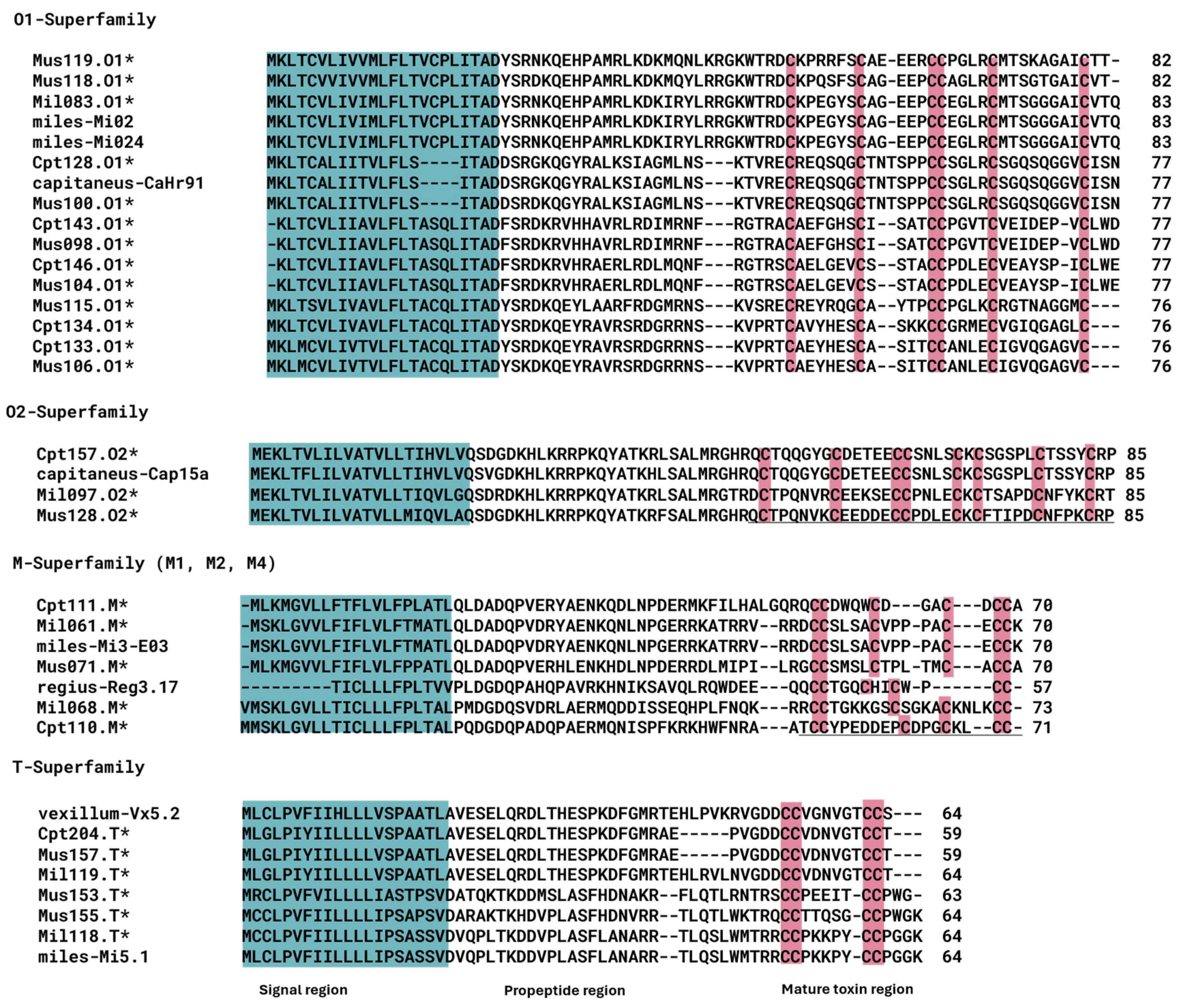
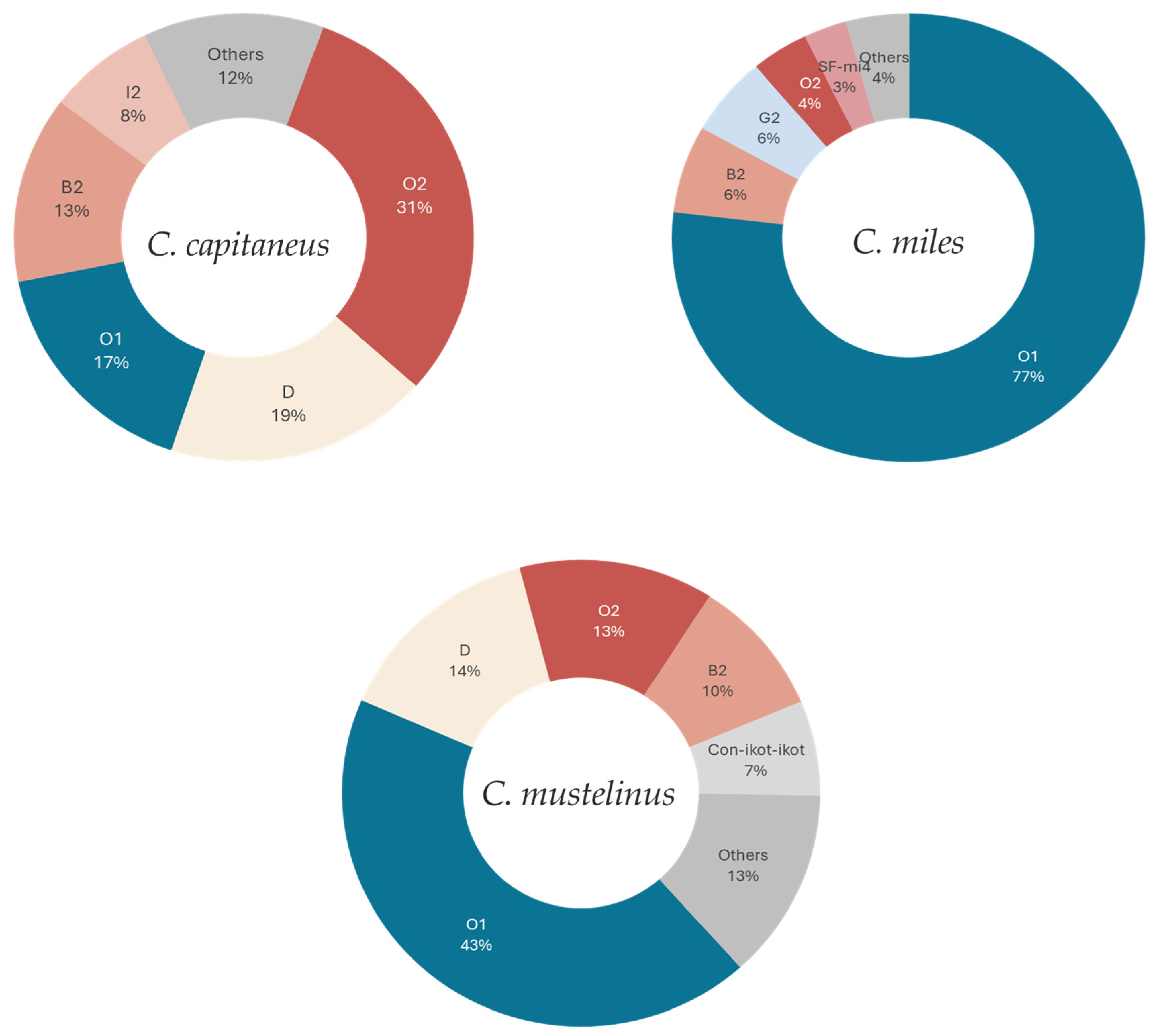


| C. capitaneus | C. miles | C. mustelinus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of transcripts | 133,698 | 56,751 | 77,764 |
| Mean length (bp) | 599.38 | 480.46 | 538.21 |
| Number of contigs >1 kb | 18,029 | 4514 | 8333 |
| N50 | 801 | 540 | 664 |
| RSEM% alignment rate | 81.48 | 88.84 | 87.57 |
| DETONATE score (×109) | −2.269 | −1.171 | −2.168 |
| Species | Number of Superfamilies | Unique Conopeptide Sequences | Shannon Diversity Index | Evenness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. capitaneus | 53 | 225 | 3.30 | 0.73 |
| C. miles | 48 | 121 | 3.43 | 0.76 |
| C. mustelinus | 45 | 168 | 3.04 | 0.78 |
| Species | Diet | No. of Unique Conopeptide Precursors | % Total TPM Attributed to Conopeptides | Sequencing Platform | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. capitaneus | V | 225 | 19.0% | Illumina | This study |
| C. miles | V | 121 | 56.1% | ||
| C. mustelinus | V | 168 | 51.5% | ||
| C. rattus | V | 102 | 35.5% | Illumina | [25] |
| C. quercinus | V | 97 | 49.5% | ||
| C. californicus | G | 185 | 26.0% | ||
| C. geographus | P | 136 | 9.33% | Illumina | [26] |
| C. rolani | P | 110 | 13.96% | ||
| C. striatus | P | 212 | 43.71% |
