Purification and Screening of the Antialgal Activity of Seaweed Extracts and a New Glycolipid Derivative against Two Ichthyotoxic Red Tide Microalgae Amphidinium carterae and Karenia mikimotoi
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Preparation and Activities of Fractions Obtained by Liquid–Liquid Extraction


| A. carterae | K. mikimotoi | |
|---|---|---|
| G. furcate | 750.6 ± 14.7 | 795.2 ± 16.9 |
| P. palmata | 153.5 ± 5.17 | 166.0 ± 6.64 |
| Sargassum sp. | 63.40 ± 1.19 | 53.70 ± 3.05 |
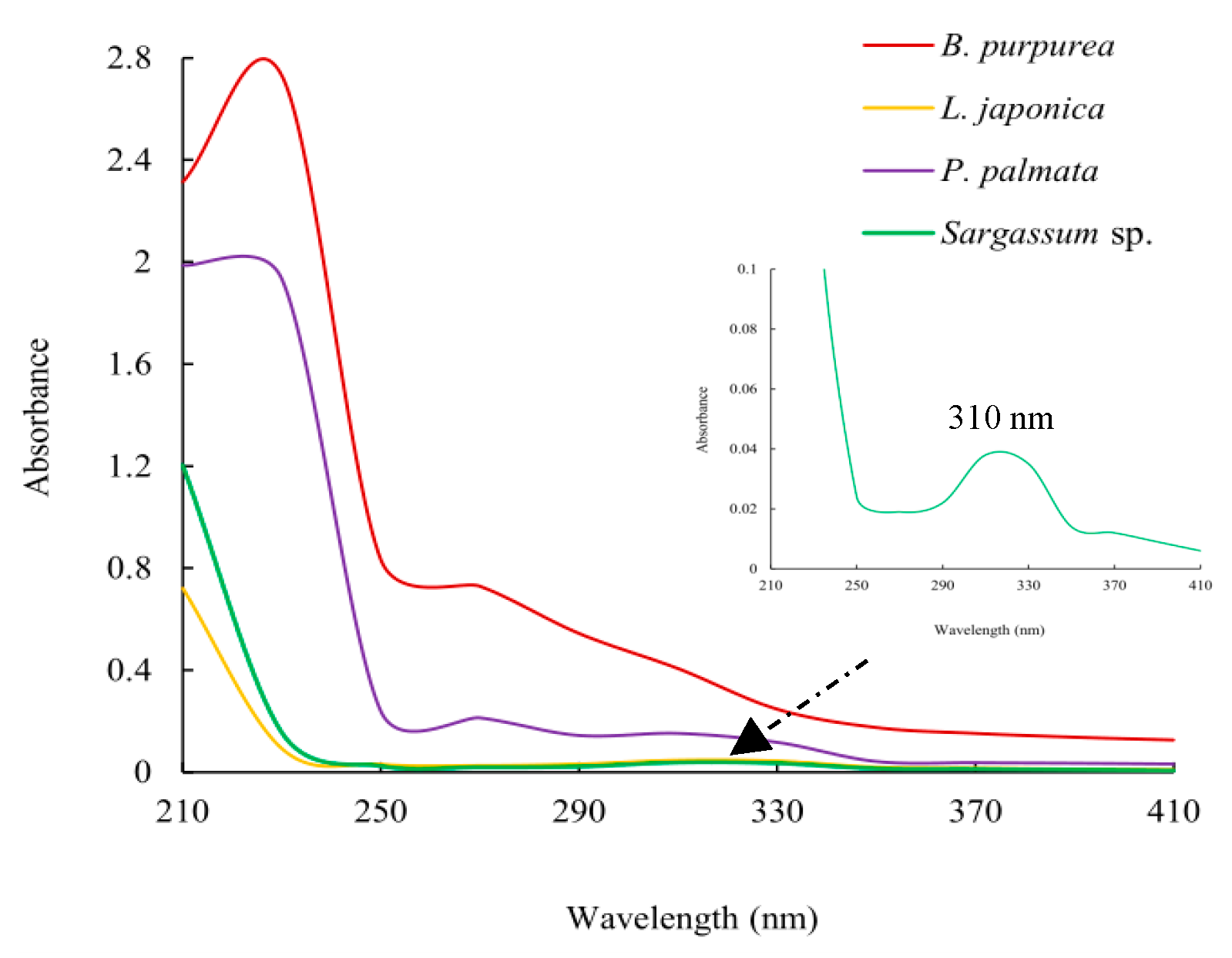
2.2. Thin-Layer Chromatography and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Analysis
2.3. Isolation and Identification
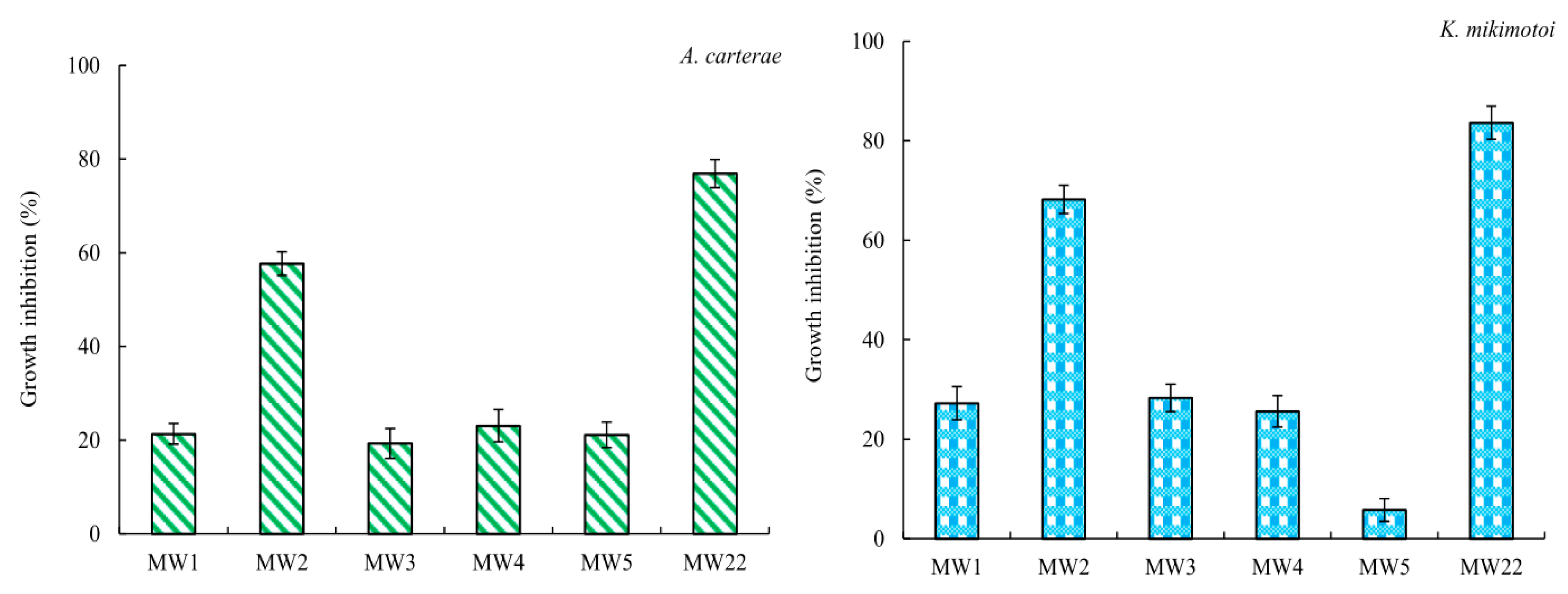
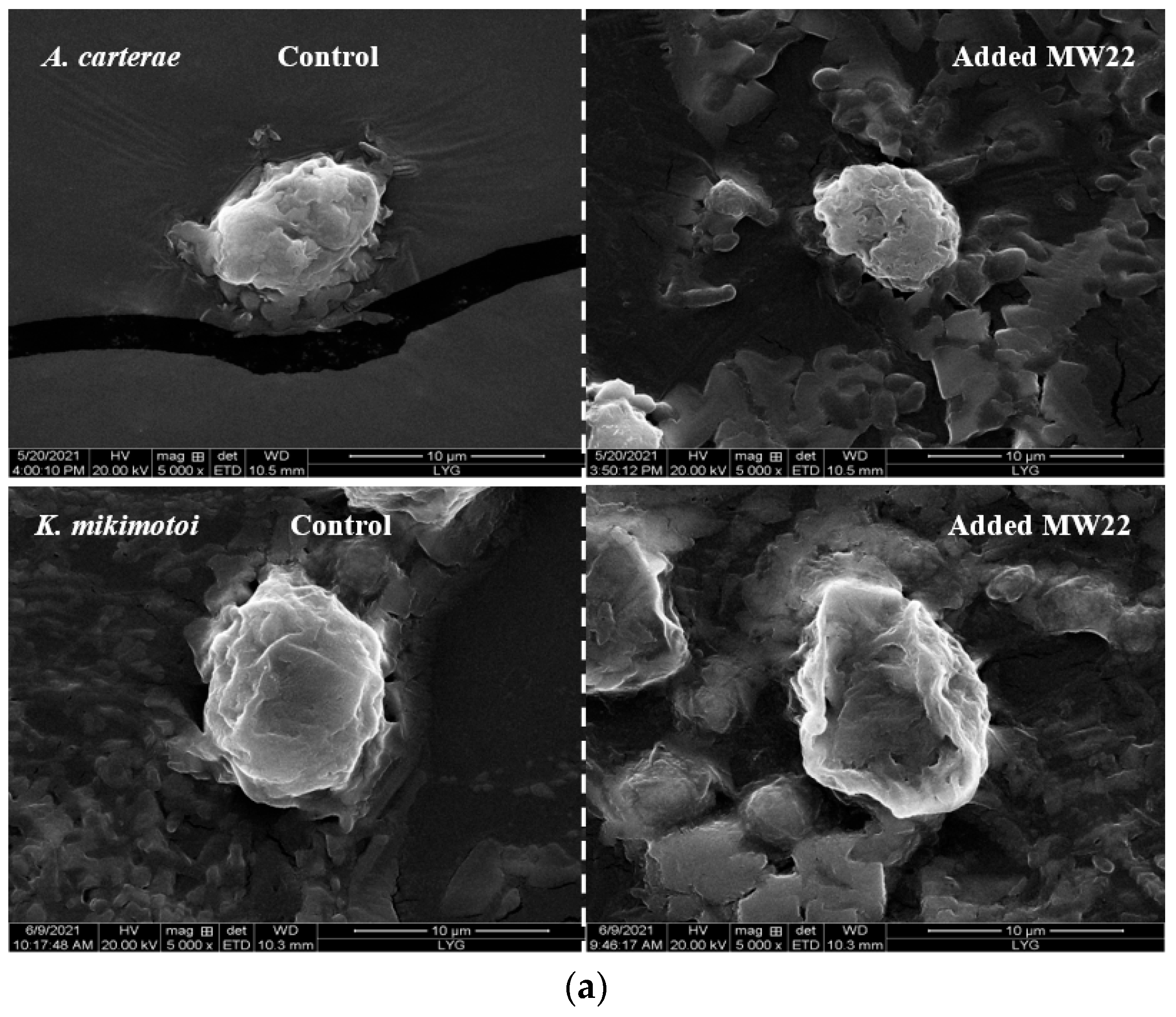
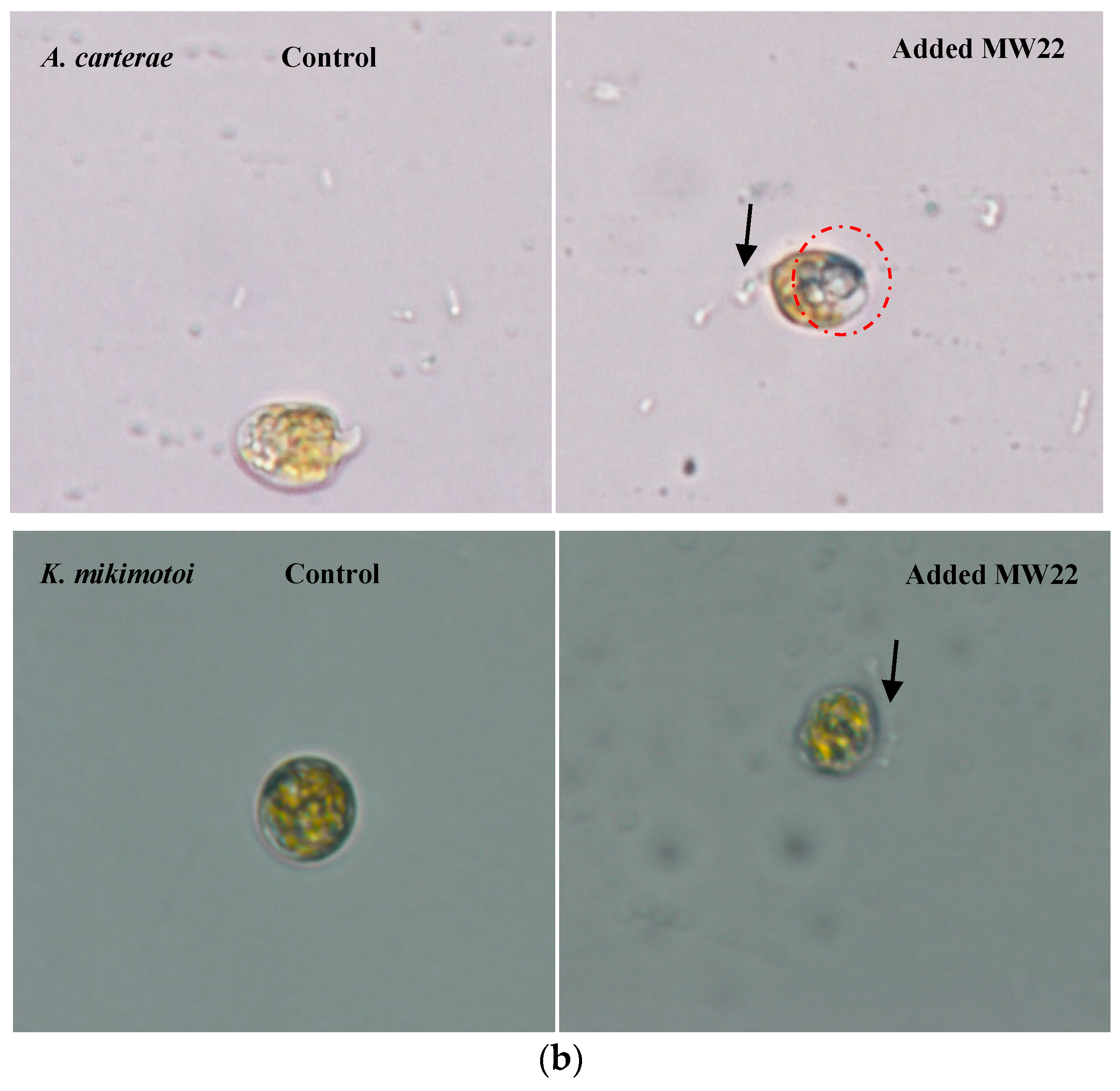
2.4. Antialgal Activity Analysis of Compound MW22
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. HAB Algae
4.2. Marine Macroalgae
4.3. Preparation of Fractions via Liquid–Liquid Extraction
4.4. Thin-Layer Chromatography Determination and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy Analysis
4.5. Infrared Spectrogram Analysis
4.6. Antialgal Activity
4.6.1. Antialgal Activity of Fractions
4.6.2. Antialgal Activity of Purified Compound
4.7. Isolation and Identification
4.8. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, X.; Zhang, H.; Huang, B.Q.; Lin, S.J. Alkaline phosphatase gene sequence and transcriptional regulation by phosphate limitation in Amphidinium carterae (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granéli, E.; Weberg, M.; Salomon, P.S. Harmful algal blooms of allelopathic microalgal species: The role of eutrophication. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, H.S.; Saifullah, S.M.; Dar, A. Occurrence and toxicity of Amphidinium carterae Hulburt in the North Arabian Sea. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentien, P.; Lunven, M.; Lazure, P.; Youenou, A.; Crassous, M.P. Motility and autotoxicity in Karenia mikimotoi (Dinophyceae). Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 1937–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, I.; Yamaguchi, M.; Hori, Y. Eutrophication and occurrences of harmful algal blooms in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan. Plankton Benthos Res. 2006, 1, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.J.; Zhu, M.Y. Progress of the project “ecology and oceanography of harmful algal blooms in China”. Adv. Earth Sci. 2006, 21, 673, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.C.; Lv, S.H.; Qi, Y.Z.; Zhou, M.J. Progress and perspectives of harmful algal bloom studies in China. Oceanol. ET Limnol. Sinaca 2020, 51, 768–788, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, J.H.; Jin, H.; Sohn, C.H.; Suh, K.H.; Hong, Y.K. Algicidal activity of the seaweed Corallina pilulifera against red tide microalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2000, 12, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.L.; You, J.G.; Wu, H.L.; Liu, Y.Y.; He, P.M. Bioremediation using Gracilaria lemaneiformis to manage the nitrogen and phosphorous balance in an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system in Yantian Bay, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Z.; Gobler, C.J. The green macroalga, Ulva lactuca, inhibits the growth of seven common harmful algal bloom species via allelopathy. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Zhou, W.J.; Wang, H.; Guo, G.L.; Su, Z.X.; Pu, Y.F. Antialgal compounds with antialgal activity against the common red tide microalgae from a green algae Ulva pertusa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Dong, S.S.; Zhou, W.J.; Guo, L.; Guo, G.L.; Zhang, X. A comprehensive review of secondary metabolites with antialgal activity from marine macroalgae against red tide microalgae. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 93, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamsjah, M.A.; Hirao, S.; Ishibashi, F.; Fujita, Y. Isolation and structure determination of algicidal compounds from Ulva fasciata. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accoroni, S.; Percopo, I.; Cerino, F.; Romagnoli, T.; Pichierri, S.; Perrone, C.; Totti, C. Allelopathic interactions between the HAB dinoflagellate Ostreopsis cf. ovata and macroalgae. Harmful Algae 2015, 49, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Dong, S.S.; Zhang, N.S.; Zhou, J.; Long, Z.K. Screening and isolation of glyceroglycolipids with antialgal activity from several marine macroalgae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 2609–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.M. Chemical Constituents of the Seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis and Their Allelopathic Effects on Skeletonema costatum. Ph.D. Thesis, Jinan University of China, Guangzhou, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Jin, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, W.; Li, Y.; Xu, N. Screening and isolation of the algicidal compounds from marine green alga Ulva intestinalis. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2016, 34, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.W.; Zhou, W.J.; Mao, Y.L.; Guo, G.L.; Wang, C.H.; Sun, Y.Y. Isolation and purification of diketopiperazines with antialgal activity from marine macroalgae. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2023, 25, 25–43. [Google Scholar]
- Hirao, S.; Tara, K.; Kuwano, K.; Tanaka, J.; Ishibashi, F. Algicidal activity of glycerolipids from brown alga Ishige sinicola toward red tide microalgae. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 372–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Cui, G.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Tan, R.X. Pinelloside, an antimicrobial cerebroside from Pinellia ternate. Phytochemistry 2008, 64, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, B.Y.; Sun, Y.M.; Yang, G.K.; Yang, H. Optimization of fermentation condition for glycolipid production by hydrocarbon degrading bacteria HB29. China Brew. 2009, 28, 83–85, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, M.Y.; Fu, B.Q. A Review of the studies on the polysaccharide structure. J. Nanchang Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2001, 25, 197–204, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.D.; Ma, C.Y.; Tan, G.; Sydara, K.; Tamez, P.; Southavong, B.; Bouamanivong, S.; Soejarto, D.D.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Harry, H.S.; et al. Rourinoside and rouremin, antimalarial constituents from Rourea minor. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Tang, X. Identification of the toxic compounds produced by Sargassum thunbergii to red tide microalgae. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Bi, W.H.; Gan, W.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, B.J.; Fu, G.W.; Jiang, T.J. Identification of ichthyotoxic red tide algae based on three-dimensional fluorescence spectra and particle swarm optimization support vector machine. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 268, 120711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leila, B.; Jyoji, G.; Sho, O.; Keita, H.; Satoshi, N.; Kiyohito, N. Sublethal and antioxidant effects of six ichthyotoxic algae on early-life stages of the Japanese pearl oyster. Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 102013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.S.; van Rijssel, M.; Yang, W.D.; Peng, X.C.; Lü, S.H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.F.; Wang, Z.H.; Qi, Y.Z. Negative effects of Phaeocystis globosa on microalgae. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2010, 28, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Ponomarev, A.V. Low-dose electron beam treatment of red tide blooms microalgae. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 179, 109–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, M.S.; Park, N.B.; Lee, C. Control of the red tide dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides by ozone in seawater. Water Res. 2017, 109, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lee, Y.; Jung, S.G.; Kim, M.J.; Eom, C.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Cho, H.; Jin, E. A novel thiazolidinedione derivative TD118 showing selective algicidal effects for red tide control. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioboo, C.; Prado, R.; Herrero, C.; Caid, A. Population growth study of the rotifer Brachionus sp. fed with triazine-exposed microalgae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 83, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Imai, I.; Fujimaru, D.; Nishigaki, T. Co-culture of fish with macroalgae and associated bacteria: A possible mitigation strategy for noxious red tides in enclosed coastal sea. Fish. Sci. 2008, 68, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Maleki, S.J.; Marcos, A.; Xu, S.S.; Shi, C.L.; Cao, M.J.; Liu, G.M. Anti food allergic activity of sulfated polysaccharide from Gracilaria lemaneiformis is dependent on immunosuppression and inhibition of p38 MAPK. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 22, 4536–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Alga Growth Inhibition Test. Test Guideline No. 201. OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, M.T.H.; Bangoura, I.; Kang, J.Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Joo, J.; Choi, Y.S.; Hwang, D.S.; Hong, Y.K. Comparison of Ecklonia cava, Ecklonia stolonifera and Eisenia bicyclis for phlorotannin extraction. J. Environ. Biol. 2014, 35, 713. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Xing, Z.; Zhang, J.S.; Zhou, W.J.; Pu, Y.F. Sesquiterpenoids with antialgal activity against the common red tide microalgae from marine macroalgae Porphyra yezoensis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 7844–7859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, G.L.; Pu, Y.F.; Yan, B.L.; Wang, C.H. Isolation, purification and identification of antialgal substances in green alga