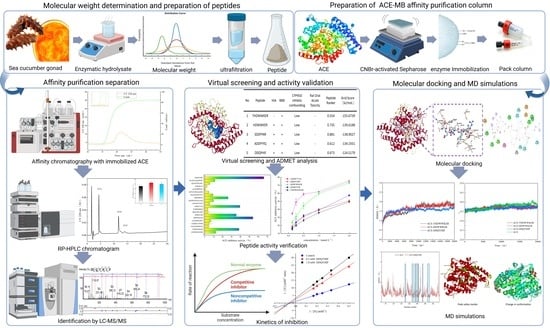
Targeted Affinity Purification and Mechanism of Action of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Sea Cucumber Gonads
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
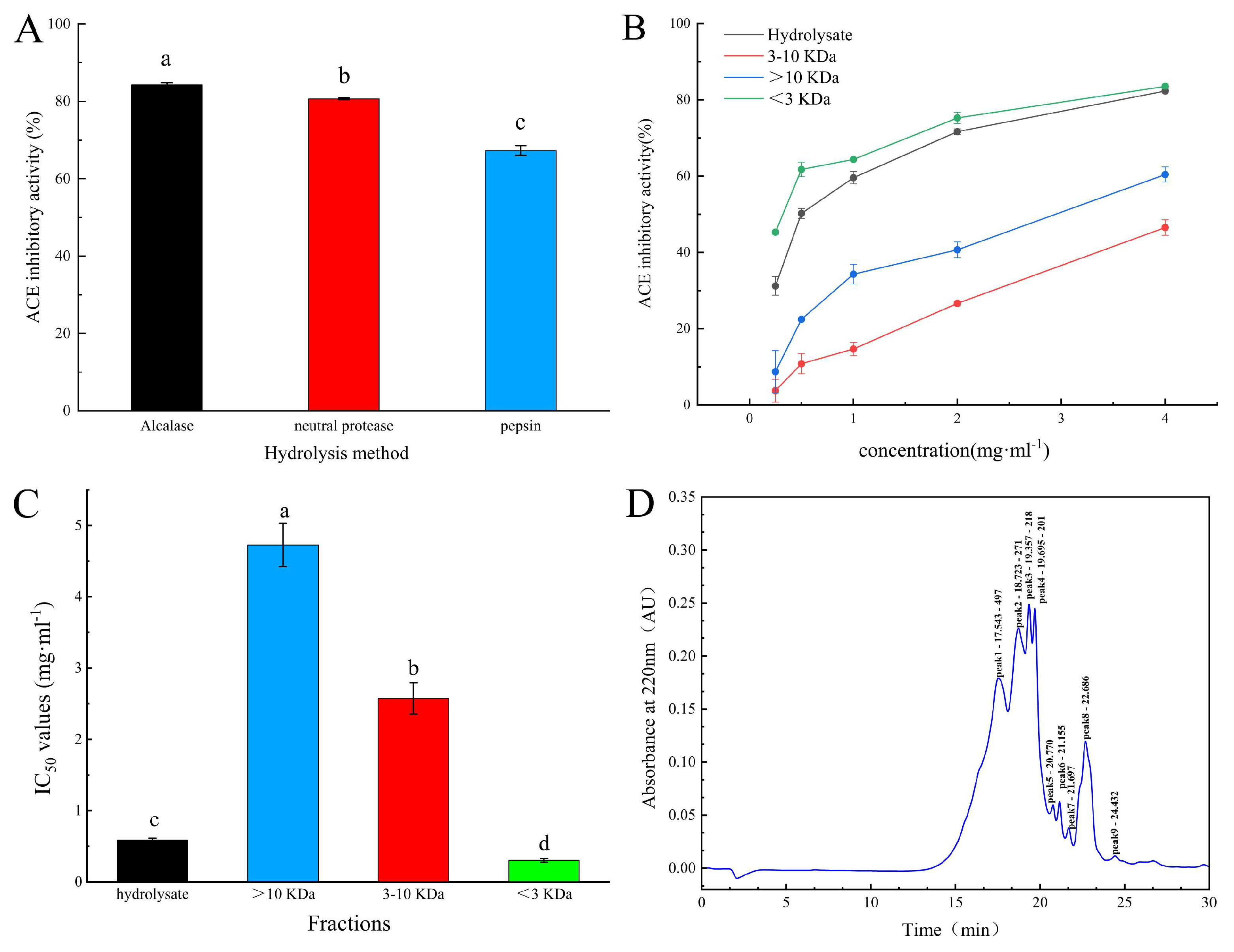
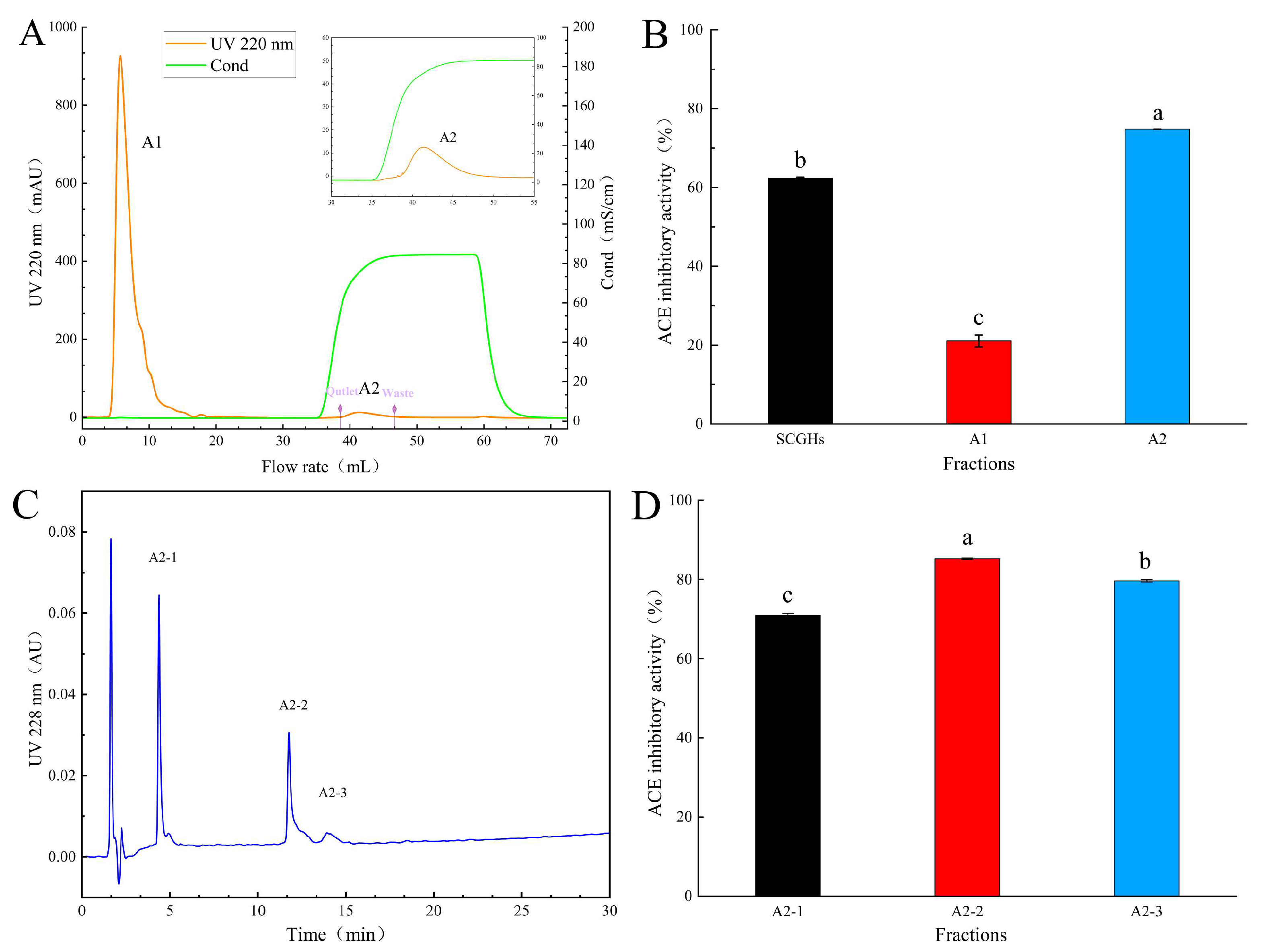
2.1. Isolation and Purification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides
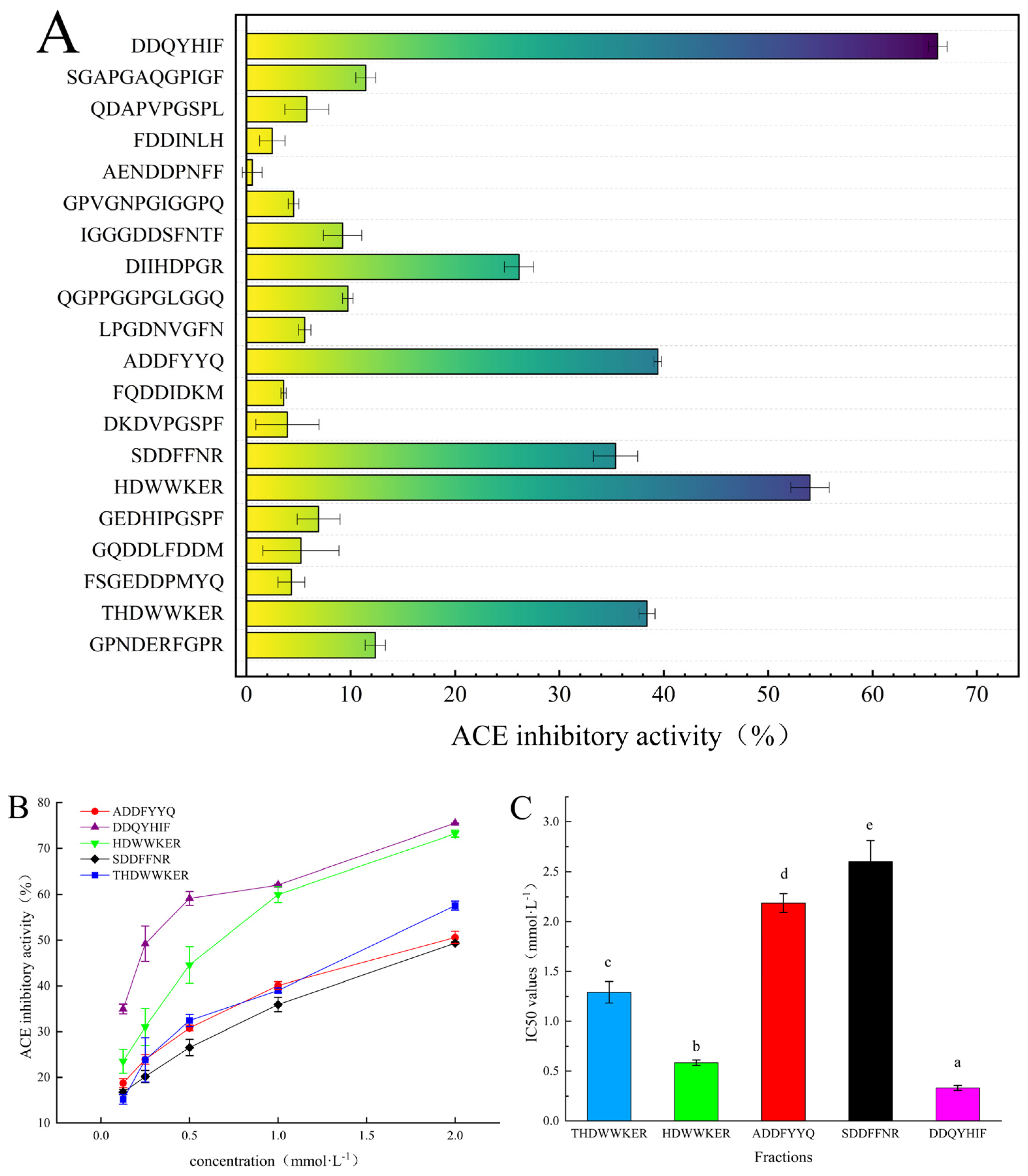
2.2. Identification and Pharmacochemical Analysis of ACE Inhibitory Peptides
2.3. Peptide Synthesis, Inhibition Rate, and Inhibition Type
2.4. Molecular Docking Simulation
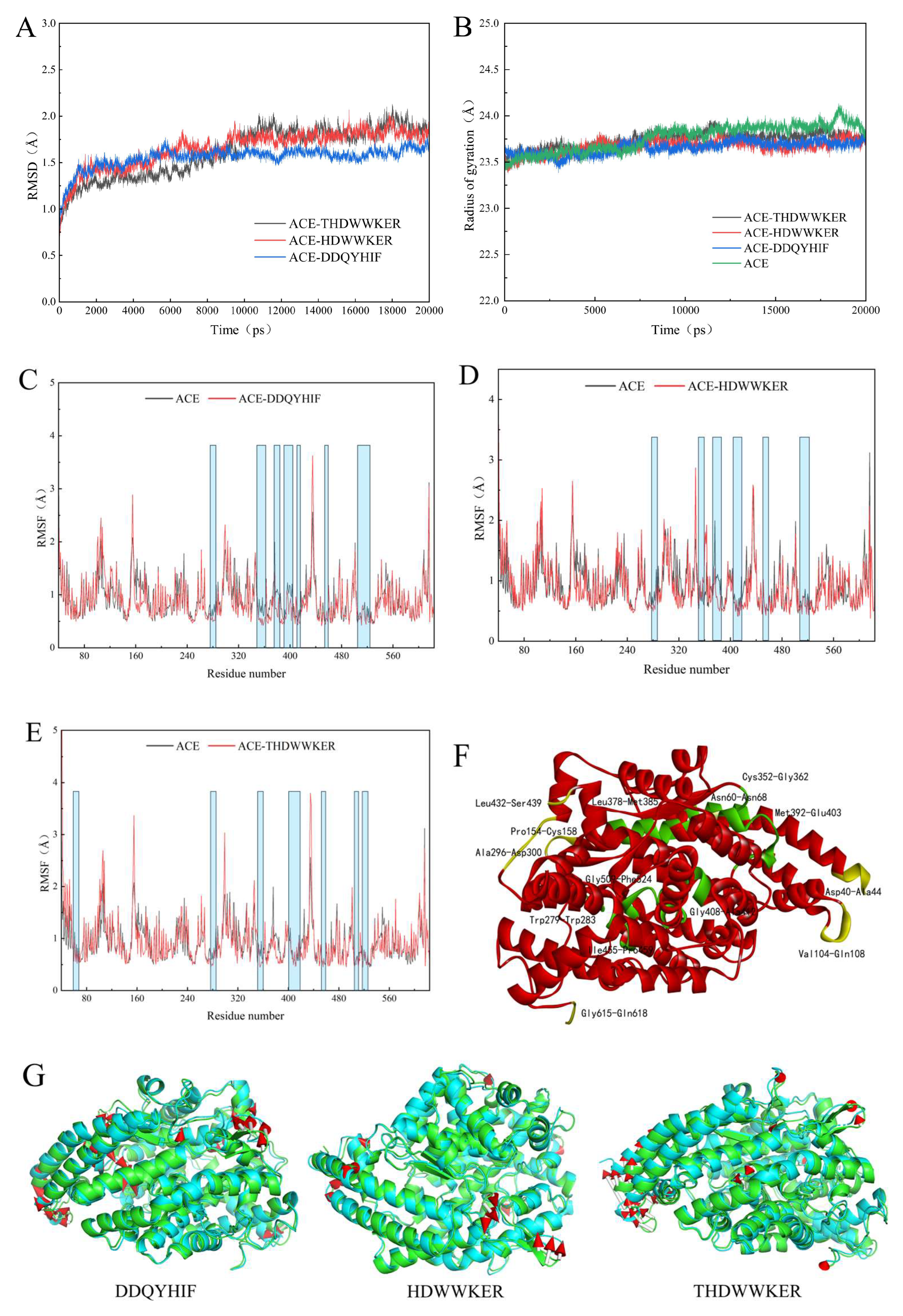
2.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
2.6. Binding Free Energy Calculations
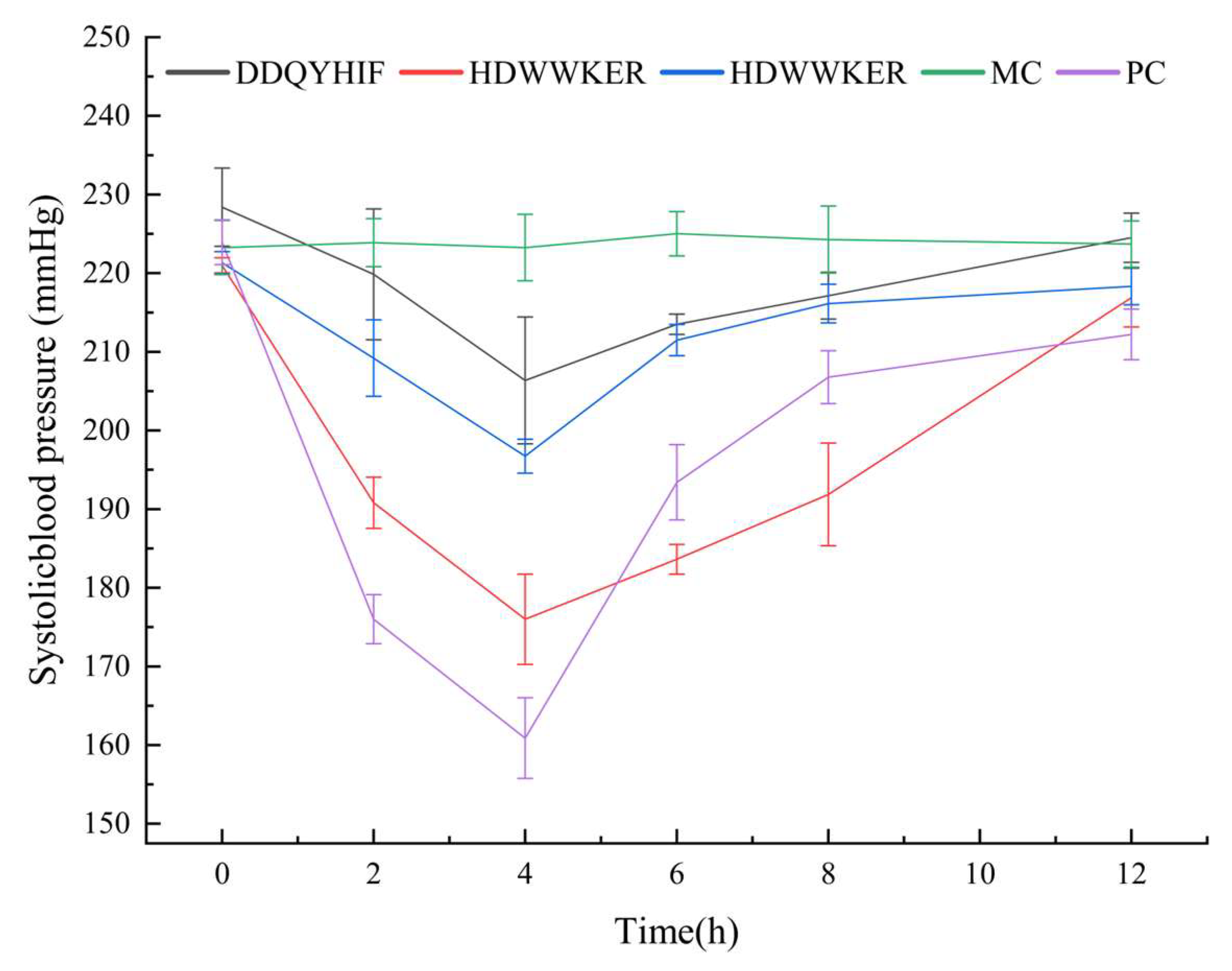
2.7. Antihypertensive Activity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Peptides from Sea Cucumber Gonads
3.3. Assay of ACE Inhibitory Activity
3.4. Determination of Molecular Weight of Hydrolysate
3.5. Targeted Affinity Purification
3.6. Analysis and Purification by RP-HPLC
3.7. Peptide Sequence Identification by LC–MS
3.8. Computer-Assisted Virtual Screening of Peptides
3.9. Peptide Synthesis, Medicinal Chemical Properties, and Activity Screening
3.10. Inhibitory Kinetic Study
3.11. Molecular Docking
3.12. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulation
3.13. Binding Free Energy Calculations
3.14. Antihypertensive Effect In Vivo
3.15. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, S.-H.; Qian, Z.-J.; Kim, S.-K. A novel angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from tuna frame protein hydrolysate and its antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem. 2010, 118, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liao, W.; Udenigwe, C.C. Revisiting the mechanisms of ACE inhibitory peptides from food proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lv, Z.; Guo, M. Research advancement of Apostichopus japonicus from 2000 to 2021. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 903–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Le, S.; Long, Y. Production, optimisation and characterisation of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus) gonad. