Heterologous Expression and Biochemical Characterization of a New α-Amylase from Nocardiopsis aegyptia HDN19-252 of Antarctic Animal Origin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Strain Identification
2.2. Identification and Sequence Analysis of Alpha-Amylase
2.3. Recombinant Expression and Purification of Alphaz
2.4. Effects of Temperature and pH on Alphaz
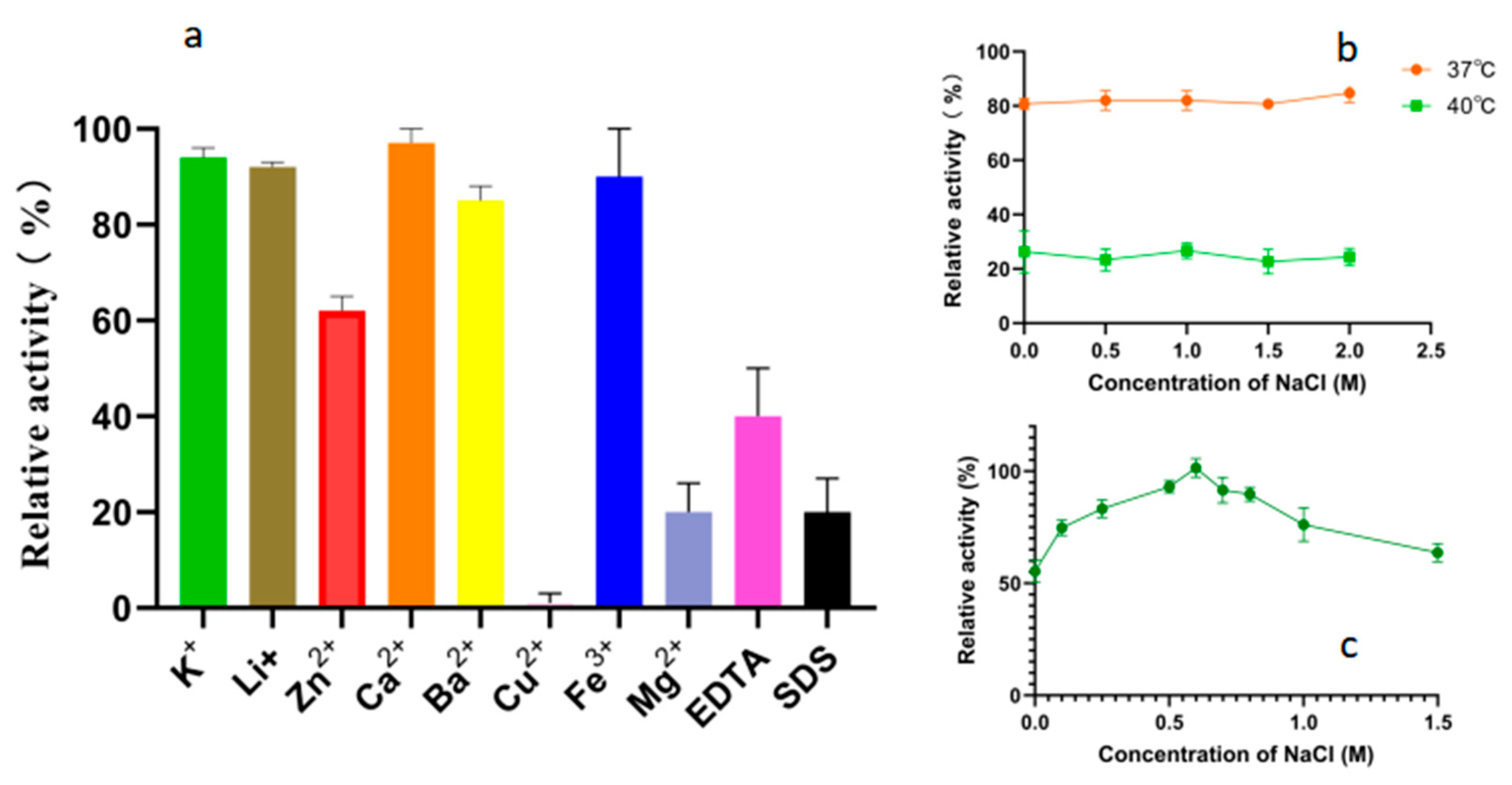
2.5. Effects of Metal Ions, Chelators, and Surfactants on Alphaz
2.6. Substrate Specificity of Alphaz
2.7. Enzymatic Kinetic Parameters
2.8. The Structure and Catalytic Site Prediction of Alphaz
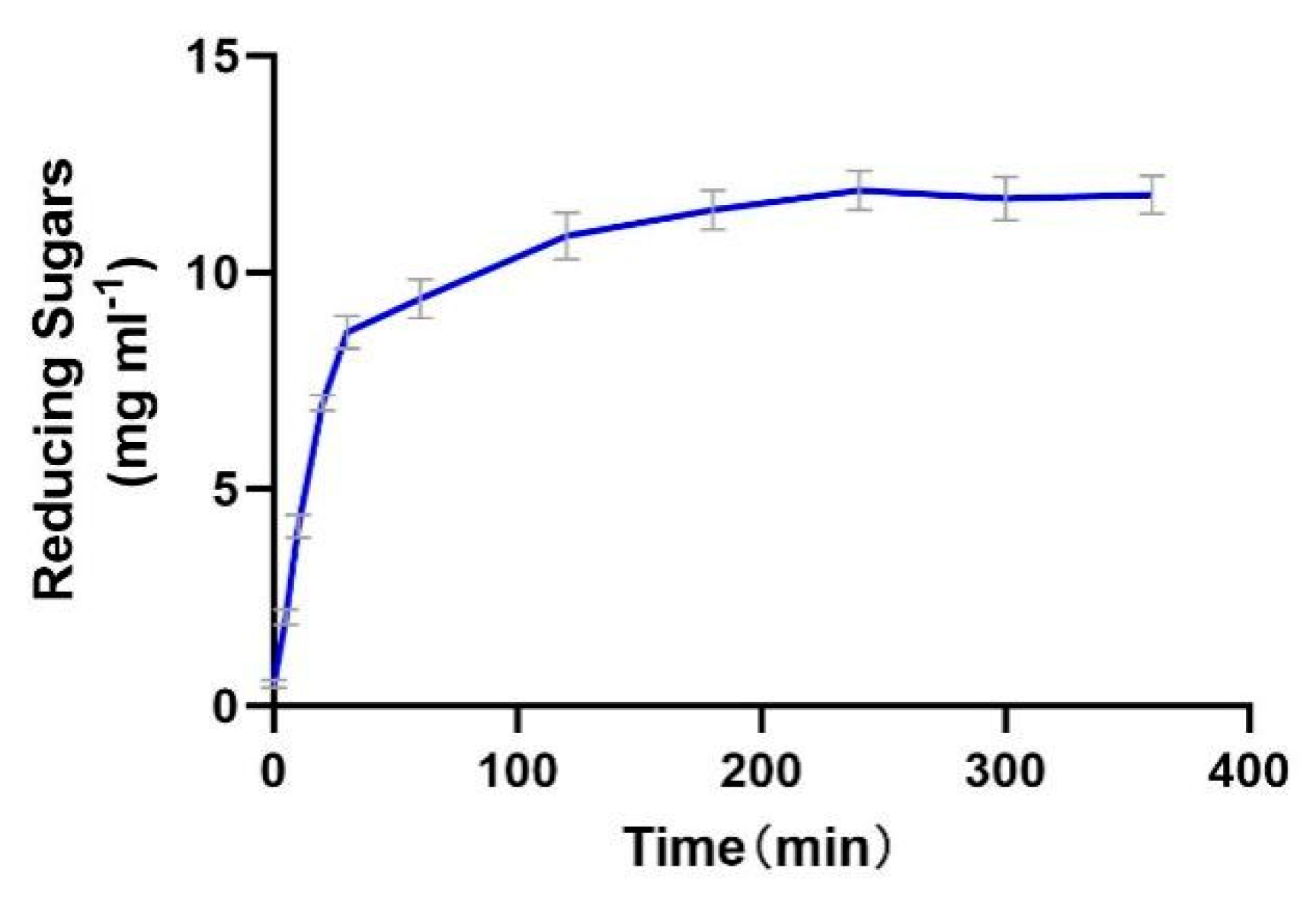
2.9. The Productivity Curve of Alphaz
2.10. Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Isolation of Nocardiopsis Aegyptia HDN19-252
3.3. Identification of Strain HDN19-252
3.4. Sequence Analysis of Alphaz
3.5. Recombinant Expression and Purification of Alphaz
3.6. Enzyme Activity Determination of Alphaz
3.7. Biochemical Characterization of Alphaz
3.8. Substrate Specificity Analysis of Alphaz
3.9. Bioinformatic Analysis
3.10. The Determination of the Productivity Curve of Alphaz
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Lombard, V.; Golaconda Ramulu, H.; Drula, E.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. The carbohydrate—Active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D490–D495. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, X.; Yang, Q. Glycoside hydrolase family 18 chitinases: The known and the unknown. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 43, 107553. [Google Scholar]
