Abstract
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) can produce a variety of noxious effects and, in some cases, the massive mortality of wild and farmed marine organisms. Some HAB species produce toxins that are released into seawater or transferred via food webs (particulate toxin fraction). The objective of the present study was to identify the toxicological effects of subacute exposure to saxitoxin (STX) during embryonic and early larval stages in Seriola rivoliana. Eggs were exposed to dissolved 19 STX (100 μg L−1). The toxic effects of STX were evaluated via the hatching percentage, the activity of three enzymes (protein and alkaline phosphatases and peroxidase), and the expression of four genes (HSF2, Nav1.4b, PPRC1, and DUSP8). A low hatching percentage (less than 5%) was observed in 44 hpf (hours post fertilization) embryos exposed to STX compared to 71% in the unexposed control. At this STX concentration, no oxidative stress in the embryos was evident. However, STX induced the expression of the NaV1.4 channel α-subunit (NaV1.4b), which is the primary target of this toxin. Our results revealed the overexpression of all four candidate genes in STX-intoxicated lecithotrophic larvae, reflecting the activation of diverse cellular processes involved in stress responses (HSF2), lipid metabolism (PPRC1), and MAP kinase signaling pathways associated with cell proliferation and differentiation (DUSP8). The effects of STX were more pronounced in young larvae than in embryos, indicating a stage-specific sensitivity to the toxin.
1. Introduction
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) have become a major environmental problem in recent decades due to their impacts on fisheries, aquaculture, wildlife, socioeconomic and recreational activities, and human health [1]. Some HAB species produce marine toxins, which are released into seawater or transferred through food webs (particulate toxin fraction). The nature of these effects depends on the marine toxins produced by harmful microalgae (e.g., dinoflagellates, diatoms, and raphidophytes), cyanobacteria, and bacteria. These toxins are metabolic compounds that can accumulate in the tissues of marine organisms, affecting both their physiology and behavior [2,3]. For example, HABs have been responsible for mass mortality events in the Gulf of California of wild (e.g., mammals, birds, fish, and invertebrates) and farmed (e.g., fish and crustaceans) marine species due to the large quantities of toxins in contaminated prey [4,5]. In addition, many human poisonings have been linked to the consumption of seafood products (filter-feeding bivalves and fish) contaminated by toxins and cases of respiratory tract irritation due to aerosolized toxins [3,6,7].
Saxitoxin (STX) and its derivatives, which are commonly referred to as paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs), are among the most studied marine toxins responsible for poisonings in both humans and marine animals [8,9]. These toxins can induce neuromuscular symptoms such as muscular paralysis, myalgia, and respiratory difficulty. In cases of severe intoxication, muscular paralysis or dyspnea may evolve into respiratory arrest and death [9,10]. Paralytic shellfish toxins act in the nervous systems of mammals by blocking voltage-gated sodium channels (NaV) [11,12] and can also bind to voltage-gated calcium (CaV) and potassium (KV) channels [13,14]. Although PSTs have been linked to the mass mortality and intoxication of diverse marine organisms, including crustaceans, fish, sea birds, sea turtles, and marine mammals, knowledge of the corresponding action mechanisms and intoxication routes remains scarce [15].
The toxins released during HAB events accumulate in food webs. Thus, marine fish are the primary group affected by these toxins. In fish, as in other vertebrates, embryonic development is controlled by different signaling pathways in which specific molecules play important roles in various processes, such as dorsal–ventral and anterior–posterior positioning [14]. Marine toxins are capable of deregulating gene expression and can disrupt embryonic development by affecting cellular metabolism [16,17] and inducing developmental delays and macroscopic organ alterations or abnormalities [18,19,20,21]. Fish embryos and larvae are susceptible to marine toxins because they have not yet developed efficient detoxification systems and exhibit high metabolic growth rates [22]. Thus, these toxins, which have lethal and sublethal effects during early life stages [4,19,20], threaten fish recruitment, fishery yields, and aquaculture production [5,23,24]. Therefore, strategies must be implemented to detect and understand the mechanisms by which marine toxins affect fish and ultimately threaten human health.
The longfin yellowtail (Seriola rivoliana) is a carnivorous, benthopelagic marine fish of the family Carangidae that is mainly found in subtropical reefs from the United States of America (USA) to Peru in the Pacific [25] and from the United States to Argentina in the Atlantic [26]. Seriola rivoliana is a top carnivore in reef-associated food webs and the main vector of Ciguatera fish poisoning in the Atlantic (Macaronesian) Islands (Canarias and Madeira archipelagos) and Azores [27,28,29]. As with other Seriola species, S. rivoliana exhibits excellent potential for aquaculture production due to its worldwide distribution, fast growth, and ability to adapt well to captivity [30]. Indeed, S. rivoliana has become one of the most important marine fish species selected to diversify aquaculture production in Japan, Australia, the United States, Spain, and Mexico [30,31]. However, information on the early life stages of S. rivoliana is needed to elucidate the causes of early mortality and develop strategies to increase egg viability and larval survival [30,32,33].
The objective of the present study was to identify the effects of saxitoxin, one of the most toxic PSTs and one of the main PSTs present in Mexico. The use of marine fish embryos and larvae as sentinels to detect the modes of action of marine toxins has been proposed in many studies mostly conducted with Zebrafish (Danio rerio) [19,20]. Previous studies have reported the negative effects of toxins on fish larvae [34,35]. In S. rivoliana, exposure to diarrhetic shellfish toxins (DSTs; okadaic acid [OA] and dinophysistoxin-1 [DTX-1]), PSTs, and saxitoxin analogs (gonyautoxin 2–3 [GTX 2–3], decarbamoyl gonyautoxin 2–3 [dc-GTX2–3], and C1–C2) has been recently shown to deregulate embryogenesis-related pathways, inhibit phosphatase activity, and induce metabolic responses in larvae by increasing gene expression and lipid metabolism enzyme activity [36,37].
The impacts of STX exposure were also evaluated in larvae from hatching until 62 h post fertilization (hpf; i.e., before mouth opening at 96 hpf) [38]. The embryotoxic effect (hatching percentage) was quantified, and the regulation of genes and enzymes involved in (i) stress responses (heat-shock proteins), (ii) ion transport (voltage-gated sodium channels), (iii) lipid metabolism (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors), (iv) digestion-related pathways (alkaline phosphatases), (v) oxidative stress (peroxidase), and (vi) key enzyme regulation (protein phosphatases) was also assessed. The results of the present study provide new information on the modes of action of PSTs during embryonic and larval development.
2. Results
2.1. Hatching Percentages
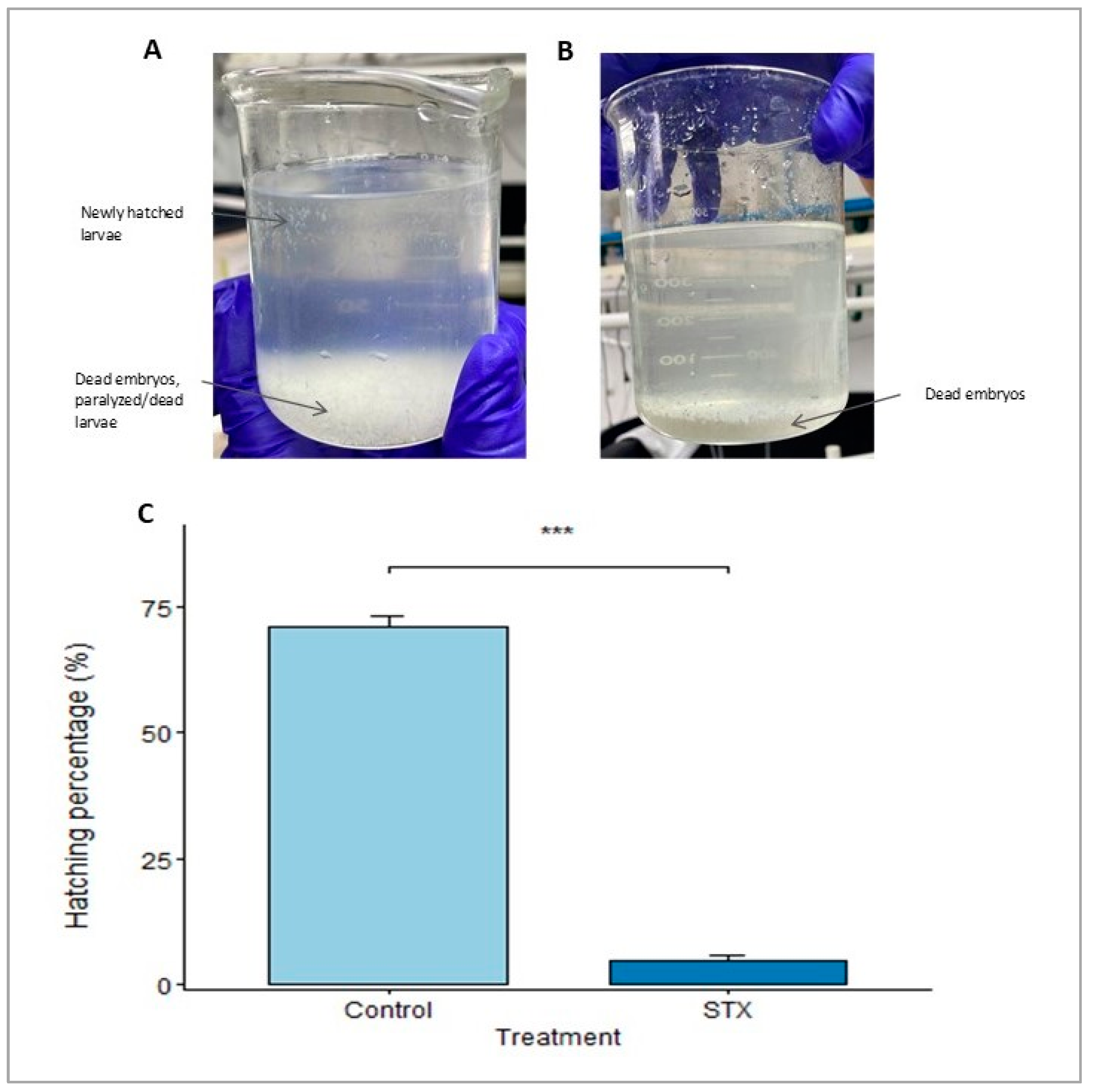
In the present study, S. rivoliana embryos and recently hatched larvae were used as models to qualitatively and quantitatively assess the impacts of PSTs during the development of early life stages. We hypothesized that PSTs would induce adverse effects on the development of S. rivoliana embryos, which could be evaluated with biochemical and molecular methods. To test this hypothesis, fish embryos were exposed to STX throughout embryonic development (8 to 44 hpf). The cellular and molecular levels in S. rivoliana were used to develop models with improved sensitivity to detect, quantify, and classify the modes of action of these molecules. The hatching percentage was assessed at 44 hpf in the control and STX treatment. The observed spawning volume (Figure S1), buoyancy, and shape indicated good egg quality. This preliminary observation was confirmed by the relatively high hatching percentage of eggs from the control group (71.16 ± 1.97%). Conversely, high mortality of STX-exposed eggs was observed in the different replicates, and the hatching percentage was 14 times lower (4.92 ± 0.80%) compared to that of the control group, with the difference being highly significant (Student’s t-test, p = 0.00018; Figure 1).
