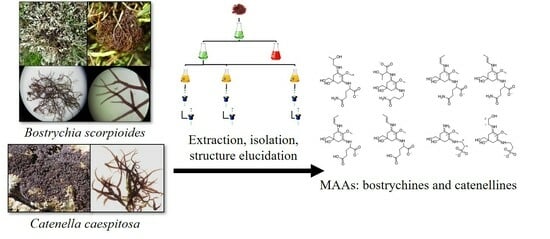
Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Novel Mycosporine-like Amino Acids from the Two Intertidal Red Macroalgae Bostrychia scorpioides and Catenella caespitosa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
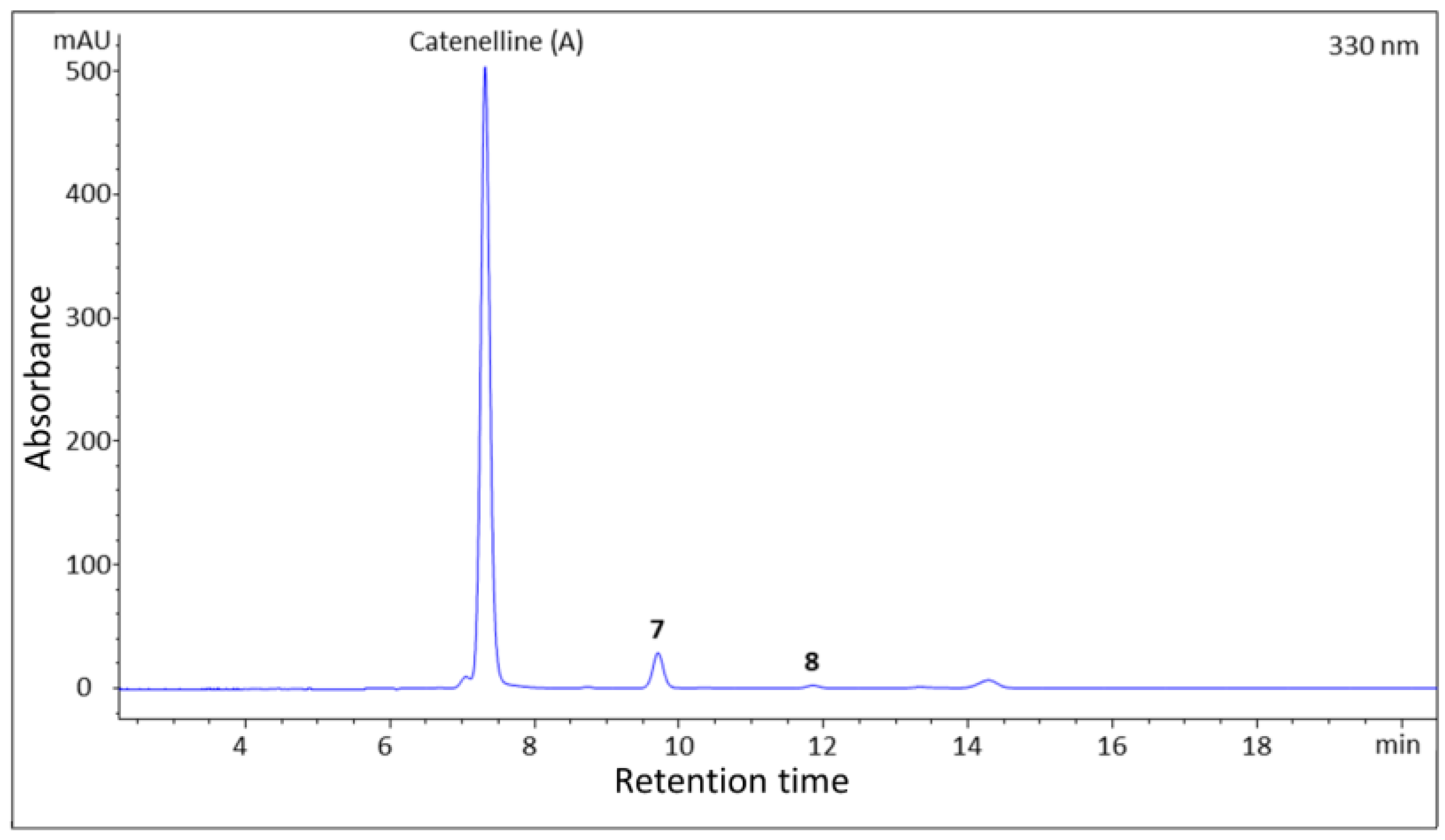
2.1. Isolation
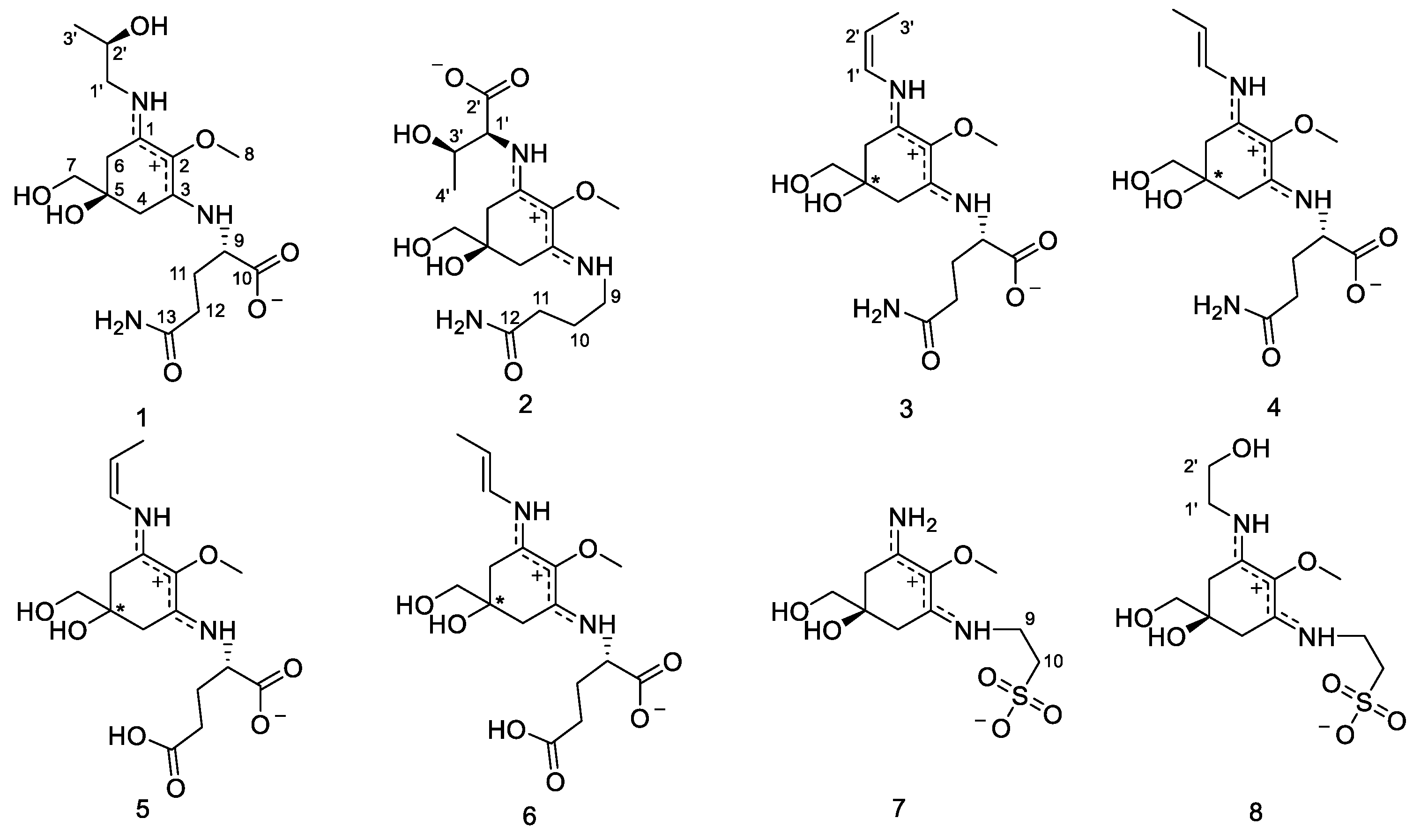
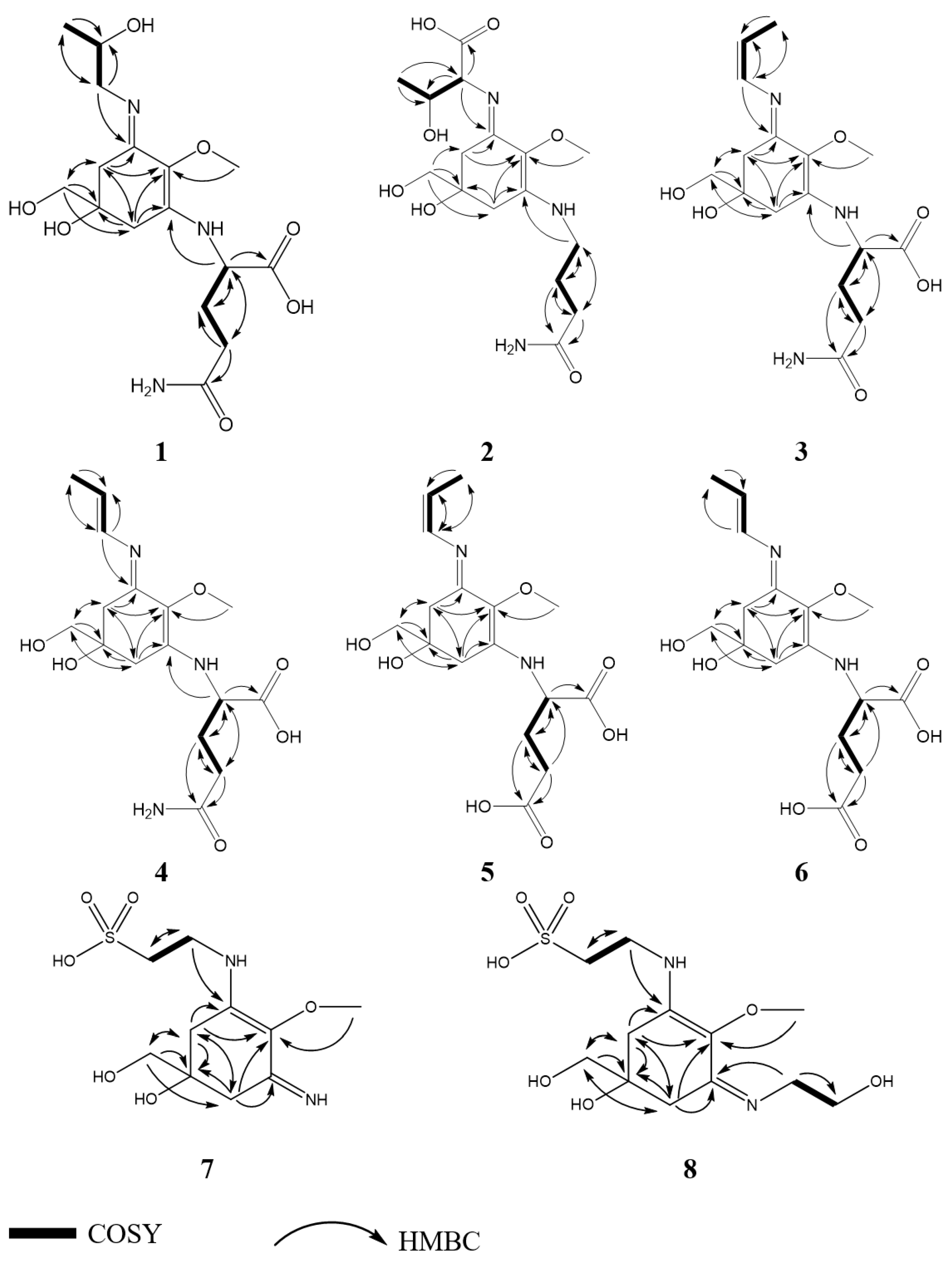
2.2. Structure Elucidation
2.3. Physical and Spectroscopic Data
2.3.1. Compound 1
2.3.2. Compound 2
2.3.3. Compound 3
2.3.4. Compound 4
2.3.5. Compound 5
2.3.6. Compound 6
2.3.7. Compound 7
2.3.8. Compound 8
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Material
4.2. Extraction and Isolation
4.3. Instrumentation
4.3.1. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
4.3.2. Mass Spectrometry
4.3.3. Other Techniques Utilized
4.4. Calculation of Electronic Circular Dichroism Spectra and Optical Rotation Calculation
4.5. Chemicals
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruiz-Nieto, M.; Fernández, J.A.; Niell, F.X.; Carmona, R. Mechanisms of inorganic carbon acquisition in two estuarine Rhodophyceans: Bostrychia scorpioides (Hudson) ex Kützing Montagne and Catenella caespitosa (Withering) L. M. Irvine. Photosynth. Res. 2014, 121, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsten, U.; Kirst, G.O. Incomplete turgor pressure regulation in the “terrestial” red alga, Bostrychia scorpioides (Huds.) Mont. Plant Sci. 1989, 61, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase. World-Wide Electronic Publication. National University of Ireland: Galway. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 24 March 2023).
- Maggs, C.A.; Hommersand, M.H. Seaweed of the British Isles; Rhodophyta. Part 3A, Ceramiales; HMSO: London, UK, 1993; Volume 1, 444p. [Google Scholar]
- Mercado, J.; Niell, F.X. Carbon dioxide uptake by Bostrychia scorpioides (Rhodophyceae) under emersed conditions. Eur. J. Phycol. 2000, 35, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfanoudaki, M.; Hartmann, A.; Miladinovic, H.; Nguyen Ngoc, H.; Karsten, U.; Ganzera, M. Bostrychines A-F, six novel mycosporine-like amino-acids and a novel betaine from the red alga Bostrychia scorpioides. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfanoudaki, M.; Hartmann, A.; Mayr, J.; Figueroa, F.L.; Vega, J.; West, J.; Bermejo, R.; Maggs, C.; Ganzera, M. Analysis of the mycosporine-like amino acid (MAA) pattern of the salt marsh red alga Bostrychia scorpioides. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreto, J.I.; Carignan, M.O. Mycosporine-like amino acids: Relevant secondary metabolites. Chemical and ecological aspects. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 387–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalegerie, F.; Lajili, S.; Bedoux, G.; Taupin, L.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Connan, S. Photo-protective compounds in red macroalgae from Brittany: Considerable diversity in mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs). Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 147, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Becker, K.; Karsten, U.; Remias, D.; Ganzera, M. Analysis of mycosporine-like amino acids in selected algae and cyanobacteria by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and a novel MAA from the red alga Catenella repens. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6291–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karentz, D.; McEuen, F.S.; Land, M.C.; Dunlap, W.C. Survey of mycosporine-like amino acid compounds in Antarctic marine organisms: Potential protection from ultraviolet exposure. Mar. Biol. 1991, 108, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shick, J.M.; Dunlap, W.C. Mycosporine-like amino acids and related gadusols: Biosynthesis, accumulation, and UV-protective functions in aquatic organisms. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2002, 64, 223–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrapusta, E.; Kaminski, A.; Duchnik, K.; Bober, B.; Adamski, M.; Bialczyk, J. Mycosporine-like amino acids: Potential health and beauty ingredients. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Čížková, M.; Bišová, K.; Vítová, M. Exploring mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) as safe and natural protective agents against UV-induced skin damage. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogany, T.; Kumari, S.; Swalaha, F.M.; Bux, F. In silico analysis of enzymes involved in mycosporine-like amino acids biosynthesis in Euhalothece sp.: Structural and functional characterization. Algal Res. 2022, 66, 102806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A.; Gunde-Cimerman, N. Mycosporines and mycosporine-like amino acids: UV protectants or multipurpose secondary