The Blockade of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 14 Activation by Marine Natural Product Crassolide Triggers ICD in Tumor Cells and Stimulates Anti-Tumor Immunity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Crassolide Stimulated the Cytotoxicity against Human Breast Cancer Cells and Murine Mammary Carcinoma Cells
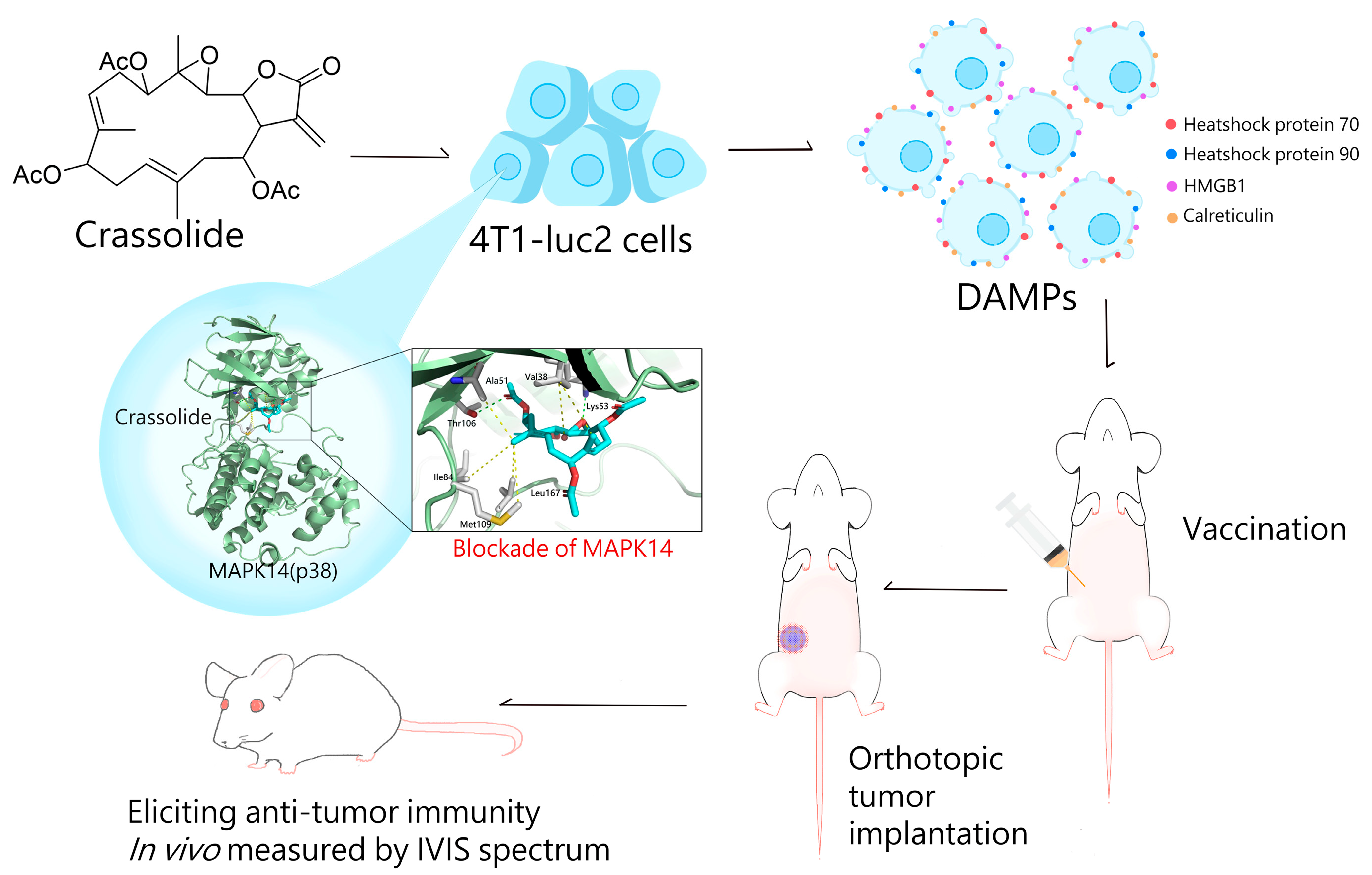
2.2. Crassolide Significantly Increases the Expression of DAMPs on the Surface of 4T1-luc2 Murine Mammary Carcinoma Cells
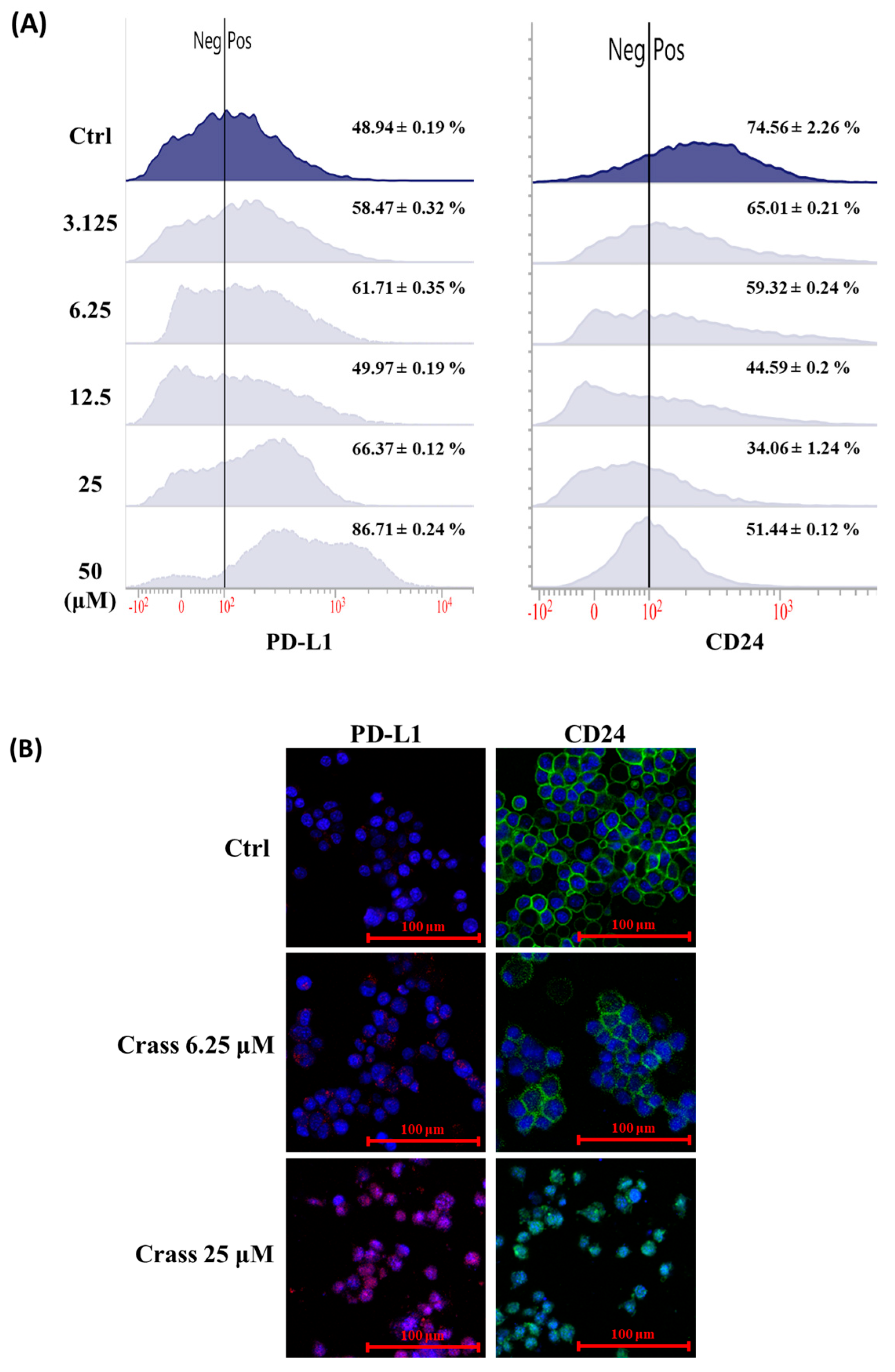
2.3. Crassolide Enhances Expression of Immune Checkpoint Molecule PD-L1 but Inhibits the Expression of Heat-Stable Antigen/CD24 on the Surface of 4T1-luc2
2.4. Crassolide Significantly Induces the Translocation of DAMPs to the Surface of 4T1-luc2 Cells
2.5. Crassolide-Treated 4T1-luc2 Cells Effectively Immunized Mice against Primary Tumors
2.6. Crassolide Inhibited MAPK14 Kinase Activity
2.7. Crassolide Up-Regulated Phosphorylation of MAPK14 and Its Downstream Targets in 4T1-luc2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Origin of Crassolide
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. Mice
4.4. Animal Model
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Immunofluorescence
4.7. Detection of DAMPs Ectolocalization
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Molecular Modeling of Crassolide and MAPK14 Interaction
4.10. Z′-LYTE Kinase Assay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, M.; Morgan, E.; Rumgay, H.; Mafra, A.; Singh, D.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Gralow, J.R.; Cardoso, F.; Siesling, S.; et al. Current and future burden of breast cancer: Global statistics for 2020 and 2040. Breast 2022, 66, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwald, R.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. The B7 family revisited. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 515–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Agata, Y.; Shibahara, K.; Honjo, T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, A.H.; Pauken, K.E. The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, C.A. CD24—A novel ‘don’t eat me’ signal. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takimoto, C.H.; Chao, M.P.; Gibbs, C.; McCamish, M.A.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.Y.; Majeti, R.; Weissman, I.L. The Macrophage ‘Do not eat me’ signal, CD47, is a clinically validated cancer immunotherapy target. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucikova, J.; Kepp, O.; Kasikova, L.; Petroni, G.; Yamazaki, T.; Liu, P.; Zhao, L.; Spisek, R.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Detection of immunogenic cell death and its relevance for cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Hua, Y.; Cai, Z. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy: Present and emerging inducers. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4854–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, C. Marine Natural Products in Medicinal Chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercolano, G.; De Cicco, P.; Ianaro, A. New Drugs from the Sea: Pro-Apoptotic Activity of Sponges and Algae Derived Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.T.; Wang, S.K.; Soong, K.; Duh, C.Y. New cytotoxic cembranolides from the soft coral Lobophytum michaelae. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, K.M.; Wang, J.H.; Lin, S.C.; Wen, Y.; Wu, C.L.; Su, J.H.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, C.C. Crassolide Induces G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, and Autophagy in Human Lung Cancer Cells via ROS-Mediated ER Stress Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmanic, A.; Sutto, L.; Saladino, G.; Nebreda, A.R.; Gervasio, F.L.; Orozco, M. Changes in the free-energy landscape of p38alpha MAP kinase through its canonical activation and binding events as studied by enhanced