Abstract
Multidrug resistance (MDR) caused by ATP-Binding Cassette Subfamily B Member 1 (ABCB1, P-glycoprotein, P-gp) is a major barrier for the success of chemotherapy in clinics. In this study, we designed and synthesized a total of 19 Lissodendrins B analogues and tested their ABCB1-mediated MDR reversal activity in doxorubicin (DOX)-resistant K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells. Among all derivatives, compounds D1, D2, and D4 with a dimethoxy-substituted tetrahydroisoquinoline fragment possessed potent synergistic effects with DOX and reversed ABCB1-mediated drug resistance. Notably, the most potent compound D1 merits multiple activities, including low cytotoxicity, the strongest synergistic effect, and effectively reversing ABCB1-mediated drug resistance of K562/ADR (RF = 1845.76) and MCF-7/ADR cells (RF = 207.86) to DOX. As a reference substance, compound D1 allows for additional mechanistic studies on ABCB1 inhibition. The synergistic mechanisms were mainly related to the increased intracellular accumulation of DOX via inhibiting the efflux function of ABCB1 rather than from affecting the expression level of ABCB1. These studies suggest that compound D1 and its derivatives might be potential MDR reversal agents acting as ABCB1 inhibitors in clinical therapeutics and provide insight into a design strategy for the development of ABCB1 inhibitors.
1. Introduction
Cancers are common and frequently occurring diseases that seriously threaten human health, and chemotherapy is still the most effective method for treating cancer [1]. However, the occurrence of termed multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer cells has led to chemotherapy being greatly ineffective [2,3]. The prime mechanism may be that increased efflux of multitudinous chemotherapeutic agents causes chemotherapy failure due to decreased intracellular drug levels and, thus, limited efficacy. Overexpression of the drug efflux ABCB1 transporter is considered to be the most pivotal reason for MDR [4,5]. Obviously, ABCB1 is an ideal and predominant target for reversing MDR by inhibiting its efflux function.
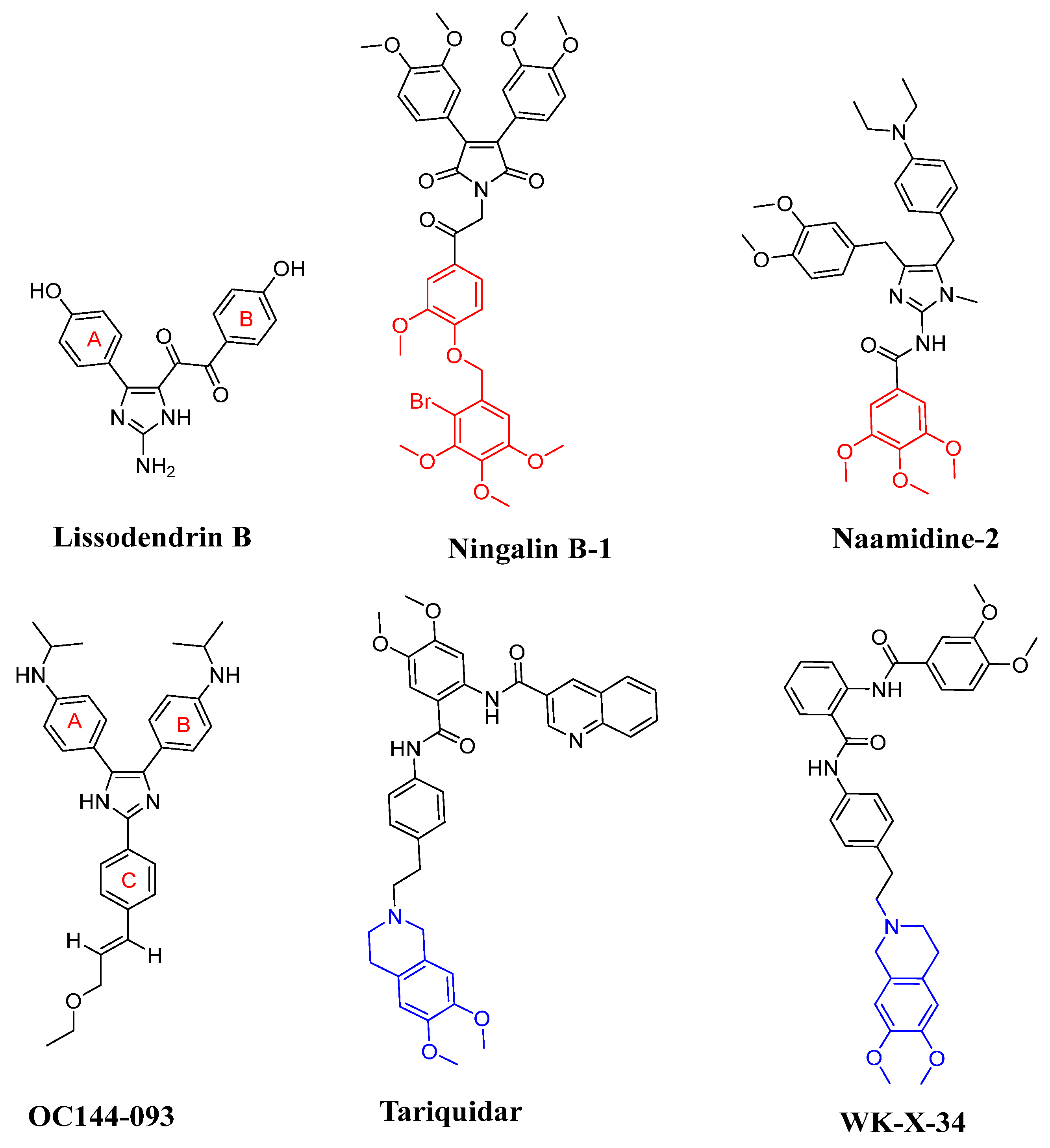
In recent years, many derivatives of natural products have been successfully reported as high-efficiency ABCB1 reversal agents, such as methylated quercetin analogues [6], methylated Ningalin B analogues [7,8], curcumin analogues [9], and methylated Naamidines analogues [10]. These compounds could effectively reverse the ABCB1-mediated tumor MDR and show low cytotoxicity. Among them, the marine alkaloids Ningalin B-1 and Naamidine-1 have preferable ABCB1 regulatory activity and reversed the tumor MDR (Figure 1). Both Ningalin B-1 and Naamidine-1 with three methoxy groups of C ring at 1 μM can sensitize LCC6MDR cells toward paclitaxel by 48- and 26.4-fold, respectively, and have non-toxic side effects on LCC6MDR cells [7,8]. On the basis of the mechanism of the ABCB1 ‘hydrophobicity vacuum cleaner’ model [11], lipid solubility is the key factor to improve the reverse tumor MDR activity. Therefore, three methoxy groups of the C ring played a significant role in the ABCB1 inhibition effect (Figure 1, shown in red).
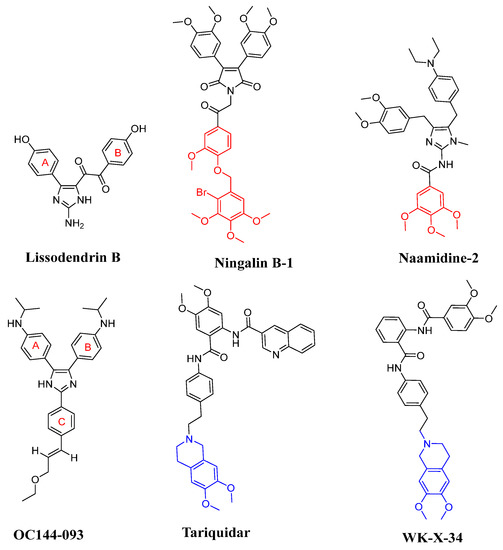
Figure 1.
Representative marine products (Lissodendrins B, Ningalin B-1 and Naamidine-1) and third-generation ABCB1 inhibitors (OC144-093, tariquidar, and WK-X-34).
2-Aminoimidazole marine alkaloids have various biological activities, including anti-cancer [12], antimicrobial [13,14], antivirus properties [15], ABCB1-mediated MDR reversal activity [16] as well as both leukotriene B4 receptor [17] and epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor antagonist activities [10]. Lissodendrins B (Figure 1) is a 2-aminoimidazole marine alkaloid first extracted from the EtOAc fraction of the sponge Lissodendoryx (Acanthodoryx) fibrosis in 2016 [18]. The compound was devoid of cytotoxicity, and its total synthesis was performed by our group [19]. OC144-093 reversed multidrug resistance to doxorubicin, paclitaxel, and vinblastine in human lymphoma, breast, ovarian, uterine, and colorectal carcinoma cell lines expressing ABCB1 with an average EC50 of 0.032 mM [20]. The structure of Lissodendrins B and the third-generation ABCB1 inhibitors OC144-093 have similar ‘Y’-type skeleton structural characteristics and may have ABCB1 inhibitory activity to reverse tumor MDR (Figure 1).
Over the past few decades, three generations of ABCB1 inhibitors have been developed [21,22]. Both the first- and second-generation inhibitors have the drawbacks of poor therapeutic efficacy and high toxicity [23], whereas the third-generation inhibitors (e.g., tariquidar and WK-X-34, Figure 1) show strong ABCB1 inhibitory activities [4,24,25]. Unfortunately, to date, none were practicable in the clinic, mainly because of the limited potency, high inherent toxicity, and adverse drug–drug interactions [26,27,28]. These failures have not concluded the development of novel ABCB1 inhibitors but reveal the evolutionary trends of their structures, where the presence of tetrahydroisoquinoline and benzene rings is important for ABCB1 inhibitors [24,29,30] (Figure 1, shown in blue). Therefore, although the discovery of novel ABCB1 inhibitors with supernal potency and low cytotoxicity is challenging, there is an enormous demand for ABCB1 inhibitors with high efficacy for clinical application.
