Anticancer Activity of the Marine Triterpene Glycoside Cucumarioside A2-2 in Human Prostate Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CA2-2 Inhibits Prostate Cancer Cell Viability
2.2. CA2-2 Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Colony Formation in PC-3 Prostate Cancer Cells
2.3. CA2-2 Arrests Cell Cycle of Prostate Cancer Cell
2.4. CA2-2 Regulates Expression of Proteins Involved in Growth, Migration, Invasion, and Cell Death in Prostate Cancer Cells
2.4.1. Proteomics Analysis of Proteins Using 2D-PAGE, MALDI-MS, and Bioinformatic Analysis
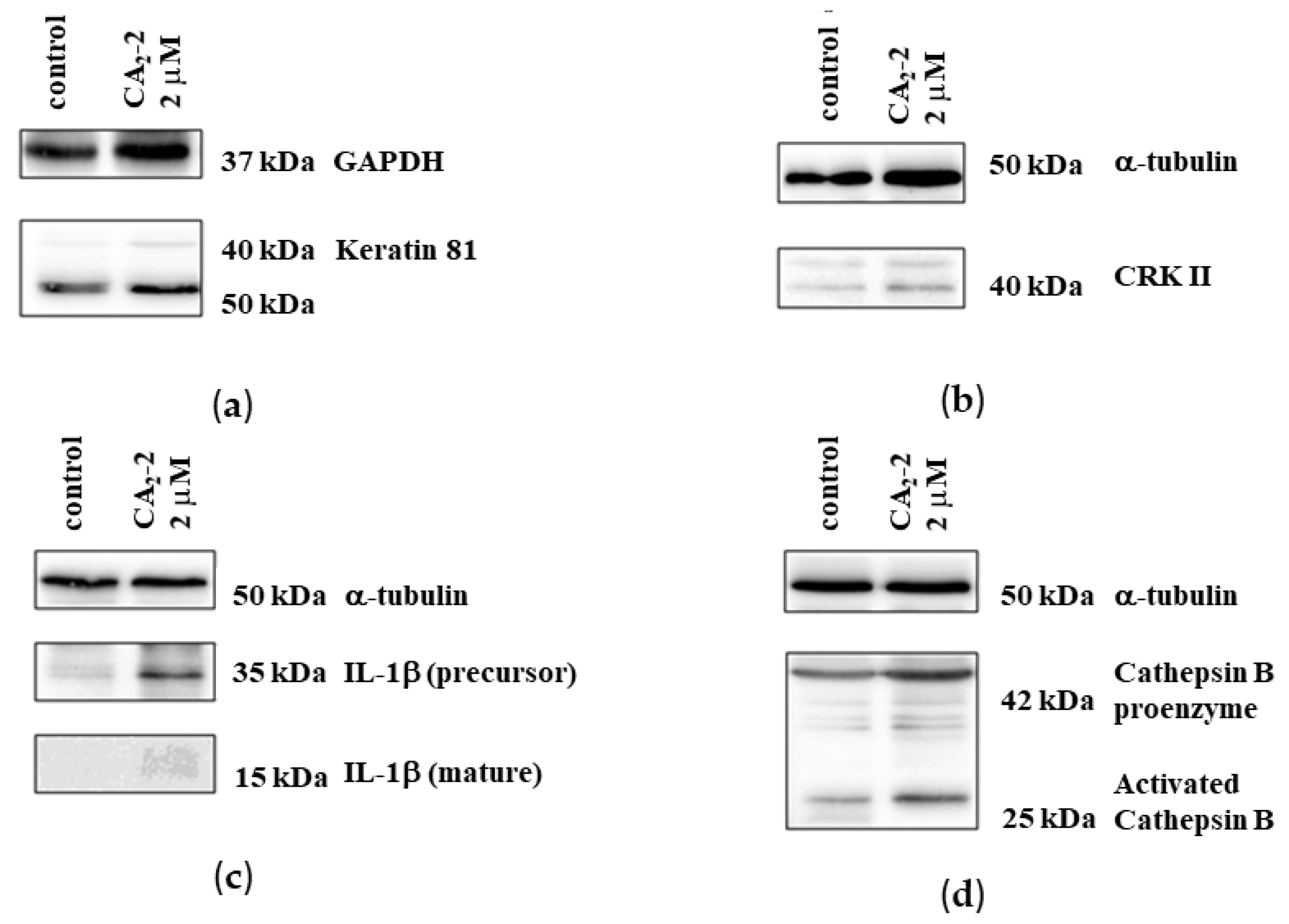
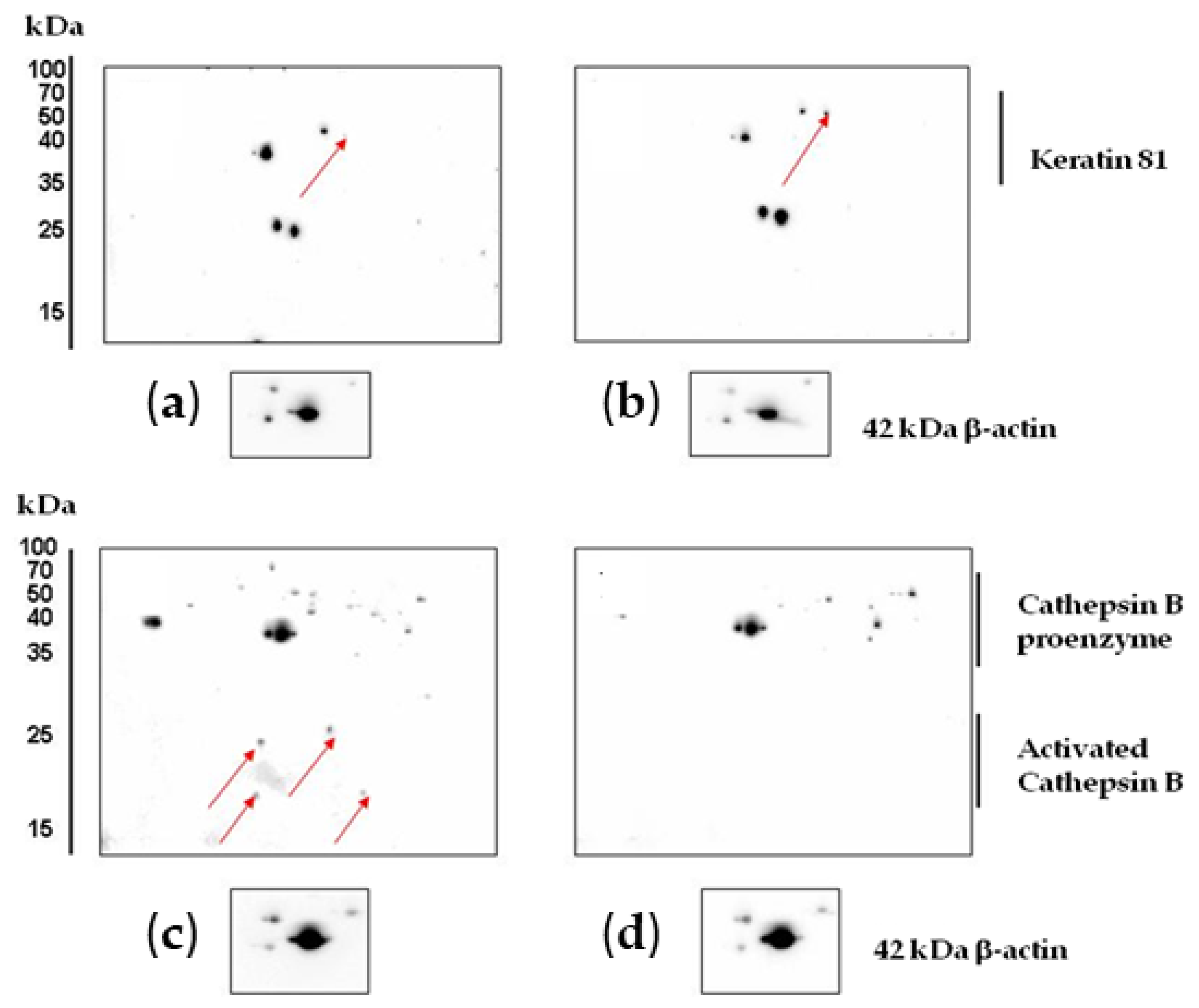
2.4.2. Verification of Protein Expression by Western Blotting and 2D Western Blotting
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. Colony Formation Assay
4.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis (2D-PAGE)
4.8. 2D-Gel Image Analysis and Protein Identification by Mass Spectrometry
4.9. Bioinformatic Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins
4.10. Mini 2D Western Blotting Analysis (2D-WB)
4.11. Statistics
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of prostate cancer. World. J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkens, L.; Sailer, V.; Lessel, D.; Janzen, E.; Greimeier, S.; Kirfel, J.; Perner, S.; Pantel, K.; Werner, S.; von Amsberg, G. Aggressive variants of prostate cancer: Underlying mechanisms of neuroendocrine transdifferentiation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2022, 41, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Honecker, F. Marine Compounds and Cancer: Updates 2022. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Honecker, F. Marine Compounds and Cancer: Updates 2020. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta Correia-da-Silva, M.; Sousa, E.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Kijjoa, A. Anticancer and cancer preventive compounds from edible marine organisms. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 46, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Aminin, D.L.; Avilov, S.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Stonik, V.A. Triterpene glycosides from sea cucucmbers (Holothurioidae, Echinodermata), biological activities and functions. In Studies in Natural Product Chemistry (Bioactive Natural Products); Rahman, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; Volume 35, pp. 135–196. [Google Scholar]