- Suriya, J.; Bharathiraja, S.; Krishnan, M.; Manivasagan, P.; Kim, S.K. Marine Microbial Amylases: Properties and Applications. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 79, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golgeri, M.D.B.; Mulla, S.I.; Bagewadi, Z.K.; Tyagi, S.; Hu, A.; Sharma, S.; Bilal, M.; Bharagava, R.N.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Gurumurthy, D.M.; et al. A systematic review on potential microbial carbohydrases: Current and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 438–455. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Bagley, D.M.; Leung, K.T.; Liss, S.N.; Liao, B.Q. Recent advances in membrane technologies for biorefining and bioenergy production. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 817–858. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wei, C. Morphology, structure, properties and applications of starch ghost: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 2084–2096. [Google Scholar]
- Morlighem, J.R.L.; Radis-Baptista, G. The Place for Enzymes and Biologically Active Peptides from Marine Organisms for Application in Industrial and Pharmaceutical Biotechnology. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 334–355. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wang, J.B.; Reetz, M.T. Biocatalysts for the pharmaceutical industry created by structure-guided directed evolution of stereoselective enzymes. Bioorg Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Scali, M.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Wu, X. Genetic Engineering of Starch Biosynthesis in Maize Seeds for Efficient Enzymatic Digestion of Starch during Bioethanol Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.P.; Morais, M.A.B.; Persinoti, G.F.; Galinari, R.H.; Yu, L.; Yoshimi, Y.; Passos Nunes, F.B.; Lima, T.B.; Barbieri, S.F.; Silveira, J.L.M.; et al. Glycoside hydrolase subfamily GH5_57 features a highly redesigned catalytic interface to process complex hetero-β-mannans. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2022, 78 Pt 11, 1358–1372. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, M.; Kumar, P.; Singh, R.; Sindhu, J.; Kataria, R. Design, synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, single crystal X-ray analysis, in vitro α-amylase inhibition assay, DPPH free radical evaluation and computational studies of naphtho[2,3-d]imidazole-4,9-dione appended 1,2,3-triazoles. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 250, 115230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biwer, A.; Antranikian, G.; Heinzle, E. Enzymatic production of cyclodextrins. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, B. Protein engineering in the alpha-amylase family: Catalytic mechanism, substrate specificity, and stability. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 25, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemhuis, H.; Dijkstra, B.W.; Dijkhuizen, L. Engineering α-amylases for cyclodextrin production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 5269–5282. [Google Scholar]