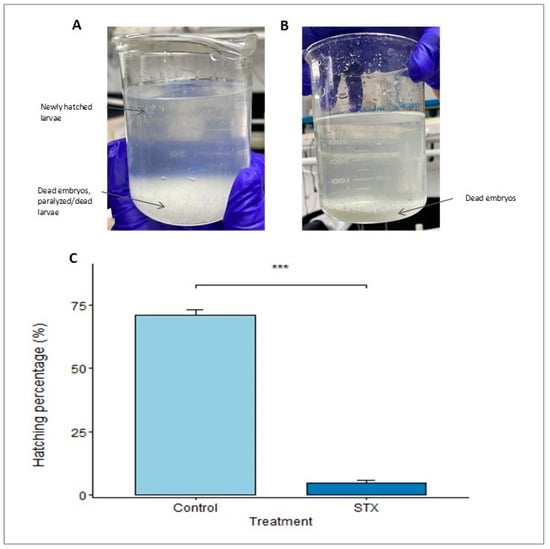
Figure 1.
(A,B) Evaluation of hatching rate and larval viability at 44 hpf in the STX treatment. (C) Hatching percentages of Seriola rivoliana embryos. Control: embryos cultivated without toxins; STX: embryos exposed to saxitoxin standard solution (100 μg L−1 STX eq.). Asterisks (***) indicate significantly different means between the control and STX treatment (Student’s t-test, p < 0.001). Bars represent the mean ± standard error (n = 3).
2.2. Gene Expression Analyses
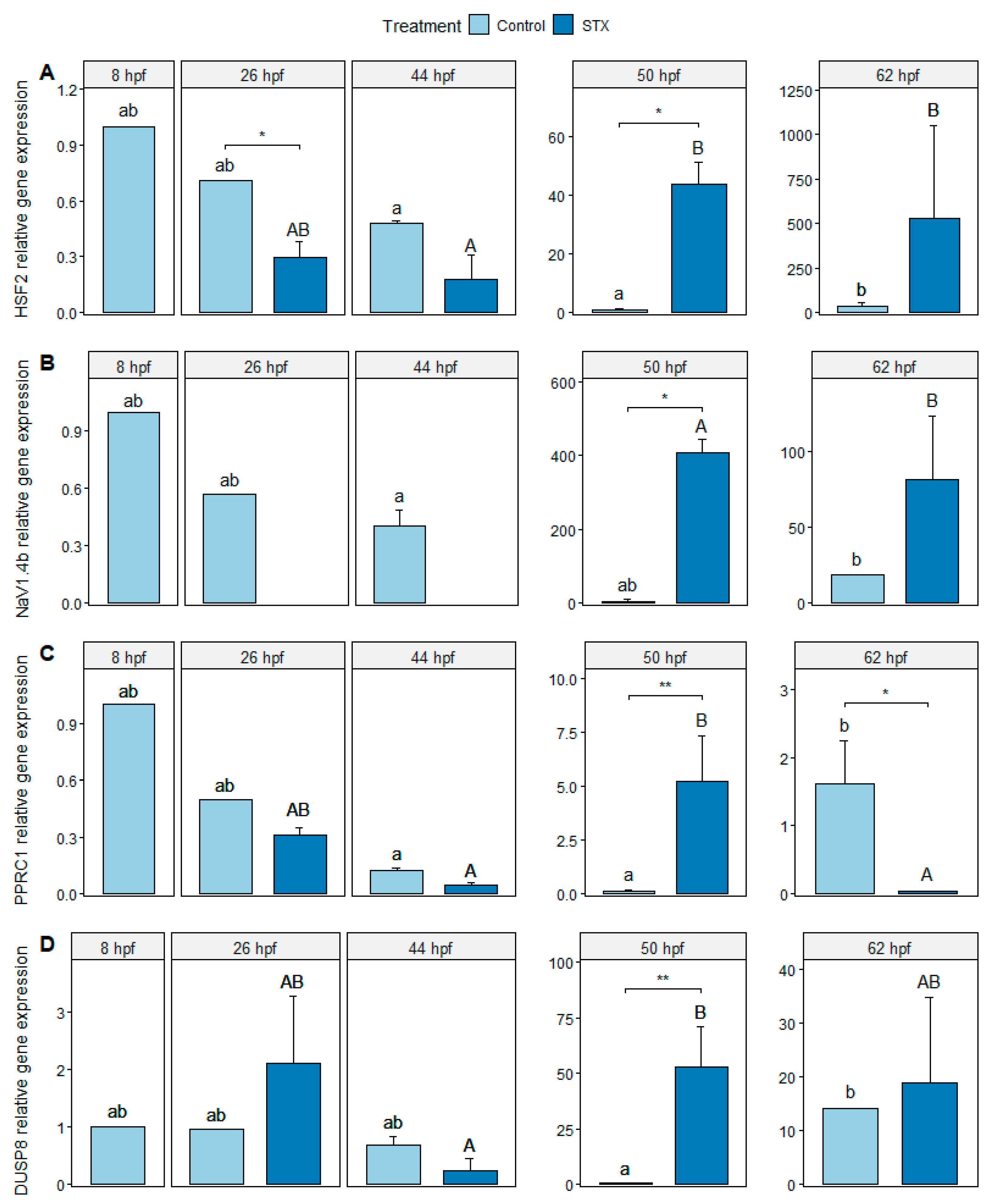
The expression of heat shock factor 2 (HSF2), sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha B (NaV1.4b), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-related protein 1 (PPRC1), and dual specificity phosphatase 8 (DUSP8) genes was detected in the control from 8 to 62 hpf. The highest expression levels were observed at 50 hpf. For the STX treatment, the expression of HSF2, PPRC1, and DUSP8 genes was detected from 26 to 62 hpf. In comparison, NaV1.4b gene expression was only detected between 50 and 62 hpf, which corresponded to the lecithotrophic larval stage (i.e., depletion of the remaining yolk reserves before mouth opening; Figure 2).
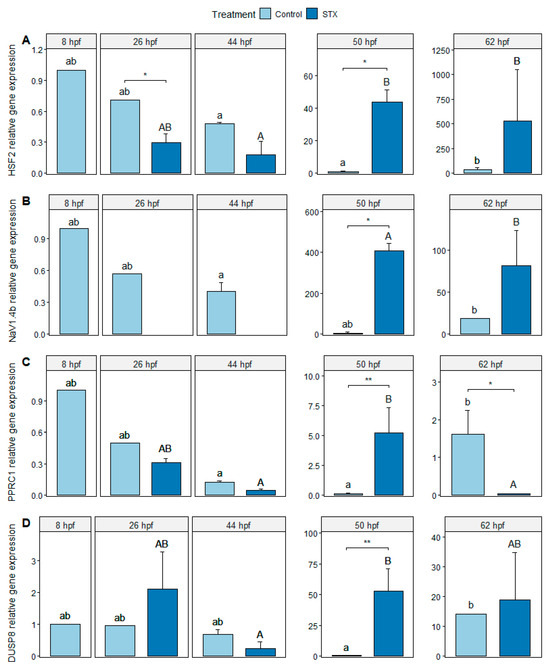
Figure 2.
Relative gene expression (A) of heat shock factor 2 (HSF2), (B) NaV1.4 channel α-subunit (NaV1.4b), (C) PPRC1 relative gene expression, and (D) dual specificity phosphatase 8 (DUSP8) genes from Seriola rivoliana embryos. Control: embryos cultivated without toxins; STX: embryos exposed to saxitoxin standard solution (100 μg L−1 STX eq.). Asterisks (* or **) indicate significant differences between treatments at 26, 50, and 62 hpf (Kruskal–Wallis p < 0.05 or p < 0.01, respectively). Letters ab and AB indicate significant differences between times under the control and STX (saxitoxin) treatments, respectively; (Kruskal–Wallis p < 0.05). Bars represent the mean ± standard error (n = 3).
A significant increase in HSF2 and DUSP8 gene expression was observed between 50 and 62 hpf in control embryos (p < 0.05) and between 44 and 50 hpf in STX-exposed embryos (p < 0.05 for HSF2, p < 0.01 for DUSP8). NaV1.4b gene expression increased significantly between 44 and 62 hpf in control embryos (p < 0.05). In exposed embryos, NaV1.4b gene expression was not detected during embryo development (between 26 and 44 hpf) but significantly increased between 50 and 62 hpf in lecithotrophic larvae (p < 0.05). The expression level of the PPRC1 gene increased significantly between 50 and 62 hpf in control embryos (p < 0.05). In exposed embryos, PPRC1 gene expression increased significantly between 44 and 50 hpf (p < 0.05) and then decreased significantly between 50 and 62 hpf (p < 0.05).
At 26 hpf, the expression of the HSF2 and NaV1.4b genes was significantly lower in STX-exposed embryos compared to the control (p < 0.05), but no significant change was observed for the other genes (p > 0.05; Figure 2). At 44 hpf, only the expression of NaV1.4b was significantly different between the two treatments (p < 0.05). At 50 hpf, the expression levels of the four genes were significantly higher in STX-exposed larvae than in the control (p < 0.05). At 62 hpf, a significant decrease in PPRC1 gene expression was observed in intoxicated larvae compared to that of the control (p < 0.05). In contrast, no significant changes were noted for the other genes (p > 0.05).