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abachi, S.; Bazinet, L.; Beaulieu, L. Antihypertensive and Angiotensin-I-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from Fish as Potential Cardioprotective Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megías, C.; Pedroche, J.; Yust, M.d.M.; Alaiz, M.; Girón-Calle, J.; Millán, F.; Vioque, J. Affinity Purification of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Using Immobilized ACE. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 7120–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Lan, X.; Yaseen, M.; Chai, K.; Zhou, L.; Sun, J.; Lan, P.; Tong, Z.; Liao, D.; Sun, L. Immobilized metal affinity chromatography matrix modified by poly (ethylene glycol) methyl ether for purification of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from casein hydrolysate. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1143, 122042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Liao, D.; Sun, L.; Wu, S.; Lan, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, Y.; Lan, X. Affinity Purification of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides from Wakame (Undaria Pinnatifida) Using Immobilized ACE on Magnetic Metal Organic Frameworks. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Liao, D.; Wu, S.; Wang, F.; Sun, J.; Tong, Z. Rapid purification and characterization of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from lizard fish protein hydrolysates with magnetic affinity separation. Food Chem. 2015, 182, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Miguel, A.; Lan, T. Big data and artificial intelligence (AI) methodologies for computer-aided drug design (CADD). Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2022, 50, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, N.-N.; Yao, Z.-J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Lu, A.-P.; Cao, D.-S. ADMETlab: A platform for systematic ADMET evaluation based on a comprehensively collected ADMET database. J. Chemin. 2018, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghislat, G.; Rahman, T.; Ballester, P.J. Recent progress on the prospective application of machine learning to structure-based virtual screening. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 65, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y. Isolation, virtual screening, action mechanisms, chelation with zinc ions, and stability of ACE-inhibitory peptides from ginkgo seed globulin. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 30528–30538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Feng, Y.; Miao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Tang, S.