Abstract
The JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway is aberrantly hyperactivated in many cancers, promoting cell proliferation, survival, invasiveness, and metastasis. Thus, inhibitors targeting JAK/STAT3 have enormous potential for cancer treatment. Herein, we modified aldisine derivatives by introducing the isothiouronium group, which can improve the antitumor activity of the compounds. We performed a high-throughput screen of 3157 compounds and identified compounds 11a, 11b, and 11c, which contain a pyrrole [2,3-c] azepine structure linked to an isothiouronium group through different lengths of carbon alkyl chains and significantly inhibited JAK/STAT3 activities. Further results showed that compound 11c exhibited the optimal antiproliferative activity and was a pan-JAKs inhibitor capable of inhibiting constitutive and IL-6-induced STAT3 activation. In addition, compound 11c influenced STAT3 downstream gene expression (Bcl-xl, C-Myc, and Cyclin D1) and induced the apoptosis of A549 and DU145 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The antitumor effects of 11c were further demonstrated in an in vivo subcutaneous tumor xenograft experiment with DU145 cells. Taken together, we designed and synthesized a novel small molecule JAKs inhibitor targeting the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway, which has predicted therapeutic potential for JAK/STAT3 overactivated cancer treatment.
1. Introduction
Cancer presenting as an incurable advanced or metastatic disease is common, and the development of new targeted antitumor drugs is of great significance to human health [1]. The Janus kinase (JAK) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway is aberrantly hyperactivated in many types of cancer, and such hyperactivation is generally associated with a poor clinical prognosis [2,3]. It plays a central role in immune response, cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival [4,5]. In the tumor microenvironment, numerous cytokines, such as IL-6 and IFNα/β, can activate JAKs by phosphorylating tyrosine residues, which in turn phosphorylate and activate STAT3 to regulate the transcription of downstream target genes [6,7]. Examples of these genes include those which drive cell proliferation (cyclin D1), promote tumor survival BCL2-like protein 1 (BCL-xL), and regulate immune response (IFN-γ) [2,8]. There are 11 JAK inhibitors approved for the treatment of various diseases that exert inhibitory effects through competitive and non-competitive reactions with the amino acid residues in JAKs [9]. An example of a JAK inhibitor used in treatment is ruxolitinib, which has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of myelofibrosis and polycythemia vera [10]. In addition, dozens of potential JAK inhibitors are under clinical trials to further evaluate their antitumor activity; for example, DZD4205 in the treatment of T-cell lymphoma [11]. Therefore, the JAK/STAT pathway is a potential therapeutic target with great value for cancer treatment; among these, small molecules to inhibit JAK activity have attracted much attention.
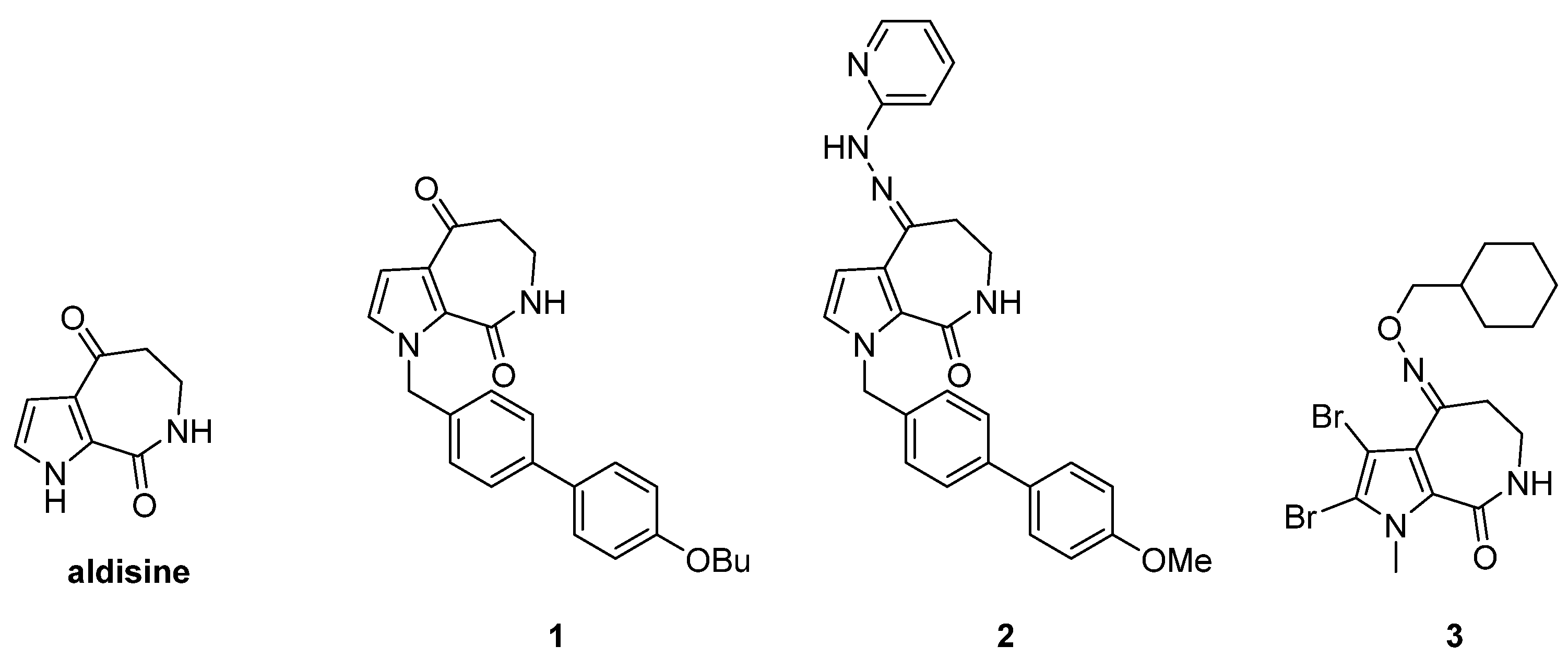
Marine sponges are an important source of potential natural bioactive ingredients that have formed natural secondary metabolites with complex and unique structures to adapt to the harsh marine survival conditions [12,13]. Aldisine (Figure 1) and its derivatives are the secondary metabolites from sponges with unique pyrrolo [2,3-c] azepine skeleton structural features that exhibit antitumor activity by inhibiting protein kinase [14,15]. It was reported that the oximes, oxime ethers, and hydrazones groups in aldisine can provide numerous hydrogen bond donor and acceptor moieties, which showed antiviral, larvicidal, and anti-phytopathogenic-fungus activities [16]. Modified aldisine at N-1 and C-4 positions obtained compounds 1 to 3 (Figure 1), which could enhance its antiproliferative activity [17,18,19,20]. The extensive antiproliferative properties of aldisine have made it a significant drug for cancer therapy. Due to its promising biological activities and multi-site modification, aldisine has become a focus of pharmaceutical chemistry as a lead compound, especially in antitumor aspects.
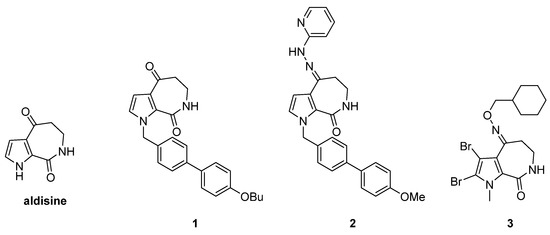
Figure 1.
The structures of aldisine and its derivatives.
These previous results guide us to put our efforts into designing and modifying aldisine. Isothiouronium is a positively charged group that induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and promotes cell apoptosis [21,22]. Previous studies have shown that isothiouronium-modified analogs may be promising anticancer agents, novel Golgi staining reagents, and useful research tools for studying Golgi functions in normal or cancer cells [23]. Therefore, compounds 10a, 10b, 10c, 11a, 11b, and 11c were obtained by introducing the isothiouronium groups to aldisine at the N-1 and N-7 positions with different lengths of carbon alkyl chains. The carbon alkyl chains increase their flexibility and liposolubility, and the introduction of isothiouronium makes it easier to enter cells to enhance antitumor activity.
Therefore, we first tested the antitumor activities of aldisine and its derivatives and found that compounds 11a, 11b, and 11c significantly reduced cell viability in the treatment of cancer cells. In parallel, we screened tens of thousands of collected compounds in a STAT3 binding promoter driving luciferase reporter system according to the method reported in references [20,21], in which compounds 11a, 11b, and 11c showed remarkable STAT3 inhibitory activity, with compound 11c showing the optimal activity. Further experiments focused on compound 11c revealed its inhibitory efficacy against JAKs. In addition, inhibition of JAK/STAT3 signaling by compound 11c induced substantial tumor cell apoptosis and influenced cell proliferation. Notably, compound 11c significantly reduced tumor growth by induced apoptosis in a mouse subcutaneous tumor implantation model in vivo, suggesting a potential for compound 11c to be further developed as a JAK/STAT3 signaling inhibitor for the treatment of cancer.