Based on the structural characteristics of marine products and known third-generation ABCB1 inhibitors, the structure–activity relationships of these compounds reversing ABCB1-meidated drug resistance are as follows: (1) similar ‘Y’-type skeleton structural characteristics may have ABCB1 inhibitory activity; (2) three methoxy groups of C ring, dimethoxy-substituted tetrahydroisoquinoline fragment and benzene rings are the key groups to improve the reversal resistance activity; (3) lipid solubility is the key factor to improve the ABCB1 inhibitory activities. They provide effective guidance for future studies of Lissodendrins B reversing resistance activity through derivatives. In this work, we intended to use 2-aminoimidazole as the ‘Y’ scaffold for the design of a series of Lissodendrins B derivatives. These designed compounds were synthesized, and their ABCB1 inhibitory activities as well as their synergic effects with DOX were evaluated using MCF-7/ADR and K562/ADR cells. Furthermore, we studied the mechanisms underlying the ABCB1 inhibitory activities and revealed that the presentative compounds could enhance the intracellular concentration of DOX via inhibiting the transporting function of ABCB1 rather than its expression.
2. Results
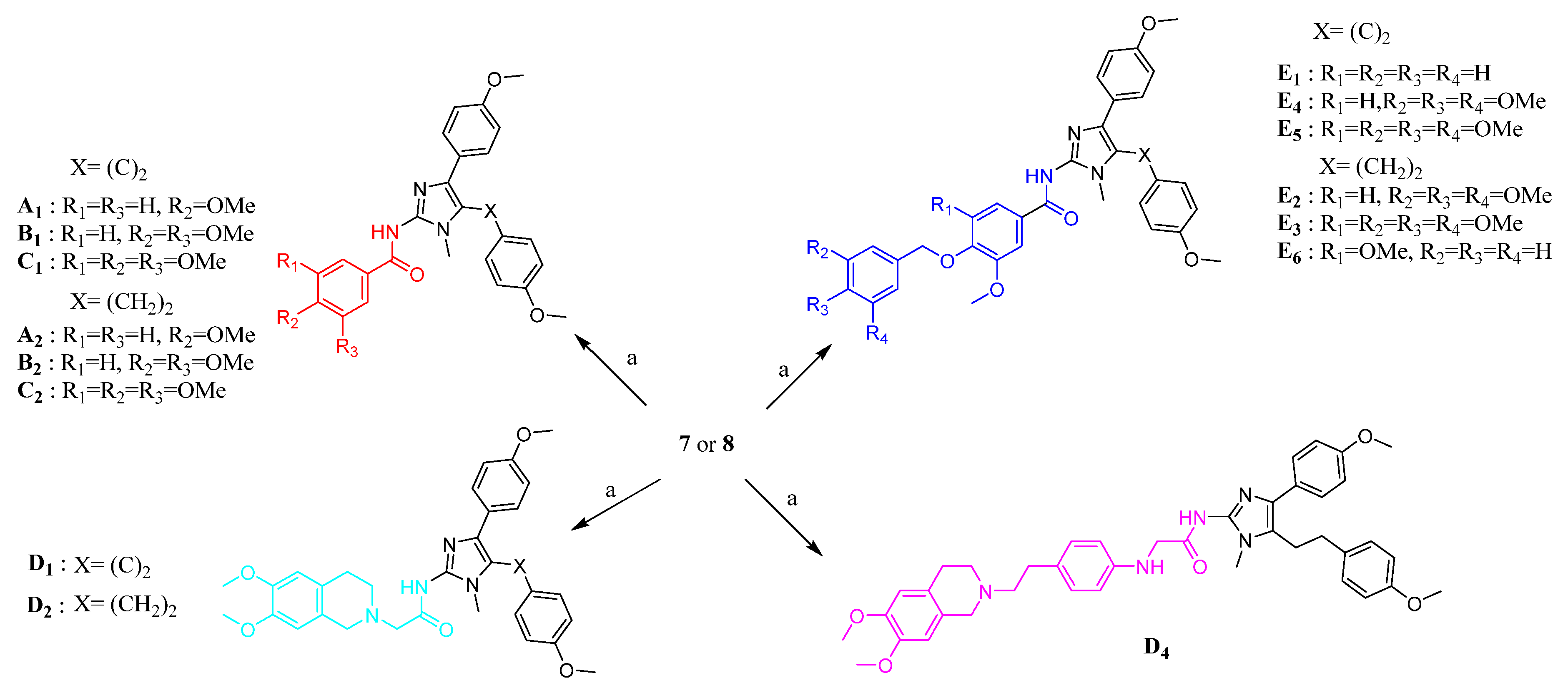
A series of Lissodendrins B analogues was designed, in which the 2-positions of 1-methyl-1H-imidazole rings were substituted with different functional groups. The key intermediates 7 and 8 were prepared and reported by our groups previously [19,31], as depicted in Scheme S1. Based on the structural characteristics of marine products and the third-generation ABCB1 inhibitors, the numbers of the methoxy group of the C ring, dimethoxy-substituted tetrahydroisoquinoline fragment, benzene rings and the different linkers between the imidazole ring and B ring were the key groups to improve the reversal resistance activity, and the typical moieties were synthesized as follows.
The key intermediates 13 and 14 were synthesized, as illustrated in Scheme S2. For example, compound 11 was prepared via the Williamson reaction from the starting material benzyl bromide in the mixture of CH3CN with K2CO3 for 5 h. Compound 11 was saponified in the presence of LiOH to produce lithium salt, followed by the hydrochloride acidification of compound 13.
The key intermediates 17 and 18 were synthesized using methods shown depicted in Scheme S3. Compound 15 was prepared via the Mitsunobu reaction from the starting material 3,4-dimethoxymethylbenzoate in the mixture of THF with DIAD and PPh3. Compound 15 was saponified in the presence of LiOH to produce lithium salt, followed by the hydrochloride acidification of compound 17.
The key intermediate 21 was synthesized using the method depicted in Scheme S4. The key intermediate 21 was prepared and reported by our groups previously [31]. Compound 20 was prepared from the starting material 6,7-dimethoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline hydrochloride refluxed in the mixture of CH3CN with methyl bromoacetate and potassium carbonate for 8 h. Then, compound 20 with lithium hydroxide in the mixture of THF and H2O gave the corresponding lithium carboxylate, which was protonated with hydrochloric acid to generate key intermediate 21.
The key intermediate 25 was synthesized using the methods described in Scheme S5. Firstly, intermediates 22 and 23 were successfully synthesized, as reported in the literature [29]. Then, compound 24 was prepared from the starting compound 23, refluxed in the mixture of EtOH with methyl bromoacetate and CH3COONa for 24 h. Finally, compound 24 was saponified in the presence of LiOH to produce lithium salt, followed by the hydrochloride acidification of compound 25.
As shown in Scheme 1, the target products could be synthesized through the acylation reaction of compound 7 or 8 with different methoxy-substituted benzoyl acid and tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives. The compounds A1–A2, B1–B2, C1–C2, D1–D2, and E1–E5 were prepared and reported by our groups previously [31]. Compound 7 or 8 was coupled with compound 14 or 25 to yield, respectively, D4 and E6, catalyzed by EDCI and HOAt in CH2Cl2.
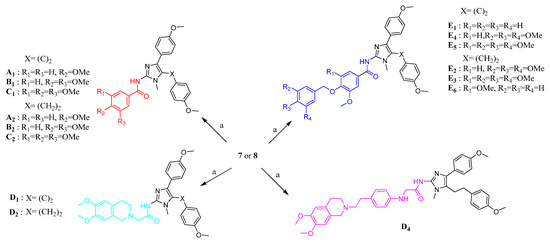
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of target products. Reagent and conditions: (a) appropriate carboxylic acid, EDCI, HOAt, DIPEA, CH2Cl2, reflux.
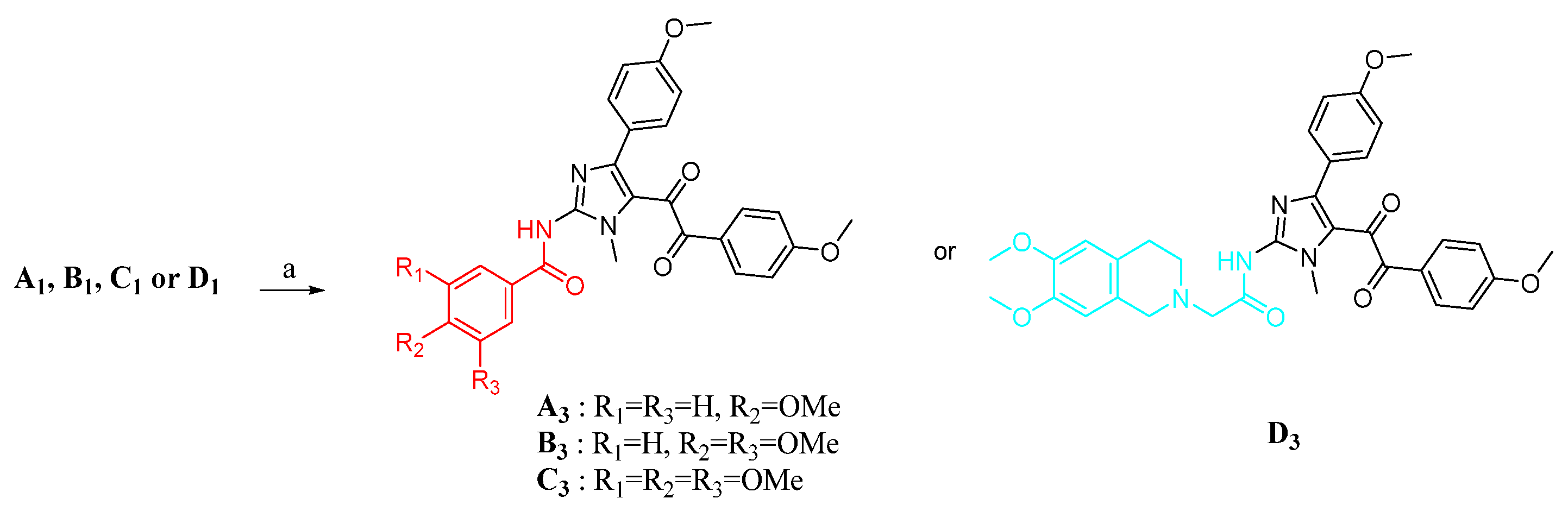
The synthetic routes for compounds A3, B3, C3, and D3 are shown in Scheme 2. Successive oxidation of A1, B1, C1, and D1 with mercuric nitrate hydrate (2 equiv) gave α-diketones compounds A3, B3, C3, and D3, respectively. The compounds A3, B3, C3, and D3 were prepared and reported by our groups previously [31].
