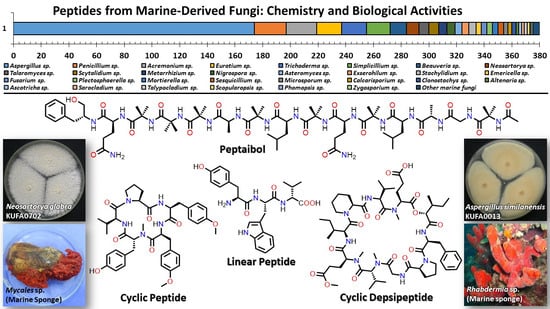
Peptides from Marine-Derived Fungi: Chemistry and Biological Activities †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Importance of Marine-Derived Peptides in Drug Discovery
3. Peptides from Marine-Derived Fungi
3.1. Linear Peptides
3.1.1. Linear Dipeptides
3.1.2. Linear Tripeptides
3.1.3. Linear Tetra- and Hexapeptides
3.1.4. Linear Octapeptides
3.1.5. Linear Nonapeptides
3.1.6. Linear Undecapeptides
3.1.7. Linear Dodecapeptides
3.1.8. Linear Pentadecapeptides
3.1.9. Linear Octadecapeptides
3.1.10. Linear Lipopeptides
3.1.11. Other Linear Peptides
3.2. Cyclic Peptides
3.2.1. Cyclic Dipeptides
3.2.2. Cyclic Tripeptides
3.2.3. Cyclic Tetrapeptides
3.2.4. Cyclic Pentapeptides
3.2.5. Cyclic Hexapeptides
3.2.6. Cyclic Heptapeptides
3.2.7. Cyclic Nonapeptides
3.2.8. Cyclic Decapeptides
3.3. Depsipeptides
3.3.1. Linear Depsipeptides
3.3.2. Cyclic Depsipeptides
4. Biological and Pharmacological Activities
4.1. Cytotoxic Activity
4.2. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities
4.3. Antifungal Activity
4.4. Antiviral Activity
4.5. Antiparasite Activity
4.6. Anti-Dinoflagellate Activity
4.7. Algicidal Activity
4.8. Enzyme Inhibitory Activity
4.8.1. Inhibition of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase (IDO) Activity
4.8.2. Inhibition of Acethylcholinesterase (AChE) Activity
4.8.3. Inhibition of Histone Deacethylase Activity
4.8.4. Inhibition of Sortase A (SrtA) and Isocitrate Lyase (ICL) Activities
4.8.5. Inhibition of Pancreatic Lipase (PL) Activity
4.8.6. Inhibition of Tankyrase1/2 Activity
4.8.7. Inhibition of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) Activity
4.8.8. Inhibition of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4 (CDK-4) Activity
4.9. Anti-Fouling Activity
4.10. Lipid-Lowering Activity
4.11. Anti-Angiogenesis Activity
4.12. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
4.13. Inhibition of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors
4.14. Inhibition of Transporter Proteins
4.15. Anti-Diabetic Activity
4.16. Antioxidant Activity
4.17. Wound-Healing Activity
4.18. Larvicidal Activity
5. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hafez Ghoran, S.; Taktaz, F.; Ayatollahi, S.A.; Kijjoa, A. Anthraquinones and their analogues from marine-derived fungi: Chemistry and biological activities. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez Ghoran, S.; Kijjoa, A. Marine-derived compounds with anti-Alzheimer’s disease activities. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, D.; Costantini, M.; Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Pons, L.N.; Ruocco, N.; di Prisco, G.; Ianora, A.; Verde, C. Biotechnological applications of bioactive peptides from marine sources. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2018, 73, 171–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, N.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, X.; Yan, Z.; Shao, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Fu, C. Therapeutic peptides: Current applications and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, F.S.; Ashour, M.L.; Singab, A.N.B.; Wink, M. A comprehensive review of bioactive peptides from marine fungi and their biological significance. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, C. Overcoming the shortcomings of peptide-based therapeutics. Future Drug Discov. 2022, 4, FDD75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Luo, D.; Luesch, H. Advances in exploring the therapeutic potential of marine natural products. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 147, 104373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, K.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.H. Recent developments on production, purification and biological activity of marine peptides. Food Res. Inter. 2021, 147, 110468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sable, R.; Parajuli, P.; Jois, S. Peptides, peptidomimetics, and polypeptides from marine sources: A wealth of natural sources for pharmaceutical applications. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, J.A.; Donia, M.S.; Schmidt, E.W. Ribosomal peptide natural products: Bridging the ribosomal and nonribosomal worlds. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetrick, K.J.; van der Donk, W.A. Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural product discovery in the genomic era. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 38, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, P.; Putz, A.; Ortlepp, S.; Kjer, J.; Bayer, M. Bioactive natural products from marine sponges and fungal endophytes. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 475–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ruiz, F.; Mancera-Andrade, E.I.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Marine-derived bioactive peptides for biomedical sectors: A review. Protein Pep. Lett. 2017, 24, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlicevic, M.; Maestri, E.; Marmiroli, M. Marine bioactive peptides—An overview of generation, structure and application with a focus on food sources. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogineni, V.; Hamann, M.T. Marine natural product peptides with therapeutic potential: Chemistry, biosynthesis, and pharmacology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Sub. 2018, 1862, 81–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmy, N.M.; Parang, K. Cyclic peptides with antifungal properties derived from bacteria, fungi, plants, and synthetic sources. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, C.; Ribeiro, R.; Pinto, M.; Kijjoa, A. Absolute Stereochemistry Determination of bioactive marine-derived cyclopeptides by liquid chromatography methods: An update review (2018–2022). Molecules 2023, 28, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, J.E.; Deer, T.R. Ziconotide: A clinical update and pharmacologic review. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2013, 14, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, L.J. Brentuximab vedotin: A review in CD30-positive Hodgkin lymphoma. Drugs 2017, 77, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malecek, M.K.; Watkins, M.P.; Bartlett, N.L. Polatuzumab vedotin for the treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2021, 21, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.; Weinstock, C.; Zhang, L.; Charlab, R.; Dorff, S.E.; Gong, Y.; Hsu, V.; Li, F.; Ricks, T.K.; Song, P.; et al. FDA approval summary: Enfortumab vedotin for locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, E.D. Disitamab Vedotin: First approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markham, A. Tisotumab Vedotin: First approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Approved Marine Drugs. Available online: https://www.marinepharmacology.org/approved (accessed on 27 August 2023).
- van Andel, L.; Fudio, S.; Rosing, H.; Munt, S.; Miguel-Lillo, B.; González, I.; Tibben, M.M.; de Vries, N.; de Vries Schultink, A.H.M.; Schellens, A.H.M.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and excretion of 14C–Plitidepsin in patients with advanced cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2017, 35, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, M.W.; Czerwinski, A.; Norton, R.S. Peptide therapeutics from venom: Current status and potential. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2738–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poth, A.G.; Chiu, F.C.K.; Stalmans, S.; Hamilton, B.R.; Huang, Y.-H.; Shackleford, D.M.; Patil, R.; Le, T.T.; Kan, M.-W.; Durek, T.; et al. Effects of backbone cyclization on the pharmacokinetics and drug efficiency of the orally active analgesic conotoxin cVc1.1. Med. Drug Discov. 2021, 10, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kineta Announces First Participant Dosed in Phase 1 Multiple Ascending Dose Clinical Trial of KCP506. Available online: https://kinetabio.com/2021/07/14/kineta-announces-first-participant-dosed-in-phase-1-multiple-ascending-dose-clinical-trial-of-kcp506/ (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- Martín-Algarra, S.; Espinosa, E.; Rubió, J.; López, J.J.L.; Manzano, J.L.; Carrión, L.A.; Plazaola, A.; Tanovic, A.; Paz-Ares, L. Phase II study of weekly kahalalide F in patients with advanced malignant melanoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratain, M.J.; Geary, D.; Undevia, S.D.; Coronado, C.; Alfaro, V.; Iglesias, J.L.; Schilsky, R.L.; Miguel-Lillo, B. First-in-human, phase I study of elisidepsin (PM02734) administered as a 30-min or as a 3-hour intravenous infusion every three weeks in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.M.; Glaser, K.B.; Cuevas, C.; Jacobs, R.S.; Kem, W.; Little, R.D.; McIntosh, J.M.; Newman, D.J.; Potts, B.C.; Shuster, D.E. The odyssey of marine pharmaceuticals: A current pipeline perspective. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaklavas, C.; Forero, A. Management of metastatic breast cancer with second-generation antibody–drug conjugates: Focus on glembatumumab vedotin (cdx-011, cr011-vcmmae). BioDrugs 2014, 28, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Keohan, M.L.; Saif, M.W.; Rushing, D.; Baez, L.; Feit, K.; DeJager, R.; Anderson, S. Phase II study of intravenous TZT-1027 in patients with advanced or metastatic soft-tissue sarcomas with prior exposure to anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Cancer 2006, 107, 2881–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha-Lima, C.M.; Bayraktar, S.; MacIntyre, J.; Raez, L.; Flores, A.M.; Ferrell, A.; Rubin, E.H.; Poplin, E.A.; Tan, A.R.; Lucarelli, A.; et al. A phase 1 trial of E7974 administered on day 1 of a 21-day cycle in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer 2012, 118, 4262–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadaschik, B.A.; Ettinger, S.; Sowery, R.D.; Zoubeidi, A.; Andersen, R.J.; Roberge, M.; Gleave, M.E. Targeting prostate cancer with HTI-286, a synthetic analog of the marine sponge product hemiasterlin. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 2368–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordon, K.C.F.; Cologna, C.T.; Fornari-Baldo, E.C.; Pinheiro-Júnior, E.L.; Cerni, F.A.; Amorim, F.G.; Anjolette, F.A.P.; Cordeiro, F.A.; Wiezel, G.A.; Cardoso, I.A.; et al. From animal poisons and venoms to medicines: Achievements, challenges and perspectives in drug discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Phat, C.; Hong, S.C. Structural diversity of marine cyclic peptides and their molecular mechanisms for anticancer, antibacterial, antifungal, and other clinical applications. Peptides 2017, 95, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Nong, X.H.; Wang, J.; Huang, Z.H.; Qi, S.H. Eight linear peptides from the deep-sea-derived fungus Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 3092–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, C.V.; Yoon, Y.D.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, H.S.; Heo, C.S.; Shin, H.J. Nitrogen-containing secondary metabolites from a deep-sea fungus Aspergillus unguis and their anti-inflammatory activity. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.H.; Liang, X.; Qi, S.H. Two new linear peptides from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO 41512. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 25, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Nong, X.H.; Ren, Z.; Wang, J.; Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Qi, S.H. Antiviral peptides from marine gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao-Wei, L.; Yun, L.; Yong-Jun, L.; Xue-Feng, Z.; Yong-Hong, L. Peptides and polyketides isolated from the marine sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus SCSIO 41008. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girich, E.V.; Rasin, A.B.; Popov, R.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Chingizova, E.A.; Trinh, P.T.H.; Ngoc, N.T.D.; Pivkin, M.V.; Zhuravleva, O.I.; Yurchenko, A.N. New tripeptide derivatives asterripeptides A–C from Vietnamese mangrove-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus LM. 5.2. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Cao, X.; Ge, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Dickschat, J.S.; Wu, B. Talaropeptins A and B, tripeptides with an N-trans-cinnamoyl moiety from the marine-derived fungus Talaromyces purpureogenus CX11. J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 2620–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.W.; Mordhorst, T.F.; Lee, C.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W.; Köck, M. Penilumamide, a novel lumazine peptide isolated from the marine-derived fungus, Penicillium sp. CNL-338. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 2158–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Shao, C.L.; Fu, X.M.; Kong, C.J.; She, Z.G.; Wang, C.Y. Lumazine peptides penilumamides B–D and the cyclic pentapeptide asperpeptide A from a gorgonian-derived Aspergillus sp. fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.J.; Wu, L.Y.; Li, X.B.; Song, X.M.; Niu, Z.G.; Song, X.P.; Chen, G.Y.; Wang, C.Y. Structure and absolute configuration of aspergilumamide A, a novel lumazine peptide from the mangrove-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. Helv. Chim. Acta 2015, 98, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Liao, L.; Hong, S.H.; Park, W.; Kwon, D.I.; Lee, J.; Noh, M.; Oh, D.-C.; Oh, K.-B.; Shin, J. Lumazine peptides from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1290–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Nong, X.H.; Huang, Z.H.; Qi, S.H. Antifungal and antiviral cyclic peptides from the deep-sea-derived fungus Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5114–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.H.; Liang, X.; Cheng, X.; Ling, J.; Dong, J.D.; Qi, S.H. Antifungal peptides from the marine gorgonian-associated fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO41501. Phytochemistry 2021, 192, 112967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.C.; Lee, J.; Oh, D.C.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. New peptides from the marine-derived fungi Aspergillus allahabadii and Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, C.M.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Crews, P. Highly N-methylated linear peptides produced by an atypical sponge-derived Acremonium sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, C.M.; Amagata, T.; Tenney, K.; Compton, J.E.; Pietraszkiewicz, H.; Valeriote, F.A.; Crews, P. Four classes of structurally unusual peptides from two marine-derived fungi: Structures and bioactivities. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 9903–9914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Xue, C.; Tian, L.; Xu, M.; Chen, J.; Deng, Z.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Asperelines A−F, peptaibols from the marine-derived fungus Trichoderma asperellum. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewapriya, P.; Khalil, Z.G.; Prasad, P.; Salim, A.A.; Cruz-Morales, P.; Marcellin, E.; Capon, R.J. Talaropeptides A-D: Structure and biosynthesis of extensively N-methylated linear peptides from an Australian marine tunicate-derived Talaromyces sp. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, K.; Shigemori, H.; Kobayashi, J. Dictyonamides A and B, new peptides from marine-derived fungus. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 6189–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morehouse, N.J.; Flewelling, A.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Cavanagh, H.; Linington, R.G.; Johnson, J.A.; Gray, C.A. Tolypocaibols: Antibacterial lipopeptaibols from a Tolypocladium sp. endophyte of the marine macroalga Spongomorpha arcta. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Bohemen, A.-I.; Ruiz, N.; Zalouk-Vergnoux, A.; Michaud, A.; du Pont, T.R.; Druzhinina, I.; Atanasova, L.; Prado, S.; Bodo, B.; Meslet-Cladiere, L.; et al. Pentadecaibins I–V: 15-residue peptaibols produced by a marine-derived Trichoderma sp. of the Harzianum clade. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Tang, Z.; Gan, Y.; Li, Z.; Luo, X.; Gao, C.; Zhao, L.; Chai, L.; Liu, Y. 18-Residue peptaibols produced by the sponge-derived Trichoderma sp. GXIMD 01001. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, D.C.; Kelly, S.; Kauffman, C.A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Halovirs A–E, new antiviral agents from a marine-derived fungus of the genus Scytalidium. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 11, 4263–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.H.; Xu, Q.H.; Ge, G.B.; Shang, R.Y.; Zhu, H.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Cui, J.; Sun, F.; Lin, H.W. Flavipesides A–C, PKS-NRPS hybrids as pancreatic lipase inhibitors from a marine sponge symbiotic fungus Aspergillus flavipes 164013. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 1825–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Bae, S.Y.; Won, T.H.; You, M.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, D.C.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Asperphenins A and B, lipopeptidyl benzophenones from a marine-derived Aspergillus sp. fungus. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 2066–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigemori, H.; Wakuri, S.; Yazawa, K.; Nakamura, T.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Fellutamides A and B, cytotoxic peptides from a marine fish-possessing fungus Penicillium fellutanum. Tetrahedron 1991, 47, 8529–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopel, M.; Abraham, W.R.; Henriques, A.T.; Macedo, A.J. Dipeptide cis-cyclo (Leucyl-Tyrosyl) produced by sponge associated Penicillium sp. F37 inhibits biofilm formation of the pathogenic Staphylococcus epidermidis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchoa, P.K.S.; Pimenta, A.T.A.; Braz-Filho, R.; de Oliveira, M.C.F.; Saraiva, N.N.; Rodrigues, B.S.F.; Pfenning, L.H.; Abreu, L.M.; Wilke, D.V.; Florêncio, K.G.; et al. New cytotoxic furan from the marine sediment-derived fungi Aspergillus niger. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2599–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wei, J.; Tang, J.; Wu, B. Two new prenylated glycine derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Fusarium sp. TW56-10. Chem. Biodivers. 2022, 19, e202100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, L.; Sun, S.; Chang, A.; Dai, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H. A cyclic dipeptide from marine fungus Penicillium chrysogenum DXY-1 exhibits anti-quorum sensing activity. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 7693–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Cui, C.B.; Li, C.W. A new cyclic dipeptide penicimutide: The activated production of cyclic dipeptides by introduction of neomycin-resistance in the marine-derived fungus Penicillium purpurogenum G59. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.R.; Li, D.Y.; Wang, P.L.; Hua, H.M.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.L. A new 3,4-seco-lanostane triterpenoid from a marine-derived fungus Ascotricha sp. ZJ-M-5. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2013, 48, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- May Zin, W.W.; Buttachon, S.; Dethoup, T.; Fernandes, C.; Cravo, S.; Pinto, M.M.; Gales, L.; Pereira, J.A.; Silva, A.M.S.; Sekeroglu, N.; et al. New cyclotetrapeptides and a new diketopiperzine derivative from the marine sponge-associated fungus Neosartorya glabra KUFA 0702. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Skene, C.; Stewart, M.; Ford, J.; Richard, A.; Williams, L.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Heiland, K.; Friedel, T. Aspergillicins A–E: Five novel depsipeptides from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus carneus. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May Zin, W.W.; Buttachon, S.; Buaruang, J.; Gales, L.; Pereira, J.A.; Pinto, M.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Kijjoa, A. A new meroditerpene and a new tryptoquivaline analog from the algicolous fungus Neosartorya takakii KUFC 7898. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3776–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovio, E.; Fauchon, M.; Toueix, Y.; Mehiri, M.; Varese, G.C.; Hellio, C. The sponge-associated fungus Eurotium chevalieri MUT 2316 and its bioactive molecules: Potential applications in the field of antifouling. Mar. Biotechnol. 2019, 21, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesekara, I.; Li, Y.-X.; Vo, T.S.; Ta, Q.V.; Ngo, D.H.; Kim, S.K. Induction of apoptosis in human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells by neoechinulin A from marine-derived fungus Microsporum sp. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetanina, O.F.; Kalinovskii, A.I.; Khudyakova, Y.V.; Slinkina, N.N.; Pivkin, M.V.; Kuznetsova, T.A. Metabolites from the marine fungus Eurotium repens. Chem. Nat. Comp. 2007, 43, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.M.; Feng, Y.; Wang, B.G. Phenethyl-α-pyrone derivatives and cyclodipeptides from a marine algous endophytic fungus Aspergillus niger EN–13. Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 24, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttachon, S.; Ramos, A.A.; Inácio, Â.; Dethoup, T.; Gales, L.; Lee, M.; Costa, P.M.; Silva, A.M.S.; Sekeroglu, N.; Rocha, E.; et al. Bis-indolyl benzenoids, hydroxypyrrolidine derivatives and other constituents from cultures of the marine sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus candidus KUFA0062. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Hong, X.; Yang, J.; Qin, J.J.; Zhang, B.; Lin, J.; Shao, Z.; Wang, W. Structure elucidation of a novel cyclic tripeptide from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis DSW-2. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 3572–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Fang, P.; Tang, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; He, Z.; Gou, D.; et al. A novel cyclic dipeptide from deep marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIOW2. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.U.; Asami, Y.; Lee, D.; Jang, J.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Oh, H. Protuboxepins A and B and protubonines A and B from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SF-5044. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebada, S.S.; Fischer, T.; Hamacher, A.; Du, F.Y.; Roth, Y.O.; Kassack, M.U.; Wang, B.G.; Roth, E.H. Psychrophilin E, a new cyclotripeptide, from co-fermentation of two marine alga-derived fungi of the genus Aspergillus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, Z.G.; Huang, X.; Raju, R.; Piggott, A.M.; Capon, R.J. Shornephine A: Structure, chemical stability, and P-glycoprotein inhibitory properties of a rare diketomorpholine from an Australian marine-derived Aspergillus sp. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 8700–8705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulder, T.A.M.; Hong, H.; Correa, J.; Egereva, E.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F.; Gross, H. Isolation, structure elucidation and total synthesis of lajollamide A from the marine fungus Asteromyces cruciatus. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2912–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.; He, H.; Dai, H.; Xia, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Song, F. New diketopiperazines from a marine-derived fungus strain Aspergillus versicolor MF180151. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.X.; Jensen, P.R.; Williams, P.G.; Fenical, W. Isolation and structure assignments of rostratins A− D, cytotoxic disulfides produced by the marine-derived fungus Exserohilum rostratum. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, R.; Yang, Y. Antitumor metabolites from marine sediment derived Penicillium sp. WF-06. World Notes Antibiots 2011, 2, 86–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.X.; Crews, M.S.; Draskovic, M.; Sohn, J.; Johnson, T.A.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Yao, X.J.; Bjeldanes, L.F.; Crews, P. Azonazine, a novel dipeptide from a Hawaiian marine sediment-derived fungus, Aspergillus insulicola. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4458–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May Zin, W.W.; Buttachon, S.; Dethoup, T.; Pereira, J.A.; Gales, L.; Inácio, Â.; Costa, P.M.; Lee, M.; Sekeroglu, N.; Silva, A.M.S.; et al. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of the metabolites isolated from the culture of the mangrove-derived endophytic fungus Eurotium chevalieri KUFA 0006. Phytochemistry 2017, 141, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Liu, X.; Guo, H.; Ren, B.; Chen, C.; Piggott, A.M.; Yu, K.; Gao, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; et al. Brevianamides with antitubercular potential from a marine-derived isolate of Aspergillus versicolor. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 4770–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chang, Q.H.; Zhang, S.S.; Yang, K.; Chen, F.L.; Zhu, H.J.; Cao, F.; Liu, Y.F. (±)-Brevianamides Z and Z1, New diketopiperazine alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1261, 132904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.J.; Li, X.M.; Li, C.S.; Wang, B.G. Alkaloid and anthraquinone derivatives produced by the marine-derived endophytic fungus Eurotium rubrum. Helv. Chim. Acta 2012, 95, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.Q.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Y.; Yao, G.S. Sclerotioloids A–C: Three new alkaloids from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum ST0501. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, D.T.; Shaala, L.A.; Genta-Jouve, G. Asperopiperazines A and B: Antimicrobial and cytotoxic dipeptides from a tunicate-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. DY001. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.-H.; Du, F.Y.; Li, X.M.; Pedpradab, P.; Xu, G.M.; Wang, B.G. Rubrumazines A–C, indolediketopiperazines of the isoechinulin class from Eurotium rubrum MA-150, a fungus obtained from marine mangrove-derived rhizospheric soil. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W. Indole diketopiperazine alkaloids from the deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. FS445. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 5213–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.H.; Du, F.Y.; Li, X.M.; Yang, S.Q.; Wang, B.G.; Li, X. Antibacterial indole diketopiperazine alkaloids from the deep-sea cold seep-derived fungus Aspergillus chevalieri. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varoglu, M.; Crews, P. Biosynthetically diverse compounds from a saltwater culture of sponge-derived Aspergillus niger. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, G.; Tay, W.; Bottriell, H.; Andersen, S.K.; Mauk, A.G.; Andersen, R.J. Plectosphaeroic acids A, B, and C, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitors produced in culture by a marine isolate of the fungus Plectosphaerella cucumerina. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 2996–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gu, B.; Yang, L.; Yang, F.; Lin, H. New anti-inflammatory cyclopeptides from a sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus violaceofuscus. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Chen, Y.; Fu, T.; Xiang, Y.; Huang, X.; Tian, X.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, W.; et al. Variecolortins A–C, three pairs of spirocyclic diketopiperazine enantiomers from the marine-derived fungus Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 4593–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, C.; Gu, Q.; Guo, P.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. Psychrophilins E–H and versicotide C, cyclic peptides from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor ZLN-60. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2218–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hong, K.; Liu, P.; Zhu, W. Cyclic tripeptides from the halotolerant fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Maddah, F.E.; Kehraus, S.; Schnakenburg, G.; König, G.M. Endolides A and B, vasopressin and serotonin-receptor interacting N-methylated peptides from the sponge-derived fungus Stachylidium sp. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Maddah, F.; Kehraus, S.; Nazir, M.; Almeida, C.; König, G.M. Insights into the biosynthetic origin of 3-(3-furyl) alanine in Stachylidium sp. 293 K04 tetrapeptides. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2838–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, J.; Luo, C.; Ding, W.; Cox, D.G. A new cyclopeptide with antifungal activity from the co-culture broth of two marine mangrove fungi. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Seo, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Rho, J.R.; Mo, S.J. A new cyclic peptide from a marine-derived bacterium of the genus Nocardiopsis. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 883–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.F.; Yang, X.H.; Liu, H.L.; Gu, Y.C.; Ye, B.P.; Guo, Y.W. A new cyclic peptide and a new steroid from the fungus Penicillium sp. GD6 isolated from the mangrove Bruguiera gymnorrhiza. Helv. Chim. Acta 2014, 97, 1564–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Bao, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tu, Z.C.; Shi, Y.M.; Qi, S.H. Asperterrestide A, a cytotoxic cyclic tetrapeptide from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus SCSGAF0162. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1182–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, S.; Yang, X. A new cyclopeptide metabolite of marine gut fungus from Ligia oceanica. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Cueto, M.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W.; Silverman, R.B. Microsporins A and B: New histone deacetylase inhibitors from the marine-derived fungus Microsporum cf. gypseum and the solid-phase synthesis of microsporin A. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 6535–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Cuevas, M.A.; González, M.C.; Raja, H.A.; Rivero-Cruz, I.; Kurina, S.J.; Burdette, J.E.; Oberlies, N.H.; Figueroa, M. Metabolites from the marine-facultative Aspergillus sp. MEXU 27854 and Gymnoascus hyalinosporus MEXU 29901 from Caleta Bay, Mexico. Tetrahedron Lett. 2019, 60, 1649–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fremlin, L.J.; Piggott, A.M.; Lacey, E.; Capon, R.J. Cottoquinazoline A and cotteslosins A and B, metabolites from an Australian marine-derived strain of Aspergillus versicolor. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.R.; Zhu, H.R.; Gu, B.B.; Wu, Y.; Sun, F.; Wang, S.P.; Zhang, A.; Jiao, W.H.; Xu, S.H.; Lin, H.W. Asperflomide and asperflosamide, new N-methylated cyclopeptides from the marine sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus flocculosus 16D-1. Tetrahedron 2022, 109, 132579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xia, Z.; Wang, B.; Lai, L.; Wang, J.; Jiang, L.; Li, T.; Wu, J.; Wang, L. Malformin C, an algicidal peptide from marine fungus Aspergillus species. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.N.; Gao, H.Q.; Cai, S.X.; Zhu, T.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Li, D.H. Two new cyclic pentapeptides from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Helv. Chim. Acta 2011, 94, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Tian, D.; Chen, M.; Xia, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wei, J.; Li, X.; Yao, X.; Wu, B.; et al. Molecular networking-guided isolation of cyclopentapeptides from the hydrothermal Vent sediment derived fungus Aspergillus pseudoviridinutans TW58-5 and their anti-inflammatory effects. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 1919–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Hai, Y.; Zheng, J.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. Aspersymmetide A, a new centrosymmetric cyclohexapeptide from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, F.; Liang, X.; Qi, S.-H. Bioassay-guided isolation of antifungal cyclopeptides from the deep-sea-derived fungus Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020. Phytochem. Lett. 2022, 48, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhu, H.; Hong, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Zhu, W. Novel cyclic hexapeptides from marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5262–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y. Cyclic peptides from the soft coral-derived fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum SCSIO 41031. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prompanya, C.; Fernandes, C.; Cravo, S.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Dethoup, T.; Silva, A.M.S.; Kijjoa, A. A new cyclic hexapeptide and a new isocoumarin derivative from the marine sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus similanensis KUFA 0013. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1432–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zang, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Song, X.; Ju, J.; Huang, H. Natural hydroxamate-containing siderophore acremonpeptides A–D and an aluminum complex of acremonpeptide D from the marine-derived Acremonium persicinum SCSIO 115. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2594–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.Z.; Liu, J.T.; Hu, Q.; He, R.J.; Guan, X.Q.; Ge, G.B.; Han, H.; Yang, F.; Lin, H.-W. Pancreatic lipase inhibitory cyclohexapeptides from the marine sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. 151304. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2287–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.M.; Liang, T.M.; Guo, Z.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. Discovery, absolute assignments, and total synthesis of asperversiamides A–C and their potent activity against Mycobacterium marinum. Chem. Comm. 2019, 55, 1104–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, R.; Hou, X.M.; Xu, W.F.; Hai, Y.; Wei, M.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Shao, C.L. Targeted isolation of asperheptatides from a coral-derived fungus using LC-MS/MS-based molecular networking and antitubercular activities of modified cinnamate derivatives. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 84, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, W.; Ju, J. Cyclic heptapeptides, cordyheptapeptides C–E, from the marine-derived fungus Acremonium persicinum SCSIO 115 and their cytotoxic activities. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewapriya, P.; Prasad, P.; Damodar, R.; Salim, A.A.; Capon, R.J. Talarolide A, a cyclic heptapeptide hydroxamate from an Australian marine tunicate-associated fungus, Talaromyces sp. (CMB-TU011). Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 2046–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunwald, A.L.; Berrue, F.; Robertson, A.W.; Overy, D.P.; Kerr, R.G. Mortiamides A–D, cyclic heptapeptides from a novel Mortierella sp. obtained from Frobisher Bay. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2677–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrøm, J. Unguisins A and B: New cyclic peptides from the marine-derived fungus Emericella unguis. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.C.; Bao, H.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Nie, Y.Y.; Yang, J.M.; Hong, P.Z.; Zhang, Y. Depsidone derivatives and a cyclopeptide produced by marine fungus Aspergillus unguis under chemical induction and by its plasma induced mutant. Molecules 2018, 23, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shen, Y. A new cyclic peptide from the marine fungal strain Aspergillus sp. AF119. Chem. Nat. Comp. 2011, 47, 786–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.T.; Cheng, X.C.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Scytalidamides A and B, new cytotoxic cyclic heptapeptides from a marine fungus of the genus Scytalidium. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 8767–8773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, K.; Kanoh, K.; Wisespongp, P.; Nishijima, M.; Shizuri, Y. Clonostachysins A and B, new anti-dinoflagellate cyclic peptides from a marine-derived fungus. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, A.L.; Cartmell, C.; Kerr, R.G. Auyuittuqamides A–D, cyclic decapeptides from Sesquicillium microsporum RKAG 186 isolated from frobisher bay sediment. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 84, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quezada, M.; Shang, Z.; Kalansuriya, P.; Salim, A.A.; Lacey, E.; Capon, R.J. Waspergillamide A, a nitro depsi-tetrapeptide diketopiperazine from an Australian mud dauber wasp-associated Aspergillus sp. (CMB-W031). J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1192–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Wang, S.; Li, N.; Li, F.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Guo, P.; Li, D. Saroclides A and B, cyclic depsipeptides from the mangrove-derived fungus Sarocladium kiliense HDN11-112. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1050–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnayake, R.; Fremlin, L.J.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Capon, R.J. Acremolides A−D, lipodepsipeptides from an Australian marine-derived fungus, Acremonium sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, J.; Ohlendorf, B.; Labes, A.; Näther, C.; Imhoff, J.F. Calcaripeptides A–C, cyclodepsipeptides from a Calcarisporium strain. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, L. Beauvericin, a bioactive compound produced by fungi: A short review. Molecules 2012, 17, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.M.; Liu, S.X.; Huang, C.H.; Pang, J.Y.; Lin, Y.C. Secondary metabolites of a mangrove endophytic fungus Aspergillus terreus (No. GX7-3B) from the South China Sea. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2616–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.W.; Lin, Y.C.; She, Z.G.; Lin, M.T.; Chen, P.X.; Zhang, J.Y. Anticancer activity and mechanism investigation of beauvericin isolated from secondary metabolites of the mangrove endophytic fungi. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagata, T.; Morinaka, B.I.; Amagata, A.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Lobkovsky, E.; Clardy, J.; Crews, P. A chemical study of cyclic depsipeptides produced by a sponge-derived fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1560–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnoff, S.B.; Gibson, D.M.; Belofsky, G.N.; Gloer, K.B.; Gloer, J.B. New destruxins from the entomopathogenic fungus Aschersonia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoo, A.; Kamijo, M.; Taketomo, N.; Sato, Y.; Ajisaka, K. Roseocardin, a novel cardiotonic cyclodepsipeptide from Trichothecium roseum TT103. J. Antibiot. 1997, 50, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belofsky, G.N.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Sansalvamide: A new cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptide produced by a marine fungus of the genus Fusarium. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 2913–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto, M.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. N-Methylsansalvamide, a cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptide from a marine fungus of the genus Fusarium. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, C.W.; Park, S.Y.; Asolkar, R.N.; Kim, H.; Kim, G.J.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, E.Y.; Oh, D.C.; et al. Acremonamide, a cyclic pentadepsipeptide with wound-healing properties isolated from a marine-derived fungus of the genus Acremonium. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.C.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Zygosporamide, a cytotoxic cyclic depsipeptide from the marine-derived fungus Zygosporium masonii. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 8625–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Sohn, J.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Oh, H. Alternaramide, a cyclic depsipeptide from the marine-derived fungus Alternaria sp. SF-5016. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2065–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, S.F.; Pan, W.; Ong, G.T.; Chiou, A.J.; Chuang, C.C.; Chiou, S.H.; Wu, S.H. Study of structure–activity correlation in destruxins, a class of cyclodepsipeptides possessing suppressive effect on the generation of hepatitis B virus surface antigen in human hepatoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 1996, 229, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Lang, G.; Kajahn, I.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Scopularides A and B, cyclodepsipeptides from a marine sponge-derived fungus, Scopulariopsis brevicaulis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1052–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singab, A.N.B.; Mostafa, N.M.; Elkhawas, Y.A.; Al-Sayed, E.; Bishr, M.M.; Elissawy, A.M.; Elnaggar, M.S.; Fawzy, I.M.; Salama, O.M.; Tsai, Y.H. Cyclodepsipeptides: Isolation from endophytic fungi of Sarcophyton ehrenbergi and verification of their larvicidal activity via in-vitro and in-silico studies. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.J.; Yuan, W.; Liao, X.J.; Han, B.N.; Wang, S.P.; Li, Z.Y.; Xu, S.H.; Zhang, W.; Lin, H.W. Oryzamides A–E, cyclodepsipeptides from the sponge-derived fungus Nigrospora oryzae PF18. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langenfeld, A.; Blond, A.; Gueye, S.; Herson, P.; Nay, B.; Dupont, J.; Prado, S. Insecticidal cyclodepsipeptides from Beauveria felina. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindra, G.; Ranganayaki, R.S.; Raghothama, S.; Srinivasan, M.C.; Gilardi, R.D.; Karle, I.L.; Balaram, P. Two novel hexadepsipeptides with several modified amino acid residues isolated from the fungus Isaria. Chem. Biodiver. 2004, 1, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabareesh, V.; Ranganayaki, R.; Raghothama, S.; Bopanna, M.; Balaram, H.; Srinivasan, M.; Balaram, P. Identification and characterization of a library of microheterogeneous cyclohexadepsipeptides from the fungus Isaria. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.M.; Li, C.S.; Cui, C.M.; Wang, B.G. Cyclohexadepsipeptides of the isaridin class from the marine-derived fungus Beauveria felina EN-135. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.M.; Lin, L.P.; Xu, Q.L.; Han, W.B.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.W.; Mei, Y.N.; Yao, Z.J.; Tan, R.X. Nodupetide, a potent insecticide and antimicrobial from Nodulisporium sp. associated with Riptortus pedestris. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Shi, Y.W.; Fang, Y.W.; Chao, R.; Gu, Y.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Shao, C.L. Integrating molecular networking and 1H NMR to target the isolation of chrysogeamides from a library of marine-derived Penicillium fungi. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.C.; Kauffman, C.A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Induced production of emericellamides A and B from the marine-derived fungus Emericella sp. in competing co-culture. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, S.; Lu, X.; Guo, H.; Chen, S.; Yin, X.; Li, H.; Dai, G.; Liu, L. Integrating genomics and metabolomics for the targeted discovery of new cyclopeptides with antifungal activity from a marine-derived fungus Beauveria felina. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 9782–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, L.J.; Insua, M.M.; Baz, J.P.; Trujillo, M.; Rodriguez-Mias, R.A.; Oliveira, E.; Giralt, E.; Albericio, F.; Canedo, L.M. IB-01212, a new cytotoxic cyclodepsipeptide isolated from the marine fungus Clonostachys sp. ESNA-A009. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 3335–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, V.R.; Puar, M.S.; Chan, T.M.; Dai, P.; Das, P.R.; Patel, M. Sch 217048: A novel cyclodepsipeptide with neurokinin antagonist activity. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 9584–9586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; He, J.; Huang, S.; Wu, S.; Zeng, L.; Wang, J.; Hong, B.; Chen, Z. Phaeosphamides A and B, cytotoxic cyclodecadepsipeptides from the mangrove-derived fungus Phaeosphaeriopsis sp. S296. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahar, A.A.; Ren, D. Antimicrobial peptides. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1543–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque-Ortega, J.R.; Cruz, L.J.; Albericio, F.; Rivas, L. The antitumoral depsipeptide IB-01212 kills Leishmania through an apoptosis-like process involving intracellular targets. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 608–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokmanovic, M.; Clarke, C.; Marks, P.A. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Overview and perspectives. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birari, R.B.; Bhutani, K.K. Pancreatic lipase inhibitors from natural sources: Unexplored potential. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.J.; Hsiao, S.J.; Yver, D.; Cushman, S.W.; Tessarollo, L.; Smith, S.; Hodes, R.J. Tankyrase 1 and tankyrase 2 are essential but redundant for mouse embryonic development. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.O.; Ermolieff, J.; Jirousek, M.R. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors for diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002, 1, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blayney, D.W.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Bondarenko, I.; Vynnychenko, I.; Kovalenko, N.; Nair, S.; Ibrahim, E.; Udovista, D.P.; et al. Efficacy of plinabulin vs pegfilgrastim for prevention of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia in adults with non–small cell lung cancer: A phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, e204429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




























| Compound | Fungal Species/Strain No. | Source of Marine-Derived Fungi | Bioactivity | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear dipeptides | ||||
| Simplicilliumtide G (1) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifouling and cytotoxic activities. | [38] |
| Simplicilliumtide H (2) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifouling and cytotoxic activities. | [38] |
| Coniosulfide E (3) | Aspergillus unguis IV17-109 | Deep-sea shrimp. | - | [39] |
| Penicamide A (4) | Penicillium sp. SCSIO 41512 | Marine. | - | [40] |
| Penicamide B (5) | Penicillium sp. SCSIO 41512 | Marine. | - | [40] |
| Linear tripeptides | ||||
| Simplicilliumtide C (6) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifouling activity. | [38] |
| Simplicilliumtide D (7) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifouling activity. | [38] |
| Simplicilliumtide E (8) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifouling and cytotoxic activities. | [38] |
| Simplicilliumtide F (9) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifouling activity. | [38] |
| Aspergillipeptide E (10) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata. | Antiviral activity. | [41] |
| Aspergillamides C (11) | Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41008 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. | - | [42] |
| Aspergillamide D (12) | Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41008 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. | - | [42] |
| Aspergillamides A (13) | Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41008 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. | - | [42] |
| Aspergillamides B (14) | Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41008 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. | - | [42] |
| cis-L-phenylalaninamide (15) | Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41008 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. | - | [42] |
| trans-L-phenylalaninamide (16) | Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41008 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. | - | [42] |
| Asterripeptide A (17) | Aspergillus terreus LM.5.2 | Marine mangrove Kandelia candel. | Cytotoxic activity. | [43] |
| Asterripeptide B (18) | Aspergillus terreus LM.5.2 | Marine mangrove Kandelia candel. | Cytotoxic and inhibition of SrtA activities. | [43] |
| Asterripeptide C (19) | Aspergillus terreus LM.5.2 | Marine mangrove Kandelia candel. | Cytotoxic and inhibition of SrtA activities. | [43] |
| Talaropeptin A (20) | Talaromyces purpureogenus CX11 | Marine. | Antifungal activity. | [44] |
| Talaropeptin B (21) | Talaromyces purpureogenus CX11 | Marine. | Antifungal activity. | [44] |
| Penilumamide (22) | Penicillium sp. (strain CNL-338) | Marine red alga Laurencia sp. | - | [45] |
| Aspergillus sp. XS-20090B15 | Marine gorgonian Muricella abnormaliz. | - | [46] | |
| Aspergillus sp. (33241) | Marine mangrove Bruguiera sexangula var. rhynchopetala. | - | [47] | |
| Penilumamide B (23) | Aspergillus sp. XS-20090B15 | Marine gorgonian Muricella abnormaliz. | - | [46] |
| Penilumamide C (24) | Aspergillus sp. XS-20090B15 | Marine gorgonian Muricella abnormaliz. | - | [46] |
| Penilumamide D (25) | Aspergillus sp. XS-20090B15 | Marine gorgonian Muricella abnormaliz. | - | [46] |
| Aspergilumamide A (26) | Aspergillus sp. (33241) | Marine mangrove Bruguiera sexangula var. rhynchopetala. | - | [47] |
| Terrelumamide A (27) | Aspergillus terreus FA009 | Marine sediment. | Anti-diabetic and anticancer activities. | [48] |
| Terrelumamide B (28) | Aspergillus terreus FA009 | Marine sediment. | Anti-diabetic and anticancer activities. | [48] |
| Linear tetrapeptides | ||||
| Simplicilliumtide A (29) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine sediment. | Antifouling and cytotoxic activities. | [38] |
| Simplicilliumtide B (30) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifouling activity. | [38] |
| Simplicilliumtide I (31) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | - | [49] |
| Aspergillipeptide F (32) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata. | - | [41] |
| Aspergillipeptide G (33) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata. | - | [41] |
| Aspergillipeptide H (34) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata Nutting. | - | [50] |
