A Comparative Study about the Neuroprotective Effects of DHA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine and EPA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine against Oxidative Damage in Primary Hippocampal Neurons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
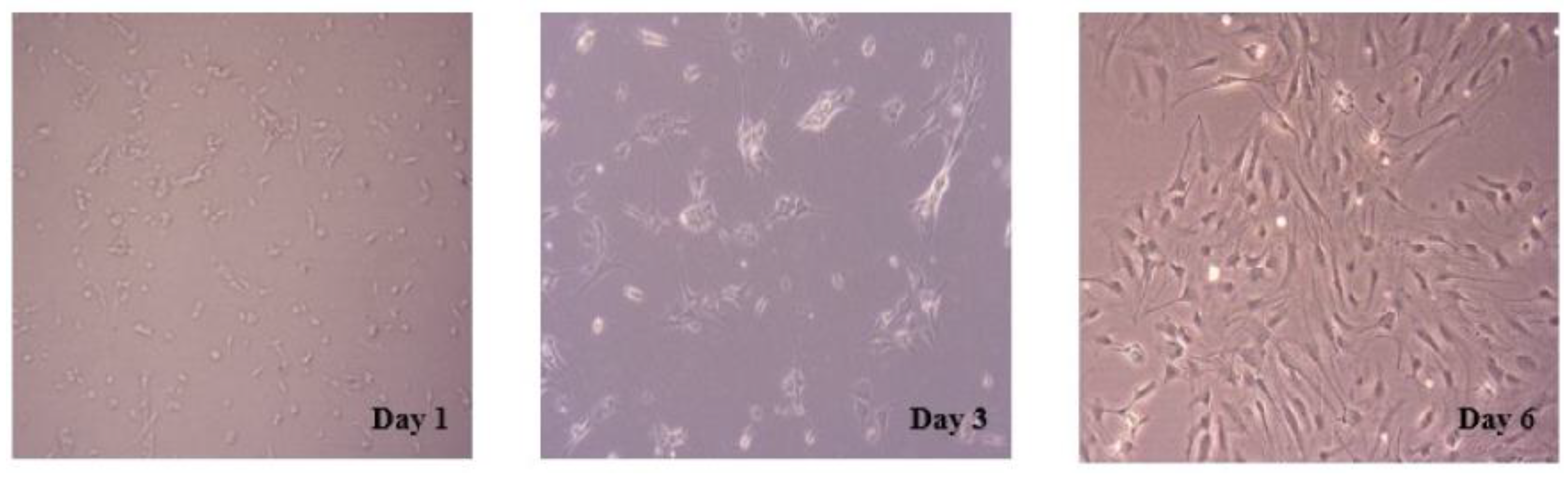
2.1. Morphology and Purity of Primary Cultured Hippocampal Neurons
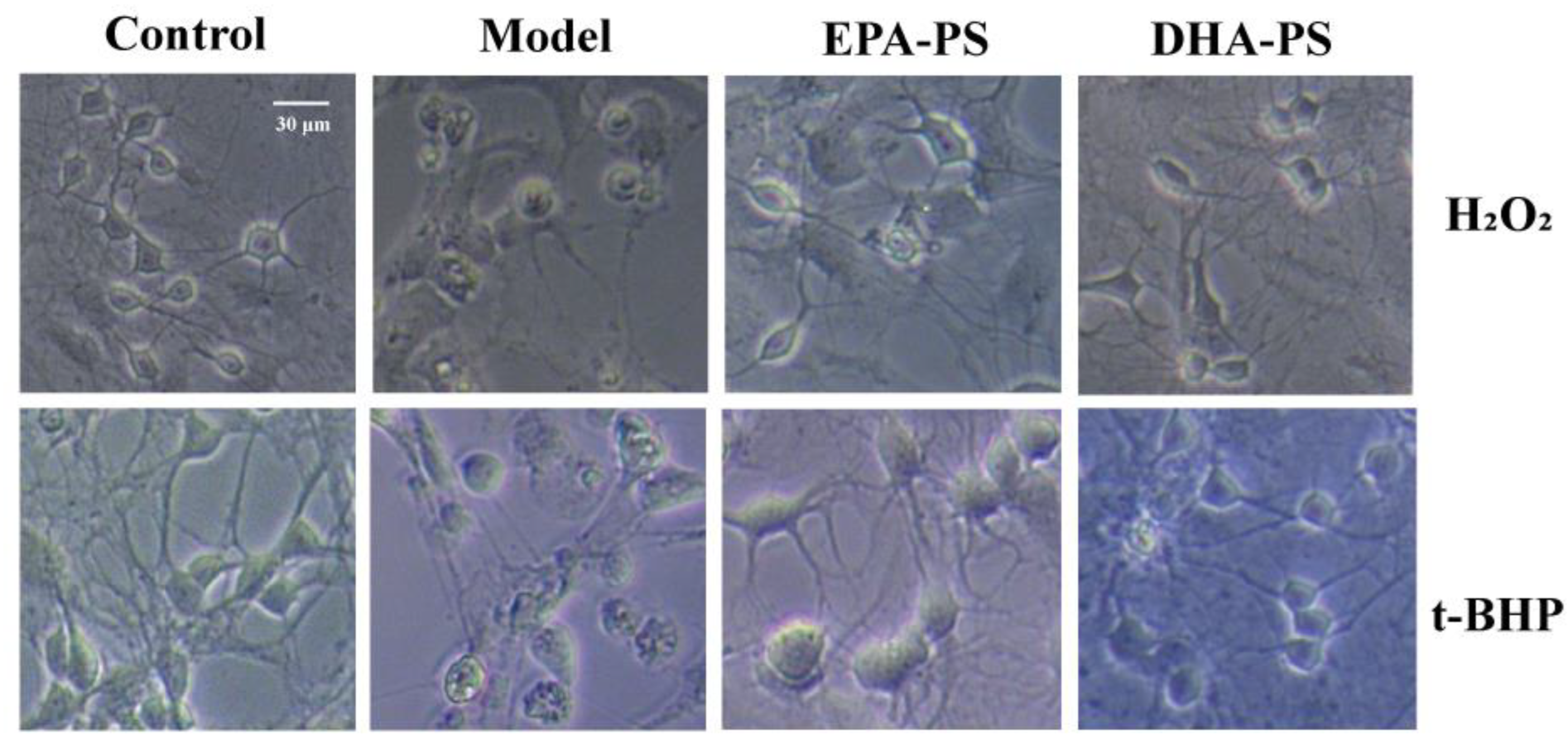
2.2. The Effects of EPA-PS and DHA-PS on H2O2-Induced or t-BHP-Induced Morphological Damage in Primary Hippocampal Neurons
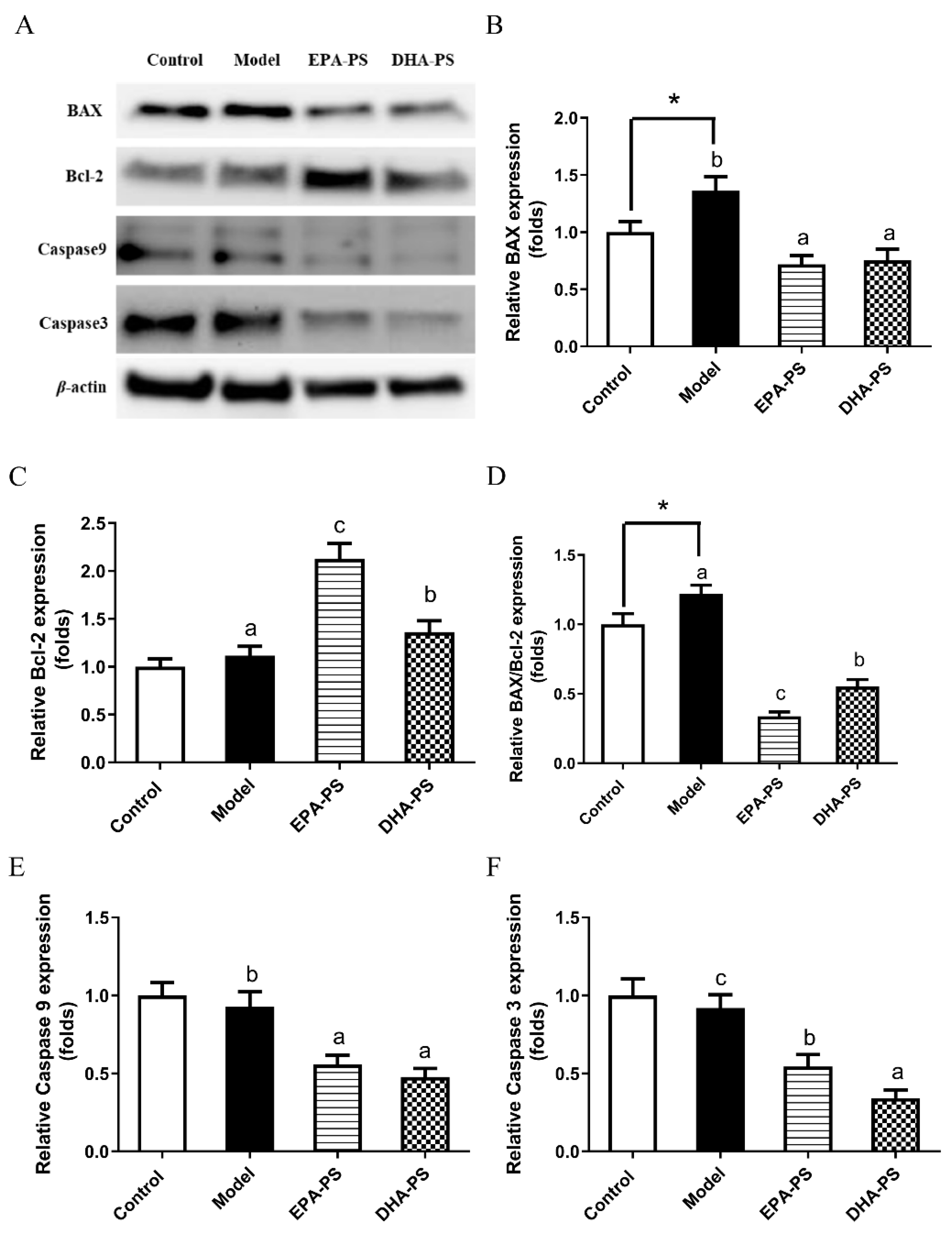
2.3. Effects of EPA-PS and DHA-PS on the Expression of Proteins Related to Apoptosis in Primary Hippocampal Neurons
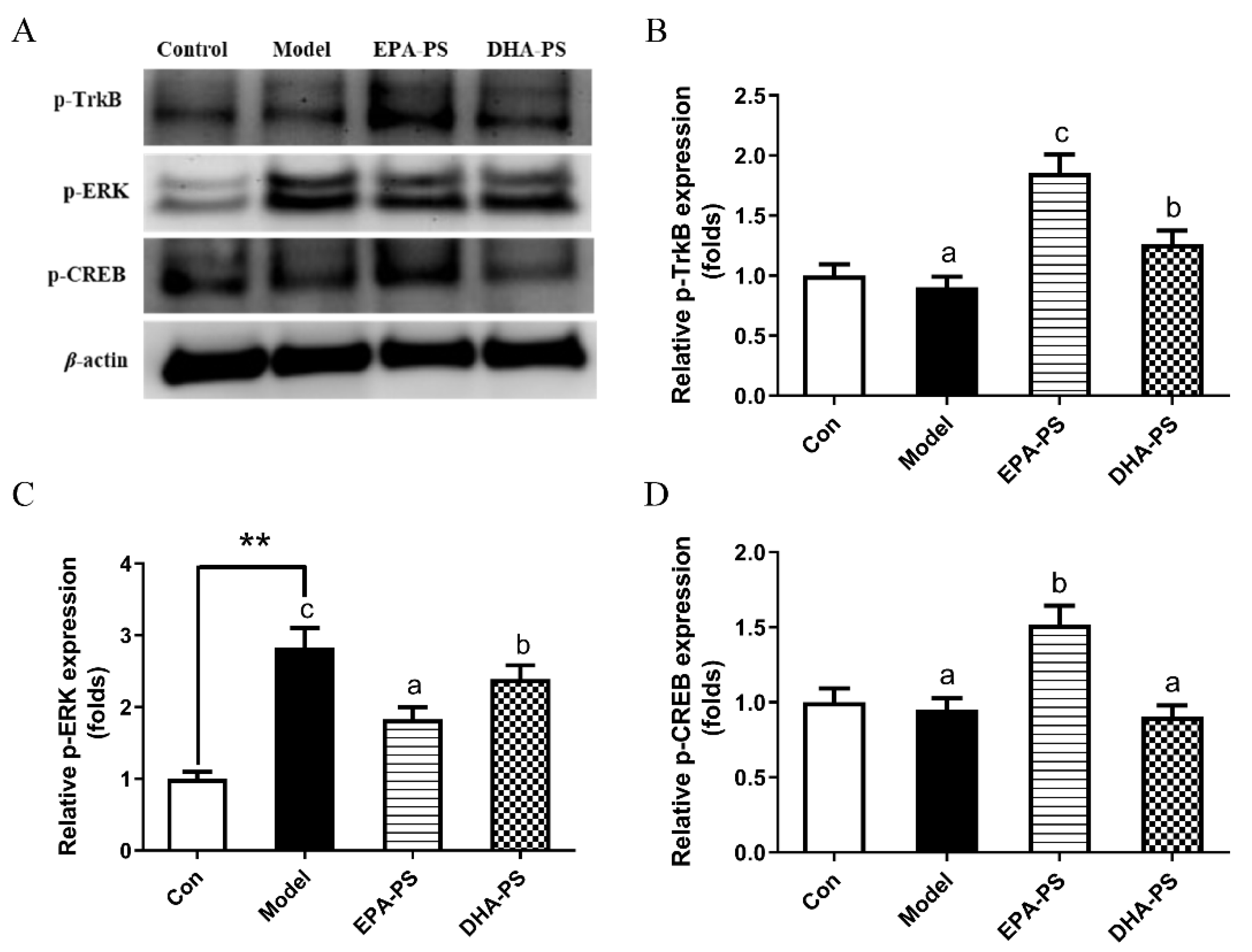
2.4. Effects of EPA-PS and DHA-PS on the TrkB/ERK/CREB Signaling Pathway and Synaptic Associated Proteins
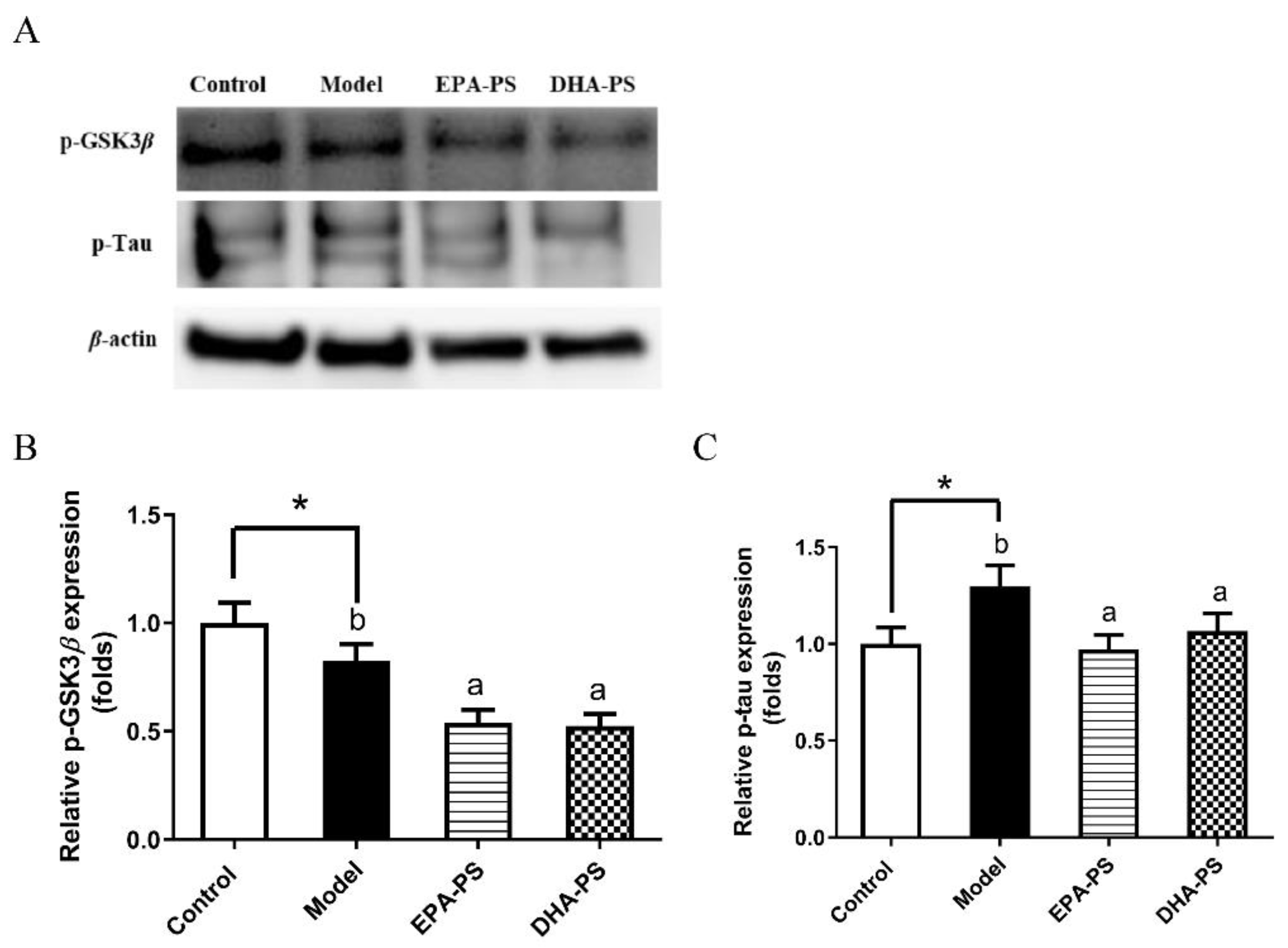
2.5. Effects of EPA-PS and DHA-PS on Tau Protein Phosphorylation
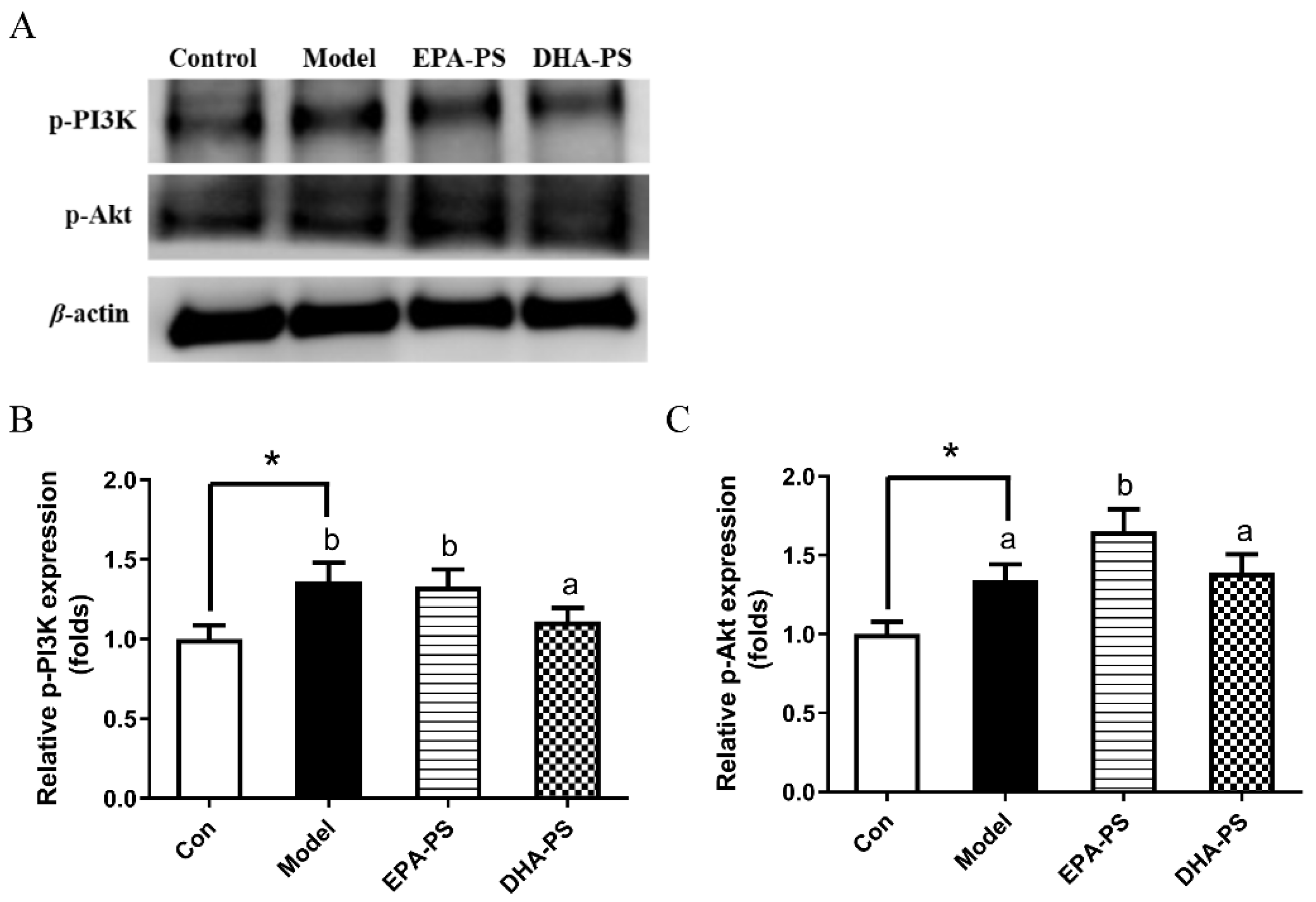
2.6. Effects of EPA-PS and DHA-PS on the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of EPA-PS and DHA-PS
3.3. Preparation of EPA-PS and DHA-PS Liposomes
3.4. Preparation of Primary Hippocampal Neurons
3.5. Morphological Observation of Primary Hippocampal Neurons
3.6. Western Blotting Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
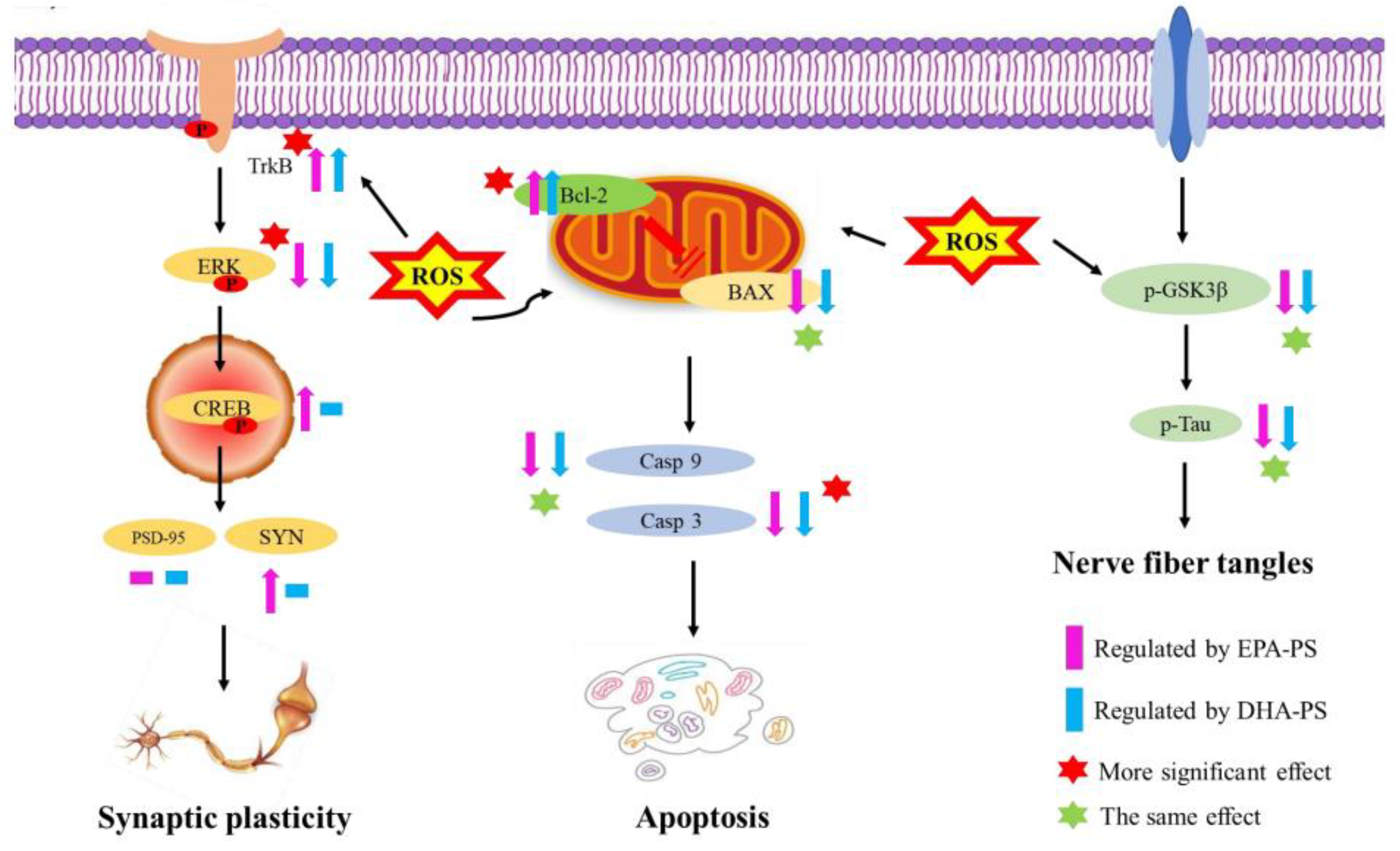
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johri, A. Disentangling Mitochondria in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, C.A.; Hardy, J.; Schott, J.M. Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2018, 25, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yiannopoulou, K.G.; Papageorgiou, S.G. Current and Future Treatments in Alzheimer Disease: An Update. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2020, 12, 370273395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingston, G.; Huntley, J.; Sommerlad, A.; Ames, D.; Ballard, C.; Banerjee, S.; Brayne, C.; Burns, A.; Cohen-Mansfield, J.; Cooper, C.; et al. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care: 2020 report of the Lancet Commission. Lancet Comm. 2020, 396, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Atluri, V.; Kaushik, A.; Yndart, A.; Nair, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Pathogenesis, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5541–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer’s disease. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ding, L.; Shi, H.; Xue, C.; Xie, W.; Che, H.; Wang, Y. A Comparative Study About the Neuroprotective Effects of EPA-Enriched Phosphoethanolamine Plasmalogen and Phosphatidylethanolamine Against Oxidative Damage in Primary Hippocampal Neurons. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2021, 20, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu-Tucker, A.; Cotman, C.W. Emerging Roles of Oxidative Stress in Brain Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2021, 107, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, I.; Arola, L.; Caimari, A.; Escoté, X.; Puiggròs, F. Structured Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Improvement of Cognitive Function during Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Xu, J.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C. Eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phospholipids improve Aβ1–40-induced cognitive deficiency in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 24, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Ding, L.; Yanagita, T.; Xu, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y. Comparative study of the effects of phosphatidylcholine rich in DHA and EPA on Alzheimer’s disease and the possible mechanisms in CHO-APP/PS1 cells and SAMP8 mice. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.T.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.M.; Xue, C.H. Health benefits of dietary marine DHA/EPA-enriched glycerophospholipids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2019, 75, 100997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Ding, L.; Wen, M.; Che, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, T.; Xue, C.; Mao, X.; Wang, Y. Mechanisms of DHA-enriched phospholipids in improving cognitive deficits in aged SAMP8 mice with high-fat diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 59, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Z.; Pathak, D.; Venkatesan Kalavai, S.; Yoshii-Kitahara, A.; Muraoka, S.; Bhatt, N.; Takamatsu-Yukawa, K.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Hersh, S.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease brain-derived extracellular vesicles spread tau pathology in interneurons. Brain 2021, 144, 288–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Q.; Ding, L.; Shi, H.; Xue, C.; Mao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T. A comparative study of the effects of phosphatidylserine rich in DHA and EPA on Aβ-induced Alzheimer’s disease using cell models. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4411–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, N.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Q.; Huang, H.; Chen, X. Microglial phagocytosis induced by fibrillar b-amyloid is attenuated by oligomeric b-amyloid: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 45, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, L.; Ding, L.; Xie, W.; Jiang, X.; Xue, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y. EPA-enriched ethanolamine plasmalogen and EPA-enriched phosphatidylethanolamine enhance BDNF/TrkB/CREB signaling and inhibit neuronal apoptosisin vitro andin vivo. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Fu, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Wen, M.; Du, L.; Xue, C.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y. Neuroprotective Effects of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Enriched Phosphatidylserine Against Oxidative Damage in PC12 Cells. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Huang, B.X.; Spector, A.A. Phosphatidylserine in the brain: Metabolism and function. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 56, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.X.; Akbar, M.; Kevala, K.; Kim, H. Phosphatidylserine is a critical modulator for Akt activation. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, L.; Nie, G.; Li, H. Inhibiting DNA methylation alleviates cisplatin-induced hearing loss by decreasing oxidative stress-induced mitochondria-dependent apoptosis via the LRP1–PI3K/AKT pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Xu, S.; Khan, M.A.; Shi, Y.; Qu, W.; Gao, J.; Liu, G.; Kastelic, J.P.; Han, B. Mycoplasma bovis-generated reactive oxygen species and induced apoptosis in bovine mammary epithelial cell cultures. J. Dairy. Sci. 2020, 103, 10429–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yang, W.; He, Z.; Guo, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.; Li, H. Kaempferol Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis Through Mitochondria-dependent Pathway During Lung Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 624402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Sui, C.; Wang, W.; Yan, J.; Deng, N.; Du, X.; Cheng, F.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q. Baicalin Attenuates Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation–Induced Injury by Modulating the BDNF-TrkB/PI3K/Akt and MAPK/Erk1/2 Signaling Axes in Neuron–Astrocyte Cocultures. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 599543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amidfar, M.; De Oliveira, J.; Kucharska, E.; Budni, J.; Kim, Y. The role of CREB and BDNF in neurobiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Réus, G.Z.; Stringari, R.B.; Ribeiro, K.F.; Ferraro, A.K.; Vitto, M.F.; Cesconetto, P.; Souza, C.T.; Quevedo, J. Ketamine plus imipramine treatment induces antidepressant-like behavior and increases CREB and BDNF protein levels and PKA and PKC phosphorylation in rat brain. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 221, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Che, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y. Comparative Study of Different Polar Groups of EPA-Enriched Phospholipids on Ameliorating Memory Loss and Cognitive Deficiency in Aged SAMP8 Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, H.; Das, R.; Chinnathambi, S. Interaction of Tau with the chemokine receptor, CX3CR1 and its effect on microglial activation, migration and proliferation. Cell Biosci. 2020, 10, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauretti, E.; Dincer, O.; Praticò, D. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viet Hoang Man, X.H.J.G. Phosphorylation of Tau R2 Repeat Destabilizes Its Binding to Microtubules: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study. Acs Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, T.; Li, P.; Wei, N.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, H.; Ji, X.; Chen, W.; Xue, M.; Wei, J. The Ambiguous Relationship of Oxidative Stress, Tau Hyperphosphorylation, and Autophagy Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2015, 2015, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Iqbal, K.; Gong, C. Deficient brain insulin signalling pathway in Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. J. Pathol. 2011, 225, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Z.; Qu, M.; Gao, D.; Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J. Stimulation of EphB2 attenuates tau phosphorylation through PI3K/Akt-mediated inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyashenko, E.; Niepel, M.; Dixit, P.D.; Lim, S.K.; Sorger, P.K.; Vitkup, D. Receptor-Based Mechanism of Cell Memory and Relative Sensing in Mammalian Signaling Networks. Elife 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, A.; Orlando, P.; Mietto, L.; Viola, G. Phospholipid metabolism in rat intestinal mucosa after oral administration of lysophospholipids. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1992, 318, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturbois-Balcerzak, B.; Stone, S.J.; Sreenivas, A.; Vance, J.E. Structure and Expression of the Murine Phosphatidylserine Synthase-1 Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8205–8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, J.E. Thematic Review Series: Glycerolipids. Phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine in mammalian cells: Two metabolically related aminophospholipids. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, J.E. Phospholipid synthesis in a membrane fraction associated with mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 7248–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aporti, F.; Borsato, R.; Calderini, G.; Rubini, R.; Toffano, G.; Zanotti, A.; Valzelli, L.; Goldstein, L. Age-dependent spontaneous EEG bursts in rats: Effects of brain phosphatidylserine. Neurobiol. Aging 1986, 7, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosadini, G.; Sannita, W.G.; Nobili, F.; Cenacchi, T. Phosphatidylserine: Quantitative EEG Effects in Healthy Volunteers. Neuropsychobiology 1990, 24, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenacchi, T.; Bertoldin, T.; Farina, C.; Fiori, M.G.; Crepaldi, G. Cognitive decline in the elderly: A double-blind, placebo-controlled multicenter study on efficacy of phosphatidylserine administration. Aging 1993, 5, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, L.; Cong, P.; Xu, J.; Xue, C.; Yanagita, T.; Chi, N.; Zhang, T.; Liu, F.; et al. Recovery of brain DHA-containing phosphatidylserine and ethanolamine plasmalogen after dietary DHA-enriched phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine in SAMP8 mice fed with high-fat diet. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapar, M.L.; Ji, H.; Wang, B.; Poe, A.R.; Dubey, K.; Ren, X.; Ni, J.; Han, C. Phosphatidylserine Externalization Results from and Causes Neurite Degeneration in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 2273–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, C.A.; Popescu, A.S.; Kitchener, E.J.A.; Allendorf, D.H.; Puigdellívol, M.; Brown, G.C. Microglial phagocytosis of neurons in neurodegeneration, and its regulation. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 621–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, R.; Ajmone-Cat, M.A.; Minghetti, L. Atypical Antiinflammatory Activation of Microglia Induced by Apoptotic Neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 2004, 2, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, M.; Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, M.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, C. DHA-PC and DHA-PS improved Aβ1–40 induced cognitive deficiency uncoupled with an increase in brain DHA in rats. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 22, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Jie Cui, Z.L.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y. Comparative study of DHA-enriched phospholipids and EPA-enriched phospholipids on metabolic disorders in diet-induced-obese C57BL/6J mice. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2014, 116, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Wang, D.; Zhou, M.; Du, L.; Xu, J.; Xue, C.; Wang, Y. Comparative Study of EPA-enriched Phosphatidylcholine and EPA-enriched Phosphatidylserine on Lipid Metabolism in Mice. J. Oleo Sci. 2016, 65, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, Z.; Kurihara, H.; Hosokawa, M.; Takahashi, K. Docosahexaenoic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phosphatidylcholine liposomes enhance the permeability, transportation and uptake of phospholipids in Caco-2 cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2006, 285, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Rodríguez, M.; de la Fuente, C.; García-Durillo, M.; García-Rodríguez, C.; Villalobos, C.; Núñez, L. Aging and amyloid β oligomers enhance TLR4 expression, LPS-induced Ca2+ responses, and neuron cell death in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-W.; Li, Q.