- Ashok, P.P.; Dasgupta, D.; Ray, A.; Suman, S.K. Challenges and prospects of microbial α-amylases for industrial application: A review. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 40, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Kumar, S.; Singh, R. Microbial α-amylases: Innovations and industrial applications. Biotechol. Adv. 1999, 42, 107579. [Google Scholar]
- Demain, A.L.; Elander, R.P. The β-lactam antibiotics: Past, present, and future. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1999, 75, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Introducing the concept of prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.S.; Saini, G.K.; Kennedy, J.F. Pullulan: Microbial sources, production and applications. Carbohyd. Polym. 2008, 73, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.H.; Gomaa, A.E.F.; Atta, O.M.; Hassane, A.M.A. Characteristics and kinetics of thermophilic actinomycetes’ amylase production on agro-wastes and its application for ethanol fermentation. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 255. [Google Scholar]
- Lima Júnior, J.P.; Franco, R.R.; Saraiva, A.L.; Moraes, I.B.; Espindola, F.S. Anacardium humile St. Hil as a novel source of antioxidant, antiglycation and α-amylase inhibitors molecules with potential for management of oxidative stress and diabetes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 268, 113667. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, T.B.; Yaghoobi, M.; Davidson, B.R.; Gurusamy, K.S. Amylase in drain fluid for the diagnosis of pancreatic leak in post-pancreatic resection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 4, CD012009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F. Structures, physicochemical properties, and applications of amaranth starch. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 313–325. [Google Scholar]