molecular dynamics simulations. Elife 2017, 6, e22175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, K.P.; Wolfson, B.; Hodge, J.W. From Immunogenic Cell Death to Immunogenic Modulation: Select Chemotherapy Regimens Induce a Spectrum of Immune-Enhancing Activities in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 728018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Bai, X.; Wu, X.; Guo, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Combination of phototherapy with immune checkpoint blockade: Theory and practice in cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 955920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.A.; Lin, J.K.; Lin, S.Y. Mechanisms of immunogenic cell death and immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.A.; Minn, A.J. Combination Cancer Therapy with Immune Checkpoint Blockade: Mechanisms and Strategies. Immunity 2018, 48, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Cubillos-Ruiz, J.R. Endoplasmic reticulum stress signals in the tumour and its microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.D.; Maes, H.; van Vliet, A.R.; Agostinis, P. Targeting the hallmarks of cancer with therapy-induced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Mol. Cell Oncol. 2015, 2, e975089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.D.; Dudek-Peric, A.M.; Romano, E.; Agostinis, P. Immunogenic cell death. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2015, 59, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, H.T. MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res. 2002, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnello, M.; Roux, P.P. Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 50–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, N.J.; Cook, S.J. The role of MAPK signalling pathways in the response to endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2150–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Chang, Y.K.; Lin, S.C.; Su, J.H.; Chao, Y.H.; Tang, K.T. Crassolide Suppresses Dendritic Cell Maturation and Attenuates Experimental Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Molecules 2021, 26, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