2.3. Enzyme Analyses
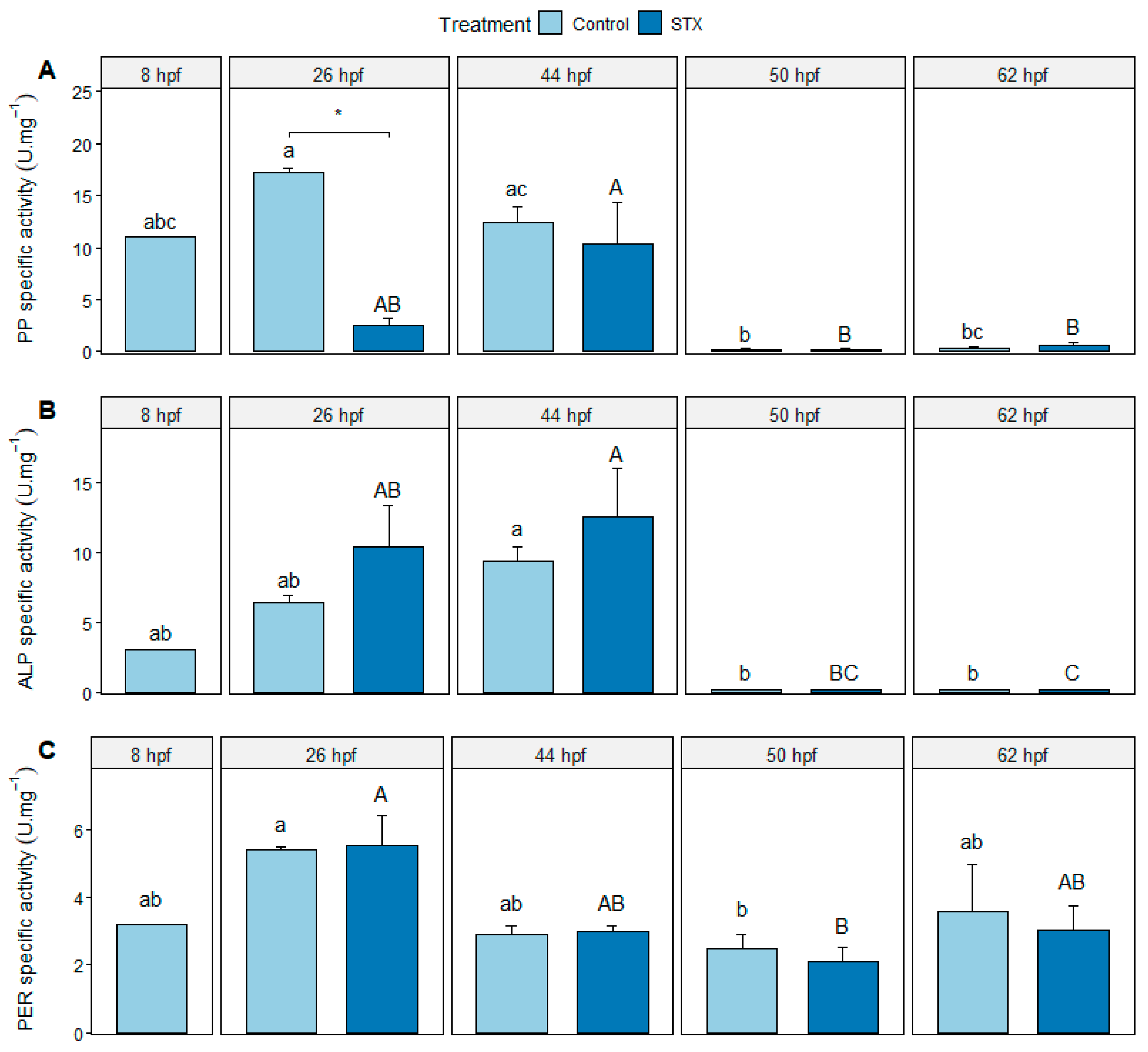
The specific activities of protein phosphatase (PP), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and peroxidase (PER) were detected from 8 to 62 hpf in the control and from 26 to 62 hpf in the STX treatment (Figure 3). A significant decrease in the activity of both types of phosphatases was observed between 44 and 50 hpf (i.e., just after larval hatching) in both treatments (p < 0.01). PER activity was significantly higher at 26 hpf than at 50 hpf in the control (p < 0.05) and in the STX-exposed embryos (p < 0.01). Nevertheless, the activity of this enzyme did not change significantly (p > 0.05) between 26 and 44 hpf or between 44, 50, and 62 hpf (Figure 3C).
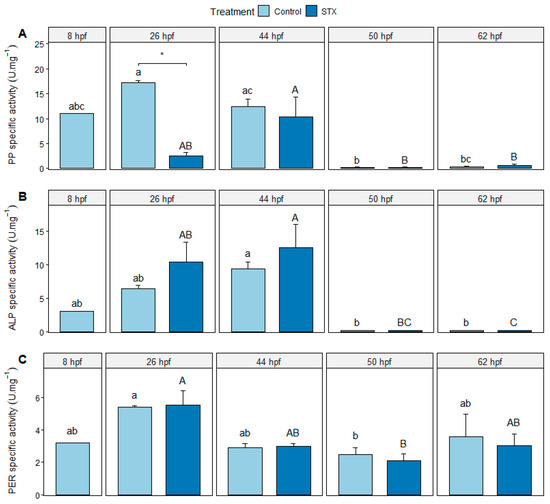
Figure 3.
Specific activity (A) of protein phosphatase (PP), (B) alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and (C) peroxidase (PER) in Seriola rivoliana embryos. Control: embryos cultivated without toxins; STX: embryos exposed to standard saxitoxin solution (100 μg L−1 STX eq.). Results are expressed as units of enzyme per milligrams of total proteins (U mg−1). Asterisk (*) indicates significant differences between treatments at 26 hpf (Kruskal–Wallis p < 0.05). Letters ab, AB, c and C indicate significant differences in times under the control and STX (saxitoxin) treatment, respectively (Kruskal–Wallis p < 0.05). Bars represent the mean ± standard error (n = 3).
At 26 hpf, PP activity was significantly lower in STX-exposed embryos compared to control embryos (p < 0.05); however, at 44, 50, or 62 hpf (p > 0.05; Figure 3B), no significant difference in the specific activities of the ALP and PER enzymes was observed in STX-exposed embryos compared to those of the control (p > 0.05), regardless of the sampling time (Figure 3A,C).
3. Discussion
3.1. Reduction of Hatching Percentage due to STX Exposure
The high hatching percentage (71.16 ± 1.97%) observed in the control indicates that the majority of eggs were able to complete embryonic development and hatch into larvae. In comparison, Brenta et al. [36] obtained a higher hatching percentage (78.3 ± 2.9%) in the control, which suggests that the eggs in our experiment were of slightly lower quality.
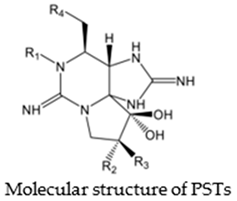
A very low hatching percentage (4.92 ± 0.80%) was observed for embryos exposed to the STX concentration of 100 µg L−1 (Figure 1C), which suggests a very high embryo mortality rate (>90%). Indeed, large quantities of dead embryos were observed at 44 hpf in the tanks with STX. Once again, these results differ from those of Brenta et al. [34], who employed an equivalent dose (100 µg L−1 STX eq.) of gonyautoxin (GTX), an analog of STX, and observed a 50% hatching rate of S. rivoliana eggs. Together with neosaxitoxin (NeoSTX), STX exhibits the highest toxicity among paralytic shellfish toxins, while GTX is less toxic (Table 1). This difference in toxicity explains why STX was able to lower the egg-hatching rate to a greater extent than GTX.

Table 1.
Molecular structure and toxic equivalency factor (TEF) of the paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs). Adapted from Leal and Cristiano [38] and Reis Costa et al. [39].
Brenta [36] also highlighted that under equivalent concentrations (90 µg L−1 OA eq. and 100 µg L−1 STX eq.), hatching was more affected by OA, which is responsible for diarrhetic shellfish poisoning, than by STX, suggesting that S. rivoliana embryos are more sensitive to OA than to GTX. Thus, it can be hypothesized that in embryos, toxicity depends on the roles targeted substrates play in cellular mechanisms and their relative importance. Within a given family of toxins, which exhibit the same modes of action with specific substrates, the elevated toxicity of some members could be related to molecular structures that increase binding affinity to certain molecular receptors [5,9].
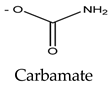
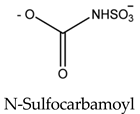
Paralytic shellfish toxins have a common molecular structure and variable R1-4 functional groups that influence their net charge and polarity, increasing the binding ability of PSTs to ion channel sites [9]. At the R4 position, the carbamate moiety common to STX and GTXs confers higher toxicity than the N-sulfocarbamoyl moiety present in C1 and C2 toxins or the decarbamate moiety characteristic of dc-GTXs. On the other hand, the lower toxicity of GTXs compared to that of STX is due to the presence of HOSO3 groups in positions R2 and R3, which decreases ion channel binding affinity and, consequently, the toxicity of the molecule (Table 1). PSTs can be classified according to their relative toxicity with the toxic equivalency factor (TEF): STX > GTX3 > GTX2 > C2 > C1 > dcGTX3 > dcGTX2. Given that STX has a higher toxicity than its analogs, it seems clear that the embryo hatching rate was more strongly impacted by STX exposure in this study than by GTX2-3, C1-2, or dcGTX2-3 exposure [36]. However, the hypothesis that high embryo sensitivity to STX results from the ability of this toxin to cross the chorion and directly reach the embryo within the egg must be confirmed in future studies. STX exposure increases the expression of various apoptosis-related genes in bivalves [40,41] and fish [42]. Thus, the results suggest that the exposure of embryos to STX, either by simple external contact or by incorporating the toxin into the egg, activates cellular mechanisms related to apoptosis, triggering embryo death. Nevertheless, other factors besides STX exposure, such as culture conditions or egg quality, may also influence the sensitivity of fish embryos to toxins and help explain the drastic embryo mortality observed in the present study (Table S1).