2. Results
2.1. Chemistry
Design and Synthesis of Aldisine Derivatives
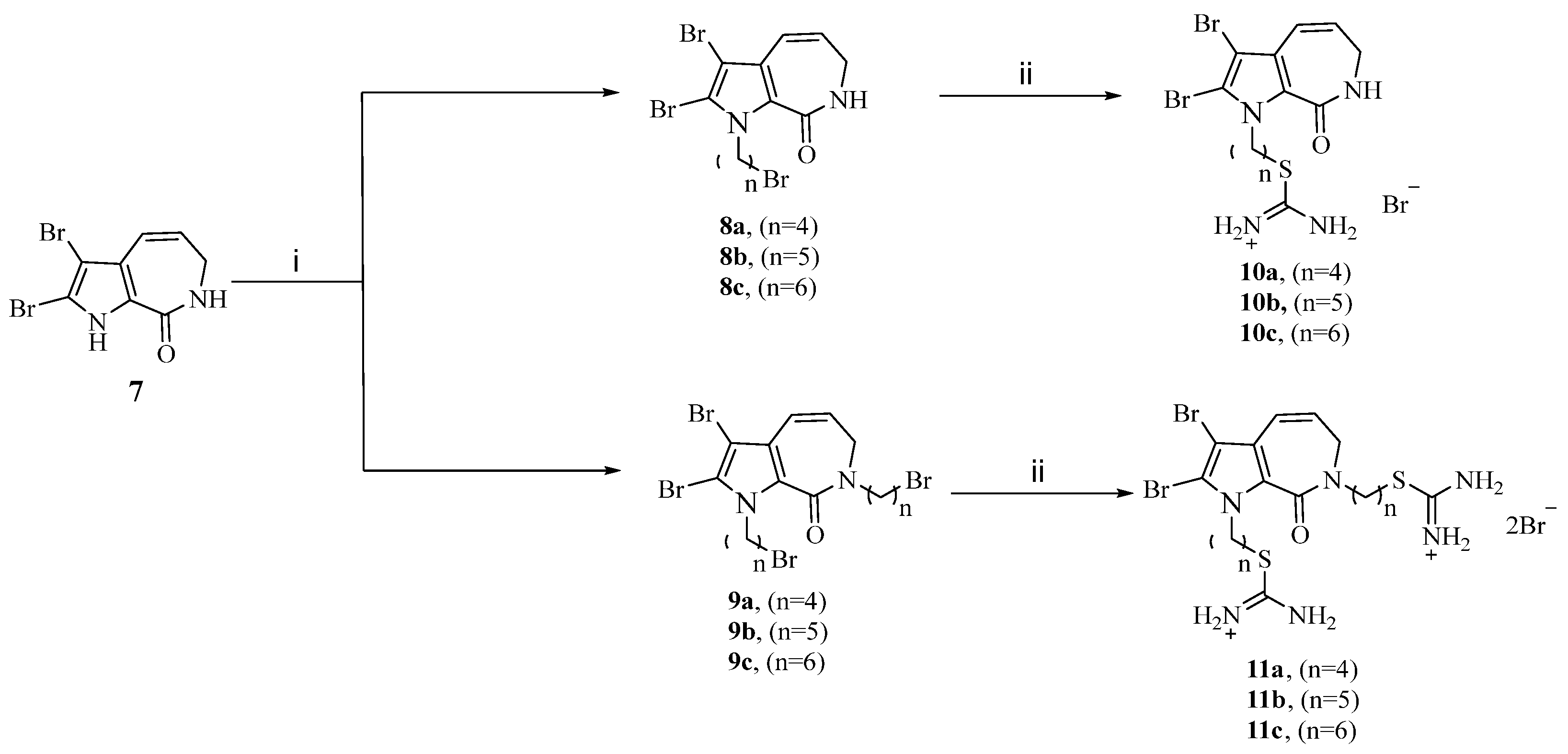
Considering the rotatability of different lengths of carboxyalkyl chains (n = 4,5,6) and the positive charge of the isothiouronium group, which can easily approach the cell membrane, we first designed and synthesized isothiouronium-modified aldisine derivatives at N1 positions in two steps as outlined in Scheme 1. Compound 7 was prepared from the 2-(trichloroacetyl) pyrrole according to the synthesis procedure of marine natural products Stevensine [24]. Subsequently, compound 7 reacts with excessive dibromoalkanes (n = 4,5,6) in DMSO for 1.5 h under the basic condition of KOH to obtain bromoalkyl derivatives 8a, 8b, 8c, 9a, 9b, and 9c, which were separated by silica gel chromatography with a 39~56% yield. Then 8a, 8b, 8c, 9a, 9b, and 9c were reacted with thiourea reflux for 12 h in ethanol to produce the target compounds 10a, 10b, 10c, 11a, 11b, and 11c with a yield of 57~67%.
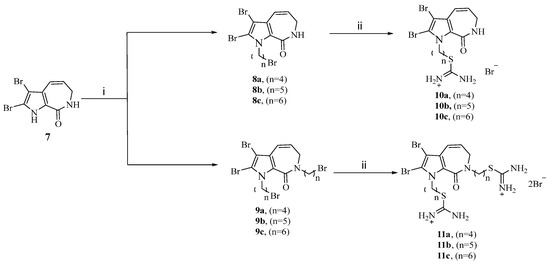
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of the isothiouronium-modified aldisine derivatives. Reagents and conditions: (ⅰ) Br-(CH2)n-Br, KOH, DMSO, 25 °C, 1.5 h, 39–56%; (ⅱ) Thiourea, EtOH, 80 °C, 12 h, 57–67%.
The general synthesized procedures for compounds 8a, 8b, 8c, 9a, 9b, 9c and 10a, 10b, 10c, 11a, 11b, 11c are in the Supplementary Materials.
2.2. Biological Activity Assessment of Compound 11c
2.2.1. Compound 11c Exhibited Antiproliferative Activity and was Identified as a JAK-STAT3 Signaling Inhibitor
After a series of aldisine derivatives were synthesized with similar structures and chemical properties, as shown in the chemistry section, we conducted high-throughput screening on them and found that the compound 11c, containing two six-carbon chain lengths of alkyl isothiourea groups at the N1 and N7 positions significantly inhibit JAK/STAT3 activity. Whereas compounds 10a, 10b, and 10c, containing only one different length of alkyl isothiourea at the N1 position, demonstrated lower inhibition of JAK/STAT 3 activity than 11c (Table S1; Figure S1).
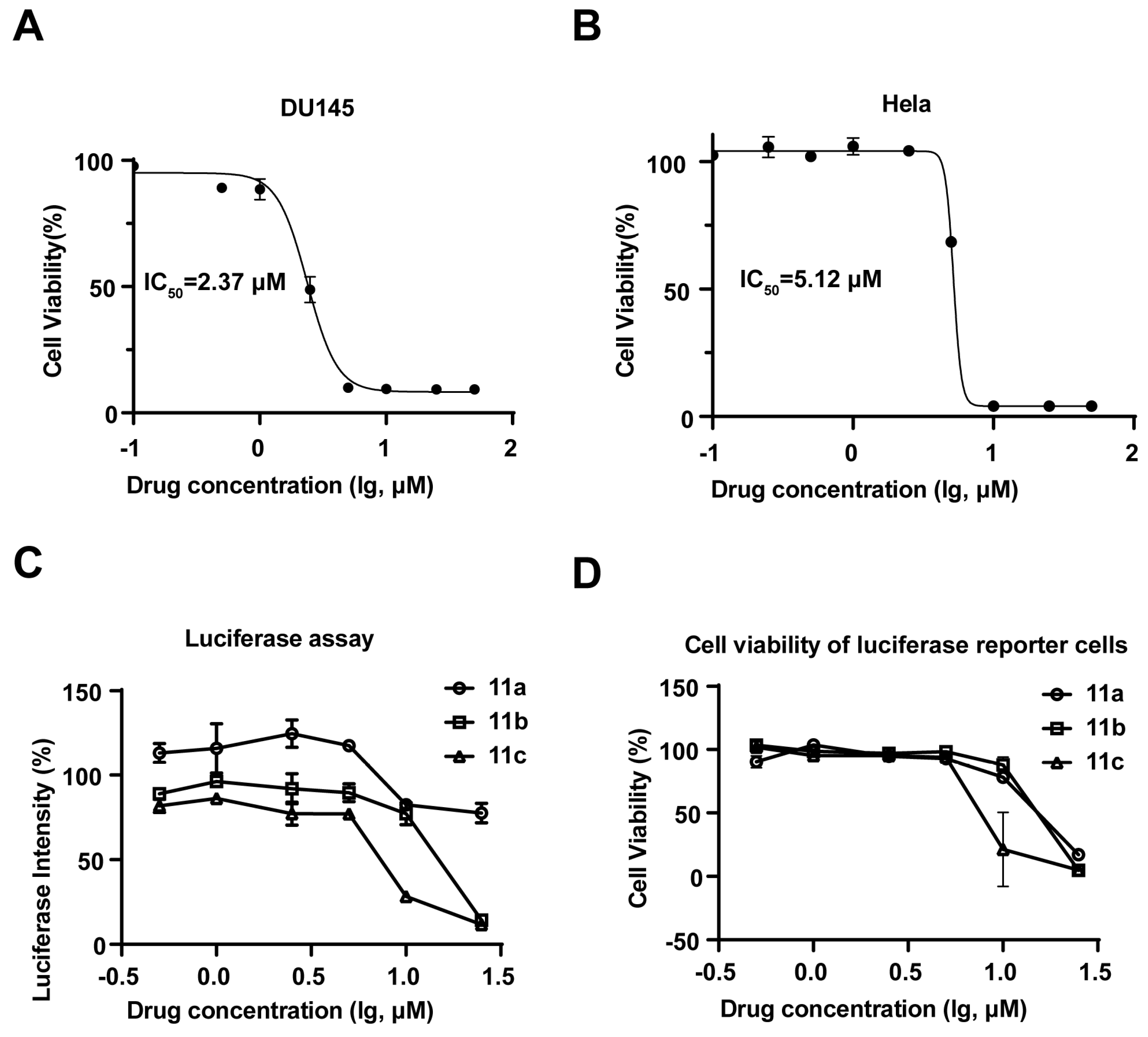
Next, for further understanding of the structure-activity relationship between aldisine derivatives, the inhibitory activities of 11a, 11b, and 11c were tested. The results showed that compounds 11a, 11b, and 11c exhibited significant antiproliferative activity against four human cancer cell lines: prostate cancer (DU145), non-small cell lung cancer (A549), breast cancer (MDA-MB-231), and cervical cancer (HeLa) (Table 1), with 11c being the most potent. Compound 11c inhibited the growth of DU145 cells with an IC50 value of 2.37 μM (Figure 2A) and HeLa cells with an IC50 value of 5.12 μM (Figure 2B). STAT3 can be activated in cancer cells in a constitutive or IL-6-induced manner [25,26]. In both DU145 and A549 cells, STAT3 is constitutively activated, whereas in Hela and MDA-MB231 cells, IL-6 can induce significant STAT3 activation [27,28,29]. Therefore, we next evaluated whether aldisine derivatives can inhibit STAT3 signaling. A STAT3 transcriptional activity-based high-throughput luciferase reporter was applied [23]. Interestingly, STAT3 luciferase inhibitory activities as well as the antiproliferative effects were indeed observed for 11a, 11b, and 11c (Figure S1; Figure 2C,D). The IC50 value of 11a, 11b, and 11c was generally lower and exhibited greater inhibitory activity as the length of alkyl carbon groups increased. Compound 11c with two six-carbon chain lengths showed the highest activity, which inhibited cancer cell growth in a dose-dependent manner and could be a potential JAK/STAT3 pathway inhibitor at a relatively low concentration.

