Abstract
Crustins are a kind of antimicrobial peptide (AMP) that exist in crustaceans. Some crustins do not have direct antimicrobial activity but exhibit in vivo defense functions against Vibrio. However, the underlying molecular mechanism is not clear. Here, the regulatory mechanism was partially revealed along with the characterization of the immune function of a type I crustin, LvCrustin I-2, from Litopenaeus vannamei. LvCrustin I-2 was mainly detected in hemocytes, intestines and gills and was apparently up-regulated after Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Although the recombinant LvCrustin I-2 protein possessed neither antibacterial activity nor agglutinating activity, the knockdown of LvCrustin I-2 accelerated the in vivo proliferation of V. parahaemolyticus. Microbiome analysis showed that the balance of intestinal microbiota was impaired after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown. Further transcriptome analysis showed that the intestinal epithelial barrier and immune function were impaired in shrimp after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown. After removing the intestinal bacteria via antibiotic treatment, the phenomenon of impaired intestinal epithelial barrier and immune function disappeared in shrimp after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown. This indicated that the impairment of the shrimp intestine after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown was caused by the dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota. The present data suggest that crustins could resist pathogen infection through regulating the intestinal microbiota balance, which provides new insights into the functional mechanisms of antimicrobial peptides during pathogen infection.
1. Introduction
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are a kind of immune effectors in innate immunity, which play essential functions in the immune defense of numerous organisms [1]. AMPs also present multiple functions including immune pathway activation, cytokine induction, endotoxin neutralization and microbiota modulation [2,3,4,5]. In invertebrates, due to the lack of adaptive immunity, the production of AMPs is an important strategy for defending against pathogens and regulating the host microbiota [6,7,8].
In crustaceans, different AMP families, including penaeidins, crustins, ALFs, etc., have been identified and characterized [9]. Crustins contain a whey acidic protein (WAP) domain and exhibit broad-spectrum activities against various microorganisms [10]. Since the first crustin gene was isolated from the hemocytes of Carcinus maenas, a variety of crustin genes have been identified in different crustaceans, including shrimp, crab, lobster, crayfish, etc. [11,12,13,14]. Crustins are classified into seven types of which type V is only found in insects and other types exist in crustaceans [15,16].
To date, the reported diverse types of crustins show different antimicrobial functions. Type I crustins show antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, and weak activity against yeasts [9,17]. Type II, type III and type IV crustins show activities against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria [9,17,18]. Some crustins not only exhibit strong antimicrobial activities in vitro but also show immune defense function in vivo during pathogen infection [19,20].
Besides their direct antimicrobial activities against various microorganisms, other functions have been reported. A type III crustin from L. vannamei shows protease inhibition activity [21]. A type I crustin accumulates in damaged tissues in C. maenas, indicating a probable role in wound healing and tissue regeneration [22]. One type VII crustin from L. vannamei not only has antimicrobial activities against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria but also enhances hemocyte phagocytosis [23]. The expression of a type II crustin in Rimicaris exoculata spatiotemporally correlates with the establishment of ectosymbiotic microbiota [24]. The silencing of a gill-abundant type II crustin in L. vannamei results in a change in the proportion of the bacterial population in the gill microbiota [25].
Despite the multiple functions of crustins, knowledge about how they defend against pathogen infection in vivo is still limited. Previously, a type I crustin with an atypical WAP domain exhibited an intestinal microbiota-modulating function, and the knockdown of this gene accelerated the infection of V. parahaemolyticus [26]. However, the underlying molecular mechanism of how crustins affect the AHPND pathogenetic process is still unclear.
In the present study, we have characterized the function of a new type I crustin gene from L. vannamei, named LvCrustin I-2. The in vivo and in vitro activities and their effects on intestinal immune function and microbiota balance in shrimp were studied. The results suggest that LvCrustin I-2 plays important roles in maintaining the intestinal health of the shrimp by keeping the balance of microbiota, which will provide new clues for understanding the molecular mechanisms of AMPs modulating the outbreak of AHPND in shrimp aquaculture.
2. Results
2.1. LvCrustin I-2 Involved in Immune Defense during V. parahaemolyticus Infection
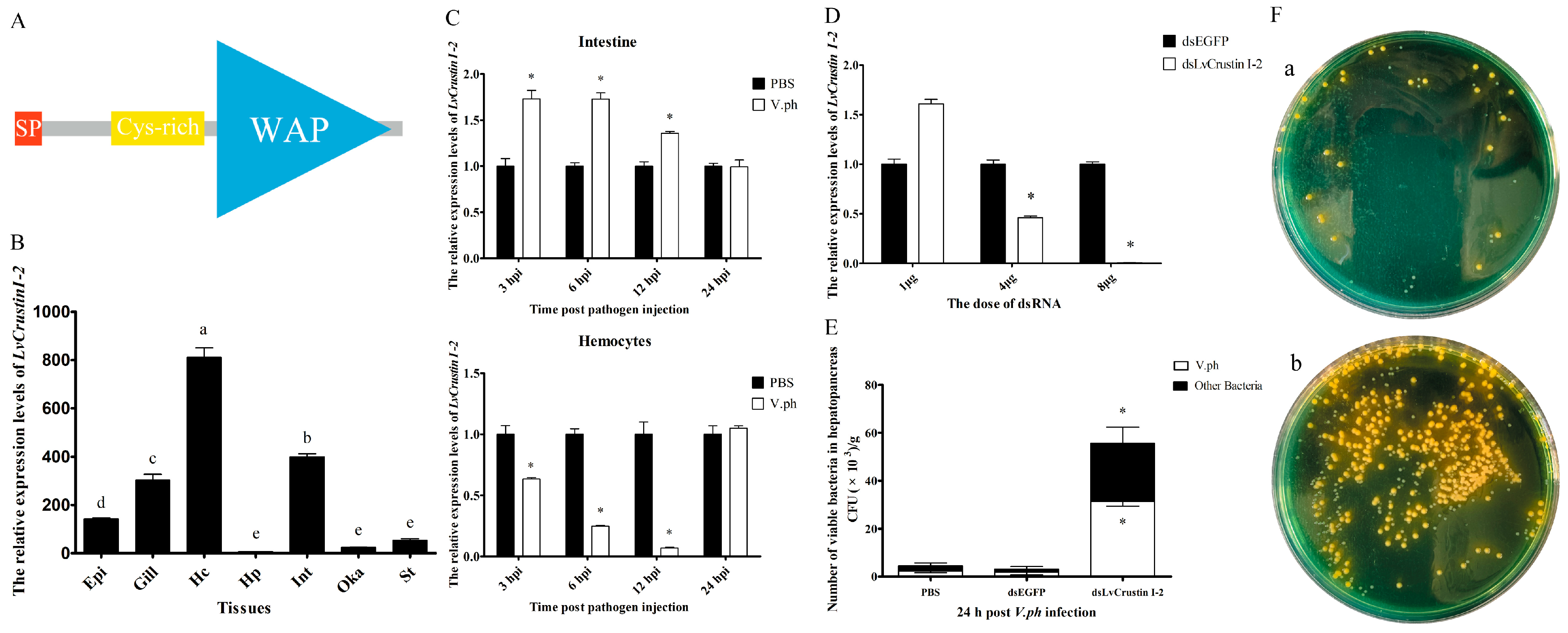
The cDNA sequence of LvCrustin I-2 (accession number: MT375558.1) contained a 345 bp open reading frame encoding 114 deduced amino acid (aa) residues (Figure S1). According to the protein sequence, which contains a 19-aa signal peptide, a cysteine-rich region (Cys31~Cys45) and a 51-aa whey acidic protein (WAP) domain (Lys58-Ser108), LvCrustin I-2 was classified as a type I crustin (Figure 1A). Tissue distribution analysis showed that LvCrustin I-2 had the highest expression level in hemocytes, followed by the intestine, gill and epidermis and a relatively low expression level in the stomach, Oka and hepatopancreas (Figure 1B).
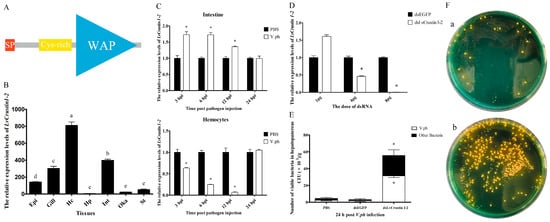
Figure 1.
Characterization of the immune function of LvCrustin I-2 in shrimp during V. parahaemolyticus infection. (A) Schematic illustration of the primary structure of LvCrustin I-2. SP, Cys-rich and WAP presented the signal peptide, cysteine-rich region, and whey acidic protein domain, respectively. (B) Tissue distribution of LvCrustin I-2 transcripts. Epi, epidermis; Hc, hemocytes; Hp, hepatopancreas; Int, intestine; Oka, lymphoid organ; St, stomach. Vertical bars represented mean ± S.E. Letters “a”, “b”, “c”, “d” and “e” represented significant differences among treatments at p < 0.05. (C) Time-course expression pattern of LvCrustin I-2 after V. parahaemolyticus challenge in intestine and hemocytes: 3, 6, 12 and 24 hpi indicate 3 h, 6 h, 12 h and 24 h after pathogen injection. Significant differences between treatment and control groups are labeled with a star at p < 0.05. (D) Silencing efficiency of LvCrustin I-2 dsRNA in different dosages. The optimal silencing dose is marked with a star at p < 0.05. (E) The total viable bacteria count in hepatopancreas of LvCrustin I-2 silenced shrimp after V. parahaemolyticus infection. The data were obtained from three independent repeats with three individuals per sample. Significant differences between treatment and control groups are labeled with a star at p < 0.05. (F) Spread plates of hepatopancreas homogenate of shrimp infected with V. parahaemolyticus after dsEGFP injection (a) or dsLvCrustin I-2 injection (b).
