Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits Inflammatory Response, Both In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Characterization of Fucoidan Extract (FE)
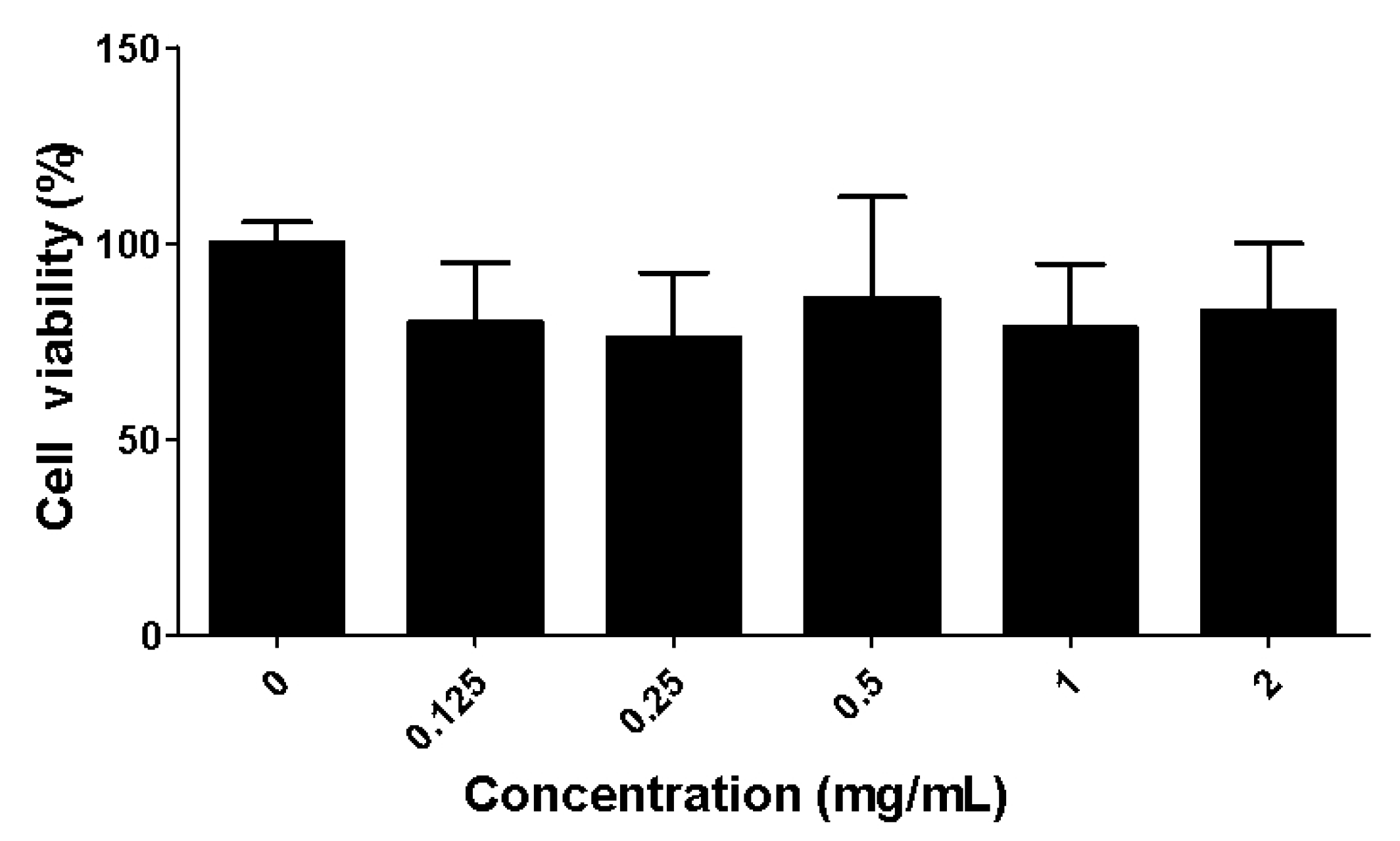
2.2. Toxicity of the Fucoidan Extract (FE) over RAW 264.7 Macrophages
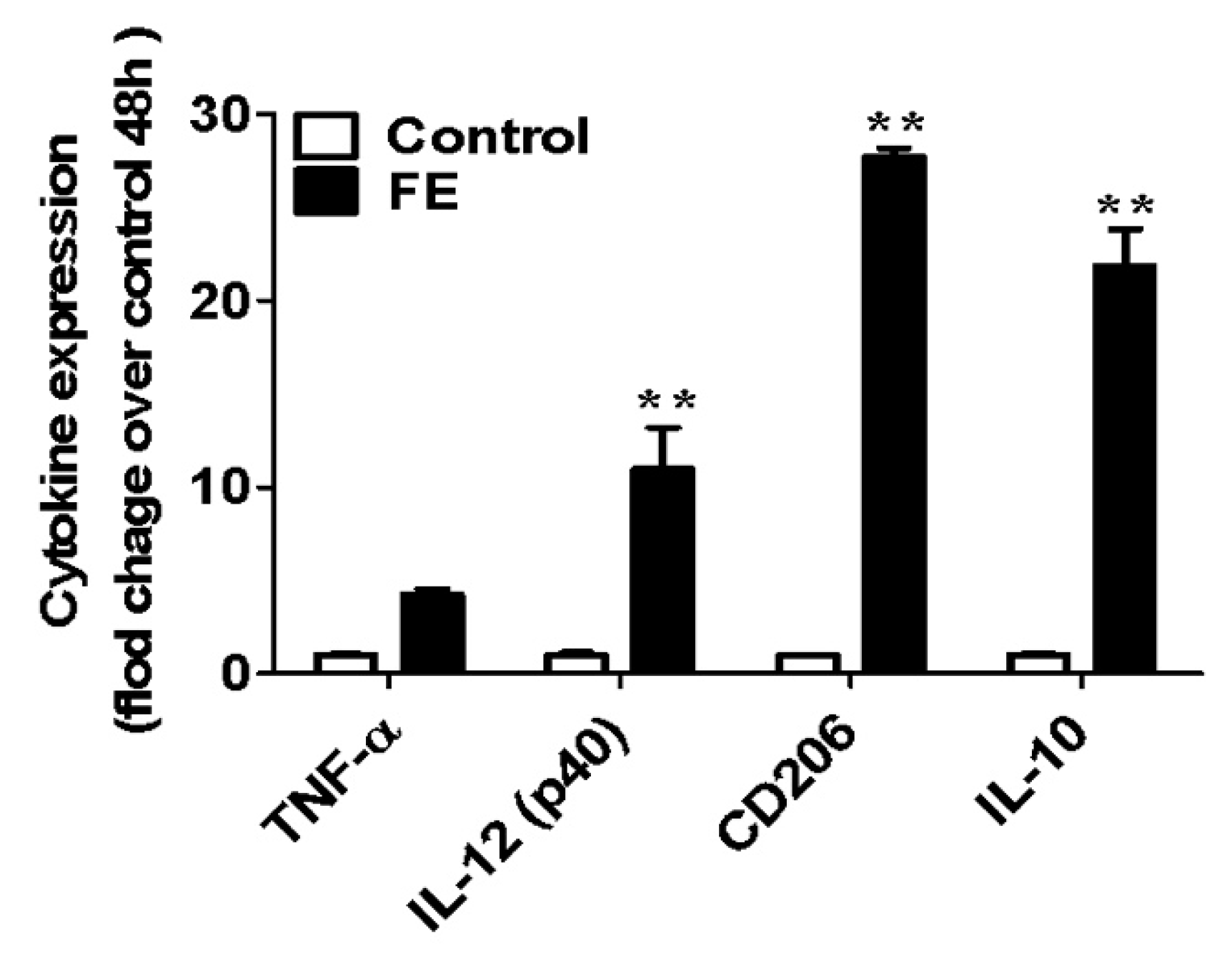
2.3. Expression of Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines
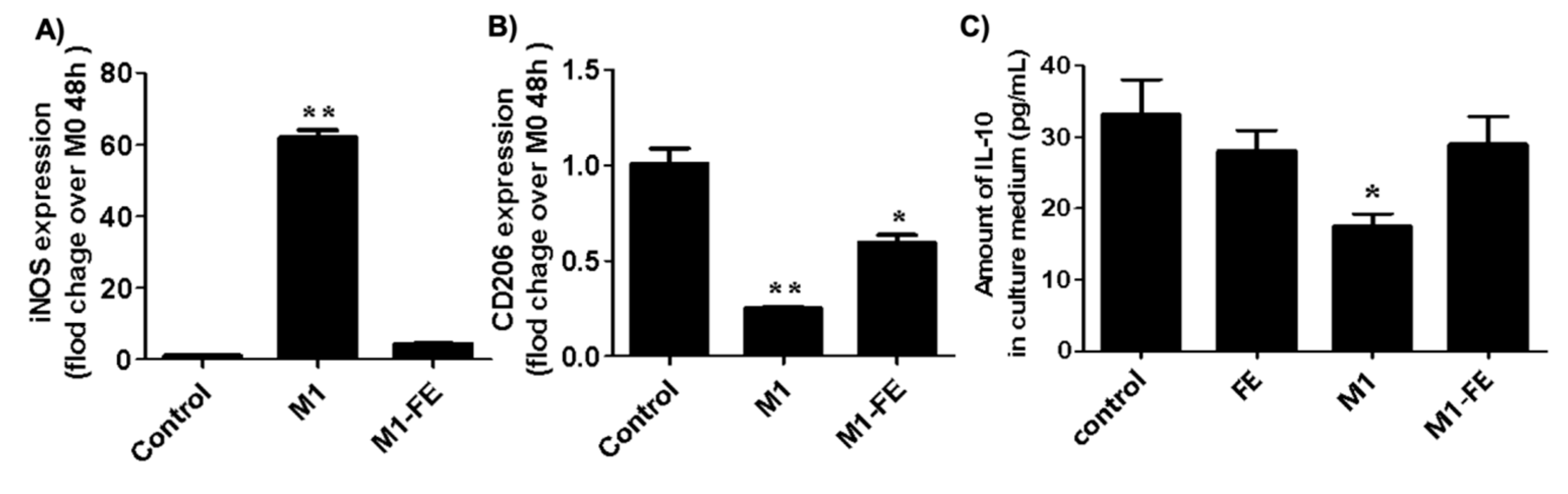
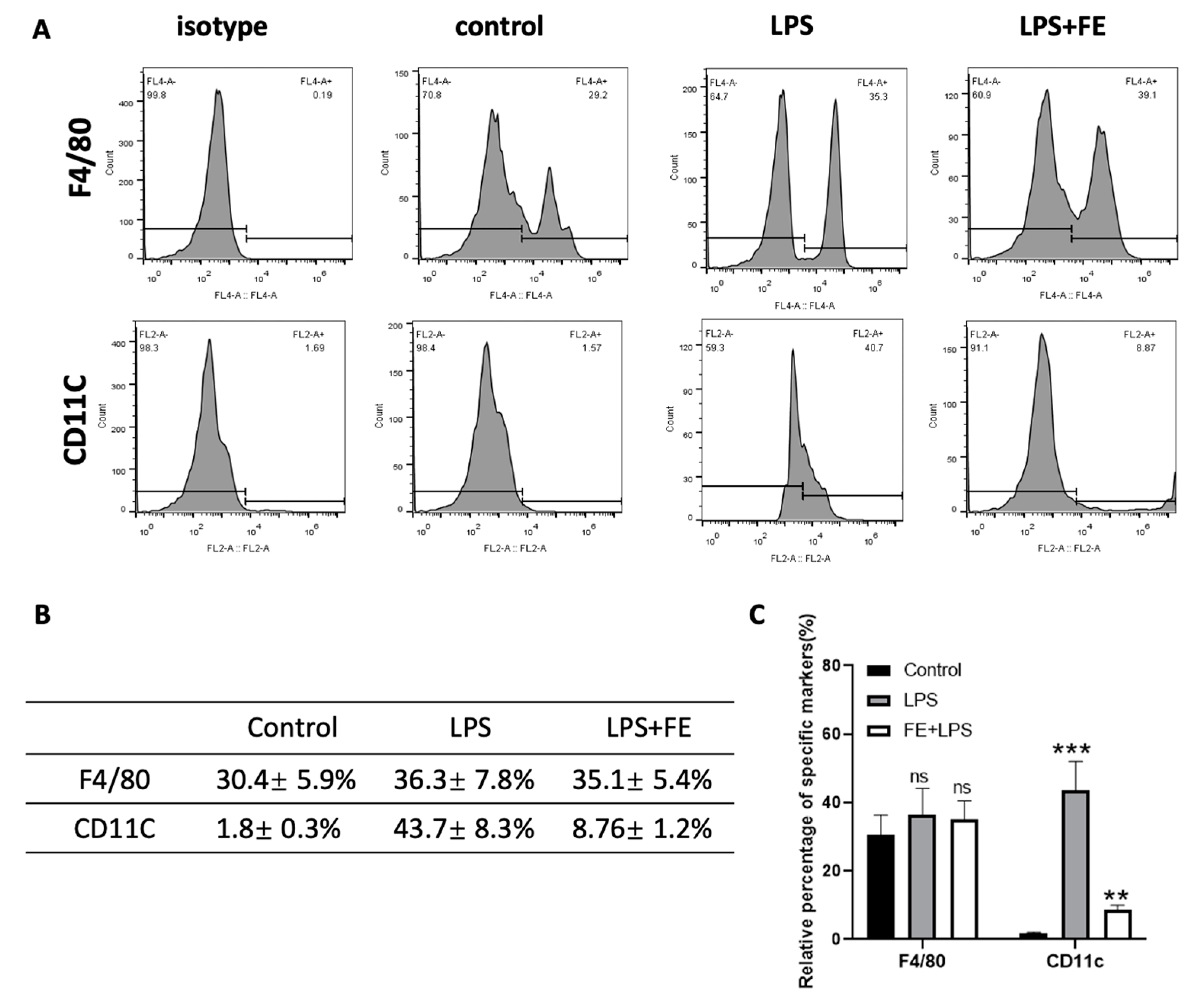
2.4. Reversed Inflammation in M1 Phenotype
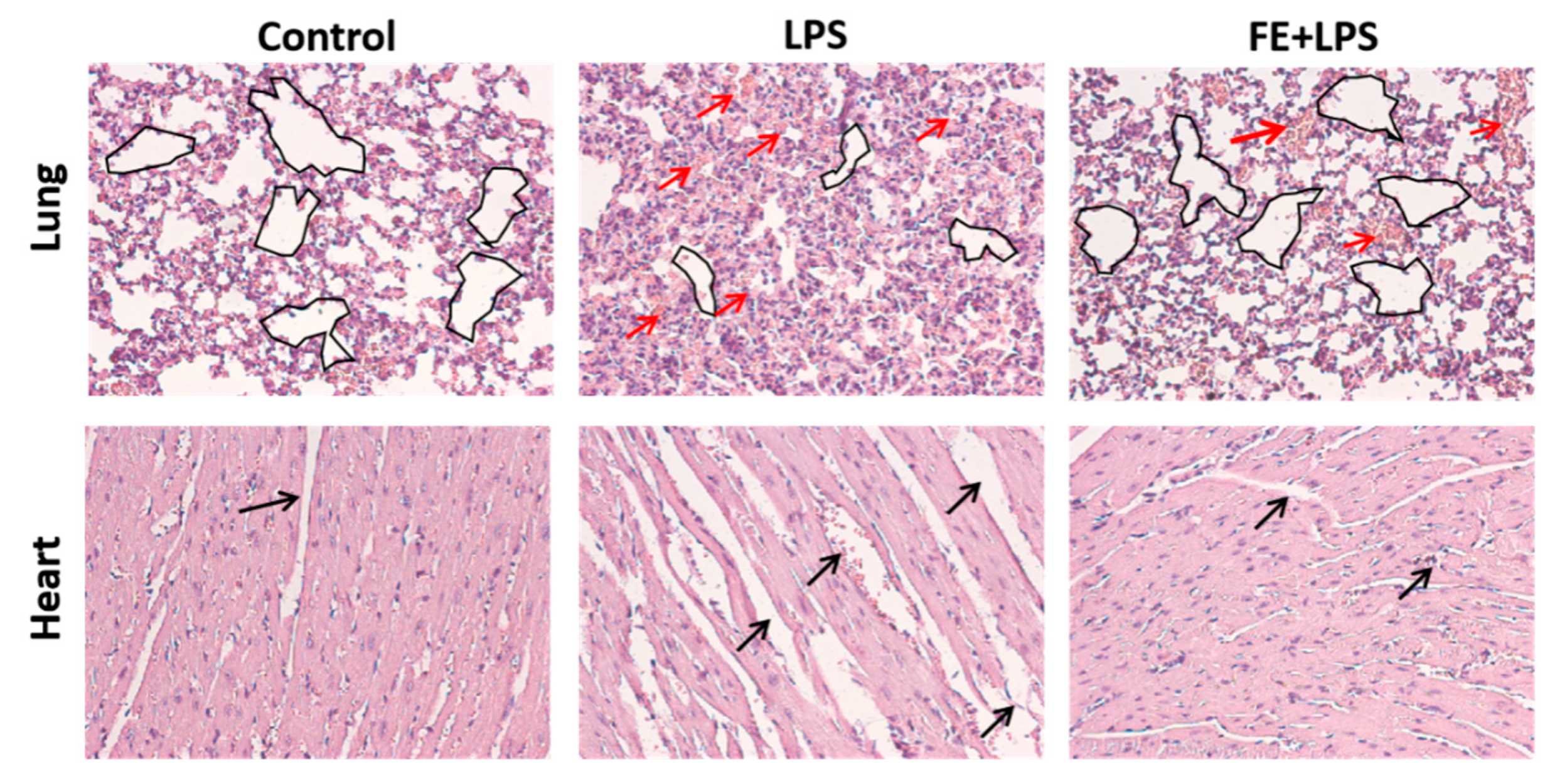
2.5. FE Anti-Inflammatory Response in a Mouse Model
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. FE Characterization
3.2.1. Molecular Weight
3.2.2. Sulfate Content
3.2.3. Monosaccharide Composition
3.2.4. Glycosidic Linkage and Substitution Analysis
3.3. Biological Assays
3.3.1. Assessment of Cytotoxic Effects of FE on the RAW264.7 Cell Line
3.3.2. Assessment of the Pro-/Anti-Inflammation Effects of FE on Mouse Bone-Marrow-Derived Macrophages
3.3.3. Assessment of Anti-Inflammatory Effects of FE on Mice
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Nah, J.-W.; Jeon, Y.-J. Potential anti-inflammatory natural products from marine algae. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, C.; Coimbra, M.A. The Potential of Fucose-Containing Sulfated Polysaccharides As Scaffolds for Biomedical Applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 6399–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, M.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A. Important Determinants for Fucoidan Bioactivity: A Critical Review of Structure-Function Relations and Extraction Methods for Fucose-Containing Sulfated Polysaccharides from Brown Seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2106–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.; Granja, S.; Neves, N.M.; Reis, R.L.; Baltazar, F.; Silva, T.H.; Martins, A. Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus inhibits new blood vessel formation and breast tumor growth in vivo. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.; Neves, N.M.; Reis, R.L.; Martins, A.; Silva, T.H. A review on fucoidan antitumor strategies: From a biological active agent to a structural component of fucoidan-based systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Hao, C.; Zhao, X.; Jiao, G.; Shan, X.; Tai, W.; Yu, G. Inhibition of Influenza A Virus Infection by Fucoidan Targeting Viral Neuraminidase and Cellular EGFR Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phull, A.R.; Kim, S.J. Fucoidan as bio-functional molecule: Insights into the anti-inflammatory potential and associated molecular mechanisms. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.L.; Lee, B.Y.; You, S.G. Relationship between oversulfation and conformation of low and high molecular weight fucoidans and evaluation of their in vitro anticancer activity. Molecules 2010, 16, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.; Ferreira, A.S.; Novoa-Carballal, R.; Nunes, C.; Pashkuleva, I.; Neves, N.M.; Coimbra, M.A.; Reis, R.L.; Martins, A.; Silva, T.H. The Key Role of Sulfation and Branching on Fucoidan Antitumor Activity. Macromol. Biosci. 2017, 17, 1600340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, M.; Cao, Q.; Ji, A.; Liang, H.; Song, S. Biological Activities of Fucoidan and the Factors Mediating Its Therapeutic Effects: A Review of Recent Studies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Kawaguchi, M.; Kitamura, K.; Narumiya, S.; Kawamura, M.; Tengan, I.; Nishimoto, S.; Hanamure, Y.; Majima, Y.; Tsubura, S.; et al. An Exploratory Study on the Anti-inflammatory Effects of Fucoidan in Relation to Quality of Life in Advanced Cancer Patients. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolova, E.; Lukova, P.; Baldzhieva, A.; Katsarov, P.; Nikolova, M.; Iliev, I.; Peychev, L.; Trica, B.; Oancea, F.; Delattre, C.; et al. Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fucoidan: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.-W.; Hwang, S.J.; Han, M.H.; Lee, D.-S.; Yoo, J.S.; Choi, I.-W.; Cha, H.-J.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, G.-Y.; et al. Fucoidan inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages and zebrafish larvae. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.L.; Mawad, D.; Dokos, S.; Koshy, P.; Martens, P.J.; Sorrell, C.C. Immunomodulatory properties of photopolymerizable fucoidan and carrageenans. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.Y.; Han, M.H.; Park, C.; Jin, C.-Y.; Kim, G.-Y.; Choi, I.-W.; Kim, N.D.; Nam, T.-J.; Kwon, T.K.; Choi, Y.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of fucoidan through inhibition of NF-κB, MAPK and Akt activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglia cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, M.J.; Chung, H.S. Anti-inflammatory activity of fucoidan with blocking NF-κB and STAT1 in human keratinocytes cells. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2015, 21, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Bahar, B.; O’Doherty, J.V.; Smyth, T.J.; Ahmed, A.M.; Sweeney, T. A cold water extract of Fucus vesiculosus inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced pro-inflammatory responses in the porcine colon ex-vivo model. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 37, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozharitskaya, O.; Obluchinskaya, E.; Shikov, A. Mechanisms of Bioactivities of Fucoidan from the Brown Seaweed Fucus vesiculosus L. of the Barents Sea. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.; Pozharitskaya, O.; Shikov, A. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Fucoidans from Five Species of Brown Seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.C.; Sousa, R.B.; Franco, Á.X.; Costa, J.V.; Neves, L.M.