Table 1.
Antiproliferative activity of aldisine derivatives against human cancer cell lines.
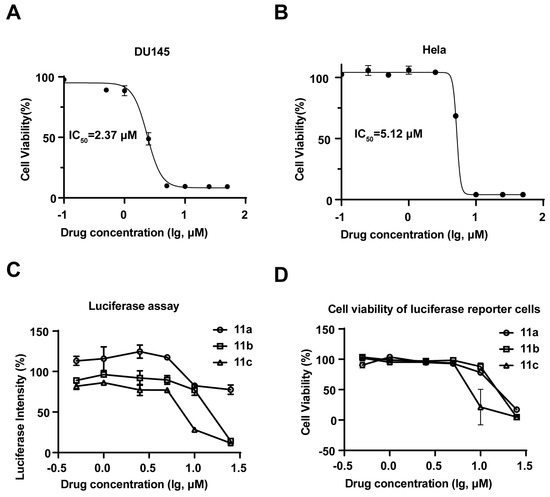
Figure 2.
Compound 11c was indicated as a JAK/STAT3 pathway inhibitor and exhibited antiproliferative activity. (A,B) Cell viability assay was determined by resazurin on DU145 (A) and Hela (B) cells after being treated with 11c for 72 h at the indicated concentrations (n = 3). (C) SKA cells (8000 cells/well) were seeded in 96-well plates and cultured overnight. Cells were then treated with 11a, 11b, and 11c at the indicated concentrations for 24 h before the STAT3-driven luciferase activity was measured. (D) Cell viability assay was determined by resazurin on SKA cells after being treated with 11c for 72 h at the indicated concentrations (n = 3).
2.2.2. 11c Inhibits Constitutive and IL-6-induced STAT3 Activation
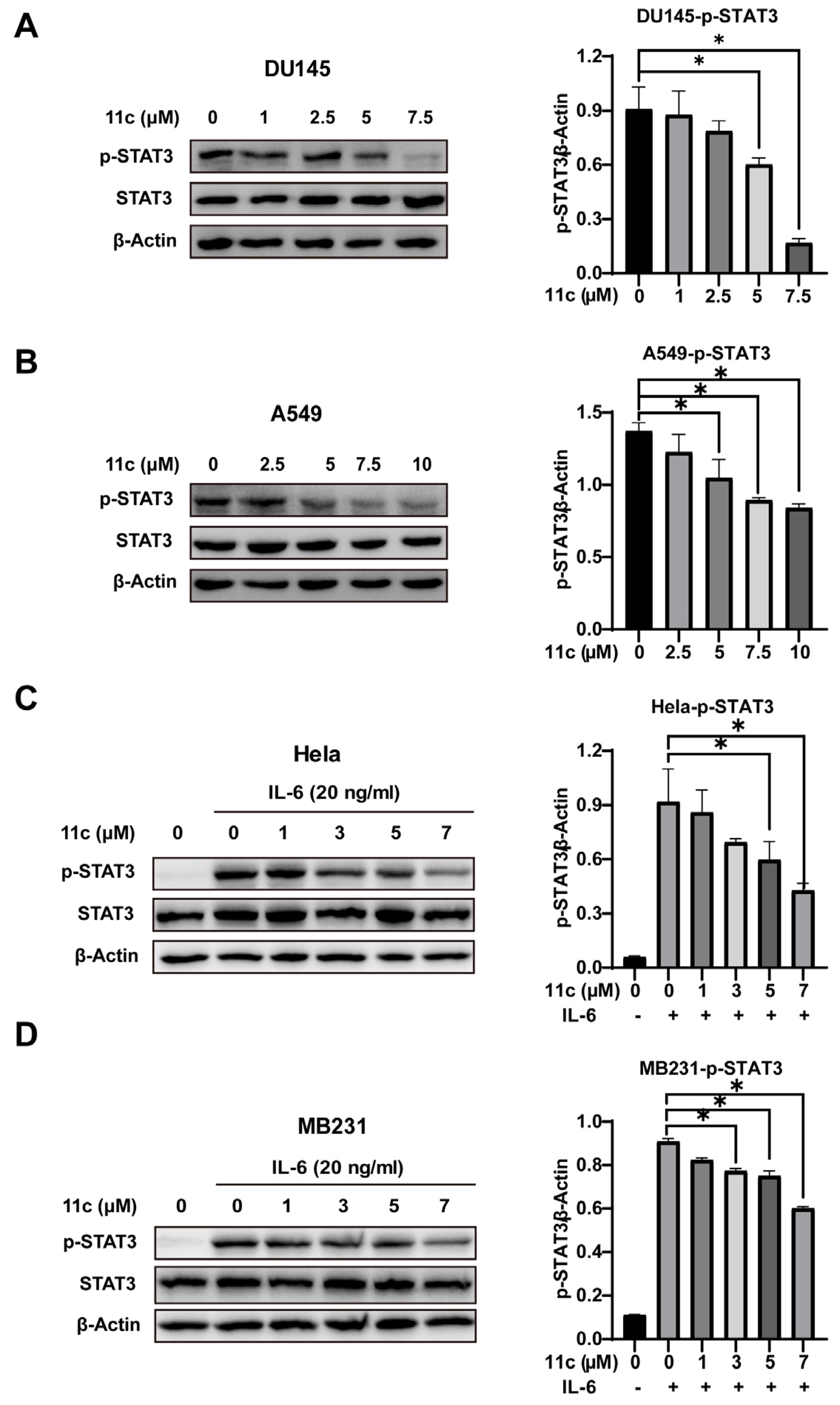
To further determine whether 11c can inhibit the activation of STAT3, we first treated DU145 and A549 cells with 11c at the indicated concentrations for 2 h and then analyzed the phosphorylation of STAT3 by Western blot (Figure 3A,B). Compound 11c inhibited constitutively activated STAT3 at the concentration of 5 μM both in DU145 and A549 cell lines. In consideration of IL-6 as the major cytokine participant in STAT3 activation and its significance in cancer formation and suppressing the antitumor immune response [4,30], we further examined the effect of 11c on IL-6-induced STAT3 activation cell lines such as Hela and MB231 cells (Figure 3C,D). The results indicated that 11c inhibited non-constitutive STAT3 activation at the concentration of 7 μM in a dose-dependent manner. Taken together, the Western blot analysis results suggested that 11c treatment inhibits the constitutive and IL-6-induced STAT3 phosphorylation in cancer cells.
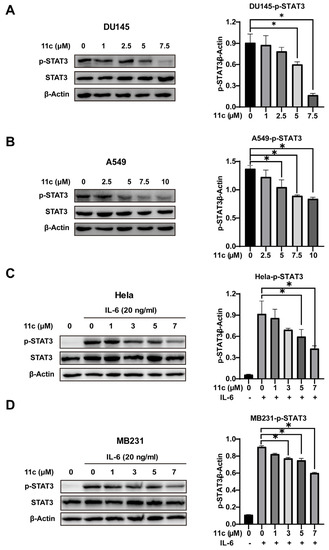
Figure 3.