Ulva prolifera for antialgal activity against the common harmful red tide microalgae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premarathna, A.D.; Ahmed, T.A.E.; Kulshreshtha, G.; Humayun, S.; Darko, C.N.S.; Rjabovs, V.; Hammami, R.; Critchley, A.T.; Tuvikene, R.; Hincke, M.T. Polysaccharides from red seaweeds: Effect of extraction methods on physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant activities. Food Hydrocolloids 2024, 47, 109307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.H.; Je, J.G.; Sim, J.H.; Ryu, B.; Heo, S.J.; Jeon, Y.J. Quantitative analysis of fucose in fucoidans from Sargassum spp. in Jeju Island, South Korea using 3-methyl-1-phenyl-5-pyrazolone derivatization and RP-HPLC-UV method. Algal Res. 2024, 79, 103441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, R.N.; Zhai, H.L.; Qi, B.; Yang, X.Q. Optimization of multi-enzymatic extraction of polysaccharide from Gelidium amansii by response surface methodology. South China Fish. Sci. 2019, 15, 88–95, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.L.; Hu, Y.N.; Yang, B.; Zhao, X.; Wang, P.P.; Ji, G.L.; Wu, J.D.; Guan, H.S. Extraction‚ isolation and structural characterization of polysaccharides from a red alga Gloiopeltis furcate. Period. Ocean. Univ. China 2009, 39, 925–929, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.D.; He, P.P.; Wu, L.; Yu, G.; Zhu, Y.B.; Li, L.J.; Ni, H.; Oda, T.; Li, Q.B. Structural characterization and pro-angiogenic property of a polysaccharide isolated from red seaweed Bangia fusco-purpurea. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 18, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Xu, J.; Xu, X. Bioactivity of fucoidan extracted from Laminaria japonica using a novel procedure with high yield. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OuYang, D.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Su, L.J. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme prepared by six combined enzymatic methods. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2024. (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, G.L.; Pu, Y.F.; Yan, B.L.; Wang, C.H. Green alga Ulva pertusa—A new source of bioactive compounds with antialgal activity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10351–10359. [Google Scholar]
