Anticoagulant Property of a Sulfated Polysaccharide with Unique Structural Characteristics from the Green Alga Chaetomorpha aerea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
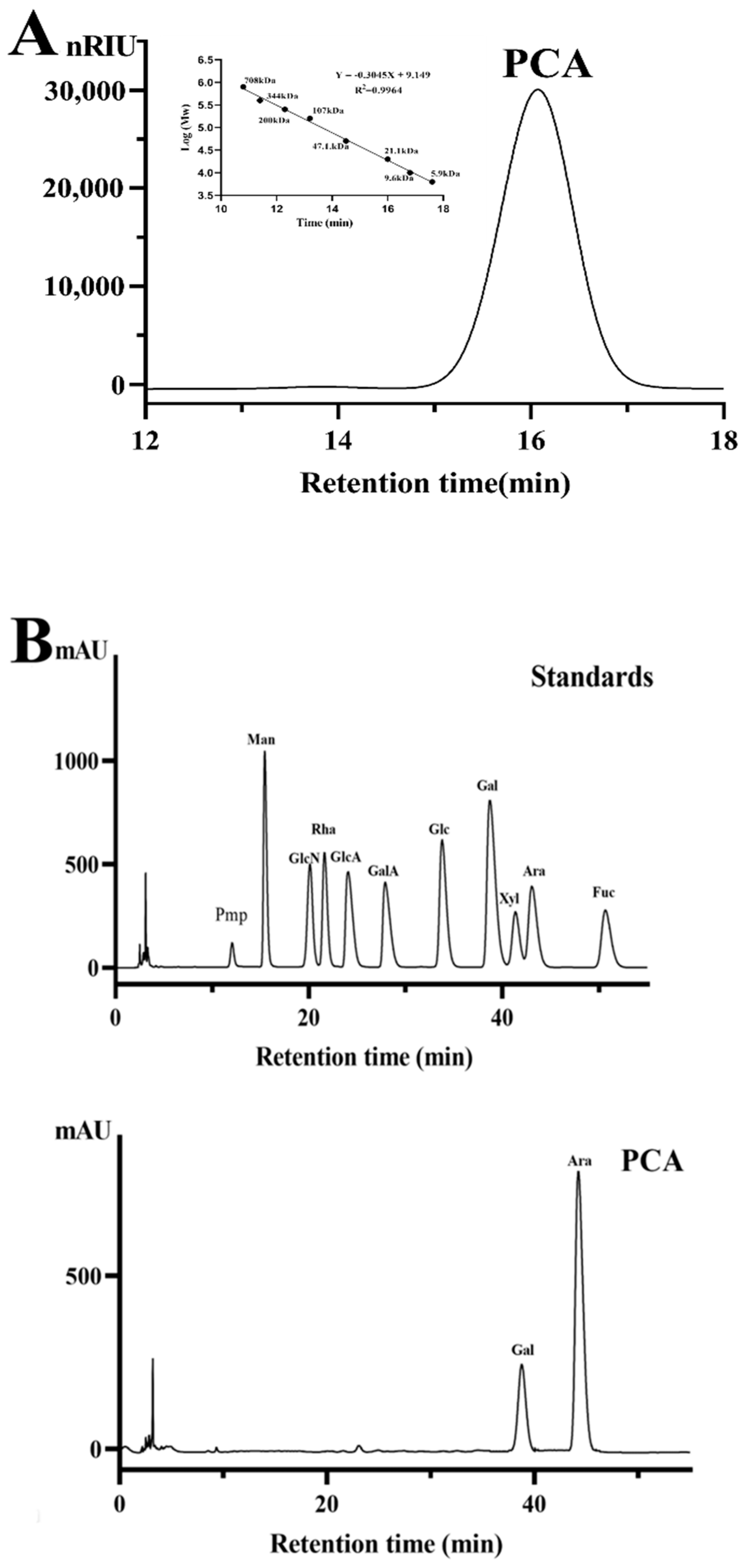
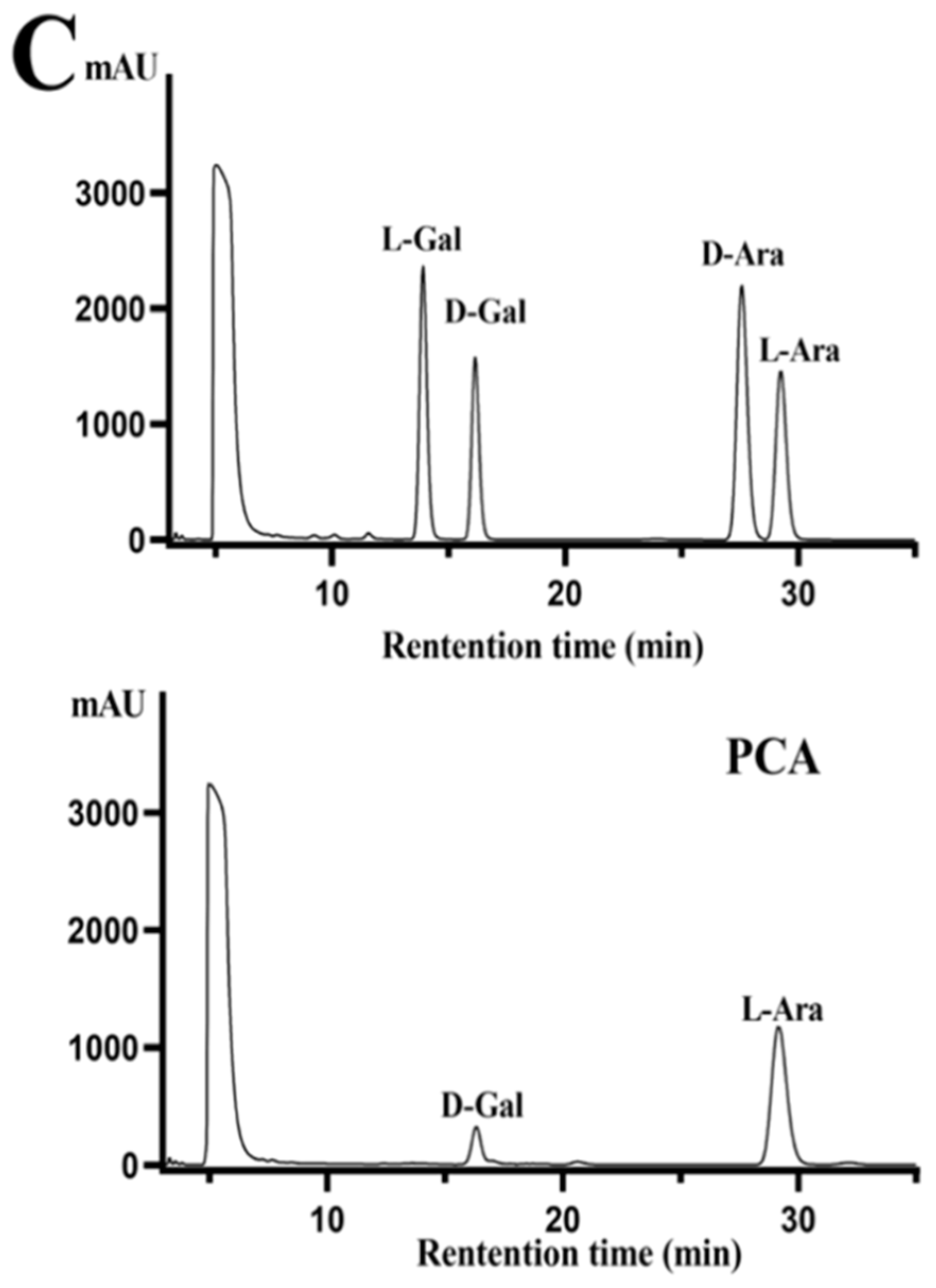
2.1. Structural Characteristics of the Sulfated Polysaccharide PCA
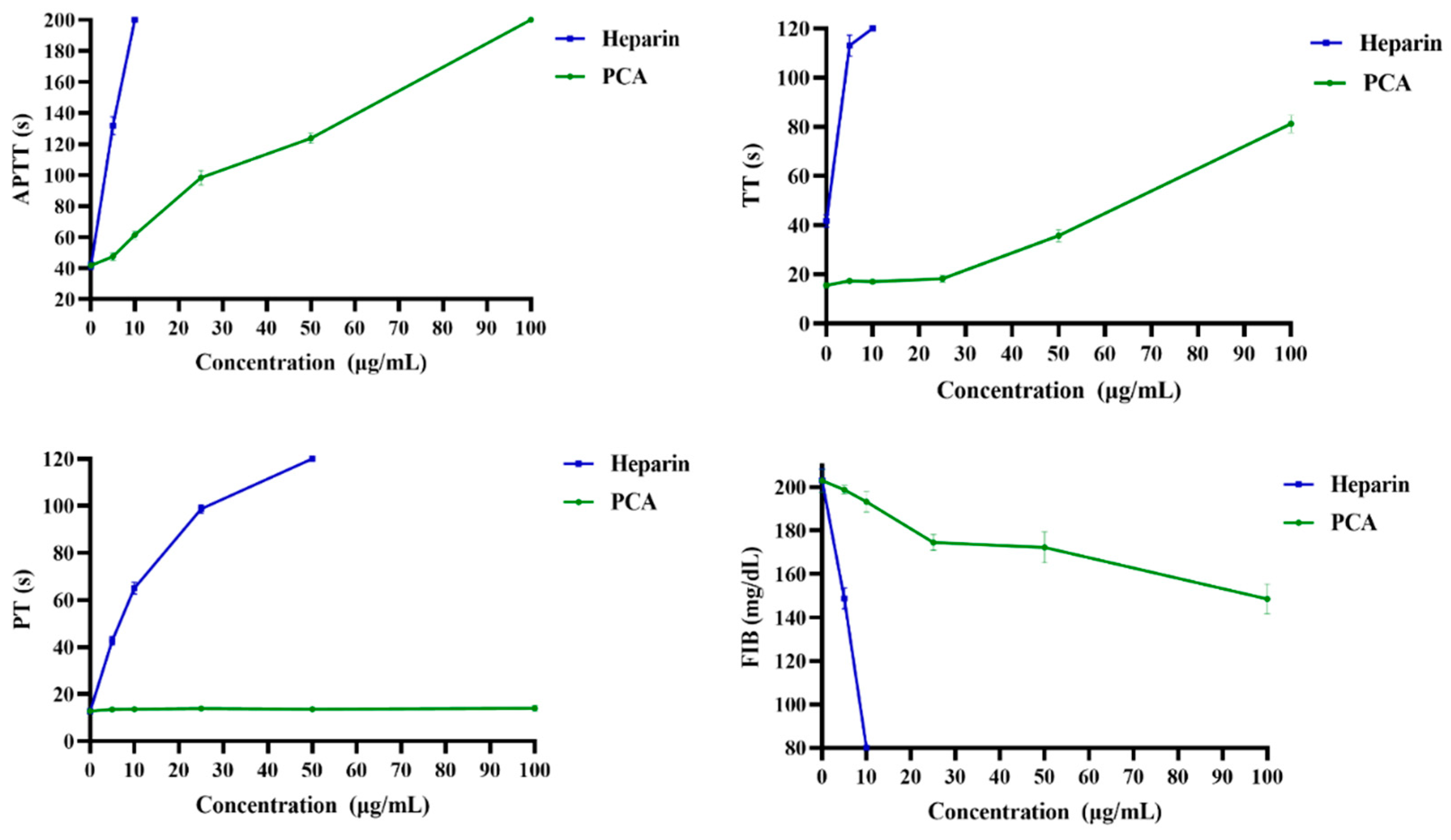
2.2. Anticoagulant Activity In Vitro and In Vivo of PCA
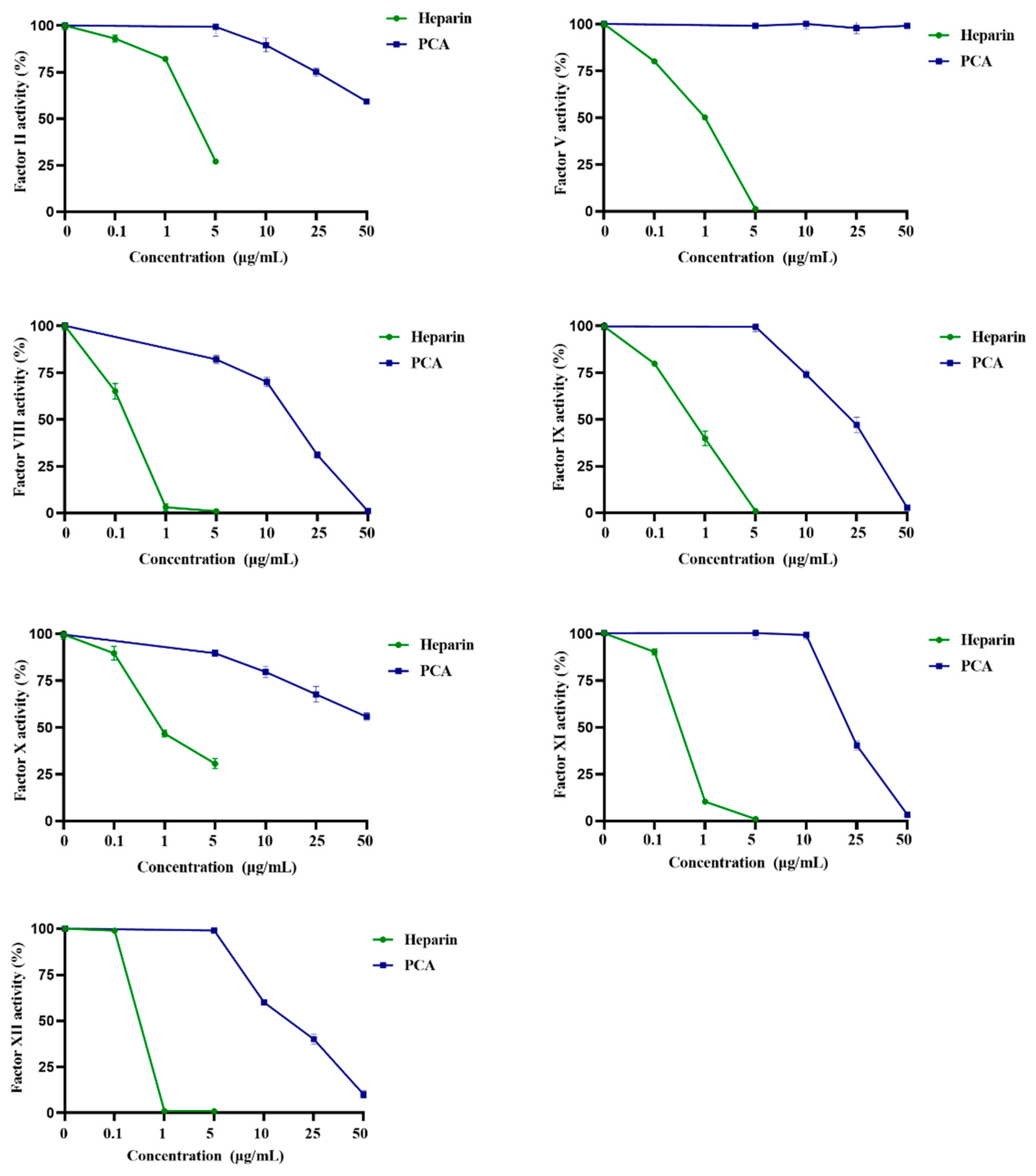
2.3. Effects of PCA on the Coagulation Factors II, V, VIII, X, IX, XI and XII
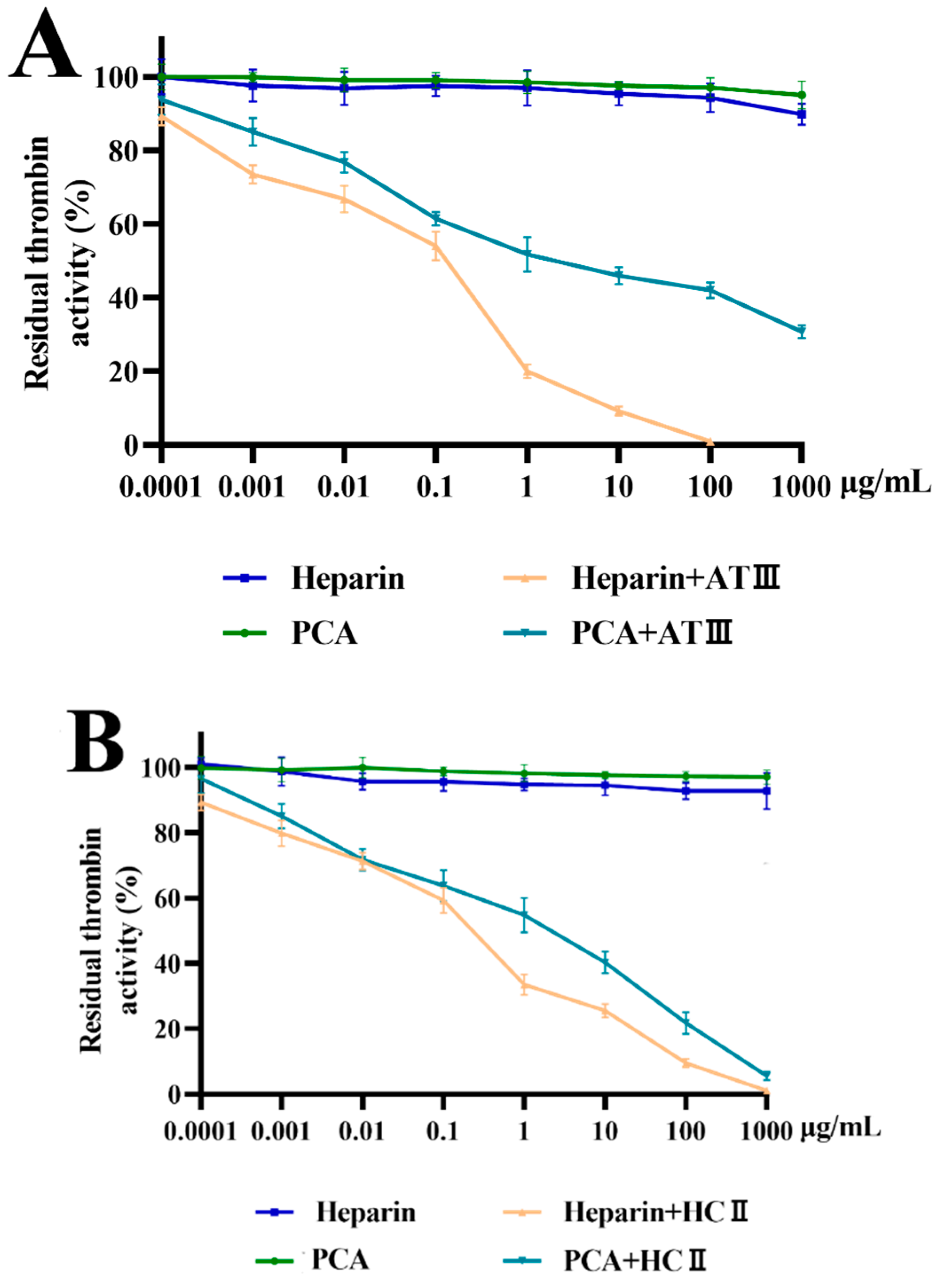
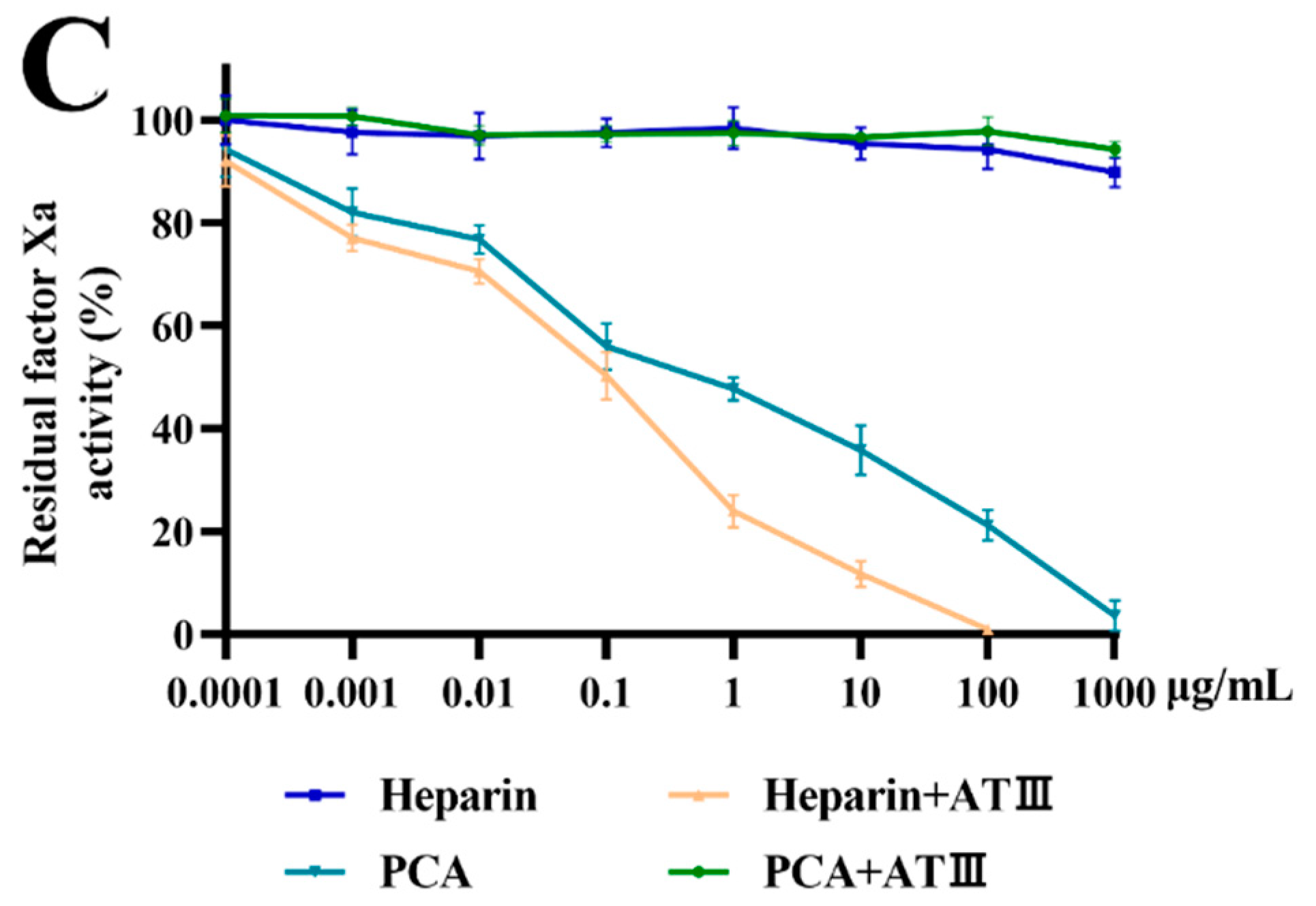
2.4. Effects of PCA on Thrombin and Factor Xa Inhibition Mediated by HCII or ATIII
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Isolation and Purification of the Sulfated Polysaccharide PCA
3.3. Assay of Physicochemical Property
3.4. Desulfation
3.5. Methylation Analysis
3.6. NMR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.7. Analysis of Anticoagulant Activity In Vitro
3.8. Animals
3.9. Determination of Anticoagulant Activity In Vivo
3.10. Assay of Coagulation Factor II, V, X, VIII, IX, XI, or XII Activity
3.11. Effects of PCA on Thrombin and Factor Xa Inhibition Mediated by ATIII or HCII
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akins, P.T.; Glenn, S.; Nemeth, P.M.; Derdeyn, C.P. Carotid artery thrombus associated with severe iron-deficiency anemia and thrombocytosis. Stroke 1996, 27, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H. Review: An overview about the structure-function relationship of marine sulfated homopolysaccharides with regular chemical structures. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesekara, I.; Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.K. Biological activities and potential health benefits of sulfated polysaccharides derived from marine algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasantharaja, R.; Stanley Abraham, L.; Gopinath, V.; Hariharan, D.; Smita, K.M. Attenuation of oxidative stress induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cytotoxicity in fibroblast cells by sulfated polysaccharide from Padina gymnospora. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassolato, J.E.F.; Noseda, M.D.; Pujol, C.A.; Pellizzari, F.M.; Damonte, E.B.; Duarte, M.E.R. Chemical structure and antiviral activity of the sulfated heterorhamnan isolated from the green seaweed Gayralia oxysperma. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 3085–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Liu, H.; Song, W.; Zhu, L.; Yin, X.Q. Polysaccharide from Caulerpa lentillifera: Extraction optimization with response surface methodology, structure and antioxidant activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 3417–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.R.; Pereira, M.S.; Fogue, D.; Mourao, P.A.S. Antithrombin-mediated anticoagulant activity of sulfated polysaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 20824–20835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolova, E.V.; Byankina, A.O.; Kalitnik, A.A.; Kim, Y.H.; Bogdanovich, L.N.; Soloveva, T.F.; Yermak, I.M. Influence of red algal sulfated polysaccharides on blood coagulation and platelets activation in vitro. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2014, 102, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, F.N.; Mou, R.R.; Zhang, Z.D.; Gao, N.; Lin, L.S.; Li, Z.K.; Wu, M.Y.; Zhao, J.H. Structural analysis and anticoagulant activities of three highly regular fucan sulfates as novel intrinsic factor Xase inhibitors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 195, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Y.; Wen, D.D.; Gao, N.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Xu, L.; Lian, W.; Peng, W.L.; Jiang, J.M.; Zhao, J.H. Anticoagulant and antithrombotic evaluation of native fucosylated chondroitin sulfates and their derivatives as selective inhibitors of intrinsic factor Xase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 92, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Pyun, Y.R.; Hwang, J.K.; Mourao, P.A.S. A sulfated fucan from the brown alga Laminaria cichorioides has mainly heparin cofactor II-dependent anticoagulant activity. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 2326–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, M.; Uehara, T.; Harada, N.; Sekiguchi, M.; Hiraoka, A. Heparinoid-active sulphated polysaccharidesfrom Monostroma nitidum and their distribution in the Chlorophyta. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 3611–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arata, P.X.; Quintana, I.; Canelon, D.J.; Vera, B.E.; Compagnone, R.S.; Ciancia, M. Chemical structure and anticoagulant activity of highly pyruvylated sulfated galactans from tropical green seaweeds of the order Bryopsidales. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, S.Y.; Cao, S.J.; He, X.X.; Qin, L.; He, M.J.; Yang, Y.J.; Hao, J.J.; Mao, W.J. Structural characteristics and anticoagulant property in vitro and in vivo of a seaweed sulfated rhamnan. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Mao, W.J.; Zhang, X.L.; Qi, X.H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Xu, J.; Zhao, C.Q.; Hou, Y.J.; Yang, Y.P. Structural characterization of an anticoagulant-active sulfated polysaccharide isolated from green alga Monostroma latissimum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 85, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, X.; He, X.X.; Wang, S.Y.; Cao, S.J.; Xia, Z.; Xian, H.L.; Qin, L.; Mao, W.J. Structure and anticoagulant property of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from the green seaweed Monostroma angicava. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 159, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Lee, J.B.; Srisomporn, P.; Maeda, M.; Ozawa, T.; Sakuragawa, N. Inhibition of thrombin by sulfated polysaccharides isolated from green algae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1543, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Mao, W.J.; Yan, M.X.; Liu, X.; Xia, Z.; Wang, S.Y.; Xiao, B.; Chen, C.L.; Zhang, L.F.; Cao, S.J. Structural characterization and anticoagulant activity of a sulfated polysaccharide from the green alga Codium divaricatum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; He, M.J.; Yang, Y.J.; Fu, Z.T.; Tang, C.C.; Shao, Z.L.; Zhang, J.Y.; Mao, W.J. Anticoagulant-active sulfated arabinogalactan from Chaetomorpha linum: Structural characterization and action on coagulation factors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 242, 116394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arata, P.X.; Quintana, I.; Raffo, M.P.; Ciancia, M. Novel sulfated xylogalactoarabinans from green seaweed Cladophora falklandica: Chemical structure and action on the fibrin network. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Yang, Y.J.; Hao, J.J.; He, X.X.; Liu, S.; Chu, X.; Mao, W.J. Antidiabetic-activity sulfated polysaccharide from Chaetomorpha linum: Characteristics of its structure and effects on oxidative stress and mitochondrial function. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surayot, U.; Lee, J.H.; Park, W.; You, S. Structural characteristics of polysaccharides extracted from Cladophora glomerata Kützing affecting nitric oxide releasing capacity of RAW 264.7 cells. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2016, 7, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.J.; Hao, J.J.; Feng, C.N.; Yang, Y.J.; Shao, Z.L.; Wang, L.; Mao, W.J. Anti-diabetic activity of a sulfated galactoarabinan with unique structural characteristics from Cladophora oligoclada (Chlorophyta). Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, A.P.; Gailani, D. The intrinsic pathway of coagulation as a target for antithrombotic therapy. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 1099–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, P.V.; Quintana, I.; Cerezo, A.S.; Caramelo, J.J.; Pol-Fachin, L.; Verli, H.; Estevez, J.M.; Ciancia, M. Anticoagulant activity of a unique sulfated pyranosic (1→3)-β-l-arabinan through direct interaction with thrombin. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclellan, D.S.; Jurd, K.M. Anticoagulants from marine algae. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1992, 3, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.J.; He, X.X.; Qin, L.; He, M.J.; Yang, Y.J.; Liu, Z.C.; Mao, W.J. Anticoagulant and antithrombotic properties in vitro and in vivo of a novel sulfated polysaccharide from marine green alga Monostroma nitidum. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.G.; Noseda, M.D.; Goncalves, A.G.; Ducatti, D.R.; Fujii, M.T.; Duarte, M.E. Chemical structure of the complex pyruvylated and sulfated agaran from the red seaweed Palisada flagellifera (Ceramiales, Rhodophyta). Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 347, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.A.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Chem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therho, T.T.; Hartiala, K. Method for determination of the sulfate content of glycosaminoglycans. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 41, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Nakashima, T.; Ueda, T.; Tomii, K.; Kouno, I. Facilediscrimination of aldose enantiomers by reversed-phase HPLC. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, I.J.; Blunt, J.W. Desulfation of algal galactans. Carbohydr. Res. 1998, 309, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.J.; Henry, R.J.; Blakeney, A.B.; Stone, B.A. An improved procedure for the methylation analysis of oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Res. 1984, 127, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourao, P.A.S.; Pereira, M.S.; Pavao, M.S.G.; Mulloy, B.; Tollefsen, D.M.; Mowinckel, M.C. Structure and anticoagulant activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from echinoderm-sulfated fucose branches on the polysaccharide account for its high anticoagulant action. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23973–23984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackie, I.J.; Lawrie, A.S.; Kitchen, S.; Gaffney, P.J.; Howarth, D.; Lowe, G.D.O. A performance evaluation of commercial fibrinogen reference preparations and assays for clauss and PT-derived fibrinogen. Thromb. Haemost. 2002, 87, 997–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, O.; Hiraga, K. Haemorrhagic toxicosis in rats given butylated hydroxytoluene. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1981, 49, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H. Anticoagulant motifs of marine sulfated glycans. Glycoconj. J. 2014, 31, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Methylated Alditol Acetate | Molar Percent Ratio | Linkage Pattern | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCA | dsPCA | ||
| 1,5-Di-acetyl-2,3,4-tri-O-methyl-arabinitol | 3.96 | 3.08 | Arap-(1→ |
| 1,4-Di-acetyl-2,3,5-tri-O-methyl-arabinitol | 6.18 | 6.13 | Araf-(1→ |
| 1,4,5-Tri-acetyl-2,3-di-O-methyl-arabinitol | 28.21 | 50.98 | →4)-Arap-(1→/→5)-Araf-(1→ |
| 1,3,4,5-Tetra-acetyl-2-O-methyl-arabinitol | 24.00 | - a | →3,4)-Arap-(1→ |
| 1,2,4,5-Tetra-acetyl-3-O-methyl-arabinitol | 10.77 | 10.89 | →2,4)-Arap-(1→/→2,5)-Araf-(1→) |
| 1,5,6-Tri-acetyl-2,3, 4-tri-O-methyl-galactitol | - a | 16.98 | →6)-Galp-(1→ |
| 1,4,5-Tri-acetyl-2,3, 6-tri-O-methyl-galactitol | 10.81 | 11.00 | →4)-Galp-(1→ |
| 1,4,5,6-Tetra-acetyl-2,3-di-O-methyl-galactitol | 16.88 | - a | →4,6)-Galp-(1→ |
| Residues | Chemical Shifts (ppm) a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1/C1 | H2/C2 | H3/C3 | H4/C4 | H5/C5 | H6/C6 | ||
