Biodiversity and Biological Interactions of Actinobacteria Associated with Deep Sea and Intertidal Marine Invertebrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
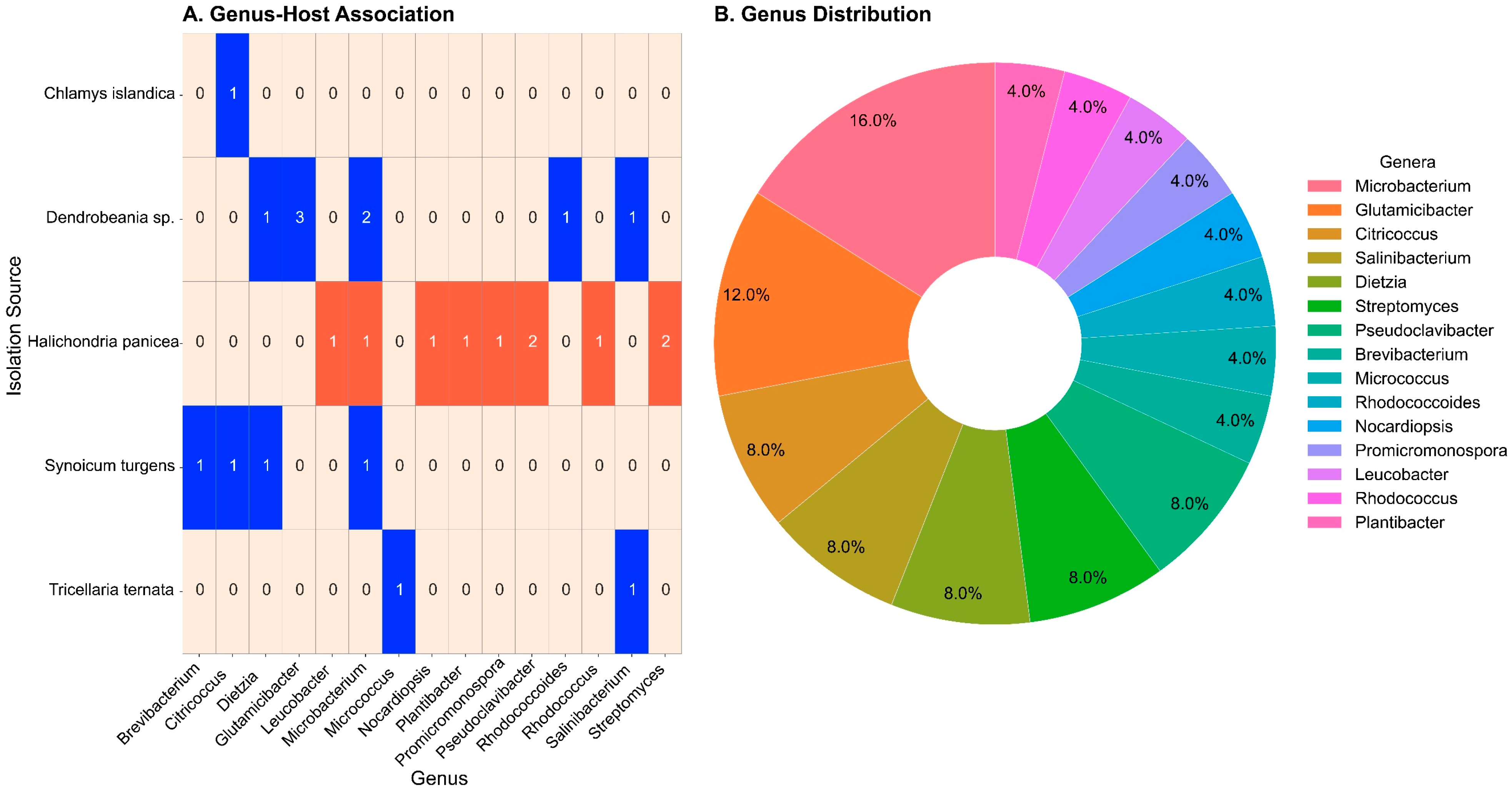
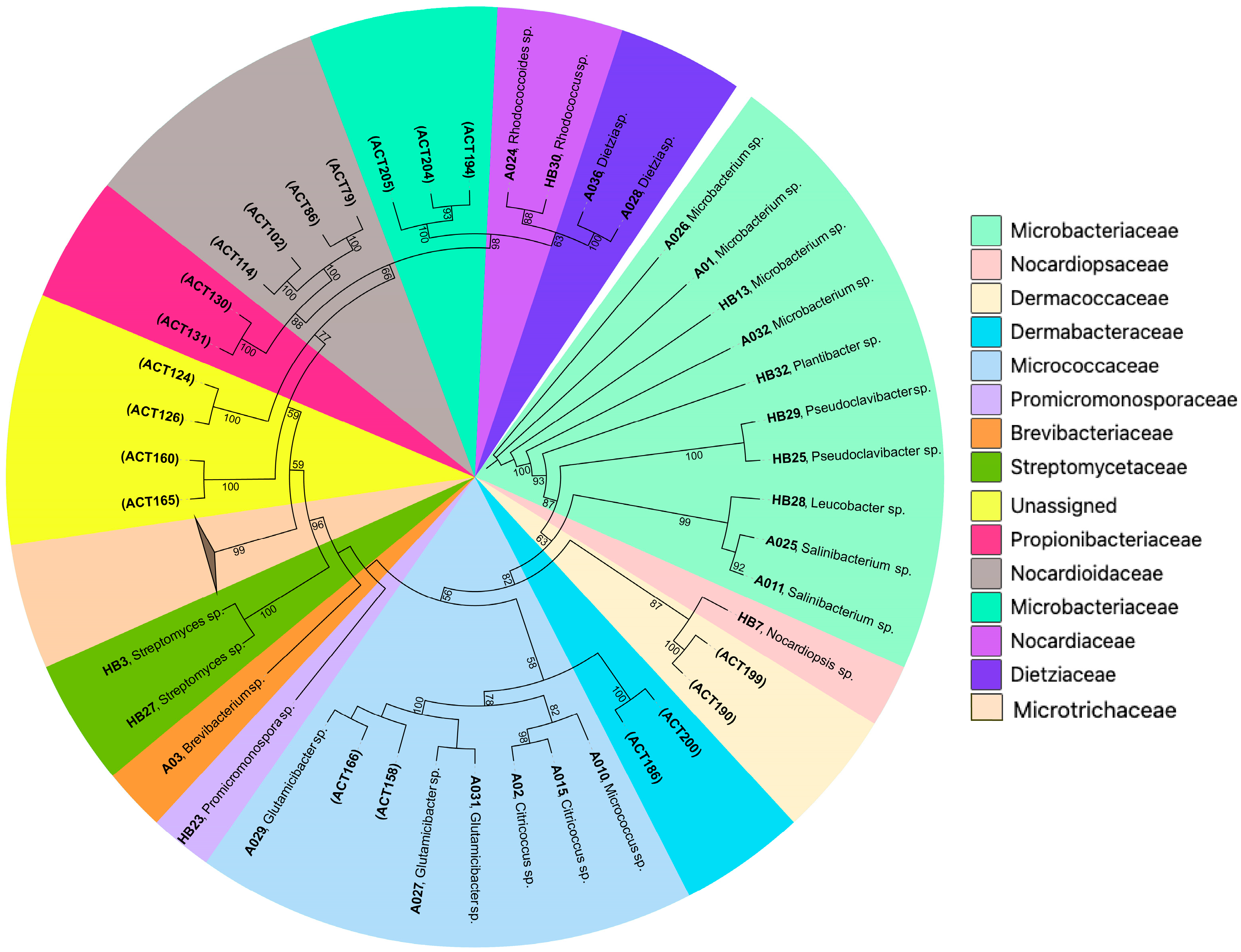
2.1. Taxonomy and Distribution of Cultured Actinobacteria
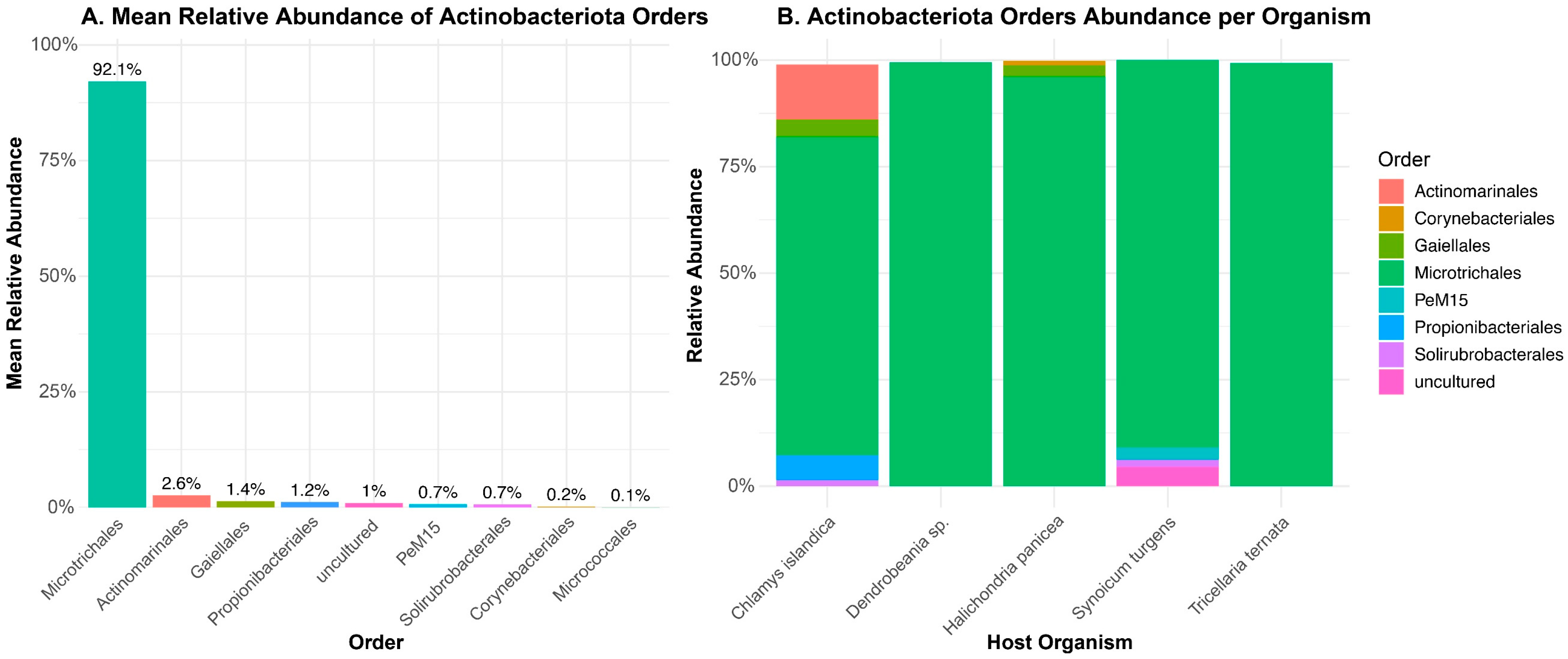
2.2. Taxonomic Composition of Actinobacteriota Across Metabarcoding Samples
2.3. Alpha Diversity Analysis of Marine Actinobacteria Communities
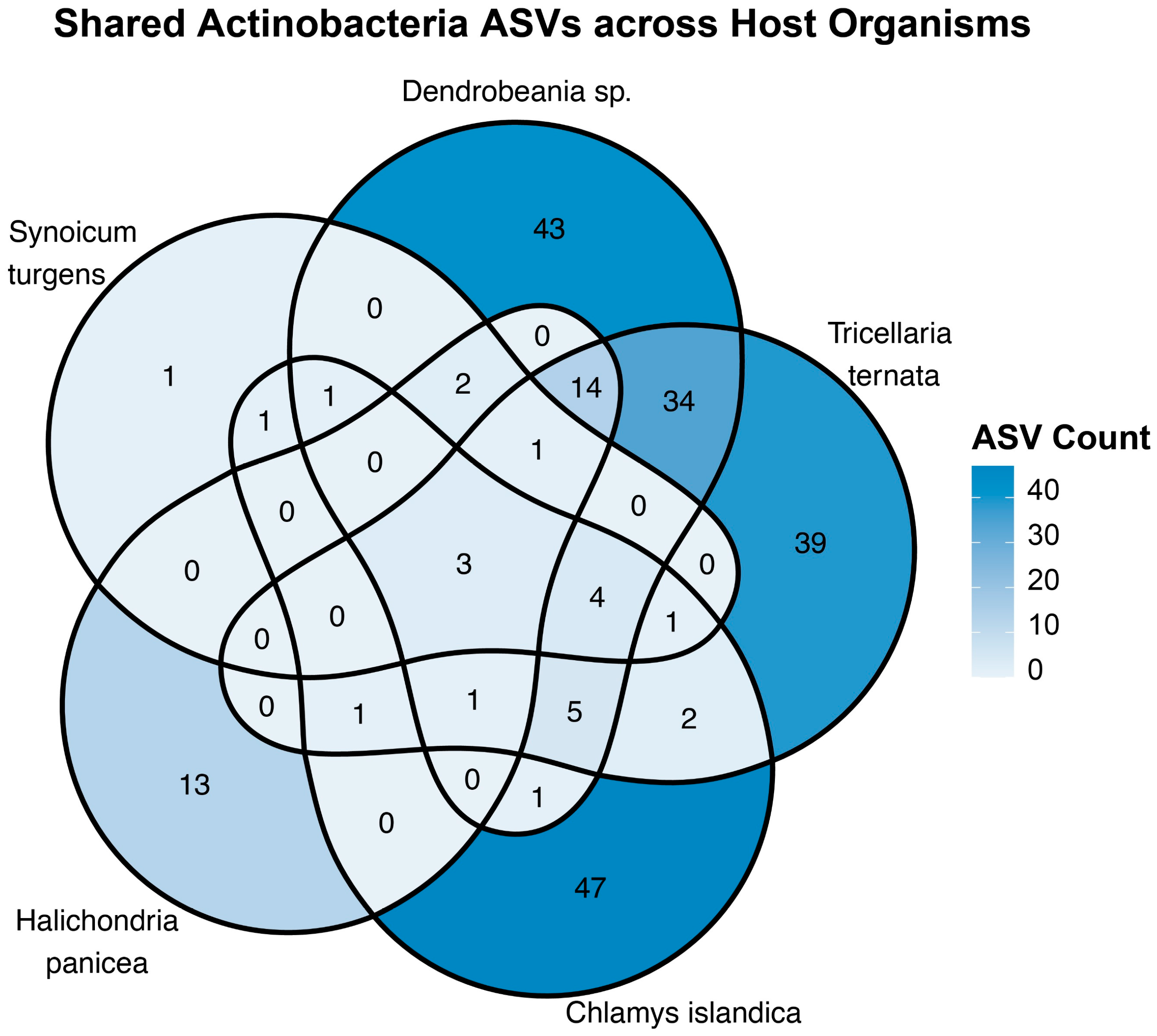
2.4. Distribution of Shared and Unique Actinobacteria ASVs Among Marine Host Organisms
2.5. Comparative Evaluation of Culture-Dependent and Culture-Independent Methods for Actinobacteria Recovery
2.6. High-Throughput Screening of Culturable Actinobacterial Interactions
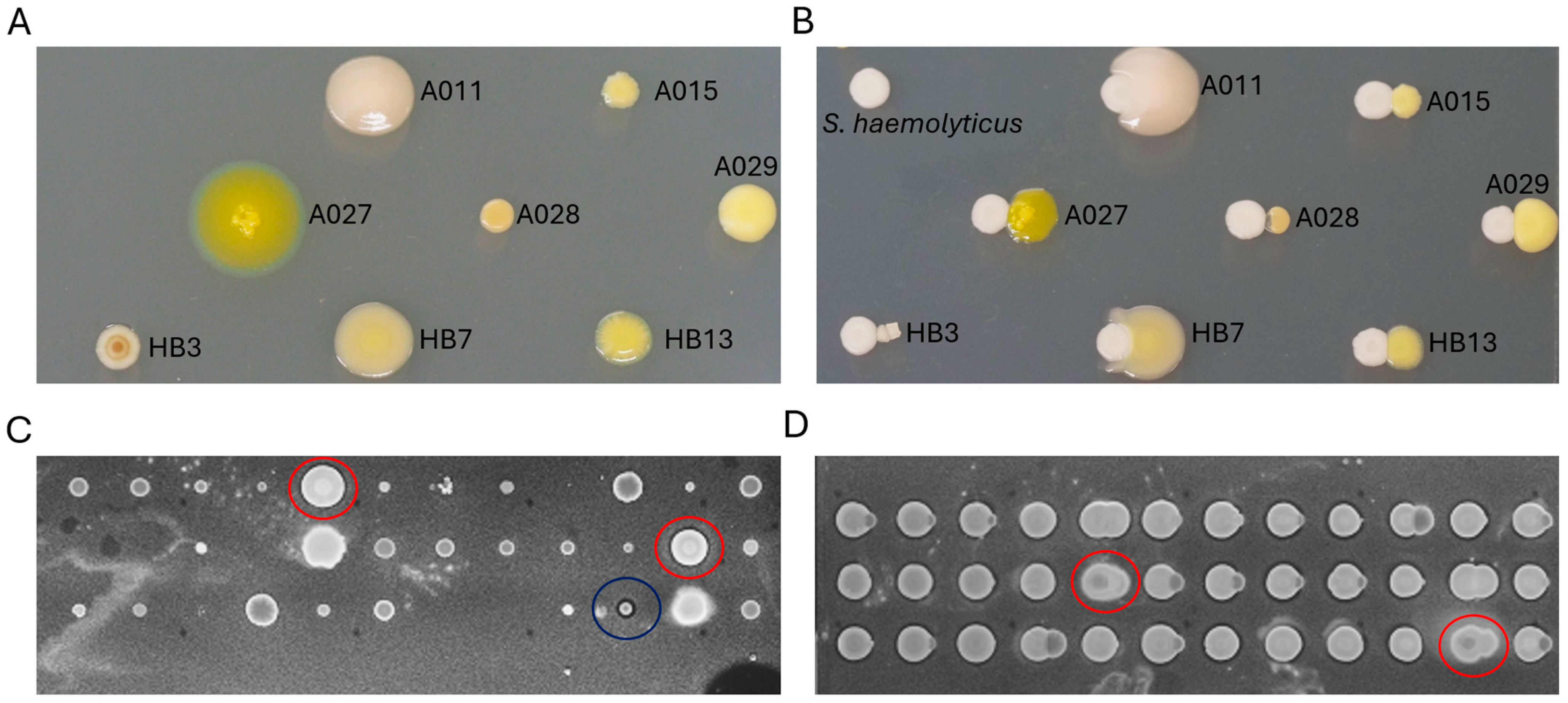
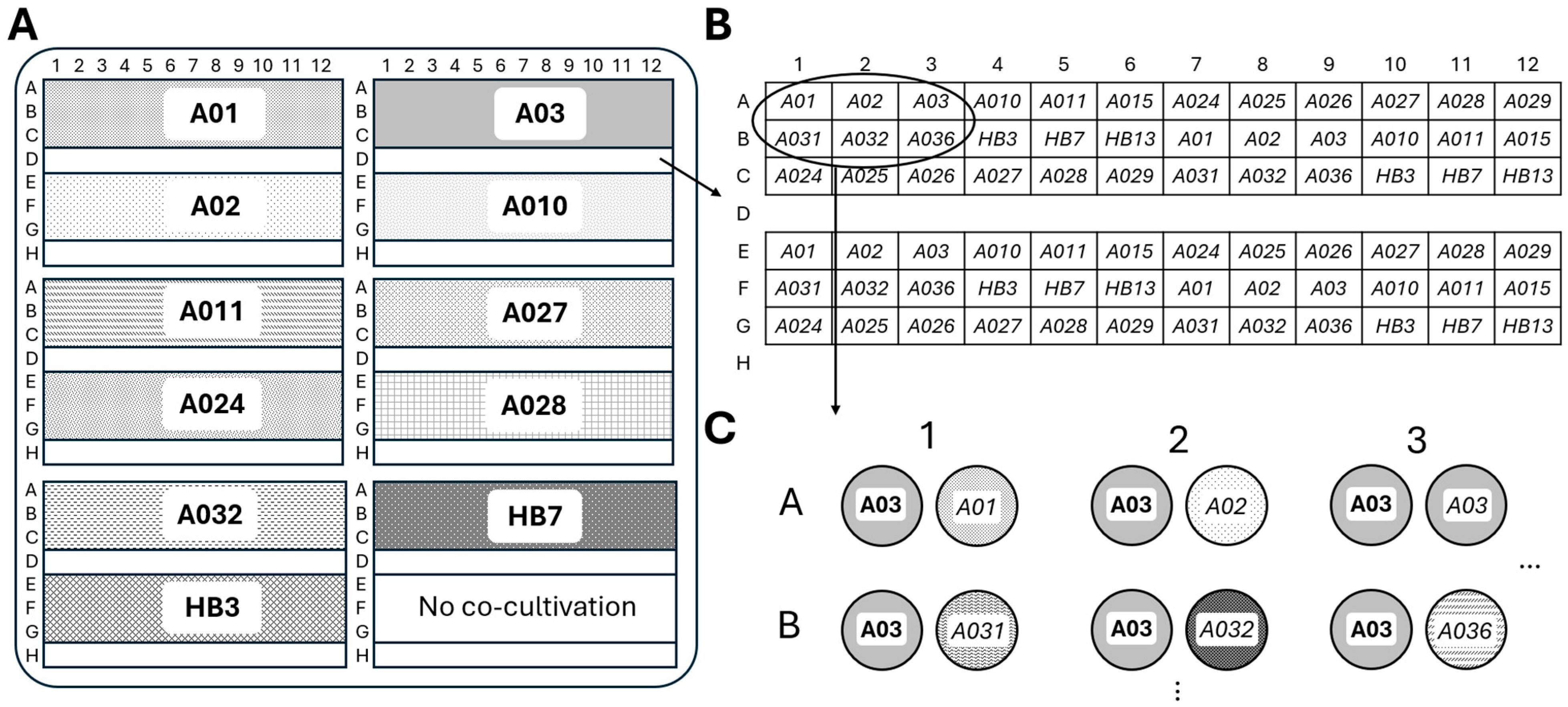
3. Discussion
3.1. Isolation of Culturable Actinobacteria Associated with Marine Invertebrates
3.2. Actinobacteria Community in the Culture-Independent Approach
3.3. Evaluation of Culture-Dependent and Culture-Independent Methods for Actinobacteria Recovery
3.4. Morphological Responses of Culturable Actinobacteria to Co-Cultivation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Processing
4.2. Media for Isolation and Subculturing
4.3. Sample Pre-Treatment and Actinobacteria Isolation Strategy
4.4. DNA Extraction, 16S rRNA Gene Amplification, and Sequencing of Culturable Actinobacteria
4.5. Phylogenetic Analysis and Taxonomic Identification of Actinobacteria Cultures
4.6. Environmental DNA (eDNA) Extraction and Amplification of the V4/V5 Region of the 16S rRNA Gene for Metabarcoding
4.7. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis of Metabarcoding Data
4.8. Comparing Culture-Dependent and Culture-Independent Methods for Recovering Actinobacteria
4.9. High-Throughput Screening of Actinobacteria Interactions in Culture Using Automated Colony Handling
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louca, S.; Mazel, F.; Doebeli, M.; Parfrey, L.W. A Census-Based Estimate of Earth’s Bacterial and Archaeal Diversity. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salwan, R.; Sharma, V. Molecular and Biotechnological Aspects of Secondary Metabolites in Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 231, 126374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertsen, H.L.; Musiol-Kroll, E.M. Actinomycete-Derived Polyketides as a Source of Antibiotics and Lead Structures for the Development of New Antimicrobial Drugs. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macagnan, D.; Romeiro, R.S.; De Souza, J.T.; Pomella, A.W.V. Isolation of Actinomycetes and Endospore-Forming Bacteria from the Cacao Pod Surface and Their Antagonistic Activity against the Witches’ Broom and Black Pod Pathogens. Phytoparasitica 2006, 34, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, C.I.; Williams, S.T.; Ruddick, S.M.; Hatfield, H.L. Studies on the Ecology of Actinomycetes in Soil IV. Observations on the Form and Growth of Streptomycetes in Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embley, T.M.; Stackebrandt, E. The Molecular Phylogeny and Systematics of the Actinomycetes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1994, 48, 257–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérdy, J. Thoughts and Facts about Antibiotics: Where We Are Now and Where We Are Heading. J. Antibiot. 2012, 65, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barka, E.A.; Vatsa, P.; Sanchez, L.; Gaveau-Vaillant, N.; Jacquard, C.; Klenk, H.-P.; Clément, C.; Ouhdouch, Y.; van Wezel, G.P. Taxonomy, Physiology, and Natural Products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotter, A.; Barbier, M.; Bertoni, F.; Bones, A.M.; Cancela, M.L.; Carlsson, J.; Carvalho, M.F.; Cegłowska, M.; Chirivella-Martorell, J.; Conk Dalay, M.; et al. The Essentials of Marine Biotechnology. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 629629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, R.; Aalbersberg, W. Marine Actinomycetes: An Ongoing Source of Novel Bioactive Metabolites. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, S.; Jóhannsson, R.; Marteinsson, V. Co-Cultivation of the Marine Sponge Halichondria Panicea and Its Associated Microorganisms. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, P.J.; Challis, G.L. Discovery of Microbial Natural Products by Activation of Silent Biosynthetic Gene Clusters. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.Y.; Wu, J.T.; Shao, C.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, C.Y. Co-Culture: Stimulate the Metabolic Potential and Explore the Molecular Diversity of Natural Products from Microorganisms. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2021, 3, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoore, R.V.; Padmaperuma, G.; Maneein, S.; Vaidyanathan, S. Co-Culturing Microbial Consortia: Approaches for Applications in Biomanufacturing and Bioprocessing. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 46–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patricia, G.; Olaf, T.; Kirsten, K.; Martin, T.; van de Velde, C.; Swatantar, K.; Paolina, G. Growth Promotion and Inhibition Induced by Interactions of Groundwater Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fiy164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyc, O.; van den Berg, M.; Gerards, S.; van Veen, J.A.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; de Boer, W.; Garbeva, P. Impact of Interspecific Interactions on Antimicrobial Activity among Soil Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.R.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Wang, Q.; Kulam-Syed-Mohideen, A.S.; McGarrell, D.M.; Bandela, A.M.; Cardenas, E.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M. The Ribosomal Database Project (RDP-II): Introducing MyRDP Space and Quality Controlled Public Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Oh, H.S.; Park, S.C.; Chun, J. Towards a Taxonomic Coherence between Average Nucleotide Identity and 16S RRNA Gene Sequence Similarity for Species Demarcation of Prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HAMEŞ-KOCABAŞ, E.E.; UZEL, A. Isolation Strategies of Marine-Derived Actinomycetes from Sponge and Sediment Samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 88, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, Y.K.; Hagestad, O.C.; Li, C.; Hansen, E.H.; Andersen, J.H. Selective Isolation of Arctic Marine Actinobacteria and a Down-Scaled Fermentation and Extraction Strategy for Identifying Bioactive Compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1005625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, U.; Piel, J.; Degnan, S.M.; Taylor, M.W. Genomic Insights into the Marine Sponge Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Jin, Y.; Jin, M.; Yu, X. A Comparative Study on the Phylogenetic Diversity of Culturable Actinobacteria Isolated from Five Marine Sponge Species. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek Int. J. General. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 93, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneemann, I.; Nagel, K.; Kajahn, I.; Labes, A.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Comprehensive Investigation of Marine Actinobacteria Associated with the Sponge Halichondria Panicea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3702–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anteneh, Y.S.; Yang, Q.; Brown, M.H.; Franco, C.M.M. Factors Affecting the Isolation and Diversity of Marine Sponge-Associated Bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 1729–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versluis, D.; McPherson, K.; van Passel, M.W.J.; Smidt, H.; Sipkema, D. Recovery of Previously Uncultured Bacterial Genera from Three Mediterranean Sponges. Mar. Biotechnol. 