3.2. Heat Shock Protein Induction
HSF2 gene expression significantly increased between 50 and 62 hpf in control larvae and 50 hpf in STX-exposed larvae (Figure 2A). These results suggest that STX exposure resulted in the early induction of the HSF2 gene during larval development in S. rivoliana. The HSF2 gene is a member of the heat shock factor (HSF) family, which are activators of heat shock protein (HSP) transcription [43,44]. Heat shock proteins act as molecular chaperones to assist misfolded proteins in stressed cells and are involved in the responses to multiple environmental stressors, including heat shock [45] and exposure to contaminants [46] or toxins [47,48]. Thus, HSF2 induction could indicate the probable accumulation of misfolded proteins within cells exposed to saxitoxin, as well as other processes involved in morphogenetic changes. In this study, HSF2 induction occurred early during development in STX-exposed larvae at 50 and 62 hpf. These gene expression results provide evidence for STX-related stress response in S. rivoliana larvae and suggest high transcription of HSP coding genes. Saxitoxin exposure has been reported to induce an increase in HSPs in Medaka (Oryzias latipes) embryos, although during later embryonic-larval stages (i.e., 16 days post-fertilization) [49] Figure S1. Similarly, in juvenile gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata), notable induction of HSP70 proteins was observed with PST exposure and warming [50].
In addition, HSF2 gene expression increased during embryo development in the control (Figure 2A). This result highlights the multiple roles of HSP and HSF proteins that are synthesized in response to environmental stress and during normal embryonic development. Thus, HSF proteins and HSP play vital roles in providing protection from multiple environmental stressors during the larval phase, one of the most vulnerable life stages of fish development [51]. HSF2 has also been shown to be involved in the constitutive transcription of HSP genes [52], which would explain its presence in both the control and STX-exposed embryos. Although the differences were not statistically significant, lower HSF2 expression at 26 hpf and higher expression of the same at 62 hpf can be visually noted in the exposed embryos compared to those in the control.
3.3. Regulation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels via Gene Expression
The primary mode of action of STX is to block voltage-gated sodium (NaV) channels by binding to site 1 of the α-subunit that forms the channel pore [11]. To highlight the impact of STX on NaV channels at the molecular level, we studied the expression of the NaV1.4b gene, which encodes the α-subunit of the NaV1.4 isoform. This isoform promotes electrogenesis in non-neuronal cells (e.g., skeletal muscle cells) and non-excitable cells (e.g., endothelial cells and red blood cells) [53]. The results revealed an absence of NaV1.4b gene expression between 26 and 44 hpf in STX-exposed embryos, followed by a 120-fold increase in expression between 50 and 62 hpf in STX-exposed larvae compared to that of the control (Figure 2B). These results suggest that the STX-associated stress response occurs in two phases during embryo and larval development: (i) STX completely inhibits the expression of the NaV1.4b gene at the embryo stage and (ii) an up-regulation of this gene occurs during the larval stage in response to this inhibition.
By regulating Na+ flow across the cell membrane to initiate and propagate action potentials, NaV channels are responsible for the electrical excitability of cells and play crucial roles in ion regulation, neuromuscular communication, and digestion [54,55]. In addition, NaV channels are involved in regulating the cellular K+ flux [56], which is required for the continuous functioning of the sodium-potassium pump (Na+/K+ATPase). Therefore, the inhibition of the NaV1.4b gene observed before and after hatching (26 and 44 hpf) may be a way of preserving the ATP pool, given that pre- and post-hatching phases are critical periods during fish development and are energetically costly [57]. In a broader context, the over-expression of the NaV1.4b gene could protect the cellular machinery of young larvae, as Na+ ions play key roles in many cellular mechanisms (e.g., neurotransmission, osmoregulation, and immunity) [58,59]. It would be useful to study the adenylate energy charge (AEC) by estimating the variation in energy content (in terms of ATP, ADP, and AMP concentrations) throughout the development of STX-exposed embryos to assess the impact of toxic stress on cellular metabolism, especially in these energy-related pathways.
To our knowledge, no study has identified the different NaV channel isoforms found in Seriola species or, more generally, in fish of the family Carangidae. In the case of the NaV1.4 isoform, which is primarily found in skeletal muscle cells, amino acid substitutions in the alpha subunit have been reported to confer resistance to toxins with positively charged guanidinium, including saxitoxin (STX), tetrodotoxin (TTX), and their derivatives. In particular, these substitutions alter the pore structure of the channels and electrostatic interactions between the toxin and pore, thus preventing the toxin from binding to the channel. This phenomenon has been described in several pufferfish species, the blue-ringed octopus (Hapalochlaena sp.), and soft-shell clam (Mya areneria) [60]. In the future, it would be interesting to identify the different isoforms of the NaV channels in S. rivoliana, the way they are related to ontogenetic development, and their distributions within tissues. The sensitivity and resistance of the different NaV channels to guanidinium toxins should also be assessed in this species.
3.4. No STX-Induced Oxidative Stress
Specific peroxidase activity was detected as early as 8 hpf and then significantly decreased between 26 and 50 hpf in both control and STX-exposed embryos (Figure 3C). Peroxidases are antioxidant enzymes capable of degrading hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a reactive oxygen species (ROS) that oxidizes lipids, DNA, and proteins. These enzymes are integral to the antioxidant defense systems of aquatic organisms and protect cell membranes and various molecules within cells [61]. In the present study, peroxidase (PER) activation suggests the presence of H2O2 in both control and STX-exposed embryos. However, PER activity was not significantly higher in exposed embryos than in the control. In adult fish, PSTs are known to induce oxidative stress, which can be observed in the modulation of antioxidant enzymes such as catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) [49,62,63] Table S2. The results of PER activity do not suggest that STX induced oxidative stress in fish embryos and larvae. The overproduction of ROS is importantly related to cytotoxicity and cell apoptosis [64].
3.5. Activation of Lipid Metabolism and Digestion-Related Pathways
The regulation of lipid metabolism was assessed by measuring the expression of the PPRC1 gene, which encodes the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) coactivator relative protein 1. PPRC1 gene expression was detected as early as 8 hpf in control embryos and significantly increased between 50 and 62 hpf in control larvae (Figure 2C). PPARγ is not only a key component in adipogenesis and lipid storage, biosynthesis, and metabolism but also helps regulate inflammatory responses, cell differentiation, and cell proliferation [65,66,67]. Lipid metabolism, and, more specifically, the β-oxidation of fatty acids, is an essential metabolic pathway for the consumption of yolk reserves during embryo development and the development of lecithotrophic larvae, which depend on lipid droplets because these are the only endogenous reserves available after yolk sac depletion [68].
The results obtained in this study indicate a metabolic activation at 62 hpf (i.e., 26 h old larvae) and provide evidence of the consumption of the remaining endogenous reserves prior to mouth opening and the first exogenous feeding. Similarly, Brenta et al. [36] found an increase in lipase activity in control larvae between 0 and 3 days post-hatching (i.e., before the onset of exogenous feeding), which may be a mechanism to initiate the digestion of exogenous food. Given that PPARγ is also involved in cell differentiation and proliferation, the induction of the PPRC1 gene at 62 hpf may also indicate tissue development in young lecithotrophic larvae. Thus, the PPRC1 gene expression results provide evidence that 26 h old lecithotrophic larvae are metabolically more active than embryos.
The activation of digestion-related pathways was investigated using the activity of ALP. In both the control and STX treatments, ALP activity was detected throughout embryo development (from 8 to 44 hpf) and then dropped to near-zero levels at 50 and 62 hpf. ALPs are intrinsic membrane proteins that are involved in digestion, membrane transport, innate immunity, and bone mineralization [69,70,71]. Thus, the increase in ALP activity in embryos may, in part, indicate the need to regulate the activity of enzymes involved in these various mechanisms, including digestion. Indeed, although the digestive system is not complete and functional at the embryonic stage, some digestive enzymes, such as ALP and lipase, have been detected in fish embryos and could potentially play roles in the absorption of lipids from maternal yolk [36,37]. In contrast, during the early larval stages of both treatments, ALP activity was almost zero at 50 and 62 hpf, indicating that either these enzymes exhibited little or no involvement in the lipid metabolism of lecithotrophic S. rivoliana larvae or that they were inactivated via other phosphatases or degraded via external stress.
STX exposure triggered an up-regulation of the PPRC1 gene at 50 hpf followed by down-regulation at 62 hpf in STX-exposed larvae (Figure 2C). However, no significant changes in ALP activity were observed between the control and STX treatments. The present results of PPRC1 gene expression suggest that the response to STX exposure occurs in two phases in lecithotrophic larvae. The first phase is characterized as active lipid metabolism that results in the rapid consumption of yolk reserves, which reflects a short-term stress response to meet energetic demands. During the second phase, the inhibition of lipid metabolism indicates either an inability of larvae to maintain a high metabolic rate when stress is prolonged or the total depletion of endogenous energy reserves at 62 hpf. Considering the results of the present study and those of Le Du et al. [37] and Brenta et al. [36], the pathways involved in lipid metabolism and digestion in S. rivoliana larvae are more affected by OA+DTX-1, followed by STX and GTX and their analogs.
As a consequence of the inhibition of fatty acid β-oxidation, stress resistance, and immune functions may be impaired in fish. However, to our knowledge, this hypothesis has only been proposed in adult fish [72] but not in lecithotrophic larvae. This may be because the innate immune response of stress resistance is not well developed at this larval stage and only becomes active at the larval mouth opening. Lecithotrophic larvae are more vulnerable than embryos to toxins because they do not have a protective envelope (chorion) and are consequently more vulnerable to toxin exposure. Moreover, the mechanisms for STX detoxification may not yet be developed in the early larval stages of S. rivoliana and only become activated later in development. In the larval stages of marine fish, adaptive mechanisms for detoxification or sequestration may have evolved as proposed for Pacific herring (Clupea harengus pallasi) [73].
3.6. Regulation of Protein Phosphatases
Protein phosphatases (PPs) are phosphatases that reverse the action of protein kinases by dephosphorylating amino acids in proteins, primarily serine (Ser), threonine (Thr), and tyrosine (Tyr) residues. For example, protein Ser/Thr phosphatases remove phosphate from Ser and Thr residues in proteins [74]. Protein phosphatases have been well studied in ecotoxicology, especially PP1 and PP2A, which are known to be inhibited by marine toxins such as OA and microcystin-LR (MC-LR) [75]. In the present study, PP activity was detected in control embryos from 8 hpf onwards (i.e., before hatching; Figure 3A and Figure 4), which was also observed in a previous study of S. rivoliana embryos [35]. Similarly, Shi et al. [76] found pre-hatching phosphatase activity in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) embryos. In the present study, PP activity was detected throughout embryonic development (from 8 to 44 hpf) and then drastically decreased to near-zero levels at 50 and 62 hpf during the early larval stages. This inhibition of PP activity in both control and STX-exposed larvae may result from the regulation of these enzymes via ontogenetic processes, which could be genetically programmed, or oxidative stress-related processes in cells. To date, the inhibition of PP by oxidative stress has never been described in marine organisms. On the other hand, in some cell lines, it has been demonstrated that H2O2 is able to inhibit PP activity rapidly [77,78]. Although PP activity was significantly lower in exposed embryos than those in the control at 26 hpf, it is unlikely that STX inhibits the activity of PPs, as this inhibitory capacity is linked to a particular molecular structure (i.e., an extended aliphatic chain with a circular component), which is common to OA and MC-LR [72] but not to STX (Table S2).