The time-course expression pattern of LvCrustin I-2 was analyzed in the hemocytes and intestine of shrimp after V. parahaemolyticus challenge. The expression level of LvCrustin I-2 was up-regulated by 1.73-fold, 1.73-fold and 1.35-fold in intestine at 3, 6 and 12 hpi, respectively. However, it decreased to 0.64-fold, 0.25-fold and 0.07-fold in hemocytes at 3, 6 and 12 hpi (Figure 1C).
RNAi was used to investigate the immune function of LvCrustin I-2 during V. parahaemolyticus infection. The interference efficiency of LvCrustin I-2 was 54% and 99.16% at the dosages of 4 μg and 8 μg dsRNA per shrimp, respectively (Figure 1D). Therefore, the dosage of 8 μg dsRNA per shrimp was used to study the immune function of LvCrustin I-2. The number of bacteria in the hepatopancreas could reflect the health status of shrimp. To study the impact of LvCrustin I-2 silencing on the V. parahaemolyticus infection process, the amount of Vibrio in the hepatopancreas of LvCrustin I-2-silenced shrimp was detected. After LvCrustin I-2 knockdown, the amount of total viable V. parahaemolyticus in hepatopancreas was 3.15 × 104 cfu/g, which was significantly higher than those from the PBS group (2.34 × 103 cfu/g) and dsEGFP group (1.82 × 103 cfu/g) (Figure 1E). In addition, the amount of other viable bacteria, including V. harveyi and P. damselae, was also higher in LvCrustin I-2-silenced shrimp (2.41 × 104 cfu/g) than those from the PBS group (2.11 × 103 cfu/g) and dsEGFP group (1.36 × 103 cfu/g) (Figure 1E).
To further study the immune function of LvCrustin I-2, in vitro activities were analyzed. The recombinant protein (rLvCrustin I-2) was expressed in E. coli with a predicted molecular mass of 28.53 kDa (Figure S2, lanes 1 and 2). rLvCrustin I-2 was mainly produced in a soluble form (Figure S2, lines 3 and 4) and then purified (Figure S2, lane 5). The MIC assay and microorganism-binding assay showed that rLvCrustin I-2 had no antibacterial activity (Table S1) or binding activity (Figure S2) on pathogens, including V. parahaemolyticus, V. harveyi and P. damselae. A further agglutination test showed that rLvCrustin I-2 had no agglutinating activity to V. parahaemolyticus (Figure S3).
2.2. Imbalance of the Intestinal Microbiota after LvCrustin I-2 Knockdown
The microbiota between the PBS group and dsEGFP group were first compared. The alpha diversity analysis showed there was no significant difference in all the alpha indexes including Ace, Chao1, Simpson and Shannon through Welch’s t-test (p-values were 0.92, 0.62, 0.71 and 0.96, respectively) or by Wilcoxon rank test (p-values were 1, 0.7, 0.7 and 0.7, respectively). The beta diversity analysis showed that the inter-group difference between the PBS group and dsEGFP group was less than the intra-group difference, as compared by the ANOSIM test (p-value was 0.2) and ADONIS test (p-value was 0.4). To facilitate the subsequent analysis, we combined the samples from the PBS group and dsEGFP group into the “control group”.
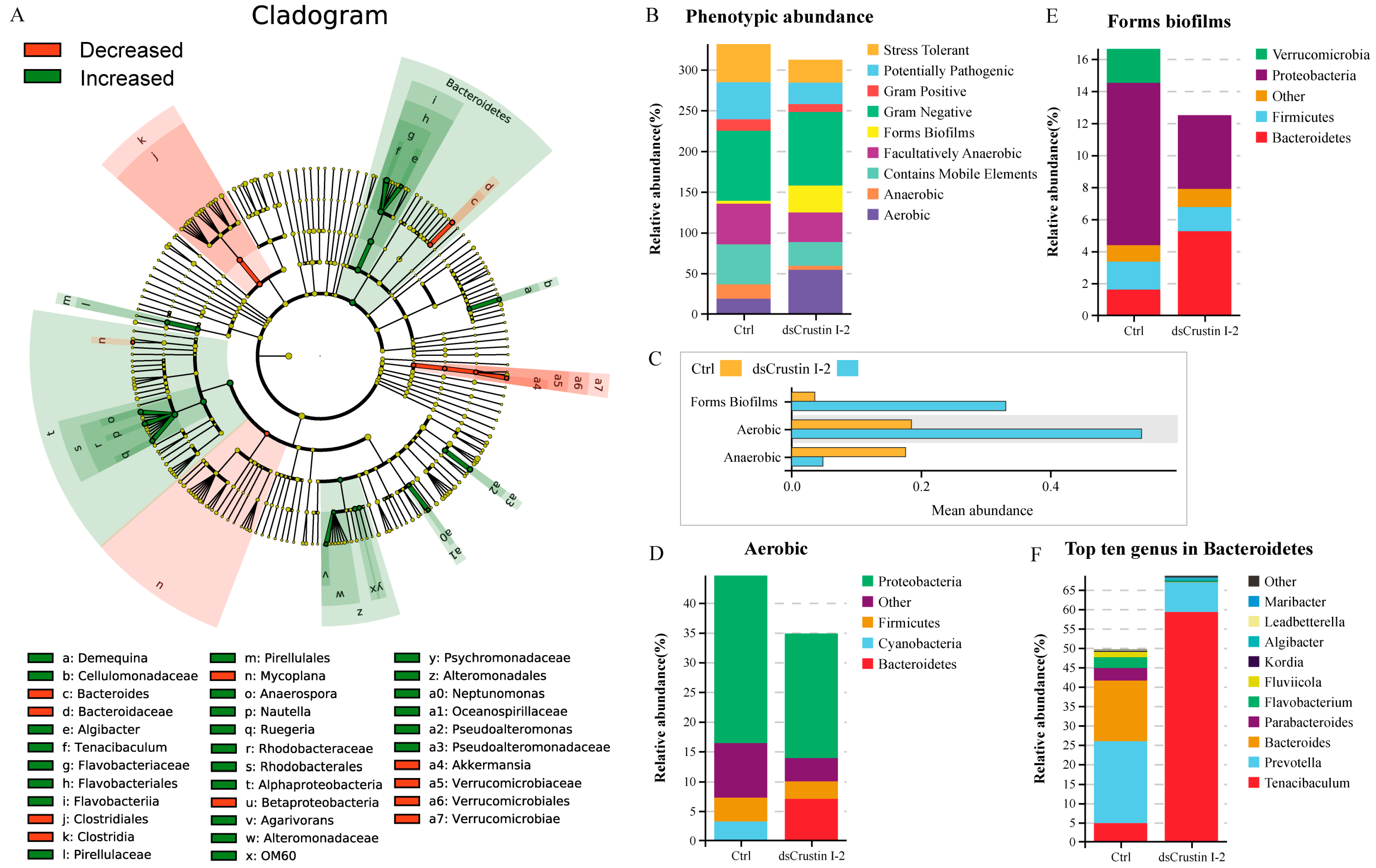
The alpha diversity analysis showed that the Ace index increased from 785.58 in the control group to 876.86 in the dsLvCrustin I-2 group (Table S2). However, the Chao1 index, Simpson index and Shannon index had no significant change (Table S2). The result of principal co-ordinate analysis (PCoA) based on weighted UniFrac distance showed that the samples in the dsLvCrustin I-2 group and the control group could be obviously divided into two clusters through ADONIS analysis (Figure S4, p-value is 0.023). After LvCrustin I-2 knockdown, the proportion of bacteria at different taxonomic levels significantly changed in the intestinal microbiota of shrimp (Figure 2A and Figure S5). Among the top ten genera, the proportion of Tenacibaculum, Anaerospora, Nautella and Pseudoalteromonas increased from 0.30%, 0.12%, 0.39% and 0.22% to 9.11%, 2.9%, 1.83% and 4.23%, respectively (Figure S5E and Figure 2A, f, o, p and a2), followed by Demequina, Algibacter, Ruegeria, Agarivorans and Neptunomonas (Figure 2A, a, e, q, v and a0). However, the proportion of Bacteroides, Mycoplana and Akkermansia significantly decreased (Figure 2A, c, n and a4).
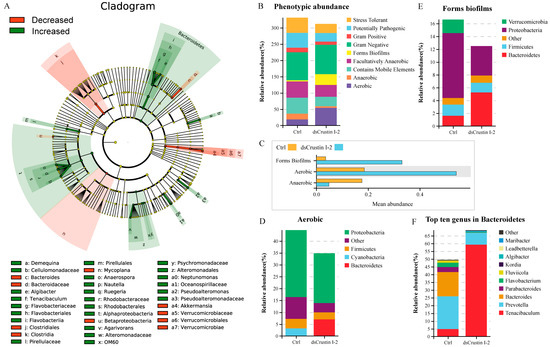
Figure 2.
Intestinal microbiota analysis in shrimp after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown. (A) LEFse analysis of the intestinal microbiota of the control group and dsLvCrustin I-2 group. The green and red colors indicate increased and decreased bacteria in different taxa, respectively. The “Decreased” indicate the bacteria have higher proportion in the control group than that in the dsLvCrustin I-2 group. The “Increased” indicate the bacteria have higher proportion in the dsLvCrustin I-2 group than that in the control group. (B) Predicted functional profile of intestinal microbial community was classified into nine phenotypes. (C) Mean abundance of phenotypes at p < 0.05. (D) Relative abundance of different phyla in biofilm-forming phenotype. (E) Relative abundance of different phyla in aerobic phenotype. (F) Top ten genera in Bacteroidetes.