2017, 19, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miksch, S.; Meiners, M.; Meyerdierks, A.; Probandt, D.; Wegener, G.; Titschack, J.; Jensen, M.A.; Ellrott, A.; Amann, R.; Knittel, K. Bacterial Communities in Temperate and Polar Coastal Sands Are Seasonally Stable. ISME Commun. 2021, 1, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampous, G.; Kormas, K.A.; Antoniou, E.; Kalogerakis, N.; Gontikaki, E. Distinct Communities of Bacteria and Unicellular Eukaryotes in the Different Water Masses of Cretan Passage Water Column (Eastern Mediterranean Sea). Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reveillaud, J.; Maignien, L.; Eren, M.A.; Huber, J.A.; Apprill, A.; Sogin, M.L.; Vanreusel, A. Host-Specificity among Abundant and Rare Taxa in the Sponge Microbiome. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.L.; Biddanda, B.A.; Weinke, A.D.; Chiang, E.; Januska, F.; Props, R.; Denef, V.J. Microhabitats Are Associated with Diversity-Productivity Relationships in Freshwater Bacterial Communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuerl, T.; Hopkins, M.; Nowell, R.W.; Rivett, D.W.; Barraclough, T.G.; Bell, T. Bacterial Adaptation Is Constrained in Complex Communities. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Manchanda, G.; Bhattacharjee, K.; Panosyan, H. Microbes in Microbial Communities: Ecological and Applied Perspectives; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; ISBN 9789811656170. [Google Scholar]
- Schwaha, T.; Hirose, M.; Wanninger, A. The Life of the Freshwater Bryozoan Stephanella Hina (Bryozoa, Phylactolaemata)—A Crucial Key to Elucidating Bryozoan Evolution. Zool. Lett. 2016, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, L.; Kjeldsen, K.U.; Funch, P.; Jensen, J.; Obst, M.; López-Legentil, S.; Schramm, A. Endozoicomonas Are Specific, Facultative Symbionts of Sea Squirts. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, J.S.; Xu, J.L.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, G.Y. Biological and Chemical Diversity of Ascidian-Associated Microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Hao, H.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, L.P. Environmental Controls over Actinobacteria Communities in Ecological Sensitive Yanshan Mountains Zone. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, X.; Tai, X.; Sun, L.; Wu, M.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Chen, T.; Liu, G.; et al. Variation in Actinobacterial Community Composition and Potential Function in Different Soil Ecosystems Belonging to the Arid Heihe River Basin of Northwest China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.N.; Fu, C.M.; Wang, G.Y. Phylogenetic Analysis and Screening of Antimicrobial and Antiproliferative Activities of Culturable Bacteria Associated with the Ascidian Styela Clava from the Yellow Sea, China. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7851251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Yang, H.O.; Sohn, Y.C.; Kwon, H.C. Aeromicrobium Halocynthiae Sp. Nov., a Taurocholic Acid-Producing Bacterium Isolated from the Marine Ascidian Halocynthia Roretzi. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 2793–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.S.; Spakowicz, D.J.; Hong, B.Y.; Petersen, L.M.; Demkowicz, P.; Chen, L.; Leopold, S.R.; Hanson, B.M.; Agresta, H.O.; Gerstein, M.; et al. Evaluation of 16S RRNA Gene Sequencing for Species and Strain-Level Microbiome Analysis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Darveekaran Nair, S.S.; Zhu, P.; Li, S.; Huang, S.; Li, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, F. Impact of DNA Extraction Method and Targeted 16S-RRNA Hypervariable Region on Oral Microbiota Profiling. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrigg, C.; Rice, O.; Kavanagh, S.; Collins, G.; O’Flaherty, V. DNA Extraction Method Affects Microbial Community Profiles from Soils and Sediment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 77, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aßhauer, K.P.; Wemheuer, B.; Daniel, R.; Meinicke, P. Tax4Fun: Predicting Functional Profiles from Metagenomic 16S RRNA Data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2882–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Guan, T.; Jiang, H.; Zhi, X.; Tang, S.; Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, W. Diversity of Actinobacterial Community in Saline Sediments from Yunnan and Xinjiang, China. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, D.; Lewis, K.; Orjala, J.; Mo, S.; Ortenberg, R.; O’Connor, P.; Zhao, C.; Vouros, P.; Kaeberlein, T.; Epstein, S.S. Short Peptide Induces an “Uncultivable” Microorganism to Grow in Vitro. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4889–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Dolfing, J.; Guo, Z.; Chen, R.