| A | →4)-β-d-Galp-(1→ | 4.49/105.02 | 3.38/74.70 | 3.83/69.95 | 4.20/77.82 | 3.86/72.38 | 3.80/62.10 |
| B | →2,5)-α-l-Araf-(1→ | 5.07/109.43 | 4.09/84.30 | 4.08/78.74 | 4.10/82.57 | 3.92/71.05 | |
| C | →4)-β-l-Arap-(1→ | 5.13/97.96 | 4.01/69.99 | 4.14/69.89 | 4.10/76.97 | 3.85/61.60 | |
| D | →6)-α-d-Galp-(1→ | 5.19/98.28 | 4.19/72.32 | 3.68/72.46 | 4.03/69.52 | 3.89/69.75 | 3.70/65.12 |
| E | →5)-α-l-Araf-(1→ | 5.24/110.76 | 4.50/82.28 | 4.08/78.74 | 4.20/82.84 | 3.92/71.05 | |
| F | →2,4)-β-l-Arap-(1→ | 5.25/97.96 | 4.01/75.86 | 4.25/68.38 | 4.10/76.97 | 3.85/61.09 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, L.; Yang, Y.; Mao, W. Anticoagulant Property of a Sulfated Polysaccharide with Unique Structural Characteristics from the Green Alga Chaetomorpha aerea. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020088
Qin L, Yang Y, Mao W. Anticoagulant Property of a Sulfated Polysaccharide with Unique Structural Characteristics from the Green Alga Chaetomorpha aerea. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(2):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020088
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Ling, Yajing Yang, and Wenjun Mao. 2023. "Anticoagulant Property of a Sulfated Polysaccharide with Unique Structural Characteristics from the Green Alga Chaetomorpha aerea" Marine Drugs 21, no. 2: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020088
APA StyleQin, L., Yang, Y., & Mao, W. (2023). Anticoagulant Property of a Sulfated Polysaccharide with Unique Structural Characteristics from the Green Alga Chaetomorpha aerea. Marine Drugs, 21(2), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21020088