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J.Z.H.; Zhang, L. Revealing the Sequence Characteristics and Molecular Mechanisms of ACE Inhibitory Peptides by Comprehensive Characterization of 160,000 Tetrapeptides. Foods 2023, 12, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y. Novel Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides Identified from Walnut Glutelin-1 Hydrolysates: Molecular Interaction, Stability, and Antihypertensive Effects. Nutrients 2021, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehseen, M.; Raducanu, V.-S.; Rashid, F.; Shirbini, A.; Takahashi, M.; Hamdan, S.M. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen-agarose column: A tag-free and tag-dependent tool for protein purification affinity chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1602, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, M.; Cai, S.; Pan, N.; Qiao, K.; Chen, B.; et al. Affinity Purification and Molecular Characterization of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides from Takifugu flavidus. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado-Cáceres, L.J.; Rabadán-Chávez, G.; Mojica, L.; Hernández-Ledesma, B.; Quevedo-Corona, L.; Cervantes, E.L. Cocoa (Theobroma cacao L.) Seed Proteins’ Anti-Obesity Potential through Lipase Inhibition Using In Silico, In Vitro and In Vivo Models. Foods 2020, 9, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, M.V.; Panchagnula, R. Prediction of in vivo intestinal absorption enhancement on P-glycoprotein inhibition, from rat in situ permeability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1694–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagoor Meeran, M.F.; Goyal, S.N.; Suchal, K.; Sharma, C.; Patil, C.R.; Ojha, S.K. Pharmacological Properties, Molecular Mechanisms, and Pharmaceutical Development of Asiatic Acid: A Pentacyclic Triterpenoid of Therapeutic Promise. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Lu, Z.; Sun, Y. Molecular Design, Structural Analysis and Antifungal Activity of Derivatives of Peptide CGA-N46. Interdiscip. Sci. 2016, 8, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wei, Y.; Chang, Q.; Sun, H.; Chai, K.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Z. Ultrafast Screening of a Novel, Moderately Hydrophilic Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme-Inhibitory Peptide, RYL, from Silkworm Pupa Using an Fe-Doped-Silkworm-Excrement-Derived Biocarbon: Waste Conversion by Waste. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 11202–11211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M.; Mogut, D.; Minkiewicz, P. Elucidation of the role of in silico methodologies in approaches to studying bioactive peptides derived from foods. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 61, 103486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, P.; Artursson, P. Oral absorption of peptides and nanoparticles across the human intestine: Opportunities, limitations and studies in human tissues. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 106, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Xing, L.; Wang, Z.; Cai, J.; Toldrá, F.; Zhang, W. Study on the anti-inflammatory activity of the porcine bone collagen peptides prepared by ultrasound-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 101, 106697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ai, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Pan, F.; Yang, Z.; Wang, O.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, L. Pancreatic lipase inhibitory effects of peptides derived from sesame proteins: In silico and in vitro analyses. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.-F.; Wang, H.; Wei, C.-K.; Thakur, K.; Wei, Z.-J.; Jiang, L. Three Novel ACE Inhibitory Peptides Isolated From Ginkgo biloba Seeds: Purification, Inhibitory Kinetic and Mechanism. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 9, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, I.; Valiente, P.A.; García, G.; Valdés-Tresanco, M.E.; Arrebola, Y.; Díaz, L.; Bounaadja, L.; Uribe, R.M.; Pacheco, M.C.; Florent, I.; et al. Discovery of novel non-competitive inhibitors of mammalian neutral M1 aminopeptidase (APN). Biochimie 2017, 142, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniak, A.; Minkiewicz, P.; Darewicz, M. Food-Originating ACE Inhibitors, Including Antihypertensive Peptides, as Preventive Food Components in Blood Pressure Reduction. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 114–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wu, J. LC–MS/MS coupled with QSAR modeling in characterising of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from soybean proteins. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2682–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, C.; Phillips, R.D. Plant Food-Derived Angiotensin I Converting Enzyme Inhibitory Peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5113–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Xu, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, N. Preparation and Identification of ACE Inhibitory Peptides from the Marine Macroalga Ulva intestinalis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins: Biochemistry, bioactivity and production. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 773–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yan, W.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Dai, Z.-Y. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from tilapia skin: Preparation, identification and its potential antihypertensive mechanism. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 137074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, C.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhao, T.; Waterhouse, G.I.; Zhao, M.; Su, G. Identification of post-digestion angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from soybean protein Isolate: Their production conditions and in silico molecular docking with ACE. Food Chem. 2020, 345, 128855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Alashi, A.M.; Young, J.F.; Therkildsen, M.; Aluko, R.E. Enzyme inhibition kinetics and molecular interactions of patatin peptides with angiotensin I-converting enzyme and renin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Zhang, R.; Liu, F.; Zheng, T.; Wu, W. Molecular mechanism of interactions between inhibitory tripeptide GEF and angiotensin-converting enzyme in aqueous solutions by molecular dynamic simulations. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikumar, P.S.; Rohini, K.; Rajesh, P.K. Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Principal Component Analysis on Human Laforin Mutation W32G and W32G/K87A. Protein J. 2014, 33, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, G.; Rajasekaran, R. Investigating the pernicious effects of heparan sulfate in serum amyloid A1 protein aggregation: A structural bioinformatics approach. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 40, 1776–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poli, G.; Granchi, C.; Rizzolio, F.; Tuccinardi, T. Application of MM-PBSA Methods in Virtual Screening. Molecules 2020, 25, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-X.; Sheng, Y.-J.; Ma, Y.-Q.; Ding, H.