The functional profile of the intestinal microbial community was predicted. The intestinal microbiota was classified into nine phenotypes. The proportions of biofilm-forming and aerobic bacteria were significantly higher in the dsLvCrustin I-2 group (Figure 2B,C), which was attributed to the abundance of Bacteroidetes (Figure 2D,E). Whereas the proportion of anaerobic bacteria was significantly higher in the control group (Figure 2B,C). Therefore, we further analyzed the bacteria in Bacteroidetes. Among the top ten genera in Bacteroidetes, Tenacibaculum and Algibacter were also the biomarkers of the dsLvCrustin I-2 group (Figure 2A, f and e). The proportions of Tenacibaculum and Algibacter in Bacteroidetes increased from 4.83% and 0.03% to 59.26% and 0.50%, respectively, after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown (Figure 2F).
2.3. Dysfunction of the Intestinal Epithelium after LvCrustin I-2 Knockdown
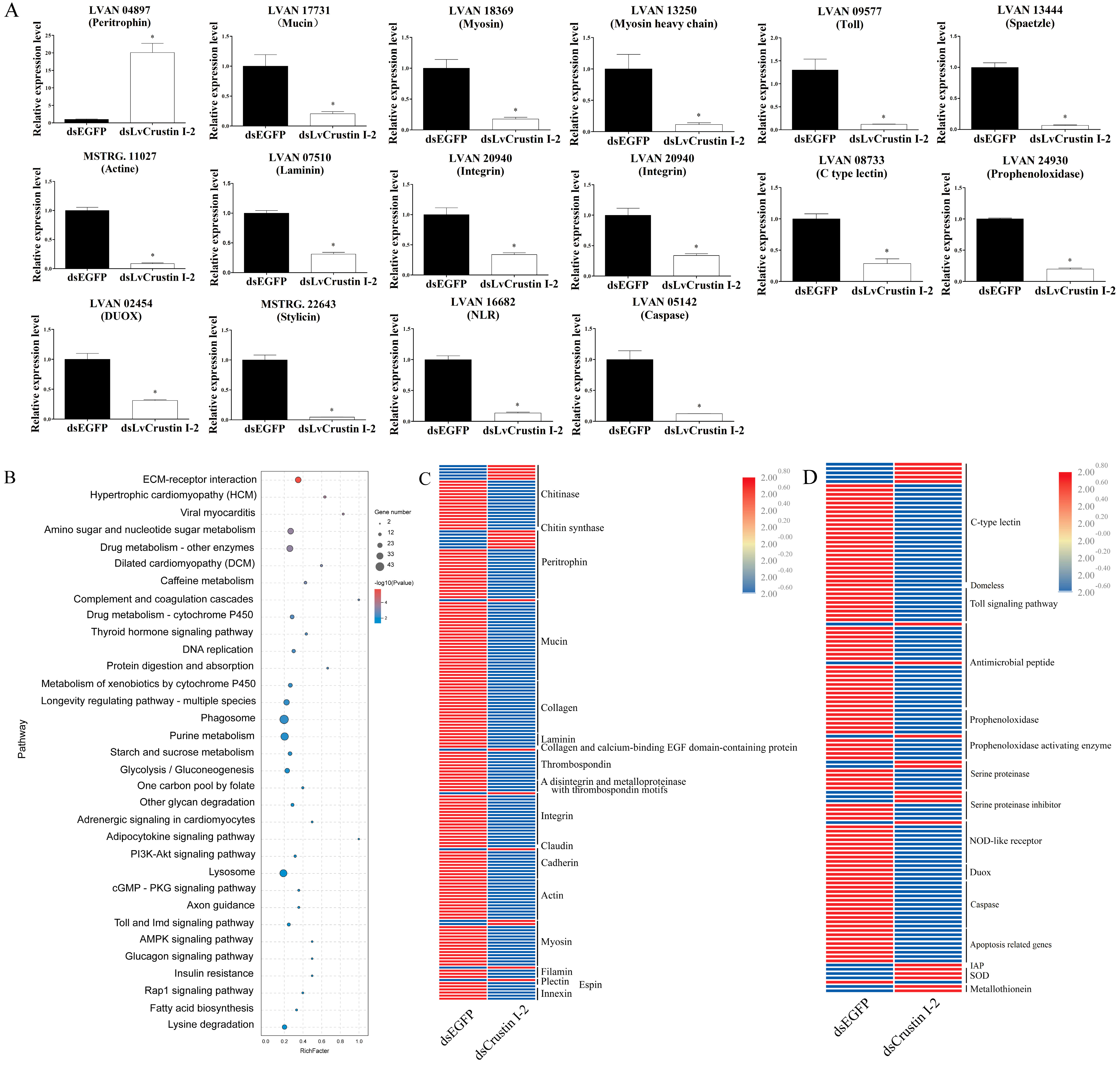
In order to further investigate the functional mechanism of LvCrustin I-2, the intestinal transcriptomes of shrimp before and after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown were compared. Detailed information on the sequencing and assembly of the intestinal transcriptome is shown in Table S3. A total of 3329 DEGs were obtained, including 2396 differentially down-regulated genes (DDGs) and 933 differentially up-regulated genes (DUGs) in the dsLvCrustin I-2 group. QPCR analysis of 16 selected DEGs showed that they were all consistent with the transcriptome data (Figure 3A).
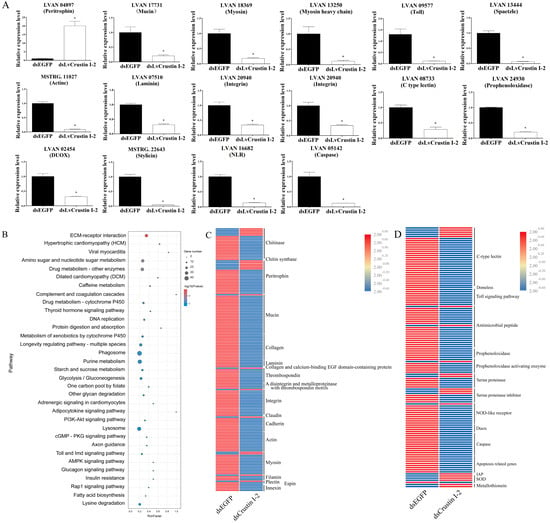
Figure 3.
(A) Real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis of candidate genes. The expression levels of these genes are presented as mean ± S.D. The gene 18S rRNA was used as the reference gene. The expression levels are all obtained from three biological replicates. Star (*) indicates statistical difference between dsLvCrustin I-2 group and dsEGFP group (One-way ANOVA, p < 0.05). The accession numbers of these selected genes are shown in Tables S3 and S4. (B) KEGG pathway enrichment analysis. “GeneNumber” represents the number of DEGs enriched in certain pathways. “p value” is the value obtained via hypergeometric test to define the significance of enriched pathways, and its colors represent the significance from low (blue) to high (red). (C) The DEGs involved in intestinal epithelial barrier integrity. (D) The DEGs involved in immune and oxidative stress. The colors represent the relative expression levels from low (blue) to high (red).
KEGG analysis showed that many enriched pathways were associated with cell and extracellular matrix interactions, including “ECM-receptor interaction”, “Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)”, “Viral myocarditis” and “Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM)” (Figure 3B). The genes in these pathways, including integrin, actin, myosin and many components of the extracellular matrix, were associated with the cell morphology and structural integrity of the intestinal epithelial barrier. Pathways including the “Toll and Imd signaling pathway”, “Phagosome” and “Lysosome” were associated with the immune and oxidized stress responses of shrimp. KEGG analysis also identified many DEGs related to intestinal epithelial barrier integrity, immunity and the oxidized stress response (Tables S4 and S5). Most of the DEGs involved in cell junction and adhesion and enterocyte microvilli structure were significantly down-regulated in the dsLvCrustin I-2 group (Figure 3C). Most of the DEGs involved in immune responses and cell apoptosis were also significantly down-regulated in the dsLvCrustin I-2 group, while the apoptosis-inhibiting related genes and antioxidant genes were significantly up-regulated (Figure 3D).