11c inhibited constitutive and IL6-induced activation of STAT3. (A,B) Constitutive STAT3 activation cells DU145 (A) and A549 (B) were treated with 11c at the specific concentration for 2 h. (C,D) Hela (C) and MB231 (D) cells were pretreated with 11c at the indicated concentrations for 2 h before treatment with IL-6 (20 ng/mL) for 10 min. Whole cell lysates were processed for Western blot and probed with anti-p-STAT3 (Tyr 705) antibody. The relative expressions compared to the loading control protein β-Actin were measured by ImageJ from 3 individual experiments and shown as bar graphs on the right side of each Western blot. Error bars indicate means ± SD. p < 0.05 (*), significant, Student’s t-test, one-way ANOVA.
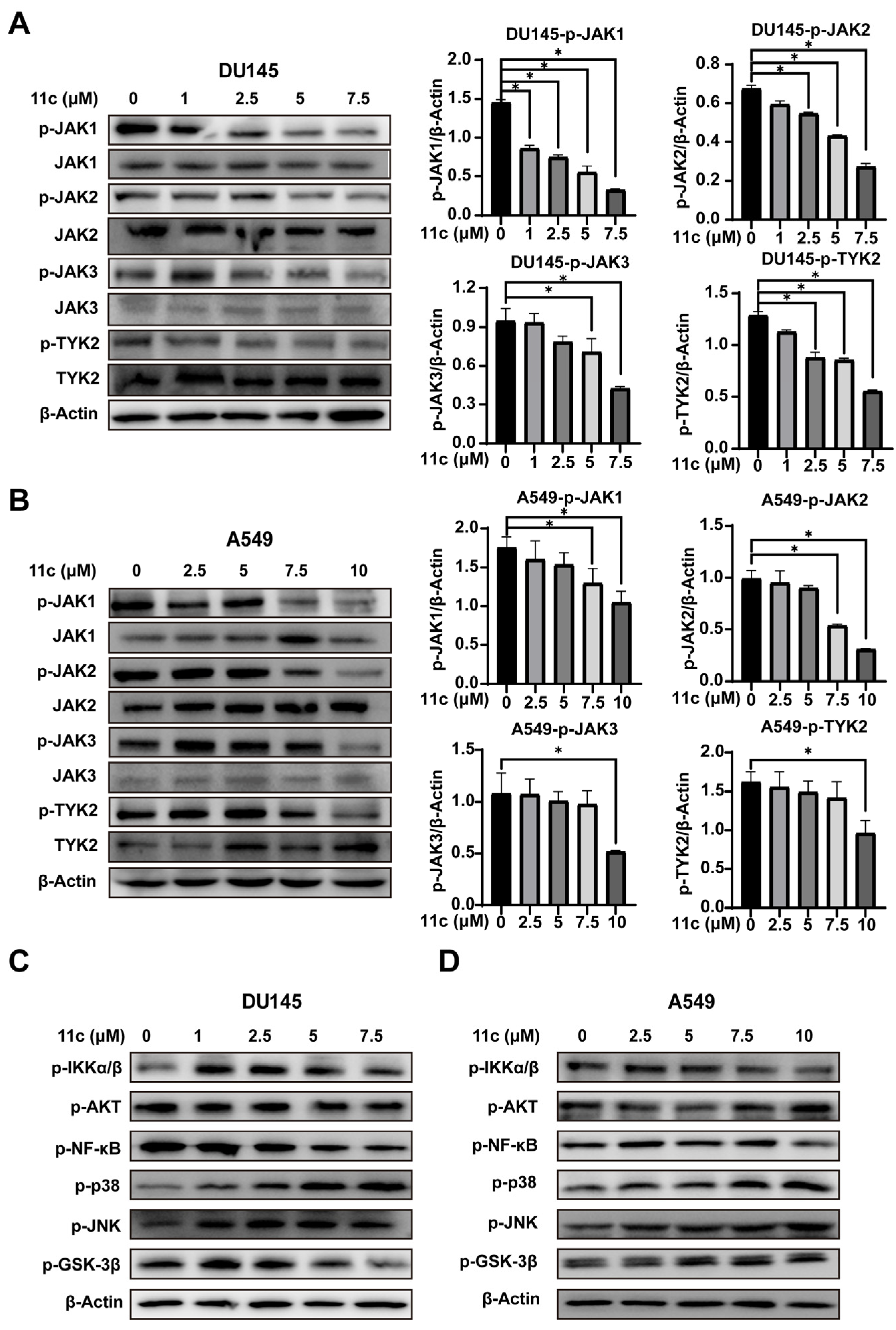
2.2.3. 11c Inhibits the Phosphorylation of JAK Family Members
The activation of STAT3 is usually regulated by its upstream JAK kinases phosphorylation [31]. To further explore whether 11c inhibits STAT3 phosphorylation by influencing JAK kinases, DU145 and A549 cells were treated with 11c for 1 h and JAK kinase phosphorylation was determined (Figure 4A,B). Phosphorylation of JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2 were decreased after 11c treatment at 5 μM in DU145 and 7.5 μM in A549 cells. These data suggest that 11c is a pan-JAK inhibitor and has a higher affinity. Then, to determine whether 11c specifically inhibited the JAK/STAT3 pathway or not, we analyzed other signaling kinases including IKK, AKT, NF-κB, p38, p-JNK, and GSK-3β (Figure 4C,D). The results indicated that 11c had no substantial inhibitory effect on the phosphorylation of IKK, AKT, and GSK-3β, with slight inhibitory activities on NF-κB at the higher concentration and stimulatory effects on the phosphorylation of p38 and JNK. In conclusion, the above data demonstrate that 11c inhibits the activation of JAK kinases in constitutively activated STAT3 cancer cells.
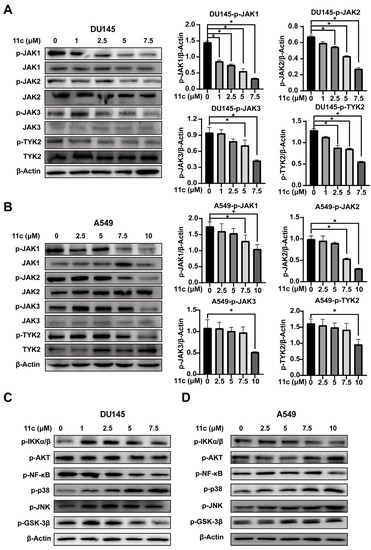
Figure 4.
11c was indicated as a pan-JAK inhibitor. Constitutive STAT3 activation cells DU145 and A549 were treated with 11c at the indicated concentration for 1 h and then total protein was analyzed by Western blot. (A,B) Phosphorylation and total expression of four JAK members were detected. (C,D) Phosphorylation of IKKα/β, AKT, NF-κB, p38, JNK, and GSK-3β were detected. The relative expressions compared to the loading control protein β-Actin were measured by ImageJ from 3 individual experiments and shown as bar graphs on the right side of each Western blot. Error bars indicate means ± SD. p < 0.05 (*), significant, Student’s t-test, one-way ANOVA.