| Hormone-like Conopeptides | TPM Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C. capitaneus | C. miles | C. mustelinus | |
| C/Consomatin | 4.96 | 8.94 | 24.15 |
| Insulin | 20.76 | 9.08 | 599.34 |
| Conopressin/conophysin | 5.41 | 33.5 | 1.24 |
| G2/Granulin-like | - | 32,050.46 | - |
| Thyrostimulin | 1.46 | - | - |
| Prohormone-4 | - | - | 142.69 |
| Protein Sequence (MS/MS >99% Confidence) | C. miles ID [19] | Superfamily | ID of Identical Peptides in C. miles Transcriptome in this Study | TPM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECREKGQGCTNTALCCPGLECEGQSQGGLCVDN | Mi001 | O1 | Mil078.O1; Mil082.O1 | 424,403.49; 1070.07 |
| GGGCSQHPHCCGGTCNK | Mi023 | O1 | Mil084.O1 | 198 |
| CTDDSQFCNPSNHDCCSGKCIDEGDNGICAIVPENS | Mi027 | O1 | Mil081.O1 | 1091.49 |
| CPNLTCKCSGSPLCTRYRCKT | Mi035 | O2 | Mil1096.O2 | 11,896.05 |
| CKCTSAPDCNFYKCRT | Mi036 | O2 | Mil097.O2; Mil099.O2 | 5218.27; 1969.75 |
| DCCSLSACVPPPACECCK | Mi040 | M | Mil061.M | 6763.05 |
| SSCPPACCPTC | Mi041 | L | Mil059.L | 355.09 |
| CCPKKPYCCPG | Mi042 | T | Mil118.T | 40.53 |
| VPCQQGGGK | Mi043 | I2 | Mil052.I2 | 99.93 |
| CMPCGGECCCEPNSCIDGTCHHE | Mi045 | G2 (Granulin-like) | Mil046.G2 | 32,050.46 |
| MLKVGVVFLVFLVLLSLADSWNGDNPGRQRGEKQSPQRNVFRSNLRKYNSYQKRRCANSTPCGECTDEGKICQVQPGGKGTCGECVPNTR | Mi040 | M | Mil062.M | 258.31 |