- Aminin, D.L.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Stadnichenko, N.I.; Collin, P.D.; Kalinin, V.I. Review of patents based on triterpene glycosides of sea cucumbers. In Studies in Natural Product Chemistry (Bioactive Natural Products); Rahman, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 51, pp. 175–200. [Google Scholar]
- Aminin, D.L.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Pisliagin, E.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I. Anticancer activity of sea cucumber triterpene glycosides. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1202–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.-H.; Sim, E.-H.; Han, S.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Silchenko, A.S.; Stonik, V.A.; Park, J.-I. Holotoxin A1 induces apoptosis by activating acid sphingomyelinase and neutral sphingomyelinase in K562 and human primary leukemia cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luparello, C.; Ragona, D.; Asaro, D.M.L.; Lazzara, V.; Affranchi, F.; Celi, M.; Arizza, V.; Vazzana, M. Cytotoxic potential of the coelomic fluid extracted from the sea cucumber Holothuria tubulosa against triple-negative MDA-MB231 breast cancer cells. Biology 2019, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tang, L.; Tao, M.; Cui, C.; He, D.; Li, L.; Liao, Y.; Gao, Y.; He, J.; Sun, F.; et al. Stichoposide C exerts anticancer effects on ovarian cancer by inducing autophagy via inhibiting AKT/mTOR pathway. Onco. Targets Ther. 2022, 21, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careagaa, V.P.; Buenob, C.; Muniainc, C.; Alché, L.; Maiera, M.S. Pseudocnoside A, a new cytotoxic and antiproliferative triterpene glycoside from the sea cucumber Pseudocnus dubiosus leoninus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Popov, R.S.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Chingizova, E.A.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Panina, E.G.; Stepanov, V.G.; Kalinin, V.I.; et al. Djakonoviosides A, A1, A2, B1-B4—Triterpene monosulfated tetra- and pentaosides from the sea cucumber Cucumaria djakonovi: The first finding of a hemiketal fragment in the aglycones; activity against human breast cancer cell lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyarenko, T.V.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Kicha, A.A.