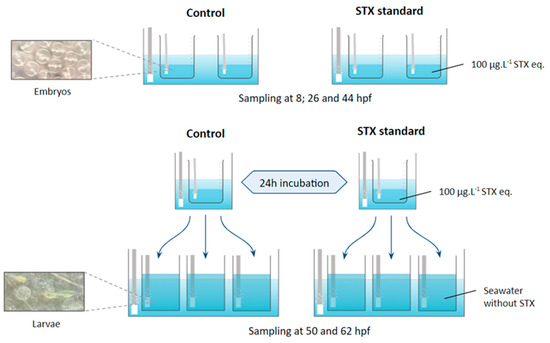
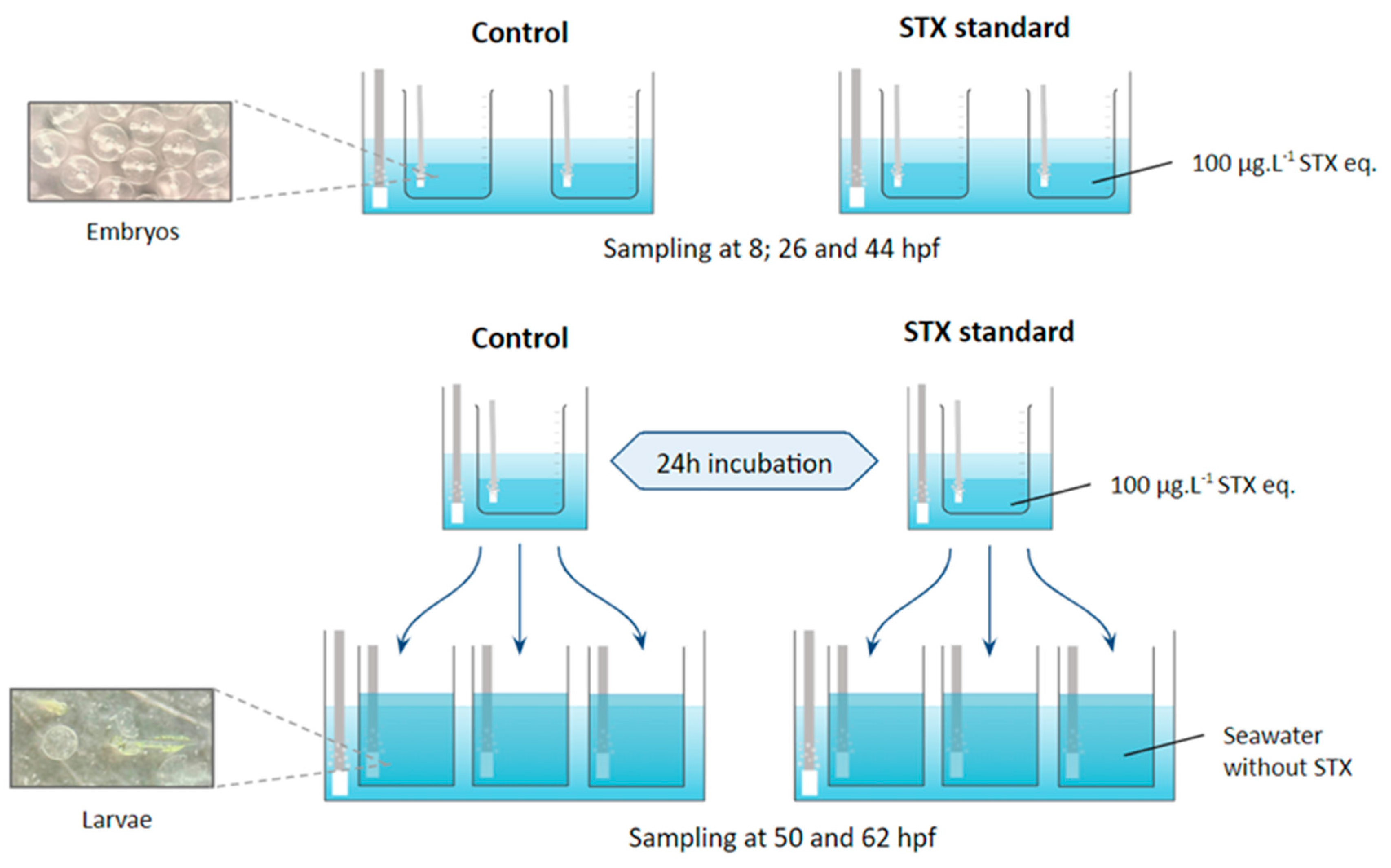
Figure 4.
Experimental design for embryo culture and sampling.
Dual-specificity phosphatases (DUSPs) are protein phosphatases that can dephosphorylate many key signaling molecules, including mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), which are associated with stress responses, immune responses, cell proliferation, and differentiation [79,80]. Through their dephosphorylation activity, DUSP8 phosphatases trigger the inactivation of stress-activated MAPK isoforms, c-Jun amino-terminal kinases (JNKs 1–3), and p38 MAPKs. By regulating the activity of both classes of MAPKs, DUSP8 plays roles in innate and adaptive immunity [81,82]. Therefore, DUSP8 activity must be properly controlled. The present results show that STX exposure during embryonic development induced an early up-regulation of DUSP8 in the first larval stages, which could indicate the need to regulate stress-activated MAPK activities or, alternatively, to release additional inorganic phosphates to produce more energy.
Nevertheless, an uncontrolled up-regulation of DUSP8 can strongly impact stress-activated MAPK signaling pathways and thus alter many key cellular processes. In the present study, the expression level was 120-fold higher in STX-exposed larvae than in control larvae at 50 hpf (p < 0.01), which may indicate the uncontrolled expression of the DUSP8 gene due to STX exposure. Consequently, the MAPK signaling pathways may be altered, leading to the inhibition of cell proliferation and differentiation. This is a likely hypothesis because some studies have reported that STX can retard growth or induce abnormal growth in fish embryos and larvae [20,49], reducing body weight and size in adult fish [63]. The results of DUSP8 gene expression do not reflect those of PP enzymatic activity. This discrepancy may be because the enzymatic assay employed in this study does not specifically target the activity of DUSP8 but measures all PPs, including PP1 and PP2A, which are known to be more prominently represented in cells than DUSP8 [75].
3.7. Implications of Other Factors in Embryonic and Larval Development
Although in vivo experiments are easier to implement and more reproducible than in situ studies, they have the disadvantage of being less relevant from an ecological point of view, as laboratory conditions cannot closely mimic natural conditions. The toxicity of STX at a concentration of 100 µg L−1 induced very high mortality in embryos. This observation is noteworthy because equivalent concentrations of PSTs may be present in the ecosystem during HABs. If true, this is a major problem for larviculture and fish reared in marine culture cages, as marine toxins can cause the massive mortality of larvae in hatcheries. Water filtration systems can control PST-producing dinoflagellate and cyanobacterial cells, but their toxins, which are dissolved in seawater due to their polar nature [83], cannot be controlled. Paralytic shellfish toxins are also highly thermostable and difficult to degrade, which results in notable bioaccumulation in tissues [84]. Although PSTs can be easily excreted via renal processes in fish due to their hydrophilic nature, they cannot be excreted in the same manner during early life stages when renal systems are not yet fully developed, making eggs and larvae highly vulnerable to HAB toxins [51]. The spatiotemporal overlap between fish spawning and HABs is critical to the success of fisheries recruitment and fish rearing. Thus, the sublethal effects of marine toxins during embryonic and larval life stages must be considered to improve the performance of fisheries and aquaculture programs.
Some authors, including Reis Costa et al. [39] and Roggatz et al. [85], have described a global climate change scenario in which the concomitant decrease in pH and increase in ocean temperatures elevate the bioavailability and toxicity of marine toxins, such as STX and TTX, negatively affecting ecosystems and human and animal health. This scenario has important implications for ecotoxicology and the chemical signals mediating interactions among marine species, such as foraging, reproduction, predation, and defense, with unknown consequences for ecosystem stability and vital ecosystem services [39].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Acquisition, Extraction, and Quantification of Marine Toxins
An STX FDA Reference Standard was obtained from the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST, RM 8642). The reference material (RM) was saxitoxin dihydrochloride (CAS No. 35554-08-6) in a solution containing hydrochloric acid at a concentration of 5 mmol L−1 in 20% ethanol in water (volume fraction). The reference value for saxitoxin dihydrochloride is 103 ± 2 μg g−1. The STX FDA standard was provided by the Marine Toxins and Amino Acids Laboratory of CIBNOR (Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas del Noroeste S.C.). Saxitoxin activity and toxicity were calculated via mouse bioassay (MBA) following the recommendations described in the official protocol of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists [86]. To prepare the toxin solution, the original STX standard was concentrated via evaporation and then diluted in sterile saline solution (0.9% NaCl), as described by Le Du et al. [37].
4.2. Assessment of Embryonic Development and Larval Viability
4.2.1. Experimental Protocol
Fertilized eggs were obtained from the natural spawning of Seriola rivoliana broodstock maintained in captivity under optimum conditions in collaboration with Ocean Era (formally Kampachi Farms) in CIBNOR. Eggs were collected with a 300 µm mesh bag and volumetrically counted to add ~15,200 eggs (i.e., 19 mL) to each 1 L glass jar (replicate). We began with three replicates containing 330 mL of seawater with embryos exposed to standard saxitoxin (100 μg L−1) and three controls containing 500 mL seawater without toxins. This concentration was chosen based on previous work with S. rivoliana embryos and larvae exposed to PSTs (GTX 2–3, dc-GTX 2–3, and C1–C2), demonstrating that this concentration is sufficient to impact embryonic and larval development without resulting in death [36]. This concentration was also chosen for its ecological relevance, as similar concentrations naturally occur during HABs. The seawater (38‰ salinity) was previously filtered (0.45 µm). All glass replicates were placed in a water bath (24.0 ± 0.4 °C) and homogenized with strong airflow to oxygenate the eggs, which were constantly mixed from top to bottom (Figure 4).