- Kakisawa, H.; Asari, F.; Kusumi, T.; Toma, T.; Sakurai, T.; Oohusa, T.; Hara, Y.; Chiharai, M. An allelopathic fatty acid from the brown alga Aladosiphon okaamuranus. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, T.; Alves, E.; Azevedo, V.; Martins, A.S.; Neves, B.; Domingues, P.; Calado, R.; Abreu, M.H.; Domingues, M.R. Lipidomics as a new approach for the bioprospecting of marine macroalgae-Unraveling the polar lipid and fatty acid composition of Chondrus crispus. Algal Res. 2015, 8, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plouguerné, E.; da Gama, B.A.P.; Pereira, R.C.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Glycolipids from seaweeds and their potential biotechnological applications. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plouguerné, E.; de Souza, L.M.; Sassaki, G.L.; Hellio, C.; Trepos, R.; da Gama, B.A.P.; Pereira, R.C.; Barreto-Bergter, E. Glycoglycerolipids from Sargassum vulgare as potential antifouling agents. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamsjah, M.A.; Ishibe, K.; Kim, D.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ishibashi, F.; Fujita, Y.; Tatsyya, O.D.A. Selective toxic effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids derived from Ulva fasciata on red tide phyotoplanker species. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jüttner, F. Liberation of 5,8,11,14,17-eicosapentaenoc acid and other polyunsaturated fatty acids from lipids as a grazer defense reaction in epilithic diatom biofilms. J. Phycol. 2001, 37, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Mizushina, Y.; Hirata, N.; Takemura, M.; Sugawara, F.; Matsukage, A.; Yoshida, S.; Sakaguchi, K. Sufoquinovosyldiacylglycerol, KM043, a new potent inhibitor of eukaryotic DNA polymerases and HIV-reverse transcriptase type 1 from a marine red alga, Gigartina tenella. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1998, 46, 684–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agafonov, A.; Gritsenko, E.; Belosludtsev, K.; Kovalev, A.; Gateau-Roesch, O.; Saris, N.E.L.; Mironova, G.D. A permeability transition in liposomes induced by the formation of Ca2+/palmiticacid complexes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2003, 1609, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, Q.; Tian, X.J. The inhibitory effects of palmitic acid and stearic acid on Microcystis aeruginosa. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 19, 291–295, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.H.; Choi, E.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.S.; Chang, S.G.; Choi, J.S.; Park, K.J.; Roh, K.B.; Lee, J.; Yoo, B.C.; et al. Oxidative stress-protective and anti-melanogenic effects of loliolide and ethanol extract from frees water green algae, Prasiola japonica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, B.D.; Nichols, P.D.; Miguel, F.