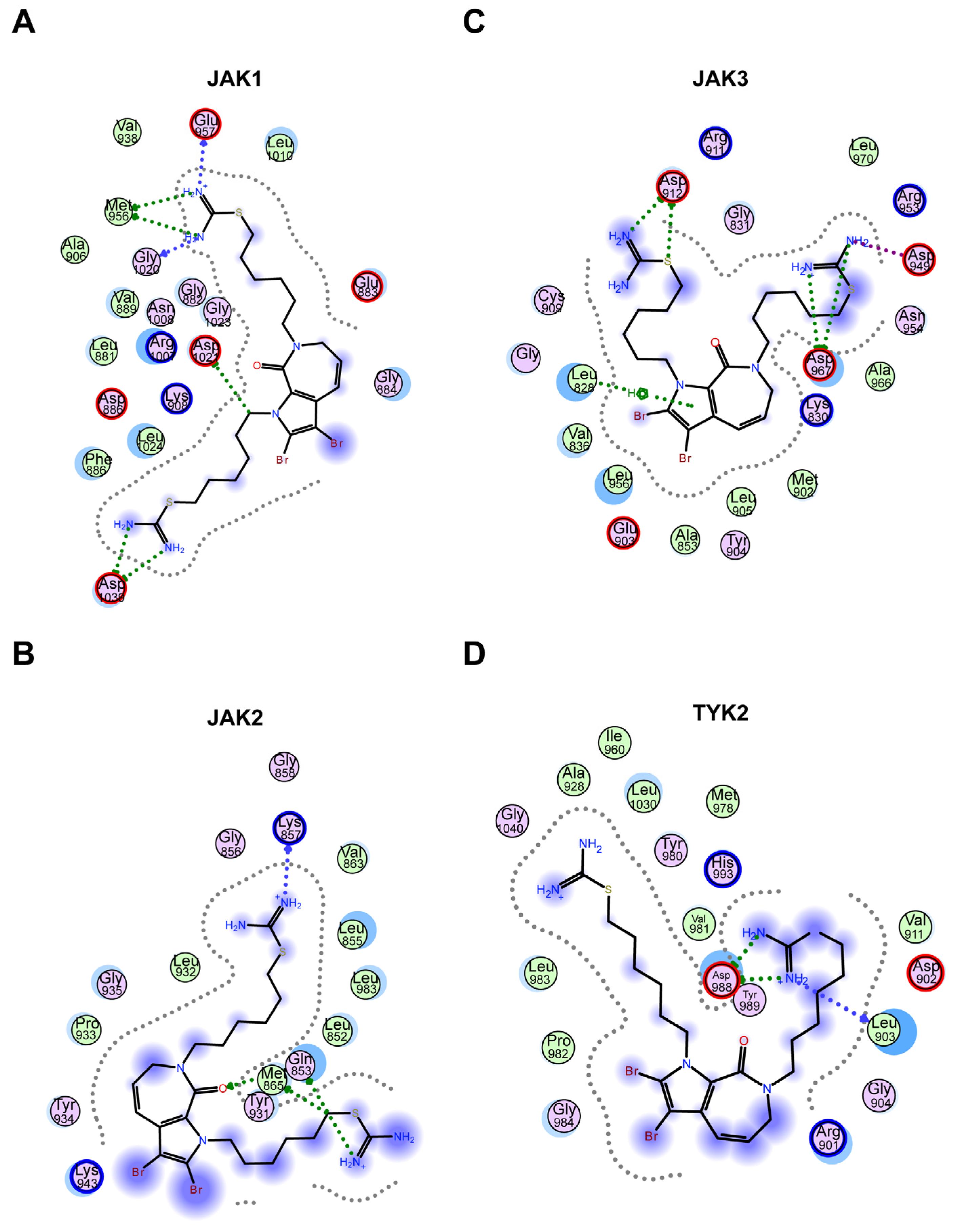
2.2.4. Molecular Docking Revealed That Hydrogen Bonding Is the Major Interaction between 11c and JAKs
JAKs, with a total length of 120–140 kD, are essential for many biological outcomes of cytokine signaling. The JAK family contains four members (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and TYK2), with the end being a catalytic or kinase domain at the carboxyl end, and the front is a pseudokinase (PK) or kinase-like domain. JAK binds to the Box1 and Box2 domains of cytokine receptors through the amino-terminal ezrin-radixin- moesin (FERM) domain and Src Homology 2 (SH2) domain [32,33,34]. Molecular docking software provides a good platform for the interaction between molecules (ligands) and target proteins (receptors) [32]. In our research, molecular docking was conducted to examine the interaction between compound 11c and JAK1 (PDB number: 4EHZ), JAK2 (PDB number: 7Q7W), JAK3 (PDB number: 4Z16), and TYK2 (PDB number: 4GJ2). The data indicated that the hydrophobic fatty chain was surrounded by a hydrophobic pocket. In addition, the isothiouronium and hydrogen interact with amino acid residues through hydrogen bonding, forming six hydrogen bonds with Glu-957, Met-956, Gly-1020, and Asp-1039 in JAK1 (Figure 5A). Similarly, in JAK2, it forms four hydrogen bonds with Lys-857, Met-865, and Gln-853 residues (Figure 5B), while in TYK2, it forms two hydrogen bonds with Asp-988 and Tyr-989 (Figure 5D). Specifically, in JAK3, in addition to four hydrogen bonds with Asp-912 and Asp-967, a π–π interaction is also formed with the indole ring of compound 11c (Figure 5C). Overall, molecular docking revealed that the hydrogen bond is the main interaction between 11c and JAK members; furthermore, the interaction intensity differences in the four JAK members were related to the inhibition effect of 11c.
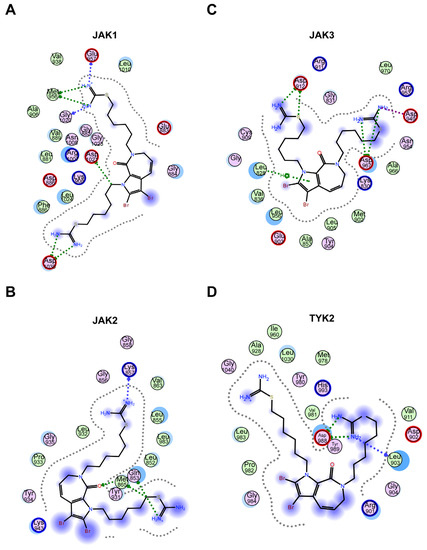
Figure 5.
Molecular docking revealed that hydrogen bonding is the main interaction between 11c and JAKs. (A–D) Molecular docking analysis 2D results of JAK1 (A), JAK2 (B), JAK3 (C), and TYK2 (D) with compound 11c by MOE software. The centered chemical structure is compound 11c. Each circle represents the amino acid residue of JAK proteins. The interaction forces between the amino acid site and the compound structure are represented by a dashed line with an arrow.
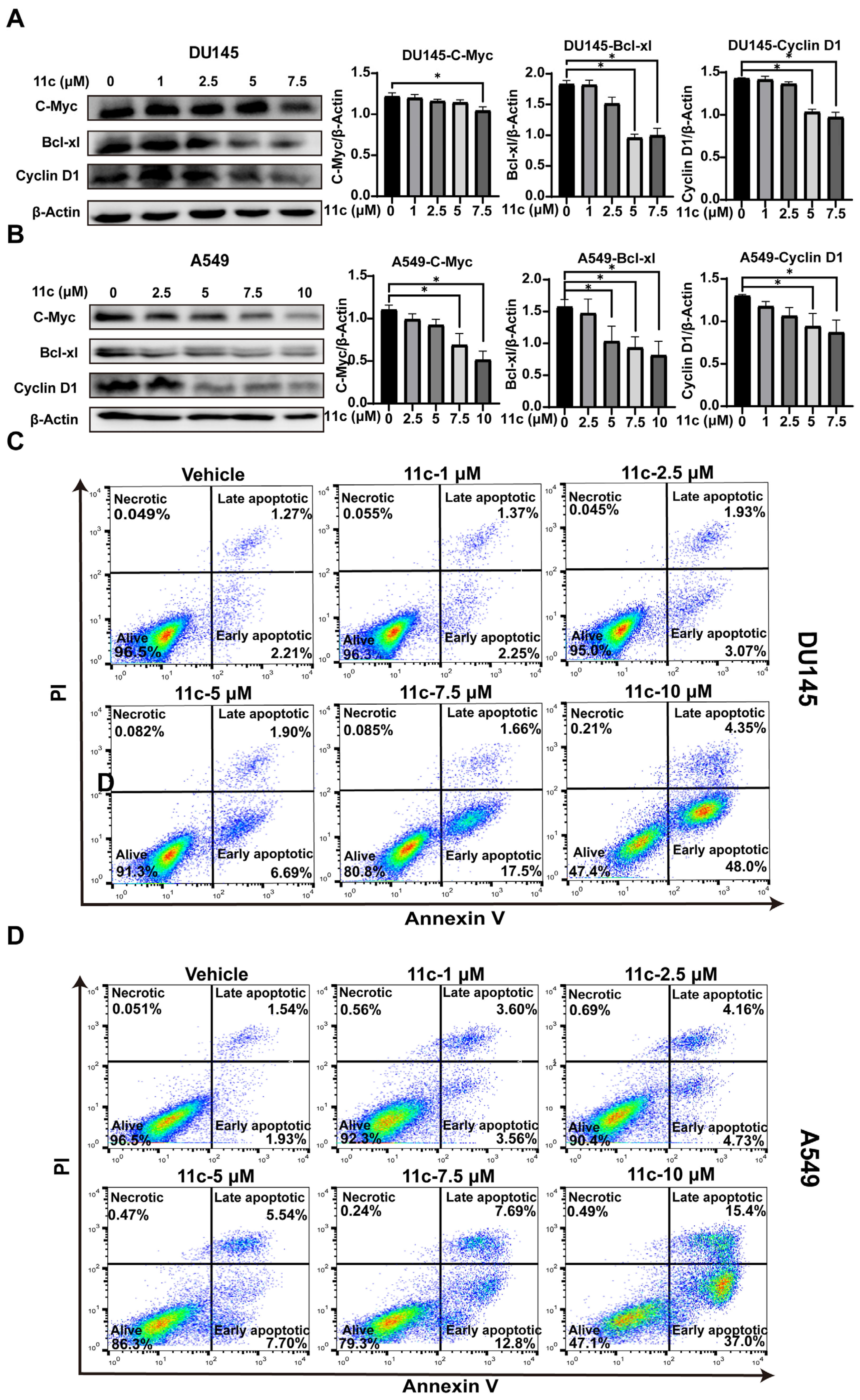
2.2.5. 11c Downregulates Anti-apoptosis Gene Expression and Induces Cancer Cell Apoptosis In Vitro
Since JAK/STAT3 signaling plays an essential role in cell proliferation and survival by reducing the expression of cell-cycle-related genes (Cyclin D) and anti-apoptotic genes (Bcl-xl) [35,36], we analyzed the effect of 11c on cell-cycle-related gene expression. As shown in Figure 6A,B, the downstream genes C-Myc, Bcl-xL, and cyclin D1 were significantly downregulated at the 11c concentration of 7.5 μM and both DU145 and A549. Furthermore, we investigated whether 11c induced apoptosis in vitro by flow cytometry. As the results show, in DU145 cells, the ratio of cells in early (Annexin V+/PI−) and late apoptosis (Annexin V+/PI+) was a total of 19.16% in the 7.5 μM 11c treatment groups and reached 52.35% in the 10 μM 11c treatment groups (Figure 6C). Similarly, in A549 cells, the ratio of cells in early and late apoptosis was a total of 20.49% in the 7.5 μM 11c treatment groups and reached 52.4% in the 10 μM 11c treatment groups (Figure 6D). Therefore, we demonstrated that 11c downregulated anti-apoptosis gene expression and induced apoptosis activities in vitro.