For each treatment (STX and control), two replicates were used to monitor embryonic development. For this purpose, 500 µL of eggs per replicate were collected at 8, 26, and 44 hpf and fixed in 500 µL of RNAlater® (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA, USA) solution for gene expression analysis. Another 500 µL of eggs per replicate were collected at the same time for enzymatic assays. The samples were stored in 2 mL Eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf® Premium U410, New Brunswick, NJ, USA) at −80 °C for molecular or enzymatic assays.
To monitor larval viability, the eggs from three replicates per treatment were incubated for 24 h and then distributed in three 2 L plastic tanks containing previously filtered seawater with a 1 µm Gaff bag. At 12 and 24 h after incubation (i.e., 50 and 62 hpf), 500 µL of larvae per replicate were collected to monitor viability with a light microscope coupled to a digital camera.
4.2.2. Hatching Percentage
Given that hatching occurs at 36 hpf in S. rivoliana [38], the hatching percentage was assessed at 44 hpf for the control and STX treatment once the majority of viable embryos had hatched and after all embryonic developmental monitoring samples had been collected. For this purpose, the remaining eggs and larvae in the different tanks were collected and preserved in Davidson’s solution. The numbers of eggs and larvae contained in 1 mL aliquots were determined and reported based on the total sample volume. The hatching percentage (HP) was calculated using Equation (1):
where NL and NE are the number of larvae and eggs, respectively.
4.3. Gene Expression
4.3.1. Primer Design
Oligonucleotides were designed in Primer 3 Plus v. 3.2.6 (https://dev.primer3plus.com/index.html (accessed on 2 February 2022)) from the target sequences derived from the transcriptome of S. rivoliana larvae [87]. Then, the self-complementarity of the selected primers was checked with Oligo Calc (http://biotools.nubic.northwestern.edu/OligoCalc.html (accessed on 2 February 2022)). The primers are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Primer sequences used for quantitative real-time PCR analysis.
4.3.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
TRizol® RNA Isolation Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) was used according to the recommendations of the manufacturer to extract total RNA. Around 100 mg (103 ± 4 mg) of embryos or larvae were manually homogenized in 1 mL of TRizol using pestles. The concentration and purity of RNA were measured using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific). RNA quantity was then visualized via electrophoresis in a 2.0% agarose gel with 1X Tris-Sodium Acetate EDTA (TAE) buffer to confirm integrity. Finally, an Improm II kit (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) was used to synthesize cDNA following the procedure provided by the manufacturer. The reaction was conducted with 1 µg of total RNA in a thermal iCycler (Bio-Rad, Berkeley, CA, USA).
4.3.3. Real-Time PCR
To quantify the target genes in S. rivoliana embryos and larvae, a standard curve was constructed to observe the dynamic range of primer detection, verify the amplification efficiency (100% efficiency corresponds to a slope of −3.32), and select the dilution at which the samples should be quantified (1:5 dilution for the NaV1.4b gene and 1:10 dilution for the other genes). Once the dilution was set, the expression level of the target genes was quantified using SsoFastTM EvaGreen® Supermix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). In each well, 5 µL of sample was mixed with 10 µL of reaction mix (0.15 µL of forward and reverse primers, 0.6 µL of MgCl2, 7.5 µL of SsoFast™ EvaGreen® Supermix (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) and 1.6 µL of water). Each assay measurement was performed in triplicate. The 18S ribosomal RNA gene was chosen as a reference to normalize the quantification cycles (Cq), which were analyzed according to CFX-Manager software algorithms (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
4.4. Protein Determination and Enzymatic Assays
Around 100 mg (103 ± 9 mg) of embryos or larvae were homogenized with 500 µL sterile deionized water in 2 mL Eppendorf PCR tubes containing grinding beads. Homogenization was performed using a FastPrep-24TM homogenizer 5G (MP Biochemicals, Santa Ana, CA, USA). Total soluble protein content was measured in the homogenates via photometry, as described by Bradford [88], using Bio-Rad Protein Assay dye reagent (Bio-Rad 500-0205) and bovine serum albumin (BSA, Sigma A7906, Madrid, Spain) as the standard. Protein and alkaline phosphatase activities were measured using a fluorometric method based on the protocol of Gee [89]. Enzyme kinetics were followed at a fluorescence wavelength of 460 nm with an excitation wavelength of 335 nm for 30 min (60 reads, 30 s each) at 30 °C. Peroxidase activity was measured via end-point spectrophotometry at 450 nm. Protein determination and enzyme activity were assessed using a 96-well plate spectrophotometer (Varioskan™, Thermo Fisher Scientific). Samples were assayed in triplicate in 96-flat bottom microplates and corrected with a blank (i.e., a sample was replaced by deionized water in the reaction mix). The following reaction mixes were employed.
Protein phosphatase: 10 μL of sample diluted 1:3, 140 μL of reaction solution (50 mM Tris-HCl, 11 mM MgCl2, 5 mM dithiothreitol, and 200 µg mL−1 serum albumin, pH = 7.0), and 50 µL of substrate solution (6, 8-Difluoro-4-methylumbelliferyl phosphate [DiFMUP] 200 µM) purchased from Molecular Probes (Eugene, OR, USA).
Alkaline phosphatase: 10 μL of sample diluted 1:3, 140 μL of reaction solution (100 mM Glycine, 1 mM MgCl2, and 1 mM ZnCl2, pH = 10.4), and 50 µL of substrate solution (DiFMUP 200 µM).
Peroxidase: 20 µL of sample diluted 1:3, 100 µL of reaction solution (0.2 M dibasic sodium phosphate, 0.1 M citric acid, one TMB [3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine, Sigma T8665], and 2 µL hydrogen peroxide for 40 mL of solution), and 50 µL of stop solution (40 mM sulfuric acid) added as soon as the mixture turned blue in the microplate wells.
4.5. Data Treatment and Statistical Analysis
Relative normalized gene expression data were obtained from CFX Manager™ v. 3.1 (Bio-Rad, Berkeley, CA, USA). Alkaline and protein phosphatase activities were calculated based on the slope of the linear regression obtained from the Abs = f(t) curve. Total enzyme activity was related to total soluble protein content to obtain the specific enzyme activity. Peroxidase activity was calculated using the following formula:
The final values for enzyme activity and gene expression correspond to the average of the experimental replicates. Considering the small sample size of each treatment (n = 2 or 3), extreme values were only eliminated from analyses when necessary.
Data are presented as mean ± standard error (SE) of 2 or 3 replicates for each representative treatment. The normality and homoscedasticity of the data were first checked using the Shapiro–Wilk and Levene tests, respectively. A parametric Student’s t-test was performed to compare the means of the hatching percentages between the control and STX treatments. Most data sets of gene expression and enzyme activity results exhibited non-normal distributions or significant differences in variance homogeneity. Thus, a non-parametric Kruskal–Wallis test was used for the overall comparison of means between groups, followed by Dunn’s post hoc test for multiple mean comparisons. The significance level was set to α = 0.05 for all statistical tests. Statistical analyses and results were performed and prepared in R v. 4.1.2 (R Core Team 2021).
5. Conclusions
The present study improves our understanding of the toxicological effects of STX during the early life stages of S. rivoliana. An STX concentration of 100 µg L−1 induced very high mortality in embryos and affected the expression of genes coding for NaV1.4b channels, the main target of this toxin, as well as the expression and activity of enzymes involved in a wide variety of cellular mechanisms—including stress responses (HSF2), lipid metabolism (PPRC1), and digestion (ALP)—and signaling pathways associated with cell proliferation and differentiation (dual-specificity MAP kinase phosphatases). No significant differences in the specific activities of the ALP and PER enzymes were observed in STX-exposed embryos compared to those in the control. For further studies, a proteomic approach in conjunction with transcriptomic analysis should be followed to determine which cellular pathways are most affected by STX exposure and which responses are primed at the molecular and cellular levels during different embryonic and larval development stages.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/md21110597/s1, Figure S1: Spawning volume obtained from S. rivoliana broodstock reared by Kampachi Farms. Table S1: Summary of the research on the effects of exposure to various concentrations of paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs), including saxitoxin (STX) and gonyautoxin (GTX), in different fish species. Table S2: Marine toxins, chemical structure, and main mode of action in the intoxicated organism [23,36,49,62,63,73,90,91,92,93].
Author Contributions
All authors contributed significantly to this study. Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing, review, and editing: C.G.; conceptualization, original draft preparation, resources, funding acquisition, methodology, investigation, writing, review, and editing: E.J.N.-V.; data curation and software, visualization and editing, review, and editing: L.J.F.-H.; methodology and review: D.A.C.-R.; conceptualization, resources, original draft preparation, funding acquisition, methodology, investigation, writing, review, and editing: D.T.-R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financed by CONAHCyT (project 319865) Ciencia Básica y/o Ciencia de Frontera Modalidad: Paradigmas y Controversias de la Ciencia 2022.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The experiment complied with the Guidelines of the European Union Council (2010/63/EU) and the Mexican Government (NOM-062—ZOO-1999) for the production, care, and use of experimental animals, and with the ARRIVE guidelines.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or Supplementary Material.