| Aspergillipeptide I (35) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata Nutting. | - | [50] |
| Aspergillipeptide J (36) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata Nutting. | - | [50] |
| Aspergillipeptide K (37) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata Nutting | - | [50] |
| Linear hexapeptides | ||||
| FJ120DPB (38) | Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis. | Marine sediment. | Inhibition of enzyme sortase A (SrtA) activity. | [51] |
| Linear octapeptides | ||||
| RHM1 (39) | Acremonium sp. (UCSC coll. no. 021172 cKZ) | Marine sponge Teichaxinella sp. (coll. no. 02172). | Antibacterial and Cytotoxic activities. | [52] |
| RHM2 (40) | Acremonium sp. (UCSC coll. no. 021172 cKZ) | Marine sponge Teichaxinella sp. (coll. no. 02172). | Cytotoxic activity. | [52] |
| RHM3 (41) | Acremonium sp. (UCSC coll. no. 021172 cKZ) | Marine sponge Teichaxinella sp. (coll. no. 02172). | - | [53] |
| RHM4 (42) | Acremonium sp. (UCSC coll. no. 021172 cKZ) | Marine sponge Teichaxinella sp. (coll. no. 02172). | - | [53] |
| Linear nonapeptides | ||||
| Aspereline A (43) | Trichoderma asperellum | Marine sediment. | - | [54] |
| Aspereline B (44) | Trichoderma asperellum | Marine sediment. | - | [54] |
| Aspereline C (45) | Trichoderma asperellum | Marine sediment. | - | [54] |
| Aspereline D (46) | Trichoderma asperellum | Marine sediment. | - | [54] |
| Aspereline E (47) | Trichoderma asperellum | Marine sediment. | - | [54] |
| Aspereline F (48) | Trichoderma asperellum | Marine sediment. | - | [54] |
| Linear undecapeptides | ||||
| Talaropeptide A (49) | Talaromyces sp. (CMB-TU011) | An unidentified marine tunicate. | Antibacterial activity. | [55] |
| Talaropeptide C (50) | Talaromyces sp. (CMB-TU011) | An unidentified marine tunicate. | - | [55] |
| Dictyonamide A (51) | The fungus strain K063. | Marine red alga Ceratodictyon spongiosum. | Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 activity. | [56] |
| Dictyonamide B (52) | The fungus strain K063. | Marine red alga Ceratodictyon spongiosum. | - | [57] |
| Tolypocaibol A (53) | Tolypocladium sp. | Marine microalga Spongomorpha arcta. | Antibacterial activity. | [57] |
| Tolypocaibol B (54) | Tolypocladium sp. | Marine microalga Spongomorpha arcta. | Antibacterial activity. | [57] |
| Linear dodecapeptides | ||||
| Talaropeptide B (55) | Talaromyces sp. (CMB-TU011) | An unidentified marine tunicate. | Antibacterial activity. | [55] |
| Talaropeptide D (56) | Talaromyces sp. (CMB-TU011) | An unidentified marine tunicate. | - | [55] |
| Linear pentadecapeptides | ||||
| Efrapeptin G (57) | Acremonium sp. (UCSC coll. no. 021172 cKZ) | Marine sponge Teichaxinella sp. (coll. no. 02172). | Antibacterial and Cytotoxic activities. | [52,53] |
| Efrapeptins Eα (58) | Acremonium sp. (UCSC coll. no. 021172 cKZ) | Marine sponge Teichaxinella sp. (coll. no. 02172). | Cytotoxic activity. | [53] |
| Efrapeptin H (59) | Acremonium sp. (UCSC coll. no. 021172 cKZ) | Marine sponge Teichaxinella sp. (coll. no. 02172). | - | [53] |
| Efrapeptin E (60) | Acremonium sp. (UCSC coll. no. 021172 cKZ) | Marine sponge Teichaxinella sp. (coll. no. 02172). | - | [53] |
| Efrapeptin F (61) | Acremonium sp. (UCSC coll. no. 021172 cKZ) | Marine sponge Teichaxinella sp. (coll. no. 02172). | Cytotoxic activity. | [53] |
| Pentadecaibin I (62) | Trichoderma sp. MMS1255 | Marine sediment. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [58] |
| Pentadecaibin II (63) | Trichoderma sp. MMS1255 | Marine sediment. | Cytotoxic activity. | [58] |
| Pentadecaibin III (64) | Trichoderma sp. MMS1255 | Marine sediment. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [58] |
| Pentadecaibin IV (65) | Trichoderma sp. MMS1255 | Marine sediment. | Cytotoxic activity. | [58] |
| Pentadecaibin V (66) | Trichoderma sp. MMS1255 | Marine sediment. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [58] |
| Linear octadecapeptides | ||||
| Trichorzins A (67) | Trichoderma sp. GXIMD 01001 | Marine sponge Haliclona sp. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [59] |
| Trichorzin B (68) | Trichoderma sp. GXIMD 01001 | Marine sponge Haliclona sp. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [59] |
| Trichorzin C (69) | Trichoderma sp. GXIMD 01001 | Marine sponge Haliclona sp. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [59] |
| Trichorzin D (70) | Trichoderma sp. GXIMD 01001 | Marine sponge Haliclona sp. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [59] |
| Trichorzin E (71) | Trichoderma sp. GXIMD 01001 | Marine sponge Haliclona sp. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [59] |
| Trichorzin F (72) | Trichoderma sp. GXIMD 01001 | Marine sponge Haliclona sp. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [59] |
| Trichorzin G (73) | Trichoderma sp. GXIMD 01001 | Marine sponge Haliclona sp. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [59] |
| Lipophilic linear hexapeptides | ||||
| Halovir A (74) | Scytalidium sp. | Marine. | Antiviral activity. | [60] |
| Halovir B (75) | Scytalidium sp. | Marine. | Antiviral activity. | [60] |
| Halovir C (76) | Scytalidium sp. | Marine. | Antiviral activity. | [60] |
| Halovir D (77) | Scytalidium sp. | Marine. | Antiviral activity. | [60] |
| Halovir E (78) | Scytalidium sp. | Marine. | Antiviral activity. | [60] |
| Other linear peptides | ||||
| Flavipeside A (79) | Aspergillus flavipes 164013 | Marine sponge Dysidea sp. | Inhibition of pancreatic lipase. | [61] |
| Flavipeside B (80) | Aspergillus flavipes 164013 | Marine sponge Dysidea sp. | Inhibition of pancreatic lipase. | [61] |
| Flavipeside C (81) | Aspergillus flavipes 164013 | Marine sponge Dysidea sp. | Inhibition of pancreatic lipase. | [61] |
| Asperphenin A (82) | Aspergillus sp. | Marine-submerged decaying wood. | Antiproliferative activity. | [62] |
| Asperphenin B (83) | Aspergillus sp. | Marine-submerged decaying wood. | Antiproliferative activity. | [62] |
| Fellutamide A (84) | Penicillium fellutanum Biourge | Marine fish Apogon endekataenta Bleeker. | Cytotoxic activity. | [63] |
| Fellutamide B (85) | Penicillium fellutanum Biourge | Marine fish Apogon endekataenta Bleeker. | Cytotoxic activity. | [63] |
| Cyclic dipeptides | ||||
| cis-cyclo(Leucyl-Tyrosyl) (86) | Penicillium sp. F37 | Marine sponge Axinella corrugate | Anti-biofilm formation. | [64] |
| cyclo-(trans-4-hydroxy-L-Pro-L-Leu) (87) | Aspergillus niger BRF-074 | Marine sediment. | - | [65] |
| cyclo-(trans-4-hydroxy-L-Pro-L-Phe) (88) | Aspergillus niger BRF-074 | Marine sediment. | - | [65] |
| cyclo-(L-Pro-L-Leu) (89) | Aspergillus niger BRF-074 | Marine sediment. | - | [65] |
| Fusarium sp. RWS56-10 | Marine hydrothermal vent sediment. | - | [66] | |
| cyclo-(L-Pro-L-Val) (90) | Aspergillus niger BRF-074 | Marine sediment. | - | [65] |
| cyclo-(Phe-Pro) (91) | Penicillium sp. WF-06 | Marine sediment. | - | [86] |
| Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41008 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. | - | [42] | |
| Aspergillus niger BRF-074 | Marine sediment. | - | [65] | |
| cyclo-(L-Pro-L-Tyr) (92) | Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis DSW-2 | Sea water. | Weak cytotoxic activity. | [78] |
| Aspergillus niger BRF-074 | Marine sediment. | - | [65] | |
| Penicillium chrysogenum DXY-1 | Marine sediment. | Antibacterial activity and anti-biofilm formation | [67] | |
| Penicimutide (93) | Penicillium purpurogenum G59 | Marine sediment. | Cytotoxic activity. | [68] |
| cyclo-(L-Ile-L-Pro) (94) | Penicillium purpurogenum G59 | Marine sediment. | - | [68] |
| cyclo-(Pro-Ala) (95) | Ascotricha sp. ZJ-M-5 | Marine. | - | [69] |
| cyclo-(Ile-Leu) (96) | Ascotricha sp. ZJ-M-5 | Marine. | - | [69] |
| cyclo-(Gly-Pro) (97) | Penicillium sp. WF-06 | Marine sediment. | - | [86] |
| Fellutanine A analogue (98) | Neosartorya glabra KUFA 0702 | Marine sponge Mycale sp. | - | [70] |
| Aszonalenin (99) | Neosartorya glabra KUFA 0702 | Marine sponge Mycale sp. | - | [70] |
| Neosartorya takakii KUFC 7898 | Marine alga Amphiroa sp. | - | [72] | |
| (3R)-3-(1H-Indol-3-ylmethyl)-3,4-dihydro-1H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2,5-dione (100) | Neosartorya glabra KUFA 0702 | Marine sponge Mycale sp. | - | [70] |
| Takakiamide (101) | Neosartorya glabra KUFA 0702 | Marine sponge Mycale sp. | - | [70] |
| Neosartorya takakii KUFC 7898 | Marine alga Amphiroa sp. | - | [72] | |
| (11aR)-2,3-Dihydro-1H-pyrrolo{2,1-c}{1,4}benzodiazepine-5,11(10H,11aH)-dione (102) | Neosartorya glabra KUFA 0702 | Marine sponge Mycale sp. | - | [70] |
| Fellutanine A (103) | Neosartorya glabra KUFA 0702 | Marine sponge Mycale sp. | - | [70] |
| Acyl aszonalenin (104) | Aspergillus carneus (MST-MF156) | Estuarine sediment. | - | [71] |
| Neosartorya takakii KUFC 7898 | Marine alga Amphiroa sp. | - | [72] | |
| Terretrione B (105) | Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41008 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. | - | [42] |
| Terretrione C (106) | Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41008 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. | - | [42] |
| Brevianamide F (107) | Aspergillus terreus SCSIO41008 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. | - | [42] |
| cyclo-(L-Trp-L-Ala) (108) | Eurotium chevalieri MUT2316 | Marine sponge Grantia compressa. | Antibacterial and algicidal activities. | [73] |
| Penicillium sp. WF-06 | Marine sediment. | - | [86] | |
| Neoechinulin A (109) | Eurotium chevalieri MUT2316 | Marine sponge Grantia compressa. | Algicidal activity. | [73] |
| Microsporum sp. | Marine red algae. | Cytotoxic activity and induction of apoptosis. | [74] | |
| Echinulin (110) | Eurotium chevalieri MUT2316 | Marine sponge Grantia compressa. | Antibacterial and algicidal activities. | [73] |
| Eurotium repens | Marine sponge Suberites domuncula | - | [75] | |
| Eurotium chevalieri KUFA 0006 | Mangrove plant Rhizophora mucronata Poir. | - | [88] | |
| cyclo-(L-Trp-L-Ile) (111) | Aspergillus niger EN-13 | Marine brown alga Colpomenia sinuosa. | - | [76] |
| cyclo-(L-Trp-L-Phe) (112) | Aspergillus niger EN-13 | Marine brown alga Colpomenia sinuosa. | - | [76] |