- Feller, G.; Lonhienne, T.; Deroanne, C.; Libioulle, C.; Van Beeumen, J.; Gerday, C. Purification, Characterization, and Nucleotide Sequence of the Thermolable a-Amylase from the Antarctic Psychrotroph Alteromonas haloplanctis A23. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 10914–10920. [Google Scholar]
- Feller, G.; Payan, F.; Theys, F.; Qian, M.; Haser, R.; Gerday, C. Stability and structural analysis of a-amylase from the antarctic psychrophile Alteromonas haloplanctis A23. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 222, 441–447. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; Sun, C.; Chang, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, G.; Che, Q.; Li, D. Saliniquinone derivatives, saliniquinones G−I and heraclemycin E, from the marine animal-derived Nocardiopsis aegyptia HDN19-252. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vértesy, L.; Barbone, F.P.; Cashmen, E.; Decker, H.; Ehrlich, K.; Jordan, B.; Knauf, M.; Schummer, D.; Segeth, M.P.; Wink, J.; et al. Pluraflavins, potent antitumor antibiotics from Saccharothrix sp. DSM 12931. J. Antibiot. 2001, 54, 718–729. [Google Scholar]
- Su, J.; Wu, H.; Yin, C.; Zhang, F.; Han, F.; Yu, W. The hydrophobic cluster on the surface of protein is the key structural basis for the SDS-resistance of chondroitinase VhChlABC. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2024, 6, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Luo, M.; Lin, J.; Lin, Y.; Yan, R.; Streit, W.R.; Ye, X.A. New Extremely Halophilic, Calcium-Independent and Surfactant-Resistant Alpha-Amylase from Alkalibacterium sp. SL3. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 765–775. [Google Scholar]