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Ivanchina, N.V. In vitro anticancer and cancer-preventive activity of new triterpene glycosides from the Far Eastern starfish Solaster pacificus. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althunibat, O.Y.; Hashim, R.B.; Taher, M.; Jamaludin, M.D.; Ikeda, M.-A.; Zali, B.I. In vitro antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of three Malaysian sea cucumber species. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 37, 376–387. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, T.-J.; Yuan, W.-P.; Cong, R.-S.; Yang, X.-X.; Wang, W.-W.; Jing, Z. Studies on the purification of water-soluble holothurian glycosides from Apostichopus japonicus and their tumor suppressing activity. Yaoxue Xuebao 2009, 44, 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Cuong, N.X.; Vien, L.T.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Thao, N.P.; Thao, D.T.; Thanh, N.V.; Nam, N.Y.; Thung, D.C.; Kiem, P.V.; Minh, C.V. Cytotoxic triterpene saponins from Cercodemas anceps. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3151–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vien, L.T.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Quang, T.H.; Thanh, N.V.; Thao, D.T.; Cuong, N.X.; Nam, N.H.; Thung, D.C.; Kiem, P.V. Triterpene tetraglycosides from Stichopus Herrmanni Semper, 1868. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2022, 17, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Miao, Z.H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Q.; Gui, M.; Lin, L.P.; Sun, P.; Yi, Y.H.; Ding, J. Echinoside A, a new marine-derived anticancer saponin, targets topoisomerase 2α by unique interference with its DNA binding and catalytic cycle. Ann. Oncol. 2010, 21, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Venz, S.; Rast, S.; Amann, K.; Hauschild, J.; Otte, K.; Kalinin, V.I.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; et al. The marine triterpene glycoside frondoside A exhibits activity in vitro and in vivo in prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2450–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Madanchi, R.; Hauschild, J.; Otte, K.; Alsdorf, W.H.; Schumacher, U.; Kalinin, V.I.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Honecker, F.; et al. The marine triterpene glycoside frondoside A induces p53-independent apoptosis and inhibits autophagy in urothelial carcinoma cells. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminin, D.L.; Chaykina, E.L.; Agafonova, I.G.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Stonik, V.A. Antitumor activity of the immunomodulatory lead Cumaside. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchinskaya, E.S.; Pislyagin, E.A.; Kovalchyk, S.N.; Davydova, V.N.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Aminin, D.L. Antitumor activity of cucumarioside A2-2. Chemotherapy 2013, 59, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reunov, A.A.; Reunov, A.V.; Pimenova, E.A.; Reunova, Y.A.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Lapshina, L.A.; Aminin, D.L. Cucumarioside A2-2 stimulates apoptotic necrosis in Ehrlich ascites carcinoma cells. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2015, 462, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reunov, A.; Reunov, A.; Pimenova, E.; Reunova, Y.; Menchinskaya, E.; Lapshina, L.; Aminin, D. The study of the calpain and caspase-1 expression in ultrastructural dynamics of Ehrlich ascites carcinoma necrosis. Gene 2018, 658, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenova, E.A.; Reunova, Y.A.; Menchinskaya, E.S.; Reunov, A.A.; Aminin, D.L. An unusual pathway of mitoptosis found in Ehrlich Carcinoma Cells. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 2020, 494, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchinskaya, E.S.; Aminin, D.L.; Avilov, S.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Andryjashchenko, P.V.; Kalinin, V.I.; Stonik, V.A. Inhibition of tumor cells multidrug resistance by cucumarioside A2–2, frondoside A and their complexes with cholesterol. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchinskaya, E.; Gorpenchenko, T.; Silchenko, A.; Avilov, S.; Aminin, D. Modulation of doxorubicin intracellular accumulation and anticancer activity by triterpene glycoside cucumarioside A2-2. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franken, N.A.; Rodermond, H.M.; Stap, J.; Haveman, J.; van Bree, C. Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2315–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Shi, S.; Wu, S.; Meng, R.; Chen, H.; Jiang, Z. Deficiency of NEIL3 enhances the chemotherapy resistance of prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazzalin, C.A.; Le Panse, R.; Cano, E.; Mahadevan, L.C. Anisomycin selectively desensitizes signalling components involved in stress kinase activation and fos and jun induction. J. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 1844–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochi, S.K.; Collier, R.J. DNA fragmentation and cytolysis in U937 cells treated with diphtheria toxin or other inhibitors of protein synthesis. Exp. Cell Res. 1993, 208, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torocsik, B.; Szeberenyi, J. Anisomycin affects both pro- and antiapoptotic mechanisms in PC12 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 278, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, J.F.; Cotter, T.G. Anisomycin activates JNK and sensitises DU 145 prostate carcinoma cells to Fas mediated apoptosis. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhou, L.; Yao, L.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, Y. Elevated GRP78 expression is associated with poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep. 2015, 4, 16067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulianich, L.; Insabato, L. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in endometrial cancer. Front. Med. 2014, 1, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerushalmi, R.; Raiter, A.; Nalbandyan, K.; Hardy, B. Cell surface GRP78: A potential marker of good prognosis and response to chemotherapy in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 2149–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Berriguete, G.; Sánchez-Espiridión, B.; Cansino, J.R.; Olmedilla, G.; Martínez-Onsurbe, P.; Sánchez-Chapado, M.; Paniagua, R.; Fraile, B.; Royuela, M. Clinical significance of both tumor and stromal expression of components of the IL-1 and TNF-α signaling pathways in prostate cancer. Cytokine 2013, 64, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawada, M.; Ishizuka, M.; Takeuchi, T. Enhancement of antiproliferative effects of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on human prostate cancer LNCaP cells by coculture with normal fibroblasts through secreted interleukin-6. Jpn J. Cancer Res. 1999, 90, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Voronov, E.; Dvorkin, T.; Fima, E.; Cagnano, E.; Benharroch, D.; Shendler, Y.; Bjorkdahl, O.; Segal, S.; Dinarello, C.A.; et al. Differential effects of IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta on tumorigenicity patterns and invasiveness. J. Immunol. 