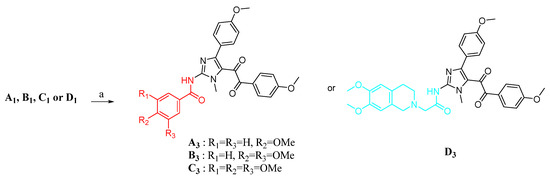
Scheme 2.
Synthesis of target products. Reagent and conditions: (a) Hg(NO3)2, DMF, rt.
2.1. Biological Evaluation
2.1.1. Biological Investigation and Structure–Activity Relationship Study
For the identification of effective ABCB1 inhibitors, we evaluated the drug resistance reversal effects of these newly synthesized compounds, using DOX-resistant K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells as screening models.
We found that when Lissodendrin B was combined with DOX, the IC50 of ABCB1 overexpressed K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells was almost unchanged, and the RF value of Lissodendrin B was about 1, indicating that it did not have an ABCB1 inhibition effect (Table 1). On the basis of the mechanism of the ABCB1 “hydrophobicity vacuum cleaner” model [11], hydrophilic Lissodendrin B was unlikely to enter the hydrophobic drug-binding cavity and, thus, high hydrophobicity was required to improve ABCB1 inhibition activity. A series of Lissodendrin B derivatives with improved hydrophobicity was designed and synthesized, and those compounds showed ABCB1 inhibition activity (Table 1). Therefore, we elaborated on the structure–activity relationship of these compounds afterwards.

Table 1.
IC50 values of DOX and the calculated theoretically reversal fold (RF) in the absence and presence of compounds (10 μM) on K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells.
In the ‘Y’-shaped skeleton compounds (A1–A3, B1–B3, and C1–C3), the RF of A1, B1, and C1 in K562/ADR cell resistance was 10.60, 21.73, and 26.04, respectively; RF values reversing MCF-7/ADR resistance were 12.61, 17.90, and 7.77, respectively (Table 1). By comparing the RF values of A1, B1, and C1, we found that the ABCB1 inhibition activity was increased with three methoxy groups of the C ring when the linker between the imidazole ring and B ring was unchanged (RFC1 > RFB1 > RFA1). When the linker was alkyne or ethyl (A1, A2) rather than α-diketone (A3) structure, ABCB1 inhibition activity was also improved (RFA1 > RFA2 > RFA3). Meanwhile, compounds B1–B3 with the different linkers and three methoxy groups of the C ring also possessed ABCB1 inhibition activities (RFB1 > RFB2 > RFB3).
When combined with DOX at 10 µM, these compounds (E1–E6) with a benzyl group or benzyl substitution could effectively reduce the IC50 value of DOX for both cancer cells (Table 1). However, their reversal multiple RF values were less than 15, and the ABCB1 inhibition activities were lower than the compounds (A1–A3, B1–B3, and C1–C3), indicating that the introduction of a benzyl group or benzyl group with three methoxy groups on the C ring was not conducive to improving the ABCB1 inhibition activity of cancer cells.
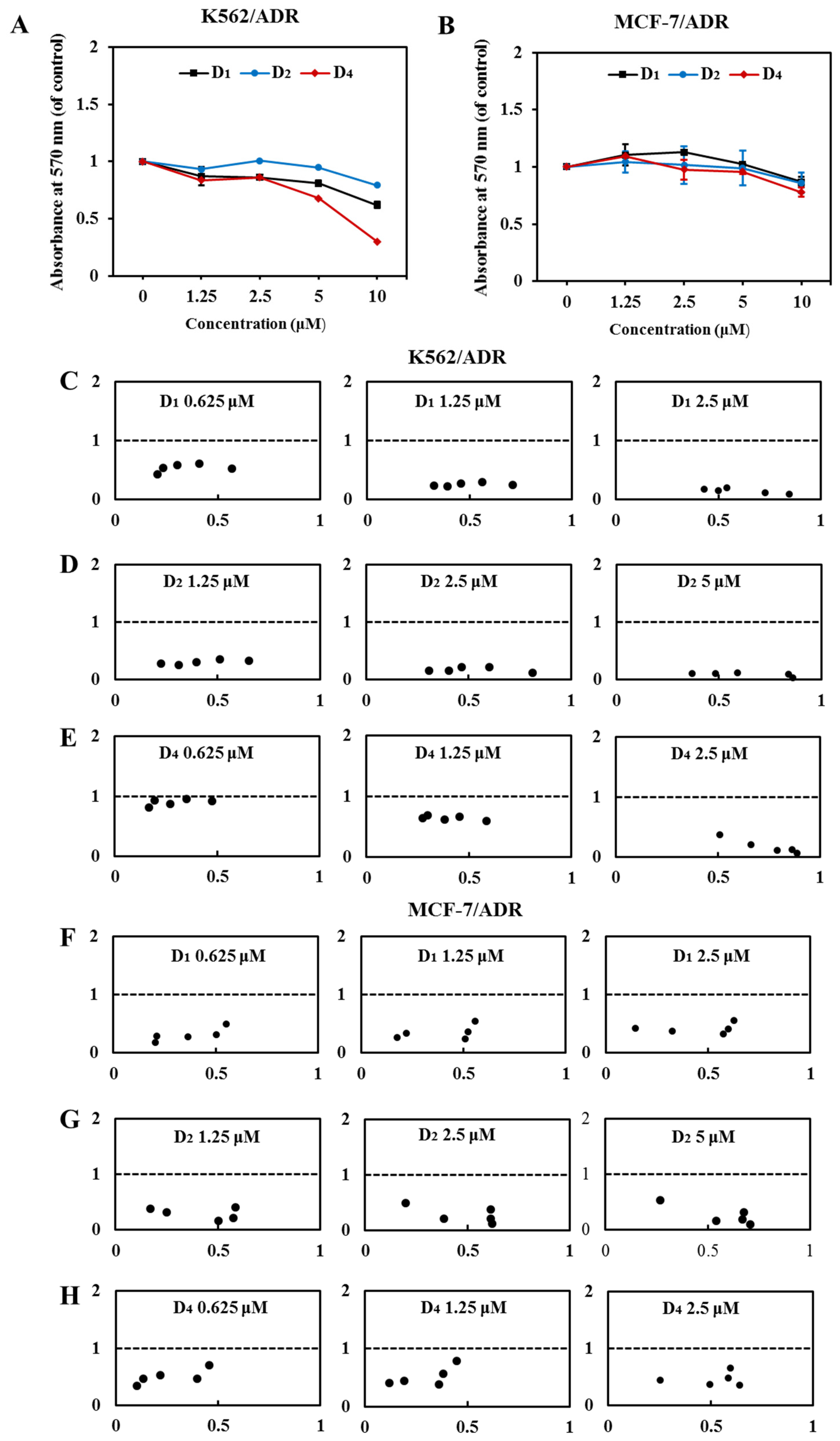
Compounds D1–D4 with the pharmacophore-6,7- dimethoxytetrahydroisoquinoline structure were obtained. Our results showed that compounds D1, D2, and D4 (10 μM) in combination with DOX for 72 h had higher reversal fold in both K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells (Table 1). At 10 µM, the calculated RF values of K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells were 1845.76 and 207.86 for D1, 80.00 and 40.63 for D2, and 1645.45 and 131.67 for D4, which were higher than other compounds. By comparing the RF values of A1, B1, C1, D1, and D2, we found that the ABCB1 inhibition activity of compounds D1 and D2 was observably increased with the pharmacophore-6,7-dimethoxytetrahydroisoquinoline structure compared to the compounds A1, B1, and C1 with methoxy groups of the C ring. Meanwhile, compound D4 displayed the most potent ABCB1 inhibition activities with an RF value of 1645.45, which was remarkably higher than compounds E1–E6 (RF values ≤ 14.3). Compounds D1, D2, and D4 with dimethoxy-substituted tetrahydroisoquinoline fragment were the most promising ABCB1 inhibitors, which indicated that the imidazole amino ligation pharmacophore was critical to improve ABCB1 inhibition activities. They provide effective guidance for future studies of Lissodendrins B inhibiting ABCB1 activity through derivatives. It should be noted that the calculated IC50 values of DOX and reversal fold in the presence of compounds D1, D2, and D4 were partly due to their own cytotoxicity of these compounds, because after the treatment of compounds D1, D2, and D4 for 72 h, a higher concentration (5 and 10 μM) of these compounds alone showed moderate cytotoxicity (Figure 2A,B).
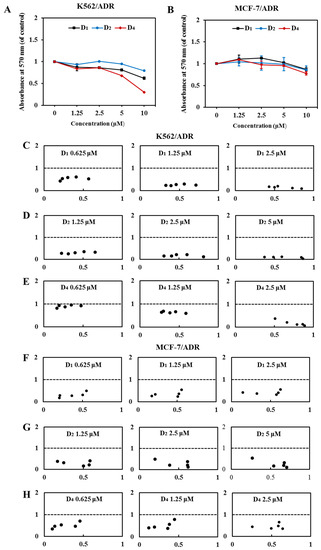
Figure 2.
Compounds D1, D2, and D4 sensitize the effect of DOX in K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells. (A) K562/ADR cells and (B) MCF-7/ADR cells were treated with compounds D1, D2, and D4 (0–10 μM), respectively, for 72 h. Cell viability was tested via MTT assay, and the value was a viability ratio relative to the control group. Treatment with DOX in the absence and presence of compounds D1, D2, and D4 for 72 h in K562/ADR cells (C–E) and MCF-7/ADR cells (F–H). The proliferation inhibition was tested via MTT assay, and the CI value was calculated in CompuSyn software. The CI values of >1, =1, and <1 indicate antagonistic, additive, and synergistic effects, respectively.
2.1.2. Compounds D1, D2, and D4 Have a Synergic Effect in Combination with DOX
Next, we investigated the synergic effect of compounds D1, D2, and D4 under sub-lethal concentrations. Our results showed that at relatively lower concentrations, 2.5 μM of D1 and D4, and 5 μM of D2 showed negligible inhibition on the cell viability (Figure 2A,B), and, therefore, we chose these sub-lethal concentrations to further evaluate their synergic combination with DOX and the concentration–response effects. As shown in Table 2, when the concentrations of compounds D1, D2, and D4 combined with DOX were decreased, the IC50 of DOX on K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells was significantly increased, and the RF values of the compounds were reduced, but they were still greater than one, indicating that they still have MDR reversal activity. Meanwhile, when DOX was combined with different concentrations of D1, D2, and D4, both in K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells, all the CI values were smaller than one and in an obvious concentration-dependent manner (Figure 2C–H), indicating that D1, D2, and D4 had strong synergic effects when in combination with DOX. Among these three compounds, compound D1 showed the strongest synergic effect, and D1 was chosen as a representative compound for the following experiments.