- Son, H.; Seo, H.; Han, S.; Kim, S.M.; Pham, L.T.M.; Khan, M.F.; Sung, H.J.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, Y.H. Extra disulfide and ionic salt bridge improves the thermostability of lignin peroxidase H8 under acidic condition. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2021, 148, 109803. [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui, K.S.; Poljak, A.; Francisci, D.D.; Guerriero, G.; Pilak, O.; Burg, D.; Raftery, M.J.; Parkin, D.M.; Trewhella, J.; Cavicchioli, R. A Chemically Modified α-Amylase with a Molten-Globule State Has Entropically Driven Enhanced Thermal Stability. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2012, 23, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Książek, E. Citric Acid: Properties, Microbial Production, and Applications in Industries. Molecules 2024, 29, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Ma, T.; Montalbán-López, M.; Li, X.; Wu, X.; Mu, D. Enhanced Production, Enzymatic Activity, and Thermostability of an α-Amylase from Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens in Lactococcus Lactis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 24587–24598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharwad, K.; Shekh, S.; Singh, N.K.; Patel, A.; Joshi, C. Heterologous Expression and Biochemical Characterization of Novel Multifunctional Thermostable α-Amylase from Hot-Spring Metagenome. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudan, S.K.; Kumar, N.; Kaur, I.; Sahni, G. Production, Purification and Characterization of Raw Starch Hydrolyzing Thermostable Acidic α-Amylase from Hot Springs, India. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Addendum: Accurate Structure Prediction of Biomolecular Interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 636, E4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wang, X.; Yin, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Yu, W.; Han, F. Identification and Biochemical Characterization of a Surfactant-Tolerant Chondroitinase VhChlABC from Vibrio hyugaensis LWW-1. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, K.S.; Ertan, H.; Poljak, A.; Bridge, W.J. Evaluating Enzymatic Productivity—The Missing Link to Enzyme Utility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

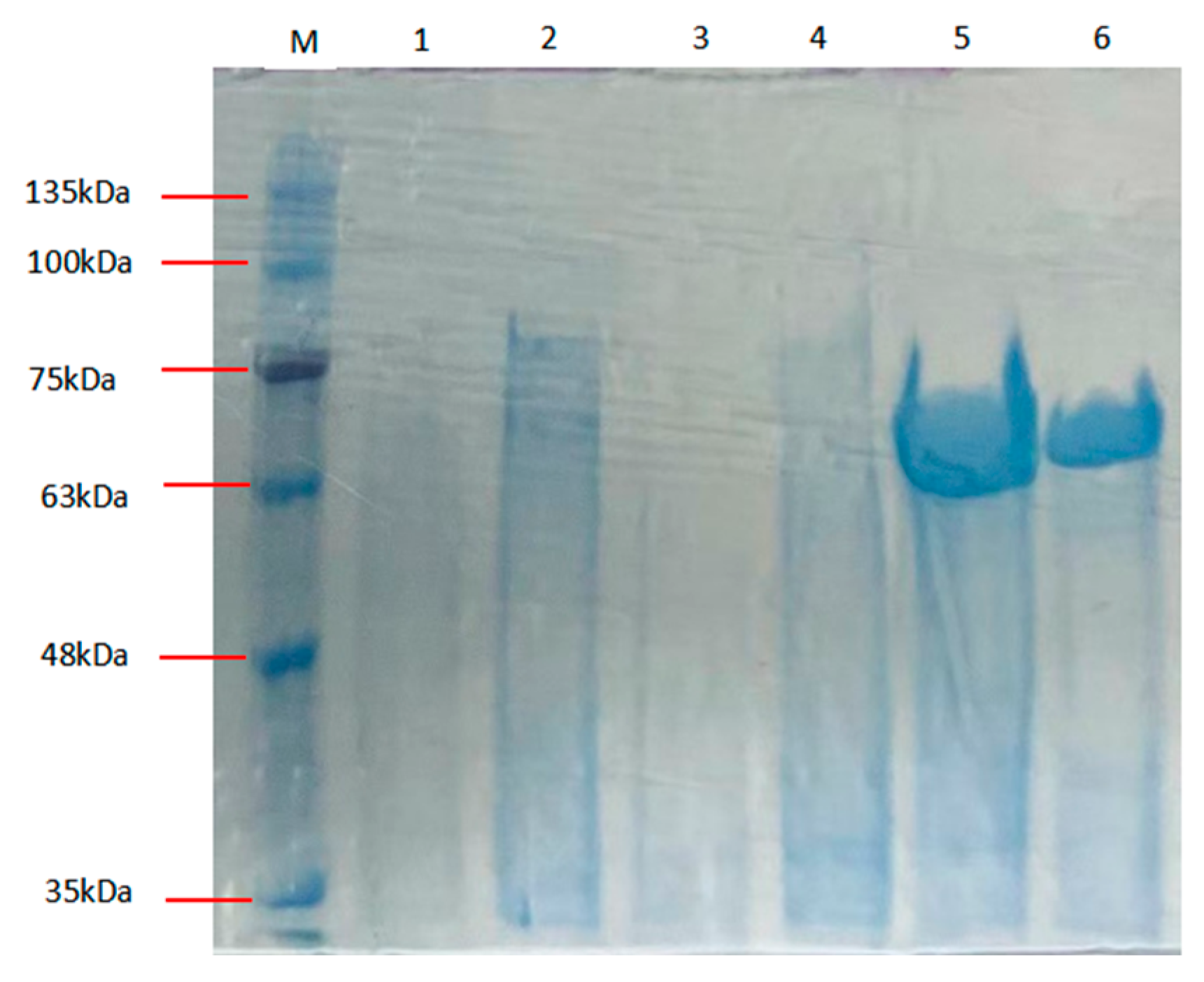
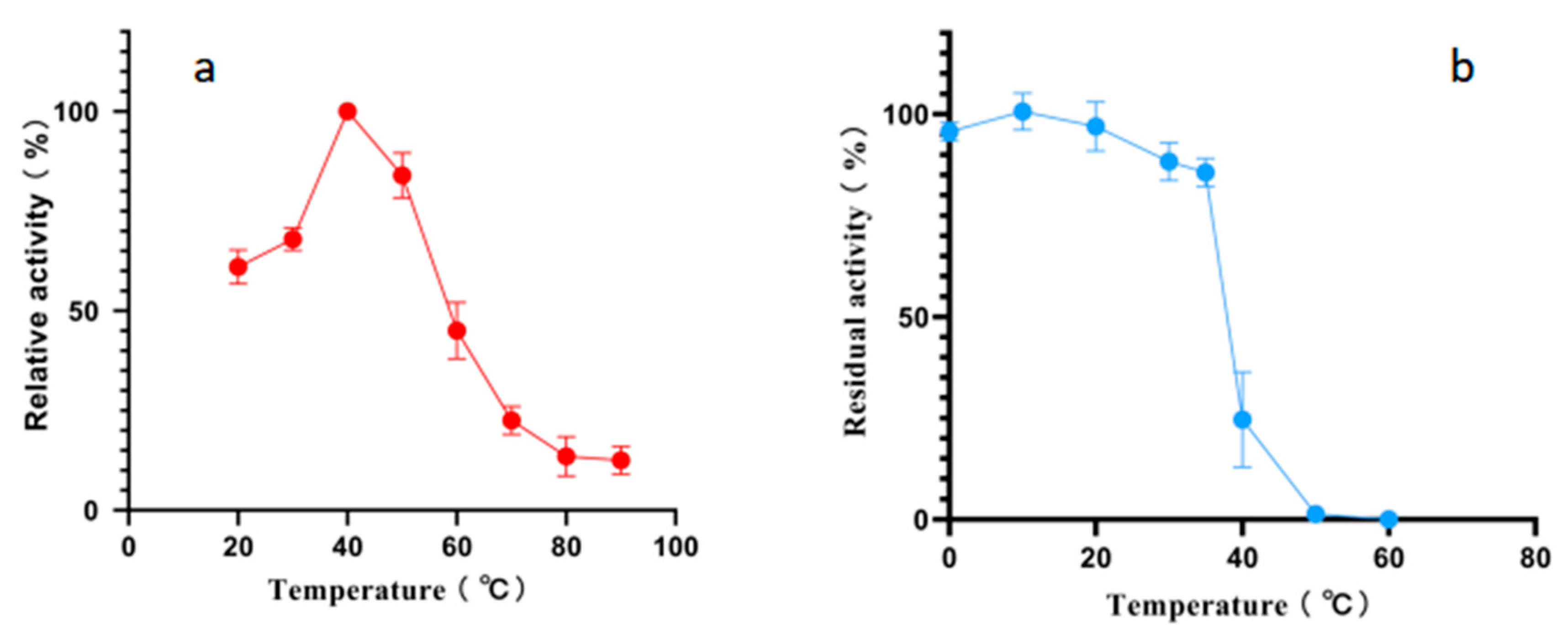
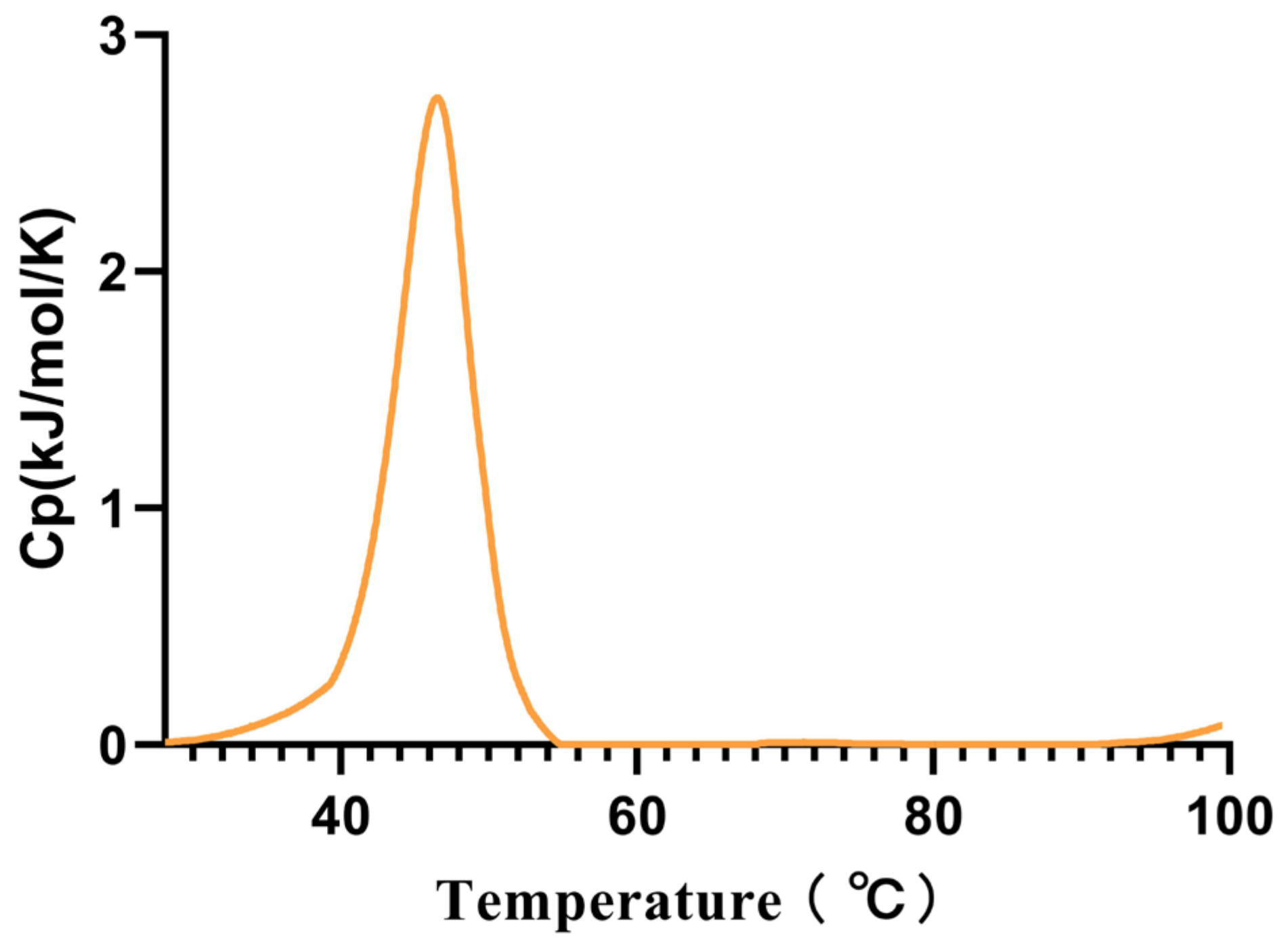
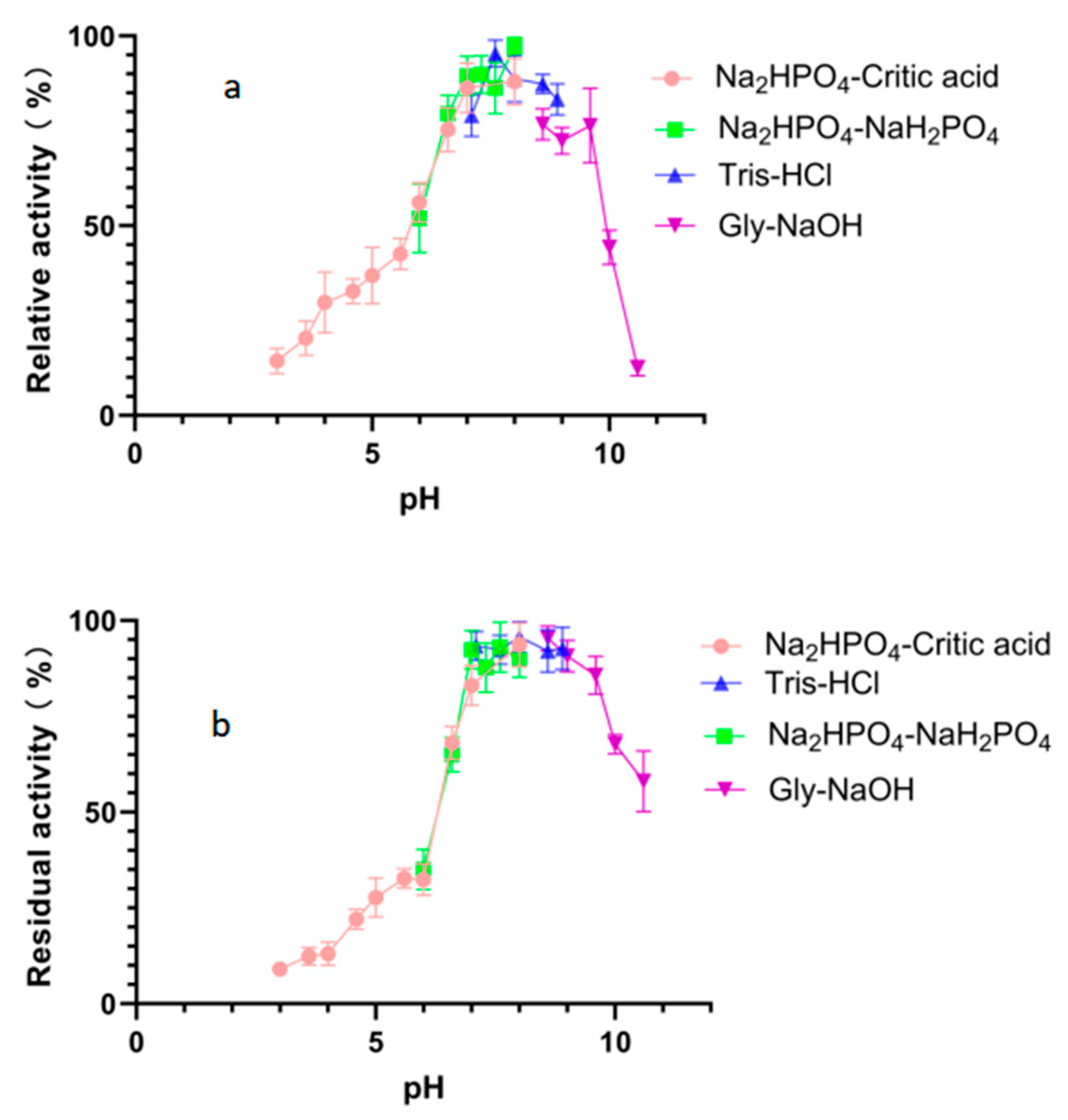


| Step | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Total Protein (mg) | Fold Purification | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fermentation broth | 286.25 ± 25.74 | 152.40 ± 13.72 | 1 | 100 |
| Nickel column | 1129.41 ± 109.83 | 9.17 ± 0.86 | 3.95 ± 0.38 | 23.74 ± 2.26 |
| Enzyme | Km (mg/mL) | kcat (s−¹) | kcat/Km (s−1 · mg−1 · mL) | Tm (°C) | Topt (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Porcine | 1.12 | 326 | 292 | - | 50 |
| A. haloplanctis AMY_PSEHA | 1.27 | 1363 | 1075 | 40 | 30 |