metabolites? FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 269, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Kuniyil, A.M.; Sreenikethanam, A.; Gugulothu, P.; Jeyakumar, R.B.; Bajhaiya, A.K. Microalgae as a source of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs); Advances and future prospects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazifi, E.; Wada, N.; Asano, T.; Nishiuchi, T.; Iwamuro, Y.; Chinaka, S.; Matsugo, S.; Sakamoto, T. Characterization of the chemical diversity of glycosylated mycosporine-like amino acids in the terrestrial cyanobacterium Nostoc commune. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 142, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaytseva, A.; Chekanov, K.; Zaytsev, P.; Bakhareva, D.; Gorelova, O.; Kochkin, D.; Lobakova, E. Sunscreen effect exerted by secondary carotenoids and mycosporine-like amino acids in the aeroterrestrial chlorophyte Coelastrella rubescens under high light and UV-A irradiation. Plants 2021, 10, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Glaser, K.; Holzinger, A.; Ganzera, M.; Karsten, U. Klebsormidin A and B, two new UV-sunscreen compounds in green microalgal Interfilum and Klebsormidium species (Streptophyta) from terrestrial habitats. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernillon, J.; Bouillant, M.-L.; Pittet, J.-L.; Favre-Bonvin, J.; Arpin, N. Mycosporine glutamine and related mycosporines in the fungus Pyronema omphalodes. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraldes, V.; Pinto, E. Mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs): Biology, chemistry and identification features. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosic, N.; Climstein, M.; Boyle, G.M.; Thanh Nguyen, D.; Feng, Y. Exploring mycosporine-like amino acid UV-absorbing natural products for a new generation of environmentally friendly sunscreens. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; Mallick, N. Mycosporine-like amino acids: Algal metabolites shaping the safety and sustainability profiles of commercial sunscreens. Algal Res. 2021, 58, 102425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, D.; Schürch, C.; Zülli, F. Mycosporine-like amino acids from red algae protect against premature skin-aging. Euro Cosmet. 2006, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Umar, S.A.; Tasduq, S.A. Ozone layer depletion and emerging public health concerns — an update on epidemiological perspective of the ambivalent effects of ultraviolet radiation exposure. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 866733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.; Schneider, G.; Moreira, B.R.; Herrera, C.; Bonomi-Barufi, J.; Figueroa, F.L. Mycosporine-like amino acids from red macroalgae: UV-photoprotectors with potential cosmeceutical applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamio, M.; Kicklighter, C.E.; Nguyen, L.; Germann, M.W.; Derby, C.D. Isolation and structural elucidation of novel mycosporine-like amino acids as alarm cues in the defensive ink secretion of the sea hare Aplysia californica. Helv. Chim. Acta 2011, 94, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, H.; Waditee-Sirisattha, R. Chapter 5—Mycosporine-like amino acids as multifunctional secondary metabolites in cyanobacteria: From biochemical to application aspects. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Attaur, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 59, pp. 153–194. [Google Scholar]
- Orfanoudaki, M.; Hartmann, A.; Alilou, M.; Gelbrich, T.; Planchenault, P.; Derbré, S.; Schinkovitz, A.; Richomme, P.; Hensel, A.; Ganzera, M. Absolute configuration of mycosporine-like amino acids, their wound healing properties and in vitro anti-aging effects. Mar. Drugs 2019, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Hartmann, A.; Ganzera, M.; Fuchs, D.; Gostner, J.M. Immunomodulatory effects of the mycosporine-like amino acids shinorine and porphyra-334. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, N.; Sakamoto, T.; Matsugo, S. Mycosporine-like amino acids and their derivatives as natural antioxidants. Antioxidants 2015, 4, 603–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Barre, S.; Roullier, C.; Boustie, J. Mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) in biological photosystems. In Outstanding Marine Molecules; La Barre, S., Kornprobst, J.M., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 333–360. [Google Scholar]
- Karsten, U. Defense Strategies of algae and cyanobacteria against solar ultraviolet radiation. In Algal Chemical Ecology; Amsler, C.D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 273–296. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.K.; Pathak, J.; Pandey, A.; Rajneesh; Singh, V.; Sinha, R.P. Purification, characterization and assessment of stability, reactive oxygen species scavenging and antioxidative potentials of mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) isolated from cyanobacteria. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 3157–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Nazifi, E.; Kunita, S.; Wada, N.; Matsugo, S.; Sakamoto, T. Novel glycosylated mycosporine-like amino acids with radical scavenging activity from the cyanobacterium Nostoc commune. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2011, 105, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbushina, A.A.; Whitehead, K.; Dornieden, T.; Niesse, A.; Schulte, A.; Hedges, J.I. Black fungal colonies as units of survival: Hyphal mycosporines synthesized by rock-dwelling microcolonial fungi. Can. J. Bot. 2003, 81, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Völler, G.; Süßmuth, R.; Dittmann, E.; Kehr, J.-C. Functional assessment of mycosporine-like amino acids in Microcystis aeruginosa strain PCC 7806. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Ludsin, S.A.; Martin, J.F.; Dittmann, E.; Lee, J. Mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs)—Producing microcystis in Lake Erie: Development of a qPCR assay and insight into its ecology. Harmful Algae 2018, 77, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C. Chapter 11—Mycosporine-like amino acids in the freshwater bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis: Detection, biosynthesis, genetic markers, and biofunctions. In Cyanobacterial Physiology; Kageyama, H., Waditee-Sirisattha, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, P.K.; Long, F.P.; Young, R.A. Mycosporine-like amino acids for skin photoprotection. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 5512–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujino, I. Isolation and structure of a 357 nm UV-absorbing substance, usujirene, from the red alga Palmaria palmata (L) O. Kuntze. Jpn. J. Phycol. 1986, 34, 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Uemura, D.; Katayama, C.; Wada, A.; Hirata, Y. Crystal and molecular structure of palythene possessing a novel 360 nm chromophore. Chem. Lett. 1980, 9, 755–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Wu, Q. Protective effects of mycosporine-like amino acids of Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 and their partial characterization. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2007, 86, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losantos, R.; Sampedro, D.; Churio, M.S. Photochemistry and photophysics of mycosporine-like amino acids and gadusols, nature’s ultraviolet screens. Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 979–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stochaj, W.R.; Dunlap, W.C.; Shick, J.M. Two new UV-absorbing mycosporine-like amino acids from the sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima and the effects of zooxanthellae and spectral irradiance on chemical composition and content. Mar. Biol. 1994, 118, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, J.; Jarrett, S.; Amaro-Ortiz, A.; Scott, T. UV radiation and the skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12222–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, G.K.; Booth, C.A.G.; Togami, K.; Chung, S.S.; Ssozi, D.; Verga, J.A.; Bouyssou, J.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Shanmugam, V.; Hornick, J.L.; et al. Ultraviolet radiation shapes dendritic cell leukaemia transformation in the skin. Nature 2023, 618, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downie, A.T.; Wu, N.C.; Cramp, R.L.; Franklin, C.E. Sublethal consequences of ultraviolet radiation exposure on vertebrates: Synthesis through meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2023; early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.; Garg, A.; Sharma, K.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, A.; Purohit, A.P. Mycosporine and mycosporine-like amino acids: A paramount tool against ultra violet irradiation. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2011, 5, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, F.L. Mycosporine-like amino acids from marine resource. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dextro, R.B.; Delbaje, E.; Geraldes, V.; Pinto, E.; Long, P.F.; Fiore, M.F. Exploring the relationship between biosynthetic gene clusters and constitutive production of mycosporine-like amino acids in Brazilian cyanobacteria. Molecules 2023, 28, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiscock, S. A Field Key to the British Red Seaweeds (Rhodophyta); Field Studies Council Publication: Birmingham, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]


| pos. | 1 (400 MHz) | 2 (600 MHz) | 3 (400 MHz) | 4 (400 MHz) | 5 (600 MHz) | 6 (600 MHz) | 7 (600 MHz) | 8 (600 MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | δH (J in Hz) | |