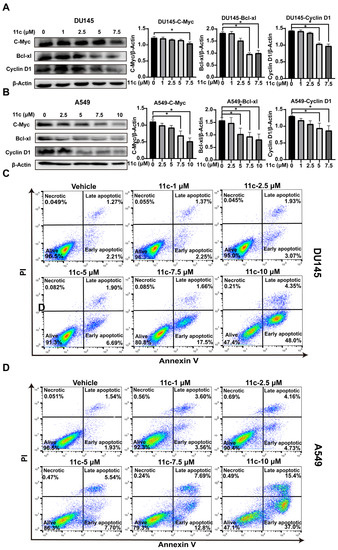
Figure 6.
11c downregulates anti-apoptosis gene expression and induces cancer cell apoptosis in vitro. (A,B) DU145 (A) and A549 (B) cells were treated with 11c at the specific concentrations for 2 h. The levels of C-Myc, Bcl-xl, and Cyclin D1 were detected by Western blot. The relative expressions compared to the loading control protein β-Actin were measured by ImageJ from 3 individual experiments and shown as bar graphs on the right side of each Western blot. Error bars indicate means ± SD. p < 0.05 (*), significant, Student’s t-test, one-way ANOVA. (C,D) DU145 (A) and A549 (B) cells were treated with 11c at specific concentrations for 24 h. After that, cell apoptosis was measured by Annexin V-FITC/PI detection assay.
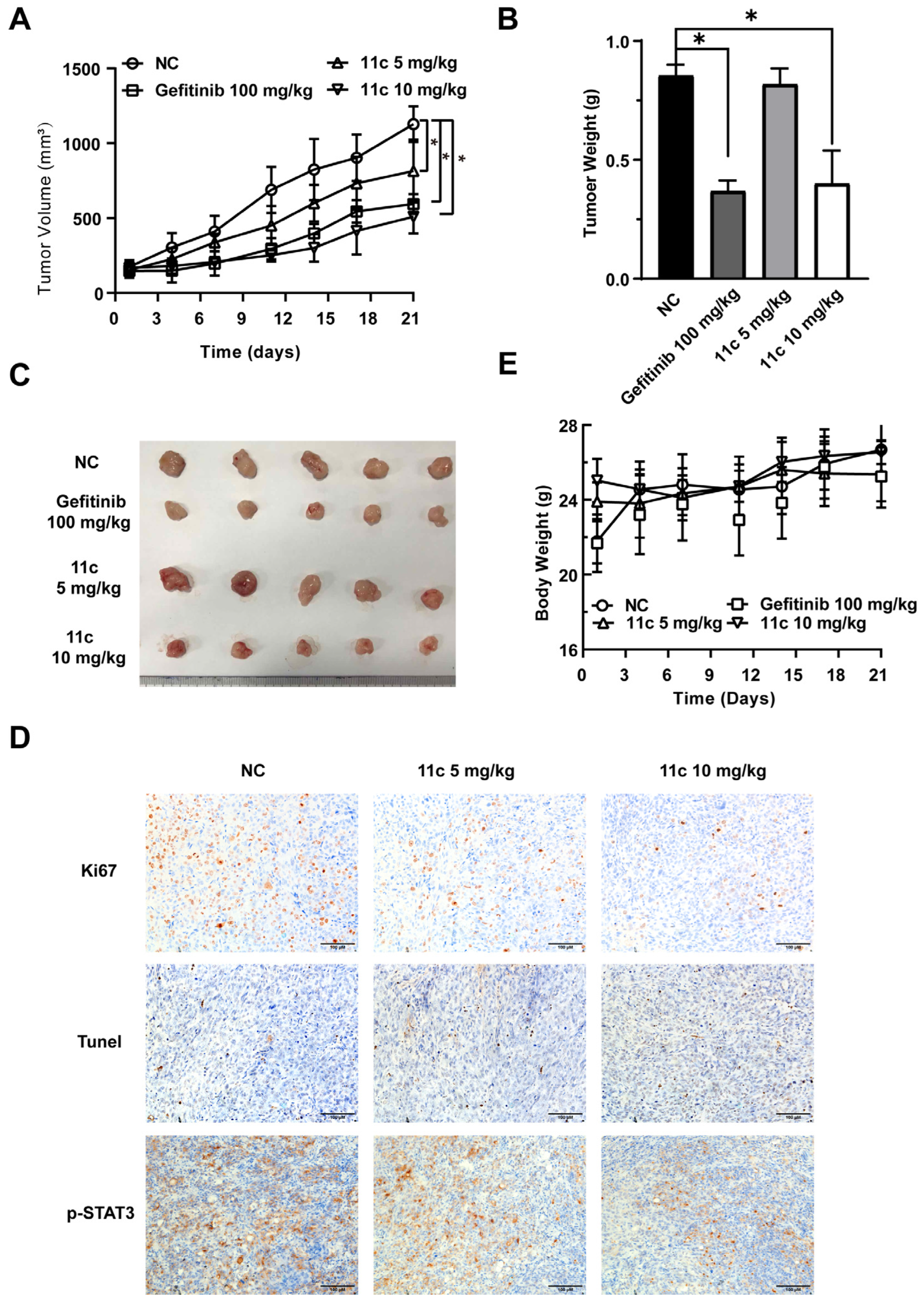
2.2.6. 11c Inhibits the Growth of DU145 Cells by Inducing Apoptosis In Vivo
To further investigate the effects of 11c on cancer cell growth in vivo, we examined the effect of compound 11c in the DU145 xenograft tumors nude model. Tumor xenograft animal models, especially subcutaneous tumor xenograft model in mice, is a widely used tool to bridge basic and clinical cancer research [37,38]. After establishing the model and drug treatment for 21 days, as shown in Figure 7A,B, 10 mg/kg 11c potently inhibited DU145 cell growth compared to the controlled vehicle group. The tumor inhibitory effects at the 10 mg/kg 11c (i.p.) dose reached more than 40% efficiency. The solid tumor images after treatment are shown in Figure 7C. In addition, we investigated whether the inhibition of 11c on tumor growth in vivo also functions via induction of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis, which is similar to the observation obtained in the in vitro experiments (Figure 6). Ki67, Tunel, and p-STAT3 staining were performed, as shown in Figure 7D, and the Ki67 positive area decreased after 11c treatment, indicating inhibited tumor proliferation. Meanwhile, an increased Tunel positive area indicated that 11c treatment caused tumor cell apoptosis in vivo. Consistent with these observations, 11c inhibited the phosphorylation of STAT3 in vivo. The body weight of the mice (Figure 7E) suggests that all treatments exhibited high efficacy without toxicity.
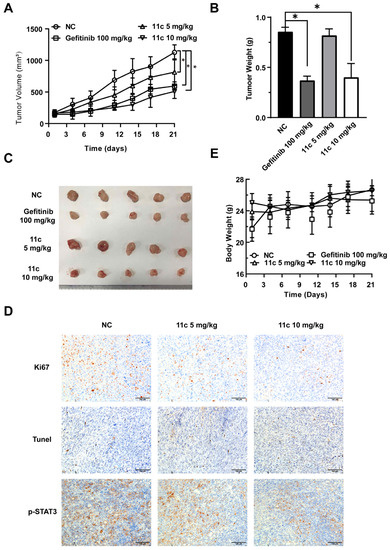
Figure 7.
11c inhibits the growth of DU145 cells in vivo. Nude mice with DU145 xenograft tumors were treated with vehicle, Gefitinib (100 mg/kg, p.o., q.2d.) or 11c (5 or 10 mg/kg, i.p., q.2d.) for 21 days. On the last day, nude mice were sacrificed. (A) The tumor volumes before excision were calculated every three days. (B) The tumor weights were measured on the day before the nude mice sacrifice. (C) Tumors were excised and photographed. (D) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tumor slices by Ki67, Tunel, and p-STAT3 staining. (E) The body weights were recorded every three days. Error bars indicate means ± SEM. p < 0.05 (*), significant, Student’s t-test, two-way ANOVA.
3. Discussion
The JAK/STAT3 is a classical intracellular signaling pathway in the regulation of tumor cell proliferation, survival, invasiveness, and metastasis [2,4,39]. Therefore, the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway was considered as an effective therapeutic target for numerous cancers [40]. In the current study, we synthesized aldisine derivatives named compounds 11a, 11b, and 11c, and their inhibitory effect on JAK/STAT3 signaling was explored in a STAT3 transcriptional activity driven luciferase reporter cell line. In particular, compound 11c with the longest carbon atom links exhibited the highest biological activity. The Western blot analysis results elucidated that 11c inhibits the phosphorylation of STAT3 and its upstream JAKs. Compound 11c was identified as a new pan-JAK kinase inhibitor. Moreover, the introduction of two isothiouronium groups contains a stronger film-breaking property with a positive charge that is superior to a single group. In addition, compound 11c induced the apoptosis of A549 and DU145 cancer cells by decreasing cell cycle and anti-apoptosis gene expression. Further in vivo antitumor studies showed that apoptosis also plays an important role in 11c suppressed xenograft tumor growth. Taken together, we have identified a novel compound 11c that inhibits the phosphorylation of JAKs that induce cell apoptosis to decrease cell proliferation based on the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway.