2.4. Epithelial Function Was Not Impaired in LvCrustin I-2-Silenced Shrimp after Removing Intestinal Microbiota
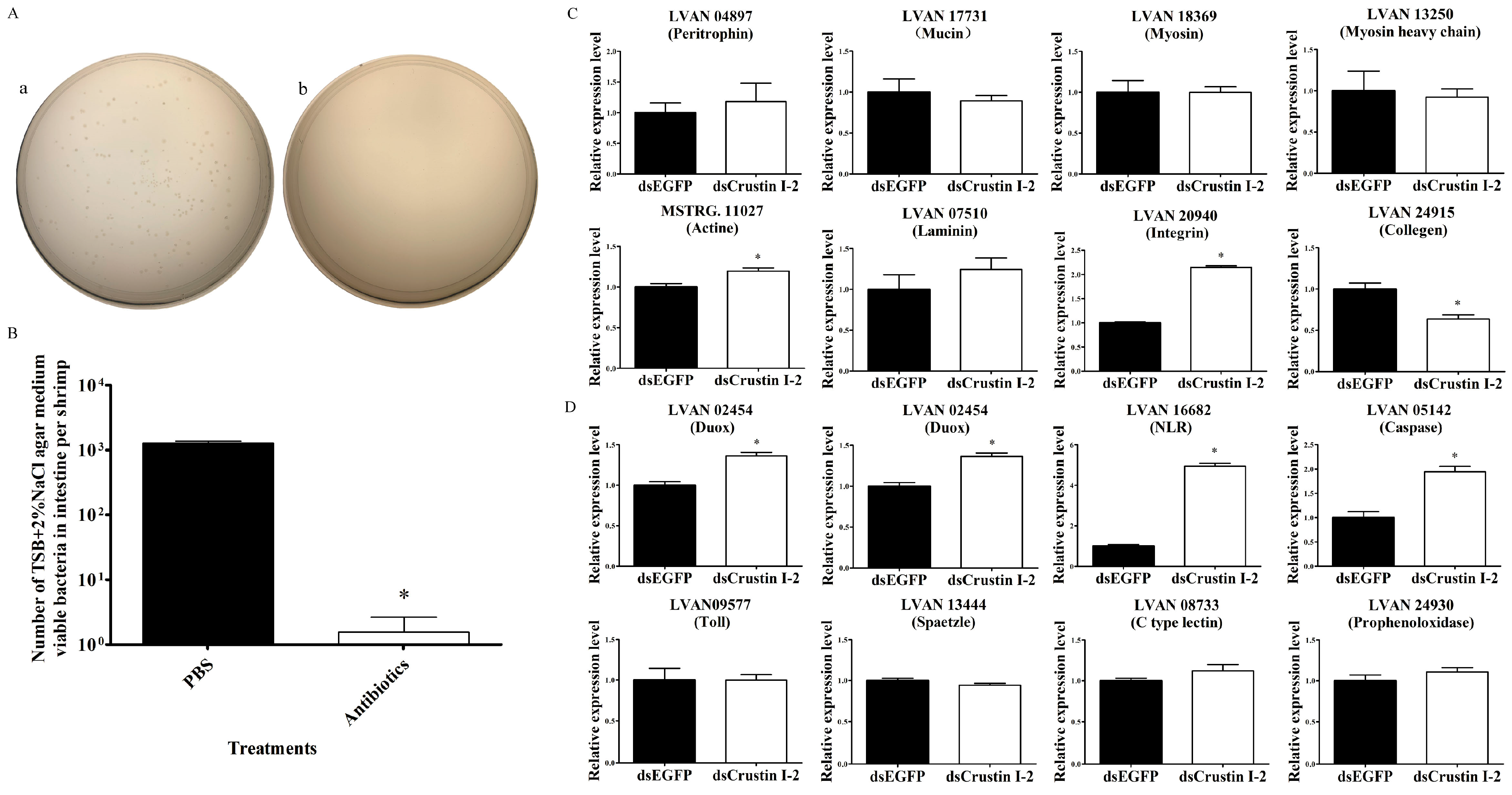
In order to find out the causal relationship between the epithelial functional impairment and microbiota imbalance in the intestine after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown, expression profiles of DEGs related to intestinal function were tested in shrimp after removing intestinal microorganisms. At 48 h after the last reverse perfusion, the TSB+2%NaCl agar medium viable bacteria dramatically decreased from 7.66 × 106 cfu/g (1275.56 bacteria per shrimp) to 9.33 × 103 cfu/g (1.56 bacteria per shrimp) (Figure 4A,B). After removing intestinal microorganisms, LvCrustin I-2 knockdown did not affect the expression of most of the intestinal epithelial barrier-related genes, including peritrophin, mucin, myosin, myosin heavy chain and laminin (Figure 4C). Some immune-related genes, including Duox, stylicine, NLR and caspase, were even upregulated after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown (Figure 4D).
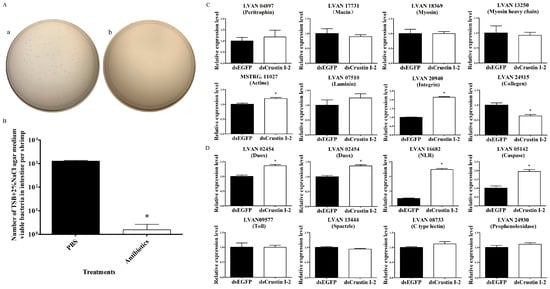
Figure 4.
Detection of intestinal epithelial barrier and immune-related genes in shrimp after removing intestinal microorganisms and LvCrustin I-2 knockdown. (A) Spread plates of intestine homogenate of shrimp. (a) Intestine homogenate of PBS buffer-treated shrimp. (b) Intestine homogenate of antibiotic-treated shrimp. (B) Total viable bacteria counts in intestines of shrimp treated with PBS buffer or antibiotics. The data were obtained from three independent repeats with three individuals per sample. Significant differences between treatment and control groups are labeled with a star at p < 0.05. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of intestinal epithelial barrier-related genes. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of immune-related genes. The expression levels of these genes are presented as mean ± S.D. The gene 18S rRNA was used as the reference gene. The expression levels were all obtained from three biological replicates. Star (*) indicates statistical difference between the dsLvCrustin I-2 group and dsEGFP group (One-way ANOVA, p < 0.05).
3. Discussion
Many crustacean AMPs have been reported to regulate pathogen infection through direct antimicrobial activity. The knockdown of AMPs with antibacterial activity against the pathogens led to an increase in bacterial count in tissues or a higher mortality rate after infection [27,28,29]. In the present study, the knockdown of LvCrustin I-2 accelerated the propagation of V. parahaemolyticus and other viable bacteria in the hepatopancreas of infected shrimp. However, LvCrustin I-2 did not show antibacterial activity or agglutinating activity against the pathogenic bacteria V. parahaemolyticus. Therefore, the in vivo inhibition of LvCrustin I-2 on V. parahaemolyticus propagation might be attributed to its influence on the host defense and microbial balance of target tissues.
In addition to direct antimicrobial activity, AMPs also play a major role in regulating the balance between homeostasis and pathogenesis in crustaceans [9]. The interaction between internal microorganisms and the host immune system is essential to the health and survival of crustaceans [30]. The silencing of AMP genes led to an increase in the internal bacteria in tissues and resulted in crustacean death [31,32]. The expression of AMPs affects not only the amount but also the composition of bacteria in tissues of crustaceans [25]. In the present study, the intestinal microbiota composition significantly changed in shrimp after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown. The proportion of potentially pathogenic bacteria, including Tenacibaculum, Nautella and Demequina [33,34,35,36], significantly increased in shrimp after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown.
Stability and diversity are essential to a healthy intestinal microbial community [37]. A change in composition may affect the function of the microbial community. The proportion of strictly anaerobic bacteria and aerobe bacteria is an indicator of healthy intestinal microbiota [38]. The overgrowth of aerobe bacteria is independently linked with intestinal diseases [39]. In addition, the formation of biofilm facilitates pathogens’ resistance against the host immune system [40]. In our results of functional prediction, the high abundance of biofilm-forming and aerobic bacteria in shrimp after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown was attributed to the abundance of Bacteroidetes. Among the top ten genera in Bacteroidetes, the proportion of Tenacibaculum in the LvCrustin I-2 knockdown group was significantly higher than that in the control group. Tenacibaculum is a kind of pathogen that infects various marine organisms [33,41]. To date, there is no direct evidence showing that Tenacibaculum is a kind of shrimp pathogen. However, in the intestine of “cotton shrimp-like” diseased shrimp, the Tenacibaculum levels significantly increased, along with the down-regulated expression of immune genes [42]. In addition, many recent studies have shown that the supplementation of probiotics decreases the proportion of Tenacibaculum in the microbiota and improves intestinal health, the immune response and resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection [43,44,45]. Therefore, we considered Tenacibaculum to have an important role in microbiota dysbiosis and to be an indicator of the intestinal health of shrimp.
Intestinal dysbiosis can result in adverse effects on the host’s health [46]. The controlled production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is an important way for regulating intestinal microorganisms and the induction of epithelial renewal and immune response in invertebrates [47,48]. However, an excessive ROS level could be deleterious and trigger oxidative stress, which damages the epithelial barrier along with pathogenic bacteria invasion [49]. In the present study, the up-regulated expression of antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and metallothionein implied that more ROS was probably produced in the intestine of shrimp after LvCrustin I-2 knockdown. It was reported that the high ROS level could inhibit the expression of Duox in shrimp [50]. The down-regulation of Duox and apoptosis-related genes as well as the up-regulation of inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP) indicated the suppression of ROS production and apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells. Consequently, we speculated that the suppression of ROS production and apoptosis caused by the negative regulation of organisms was due to the excessive ROS level.
The integrity of the intestinal barrier, which includes the basal lamina, intestinal epithelium, mucus and peritrophic matrix, is important for maintaining the functions of the intestine in invertebrates [51]. After LvCrustin I-2 knockdown, genes involved in the intestinal epithelial barrier and immune response were down-regulated, indicating that the integrity and function of the intestinal barrier were impaired. Pathogens could disrupt or cross the barriers and cause infection by interacting with and manipulating components of epithelial barriers [52]. The impairment of the epithelial barrier and immune function may facilitate V. parahaemolyticus crossing the intestinal epithelium of shrimp and accelerate the infection progress.
As one kind of immune effector, crustins are the downstream molecules of immune signaling pathways. It is interesting to know why the knockdown of a single downstream gene could cause such a high level of gene expression changes. According to the above analysis, we proposed a hypothesis that the knockdown of LvCrustin I-2 influenced the intestinal microorganisms, and then the rupture of gut homeostasis by the microorganisms induced excessive ROS production and damaged the integrity of the intestinal barrier. In order to prove the hypothesis, the LvCrustin I-2 RNAi assay was performed in antibiotic-treated shrimp. After intestinal bacteria were removed, the knockdown of LvCrustin I-2 did not lead to a wide down-regulation of the intestinal epithelial barrier or immune-related genes, indicating the impairment of the epithelial barrier and immune function was directly caused by the dysbiotic microbiota.