| MSKTGLVLVVLYLLSSPVNLQQNEDDQAFSKIETRDRPECYNCFPNDDGHCVGTCCGEDSCKGGIRGCGCL | Mi044 | SF-mi1 | Mil113.SF-mi1 | 20.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Florece, C.M.C.; Kaas, Q.; Barghi, N.; Lluisma, A.O. Diversity and Novelty of Venom Peptides in Vermivorous Cone Snails, Subgenus Rhizoconus (Gastropoda: Mollusca). Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070266
Florece CMC, Kaas Q, Barghi N, Lluisma AO. Diversity and Novelty of Venom Peptides in Vermivorous Cone Snails, Subgenus Rhizoconus (Gastropoda: Mollusca). Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(7):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070266
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlorece, Christine Marie C., Quentin Kaas, Neda Barghi, and Arturo O. Lluisma. 2025. "Diversity and Novelty of Venom Peptides in Vermivorous Cone Snails, Subgenus Rhizoconus (Gastropoda: Mollusca)" Marine Drugs 23, no. 7: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070266
APA StyleFlorece, C. M. C., Kaas, Q., Barghi, N., & Lluisma, A. O. (2025). Diversity and Novelty of Venom Peptides in Vermivorous Cone Snails, Subgenus Rhizoconus (Gastropoda: Mollusca). Marine Drugs, 23(7), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23070266