-M. Assessing the Performance of Screening MM/PBSA in Protein–Ligand Interactions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompella, U.B.; Lee, V.H. Delivery systems for penetration enhancement of peptide and protein drugs: Design considerations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 211–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Kapoor, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Gautam, A.; Kumar, R.; Raghava, G.P.S. In Silico Approach for Predicting Toxicity of Peptides and Proteins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Zhang, L.-W.; Han, X.; Cheng, D.-Y. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from protease hydrolysates of Qula casein: Quantitative structure-activity relationship modeling and molecular docking study. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 32, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, D.; Aktulga, H.; Belfon, K. AmberTools. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2023, 63, 6183–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Belfon, K.A.A.; Raguette, L.; Huang, H.; Migues, A.N.; Bickel, J.; Wang, Y.; Pincay, J.; Wu, Q.; et al. ff19SB: Amino-Acid-Specific Protein Backbone Parameters Trained against Quantum Mechanics Energy Surfaces in Solution. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 16, 528–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, T.E., III. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: Software for Processing and Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Trajectory Data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.R.; McGee, T.D.; Swails, J.M.; Homeyer, N.; Gohlke, H.; Roitberg, A.E. MMPBSA.py: An Efficient Program for End-State Free Energy Calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| No | Peptide | Mass (Da) | Water Solubility | Isoelectric Point | GRAVY | −10lgP | Peptide Ranker | Grid Score (kJ/mol.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GPNDERFGPR | 1144.21 | Insoluble | 6.07 | −2.07 | 34.50 | 0.814 | −164.7258 |
| 2 | THDWWKER | 1157.25 | Soluble | 6.42 | −2.64 | 29.53 | 0.554 | −155.6739 |
| 3 | FSGEDDPMYQ | 1188.23 | Soluble | 3.49 | −1.34 | 32.13 | 0.531 | −144.8246 |
| 4 | GQDDLFDDM | 1055.08 | Insoluble | 3.32 | −1.04 | 39.68 | 0.653 | −144.1646 |
| 5 | GEDHIPGSPF | 1055.11 | Soluble | 4.35 | −0.77 | 29.06 | 0.667 | −140.5179 |
| 6 | HDWWKER | 1056.15 | Soluble | 6.75 | −2.91 | 28.1 | 0.735 | −139.6188 |
| 7 | SDDFFNR | 899.92 | Soluble | 4.21 | −1.46 | 28.21 | 0.881 | −138.9027 |