2003, 15, 6448–6456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Russell, M.R.; Shahriari, K.; Jernigan, D.L.; Lioni, M.I.; Garcia, F.U.; Fatatis, A. Interleukin-1β promotes skeletal colonization and progression of metastatic prostate cancer cells with neuroendocrine features. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, P.; Galea, V.; Augenlicht, L.; Klampfer, L. Tumor associated macrophages protect colon cancer cells from TRAIL-Induced apoptosis through IL-1β- Dependent stabilization of snail in tumor cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karantza, V. Keratins in health and cancer: More than mere epithelial cell markers. Oncogene 2011, 30, 27–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirman, T.; Oresić, K.; Mazovec, G.D.; Turk, V.; Reed, J.C.; Myers, R.M.; Salvesen, G.S.; Turk, B. Selective disruption of lysosomes in HeLa cells triggers apoptosis mediated by cleavage of Bid by multiple papain-like lysosomal cathepsins. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 3578–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaowu, H.; Brown, M.A.; Rothnagel, J.A.; Saunders, N.A.; Smith, R. Roles of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A and B in cell proliferation. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 3173–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.P.; Fathers, K.E.; Chan, G.; Zuo, D.; Halwani, F.; Meterissian, S.; Park, M. CrkI and CrkII function as key signaling integrators for migration and invasion of cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2005, 3, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilov, S.A.; Stonik, V.A.; Kalinovskii, A.I. Structures of four new triterpene glycosides from the holothurians Cucumaria japonica. Chem. Nat. Compd. 1990, 26, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
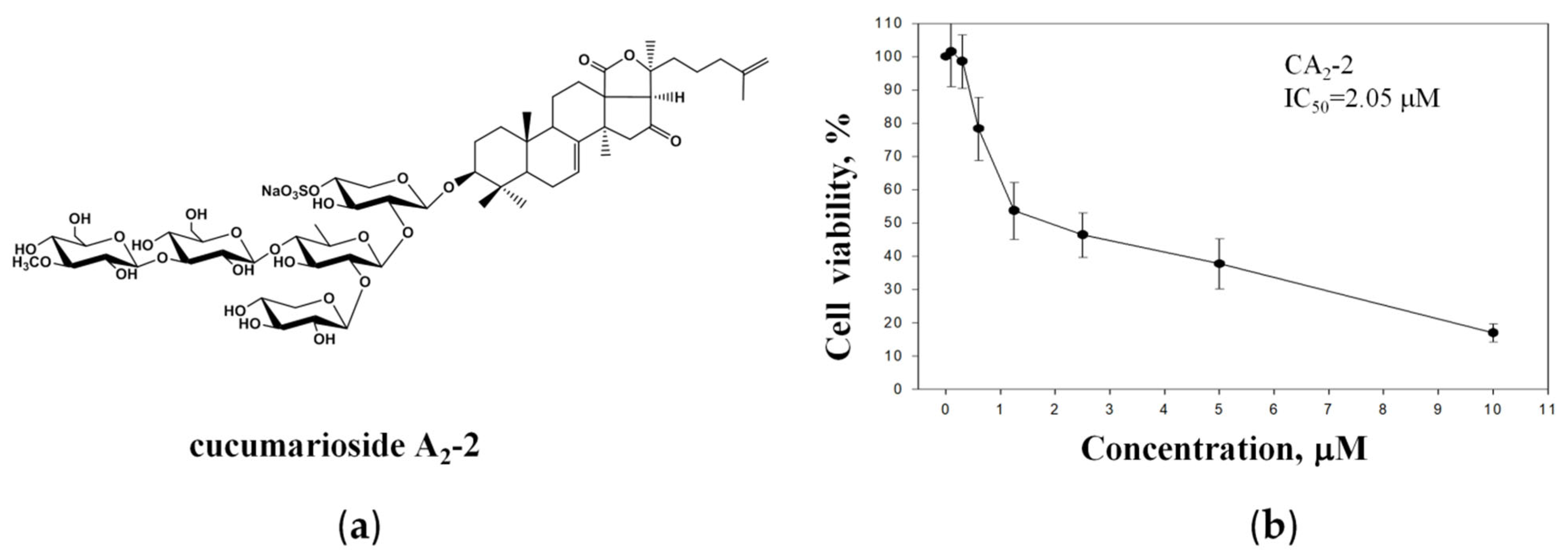
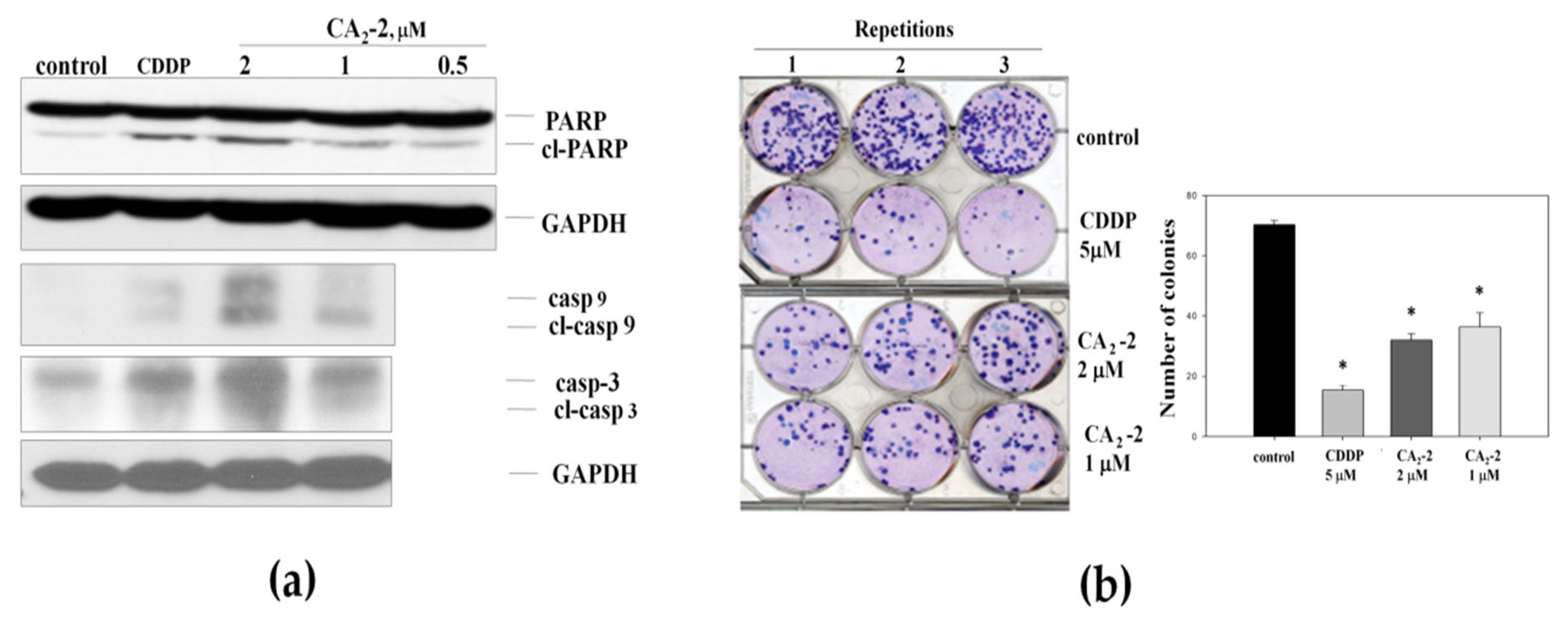
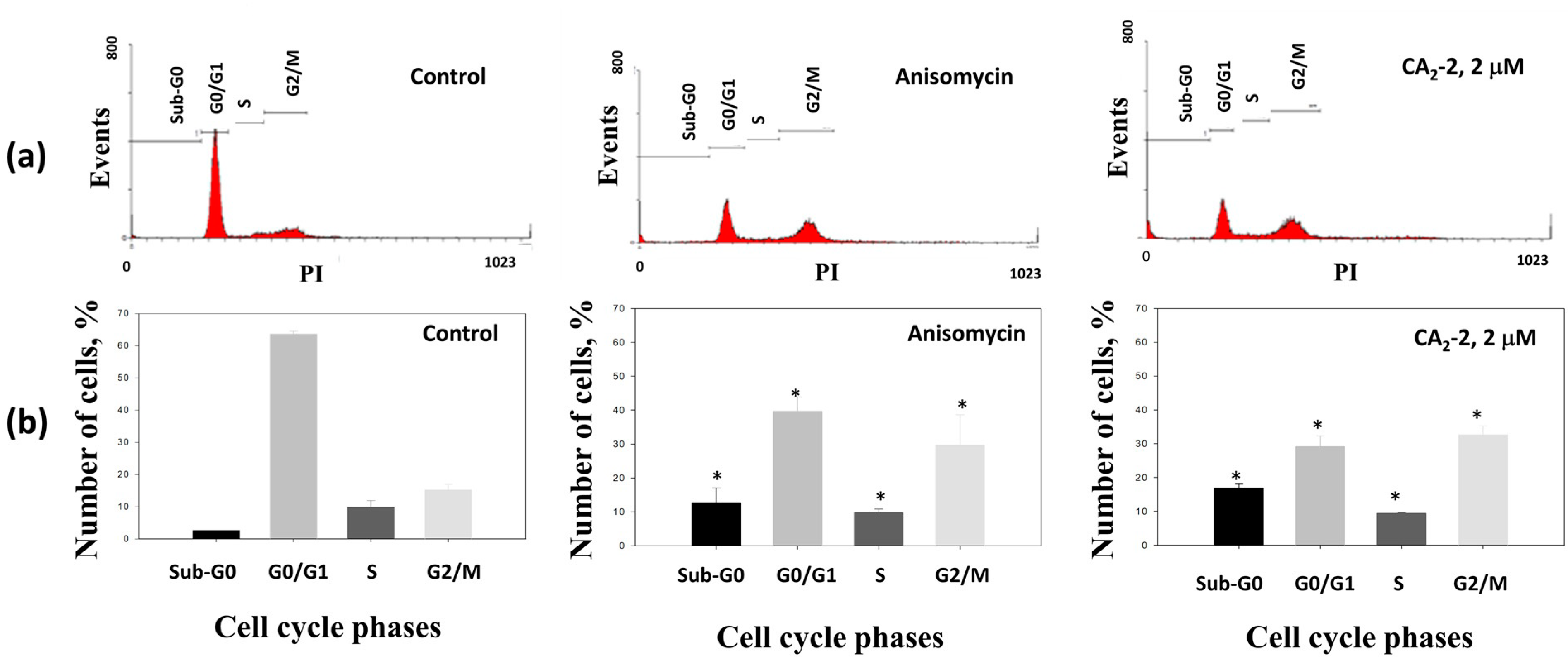
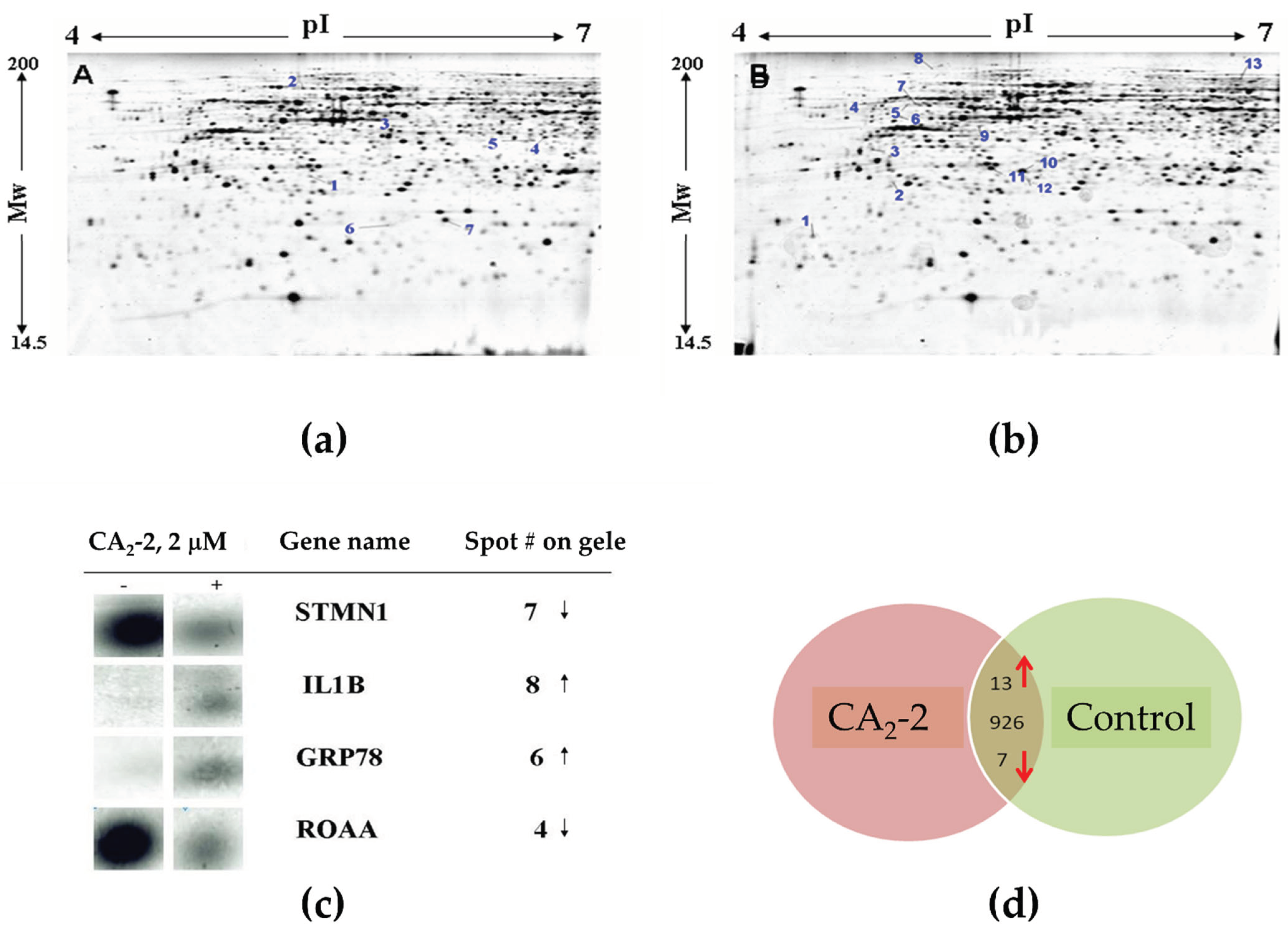

| Substance | Cell Cycle Phases (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SubG0 | G0/G1 | S | G2/M | |
| Control (untreated) | 2.59 ± 0.08 | 63.54 ± 1.01 | 9.85 ± 2.05 | 15.22 ± 1.71 |
| CA2-2 (1 μM) | 8.78 ± 0.23 * | 36.87 ± 1.53 * | 9.22 ± 0.04 | 32.14 ± 0.30 * |