Table 2.
IC50 values of DOX and the reversal fold (RF) in the absence and presence of compounds D1, D2, and D4 on K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells.
2.1.3. Molecular Docking of D1 with ABCB1
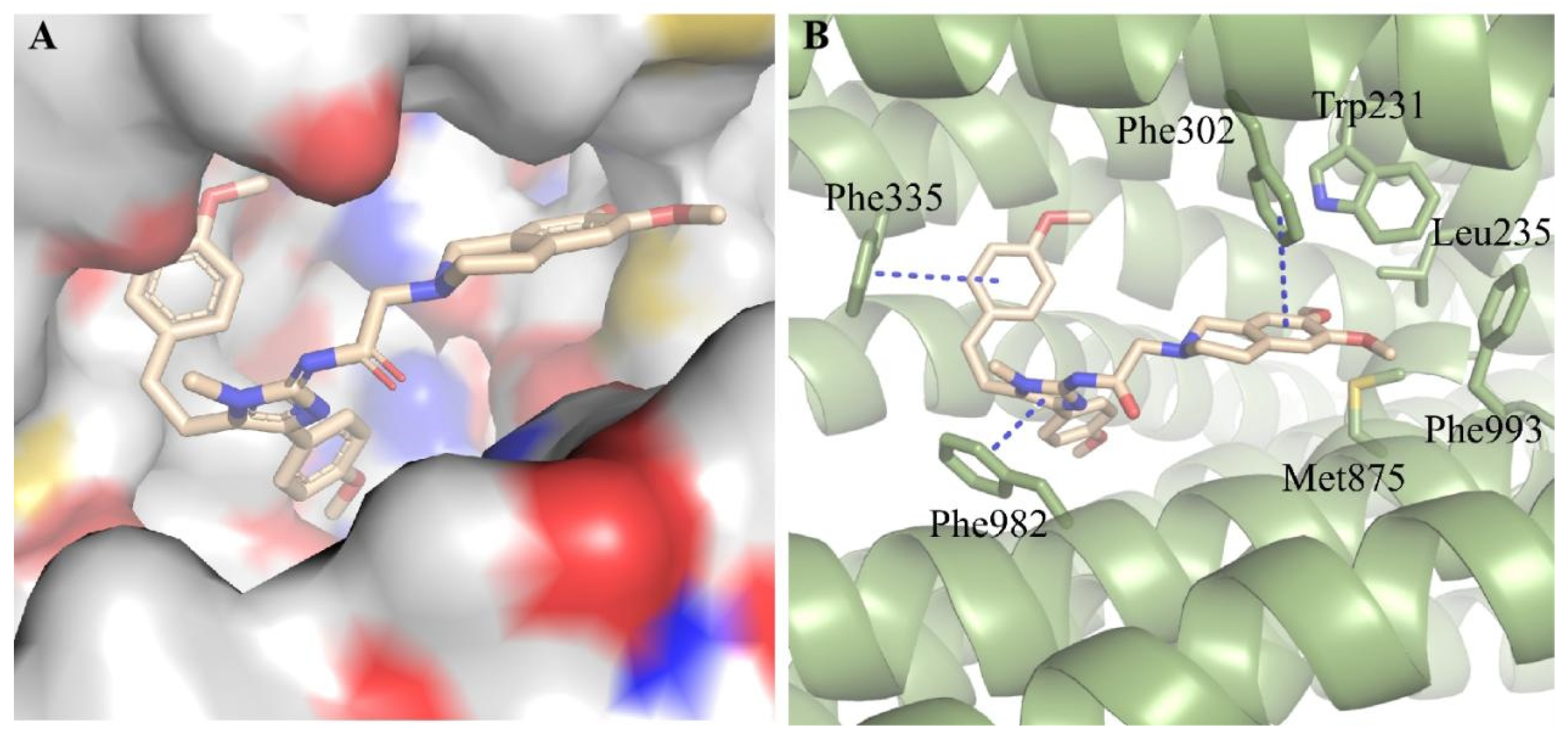
We subsequently conducted docking analysis to investigate the interacting binding mode of compound D1 with ABCB1 (PDB: 6FN1) [32,33]. The result showed that compound D1 well fitted into the hydrophobic binding pocket formed by Trp231, Leu235, Phe302, Phe335, Phe982, Met875, and Phe993 of ABCB1 (Figure 3A,B). T-π stacking interactions were found between the phenyl ring of compound D1 and Phe335, and between the tetrahydroisoquinoline ring of D1 and Phe302, while π-π stacking was formed between the imidazole ring of D1 and Phe982 (Figure 3B). Meanwhile, the tetrahydroisoquinoline ring of D1 was also stabilized through hydrophobic interaction with the side chains of Trp231, Leu235, Met875, and Phe993. We conducted docking analysis to investigate the interacting binding modes of zosuquidar and compound D1 with ABCB1. We found that zosuquidar and compound D1 had the same binding pocket and similar binding patterns (Figure S1A,B). Meanwhile, the stable binding pattern of compound D1 with ABCB1 was demonstrated by root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) in 50 ns molecular dynamic simulations (Figure S1C). These interactions contribute greatly to the high binding affinity of compound D1 to ABCB1 and provide a fundamental structural basis for the further structure-based design of novel ABCB1 inhibitors.
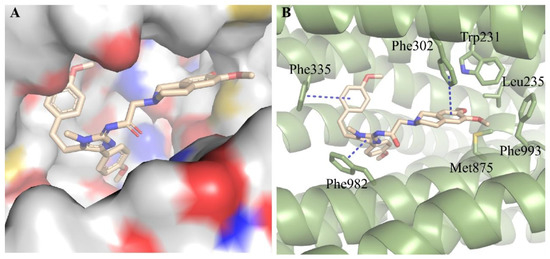
Figure 3.
Predicted binding mode of compound D1 with ABCB1 (PDB code: 6FN1). (A) Compound D1 well fitted into the hydrophobic cavity of the binding pocket. (B) 3D view of the interaction of compound D1 (yellow) with ABCB1 (green, shown as cartoon). The π-π stacking interactions showed in blue dash line.
2.1.4. Compound D1 Increases the Intracellular Accumulation of DOX in K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR Cells
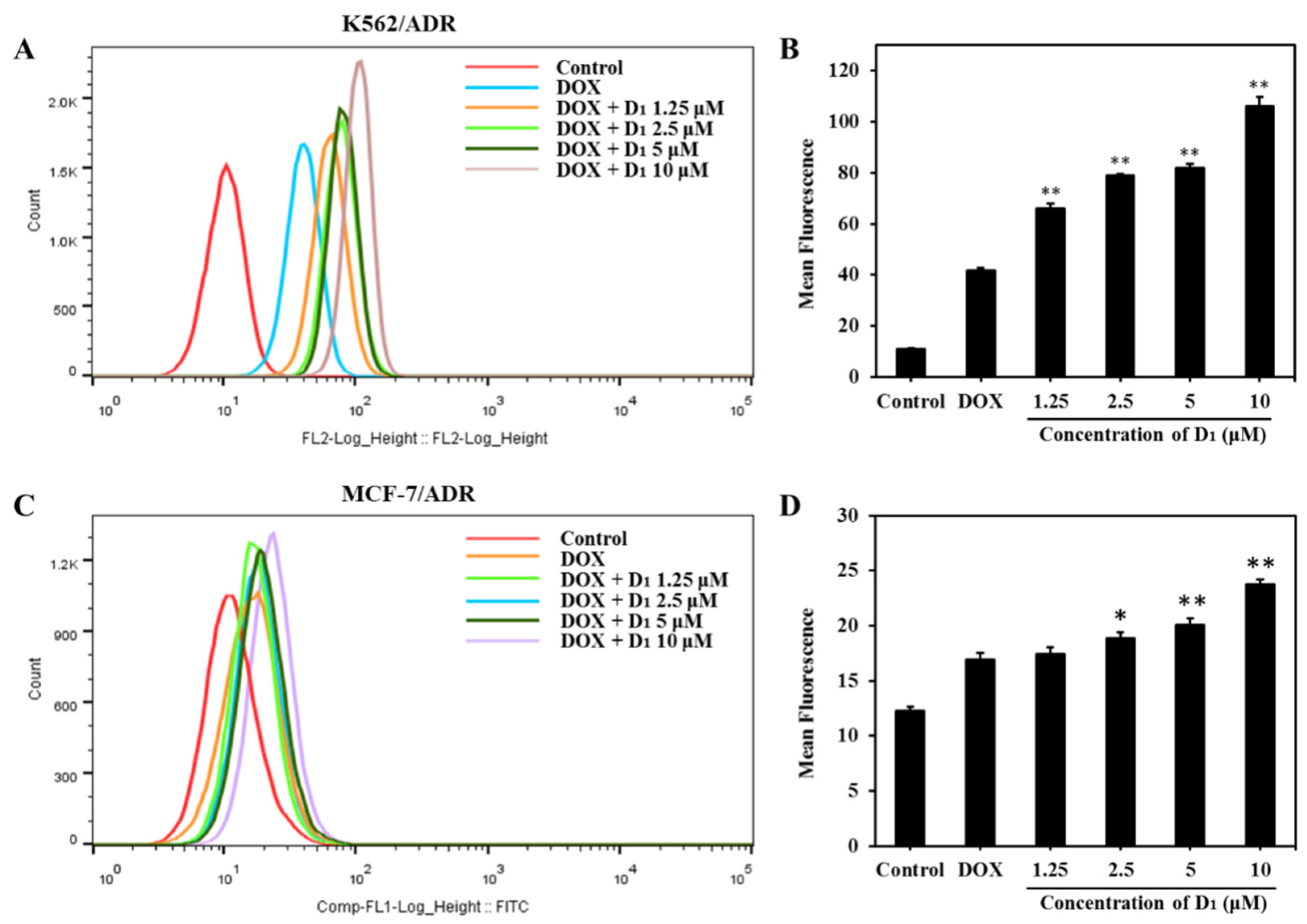
To further investigate the mechanisms underlying the MDR reversal effect of compound D1, we analyzed the intracellular accumulation of DOX in K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells using flow cytometry. As shown in Figure 4A,B, a relatively lower concentration of DOX was accumulated in DOX-alone-treated K562/ADR cells. However, in the presence of different concentrations of compound D1, the accumulation of DOX significantly increased, and the accumulation effect was shown in a concentration-dependent manner. The effect of D1 enhancing intracellular accumulation of DOX was also observed in MCF-7/ADR cells (Figure 4C,D). These results indicate that the mechanisms underlying the reversal effect of D1 are possibly related to the inhibition of the ABCB1 transporting function, as ABCB1 is the major transporter that mediates the DOX efflux and drug resistance.