In humans, intestinal dysbiosis is associated with host health and raises the risk of developing diseases [53,54]. In aquatic invertebrates, dysbiosis also leads to diseases. Dysbiosis was detected in the sea cucumber with skin ulceration syndrome due to a decrease in microbiota diversity [55]. The dysbiosis in the host intestinal microbiota played the causative role in the occurrence of shrimp white feces syndrome [56]. A study showed dysbiotic microbiota associated with an early development of AHPND [57]. To date, studies on the pathogenesis of AHPND have made progress [58,59]. However, it is still largely unknown how V. parahaemolyticus and the toxin migrated into the hepatopancreas. Many researchers have proposed hypotheses in response to this question [60]. A comprehensive model that incorporated dysbiotic microbiota was proposed by Kumar [61]. In this model, the entry of V. parahaemolyticus leads to dysbiosis of the microbiota, which enables the pathogen to further replicate and colonize, which in turn causes inflammation and an increased immune response. At the same time, the Rho pathway is activated by an unknown mechanism, which causes disruption of the cell junctions and disintegrates the epithelial barrier. In the present study, the dysbiotic microbiota impaired epithelial barrier function, which provided experimental evidence for the “unknown mechanism” in Kumar’s model.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Tissue Collection
Experimental shrimp L. vannamei with an average body length of 6.56 ± 0.54 cm and body weight of 3.42 ± 0.70 g obtained from Xingguang Marine Ranch Fishery Co., Ltd (Rizhao, Shandong, China). were cultured in our aquarium with aerated seawater at 25 °C and 27‰ salinity and fed with sterile commercial feed (DaLe, Yantai, Shandong, China) more than two months before being used. To paralyze and kill the shrimp, the nerves were cut off and the cephalothoraxes were removed. Tissues including lymphoid organ (Oka), hepatopancreas, intestine, stomach, gills, and epidermis from 12 shrimp were collected. Hemolymph was drawn and centrifuged at 800× g, 4 °C for 10 min to collect hemocytes. Each kind of tissue contained three samples, and each sample included the same tissues from 15 individuals. All the samples were stored at −80 °C for detection of the expression levels of the target genes.
4.2. Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis
Total RNA from 100 mg tissue sample was extracted using RNAiso Plus reagent (TaKaRa, kusatsu, Shiga, Japan). The concentration and quality of RNA samples were assessed using Nanodrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel. The first-strand cDNA was synthesized using PrimeScript™ RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (TaKaRa, kusatsu, Shiga, Japan).
Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) was performed to detect the expression levels of LvCrustin I-2 in different samples with primers qLvCrustin I-2-F and qLvCrustin I-2-R (Table S6). A pair of primers, 18S-F/R (Table S6), was designed to amplify 18S rRNA, which was used as an internal reference gene. The program of qPCR was set as follows: 95 °C for 1 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15 s, at the annealing temperature for 15 s, 72 °C for 30 s, and a melting curve analysis was used to verify the specificity of the product. The data were processed using 2−ΔΔCT method [62].
4.3. Gene Cloning and Sequence Analysis
The cDNA sequence of LvCrustin I-2 was obtained from a transcriptome database of L. vannamei [63]. Primers LvCrustin I-2-F and LvCrustin I-2-R were synthesized to amplify the open reading frame (ORF) sequence of LvCrustin I-2. The PCR program was as follows: 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 55 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 30 s, followed by an extension at 72 °C for 10 min. The PCR product was purified using MiniBEST DNA Fragment Purification Kit (TaKaRa, kusatsu, Shiga, Japan) and sub-cloned into the pMD19-T vector (TaKaRa, kusatsu, Shiga, Japan). The ORF sequence of the target gene was confirmed through Sanger sequencing with universal primers RV-M and M13-47 (Table S6).
The nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acid sequence of LvCrustin I-2 were analyzed using BLAST algorithm (NCBI, blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 15 March 2022). The signal peptide was predicted via CBS prediction servers (http://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?SignalP-5.0, accessed on 15 March 2022). The WAP domain was predicted with the InterPro servers (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/, accessed on 15 March 2022). Multiple sequence alignment was calculated using DNAMAN software (Version 7.0).
4.4. Pathogen Challenge and Gene Expression Analysis
The cDNA samples of V. parahaemolyticus-challenged shrimp were obtained as previously described [26]. Briefly, each shrimp in bacterial challenge group was injected with 2 × 105 CFU V. parahaemolyticus. The shrimp in the control group were injected with equal volume of PBS buffer. The hemocytes and intestines were collected at 3 h, 6 h, 12 h and 24 h post-injection (hpi). Each time point contained three repeats of 15 shrimp. The total RNA of each sample was extracted, and the cDNA was synthesized as described in section “Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis”. The expression levels of LvCrustin I-2 in different samples were detected via qRT-PCR as described in section “Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis”.
4.5. Total Viable Bacteria Count after DsRNA and V. parahaemolyticus Injection
Primers dsLvCrustin I-2-F and dsLvCrustin I-2-R (Table S6) were designed to amplify the DNA template for LvCrustin I-2 dsRNA synthesis. The PCR was performed using the ExTaq (TaKaRa, Japan) with the program set as: 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, 60 °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 40 s, followed by an extension at 72 °C for 10 min. The PCR product was purified with the Gel Extraction Kit (OMEGA, Norcross, GA, USA). The LvCrustin I-2 dsRNA was synthesized with the TranscriptAid T7 High Yield Transcription Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and purified with phenol–chloroform solution. The dsRNA of a 289 bp fragment of enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene was also synthesized as negative control. The template for EGFP dsRNA was amplified from the pEGFP-N1 plasmid with a pair of primers, dsEGFP-F/R (Table S6). To optimize the interference doses, 30 individuals with a body weight of 4.75 ± 0.92 g were equally divided into two groups: dsLvCrustin I-2 group and dsEGFP group. Each group contained three dosages, including 1 μg, 4 μg and 8 μg dsRNA per shrimp. The intestines of five shrimp in each subgroup were collected as one sample 48 h after dsRNA interference. Total RNA extraction and qRT-PCR analysis were performed according to section “Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis”.
After dose optimization, 60 shrimp were equally divided into three groups: the PBS, dsEGFP, and dsLvCrustin I-2 groups. The shrimp in dsLvCrustin I-2 group and dsEGFP group were injected with 8 µg corresponding dsRNA per shrimp, respectively. The shrimp in PBS group were injected with equal volume of PBS buffer. At 48 h after dsRNA interference, the shrimp were injected with 2 × 104 cfu V. parahaemolyticus. The hepatopancreas from three individuals was collected and crushed in sterile PBS buffer as one sample 24 h after bacterial infection. Each group contained three biological replicates. The tissue homogenate was seeded onto the TCBS (LuQiao, Beijing, China) agar medium and cultured at 28 °C overnight. The total viable bacteria were counted, and the dominant bacteria were identified with bacterial 16S rDNA sequencing method.
4.6. Recombinant Expression and Purification of rLvCrustin I-2
The vector pET32a, digested by restriction enzymes Nco I and EcoR I (TaKaRa, kusatsu, Shiga, Japan), was used to construct the recombinant protein expression plasmid. The DNA fragment encoding LvCrustin I-2 mature protein was amplified from the plasmid that contained the ORF sequence of target gene with primers rLvCrustin I-2-F/R (Table S6). The linearized vector and the DNA fragment were purified and linked using MiniBEST DNA Fragment Purification Kit (TaKaRa, kusatsu, Shiga, Japan) and In-Fusion HD Cloning Kit (TaKaRa, kusatsu, Shiga, Japan) according to the protocol from the manufacturer. The plasmid was transformed into TransB Competent Cell (TransGen, Beijing, China). The soluble rLvCrustin I-2 was induced to express by addition of 1 mM Isopropyl-b-d-thio-galactoside (IPTG) at 37 °C for 4 h and purified using HisTALON Gravity Column Purification Kit (Clontech, Mountain View, CA, USA). The tag protein of pET32a, thioredoxin (Trx), was also expressed and purified as a control. Purity of rLvCrustin I-2 and rTrx was verified using sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and visualized with Coomassie brilliant blue R250. The concentration of recombinant proteins was detected with the BCA Protein Quantification Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China).
4.7. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assay
The concentration of imidazole in protein solution (50 mM sodium phosphate, 300 mM sodium chloride and 150 mM imidazole) was diluted 300-fold using a centrifugal filter device (Millipore, Cork, Ireland) by adding desalting buffer (50 mM sodium phosphate, 300 mM sodium chloride) and centrifuging. The concentration of recombinant proteins was also adjusted to 1 mg/mL with the centrifugal filter device.
Bacterium strains including V. parahaemolyticus, Vibrio harveyi, Photobacterium damselae and Escherichia coli were cultured to logarithmic phase and counted on a blood cell counting plate under a microscope. The recombinant proteins were diluted to concentrations of 1 mg/mL, 0.500 mg/mL, 0.250 mg/mL, 0.125 mg/mL, 0.0625 mg/mL and 0.0313 mg/mL. A total of 50 μL of recombinant proteins with density gradient was incubated with 50 μL of 5 × 103 cfu/mL bacterial suspension of each strain for 2 h in the 96-well plates at room temperature. After incubation, 150 μL TSB + 2% NaCl or LB liquid medium was added, and the plates were incubated at 28 °C or 37 °C for 8 h depending on different bacterial strains. The absorbance at 560 nm was detected via the precision micro-plate reader (TECAN infinite M200 PRO, Salzburg, Austria). The experiment was performed in triplicate.