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Lipid, fatty acid, and sterol composition of eight species of Kareniaceae (Dinophyta): Chemotaxonomy and putative lipid phycotoxins. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.W. Effects of the Variously Ambient Nitrogen, Phosphorus Concentrations and Niturogen Sources on Growth of Karenia mikimotoi under Laboratory Conditions. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, 2010; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Armando, M.F.; del Pilar, S.S.M. Light irradiance modifies the fatty acid composition of Amphidinium carterae (Dinophyceae). Phycologia 2023, 62, 525–531. [Google Scholar]
- Guillard, R.R.L.; Ryther, J.H. Studies of marine planktonic diatom. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 1962, 17, 309–314. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, W.T.L.; Thien, V.Y.; Misson, M.; Chin, G.J.W.L.; Hussin, S.N.I.S.; Chong, H.L.H.; Yusof, N.A.; Ma, N.L.; Rodrigues, K.F. Seaweed: A bioindustrial game-changer for the green revolution. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 183, 107122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Extracts | Fractions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethyl Acetate Fraction | N-Butanol Fraction | Aqueous Fraction | ||
| B. purpurea | 225.2 ± 12.4 | 64.1 ± 7.3 | 60.9 ± 4.7 | 81.3 ± 6.6 |
| G. amansii | 122.6 ± 11.5 | 28.3 ± 3.9 | 53.4 ± 5.3 | 35.3 ± 4.7 |
| G. furcate | 176.9 ± 10.7 | 25.2 ± 4.1 | 47.2 ± 5.7 | 53.2 ± 6.9 |
| H. fusifarme | 363.3 ± 17.7 | 247.1 ± 15.6 | 61.9 ± 6.2 | 34.1 ± 7.2 |
| L. japonica | 345.4 ± 21.6 | 50.7 ± 6.7 | 102.3 ± 9.4 | 183.2 ± 21.4 |
| P. palmata | 43.6 ± 6.4 | 21.5 ± 1.4 | 10.1 ± 2.5 | 9.3 ± 3.5 |
| Sargassum sp. | 78.6 ± 5.4 | 67.6 ± 4.9 | 2.6 ± 0.98 | 5.7 ± 1.2 |
| A. carterae | K. mikimotoi | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethyl Acetate Fraction | N-Butanol Fraction | Aqueous Fraction | Ethyl Acetate Fraction | N-Butanol Fraction | Aqueous Fraction | |
| B. purpurea | ++ | - | - | ++ | - | ++ |
| G. amansii | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| G. furcate | ++ | - | - | ++ | - | - |
| H. fusifarme | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | - | + |
| L. japonica | - | + | ++ | - | - | ++ |
| P. palmata | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | - |
| Sargassum sp. | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ |
| C. No. | δ13C NMR | H. No. | δ 1H NMR | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-1 | 62.9 | H-1 | 3.30–3.45 (2H, m) | 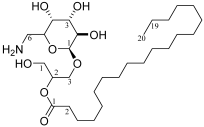 |
| C-2 | 69.5 | H-2 | 3.67 (1H, m) | |
| C-3 | 65.2 | H-3a | 3.51 (1H, dd, J = 6.0, 10.4, Hz) | |
| Sug-1 | 98.7 | H-3b | 3.91 (1H, dd, J = 4.8, 10.4, Hz) | |
| Sug-2 | 71.8 | Sug-1 | 4.57 (1H, d, J = 4.2) | |
| Sug-3 | 72.8 | Sug-2 | 3.16 (1H, m) | |
| Sug-4 | 74.1 | Sug-3 | 3.35 (1H, d, J = 7.8) | |
| Sug-5 | 68.3 | Sug-4 | 2.91 (1H, m) | |
| Sug-6 | 54.8 | Sug-5 | 3.80 (1H, m) | |
| fatty-1 | 172.9 | Sug-6a | 2.92 (1H, m) | |
| fatty-2 | 33.3 | Sug-6b | 2.56 (1H, m) | |
| fatty-3 | 24.3 | fatty-2 | 2.29 (2H, m) | |
| fatty-4~18 | 28.6–29.5 | fatty-3 | 1.52 (2H, m) | |
| fatty-19 | 22.0 | fatty-4~19 | 1.23–1.25 (32H, m) | |
| fatty-20 | 13.1 | fatty-20 | 0.86 (3H, t, J = 7.0 Hz) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, X.; Pu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.; He, P.; Zheng, S. Purification and Screening of the Antialgal Activity of Seaweed Extracts and a New Glycolipid Derivative against Two Ichthyotoxic Red Tide Microalgae Amphidinium carterae and Karenia mikimotoi. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060279
Sun Y, Li H, Ma X, Pu M, Zhang Y, Dong Z, He P, Zheng S. Purification and Screening of the Antialgal Activity of Seaweed Extracts and a New Glycolipid Derivative against Two Ichthyotoxic Red Tide Microalgae Amphidinium carterae and Karenia mikimotoi. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(6):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060279
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Yingying, Hui Li, Xiao Ma, Mengxuan Pu, Yuqi Zhang, Zhuohan Dong, Peicong He, and Shiyan Zheng. 2024. "Purification and Screening of the Antialgal Activity of Seaweed Extracts and a New Glycolipid Derivative against Two Ichthyotoxic Red Tide Microalgae Amphidinium carterae and Karenia mikimotoi" Marine Drugs 22, no. 6: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060279
APA StyleSun, Y., Li, H., Ma, X., Pu, M., Zhang, Y., Dong, Z., He, P., & Zheng, S. (2024). Purification and Screening of the Antialgal Activity of Seaweed Extracts and a New Glycolipid Derivative against Two Ichthyotoxic Red Tide Microalgae Amphidinium carterae and Karenia mikimotoi. Marine Drugs, 22(6), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22060279