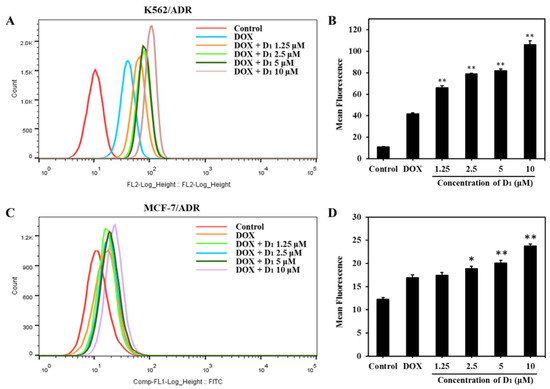
Figure 4.
Compound D1 increases the intracellular accumulation of DOX both in K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells. K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells were treated with DOX (3 μM) in the presence or absence of compound D1 (1.25–10 μM) for 12 h. (A) Intracellular DOX accumulation in K562/ADR cells was detected through flow cytometry (Beckman Coulter MoFlo XDP). (B) The mean of DOX fluorescent intensity in K562/ADR cells shown in the histograms. (C) Intracellular accumulation of DOX was detected via flow cytometry, and (D) histograms show the mean fluorescence of DOX in MCF-7/ADR cells. Values represent the means ± SD of three experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
2.1.5. Compound D1 increases the Intracellular Accumulation of ABCB1 Substrate Rho123 in K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR Cells
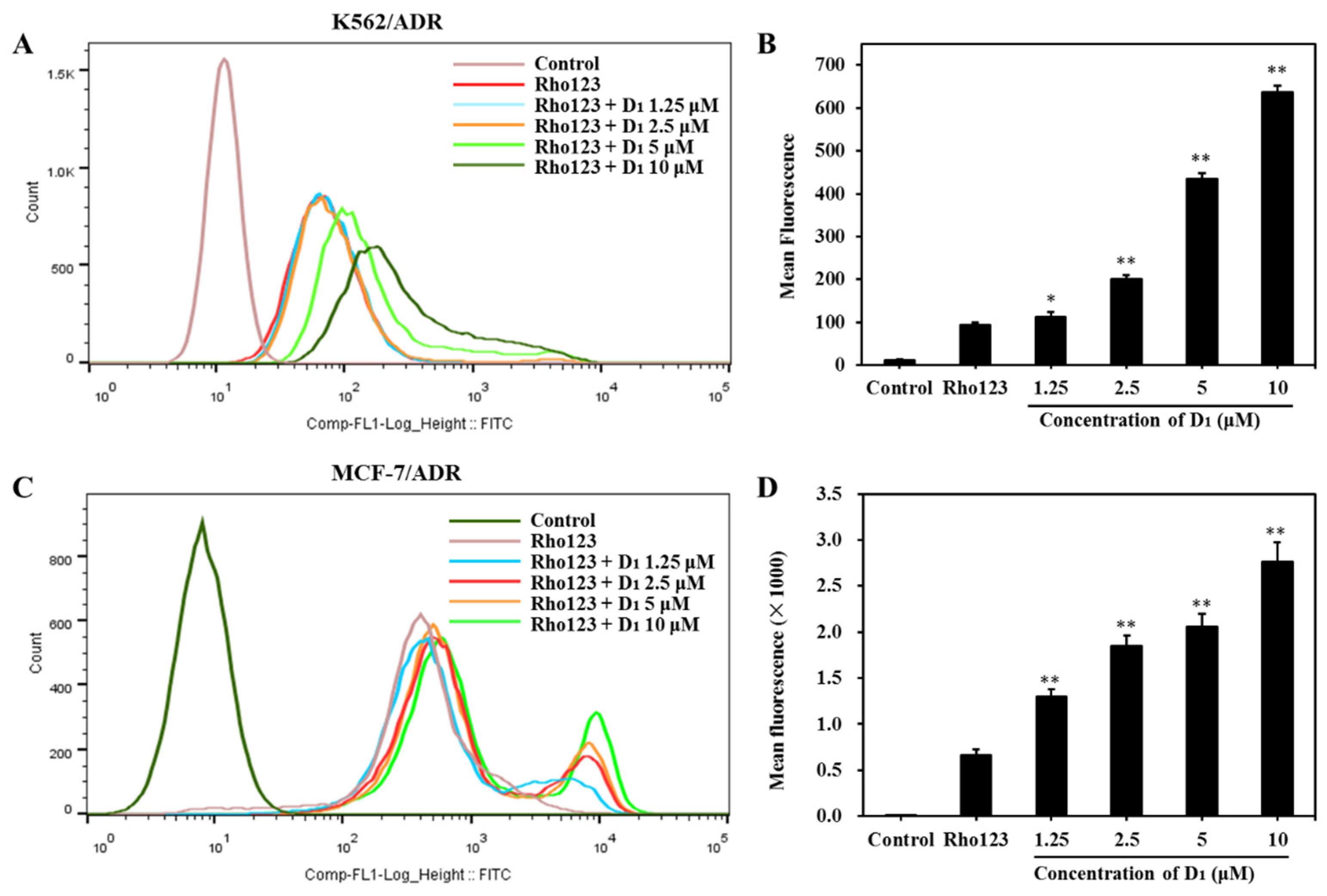
To confirm whether D1 affects the ABCB1 transporting function, we next analyzed the efflux and intracellular accumulation of Rho123, which is a classical substrate of ABCB1. As shown in Figure 5A,B, in the presence of compound D1, in K562/ADR cells, the intracellular Rho123 fluoresces increased in a concentration-dependent manner. The same phenomenon was also observed in MCF-7/ADR cells (Figure 5C,D), confirming that compound D1 could significantly increase the intracellular accumulation of Rho123. These results further revealed that compound D1 could inhibit the efflux function of ABCB1.
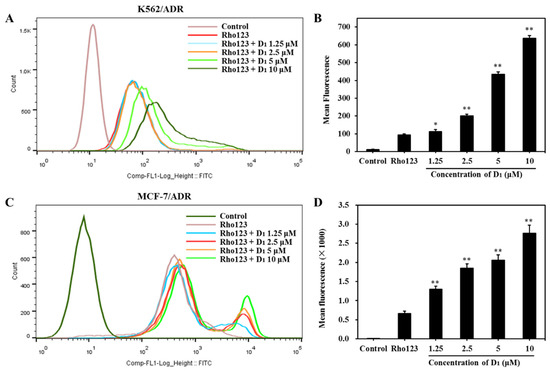
Figure 5.
Compound D1 inhibits the efflux of Rho123 both in K562/ADR cells and MCF-7/ADR cells. Cells were treated with compound D1 (1.25–10 μM) for 6 h, then incubation with Rho123 (10 μM) for another 2 h. (A) The intracellular accumulation of Rho123 in K562/ADR cells was analyzed via flow cytometry, and (B) the mean fluorescence of Rho123 is shown in the histograms. (C) The intracellular accumulation of Rho123 in MCF-7/ADR cells was detected via flow cytometry, and (D) histograms show the increasing mean fluorescence of Rho123. Values represent the means ± SD of three experiments. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
2.1.6. ABCB1 Is Involved in Compound D1-Mediated MDR Reversal
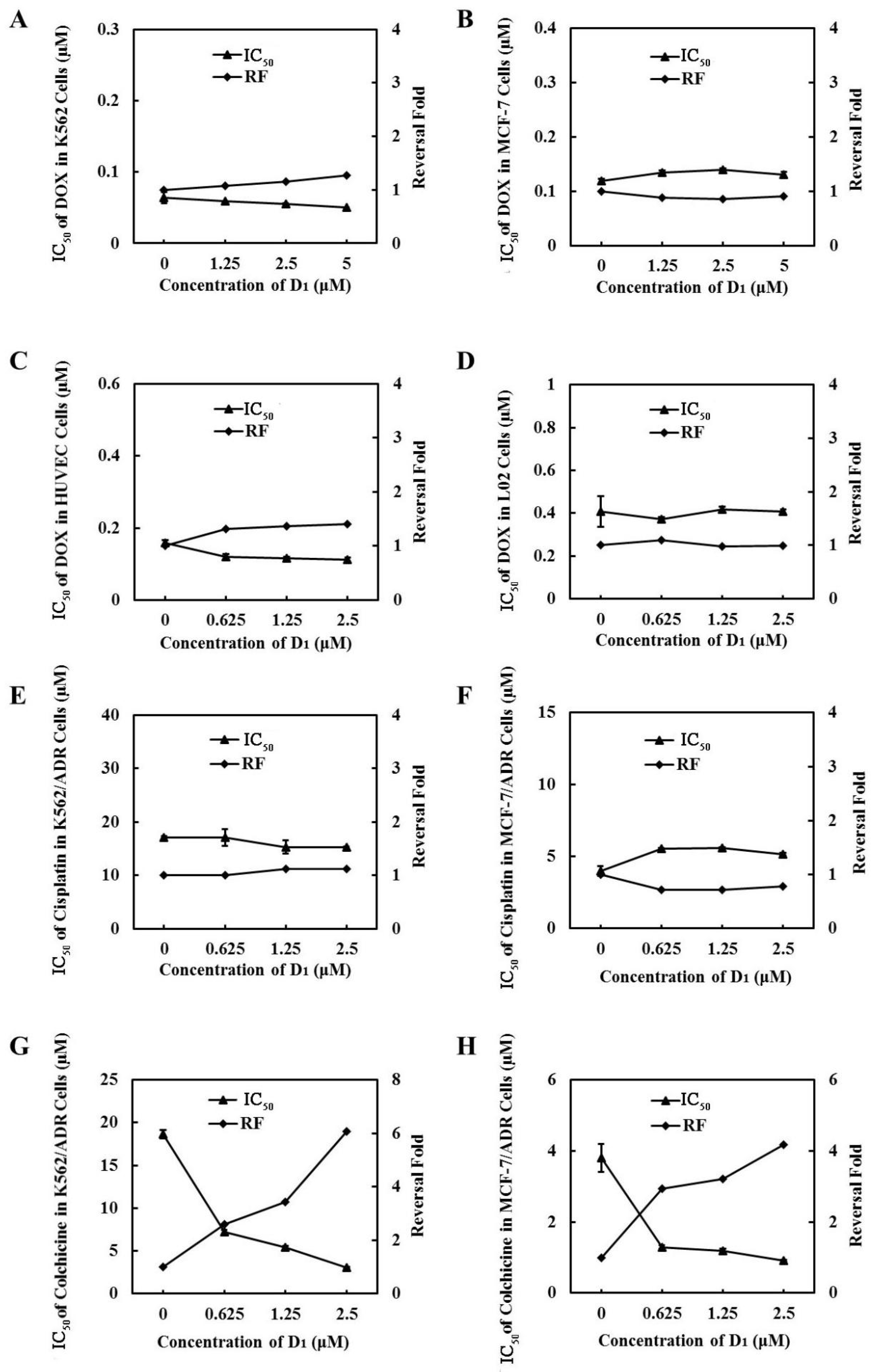
To further demonstrate that ABCB1 was involved in compound D1-mediated MDR reversal, we used DOX-sensitive cell line MCF-7 cells and K562 cells, which express low ABCB1, to evaluate the synergic effect of DOX and D1. We found that compound D1 did not enhance the sensitivity of DOX in these two DOX-sensitive cell lines (Figure 6A,B). Meanwhile, the synergic effect was not observed in normal human liver L02 cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) (Figure 6C,D). Moreover, when combined with cisplatin, which is not a substrate of ABCB1 in K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells, compound D1 did not decrease the IC50 of cisplatin and showed no synergic effect (Figure 6E,F). However, when combined with colchicine, which is a substrate of ABCB1, as expected, D1 could significantly enhance the sensitivity of colchicine, both in K562/ADR and in MCF-7/ADR cells (Figure 6G,H). Taken together, compound D1 sensitized the chemotherapeutic agents in MDR cells via inhibition of the efflux function of ABCB1.