4.8. Microorganism-Binding Assay
The microorganism-binding activity of rLvCrustin I-2 was detected through Western blot assay. The bacteria including V. parahaemolyticus, V. harveyi, P. damselae and E. coli were cultured to logarithmic phase. The number of each bacterial strain was counted using a blood cell counting plate under a microscope. About 1 × 108 cfu of each kind of bacteria was washed with phosphate buffer saline (PBS) (Sangon, Shanghai, China) and then resuspended with 450 μL PBS. A total of 50 μL of rLvCrustin I-2 or rTrx was added to the bacterial suspension, with a final concentration of 200 μg/mL. One hour after incubation with the recombinant protein, the bacterial suspension was centrifuged and washed six times with PBS. The bacterial pellet was resuspended in 200 μL PBS. The pellet samples were loaded onto the SDS-PAGE and transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane. The membrane was blocked with 5% skim milk and incubated with Mouse Anti-Trx-Tag mAb (ABclonal, Wuhan, Hubei, China). After washing three times with TBST, the membrane was incubated with HRP Goat Anti-Mouse IgG Antibody (ABclonal, Wuhan, Hubei, China). The proteins were visualized using the BeyoECL Plus Kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) following the manufacturer’s protocol. The experiment was performed in triplicate.
4.9. Bacterial Agglutination Experiment
The bacteria V. parahaemolyticus in their logarithmic growth phase were labeled with 0.1 mg/mL FITC. The FITC-labeled bacteria were diluted to 107 cfu/mL and mixed with equal volume of 1 mg/mL rLvCrustin I-2 or rTrx. After incubation at room temperature for 1 h, the bacteria were observed under an optical Nikon TS100 microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). The experiment was performed in triplicate.
4.10. Intestinal Microbiome Analysis of LvCrustin I-2-Silenced Shrimp
Three groups including dsLvCrustin I-2 group, dsEGFP group and PBS group were devised in this experiment. A total of 45 shrimp were equally divided into these three groups and were injected with corresponding dsRNA and equal volume of PBS buffer, respectively, as described in section “Total viable bacteria count after dsRNA and V. parahaemolyticus injection”. At 48 h after injection, the intestines from five individuals were collected and pooled as one sample. Each group contained three replicate samples.
The microbial DNA of all the samples was extracted with the HiPure Stool DNA Kits (Magen, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China) following the protocol from the manufacturer. The PCR was performed to amplify the 16S rDNA V3-V4 region of the ribosomal RNA gene with primers 341F and 806R (Table S6). The PCR program was set as follows: 95 °C for 2 min, followed by 27 cycles at 98 °C for 10 s, 62 °C for 30 s, 68 °C for 30 s and a final extension at 68 °C for 10 min. The PCR fragments were purified with the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biosciences, Wujiang, Jiangsu, China) following the instructions from the manufacturer. The purified fragments were adjusted in equimolar and paired-end sequenced (2 × 250) on an Illumina platform according to the standard protocol.
The low-quality reads were removed with FASTP (version 0.18.0). The raw tags were generated and filtered with FLSAH (version 1.2.11) and QIIME (version 1.9.1), respectively. The chimeric sequences were checked via UCHIME algorithm (http://www.drive5.com/usearch/manual/uchime_algo.html, accessed on 16 June 2022). The effective tags were clustered into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) of ≥ 97% similarity with UPARSE pipeline. Taxonomies were assigned using a naive Bayesian model with RDP classifier based on SILVA Database (https://www.arb-silva.de/, accessed on 16 June 2022). The alpha diversity indexes and weighted unifrac distance matrix were calculated via QIIME. PCoA (Principal Co-ordinate Analysis) of weighted unifrac distances was calculated and plotted using R project. The biomarker features in different groups were screened with Metastats and LEfSe software. The functional prediction and phenotype classification were performed using BugBase.
4.11. Intestinal Transcriptome Analysis of LvCrustin I-2-Silenced Shrimp
A total of 30 shrimp were divided into two groups. The shrimp in LvCrustin I-2 silencing group were each injected with 8 μg LvCrustin I-2 dsRNA, and the shrimp in control group were injected with equal dose of EGFP dsRNA. At 48 h after dsRNA injection, the intestines from five individuals were collected and set as one sample. Six biological replicates were finally prepared for each group, designated as dsCru_1-6 and dsEGFP_1-6, respectively. The total RNA of these samples was extracted with RNAiso Plus reagent (TaKaRa, kusatsu, Shiga, Japan). RNA samples from dsCru_1-3 and dsEGFP_1-3 samples were used for transcriptome sequencing, and those from dsCru_4-6 and dsEGFP_4-6 samples were used to synthetize cDNA for qPCR analysis.
For Illumina sequencing, the mRNA was enriched using Oligo (dT) beads from the RNA samples and fragmented into short fragments and reverse transcribed into cDNA with random primers. The second-strand cDNA was synthesized and purified using QiaQuick PCR extraction kit (Qiagen, Venlo, The Netherlands). The short fragments were operated with end repair and the addition of poly (A). The cDNA library was constructed after the fragments were ligated with sequencing adapters and enriched by PCR amplification. The paired-end library was sequenced using Illumina HiSeq2500 by Gene Denovo Biotechnology Co. (Guangzhou, Guangdong, China).
The raw reads were filtered via FASTP (version 0.18.0) to obtain high-quality clean reads and mapped to ribosomal RNA (rRNA) database using Bowtie2 (version 2.2.8). Then the rRNA-mapped reads were removed. The paired-end clean reads were mapped to the reference genome (QCYY00000000) via HISAT2.2.4. The mapped reads of samples were assembled by reference-based approach using StringTie (version 1.3.1). To quantify the expression abundance of genes, the FPKM (fragment per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads) value was calculated with StringTie software. The differential expression of genes between two different groups was performed using DESeq2 software. The genes with a false discovery rate (FDR) below 0.05 and absolute fold change above 2 were defined as differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The KEGG analysis was carried out with KEGG Automatic Annotation Server (http://www.genome.jp/tools/kaas/, accessed on 16 June 2022).
4.12. Elimination of Intestinal Microorganisms in Shrimp
The antibiotic-treated shrimp were obtained via reverse perfusion with antibiotic mixture (1 mg/mL ampicillin, 1 mg/mL neomycin, 1 mg/mL enrofloxacin, 1 mg/mL metronidazole and phenol red in PBS buffer) every 12 h for 48 h, and were cultured in sterile seawater at 25 °C. To verify the effectiveness of antibiotic treatment, the shrimp that were reverse perfused with equal volume of PBS buffer were set as controls. At 48 h after reverse perfusion, the intestines from three individuals were dissected and crushed in sterile PBS buffer as one sample, and the assay was performed in triplicate. The intestinal homogenate was diluted and seeded onto the TSB (LuQiao, Beijing, China) + 2% NaCl agar medium and cultured at 28 °C overnight, and then the total viable bacteria were counted.
A total of 30 antibiotic-treated shrimp with a body weight of 5.16 ± 1.04 g were divided into two groups: the dsLvCrustin I-2 group and dsEGFP group. The shrimp in the two groups were each injected with 8 µg corresponding dsRNA. The interference efficiency of LvCrustin I-2 dsRNA and the expression level of selected genes were detected via qRT-PCR analysis, as described in section “Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Analysis”.
4.13. Statistical Analysis
The statistical significance between treatments and controls was analyzed using SPSS statistics 20 software by variance (ANOVA) and Duncan’s multiple comparisons. The significant differences were labeled with lowercase letters or stars at p < 0.05. In the microbiome analysis, the Alpha index comparison and BugBase analysis were calculated with t-test in R project. The PCoA analysis was calculated with ADONIS test. The significance was set at p < 0.05. The biomarker features in different groups at LDA score ≥ 2 were analyzed using LEfSe software.