| CA2-2 (2 μM) | 16.92 ± 1.10 * | 29.19 ± 3.11 * | 9.43 ± 0.20 | 32.56 ± 2.72 * |
| Anisomycin (1 μM) | 12.71 ± 4.32 * | 39.63 ± 4.34 * | 9.81 ± 1.09 | 29.62 ± 9.04 |
| Spot No on Gel | Gene Name | Protein | Up/Down Regulation, Fold Change | Protein Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein metabolism, enzymatic activity | ||||
| 4 | PDIA1 | Protein disulfide-isomerase | 2.44 ↑ | Catalyzes the formation and destruction of disulfide bonds during protein folding |
| 1 | CATB | Cathepsin B | 3.2 ↓ | Takes part in apoptosis, and is a mediator of the lysosomal pathway of cell death |
| 6 | GRP78 | 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein | 2.43 ↑ | Controls the processes of invasion, apoptosis, and inflammation |
| Metabolism of carbohydrates | ||||
| 5 | PGP | Phosphoglycolate phosphatase | 2.12 ↓ | Takes part in the metabolism of carbohydrates |
| Cytoskeletal organization, cell motility, and division | ||||
| 2 | K2C1 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 | 2.35 ↑ | Participates in the formation of intermediate filaments |
| 11 | KRT81 | Keratin, type II cuticular Hb1 | 2.96 ↑ | Participates in the formation of intermediate filaments |
| 10 | KRT81 | Keratin, type II cuticular Hb1 | 2.52 ↑ | Participates in the formation of intermediate filaments |
| 7 | STMN1 | Stathmin | 2.16 ↓ | Regulates rapid cytoskeletal remodeling in response to cell needs |
| 5 | KINH | Kinesin-1 heavy chain | 2.22 ↑ | Supports mitosis, meiosis, and transport of intracellular molecules |
| 13 | CALD1 | Caldesmon | 2,18 ↑ | Binds calmodulin, and inhibits the ATPase activity of myosin |
| 12 | CRK II | Adapter molecule crk | 2.93 ↑ | Involved in phagocytosis of apoptotic cells, and may regulate EFNA5-EPHA3 signaling |
| Immune response | ||||
| 9 | IL1B | Interleukin-1 beta | 3.32 ↑ (precursor) | Development and regulation of the body’s defense response to a pathogen |
| 3 | IL1B | Interleukin-1 beta | 3.09 ↑ (mature) | Development and regulation of the body’s defense response to a pathogen |
| mRNA processing | ||||
| 4 | ROAA | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B | 2.04 ↓ | Regulates the formation of telomeres and/or their stabilization, and also takes part in the control of apoptosis |
| 8 | HNRL2 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U-like protein 2 | 2.27 ↑ | Process heteronuclear RNA into mature mRNAs, and regulates of gene expression |