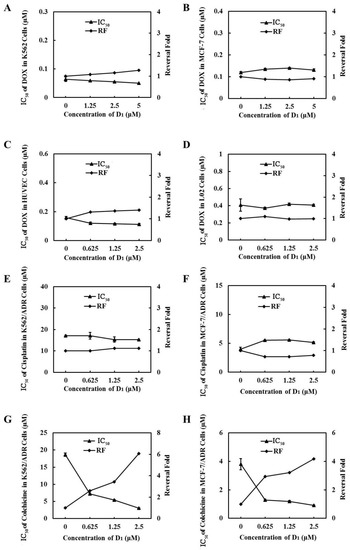
Figure 6.
The inhibition effect of MDR is related to ABCB1. Compound D1 does not enhance the sensitization of DOX in MCF-7 cells (A), K562 cells (B), HUVECs (C), and L02 cells (D). MCF-7 cells and K562 cells were incubated with DOX in absence or presence of certain concentrations of compound D1 (1.25–5 μM) for 72 h; HUVECs and L02 cells were treated with DOX in absence and presence of compound D1 (0.625–2.5 μM). Cell viability was assayed via MTT method, and the IC50 values of DOX and the reversal fold were calculated. Compound D1 does not reverse the resistance of cisplatin in K562/ADR cells (E) and MCF-7/ADR cells (F). Compound D1 enhances the sensitivity of ABCB1 substrate COL in K562/ADR cells (G) and MCF-7/ADR cells (H). Cells were treated with cisplatin or COL in absence and presence of compound D1 (0.625–2.5 μM). Cell viability was assayed via MTT method; the IC50 values of DOX and the reversal fold were calculated.
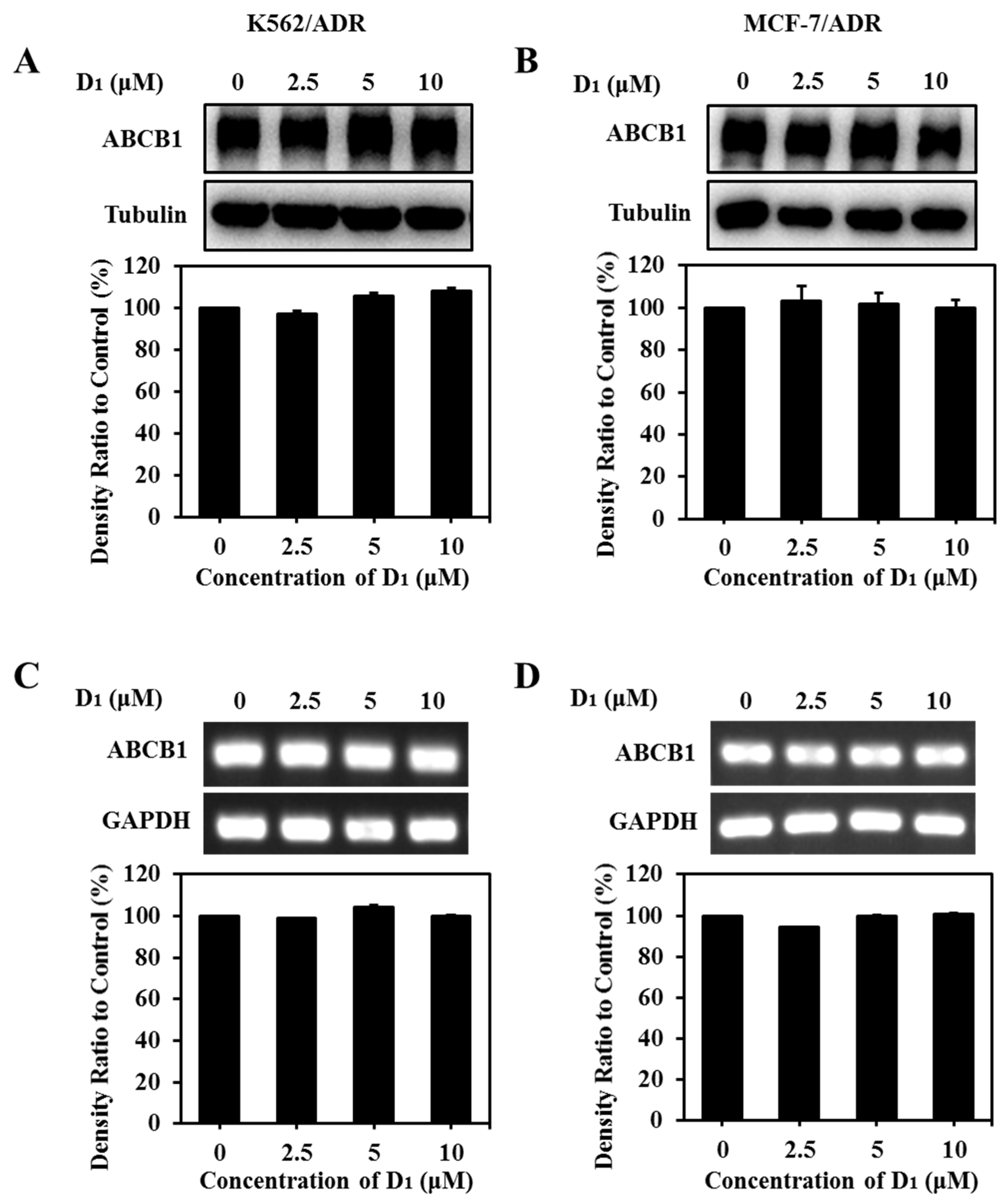
2.1.7. Compound D1 Did Not Have an Obvious Effect on the Expression Levels of ABCB1
Both the expression downregulation and the functional inhibition can decrease the ABCB1 transporting function. In order to elucidate the transporting inhibition mechanism of ABCB1, the effect of compound D1 on ABCB1 expression was analyzed via WB assay and RT-PCR assay. The results showed that compound D1 did not obviously alter the protein expression level (Figure 7A,B) or mRNA expression level (Figure 7C,D) of ABCB1 in K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells under the present experimental conditions. The results revealed that reversal MDR of compound D1 was not through the downregulation of ABCB1 expression but rather through inhibiting the transport function of ABCB1.
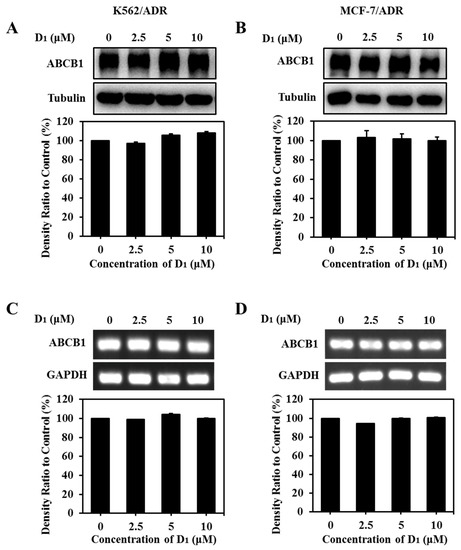
Figure 7.
Compound D1 has no significant effect on ABCB1 expression level. Cells were treated with certain concentrations of compound D1 (0–10 μM) for 24 h in K562/ADR cells and MCF-7/ADR cells, respectively. The expression levels of ABCB1 were detected via Western blotting assay, and the histograms show the expression levels of protein bands in K562/ADR cells (A) and MCF-7/ADR cells (B). The expression levels of ABCB1 mRNA were measured using RT-PCR in K562/ADR cells (C) and MCF-7/ADR cells (D). Histograms show the relative density ratio to control group.
2.2. Discussion
In this study, nineteen Lissodendrins B analogues were synthesized as ABCB1 inhibitors to overcome ABCB1-mediated MDR. A preliminary structure–activity relationship study showed that ‘Y’-type skeleton structural characteristics, three methoxy groups of the C ring, dimethoxy-substituted tetrahydroisoquinoline fragment, and the linker between the imidazole ring and B ring essentially contribute to ABCB1 inhibiting activity. The compounds (D1, D2, and D4) with the pharmacophore-6,7-dimethoxytetrahydroisoquinoline were the most promising ABCB1 inhibitors, which indicated that the tetrahydroisoquinoline as a pharmacophore was critical to improve the ABCB1 inhibition effect.