5. Conclusions
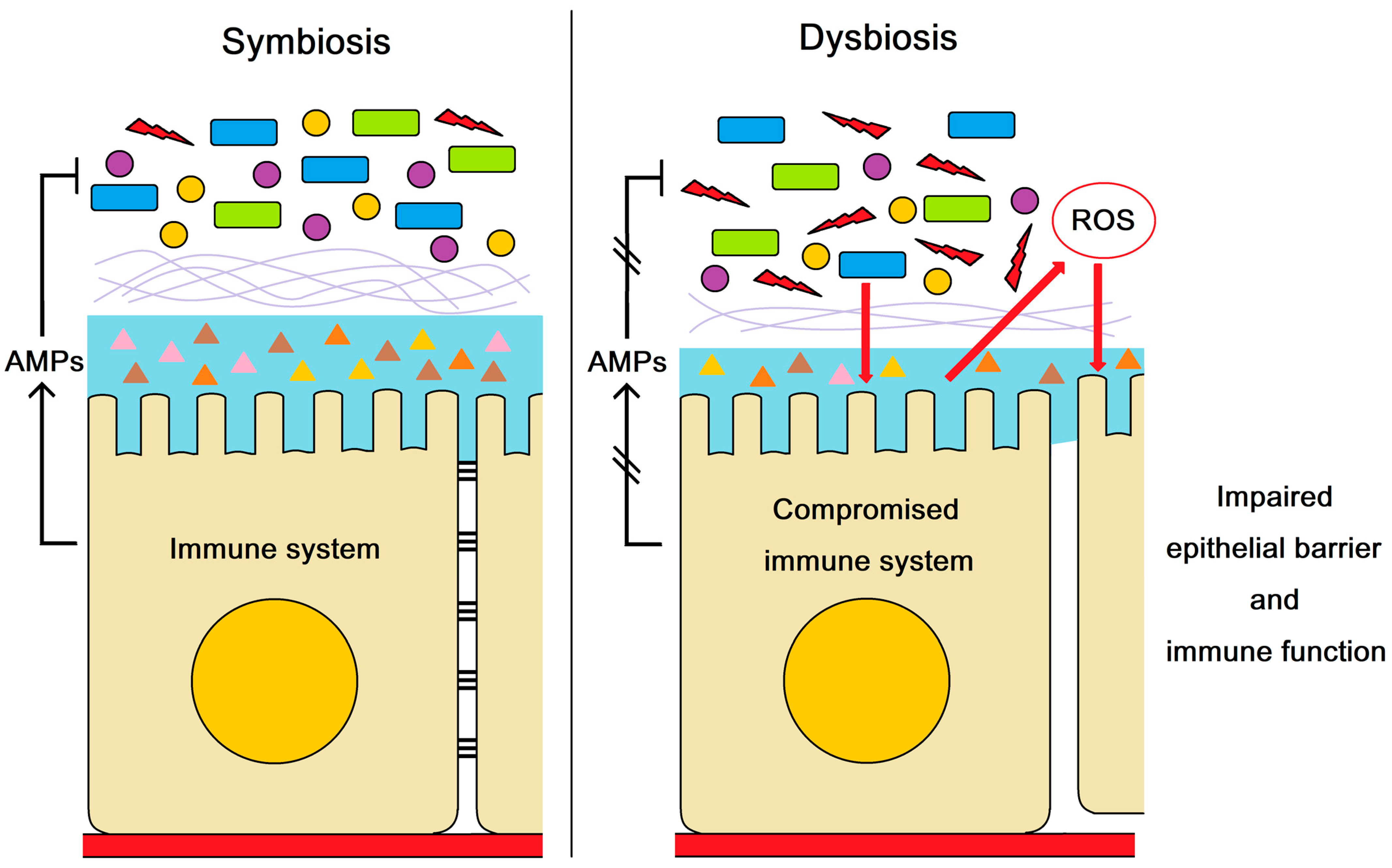
According to the above evidence, we concluded that AMPs could maintain intestinal health and resist pathogen infection by regulating intestinal microbiota balance (Figure 5). The dysbiosis of intestinal microbiota induced excessive ROS production and impaired the epithelial barrier and immune function in shrimp, which facilitated the V. parahaemolyticus invasion. The present study revealed the molecular mechanism by which AMPs modulate the outbreak of AHPND in shrimp.
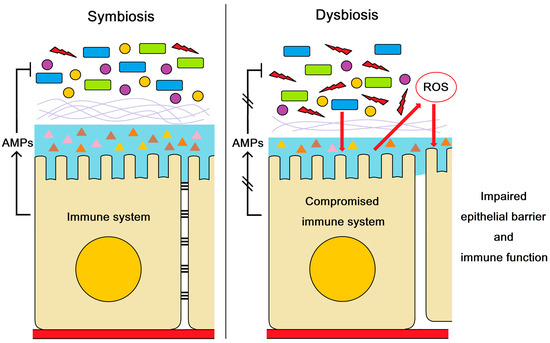
Figure 5.
The role of AMPs in maintaining intestinal health and resisting pathogen infection. AMPs regulate intestinal microbiota balance. The compromised AMP expression resulted in dysbiosis of intestinal microbiota, which impaired the epithelial barrier and immune function in shrimp. The impairment of epithelial barrier and immune function may facilitate the V. parahaemolyticus invasion and the outbreak of AHPND.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/md21020130/s1, Figure S1: Nucleotide and amino acid sequence of LvCrustin I-2. The start codon and stop codon are boxed. The predicted signal peptide is waved underlined. The WAP domain is marked with dark background. The conserved cysteine residues in cysteine-rich region and WAP domain are underlined; Figure S2: Recombinant expression and microorganism-binding activity of LvCrustin I-2. SDS-PAGE of rLvCrustin I-2 produced in E. coli expression system. The expected band of rLvCrustin I-2 is indicated by an arrow. Lane M: protein ladder marker; Lane 1: total protein of E. coli before induction; Lane 2: total protein of E. coli after induction; Lane 3: inclusion of the induced E. coli lysate; Lane 4: supernatant of the induced E. coli lysate; Lane 5: purified rLvCrustin I-2. The microorganism-binding activity of rLvCrustin I-2 detected via Western blot employing an anti-Trx tag antibody. Recombinant rLvCrustin I-2 was sampled as the positive control; Figure S3: The agglutination activities of rLvCrustin I-2 to V. parahaemolyticus. rTrx was used as negative control; Figure S4: PCoA analysis based on weighted UniFrac distance of the intestinal microbiota in different samples. The p-value of ADONIS analysis was less than 0.05; Figure S5: The comparison of relative abundance of bacterial communities between control group and dsLvCrustin I-2 group. Ctrl 1-6, the microbiota samples from dsEGFP group and PBS group; dsCru 1-3, microbiota samples from LvCrustin I-2 knockdown shrimp. (A) Top ten abundant bacteria at the phylum level. (B) Top ten abundant bacteria at the class level. (C) Top ten abundant bacteria at the order level. (D) Top ten abundant bacteria at the family level. (E) Top ten abundant bacteria at the genus level; Figure S6: The score of linear discriminant analysis (LDA). The green and red colors indicated the increased and decreased bacteria in different taxa, respectively. The “Decreased” indicates the bacteria have higher proportion in control group than dsLvCrustin I-2 group; The “Increased” indicates the bacteria have higher proportion in dsLvCrustin I-2 group than control group. The length of the bar indicates the contributing degree of differences; Table S1: Minimal inhibitory concentration of rLvCrustin I-2 on pathogens; Table S2: Alpha diversity indexes of intestinal microbiota; Table S3: Summary of sequencing and assembly of the intestinal transcriptome from L. vannamei; Table S4: Expression levels of intestinal epithelial barrier related genes; Table S5: Expression levels of immune-related genes; Table S6: Nucleotide sequences of primers used in the present study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L. and F.L.; validation, X.L. and Y.Y.; formal analysis, X.L. and X.Z.; investigation, X.L. and S.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.L.; writing—review and editing, S.L. and F.L.; supervision, S.L. and F.L.; funding acquisition, S.L. and F.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (31830100), the General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (31972829), the earmarked fund for CARS-48 and the Taishan Scholars Program.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the raw data were deposited on the website http://dx.doi.org/10.12157/IOCAS.20220907.001 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
Acknowledgments
Thanks for the data service provided by the Oceanographic Data Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CASODC).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hancock, R.E.; Sahl, H.G. Antimicrobial and host-defense peptides as new anti-infective therapeutic strategies. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funderburg, N.; Lederman, M.M.; Feng, Z.; Drage, M.G.; Jacllowsky, J.; Harding, C.V.; Weinberg, A.; Sieg, S.F. Human beta-defensin-3 activates professional antigen-presenting cells via Toll-like receptors 1 and 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18631–18635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, Y.; Papo, N.; Shai, Y. Endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide) neutralization by innate immunity host-defense peptides. Peptide properties and plausible modes of action. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibusuki, K.; Sakiyama, T.; Kanmura, S.; Maeda, T.; Iwashita, Y.; Nasu, Y.; Sasaki, F.; Taguchi, H.; Hashimoto, S.; Numata, M.; et al. Human neutrophil peptides induce interleukin-8 in intestinal epithelial cells through the P2 receptor and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, N.H.; Hung, K.C.; Haribhai, D.; Chu, H.T.; Karlsson-Sjoberg, J.; Amir, E.; Teggatz, P.; Barman, M.; Hayward, M.; Eastwood, D.; et al. Enteric defensins are essential regulators of intestinal microbial ecology. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abul, K.; Abbas, A.H.L.; Pillai, S. General Features of Immunity at Epithelial Barriers. In Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 9th ed.; Blvd, J.F.K., Ed.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; p. 299. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Bai, J.Y.; Nam, Y.D.; Bae, J.W.; Lee, D.G.; Shin, S.C.; Ha, E.M.; Lee, W.J. Innate immune homeostasis by the homeobox gene Caudal and commensal-gut mutualism in Drosophila. Science 2008, 319, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzenburg, S.; Walter, J.; Kunzel, S.; Wang, J.; Baines, J.F.; Bosch, T.C.G.; Fraune, S. Distinct antimicrobial peptide expression determines host species-specific bacterial associations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3730–E3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, G.M.; Rosa, R.D. On the silver jubilee of crustacean antimicrobial peptides. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 594–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.H.; Xiang, J.H. Recent advances in researches on the innate immunity of shrimp in China. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donpudsa, S.; Rimphanitchayakit, V.; Tassanakajon, A.; Soderhall, I.; Soderhall, K. Characterization of two crustin antimicrobial peptides from the freshwater crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 104, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauton, C.; Brockton, V.; Smith, V.J. Cloning of a crustin-like, single whey-acidic-domain, antibacterial peptide from the haemocytes of the European lobster, Homarus gammarus, and its response to infection with bacteria. Mol. Immunol. 2006, 43, 1490–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, T.C.; Cuthbertson, B.J.; Shepard, E.F.; Chapman, R.W.; Gross, P.S.; Warr, G.W. Crustins, homologues of an 11.5-kDa antibacterial peptide, from two species of penaeid shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei and Litopenaeus setiferus. Mar. Biotechnol. 2002, 4, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relf, J.M.; Chisholm, J.R.; Kemp, G.D.; Smith, V.J. Purification and characterization of a cysteine-rich 11.5-kDa antibacterial protein from the granular haemocytes of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.J.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Kemp, G.D.; Hauton, C. Crustins: Enigmatic WAP domain-containing antibacterial proteins from crustaceans. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2008, 32, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lv, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, F. Molecular and Functional Diversity of Crustin-Like Genes in the Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.J.; Dyrynda, E.A. Antimicrobial proteins: From old proteins, new tricks. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 68, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Destoumieux-Garzon, D.; Rosa, R.D.; Schmitt, P.; Barreto, C.; Vidal-Dupiol, J.; Mitta, G.; Gueguen, Y.; Bachere, E. Antimicrobial peptides in marine invertebrate health and disease. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Luo, M.; Guo, Z.; Zuo, H.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Xu, X. A shrimp gene encoding a single WAP domain (SWD)-containing protein regulated by JAK-STAT and NF-kappaB pathways. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 104, 103537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.-q.; Wang, Y.; Ma, H.-y.; Shen, X.-l.; Wang, K.; Du, J.; Yu, X.-d.; Fang, W.-h.; Li, X.-c. A new crustin homologue (SpCrus6) involved in the antimicrobial and antiviral innate immunity in mud crab, Scylla paramamosain. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 84, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visetnan, S.; Supungul, P.; Tassanakajon, A.; Donpudsa, S.; Rimphanitchayakit, V. A single WAP domain-containing protein from Litopenaeus vannamei possesses antiproteinase activity against subtilisin and antimicrobial activity against AHPND-inducing Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 68, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, S.; Smith, V.J.; Dyrynda, E.A. Unusual tissue distribution of carcinin, an antibacterial crustin, in the crab, Carcinus maenas, reveals its multi-functionality. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 76, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, S.; Lv, Q.; Miao, M.; Li, X.; Li, F. Characterization of the Dual Functions of LvCrustinVII from Litopenaeus vannamei as Antimicrobial Peptide and Opsonin. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bloa, S.; Boidin-Wichlacz, C.; Cueff-Gauchard, V.; Rosa, R.D.; Cuvillier-Hot, V.; Durand, L.; Methou, P.; Pradillon, F.; Cambon-Bonavita, M.A.; Tasiemski, A. Antimicrobial Peptides and Ectosymbiotic Relationships: Involvement of a Novel Type IIa Crustin in the Life Cycle of a Deep-Sea Vent Shrimp. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, F. Characterization of a gill-abundant crustin with microbiota modulating function in Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 105, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Xiang, J.; Li, F. The immune function of a novel crustin with an atypical WAP domain in regulating intestinal microbiota homeostasis in Litopenaeus vannamei. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 111, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lv, X.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Characterization of a Lymphoid Organ Specific Anti-lipopolysaccharide Factor from Shrimp Reveals Structure-Activity Relationship of the LPS-Binding Domain. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.R.; Jia, W.M.; Zhao, X.F.; Wang, J.X. A new group of anti-lipopolysaccharide factors from Marsupenaeus japonicus functions in antibacterial response. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 48, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, R.-R.; Fan, Z.-X.; Zhao, X.-F.; Wang, X.-W.; Wang, J.-X. Characterization of a type-I crustin with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity from red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 61, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.W.; Wang, J.X. Crustacean hemolymph microbiota: Endemic, tightly controlled, and utilization expectable. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 68, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponprateep, S.; Tharntada, S.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Tassanakajon, A. Gene silencing reveals a crucial role for anti-lipopolysaccharide factors from Penaeus monodon in the protection against microbial infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Li, S.; Liu, F.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Identification and function analysis of an anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from the ridgetail prawn Exopalaemon carinicauda. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 70, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burioli, E.A.V.; Varello, K.; Trancart, S.; Bozzetta, E.; Gorla, A.; Prearo, M.; Houssin, M. First description of a mortality event in adult Pacific oysters in Italy associated with infection by a Tenacibaculum soleae strain. J. Fish Dis. 2018, 41, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, R.A.; Cawthorn, R.J.; Summerfield, R.L.; Smolowitz, R.; Chistoserdov, A.Y. Bacterial communities associated with lesions of two forms of shell disease in the American lobster (Homarus americanus, Milne Edwards) from Atlantic Canada. Can. J. Microbiol. 2013, 59, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Yu, M.; Liu, J.W.; Qiao, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.T.; Zhang, X.H.; Yu, M.C. Bacterial Community Associated with Healthy and Diseased Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Larvae and Rearing Water across Different Growth Stages. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.S.; Xiong, D.L.; Zhang, J.S. Transcriptomic and microbiota response on Litopenaeus vannamei intestine subjected to acute sulfide exposure. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 88, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, II; Honda, K. Intestinal commensal microbes as immune modulators. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekirov, I.; Russell, S.L.; Antunes, L.C.; Finlay, B.B. Gut microbiota in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 859–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyleris, E.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Tzivras, D.; Koussoulas, V.; Barbatzas, C.; Pimentel, M. The prevalence of overgrowth by aerobic bacteria in the small intestine by small bowel culture: Relationship with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 1321–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlan, R.M.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilms: Survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Alvarez, C.; Santos, Y. Identification and typing of fish pathogenic species of the genus Tenacibaculum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 9973–9989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, C.Z.; Xie, J.; Xu, C.; Zhao, Q.; Qin, J.G.; Chen, L.Q.; Li, E.C. Intestinal bacterial signatures of the “cotton shrimp-like” disease explain the change of growth performance and immune responses in Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoah, K.; Huang, Q.C.; Tan, B.P.; Zhang, S.; Chi, S.Y.; Yang, Q.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Dong, X.H. Dietary supplementation of probiotic Bacillus coagulans ATCC 7050, improves the growth performance, intestinal morphology, microflora, immune response, and disease confrontation of Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omont, A.; Elizondo-Gonzalez, R.; Escobedo-Fregoso, C.; Tovar-Ramirez, D.; Hinojosa-Baltazar, P.; Pena-Rodriguez, A. Bacterial communities and digestive enzymatic activities of Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp fed pre-digested seaweeds as a functional ingredient. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoah, K.; Dong, X.H.; Tan, B.P.; Zhang, S.; Chi, S.Y.; Yang, Q.H.; Liu, H.Y.; Yang, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.T. Administration of probiotic Bacillus licheniformis induces growth, immune and antioxidant enzyme activities, gut microbiota assembly and resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus in Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1604–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Thaiss, C.A.; Elinav, E. Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Molina-Cruz, A.; Gupta, L.; Rodrigues, J.; Barillas-Mury, C. A peroxidase/dual oxidase system modulates midgut epithelial immunity in Anopheles gambiae. Science 2010, 327, 1644–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchon, N.; Broderick, N.A.; Lemaitre, B. Gut homeostasis in a microbial world: Insights from Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Liehl, P.; Buchon, N.; Lemaitre, B. Infection-induced host translational blockage inhibits immune responses and epithelial renewal in the Drosophila gut. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.T.; Yang, M.C.; Sun, J.J.; Shi, X.Z.; Zhao, X.F.; Wang, J.X. Dual oxidases participate in the regulation of intestinal microbiotic homeostasis in the kuruma shrimp Marsupenaeus japonicus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 59, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Lucchetta, E.; Rafel, N.; Ohlstein, B. Maintenance of the adult Drosophila intestine: All roads lead to homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2016, 40, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitas, G.; Cossart, P. Adherens junctions and pathogen entry. Sub-Cell. Biochem. 2012, 60, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miele, L.; Giorgio, V.; Alberelli, M.A.; De Candia, E.; Gasbarrini, A.; Grieco, A. Impact of Gut Microbiota on Obesity, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2015, 17, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Butcher, J.; Mack, D.; Stintzi, A. Functional impacts of the intestinal microbiome in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xing, R.; Lv, Z.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, X.; Li, C. Analysis of gut microbiota revealed Lactococcus garviaeae could be an indicative of skin ulceration syndrome in farmed sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 80, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zeng, S.; Xiong, J.; Hou, D.; Zhou, R.; Xing, C.; Wei, D.; Deng, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Microecological Koch’s postulates reveal that intestinal microbiota dysbiosis contributes to shrimp white feces syndrome. Microbiome 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornejo-Granados, F.; Lopez-Zavala, A.A.; Gallardo-Becerra, L.; Mendoza-Vargas, A.; Sanchez, F.; Vichido, R.; Brieba, L.G.; Viana, M.T.; Sotelo-Mundo, R.R.; Ochoa-Leyva, A. Microbiome of Pacific Whiteleg shrimp reveals differential bacterial community composition between Wild, Aquacultured and AHPND/EMS outbreak conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.-C.; Ng, T.H.; Ando, M.; Lee, C.-T.; Chen, I.T.; Chuang, J.-C.; Mavichak, R.; Chang, S.-H.; Yeh, M.-D.; Chiang, Y.-A.; et al. Pathogenesis of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) in shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 47, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.T.; Chen, I.T.; Yang, Y.T.; Ko, T.P.; Huang, Y.T.; Huang, J.Y.; Huang, M.F.; Lin, S.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, S.S.; et al. The opportunistic marine pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus becomes virulent by acquiring a plasmid that expresses a deadly toxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10798–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prachumwat, A.; Taengchaiyaphum, S.; Mungkongwongsiri, N.; Aldama-Cano, D.J.; Flegel, T.W.; Sritunyalucksana, K. Update on early mortality syndrome/acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease by April 2018. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2019, 50, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ng, T.H.; Wang, H.C. Acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease in penaeid shrimp. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1867–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Comparative Transcriptomic Characterization of the Early Development in Pacific White Shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).