| cyclo-(L-Trp-L-Tyr) (113) | Aspergillus niger EN-13 | Marine brown alga Colpomenia sinuosa. | - | [76] |
| (3S,6S)-3,6-dibenzylpiperazine-2,5-dione (114) | Aspergillus candidus KUFA0062 | Marine sponge Epipolasis sp. | - | [77] |
| Mactanamide (115) | Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis DSW-2 | Sea water. | Weak cytotoxic activity. | [78] |
| 14-Hydroxy-cyclopeptine (116) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIOW2 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Inhibition of nitric oxide production. | [79] |
| Protuboxepin A (117) | Aspergillus sp. SF-5044 | Marine intertidal sediment. | Cytotoxic activity. | [80] |
| Protuboxepin B (118) | Aspergillus sp. SF-5044 | Marine intertidal sediment. | - | [80] |
| Protubonine A (119) | Aspergillus sp. SF-5044 | Marine intertidal sediment. | - | [80] |
| Protubonine B (120) | Aspergillus sp. SF-5044 | Marine intertidal sediment. | - | [80] |
| Oxepinamide E (121) | Aspergillus sp. (BM-05 and BM-05ML) | Marine brown alga Sargassum sp. | [81] | |
| Shornephine A (122) | Aspergillus sp. (CMB-M081F) | Marine sediment. | Inhibition of P-glycoprotein | [82] |
| 15b-β-Hydroxy-5-N-acetyladreemin (123) | Aspergillus sp. (CMB-M081F) | Marine sediment. | - | [82] |
| 5-N-Acetyladreemin (124) | Aspergillus sp. (CMB-M081F) | Marine sediment. | - | [82] |
| 15b-β-Methoxy-5-N-acetyladreemin (125) | Aspergillus sp. (CMB-M081F) | Marine sediment. | - | [82] |
| Hyalodendrin (126) | Asteromyces cruciatus 763 | An unidentified decaying green alga. | - | [83] |
| Gliovictin (127) | Asteromyces cruciatus 763 | An unidentified decaying green alga. | - | [83] |
| 1N-norgliovictin (128) | Asteromyces cruciatus 763 | An unidentified decaying green alga. | - | [83] |
| Bis-N-norgliovictin (129) | Asteromyces cruciatus 763 | An unidentified decaying green alga. | Antibacterial and antifungal activities. | [83] |
| (±)-7,8-epoxy-brevianamide Q ((±)-130) | Aspergillus versicolor MF180151 | Marine sediment. | - | [84] |
| (±)-8-hydroxy-brevianamide R ((±)-131) | Aspergillus versicolor MF180151 | Marine sediment. | - | [84] |
| (±)-8-epihydroxy-brevianamide R ((±)-132) | Aspergillus versicolor MF180151 | Marine sediment. | - | [84] |
| (±)-Brevianamide R ((±)-133) | Aspergillus versicolor MF180151 | Marine sediment. | - | [84] |
| Aspergillus versicolor HBU-7 | Sea mud sample. | - | [90] | |
| Rostratin A (134) | Exserohilum rostratum (Drechsler) CNK-630 | Marine cyanobacterial mat. | Cytotoxic activity. | [85] |
| Rostratin B (135) | Exserohilum rostratum (Drechsler) CNK-630 | Marine cyanobacterial mat. | Cytotoxic activity. | [85] |
| Rostratin C (136) | Exserohilum rostratum (Drechsler) CNK-630 | Marine cyanobacterial mat. | Cytotoxic activity. | [85] |
| Rostratin D (137) | Exserohilum rostratum (Drechsler) CNK-630 | Marine cyanobacterial mat. | Cytotoxic activity. | [85] |
| Exserohilone (138) | Exserohilum rostratum (Drechsler) CNK-630 | Marine cyanobacterial mat. | - | [85] |
| Gliocladine C (139) | Penicillium sp. WF-06 | Marine Sediment. | Cytotoxic activity. | [86] |
| Azonazine (140) | Aspergillus insulicola | Marine sediment. | Anti-angiogenesis activity. | [87] |
| (11R,14S)-3-(1H-Indol-3ylmethyl)-6-isopropyl-2,5-piperazinedione (141) | Eurotium chevalieri KUFA 0006 | Mangrove plant Rhizophora mucronata Poir. | - | [88] |
| Preechinulin (142) | Eurotium chevalieri KUFA 0006 | Mangrove plant Rhizophora mucronata Poir. | - | [88] |
| Neoechinulin E (143) | Eurotium chevalieri KUFA 0006 | Mangrove plant Rhizophora mucronata Poir. | - | [88] |
| Eurocristatine (144) | Eurotium chevalieri KUFA 0006 | Mangrove plant Rhizophora mucronata Poir. | - | [88] |
| Brevianamide S (145) | Aspergillus versicolor (MF030) | Marine sediment. | Antibacterial activity. | [89] |
| Brevianamide T (146) | Aspergillus versicolor (MF030) | Marine sediment. | - | [89] |
| Brevianamide U (147) | Aspergillus versicolor (MF030) | Marine sediment. | - | [89] |
| Brevianamide V (148) | Aspergillus versicolor (MF030) | Marine sediment. | - | [89] |
| Aspergillus versicolor HBU-7 | Sea mud sample. | Cytotoxic activity. | [90] | |
| Brevianamide N (149) | Aspergillus versicolor (MF030) | Marine sediment. | - | [89] |
| Brevianamide K (150) | Aspergillus versicolor (MF030) | Marine sediment. | - | [89] |
| Aspergillus versicolor HBU-7 | Sea mud sample. | - | [90] | |
| Deoxy brevianamide E (151) | Aspergillus versicolor (MF030) | Marine sediment. | - | [89] |
| Aspergillus versicolor HBU-7 | Sea mud sample. | - | [90] | |
| (±)-Brevianamide Z ((±)-152) | Aspergillus versicolor HBU-7 | Sea mud sample. | - | [90] |
| (±)-Brevianamide Z1 ((±)-153) | Aspergillus versicolor HBU-7 | Sea mud sample. | - | [90] |
| (±)-Brevianamide X ((±)-154) | Aspergillus versicolor HBU-7 | Sea mud sample. | - | [90] |
| (±)-Brevianamide Q ((±)-155) | Aspergillus versicolor HBU-7 | Sea mud sample. | - | [90] |
| 12-Demethyl-12-oxo-eurotechinulin B (156) | Eurotium rubrum G2 | Marine semi-mangrove plant Hibiscus tiliaceus LINN. | Cytotoxic activity. | [91] |
| Variecolorin J (157) | Eurotium rubrum G2 | Marine semi-mangrove plant Hibiscus tiliaceus LINN | - | [91] |
| Eurotechinulin B (158) | Eurotium rubrum G2 | Marine semi-mangrove plant Hibiscus tiliaceus LINN | - | [91] |
| Variecolorin G (159) | Eurotium rubrum G2 | Marine semi-mangrove plant Hibiscus tiliaceus LINN | Cytotoxic activity. | [91] |
| Alkaloid E-7 (160) | Eurotium rubrum G2 | Marine semi-mangrove plant Hibiscus tiliaceus LINN | Cytotoxic activity. | [91] |
| Aspergillus sp. FS445 | Marine deep sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [95] | |
| Cryptoechinuline G (161) | Eurotium rubrum G2 | Marine semi-mangrove plant Hibiscus tiliaceus LINN | - | [91] |
| Aspergillus sp. FS445 | Marine deep sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [95] | |
| Isoechinulin B (162) | Eurotium rubrum G2 | Marine semi-mangrove plant Hibiscus tiliaceus LINN | - | [91] |
| Aspergillus sp. FS445 | Marine deep sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [95] | |
| 7-Isopentenylcryptoechinuline D (163) | Eurotium rubrum G2 | Marine semi-mangrove plant Hibiscus tiliaceus LINN | - | [91] |
| Sclerotioloid A (164) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum ST0501 | Inner tissue of marine sponge. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [92] |
| Sclerotioloid B (165) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum ST0501 | Inner tissue of marine sponge. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [92] |
| Sclerotioloid C (166) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum ST0501 | Inner tissue of marine sponge. | Weak anti-inflammatory activity. | [92] |
| Gartryprostatin C (167) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum ST0501 | Inner tissue of marine sponge. | - | [92] |
| Speramide C (168) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum ST0501 | Inner tissue of marine sponge. | - | [92] |
| Asperopiperazine A (169) | Aspergillus sp. DY001 | Red Sea tunicate Didemnum sp. | Antibacterial, antifungal, and cytotoxic activities. | [93] |
| Asperopiperazine B (170) | Aspergillus sp. DY001 | Red Sea tunicate Didemnum sp. | Antibacterial, antifungal, and cytotoxic activities. | [93] |
| Asperchinulin A (171) | Aspergillus sp. FS445 | Marine deep sediment. | - | [95] |
| Asperchinulin B (172) | Aspergillus sp. FS445 | Marine deep sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [95] |
| Asperchinulin C (173) | Aspergillus sp. FS445 | Marine deep sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [95] |
| Asperchinulin D (174) | Aspergillus sp. FS445 | Marine deep sediment. | - | [95] |
| Neoechinulin B (175) | Aspergillus sp. FS445 | Marine deep sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [95] |
| Antibacterial activity. | [96] | |||
| Isoechinulin A (176) | Aspergillus sp. FS445 | Marine deep sediment. | - | [95] |
| Tardioxopiperazine A (177) | Aspergillus sp. FS445 | Marine deep sediment. | - | [95] |
| 24,25-dihydroxyvariecolorin G (178) | Aspergillus chevalieri CS-122 | Marine deep-sea cold seep. | Antibacterial activity. | [96] |
| 25-hydroxyrubrumazine B (179) | Aspergillus chevalieri CS-122 | Marine deep-sea cold seep. | Antibacterial activity. | [96] |
| 22-chloro-25-hydroxyrubrumazine B (180) | Aspergillus chevalieri CS-122 | Marine deep-sea cold seep. | Antibacterial activity. | [96] |
| 25-hydroxyvariecolorin F (181) | Aspergillus chevalieri CS-122 | Marine deep-sea cold seep. | Antibacterial activity. | [96] |
| 27-epi-aspechinulin D (182) | Aspergillus chevalieri CS-122 | Marine deep-sea cold seep. | Antibacterial activity. | [96] |
| Asperazine (183) | Aspergillus niger | Caribbean sponge Hyrtiosproteus sp. | - | [97] |
| Plectosphaeroic acid A (184) | Plectosphaerella cucumerina | Marine sediment. | Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. | [98] |
| Plectosphaeroic acid B (185) | Plectosphaerella cucumerina | Marine sediment. | Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. | [98] |
| Plectosphaeroic acid C (186) | Plectosphaerella cucumerina | Marine sediment. | Inhibition of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. | [98] |
| T988 A (187) | Plectosphaerella cucumerina | Marine sediment. | - | [98] |
| Diketopiperazine dimer (188) | Aspergillus violaceofuscus | Marine Sponge Reniochalina sp. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [99] |
| Variecolortin A (189) | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | Marine sediment. | DPPH• radical scavenging activity. | [100] |
| Variecolortin B (190) | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | Marine sediment. | Cytotoxic activity. | [100] |
| Variecolortin C (191) | Eurotium sp. SCSIO F452 | Marine sediment. | Cytotoxic activity. | [100] |
| Cyclic tripeptides | ||||
| Psychrophilin E (192) | Aspergillus sp. (BN-05 & BM-05ML) | Marine brown alga Sargassum sp. | Cytotoxic activity. | [81] |
| Aspergillus versicolor ZLN-60 | Marine mud. | - | [101] | |
| Psychrophilin F (193) | Aspergillus versicolor ZLN-60 | Marine mud. | - | [101] |