Meanwhile, our present work revealed that the presentative compound D1 could significantly reverse the drug resistance of MCF-7/ADR and K562/ADR cells to DOX and indicated that D1 had the potential to develop as a good DOX and other chemotherapeutic agent sensitizer for ABCB1 transporter-mediated MDR in clinical cancer treatment. Parent compounds of D1 usually influence multiple bioactivities, e.g., DNA damage, telomerase inhibition, and senescence induction, and, thus, it is interesting to explore the effect of D1 on other bioactivities since this kind of compound has multiple activities and mechanisms in cancer therapy. A study is ongoing in our laboratory to study its effect on these bioactivities, as well as address the in vivo activity of D1 on xenograft tumor models.
A high expression of ABCB1 plays a crucial role in chemotherapeutic agent resistance, and targeting ABCB1 has become an promising strategy to reverse MDR [34]. In our previous screening work for ABCB1 inhibitors, we found that cardiotonic steroid compounds display anti-DOX resistance activity by stimulating ABCB1 ATPase activity [35]. Flavonoid compounds, e.g., xanthohumol and isoxanthohumol, also act as ABCB1 substrates and reverse MDR in MCF-7/ADR cells [36,37]. Other research groups also showed that tyrosine kinase inhibitors modulate ABCB1 functions through stimulating the ATPase activity [38]. In this work, we reported that D1 and its derivatives could reverse DOX resistance by inhibiting the efflux function of ABCB1 for the first time. It should be noted that D1-reversed ABCB1-mediated MDR possibly occurred via the modulation of ABC protein expression. In the following experiments, we then found that up to 24 h, 10 μM D1 did not affect ABCB1 expression, both in mRNA and protein levels, confirming that D1 inhibited the efflux of DOX and was not via modulation of ABCB1 expression level under our present experimental conditions.
Considering that other ABC transporters also contributed to the development of MDR, we could not eliminate the effect of D1 on other ABC transporters, such as ABCG2 and multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1). As compound D1 could inhibit the efflux function of ABCB1, it is an interesting topic to further evaluate whether D1 could interfere with the pharmacokinetics of chemotherapeutic agents, e.g., DOX or paclitaxel, which are substrates of ABCB1. Moreover, most of the present ABCB1 inhibitors in clinical trials have failed due to side effects or unpredictable pharmacokinetic drug–drug interactions. Thus, there is still a reason to develop more efficacious and non-toxic ABCB1 inhibitors in order to reverse MDR in cancer treatment [39].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Design and Synthesis Materials
Dichloromethane and tetrahydrofuran were purified conventionally. All reagents used in the experiments were obtained from commercial sources without further purification. Reactions were monitored through thin-layer chromatography (TLC). Visualization was achieved under a UV lamp (254 nm and 365 nm) and developed the plates with potassium permanganate. Flash column chromatography was performed with silica gel (200–300 mesh). 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra were taken on JnmEcp-600 spectrometer. 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra are cell lines referenced to tetramethylsilane (Me4Si). The following abbreviations are used: s = singlet, d = doublet, t = triplet, q = quartet, m = multiplet, dd = double-doublet.
3.2. Biological Evaluation
3.2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
Cells: Human breast cancer MCF-7 cells and the adriamycin-resistant cell line MCF-7/ADR, human myelogenous leukemia K562 cell lines and adriamycin-resistant cell line K562/ADR, human hepatacyte L02 cells, and Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were obtained from the Cell Bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences. K562 cells, K562/ADR cells, and L02 cells were maintained in Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s Medium (IMDM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). MCF-7 cells were maintained in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI)-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS. MCF-7/ADR cells were maintained in Eagles Minimum Essential Medium (EMEM) supplemented with 10% FBS. HUVECs were maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% FBS. All media were supplemented with antibiotics (100 IU/mL penicillin G, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin). All cell lines were maintained at 37 °C in humidified 5% CO2 incubator. Reagents: Antibody against ABCB1 was from Cell Signaling Technology (Boston, MA, USA). Antibodies against β-tubulin were purchased from Epitomics (Burlingame, CA, USA). The RNA extraction kit was purchase from Tiangen (Beijing, China). The PrimeScriptTM RT-PCR kit was purchased from Takara (Kusatsu, Shiga, Japan). The other reagents were purchased from Beyotime Biotechnology (Shanghai, China).
3.2.2. Detection of Cell Proliferation
The effect of compounds on cell proliferation was determined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Cells were seeded in 96-plate wells and incubated with the indicated concentrations of compounds for indicated periods. Then, MTT (20 μL, 5 mg/mL) was added in each well. After incubation at 37 °C for another 4 h, supernatant of adherent cells was discarded; then, 150 μL DMSO was added and incubated for about 15 min. Meanwhile, acidic isopropanol 100 μL was added into the wells of suspension cells, and plates were further incubated overnight to dissolve the formazan product. Finally, absorbance was measured at 570 nm.
The sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay was another method used to detect the effect of compounds on cell growth. Briefly, cells were seeded in 96-well plates and treated for indicated time with various concentrations of compounds. Then, the supernatant liquid was discarded; cells were immobilized by ice-cold trichloroacetic acid (TCA, 10%) for 1 h and washed with deionized water. After drying at 37 °C, 100 μL 0.4% SRB was added in every well and incubated for 15 min. SRB was discarded and washed with 1% glacial acetic acid. After drying at 37 °C, 150 μL tris-base (10 mM) was added in every well and incubated for 10 min, and the absorbance was measured at 492 nm.
3.2.3. Calculation of Combined Drug Synergistic Effects
Cells were seeded in 96-well plates and treated with DOX alone or combined with certain concentrations of tested compounds for 72 h; then, the cell viability was detected using MTT method as mentioned above. The drug combination index (CI) was calculated in CompuSyn software (ComboSyn, Inc., Paramus, NJ, USA) according to the description of Chou and Talalay [40]. The CI values of >1, =1, and <1 indicate antagonistic, additive, and synergistic effects, respectively.
3.2.4. Intracellular DOX Accumulation Assay
Cells were seeded in 6-well plates and treated with DOX (3 μM) alone or in presence of compound D1 (0–10 μM) for 12 h, and then cells were collected and washed three times with ice-cold phosphate buffered saline (PBS). The autofluoresence of DOX was detected via flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter MoFlo XDP, Fullerton, CA, USA) with an excitation wavelength of 488 nm.
3.2.5. Intracellular Rhodamine 123 (Rho123) Accumulation Assay
Cells were pre-treated with different concentrations of compound D1 (0–10 μM) for 6 h. Rho123 (10 μM) was added in the culture medium for another 2 h. Then, the cells were collected and washed 3 times with chilled PBS. Cells were resuspended in 500 μL PBS and analyzed via flow cytometry (Beckman Coulter MoFlo XDP, Fullerton, CA, USA). The excitation wavelengths of Rho 123 were 488 nm, and the emission wavelength was 530 nm.
3.2.6. ABCB1 mRNA Level and RT-PCR
Cells were seeded in 6-well plates and treated with certain concentrations of compound D1 (0–10 μM) for 24 h. After incubation, total RNA was obtained via RNA extraction kit according to the manufacturer’s instruction. Then, the RT-PCR was performed with PrimeScriptTM RT-PCR kit. ABCB1 mRNA was measured using the following primers [36]: ABCB1 FP: 5′-CCCATCATTGCAATAGCAGG-3′; RP: 5′-GTTCAAACTTCTGCTCCTGA-3′. The primer pairs for GAPDH were: FP: 5′-GAAGGTGAAGGTCGGAGTC-3′; RP: 5′-GAAGATGGTGATGGGATTTC-3′. The electrophoresis of the products running on 1% agarose gels contained gel red. The results were detected via Gel DocTM XR + (BIO-RAD, Heracles, CA, USA) and analyzed with Image LabTM Software (BIO-RAD, Heracles, CA, USA).
3.2.7. Western Blotting Assay
Cells were seeded in 6-well plates and treated with certain concentrations of compound D1 (0–10 μM) for 24 h. Then, cells were collected, washed twice with PBS, and lysed with loading buffer for 45 min at 4 °C. The total protein samples were separated by 6–8% SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and immobilized on the nitrocellulose membrane through electroblotting. The membranes were blocked in 5% milk for 2 h and incubated with specific primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight, followed by incubation with secondary antibodies for 1 h. Finally, protein bands were visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence kits and quantified by Tanon-5200 (Tanon, Shanghai, China).
3.2.8. Statistical Analysis
The results were given as mean ± SD, and Student’s t-test was employed for the statistical comparisons. p < 0.05 was considered as significant difference compared with the control group.
4. Conclusions
In summary, a series of 19 Lissodendrins B analogues was synthesized, and the ABCB1-mediated MDR reversal activity in DOX-resistant K562/ADR and MCF-7/ADR cells was evaluated. Amongst them, we revealed that these novel compounds D1, D2, and D4 possessed potent synergistic effects with DOX and reversed ABCB1-mediated drug resistance, which demonstrated that the introduction of a dimethoxy-substituted tetrahydroisoquinoline fragment was a successful strategy for the development of ABCB1 inhibitors. Notably, compound D1 exhibited low cytotoxicity and the strongest synergistic effect. The synergistic mechanisms were mainly related to the increased intracellular accumulation of DOX, via inhibiting the efflux function of ABCB1 rather than from affecting the expression level of ABCB1. Considering the potent MDR reversal activity and the relatively safe profiles, compound D1, as a potentially promising lead, deserves further investigation for developing ABCB1 inhibitors to overcome ABCB1-mediated MDR.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/md21050314/s1, General procedure for synthesis of compounds 11–18, 20 and 21. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds A1, A2, B1, B2, C1, C2, D1, D2, E1–E5. Scheme S1: Chemical synthesis of compounds 7 and 8. Scheme S2: Chemical synthesis of compounds 13 and 14. Scheme S3: Chemical synthesis of compounds 17 and 18. Scheme S4: Chemical synthesis of compound 21. Scheme S5: Chemical synthesis of compound 25. Figure S1: Predicted binding modes of zosuquidar and compound D1 with ABCB1. Figures S2–S39: Copies of 1H NMR and 13C NMR Spectra of Compounds A1–A3, B1–B3, C1–C3, D1–D4 and E1–E6.