| 4 | 2.81, d (17.2) 2.76, d (17.2) | 2.75, d (17.6) 2.90, d (17.6) | 2.79–2.93 a, d (18.0) | 2.79–2.93 a, d (18.0) | 2.75–2.92 a, d (18.0) | 2.75–2.92 a, d (18.0) | 2.92, d (16.8) 2.98, d (16.8) | 2.90, d (17.4) 2.92, d (17.4) |
| 6 | 2.91, s | 2.88, d (17.2) 2.92, d (17.2) | 2.79–2.93 a, d (18.0) | 2.79–2.93 a, d (18.0) | 2.75–2.92 a, d (18.0) | 2.75–2.92 a, d (18.0) | 2.68, d (16.8) 2.94, d (16.8) | 2.92, d (17.4) 2.97, d (17.4) |
| 7 | 3.60, s | 3.60, s | 3.60, s | 3.60, s | 3.59, s | 3.59, s | 3.59, s | 3.62, s |
| 8 | 3.64, s | 3.66, s | 3.71, s | 3.64, s | 3.68–3.70 a, s | 3.68–3.70 a, s | 3.61, s | 3.60, s |
| 9 | 4.21, dd (8.0/4.8) | 3.51, t (7. 2) | 4.28, dd (8.0/4.8) | 4.25, dd (8.0/4.8) | 4.23–4.26 a, dd (8.0/5.6) | 4.23–4.26 a, dd (8.0/5.6) | 3.87, t (6.4) | 3.87, td (6.0/1.2) |
| 10 | 1.96, m | 3.23, t (6.4) | 3.23, t (6.0) | |||||
| 11 | 2.18, m 2.27, m | 2.39, t (7.6) | 2.20, m 2.28, m | 2.20, m 2.28, m | 2.13, m 2.25, m | 2.13, m 2.25, m | ||
| 12 | 2.45, (td, 7.2/1.6) | 2.46, m | 2.46, m | 2.35, m | 2.35, m | |||
| 1′ | 3.44, dd (14.4/7.8) 3.51, dd (14.4/2.4) | 4.05, d (3.6) | 6.39, dd (8.0/1.2) | 6.57, dd (13.6/2.0) | 6.39, d (7.4) | 6.56, d (15.0) | 3.60, t (5.4) | |
| 2′ | 4.03, m | 5.42, m | 5.77, m | 5.40, m | 5.74, m | 3.77, t (5.4) | ||
| 3′ | 1.24, d (6.4) | 4.31, m | 1.78, dd (5.0/2.0) | 1.76, dd (5.2/1.6) | 1.76–1.77 a, dd (6.6/1.8) | 1.76–1.77 a, dd (6.6/1.8) | ||
| 4′ | 1.26, d (6.4) |
| pos. | 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 4 d | 5 e | 6 e | 7 e | 8 e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, Type | δC, Type | δC, Type | δC, Type | δC, Type | δC, Type | δC, Type | δC, Type | |
| 1 | 163.5, C | 163.4, C | 158.0, C | 156.6, C | 157.1, Cc | 157.1, C c | 163.3, C | 162.0, C |
| 2 | 128.5, C | 128.3, C | 129.1, C | 128.6, C | 128.7, C c | 128.7, C c | 127.5, C | 128.2, C |
| 3 | 161.7, C | 162.2, C | 163.8, C | 162.8, C | 163.8, C c | 163.8, C c | 164.3, C | 163.3, C |
| 4 | 35.9, CH2 | 35.5, CH2 | 35.8–36.1 a, CH2 | 35.8–36.1 a, CH2 | 35.7, CH2 b | 35.7, CH2 b | 36.1, CH2 | 35.8, CH2 |
| 5 | 73.9, C | 73.6, C | 73.8–73.9 a, C | 73.8–73.9 a, C | 73.9, C | 73.9, C | 74.2, C | 73.9, C |
| 6 | 35.9, CH2 | 36.1, CH2 | 35.8–36.1 a, CH2 | 35.8–36.1 a, CH2 | 35.7, CH2 b | 35.7, CH 2 b | 38.6, CH2 | 35.4, CH2 |
| 7 | 70.5, CH2 | 70.3, CH2 | 70.4, CH2 | 70.4, CH2 | 70.5, CH2 | 70.5, CH2 | 70.3, CH2 | 70.3, CH2 |