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Feng, Y. Important Ecophysiological Roles of Non-Dominant Actinobacteria in Plant Residue Decomposition, Especially in Less Fertile Soils. Microbiome 2021, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Větrovský, T.; Baldrian, P. An In-Depth Analysis of Actinobacterial Communities Shows Their High Diversity in Grassland Soils along a Gradient of Mixed Heavy Metal Contamination. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, G.V.; Victor, S. Organism Life Cycles, Predation, and the Structure of Marine Pelagic Ecosystems. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 130, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Mendez, G.; Faust, K.; Henry, N.; Decelle, J.; Colin, S.; Carcillo, F.; Chaffron, S.; Cesar Ignacio-Espinosa, J.; Roux, S.; Vincent, F.; et al. Determinants of Community Structure in the Global Plankton Interactome. Science 2015, 348, 1262073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbing, M.E.; Fuqua, C.; Parsek, M.R.; Peterson, S.B. Bacterial Competition: Surviving and Thriving in the Microbial Jungle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selegato, D.M.; Castro-Gamboa, I. Enhancing Chemical and Biological Diversity by Co-Cultivation. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1117559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Bayer, K.; Hentschel, U. Diversity, Abundance and Natural Products of Marine Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmann, A.; Aly, A.H.; Lin, W.; Wang, B.; Proksch, P. Co-Cultivation—A Powerful Emerging Tool for Enhancing the Chemical Diversity of Microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakefield, J.; Hassan, H.M.; Jaspars, M.; Ebel, R.; Rateb, M.E. Dual Induction of New Microbial Secondary Metabolites by Fungal Bacterial Co-Cultivation. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadell, C.D.; Drescher, K.; Foster, K.R. Spatial Structure, Cooperation and Competition in Biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuqua, W.C.; Winans, S.C.; Peter Greenberg, E. Quorum Sensing in Bacteria: The LuxR-LuxI Family of Cell Density-Responsive Transcriptional Regulatorst. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, S.B.; Bertolli, S.K.; Mougous, J.D. The Central Role of Interbacterial Antagonism in Bacterial Life. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R1203–R1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Sandiford, S.K.; Van Wezel, G.P. Triggers and Cues That Activate Antibiotic Production by Actinomycetes. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehe, J.; Kulesa, A.; Ortiz, A.; Ackerman, C.M.; Thakku, S.G.; Sellers, D.; Kuehn, S.; Gore, J.; Friedman, J.; Blainey, P.C. Massively Parallel Screening of Synthetic Microbial Communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12804–12809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.W.F.; Ser, H.L.; Ab Mutalib, N.S.; Saokaew, S.; Duangjai, A.; Khan, T.M.; Chan, K.G.; Goh, B.H.; Lee, L.H. Streptomyces Monashensis Sp. Nov., a Novel Mangrove Soil Actinobacterium from East Malaysia with Antioxidative Potential. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 418–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, L.; Pipite, A.; Subramani, R.; Owen, J.; Keyzers, R.A.; Taufa, T. Streptomyces: Still the Biggest Producer of New Natural Secondary Metabolites, a Current Perspective. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 418–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palkova, L.; Tomova, A.; Repiska, G.; Babinska, K.; Bokor, B.; Mikula, I.; Minarik, G.; Ostatnikova, D.; Soltys, K. Evaluation of 16S RRNA Primer Sets for Characterisation of Microbiota in Paediatric Patients with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An Integrated and Extendable Desktop Software Platform for the Organization and Analysis of Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschup, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic Local Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast Approximation for Phylogenetic Bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New Algorithms and Methods to Estimate Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (ITOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parada, A.E.; Needham, D.M.; Fuhrman, J.A. Every Base Matters: Assessing Small Subunit RRNA Primers for Marine Microbiomes with Mock Communities, Time Series and Global Field Samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize Analysis Results for Multiple Tools and Samples in a Single Report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Guerrini, C.J.; Botkin, J.R.; McGuire, A.L. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 850–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A Versatile Open Source Tool for Metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 2016, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package 2013. Available online: https://vegandevs.github.io/vegan/ (accessed on 15 October 2025).