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Sutton, R.; Criddle, D.N.; Soares, P.M.; de Souza, M.H. Protective effects of fucoidan, a P- and L-selectin inhibitor, in murine acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 2014, 43, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumashi, A.; Ushakova, N.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.; D’Incecco, A.; Piccoli, A.; Totani, L.; Tinari, N.; Morozevich, G.; Berman, A.; Bilan, M.; et al. A comparative study of the anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant, antiangiogenic, and antiadhesive activities of nine different fucoidans from brown seaweeds. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lean, Q.Y.; Eri, R.; Fitton, J.; Patel, R.; Güven, N. Fucoidan Extracts Ameliorate Acute Colitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obluchinskaya, E.; Pozharitskaya, O.; Flisyuk, E.; Shikov, A. Formulation, Optimization and In Vivo Evaluation of Fucoidan-Based Cream with Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, N.; Stortz, C. A Comprehensive and Comparative Analysis of the Fucoidan Compositional Data Across the Phaeophyceae. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 556312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Jasso, R.M.; Mussatto, S.I.; Pastrana, L.; Aguilar, C.N.; Teixeira, J.A. Microwave-assisted extraction of sulfated polysaccharides (fucoidan) from brown seaweed. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obluchinskaya, E.; Pozharitskaya, O.; Zakharov, D.; Flisyuk, E.; Terninko, I.; Generalova, Y.; Smekhova, I.; Shikov, A. The Biochemical Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Fucus vesiculosus from the Arctic Region. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, A.; Tu, C.; Shen, S.; Xu, D.; Oursler, M.; Qu, J.; Yang, S. Comparative Characterization of Osteoclasts Derived From Murine Bone Marrow Macrophages and RAW 264.7 Cells Using Quantitative Proteomics. Jbmr Plus 2018, 2, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, Y.; Xing, Y.; Zhu, H.; Shen, J.; Tian, J. Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide from brown algae, against myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats via regulating the inflammation response. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 2090–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaillon, J.M. Pro- versus anti-inflammatory cytokines: Myth or reality. Cell. Mol. Biol. (Noisy-Le-Grand Fr.) 2001, 47, 695–702. [Google Scholar]
- Parameswaran, N.; Patial, S. Tumor necrosis factor-α signaling in macrophages. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2010, 20, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, K.; Guzzo, C.; Che Mat, N.F.; Ma, W.; Kumar, A. The IL-12 family of cytokines in infection, inflammation and autoimmune disorders. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2009, 8, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, E.H.; Wang, X.; Balaji, S.; Butte, M.J.; Bollyky, P.L.; Keswani, S.G. The Role of the Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Interleukin-10 in Tissue Fibrosis. Adv. Wound Care 2020, 9, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Yasui, H.; Karayama, M.; Hozumi, H.; Furuhashi, K.; Enomoto, N.; Fujisawa, T.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Macrophage Mannose Receptor CD206 Predicts Prognosis in Community-acquired Pneumonia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, M.C.; Hvidbjerg Gantzel, R.; Clària, J.; Trebicka, J.; Møller, H.J.; Grønbæk, H. Macrophage Activation Markers, CD163 and CD206, in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Cells 2020, 9, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Ko, C.-I.; Ahn, G.; You, S.; Kim, J.-S.; Heu, M.S.; Kim, J.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.-J. Molecular characteristics and anti-inflammatory activity of the fucoidan extracted from Ecklonia cava. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskin, D.L.; Pendino, K.J. Macrophages and inflammatory mediators in tissue injury. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1995, 35, 655–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suschek, C.V.; Schnorr, O.; Kolb-Bachofen, V. The role of iNOS in chronic inflammatory processes in vivo: Is it damage-promoting, protective, or active at all? Curr. Mol. Med. 2004, 4, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.J.; Zhang, T.; Luo, D.Z.; Jia, Y.J.; Guo, Z.X.; Zhang, Q.B.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.M. Inhibitory effect of fucoidan on nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-activated primary microglia. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 37, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.; Wang, L.; Fu, X.; Duan, D.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Xu, J.; Gao, X. In vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory activities of a fucose-rich fucoidan isolated from Saccharina japonica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Phan, N.N.; Lu, W.J.; Ngoc Hieu, B.T.; Lin, Y.C. Low-molecular-weight fucoidan and high-stability fucoxanthin from brown seaweed exert prebiotics and anti-inflammatory activities in Caco-2 cells. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 32033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Anjos Cassado, A. F4/80 as a Major Macrophage Marker: The Case of the Peritoneum and Spleen. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2017, 62, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.H.; Faunce, D.E.; Stacey, M.; Terajewicz, A.; Nakamura, T.; Zhang-Hoover, J.; Kerley, M.; Mucenski, M.L.; Gordon, S.; Stein-Streilein, J. The macrophage F4/80 receptor is required for the induction of antigen-specific efferent regulatory T cells in peripheral tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, I.C.; Mathisen, S.; Schulthess, J.; Danne, C.; Hegazy, A.N.; Powrie, F. CD11c+ monocyte/macrophages promote chronic Helicobacter hepaticus-induced intestinal inflammation through the production of IL-23. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, A.; El-Aasr, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Ulber, R. Fucoidan Characterization: Determination of Purity and Physicochemical and Chemical Properties. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, M.; Feitosa, J.; Freitas, A.; de Paula, R. Isolation and characterization of soluble sulfated polysaccharide from the red seaweed Gracilaria cornea. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 49, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandeirada, C.O.; Maricato, É.; Ferreira, S.S.; Correia, V.G.; Pinheiro, B.A.; Evtuguin, D.V.; Palma, A.S.; Correia, A.; Vilanova, M.; Coimbra, M.A.; et al. Structural analysis and potential immunostimulatory activity of Nannochloropsis oculata polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 114962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Monosaccharides (mol%) | Total Sugars (%, w/w) | Sulfate (%, w/w) | Mw (kDa) | Mw/Mn | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fucose | Xylose | Galactose | Uronic Acids | |||||
| FE | 90.4 ± 2.0 | 2.4 ± 0.7 | 3.3 ± 0.7 | 3.8 ± 0.7 | 66.1 ± 2.6 | 9.9 ± 2.9 | 70 | 1.5 |
| Substitution | Native FE | Desulfated FE |
|---|---|---|
| t-Fuc | 7.2 ± 0.3 | 10.8 ± 1.1 |
| 2-Fuc | 6.7 ± 0.6 | 9.4 ± 0.3 |
| 3-Fuc | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 3.8 ± 0.2 |
| 4-Fuc | 3.4 ± 0.1 | 6.5 ± 1.0 |
| 2,3-Fuc | 4.8 ± 0.4 | 5.6 ± 0.7 |
| 2,4-Fuc | 9.9 ± 0.4 | 7.1 ± 0.5 |
| 3,4-Fuc | 11.6 ± 0.7 | 16.8 ± 0.8 |
| 2,3,4-Fuc | 49.9 ± 1.1 | 32.7 ± 2.6 |
| Total Fuc | 93.9 ± 1.2 | 92.7 ± 1.1 |
| t-Xyl | 4.0 ± 0.8 | 4.4 ± 0.5 |
| 2-Xyl | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.2 |