The improved understanding of the JAK/STAT3 signaling participation in cancer treatment has led to the increasing discovery of therapeutic intervention with JAK inhibitors [41]. Previous reports have indicated that JAK inhibitors can be used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, cancer, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, atopic dermatitis, and so on [42,43,44]. Nowadays, several JAK inhibitors have been developed, but the clinical use of pan-JAK inhibitors in cancer therapy is still limited, perhaps due to the selectivity of JAK inhibitors [45,46]. Recent research has focused on more selective JAK inhibitors because specific JAK inhibitors may reduce side effects while increasing safety and efficacy [47,48]. Our molecular docking data showed that the hydrogen bond is the major interaction route between 11c and the JAK’s amino acid residues. In addition, the hydrogen bond interaction intensity, which was different in the four JAK members, was related to the inhibitory effect of 11c. This discovery may provide evidence for the further modification of compound 11c to improve its selectivity of JAK members. At the same time, there are some therapeutic interests in the future; for example, which JAK structural motif the 11c is targeting and how it works concretely.
In conclusion, our research identified compound 11c as a novel antitumor drug by specifically targeting the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Compound 11c exhibited inhibitory activity on JAKs activation, and efficiently inhibited cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. The synthesis and modification route of compound 11c provides the potential for marine drug development in cancer treatment. In the future, compound 11c may serve as a new skeleton molecule for further development into a JAKs’ inhibitor, which has great potential for cancer treatment in clinical applications.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Design and Synthesis Materials
All raw materials required in this article were purchased from commercial channels. All reactions were tracked by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) and observed under 254 nm ultraviolet light using precoated silica gel plates. The specification of silica gel used for column chromatography is 200–300 mesh. 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra were recorded with a Jeol JNM-ECP 600 MHz spectrometer (Celes Automation Technology Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China), using TMS as an internal standard. Chemical shifts were reported on the δ scale and J values were given in Hz. High resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were recorded on a Q-TOF Global Mass Spectrum (Agilent, Beijing, China). The following abbreviations are used: s = singlet, d = doublet, t = triplet, q = quartet, m = multiplet, dd = double-doublet.
4.2. Antibodies and Reagents
Antibodies against STAT3, p-STAT3 (Tyr705), JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, TYK2, Bcl-xl, C-Myc, CyclinD1, p-JAK1 (Tyr1022/1023), p-JAK2 (Tyr1007/1008), p-TYK2 (Tyr1054/1055), p-JAK(Tyr980/981), p-IKK-α/β(Ser176/180), p-NF-κB p65(Ser536)(93H1), p-Akt (Ser473) (D9E) XP®, p-GSK-3β(Ser9)(D85E12), p-p38 (Thr180/Tyr182), p-JNK (Thr183/Tyr185), and β-Actin were all obtained from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA). Obtained recombinant human IL6 (Cat. 216-16) was from PeproTech. Protease and phosphatase inhibitors A and B were purchased from Millipore (Billerica, MA, USA). Bioactive drugs and compounds used for high-throughput screening were provided by TargetMol (Shanghai, China). Aldisine derivatives were obtained as mentioned in the chemical part.
4.3. Cell Culture
A549, DU145, MDA-MB231, and Hela were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). SKA cells were established by transfected A549 cells with a vector containing STAT3-based luciferase reporter gene as in previously reported methods [49]. The DU145 cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 complete medium (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA), the others were cultured in DMEM complete medium (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA). Prepared complete medium with added 1% streptomycin, 1% penicillin, and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA). Cells were incubated in a 37 °C temperature incubator with 5% CO2.
4.4. Animals
Nude mice (male, six-week-old, weight 17–20 g) were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology (Beijing, China). Mice were bred in a specific pathogen-free environment with controlled temperature and humidity and 12 h light and dark alternate. The Committee of Experimental Animals of the Ocean University of China (OUC-SMP-2020-11-01) has approved the animal experiments.
4.5. Luciferase Reporter Assay
SKA cells (8000 cells/well) were bedded into white 96-well plates (Corning, NY, USA) and incubated in an incubator at 37 °C containing 5% CO2 overnight and then treated with the vehicle or indicated concentrations of compounds. Twenty-four hours later, luciferase activity was detected by adding a luciferase substrate (Cat. E2510, Promega, Beijing, China) and read by a SpectraMax® L microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Shanghai, China) [49,50].
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
After stimulating with compounds, we washed the cells twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and lysed the cells with the RIPA buffer including 1% phosphatase and 1% protease inhibitors. Protein lysis was quantified by a BCA kit (Solarbio, Beijing, China) and separated by 10% SDS-PAGE. Later they were transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes (GE Healthcare) at 90v for 2 h and incubated with primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight. After that, they were incubated with anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibodies at room temperature for 1 h, detected with chemiluminescence HRP substrate (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) and photographed by Chemiluminescence Imaging System (Tanon 5200, Shanghai, China).
4.7. Cell Viability and Antiproliferation Activity Assay
Cell viability and antiproliferation activity was evaluated by the resazurin indicator [51]. Cells (3500 cells/well) were seeded into 96-well plates overnight and treated with the vehicle or indicated drug concentrations for 72 h. An amount of 10 µL of 1 mg/mL resazurin solution was added per well and, after incubating for 3 h, relative cell viability was detected using a SpectraMax Mode Plate Reader (Molecular Devices, Shanghai, China) at a 595-nm emission wavelength and a 549-nm excitation wavelength. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration value (IC50) of 11c was determined using GraphPad Prism 8 software.
4.8. Molecular Docking
The docking results of compound 11c (ligand) and JAK proteins (receptor) were calculated by the MOE (version 2020) molecular docking program. Crystal structures of all JAK proteins were obtained from the RCSB Protein Data Bank (RCSB PDB). Firstly, compound 11c was subjected to an energy minimization processing through Chemdraw 3D software (version, 14.0.0.17). Secondly, the water molecules of the receptor protein and the existing small molecule ligands in the crystal were removed. Finally, compound 11c was introduced into the protein structure and docked in the pocket of the original ligand. Based on the scores calculated by GBVI/WSA combined with free energy, the top 5 results were analyzed using MOE.
4.9. Flow cytometry Analysis of Apoptosis
A549 and DU145 cells (5 × 105 cells/well) were bedded into 6-well plates and treated with 11c at the indicated concentrations. After 24 h incubation, the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) twice followed by incubating with the eBioscience™ Annexin VFITC Apoptosis Kit (Invitrogen, City, Carlsbad, California, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Finally, cell apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry and the results were processed by flowjo software(version 10.6.2).
4.10. Subcutaneous Tumor Xenograft Model and Antitumor Assay In Vivo
Nude mice were randomly divided into 4 treatment groups (n = 5/group) before being implanted with subcutaneous tumor xenograft cells. DU145 cells were harvested, counted, and reserved on ice. About 15 × 106 cells were injected to establish a tumor transplantation nude mouse model. The four groups were treated as follows: vehicle group, Gefitinib (100 mg/kg) group, and 11c (5 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg) group. Tumor size (1/2 × length × width2) and body weight were measured every 3 days for 21 days. On the last day the mice were sacrificed, and the tumor weight was determined [6].
4.11. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Analysis
The xenograft model tumor of mice was collected and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 72 h at 4 °C and then embedded in paraffin and cut into slices. After, the slices were baked, dewaxed in xylene, gradients ethanol, and boiled in a microwave to repair antigen [31]. The inactivation of endogenous peroxidase was blocked by incubating with fresh 3% H2O2. The slices were blocked with fat free milk and incubated with the primary antibody (1:3000) at 4 °C overnight. After that, they were washed with PBS followed by incubation with the HRP-conjugated secondary antibody at room temperature (Boster, Wuhan, China). Finally, slices were dyed by DAB/H2O2 reaction, brown color in the cell membrane indicated positive staining. Images were captured using an upright fluorescence microscope (Olympus BX53, Tokyo, Japan) [6,52].