Author Contributions
C.W., J.Z., X.W., M.L. and T.J., designed research; C.W., J.Z., X.W., M.Y. and W.M., performed research; M.Y., W.M., R.Y., M.L. and T.J., contributed reagents and analytic tools; C.W., J.Z., X.W., R.Y., M.L. and T.J., analyzed data; C.W. and J.Z., wrote the paper. Our manuscript is original content and has not been submitted to other journals. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors are grateful for financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of China (82073759, 82122064), Key Project of Greater Bay Area Institute of Precision Medicine (Guangzhou) (IPM2021C009), and Special Funds of Shandong Province for Qingdao National Laboratory of Marine Science and Technology (No.2022QNLM030003).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that the supporting data of this study are available within the article and the Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fletcher, J.I.; Haber, M.; Henderson, M.J.; Norris, M.D. ABC transporters in cancer: More than just drug efflux pumps. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Ma, L.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Lei, Z.-N.; Gupta, P.-Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, Z.-H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.-H.; Li, Y.-N.; et al. Discovery of 5-cyano-6-phenylpyrimidin derivatives containing an acylurea moiety as orally bioavailable reversal agents against P-glycoprotein-mediated mutidrug resistance. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5988–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, W.-D.; Cheng, G.; Yehuda, A.G.; Ashby, C.R.; Chen, Z.-S.; Cheng, X.-D.; Qin, J.-J. Medicinal chemistry strategies to discover P-glycoprotein inhibitors: An update. Drug Resist. Updates 2020, 49, 100681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Pan, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zeng, M.; Sun, S.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Qiu, J.; Niu, M.; et al. Design and evaluation of dibenzoazepine-tetrahydroisoquinoline hybrids as potential P-glycoprotein inhibitors against multidrug resistant K562/A02 cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 249, 115150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faneyte, I.F.; Kristel, P.M.P.; Maliepaard, M.; Scheffer, G.L.; Scheper, R.J.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Vijver, M.J. Expression of the breast cancer resistance protein in breast cancer. Clin. Can. Res. 2002, 8, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J.; Wong, I.L.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S.-W.; Liu, T.; Wen, B.-J.; Chow, L.M.; Wan, S.-B. Synthesis of methylated quercetin derivatives and their reversal activities on P-gp- and BCRP-mediated multidrug resistance tumour cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.-Y.; Wong, I.L.; Yan, C.-S.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Jiang, T.; Chow, L.M.; Wan, S.-B. Design and syntheses of permethyl ningalin B analogues: Potent multidrug resistance (MDR) reversal agents of cancer cells. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5108–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wong, I.L.; Peng, K.; Liu, Z.; Wang, P.; Jiang, T.; Chow, L.M.; Wan, S.-B. Extending the structure-activity relationship study of marine natural ningalin B analogues as P-glycoprotein inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Liu, Q.; Ren, S.; Wan, S.; Jiang, T.; Wong, I.L.K.; Chow, L.M.C.; Wang, S. Synthesis of a novel series of (E,E)-4,6-bis(styryl)-2-O-glucopyranosyl-pyrimidines and their potent multidrug resistance (MDR) reversal activity against cancer cells. J. Carbohydr. Chem. 2012, 31, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copp, B.R.; Fairchild, C.R.; Cornell, L.; Casazza, A.M.; Robinson, S.; Ireland, C.M. Naamidine A is an antagonist of the epidermal growth factor receptor and an in vivo active antitumor agent. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 3909–3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, C.F.; Gottesman, M.M. Is the multidrug transporter a flippase? Trends Biochem. Sci. 1992, 17, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, K.-K.; Tang, X.-L.; Liu, Y.-S.; Li, P.-L.; Li, G.-Q. Imidazole alkaloids from the south china sea sponge pericharax heteroraphis and their cytotoxic and antiviral activities. Molecules 2016, 21, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Me’lanie, R.; Isabelle, D.C.; Alexander, E.; Chakib, D.; Thierry, P.; Marie-Lise, B.-K. Cellular localization of clathridimine, an antimicrobial 2-aminoimidazole alkaloid produced by the mediterranean calcareous sponge clathrina clathrus. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, W.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Wray, V.; Proksch, P. New imidazole alkaloids from the indonesian sponge leucetta chagosensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Guo, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Song, H.; Wang, Q. Marine natural products for drug discovery: First discovery of kealiinines A-C and their derivatives as novel antiviral and antiphytopathogenic fungus agents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7310–7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Wong, I.L.; Wan, S.; Chow, L.M.; Jiang, T. 4,5-Di-substituted benzyl-imidazol-2-substituted amines as the structure template for the design and synthesis of reversal agents against P-gp-mediated multidrug resistance breast cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 83, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.W.; Mong, S.; Hemling, M.E.; Freyer, A.J.; Westley, J.W. New leukotriene B4 receptor antagonist: Leucettamine A and related imidazole alkaloids from the marine sponge Leucetta microraphis. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhlesi, A.; Hartmann, R.; Achten, E.; Chaidir; Hartmann, T.; Lin, W.; Daletos, G.; Proksch, P. Lissodendrins A and B: 2-aminoimidazole alkaloids from the marine sponge lissodendoryx (acanthodoryx) fibrosa. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 2016, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Hu, X.; Yu, R.; Wan, S.; Jiang, T. Efficient total synthesis of lissodendrin B, 2-aminoimidazole marine alkaloids isolated from lissodendoryx (acanthodoryx) fibrosa. Mar. Drugs 2019, 18, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.J.; Rodarte, J.C.; Benbatoul, K.D.; Romano, S.J.; Zhang, C.; Krane, S.; Moran, E.J.; Uyeda, R.T.; Dixon, R.; Guns, E.S.; et al. Discovery and characterization of OC144-093, a novel inhibitor of P-glycoproteinmediated multidrug resistance. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2964–2972. [Google Scholar]
- Kathawala, R.J.; Gupta, P.; Ashby, C.R.; Chen, Z.-S. The modulation of ABC transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer: A review of the past decade. Drug Resist. Updates 2015, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhuang, W.; Sun, X.; Li, Q.; Bao, X.; Ye, X.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel phenylfuran-bisamide derivatives as P-glycoprotein inhibitors against multidrug resistance in MCF-7/ADR cell. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 248, 115092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; O’ Loughlin, K.L.; Fricke, S.M.; Williamson, N.A.; Greco, W.R.; Baer, H.; Minderman, M.R. Cyclosporin A is a broad-spectrum multidrug resistance modulator. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2320–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kairuki, M.; Qiu, Q.; Pan, M.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Ghaleb, H.; Huang, W.; Qian, H.; Jiang, C. Designed P-glycoprotein inhibitors with triazol-tetrahydroisoquinoline-core increase doxorubicin-induced mortality in multidrug resistant K562/A02 cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2019, 27, 3347–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Prasad, N.R.; Chufan, E.E.; Patel, B.A.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, Z.S.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Talele, T.T. Design and synthesis of human ABCB1 (P-glycoprotein) inhibitors by peptide coupling of diverse chemical scaffolds on carboxyl and amino termini of (S)-valine-derived thiazole amino acid. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4058–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Yin, D.; Ye, J.; Wei, X.; Pei, Y.; Li, X.; Si, G.; Chen, X.-Y.; Chen, Z.-S.; Dong, Y.; et al. Discovery of potent inhibitors against P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance aided by late-Stage functionalization of a 2-(4-(pyridin-2-yl)phenoxy)pyridine analogue. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 5458–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghray, D.; Zhang, Q. Inhibit or evade multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein in cancer treatment. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5108–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Su, W.; White, A.M.; Bin, J.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Stewart, S.; et al. Carbon nano-onion-mediated dual targeting of P-selectin and P-glycoprotein to overcome cancer drug resistance. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Shi, W.; Kairuki, M.; Huang, W.; Qian, H. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of N-(4-(2-(6,7-dimethoxy-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-yl)ethyl)phenyl)-4-oxo-3,4-dihydrophthalazine-1-carboxamide derivatives as novel P-glycoprotein inhibitors reversing multidrug resistance. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 86, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braconi, L.; Bartolucci, G.; Contino, M.; Chiaramonte, N.; Giampietro, R.; Manetti, D.; Perrone, M.G.; Romanelli, M.N.; Colabufo, N.A.; Riganti, C.; et al. 6,7-Dimethoxy-2-phenethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline amides and corresponding ester isosteres as multidrug resistance reversers. J. Enzyme. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2020, 35, 974–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wei, X.; Li, X.; Yu, R.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, C. Design, synthesis, and bioactivity study on Lissodendrins B derivatives as PARP1 inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2022, 69, 116892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, A.; Kung, R.; Kowal, J.; McLeod, R.A.; Tremp, N.; Broude, E.V.; Roninson, I.B.; Stahlberg, H.; Locher, K.P. Structure of a zosuquidar and UIC2-bound human-mouse chimeric ABCB1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shawky, A.M.; Abdalla, A.N.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Abourehab, M.A.S.; Gouda, A.M. Discovery of new pyrimidopyrrolizine/indolizine-based derivatives as P-glycoprotein inhibitors: Design, synthesis, cytotoxicity, and MDR reversal activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 218, 113403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Videira, M.; Reis, R.L.; Brito, M.A. Deconstructing breast cancer cell biology and the mechanisms of multidrug resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2014, 1846, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Lin, X. Teratogenic jervine increases the activity of doxorubicin in MCF-7/ADR cells by inhibiting ABCB1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.; Li, M.; Miao, J. Prenylflavonoid isoxanthohumol sensitizes MCF-7/ADR cells to doxorubicin cytotoxicity via acting as a substrate of ABCB1. Toxins 2017, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hoag, H.; Wu, C.; Liu, H.; Yin, H.; Dong, J.; Qian, Z.; Miao, F.; Liu, M.; Miao, J. Experimental and simulation identification of xanthohumol as an inhibitor and substrate of ABCB1. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, L.K.; Zhang, X.; To, K.K.; Zhao, H.; Wang, F.; Xia, Z.; Chen, X.; et al. Osimertinib (AZD9291) enhanced the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents in ABCB1 and ABCG2 overexpressing cells in vitro, in vivo and ex vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1845–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szakács, G.; Paterson, J.K.; Ludwig, J.A.; Booth-Genthe, C.; Gottesman, M.M. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the chou-talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).