| 8 | DKDVPGSPF | 961.04 | Soluble | 4.21 | −0.92 | 26.55 | 0.526 | −137.0551 |
| 9 | FQDDIDKM | 1011.11 | Insoluble | 3.93 | −1.09 | 27.61 | 0.582 | −134.7892 |
| 10 | ADDFYYQ | 920.93 | Insoluble | 3.56 | −1.21 | 26 | 0.612 | −134.1931 |
| 11 | LPGDNVGFN | 931.99 | Soluble | 3.8 | −0.23 | 33.28 | 0.652 | −133.1769 |
| 12 | QGPPGGPGLGGQ | 1021.09 | Soluble | 5.52 | −0.87 | 33.74 | 0.828 | −132.4893 |
| 13 | DIIHDPGR | 922.01 | Soluble | 5.21 | −0.96 | 31.59 | 0.517 | −130.6882 |
| 14 | IGGGDDSFNTF | 1129.15 | Insoluble | 3.56 | −0.28 | 42.29 | 0.607 | −130.2659 |
| 15 | GPVGNPGIGGPQ | 1049.15 | Insoluble | 5.52 | −0.42 | 45.69 | 0.625 | −129.655 |
| 16 | AENDDPNFF | 1068.06 | Insoluble | 3.49 | −1.3 | 42.99 | 0.746 | −126.6069 |
| 17 | FDDINLH | 872.93 | Insoluble | 4.2 | −0.37 | 25.82 | 0.511 | −125.8939 |
| 18 | QDAPVPGSPL | 980.09 | Soluble | 3.8 | −0.32 | 35.46 | 0.670 | −125.2897 |
| 19 | SGAPGAQGPIGF | 1058.16 | Soluble | 5.24 | 0.15 | 38.45 | 0.867 | −124.7403 |
| 20 | DDQYHIF | 936.98 | Insoluble | 4.2 | −1.1 | 30.33 | 0.673 | −124.5179 |
| No | Peptide | ADMET | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIA | BBB | CYP450 Inhibits Confounding | Rat Oral Acute Toxicity | AMES Toxicity | Carcinogenicity | ||
| 1 | GPNDERFGPR | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 2 | THDWWKER | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 3 | FSGEDDPMYQ | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 4 | GQDDLFDDM | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 5 | GEDHIPGSPF | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 6 | HDWWKER | + | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 7 | SDDFFNR | + | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 8 | DKDVPGSPF | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 9 | FQDDIDKM | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 10 | ADDFYYQ | + | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 11 | LPGDNVGFN | + | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 12 | QGPPGGPGLGGQ | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 13 | DIIHDPGR | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 14 | IGGGDDSFNTF | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 15 | GPVGNPGIGGPQ | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 16 | AENDDPNFF | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 17 | FDDINLH | + | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 18 | QDAPVPGSPL | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 19 | SGAPGAQGPIGF | - | + | Low | - | - | - |