4.12. Statistical Analysis
The data were presented as mean ± SD. GraphPad prism (version 8.0.2) was used for statistical analysis. p-value < 0.05 (*) was considered a significant difference, which was calculated by t-test, one and two-way ANOVA (analysis of variance).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/md21040218/s1, The general procedures for compounds 8a, 8b, 8c, 9a, 9b, 9c, 10a, 10b, 10c, 11a, 11b, and 11c. The data of 1H and 13C NMR of all the compounds are shown in Supplementary Materials. Table S1: The high-throughput-screen result of aldisine derivatives. Figure S1: The high-throughput screen of compounds graph.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-Y.Z. and T.J.; experimental studies performed by, D.-P.W., L.-H.W., R.L., N.H. and Q.-Y.Z.; writing–original draft preparation, L.-H.W., D.-P.W. and R.L.; writing–review and editing, C.-Y.Z. and T.J.; Our manuscript is original content and has not been submitted to other journals. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Natural Science Foundation of China: Grant No. 82073759; Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory Platform Project No. 2021ZDSYS11; Shandong Province Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project: No. 2020CXGC010503; National Natural Science Foundation of China Major Project: No. 81991525.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by Committee of Experimental Animals of the Ocean University of China (protocol code: OUC-SMP-2020-11-01 and date of approval: 2 November 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors declare that supporting data of this study are available within the article and the Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calautti, E.; Avalle, L.; Poli, V. Psoriasis: A STAT3-Centric View. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manore, S.G.; Doheny, D.L.; Wong, G.L.; Lo, H.-W. IL-6/JAK/STAT3 Signaling in Breast Cancer Metastasis: Biology and Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 866014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Mao, Q.-F.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. The Interaction Between Autophagy and JAK/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Tumors. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 880359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-Q.; Li, R.; Dong, X.-Y.; He, N.; Yin, R.-J.; Yang, M.-K.; Liu, J.-Y.; Yu, R.-L.; Zhao, C.-Y.; Jiang, T. Design, Synthesis and Structure-Activity Relationship Studies of Meridianin Derivatives as Novel JAK/STAT3 Signaling Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Fragoulis, G.; McInnes, I.B.; Siebert, S. JAK-inhibitors. New players in the field of immune-mediated diseases, beyond rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, i43–i54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, K.L.; Brockwell, N.K.; Parker, B.S. JAK-STAT Signaling: A Double-Edged Sword of Immune Regulation and Cancer Progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, A.M.; Almalki, F.A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Abdelazeem, A.H.; Gouda, A.M. A Comprehensive Overview of Globally Approved JAK Inhibitors. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, J.C.; Verstovsek, S. Overcoming treatment challenges in myelofibrosis and polycythemia vera: The role of ruxolitinib. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 1125–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Yoon, D.; Song, Y.; Koh, Y.; Cao, J.; Ji, D.; Yang, H.; Eom, H.; Jing, H.; Kwak, J.; et al. Early Safety and Efficacy Data from a Phase I/II Trial of DZD4205, a Selective Jak1 Inhibitor, in Relapsed/Refractory Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 101–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigogliuso, S.; Campora, S.; Notarbartolo, M.; Ghersi, G. Recovery of Bioactive Compounds from Marine Organisms: Focus on the Future Perspectives for Pharmacological, Biomedical and Regenerative Medicine Applications of Marine Collagen. Molecules 2023, 28, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Natural Products from the Marine Sponge Subgenus Reniera. Molecules 2021, 26, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebada, S.S.; Linh, M.H.; Longeon, A.; de Voogd, N.J.; Durieu, E.; Meijer, L.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Singab, A.N.B.; Müller, W.E.; Proksch, P. Dispacamide E and other bioactive bromopyrrole alkaloids from two Indonesian marine sponges of the genus Stylissa. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir, D.; Mallon, R.; Greenstein, M.; Feldberg, L.R.; Kim, S.C.; Collins, K.; Wojciechowicz, D.; Mangalindan, G.C.; Concepción, G.P.; Harper, M.K.; et al. Aldisine Alkaloids from the Philippine Sponge Stylissa massa Are Potent Inhibitors of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase-1 (MEK-1). J. Med. Chem. 2001, 45, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, R.; Hao, Y.; Song, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. Discovery of Aldisine and Its Derivatives as Novel Antiviral, Larvicidal, and Antiphytopathogenic-Fungus Agents. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 12355–12363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Tian, J.; Su, L.; Huang, M.; Zhu, X.; Ye, F.; Wan, Y. Pyrrolo[2,3-c]azepine derivatives: A new class of potent protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4306–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.W.; Carpenter, N.; Lottin, J.R.; McClelland, R.A.; Nicholson, R.I. Synthesis and evaluation of novel anti-proliferative pyrroloazepinone and indoloazepinone oximes derived from the marine natural product hymenialdisine. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 56, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimino, G.; De Rosa, S.; De Stefano, S.; Mazzarella, L.; Puliti, R.; Sodano, G. Isolation and X-ray crystal structure of a novel bromo-compound from two marine sponges. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Hur, W.; Cho, C.Y.; Liu, Y.; Adrian, F.J.; Lozach, O.; Bach, S.; Mayer, T.; Fabbro, D.; Meijer, L.; et al. Synthesis and target identification of hymenialdisine analogs. Chem. Biol. 2004, 11, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, B.K.; Scheidt, L.G.; Fraser, T.J. Cell cycle phase specificity of antitumor agents. Cancer Res 1972, 32, 398–407. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.; Assunção, L.S.; Silva, A.H.; Filippin-Monteiro, F.B.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B.; Sá, M.M. Allylic isothiouronium salts: The discovery of a novel class of thiourea analogues with antitumor activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 129, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Yin, R.; Yu, R.; Wan, S.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, L. Isothiouronium modification empowers pyrimidine-substituted curcumin analogs potent cytotoxicity and Golgi localization. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Z.; Yakushijin, K.; Horne, D.A. Synthesis of C11N5 marine sponge alkaloids:(±)-Hymenin, stevensine, hymenialdisine, and debromohymenialdisine. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, M.A.; Tan, N.Y.; Thiam, C.H.; Khatoo, M.; MacAry, P.A.; Angeli, V.; Gasser, S.; Zhang, Y.L. cGAS-STING cytosolic DNA sensing pathway is suppressed by JAK2-STAT3 in tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, H.-H.; Lai, W.-W.; Chen, H.H.W.; Liu, H.-S.; Su, W.-C. Autocrine IL-6-induced Stat3 activation contributes to the pathogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma and malignant pleural effusion. Oncogene 2006, 25, 4300–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schabath, M.B.; Cote, M.L. Cancer Progress and Priorities: Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. A Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2019, 28, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, J.K.; Mishra, R.; Das, B.R. Activation of Stat-3 as one of the early events in tobacco chewing-mediated oral carcinogene-sis. Cancer 2002, 94, 2393–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suradej, B.; Sookkhee, S.; Panyakaew, J.; Mungkornasawakul, P.; Wikan, N.; Smith, D.R.; Potikanond, S.; Nimlamool, W. Kaempferia parviflora Extract Inhibits STAT3 Activation and Interleukin-6 Production in HeLa Cervical Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Xu, X.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Zelnorm, an agonist of 5-Hydroxytryptamine 4-receptor, acts as a potential antitumor drug by targeting JAK/STAT3 signaling. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 38, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaronson, D.S.; Horvath, C.M. A Road Map for Those Who Don’t Know JAK-STAT. Science 2002, 296, 1653–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, S.; Dusanter-Fourt, I. The Structure, Regulation and Function of the Janus Kinases (JAKs) and the Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (STATs). JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 248, 615–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glassman, C.R.; Tsutsumi, N.; Saxton, R.A.; Lupardus, P.J.; Jude, K.M.; Garcia, K.C. Structure of a Janus kinase cytokine receptor complex reveals the basis for dimeric activation. Science 2022, 376, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.; Xu, X.; Deng, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ma, H.; Wei, D.; Sun, S. The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway and its inhibitors in diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, E.D.; Orlova, A.; Neubauer, H.A.; Bajusz, D.; Seo, H.-S.; Dhe-Paganon, S.; Keserű, G.M.; Moriggl, R.; Gunning, P.T. Structural Implications of STAT3 and STAT5 SH2 Domain Mutations. Cancers 2019, 11, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukada, T.; Ohtani, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Shirogane, T.; Nishida, K.; Nakajima, K.; Hibi, M.; Hirano, T. STAT3 orchestrates contradictory signals in cytokine-induced G1 to S cell-cycle transition. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 6670–6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.P.; Chan, C.M.; Tung, L.N.; Wang, H.K.; Law, S. Tumor xenograft animal models for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürtin, F.; Mullins, C.S.; Linnebacher, M. Mouse models of colorectal cancer: Past, present and future perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 1394–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Tong, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, W.; Tian, Y.; Fu, X. Targeting STAT3 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLornan, D.P.; E Pope, J.; Gotlib, J.; Harrison, C.N. Current and future status of JAK inhibitors. Lancet 2021, 398, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.C.; Keystone, E.C.; Van Der Heijde, D.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Del Carmen Morales, L.; Gonzaga, J.R.; Yakushin, S.; Ishii, T.; Emoto, K.; Beattie, S.; et al. Baricitinib versus Placebo or Adalimumab in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovatiya, R.; Paller, A.S. JAK inhibitors in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, C.; Nichols, K.E.; Albeituni, S. Use of the JAK Inhibitor Ruxolitinib in the Treatment of Hemophagocytic Lymphohis-tiocytosis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 614704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, B.; Yates, M.; Adas, M.; Bechman, K.; Galloway, J. The safety of JAK-1 inhibitors. Rheumatology 2021, 60, ii24–ii30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traves, P.G.; Murray, B.; Campigotto, F.; Galien, R.; Meng, A.; A Di Paolo, J. JAK selectivity and the implications for clinical inhibition of pharmacodynamic cytokine signalling by filgotinib, upadacitinib, tofacitinib and baricitinib. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, A.T.; Haikarainen, T.; Raivola, J.; Silvennoinen, O. Selective JAKinibs: Prospects in Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases. BioDrugs Clin. Immuno-Ther. Biopharm. Gene Ther. 2019, 33, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, L.A.; Collins, I. Measuring and interpreting the selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors. J. Chem. Biol. 2009, 2, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Du, Y.; Nan, J.; Zhang, X.; Qin, X.; Wang, Y.; Hou, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J. Brevilin A, a Novel Natural Product, Inhibits Janus Kinase Activity and Blocks STAT3 Signaling in Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, L.; Lu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Q.; et al. Scaffold compound L971 exhibits anti-inflammatory activities through inhibition of JAK/STAT and NFκB signalling pathways. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 6333–6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P. Analysis of Cell Viability by the alamarBlue Assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 2018, pdb.prot095489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.C.C.; Nerurkar, S.N.; Cai, H.Y.; Ng, H.H.M.; Wu, D.; Wee, Y.T.F.; Lim, J.C.T.; Yeong, J.; Lim, T.K.H. Overview of multiplex immunohistochemistry/immunofluorescence techniques in the era of cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Commun. 2020, 40, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).