| Alphaz | 1.01 | 1216.67 | 1204.62 | 45.53 | 40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, F.; Zheng, X.; Liao, W.; Ren, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, G.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; et al. Heterologous Expression and Biochemical Characterization of a New α-Amylase from Nocardiopsis aegyptia HDN19-252 of Antarctic Animal Origin. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040159
Liu F, Zheng X, Liao W, Ren X, Ma C, Zhang G, Che Q, Zhu T, Wang W, Zhang T, et al. Heterologous Expression and Biochemical Characterization of a New α-Amylase from Nocardiopsis aegyptia HDN19-252 of Antarctic Animal Origin. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(4):159. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040159
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Fuhao, Xiangnan Zheng, Wenhui Liao, Xingtao Ren, Chuanteng Ma, Guojian Zhang, Qian Che, Tianjiao Zhu, Wenxue Wang, Tao Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Heterologous Expression and Biochemical Characterization of a New α-Amylase from Nocardiopsis aegyptia HDN19-252 of Antarctic Animal Origin" Marine Drugs 23, no. 4: 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040159
APA StyleLiu, F., Zheng, X., Liao, W., Ren, X., Ma, C., Zhang, G., Che, Q., Zhu, T., Wang, W., Zhang, T., Han, F., & Li, D. (2025). Heterologous Expression and Biochemical Characterization of a New α-Amylase from Nocardiopsis aegyptia HDN19-252 of Antarctic Animal Origin. Marine Drugs, 23(4), 159. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23040159