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Boutros, P.C. VennDiagram: A Package for the Generation of Highly-Customizable Venn and Euler Diagrams in R. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R.; Teeling, E. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Isolate Id | Accession | Phylogenetic Group | Treatment | Host Source | Most Closely Related Taxon (Accession No.) | Identity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A01 | PQ814116 | Microbacteriaceae | Control | S. turgens | Microbacterium oxydans (NR_044931) | 99.03 |
| A02 | PQ814117 | Micrococcaceae | Control | S. turgens | Citricoccus parietis (NR_104498) | 98.85 |
| A03 | PQ814118 | Brevibacteriaceae | Control | S. turgens | Brevibacterium aurantiacum (NR_044854) | 98.54 |
| A010 | PQ814119 | Micrococcaceae | Control | T. ternata | Micrococcus yunnanensis (NR_116578) | 99.85 |
| A011 | PQ814120 | Microbacteriaceae | Control | T. ternata | Salinibacterium amurskyense (NR_041932) | 99.64 |
| A015 | PQ814121 | Micrococcaceae | Control | C. islandica | Citricoccus parietis (NR_104498) | 99.06 |
| A024 | PQ814122 | Nocardiaceae | Control | Dendrobeania sp. | Rhodococcoides fascians (NR_037021) | 98.83 |
| A025 | PQ814123 | Microbacteriaceae | Control | Dendrobeania sp. | Salinibacterium amurskyense (NR_041932) | 99.78 |
| A026 | PQ814124 | Microbacteriaceae | Control | Dendrobeania sp. | Microbacterium oxydans (NR_044931) | 99.96 |
| A027 | PQ814125 | Micrococcaceae | Control | Dendrobeania sp. | Glutamicibacter bergerei (NR_025612) | 99.35 |
| A028 | PQ814126 | Dietziaceae | Control | Dendrobeania sp. | Dietzia kunjamensis (NR_116684) | 99.86 |
| A029 | PQ814127 | Micrococcaceae | Control | Dendrobeania sp. | Glutamicibacter bergerei (NR_025612) | 99.93 |
| A031 | PQ814128 | Micrococcaceae | Control | Dendrobeania sp. | Glutamicibacter bergerei (NR_025612) | 99.86 |
| A032 | PQ814129 | Microbacteriaceae | Control | Dendrobeania sp. | Microbacterium invictum (NR_042708) | 97.81 |
| A036 | PQ814130 | Dietziaceae | Control | Synoicum turgens | Dietzia kunjamensis (NR_117962) | 99.55 |
| HB3 | PQ814131 | Streptomycetaceae | Heat shock 55 °C | H. panicea | Streptomyces argenteolus (NR_112300) | 99.17 |
| HB7 | PQ814132 | Nocardiopsaceae | Heat shock 55 °C | H. panicea | Nocardiopsis prasina (NR_044906) | 99.64 |
| HB13 | PQ814133 | Microbacteriaceae | Heat shock 65 °C | H. panicea | Microbacterium oxydans (NR_044931) | 99.85 |
| HB23 | PQ814134 | Promicromonosporaceae | Heat shock 65 °C | H. panicea | Promicromonospora iranensis (NR_109446) | 99.75 |
| HB25 | PQ814135 | Microbacteriaceae | Heat shock 55 °C | H. panicea | Pseudoclavibacter terrae (NR_145621) | 99.92 |
| HB27 | PQ814136 | Streptomycetaceae | Heat shock 55 °C | H. panicea | Streptomyces niveus (NR_115784) | 98.82 |
| HB28 | PQ814137 | Microbacteriaceae | Heat shock 55 °C | H. panicea | Leucobacter viscericola (NR_180647) | 98.54 |
| HB29 | PQ814138 | Microbacteriaceae | Heat shock 65 °C | H. panicea | Pseudoclavibacter terrae (NR_145621) | 99.93 |
| HB30 | PQ814139 | Nocardiaceae | Heat shock 65 °C | H. panicea | Rhodococcus qingshengii (NR_043535) | 99.92 |
| HB32 | PQ814140 | Microbacteriaceae | Heat shock 55 °C | H. panicea | Plantibacter flavus strain (NR_025462) | 99.78 |
| Sample Source | Phylum | Latitude | Longitude | Depth/Intertidal Zone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synoicum turgens (A16) | Chordata | 77.3698559 | 8.28327852 | 1400 m |
| Dendrobeania sp. (A18) | Bryozoa | 77.0797973 | 8.86340588 | 2200 m |
| Tricellaria ternata (A22) | Bryozoa | 76.1558945 | 8.49651083 | 2200 m |
| Chlamys islandica (A23) | Mollusca | 75.8646908 | 9.83376993 | 2300 m |
| Halichondria panicea (HP) | Porifera | 69.6439 | 18.7369 | Lower intertidal |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masaki, H.I.; Schneider, Y.K.-H.; Franz, O.H.; Hansen, E.H.; Andersen, J.H.; Rämä, T. Biodiversity and Biological Interactions of Actinobacteria Associated with Deep Sea and Intertidal Marine Invertebrates. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100408
Masaki HI, Schneider YK-H, Franz OH, Hansen EH, Andersen JH, Rämä T. Biodiversity and Biological Interactions of Actinobacteria Associated with Deep Sea and Intertidal Marine Invertebrates. Marine Drugs. 2025; 23(10):408. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100408
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasaki, Hosea Isanda, Yannik Karl-Heinz Schneider, Ole Hinnerk Franz, Espen Holst Hansen, Jeanette Hammer Andersen, and Teppo Rämä. 2025. "Biodiversity and Biological Interactions of Actinobacteria Associated with Deep Sea and Intertidal Marine Invertebrates" Marine Drugs 23, no. 10: 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100408
APA StyleMasaki, H. I., Schneider, Y. K.-H., Franz, O. H., Hansen, E. H., Andersen, J. H., & Rämä, T. (2025). Biodiversity and Biological Interactions of Actinobacteria Associated with Deep Sea and Intertidal Marine Invertebrates. Marine Drugs, 23(10), 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/md23100408