| 20 | DDQYHIF | + | + | Low | - | - | - |
| Active Pocket | Amino Acid Residue | Lisinopril | THDWWKER | DDQYHIF | HDWWKER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Ala354 | + | + | + | + |
| Tyr523 | + | + | + | + | |
| Glu384 | + | - | - | - | |
| S2 | Gln281 | - | + | + | + |
| His353 | - | + | - | + | |
| Lys511 | - | + | + | + | |
| His513 | + | - | - | - | |
| Tyr520 | + | + | - | + | |
| S1′ | Glu162 | - | - | - | - |
| T | His383 | + | - | + | + |
| His387 | + | - | - | - | |
| Glu411 | + | - | - | - |
| Energy Term | ACE–DDQYHIF | ACE–HDWWKER | ACE–THDWWKER |
|---|---|---|---|
| ΔGvdw | −79.8 ± 5.1 | −93.7 ± 7.5 | −85.2 ± 6.3 |
| ΔGele | 58.6 ± 16.9 | −411.8 ± 40.5 | −444.1 ± 21.9 |
| ΔGpolar | 7.6 ± 17.6 | 443.5 ± 33.8 | 470.5 ± 22.2 |
| ΔGnonpolar | −8.4 ± 0.3 | −9.6 ± 0.2 | −10.2 ± 0.3 |
| ΔGgas | −21.2 ± 17.3 | −505.5 ± 38.3 | −529.4 ± 20.1 |
| ΔGsolv | −0.7 ± 17.4 | 433.9 ± 33.8 | 460.3 ± 22.1 |
| ΔGtotal | −21.9 ± 9.4 | −71.6 ± 11.4 | −69.1 ± 11.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Shi, W.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Pan, N.; Wang, X.; Su, Y.; Liu, Z. Targeted Affinity Purification and Mechanism of Action of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Sea Cucumber Gonads. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020090
Wang Y, Chen S, Shi W, Liu S, Chen X, Pan N, Wang X, Su Y, Liu Z. Targeted Affinity Purification and Mechanism of Action of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Sea Cucumber Gonads. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(2):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020090
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yangduo, Shicheng Chen, Wenzheng Shi, Shuji Liu, Xiaoting Chen, Nan Pan, Xiaoyan Wang, Yongchang Su, and Zhiyu Liu. 2024. "Targeted Affinity Purification and Mechanism of Action of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Sea Cucumber Gonads" Marine Drugs 22, no. 2: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020090
APA StyleWang, Y., Chen, S., Shi, W., Liu, S., Chen, X., Pan, N., Wang, X., Su, Y., & Liu, Z. (2024). Targeted Affinity Purification and Mechanism of Action of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptides from Sea Cucumber Gonads. Marine Drugs, 22(2), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22020090