| Total Xyl | 5.5 ± 0.9 | 6.5 ± 0.7 |
| t-Gal | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.4 |
| Total Gal | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.4 |
| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | ACGGCATGGATCTCAAAGAC | AGATAGCAAATCGGCTGACG |
| IL-12 p40 | AGCAGTAGCAGTTCCCCTGA | AGTCCC TTTGGTCCAGTGTG |
| IL-10 | GCTCTTACTGACTGGCATGAG | CGCAGCTCTAGGAGCATGTG |
| CD206 | GCAGGTGGTTTATGGGATGT | GGGTTCAGGAGTGTTGTGG |
| iNOS | CCAAGCCCTCACCTACTTCC | CTCTGAGGGCTGACACAAGG |
| GADPH | AACGACCCCTTCATTGAC | TCCACGACATACTCAGCAC-3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Oliveira, C.; Li, Q.; Ferreira, A.S.; Nunes, C.; Coimbra, M.A.; Reis, R.L.; Martins, A.; Wang, C.; Silva, T.H.; et al. Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits Inflammatory Response, Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050302
Wang L, Oliveira C, Li Q, Ferreira AS, Nunes C, Coimbra MA, Reis RL, Martins A, Wang C, Silva TH, et al. Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits Inflammatory Response, Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(5):302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050302
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lingzhi, Catarina Oliveira, Qiu Li, Andreia S. Ferreira, Cláudia Nunes, Manuel A. Coimbra, Rui L. Reis, Albino Martins, Chunming Wang, Tiago H. Silva, and et al. 2023. "Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits Inflammatory Response, Both In Vitro and In Vivo" Marine Drugs 21, no. 5: 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050302
APA StyleWang, L., Oliveira, C., Li, Q., Ferreira, A. S., Nunes, C., Coimbra, M. A., Reis, R. L., Martins, A., Wang, C., Silva, T. H., & Feng, Y. (2023). Fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus Inhibits Inflammatory Response, Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Marine Drugs, 21(5), 302. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21050302