| Response to stress | ||||
| 3 | NDRG1 | Protein NDRG1 | 2.2 ↓ | Participates in the formation of a response to stress and hormones, and participates in cell growth and differentiation |
| Structural and functional organization of the nucleus | ||||
| 6 | CRABP2 | Cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 2 | 2.16 ↓ | Is an intracellular lipid-binding protein that interacts with cyclin D |
| 1 | NPM | Nucleophosmin | 2.16 ↑ | Takes part in the biogenesis of ribosomes, and the transport of proteins to the nucleus |
| 2 | LMNB1 | Lamin-B1 | 4.01 ↓ | Performs structural functions, and takes part in the regulation of transcription |
| 7 | SYNE1 | Nesprin-1 | 2.15 ↑ | Takes part in the nuclear organization and structural structure of the nucleus, and interacts with F-actin and with the nuclear envelope |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menchinskaya, E.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Venz, S.; Jacobsen, C.; Hauschild, J.; Rohlfing, T.; Silchenko, A.S.; Avilov, S.A.; Balabanov, S.; Bokemeyer, C.; et al. Anticancer Activity of the Marine Triterpene Glycoside Cucumarioside A2-2 in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010020
Menchinskaya ES, Dyshlovoy SA, Venz S, Jacobsen C, Hauschild J, Rohlfing T, Silchenko AS, Avilov SA, Balabanov S, Bokemeyer C, et al. Anticancer Activity of the Marine Triterpene Glycoside Cucumarioside A2-2 in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs. 2024; 22(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenchinskaya, Ekaterina S., Sergey A. Dyshlovoy, Simone Venz, Christine Jacobsen, Jessica Hauschild, Tina Rohlfing, Aleksandra S. Silchenko, Sergey A. Avilov, Stefan Balabanov, Carsten Bokemeyer, and et al. 2024. "Anticancer Activity of the Marine Triterpene Glycoside Cucumarioside A2-2 in Human Prostate Cancer Cells" Marine Drugs 22, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010020
APA StyleMenchinskaya, E. S., Dyshlovoy, S. A., Venz, S., Jacobsen, C., Hauschild, J., Rohlfing, T., Silchenko, A. S., Avilov, S. A., Balabanov, S., Bokemeyer, C., Aminin, D. L., von Amsberg, G., & Honecker, F. (2024). Anticancer Activity of the Marine Triterpene Glycoside Cucumarioside A2-2 in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Marine Drugs, 22(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/md22010020