Acknowledgments
E.J.N.-V. dedicates this work to the memory of Paul J. Scheuer (1915–2003; University of Hawaii), a pioneer in the discovery of various marine toxins and ecological research in marine chemistry, co-founder of the modern chemistry of marine natural products, and inspiring scientist who worked to develop the nascent research in Marine Toxinology in Mexico during his visit to CIBNOR in La Paz, Baja California Sur, during the early 1990s. The authors thank Kampachi Farms for providing the fertilized eggs to carry out the study; This work is also dedicated to the memory of Biol. Patricia Hinojosa-Baltazar† (1968–2023) Responsible Technician of the Laboratory of Comparative Physiology and Functional Genomics of the CIBNOR, Pablo Monsalvo-Spencer, and Carlos Ceseña for their technical assistance; and Andrea Lievana MacTavish for English editing. Colleen Guinle received financial support from the Regional Council of Brittany and LabexMER, France, during this study, and Leyberth Fernandez-Herrera received a postdoctoral fellowship (CONACyT; project 319865).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Anderson, D.M.; Cembella, A.D.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Progress in understanding harmful algal blooms: Paradigm shifts and new technologies for research, monitoring, and management. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 143–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louzao, M.C.; Vilariño, N.; Vale, C.; Costas, C.; Cao, A.; Raposo-Garcia, S.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Current Trends and New Challenges in Marine Phycotoxins. Marine Drugs 2022, 20, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumoto, T.; Murata, M. Marine Toxins. Chem. Rev. 1993, 24, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Vazquez, E.J.; Garate-Lizarraga, I.; Cordero-Tapia, A.; López-Cortes, D.J.; Hernández-Sandoval, F.E.; Heredia-Tapia, A.; Bustillos-Guzmán, J. Impact of harmful algal blooms on wild and cultured animals in the Gulf of California. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 413–423. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Hernandez-Sandoval, F.E.; Bustillos-Guzman, J.J.; López-Cortés, D.J.; Cordero-Tapia, A.; Heredia-Tapia, A.; Garcia-Mendoza, E.; Peña-Manjarrez, J.; Ruiz-de la Torre, M.; et al. Impactos de los FAN en la salud pública y animal (silvestres y de cultivo) en el Golfo de California. In Florecimientos Algales Nocivos en México; García-Mendoza, E., Quijano-Sheggia, S.I., Olivos-Ortiz, A., Núñez-Vázquez, E.J., Eds.; CICESE: Mexico City, Mexico, 2016; pp. 196–212. [Google Scholar]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Marine Biotoxins. 2. Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2004; p. 281. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dolah, F. Marine Algal Toxins: Origins, Health Effects, and Their Increased Occurrence. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, I.R.; Humpage, A.R. Health Risk Assessment of Cyanobacterial (Blue-green Algal) Toxins in Drinking Water. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 2, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.F.; Cristiano, M.L.S. Marine paralytic shellfish toxins: Chemical properties, mode of action, newer analogues, and structure-toxicity relationship. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilariño, N.; Louzao, M.C.; Abal, P.; Cagide, E.; Carrera, C.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Human Poisoning from Marine Toxins: Unknowns for Optimal Consumer Protection. Toxins 2018, 10, E324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.; Peigneur, S.; Tytgat, J. Neurotoxins and their binding areas on voltage-gated sodium channels. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thottumkara, A.P.; Parsons, W.H.; Du Bois, J. Saxitoxin. Angew. Chem. 2014, 53, 5760–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Sheets, M.; Ishida, H.; Li, F.; Barry, W.H. Saxitoxin Blocks L-Type ICa. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Salata, J.J.; Bennett, P.B. Saxitoxin Is a Gating Modifier of hERG K+ Channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2003, 121, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Duran-Riveroll, L.M.; Bustillos-Guzman, J.J.; Leyva-Valencia, I.; Lopez-Cortes, D.J.; Nunez-Vazquez, E.J.; Ramírez-Rodríguez, D.V. Paralytic toxin producing dinoflagellates in Latin America: Ecology and physiology. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schier, A.F.; Talbot, W.S. Molecular genetics of axis formation in zebrafish. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005, 39, 561–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espiña, B.; Louzao, M.C.; Cagide, E.; Alfonso, A.; Vieytes, M.R.; Yasumoto, T.; Botana, L.M. The methyl ester of okadaic acid is more potent than okadaic acid in disrupting the actin cytoskeleton and metabolism of primary cultured hepatocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillotin, S.; Delcourt, N. Marine Neurotoxins’ Effects on Environmental and Human Health: An OMICS Overview. Marine Drugs 2021, 20, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoffier, N.; Gaudin, J.; Mezhoud, K.; Huet, H.; Chateau-Joubert, S.; Turquet, J.; Crespeau, F.; Edery, M. Toxicity to medaka fish embryo development of okadaic acid and crude extracts of Prorocentrum dinoflagellates. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Trainer, V.L.; Scholz, N.L. Morphological abnormalities and sensorimotor deficits in larval fish exposed to dissolved saxitoxin. Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 66, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, W. Gene expression profiles in zebrafish (Danio rerio) liver after acute exposure to okadaic acid. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, V.; Azevedo, J.; Silva, M.; Ramos, V. Effects of marine toxins on the reproduction and early stages development of aquatic organisms. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Cortés, D.J.; Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Hernandez-Sandoval, F.E.; Bustillos-Guzman, J.J.; Leyva-Valencia, I.; Fernández Herrera, L.J. The State of Knowledge of Harmful Algal Blooms of Margalefidinium polykrikoides (a.k.a. Cochlodinium polykrikoides) in Latin America. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Heredia-Tapia, A.; Pérez-Urbiola, J.; Alonso, R.; Arellano-Blanco, J.; Cordero-Tapia, A.; Pérez-Linares, J. Ochoa, J.L Evaluation of dinoflagellate toxicity implicated in recent HAB events in the Gulf of California, México. In Proceedings from HABTech 2003 APEC: A Workshop on Technologies for Monitoring of Harmful Algal Blooms and Marine Biotoxins; Cawtron Report No. 906; Holland, P., Rhodes, L., Brown, L., Eds.; Cawthron Institute: Nelson, New Zealand, 2003; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Eschmeyer, W.N.; Herald, E.S.; Hammann, H. A Field Guide to Pacific Coast Fishes: North America; Houghton Mifflin: Boston, MA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Cervigón, F. Los peces marinos de Venezuela. In Estación de Investigaciones Marinas de Margarita; Fundación La Salle de Ciencias Naturales: Caracas, Venezuela, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Arellano, J.L.; Luzardo, O.P.; Brito, A.P.; Cabrera, M.H.; Zumbado, M.; Carranza, C.; Angel-Moreno, A.; Dickey, R.W.; Boada, L.D. Ciguatera fish poisoning, Canary Islands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1981–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Pérez, S.; Alfonso, A.; Vale, C.; Rodríguez, P.; Gouveia, N.N.; Gouveia, N.; Delgado, J.; Vale, P.; Hirama, M.; et al. First toxin profile of ciguateric fish in Madeira Arquipelago (Europe). Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6032–6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boada, L.D.; Zumbado, M.; Luzardo, O.R.; Almeida-Gonzalez, M.; Plakas, S.M.; Granade, H.R.; Abraham, A.; Jester, E.L.E.; Dickey, R.W. Ciguatera fish poisoning on the West Africa Coast: An emerging risk in the Canary Islands (Spain). Toxicon 2010, 56, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roo, J.; Fernández-Palacios, H.; Hernández-Cruz, C.M.; Mesa-Rodríguez, A.; Schuchardt, D.; Izquierdo, M. First results of spawning and larval rearing of longfin yellowtail Seriola rivoliana as a fast-growing candidate for European marine finfish aquaculture diversification. Aquac. Res. 2014, 45, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, A.; Favaloro, E.; Sarà, G. Cultivation of the Mediterranean amberjack, Seriola dumerili (Risso, 1810), in submerged cages in the Western Mediterranean Sea. Aquaculture 2000, 181, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa-Rodríguez, A.; Hernandez-Cruz, M.; Socorro, J.A.; Fernández-Palacios, H.; Izquierdo, M.; Roo, J. Skeletal Development and Mineralization Pattern of the Vertebral Column, Dorsal, Anal and Caudal Fin Complex in Seriola rivoliana (Valenciennes, 1833) Larvae. J. Aquac. Res Dev. 2014, 5, 2155–9546. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, T.; Teruya, K.; Hara, T.; Hokazono, H.; Hashimoto, H.; Suzuki, N.; Iwashita, Y.; Matsunari, H.; Furuita, H.; Mushiake, K. Nutritional evaluation of live food organisms and commercial dry feeds used for seed production of amberjack Seriola dumerili. Fish. Sci. 2008, 74, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rountos, K.J.; Kim, J.J.; Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Gobler, C.J. Effects of the harmful algae, Alexandrium catenella and Dinophysis acuminata, on the survival, growth, and swimming activity of early life stages of forage fish. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 148, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillard, S.; Réveillon, D.; Mason, P.L.; Ayache, N.; Sanderson, M.; Smith, J.L.; Giddings, S.; McCarron, P.; Séchet, V.; Hégaret, H.; et al. Mortality and histopathology in sheepshead minnow (Cyprinodon variegatus) larvae exposed to pectenotoxin-2 and Dinophysis acuminata. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 257, 106456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenta, A.; Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Asencio-Alcudia, G.; Teles, A.; Salas, J.; Álvarez-González, C.A.; Fernández-Herrera, L.J.; Tovar-Ramírez, D. Dissolved diarrhetic and paralytic shellfish toxins affects viability and lipid metabolism in Seriola rivoliana embryo. Aquatic Toxicol. 2023; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Le Du, J.; Tovar-Ramírez, D.; Núñez-Vázquez, E.J. Embryotoxic effects of dissolved okadaic acid on the development of Longfin yellowtail Seriola rivoliana. Aquat.Toxicol. 2017, 190, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, E.; Fernández-Palacios, H.; Abreu, N.; Socorro, J.A.; Roo, J.; Hernandez-Cruz, M.; Schuchardt, D. Organogénesis y morfometría de la fase lecitotrófica de larvas del medregal negro (Seriola rivoliana, Valenciennes,1883). In Proceedings of the XII Congreso Nacional de Acuicultura, Madrid, Spain, 24–26 November 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis Costa, P. Impact and effects of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins derived from harmful algal blooms to marine fish. Fish Fish. 2014, 17, 226–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi-Khalil, C.; Finkelstein, D.S.; Conejero, G.; Du Bois, J.; Destoumieux-Garzon, D.; Rolland, J.L. The paralytic shellfish toxin, saxitoxin, enters the cytoplasm and induces apoptosis of oyster immune cells through a caspase-dependent pathway. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 190, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medhioub, W.; Ramondenc, S.; Vanhove, A.S.; Vergnes, A.; Masseret, E.; Savar, V.; Amzil, Z.; Laabir, M.; Rolland, J.L. Exposure to the Neurotoxic Dinoflagellate, Alexandrium catenella, Induces Apoptosis of the Hemocytes of the Oyster, Crassostrea gigas. Marine Drugs 2013, 11, 4799–4814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Hu, T. Effect of acute exposure of saxitoxin on development of zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio). Environl. Res. 2020, 185, 109432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwama, G.; Thomas, P.; Forsyth, R.; Vijayan, M. Heat shock expression in fish. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1998, 8, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, G.; Afonso, L.; Todgham, A.; Ackerman, P.; Nakano, K. Are hsps suitable for indicating stressed states in fish? J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, D.-F.; Wang, C.; Lee, S.; Bai, S.; Hung, S.S.O. Feeding rates affect heat shock protein levels in liver of larval white sturgeon (Acipenser transmontanus). Aquaculture 2009, 287, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, H.; Xu, M.; Dai, J. The identification of heat shock protein genes in goldfish (Carassius auratus) and their expression in a complex environment in Gaobeidian Lake, Beijing, China. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 145, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, B.; Wu, H.; Nie, P. Effects of pure microcystin-LR on the transcription of immune related genes and heat shock proteins in larval stage of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Aquaculture 2009, 289, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Gu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z. Accumulation, and detoxification dynamics of microcystin-LR and antioxidant responses in male red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 177, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Cheng, J.; Chen, X.; Cheng, S.H.; Mak, Y.L.; Lam, P.K.S.; Chan, L.L.; Wang, M. Early developmental toxicity of saxitoxin on medaka (Oryzias melastigma) embryos. Toxicon 2014, 77, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, V.; Santos, M.; Anacleto, P.; Maulvault, A.L.; Pousão-Ferreira, P.; Costa, P.R.; Marques, A. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Ocean Warming: Bioaccumulation and Ecotoxicological Responses in Juvenile Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Toxins 2019, 11, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pederzoli, A.; Mola, L. The early stress responses in fish larvae. Acta Histochem. 2016, 118, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.P.; Gorzowski, J.J.; Sarge, K.D.; Phillips, B. Characterization of constitutive HSF2 DNA-binding activity in mouse embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 5309–5317. [Google Scholar]
- Bakke, M.J.; Horsberg, T.E. Kinetic properties of saxitoxin in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) and Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 152, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestèle, S.; Catterall, W.A. Molecular mechanisms of neurotoxin action on voltage-gated sodium channels. Biochimie 2000, 82, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat, A.; Klopp, C.; Payton, L.; Jeziorski, C.; Chalopin, M.; Amzil, Z.; Tran, D.; Wikfors, G.; Hégaret, H.; Soudant, P.; et al. Oyster transcriptome response to Alexandrium exposure is related to saxitoxin load and characterized by disrupted digestion, energy balance, and calcium and sodium signaling. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 199, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G. Noncanonical Roles of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels. Neuron 2013, 80, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulekbache, H. Energy Metabolism in Fish Development. Am. Zool. 1981, 21, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Iliuta, A. The role of sodium in the body. Balneo Res. J. 2011, 2, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, N.; Wang, H.; Mu, C.; Wang, C. Effects of salinity on the ions important and sodium-potassium ATPase in osmoregulation, cortisol, amino acids, digestive and immune enzymes in Scylla paramamosain during indoor overwintering. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4173–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thiel, J.; Ali Khan, M.; Wouters, R.; Harris, R.; Casewell, N.; Kini, R.; Mackessy, S.; Vonk, F.; Wüster, W.; Richardson, M. Convergent evolution of toxin resistance in animals. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2022, 97, 1823–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, D.; Signore, A.; Araneda, O.; Contreras, H.R.; Concha, M.; García, C. Toxicity and differential oxidative stress effects on zebrafish larvae following exposure to toxins from the okadaic acid group. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2020, 83, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis Costa, P.; Pereira, P.; Guilherme, S.; Barata, M.; Nicolau, L.; Santos, M.A.; Pacheco, M.; Pousão-Ferreira, P. Biotransformation modulation and genotoxicity in white seabream upon exposure to paralytic shellfish toxins produced by Gymnodinium catenatum. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 106–107, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.N.; Nam, S.-E.; Han, Y.-S.; Park, H.S.; Rhee, J.-S. Chronic exposure to sublethal concentrations of saxitoxin reduces antioxidant activity and immunity in zebrafish but does not affect reproductive parameters. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 243, 106070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Tang, X.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y. A ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway and Nrf2 pathway activation are involved in BDE-47 induced apoptosis in Neuro-2a cells. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, E.; Kaitetzidou, E.; Castellana, B.; Panteli, N.; Kyriakis, D.; Vraskou, Y.; Planas, J.V. In Vivo Effects of Lipopolysaccharide on Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Expression in Juvenile Gilthead Seabream (Sparus aurata). Biology 2017, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Poulsen, L.C.; Siersbæk, M.; Mandrup, S. PPARs: Fatty acid sensors controlling metabolism. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.-Y.; Nie, L.; Lu, X.-J.; Fei, C.-J.; Chen, J. Molecular characterization, expression, and functional analysis of large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2022, 123, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teles, A.; Salas-Leiva, J.; Alvarez-González, C.A.; Gisbert, E.; Ibarra-Castro, L.; Urbiola, J.C.P.; Tovar-Ramírez, D. Histological study of the gastrointestinal tract in longfin yellowtail (Seriola rivoliana) larvae. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1613–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atencio Genes, L.; Moreno, I.; Prieto, A.; Moyano, R.; Molina, A.; Cameán, A. Acute Effects of Microcystins MC-LR and MC-RR on Acid and Alkaline Phosphatase Activities and Pathological Changes in Intraperitoneally Exposed Tilapia Fish (Oreochromis sp.). Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 36, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.M.; Akerlund, J.; Mittge, E.; Guillemin, K. Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase Detoxifies Lipopolysaccharide and Prevents Inflammation in Zebrafish in Response to the Gut Microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynes, M.; Narisawa, S.; Millán, J.L.; Widmaier, E.P. Interactions between CD36 and global intestinal alkaline phosphatase in mouse small intestine and effects of high-fat diet. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 301, R1738–R1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Li, L.-Y.; Li, J.-M.; Wang, W.-L.; Limbu, S.M.; Degrace, P.; Li, D.-L.; Du, Z.-Y. Inhibited fatty acid β-oxidation impairs stress resistance ability in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 68, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, K.A.; Elder, N.E.; Hershberger, P.K.; Trainer, V.L.; Stehr, C.M.; Scholz, N.L. Dissolved saxitoxin causes transient inhibition of sensorimotor function in larval Pacific herring (Clupea harengus pallasi). Mar. Biol. 2005, 147, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barford, D. Molecular mechanisms of the protein serine/threonine phosphatases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996, 21, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, A.; Murata, M.; Torigoe, K.; Isobe, M.; Mieskes, G.; Yasumoto, T. Inhibitory effect of okadaic acid derivatives on protein phosphatases: A study on structure-affinity relationship. Biochem. J. 1992, 284 Pt 2, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Y.; Chen, X.W.; Gu, Y.F. Cloning, and expression pattern of alkaline phosphatase during the development of Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 37, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, H.; Nie, G.; Li, X. Responses of acid/alkaline phosphatase, lysozyme, and catalase activities and lipid peroxidation to mercury exposure during the embryonic development of goldfish Carassius aratus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 120–121, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Loghlen, A.; Pérez-Morgado, M.I.; Salinas, M.; Martín, M.E. Reversible inhibition of the protein phosphatase 1 by hydrogen peroxide. Potential regulation of eIF2 alpha phosphorylation in differentiated PC12 cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 417, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, S.G.; Chiu, D.T.; Errasfa, M.; Wang, J.M.; Qi, J.S.; Stern, A. Effects of H2O2 on protein tyrosine phosphatase activity in HER14 cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 16, 399–403. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.; Karin, M. Mammalian MAP kinase signaling cascades. Nature 2001, 410, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, D.M.; Keyse, S.M. Differential regulation of MAP kinase signalling by dual-specificity protein phosphatases. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3203–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Zhou, Y.; Long, R.; Chen, C.; Zhao, J.; Cui, P.; Guo, M.; Liang, G.; Xu, L. DUSP8 phosphatase: Structure, functions, expression regulation and the role in human diseases. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, L. Saxitoxin, a toxic marine natural product that targets a multitude of receptors. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2006, 23, 200–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso, A.; Louzao, M.C.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Comparative study of the stability of saxitoxin and neosaxitoxin in acidic solutions and lyophilized samples. Toxicon 1994, 32, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggatz, C.C.; Fletcher, N.; Benoit, D.M.; Algar, A.C.; Doroff, A.; Wright, B.; Wollenberg Valero, K.C.; Hardege, J.D. Saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin bioavailability increases in future oceans. Nat. Clim. Change 2019, 9, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Method 959.08 Paralytic Shellfish Poison, Biological Method, Final Action. In Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 16th ed.; Cunniff, P., Ed.; AOAC: Rockville, MD, USA, 1995; pp. 21–22. [Google Scholar]
- Teles, A.; Álvarez-González, C.A.; Llera-Herrera, R.; Gisbert, E.; Salas-Leiva, J.; del Rodríguez-Jaramillo, M.C.; Tovar-Ramírez, D. Debaryomyces hansenii CBS 8339 promotes larval development in Seriola rivoliana. Aquaculture 2023, 560, 738587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, K.R.; Sun, W.C.; Bhalgat, M.K.; Upson, R.H.; Klaubert, D.H.; Latham, K.A.; Haugland, R.P. Fluorogenic substrates based on fluorinated umbelliferones for continuous assays of phosphatases and beta-galactosidases. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 273, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosselin, S.; Fortier, L.; Gagné, J. Vulnerability of marine fish larvae to the toxic dinoflagellate Protogonyaulax tamarensis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salierno, J.D.; Snyder, N.S.; Murphy, A.Z.; Poli, M.; Hall, S.; Baden, D.; Kane, A.S. Harmful algal bloom toxins alter c-Fos protein expression in the brain of killifish, Fundulus heteroclitus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 78, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, C.A.; de Morais, E.C.; Costa, M.D.; Ribas, J.L.; Guiloski, I.C.; Ramsdorf, W.A. Saxitoxins induce cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and oxidative stress in teleost neurons in vitro. Toxicon 2014, 86, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva de Assis, H.C.; da Silva, C.A.; Oba, E.T.; Pamplona, J.H.; Mela, M.; Doria, H.B.; Guiloski, I.C.; Ramsdorf, W.; Cestari, M.M. Hematologic and hepatic responses of the freshwater fish Hoplias malabaricus after saxitoxin exposure. Toxicon 2013, 66, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).