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhao, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Xue, C.-H.; Wang, Y.-M.; Zhang, T.-T. A Comparative Study about the Neuroprotective Effects of DHA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine and EPA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine against Oxidative Damage in Primary Hippocampal Neurons. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070410
Wang Y-W, Li Q, Li X-Y, Zhao Y-C, Wang C-C, Xue C-H, Wang Y-M, Zhang T-T. A Comparative Study about the Neuroprotective Effects of DHA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine and EPA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine against Oxidative Damage in Primary Hippocampal Neurons. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(7):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070410
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yi-Wen, Qian Li, Xiao-Yue Li, Ying-Cai Zhao, Cheng-Cheng Wang, Chang-Hu Xue, Yu-Ming Wang, and Tian-Tian Zhang. 2023. "A Comparative Study about the Neuroprotective Effects of DHA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine and EPA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine against Oxidative Damage in Primary Hippocampal Neurons" Marine Drugs 21, no. 7: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070410
APA StyleWang, Y.-W., Li, Q., Li, X.-Y., Zhao, Y.-C., Wang, C.-C., Xue, C.-H., Wang, Y.-M., & Zhang, T.-T. (2023). A Comparative Study about the Neuroprotective Effects of DHA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine and EPA-Enriched Phosphatidylserine against Oxidative Damage in Primary Hippocampal Neurons. Marine Drugs, 21(7), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21070410