| 8 | 62.1, CH3 | 62.2, CH3 | 62.3, CH3 | 62.4, CH3 | 62.4, CH3 | 62.4, CH3 | 61.9, CH3 | 61.9, CH3 |
| 9 | 61.3, CH | 45.7, CH2 | 61.5–61.6 a, CH | 61.5–61.6 a, CH | 62.3, CH | 62.3, CH | 42.1, CH2 | 41.9, CH2 |
| 10 | 179.5, CO | 28.0, CH2 | 178.9, CO | 179.2, CO | 179.6, CO c | 179.6, CO c | 52.5, CH2 | 52.6, CH2 |
| 11 | 30.6, CH2 | 34.8, CH2 | 30.4–30.5 a, CH2 | 30.4–30.5 a, CH2 | 31.0, CH2 | 31.0, CH2 | ||
| 12 | 34.2, CH2 | 180.7, CO | 34.2, CH2 | 34.2, CH2 | 36.7, CH2 | 36.7, CH2 | ||
| 13 | 181.1, CO | 181.1, CO | 181.1, CO | 184.5, CO c | 184.5, CO c | |||
| 1′ | 52.9, CH2 | 67.2, CH | 124.7, CH | 126.5, CH | 124.1, CH b | 126.0, CH b | 48.2, CH2 | |
| 2′ | 69.5, CH | 178.3, CO | 120.3, CH | 120.4, CH | 119.5, CH b | 119.7, CH b | 63.1, CH2 | |
| 3′ | 22.2, CH3 | 71.0, CH | 13.5, CH3 | 17.3, CH3 | 13.4, CH3 | 17.3, CH3 | ||
| 4′ | 22.3, CH3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orfanoudaki, M.; Alilou, M.; Hartmann, A.; Mayr, J.; Karsten, U.; Nguyen-Ngoc, H.; Ganzera, M. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Novel Mycosporine-like Amino Acids from the Two Intertidal Red Macroalgae Bostrychia scorpioides and Catenella caespitosa. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100543
Orfanoudaki M, Alilou M, Hartmann A, Mayr J, Karsten U, Nguyen-Ngoc H, Ganzera M. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Novel Mycosporine-like Amino Acids from the Two Intertidal Red Macroalgae Bostrychia scorpioides and Catenella caespitosa. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(10):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100543
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrfanoudaki, Maria, Mostafa Alilou, Anja Hartmann, Julia Mayr, Ulf Karsten, Hieu Nguyen-Ngoc, and Markus Ganzera. 2023. "Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Novel Mycosporine-like Amino Acids from the Two Intertidal Red Macroalgae Bostrychia scorpioides and Catenella caespitosa" Marine Drugs 21, no. 10: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100543
APA StyleOrfanoudaki, M., Alilou, M., Hartmann, A., Mayr, J., Karsten, U., Nguyen-Ngoc, H., & Ganzera, M. (2023). Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Novel Mycosporine-like Amino Acids from the Two Intertidal Red Macroalgae Bostrychia scorpioides and Catenella caespitosa. Marine Drugs, 21(10), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100543