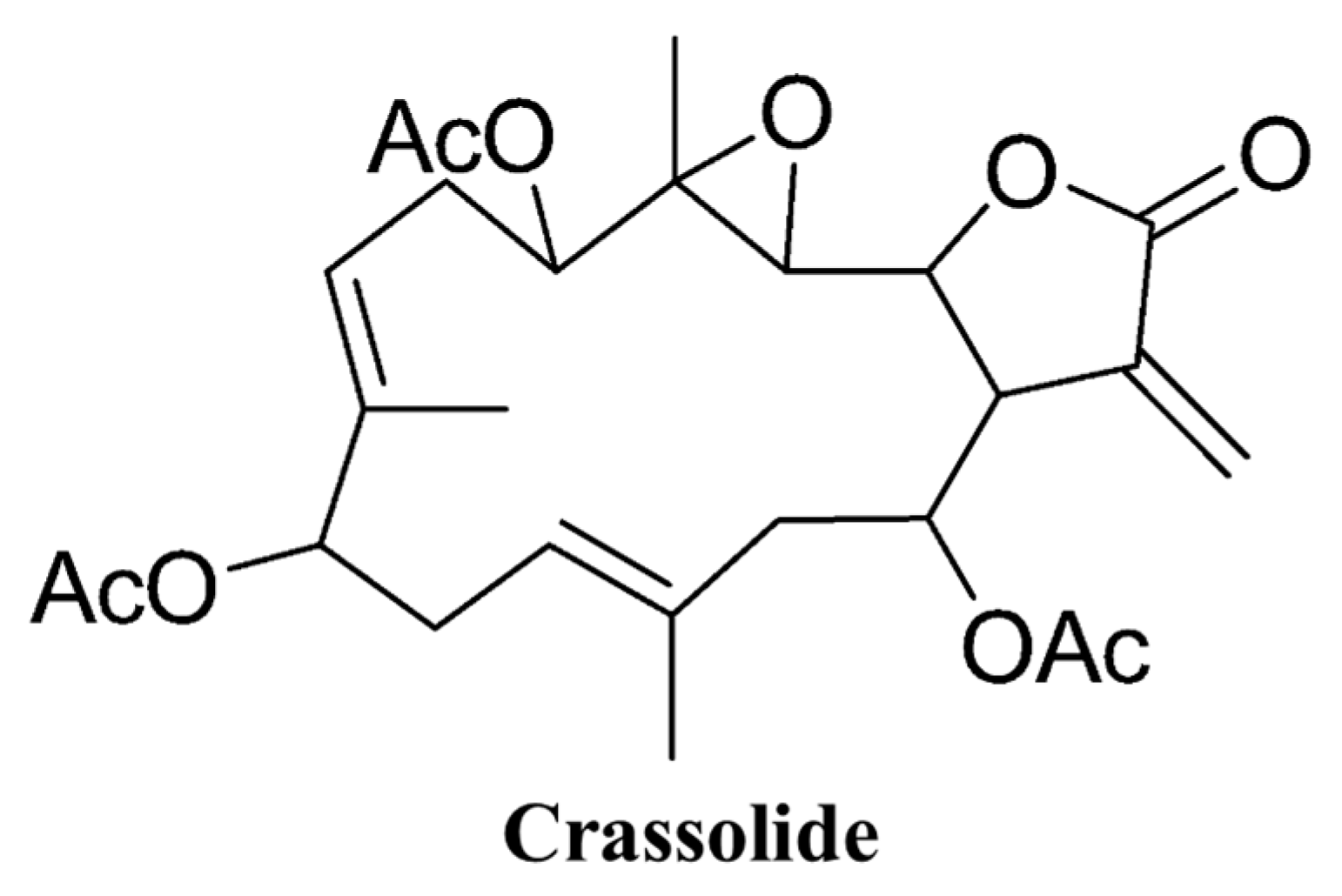






| Cell Line | IC50 |
|---|---|
| 4T1-luc2 | 24.60 |
| TS/A | 3.74 |
| MCF7 | 9.35 |
| MDA-MB-231 | 6.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, K.-C.; Chen, C.-S.; Su, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-C.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Wei, W.-C. The Blockade of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 14 Activation by Marine Natural Product Crassolide Triggers ICD in Tumor Cells and Stimulates Anti-Tumor Immunity. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21040225
Tsai K-C, Chen C-S, Su J-H, Lee Y-C, Tseng Y-H, Wei W-C. The Blockade of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 14 Activation by Marine Natural Product Crassolide Triggers ICD in Tumor Cells and Stimulates Anti-Tumor Immunity. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(4):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21040225
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Keng-Chang, Chia-Sheng Chen, Jui-Hsin Su, Yu-Ching Lee, Yu-Hwei Tseng, and Wen-Chi Wei. 2023. "The Blockade of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 14 Activation by Marine Natural Product Crassolide Triggers ICD in Tumor Cells and Stimulates Anti-Tumor Immunity" Marine Drugs 21, no. 4: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21040225
APA StyleTsai, K.-C., Chen, C.-S., Su, J.-H., Lee, Y.-C., Tseng, Y.-H., & Wei, W.-C. (2023). The Blockade of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase 14 Activation by Marine Natural Product Crassolide Triggers ICD in Tumor Cells and Stimulates Anti-Tumor Immunity. Marine Drugs, 21(4), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21040225