| Psychrophilin G (194) | Aspergillus versicolor ZLN-60 | Marine mud. | Lipid-lowering activity. | [101] |
| Psychrophilin H (195) | Aspergillus versicolor ZLN-60 | Marine mud. | - | [101] |
| Sclerotiotide A (196) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | Antifungal activity. | [102] |
| Sclerotiotide B (197) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | Antifungal activity. | [102] |
| Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis DSW-2 | Sea water. | Weak cytotoxic activity. | [78] | |
| Sclerotiotide C (198) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | - | [102] |
| Sclerotiotide D (199) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | - | [102] |
| Sclerotiotide E (200) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | - | [102] |
| Sclerotiotide F (201) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | Antifungal activity. | [102] |
| Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis DSW-2 | Sea water. | Weak cytotoxic activity. | [78] | |
| Sclerotiotide G (202) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | - | [102] |
| Sclerotiotide H (203) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | - | [102] |
| Sclerotiotide I (204) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | Antifungal activity. | [102] |
| Sclerotiotide J (205) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | - | [102] |
| Sclerotiotide K (206) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | - | [102] |
| JBIR-15 (207) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | Antifungal activity. | [102] |
| Aspochracin (208) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Marine salt sediment. | - | [102] |
| Sclerotiotide L (209) | Aspergillus violaceofuscus | Marine sponge Reniochalina sp. | Weak anti-inflammatory activity. | [99] |
| Sclerotiotide M (210) | Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis DSW-2 | Sea water. | Weak cytotoxic activity. | [78] |
| Cyclic tetrapeptides | ||||
| Endolide A (211) | Stachylidium sp. | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. sf. C. flammea. | Inhibition of G-protein-coupled receptors. | [103] |
| Endolide B (212) | Stachylidium sp. | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. sf. C. flammea. | Inhibition of G-protein-coupled receptors. | [103] |
| Endolide C (213) | Stachylidium sp. 293 K04 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. sf. C. flammea. | - | [104] |
| Endolide D (214) | Stachylidium sp. 293 K04 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. sf. C. flammea. | - | [104] |
| Hirsutide (215) | Stachylidium sp. 293 K04 | Marine sponge Callyspongia sp. sf. C. flammea. | - | [104] |
| Violaceomide A (216) | Aspergillus violaceofuscus | Marine Sponge Reniochalina sp. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [99] |
| Sartoryblabramide A (217) | Neosartorya glabra KUFA 0702 | Marine sponge Mycale sp. | - | [70] |
| Sartoryblabramide B (218) | Neosartorya glabra KUFA 0702 | Marine sponge Mycale sp. | - | [70] |
| cyclo-(L-leucyl-trans-4-hydroxy-L-prolyl-D-leucyl-trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline) (219) | Co-culture of Phomopsis sp. K38 & Altenaria sp. E33 | Mangrove. | Antifungal activity. | [105] |
| 5,5ʹ-epoxy-MKN-349A (220) | Penicilluim sp. GD6 | Marine mangrove Bruguiera gymnorrhiza. | - | [107] |
| Asperterrestide A (221) | Aspergillus terreus SCSGAF0162 | Marine gorgonian Echinogorgia aurantiaca. | Antiviral and cytotoxic activities. | [108] |
| Compound (222) | Aspergillus flavipes | Marine isopod Ligia oceanica. | - | [109] |
| Microsporin A (223) | Microsporum cf. gypseum | Marine bryozoan Bugula sp. | Cytotoxic and histone deacethylase inhibitory activities. | [110] |
| Microsporin B (224) | Microsporum cf. gypseum | Marine bryozoan Bugula sp. | Cytotoxic activity. | [110] |
| Cyclic penapeptides | ||||
| Caletasin (225) | Aspergillus sp. MEXU27854 | Marine intertidal sand. | - | [111] |
| Asperpeptide A (226) | Aspergillus sp. XS-20090B15 | Marine gorgonian Muricella abnormaliz. | Antibacterial activity. | [46] |
| Cotteslosin A (227) | Aspergillus versicolor (MST-MF495) | Low-tide region. | Cytotoxic activity. | [112] |
| Cotteslosin B (228) | Aspergillus versicolor (MST-MF495) | Low-tide region. | - | [112] |
| Lajollamide A (229) | Asteromyces cruciatus 763 | An unidentified decaying green alga. | Antibacterial activity. | [83] |
| JG002CPA (230) | Aspergillus allahabadii | Marine sediment. | Inhibition of enzyme sortase A (SrtA) activity. | [51] |
| JG002CPA (231) | Aspergillus allahabadii | Marine sediment. | Inhibition of sortase A (SrtA) and isocitrate lyase (ICL) activities. | [51] |
| Asperflomide (232) | Aspergillus flocculosus 16D-1 | Marine sponge Phakellia fusca. | Inhibition of tankyrase1/2 activity. | [113] |
| Malformin C (233) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIOW2 | Marine sediment. | Algicidal activity. | [114] |
| Aspergillus niger BRF-074 | Marine sediment. | - | [65] | |
| Aspergillus niger | Marine sponge Hyrtiosproteus sp. | - | [97] | |
| Malformin A1 (234) | Aspergillus niger BRF-074 | Marine sediment. | - | [65] |
| Aspergillipeptide D (235) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata. | Antiviral activity. | [41] |
| Versicotide A (236) | Aspergillus versicolor ZLN-60 | Marine mud. | - | [115] |
| Versicotide B (237) | Aspergillus versicolor ZLN-60 | Marine mud. | - | [115] |
| Pseudoviridinutan A (238) | Aspergillus pseudoviridinutans TW58-5 | Marine hydrothermal vent sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [116] |
| Pseudoviridinutan B (239) | Aspergillus pseudoviridinutans TW58-5 | Marine hydrothermal vent sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [116] |
| Pseudoviridinutan C (240) | Aspergillus pseudoviridinutans TW58-5 | Marine hydrothermal vent sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [116] |
| Pseudoviridinutan D (241) | Aspergillus pseudoviridinutans TW58-5 | Marine hydrothermal vent sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [116] |
| Pseudoviridinutan E (242) | Aspergillus pseudoviridinutans TW58-5 | Marine hydrothermal vent sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [116] |
| Pseudoviridinutan F (243) | Aspergillus pseudoviridinutans TW58-5 | Marine hydrothermal vent sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [116] |
| Pseudoviridinutan G (244) | Aspergillus pseudoviridinutans TW58-5 | Marine hydrothermal vent sediment. | Anti-inflammatory activity. | [116] |
| Cyclic hexapeptides | ||||
| Aspersymmetide A (245) | Aspergillus versicolor (TA01-14) | Marine gorgonian coral Carijoa sp. (GX-WZ-2010001). | Cytotoxic activity. | [117] |
| Simplicilliumtide J (246) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifungal and antiviral activities. | [49] |
| Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifungal activity. | [118] | |
| Simplicilliumtide K (247) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | - | [49] |
| Simplicilliumtide L (248) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | - | [49] |
| Simplicilliumtide M (249) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | - | [49] |
| Verlamelin A (250) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifungal and antiviral activities. | [49] |
| Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifungal activity. | [118] | |
| Verlamelin B (251) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifungal and antiviral activities. | [49] |
| Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifungal activity. | [118] | |
| Simplicilliumtide N (252) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifungal activity. | [118] |
| Simplicilliumtide O (253) | Simplicillium obclavatum EIODSF 020 | Marine deep-sea sediment. | Antifungal activity. | [118] |
| Versicotide C (254) | Aspergillus versicolor ZLN-60 | Marine mud. | - | [101] |
| Sclerotide A (255) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Putain sea salt filed. | Antifungal activity. | [119] |
| Aspergillus sclerotiorum SCSIO41031 | Marine soft coral. | - | [120] | |
| Sclerotide B (256) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1 | Putain sea salt filed. | Antifungal, antibacterial, and cytotoxic activities. | [119] |
| Sclerotide C (257) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum SCSIO41031 | Marine soft coral. | - | [120] |
| Sclerotide D (258) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum SCSIO41031 | Marine soft coral. | - | [120] |
| Sclerotide E (259) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum SCSIO41031 | Marine soft coral. | - | [120] |
| Similanamide (260) | Aspergillus similanensis KUFA0013 | Marine sponge Rhabdermia sp. | Cytotoxic activity. | [121] |
| Acremonpeptide A (261) | Acremonium persicinum SCSIO115. | Marine sediment. | Antiviral activity. | [122] |
| Acremonpeptide B (262) | Acremonium persicinum SCSIO115. | Marine sediment. | Antiviral activity. | [122] |
| Acremonpeptide C (263) | Acremonium persicinum SCSIO115. | Marine sediment. | Antiviral activity. | [122] |
| Acremonpeptide D 264) | Acremonium persicinum SCSIO115. | Marine sediment. | Antiviral activity. | [122] |
| Al(III)-acremonpeptide D (265) | Acremonium persicinum SCSIO115. | Marine sediment. | Antiviral activity. | [122] |
| Petrosamide A (266) | Aspergillus sp. 151304 | Marine sponge Petrosia sp. | Inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity. | [123] |
| Petrosamide A (267) | Aspergillus sp. 151304 | Marine sponge Petrosia sp. | Inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity. | [123] |
| Petrosamide A (268) | Aspergillus sp. 151304 | Marine sponge Petrosia sp. | Inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity. | [123] |
| Cyclic heptapeptides | ||||
| Asperversiamide A (269) | Aspergillus versicolor (CHNSCLM-0063) | Marine coral. | Antibacterial activity. | [124] |
| Asperversiamide B (270) | Aspergillus versicolor (CHNSCLM-0063) | Marine coral. | Antibacterial and anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis activities. | [124] |
| Asperversiamide C (271) | Aspergillus versicolor (CHNSCLM-0063) | Marine coral. | Antibacterial activity. | [124] |
| Asperheptatide A (272) | Aspergillus versicolor (CHNSCLM-0063) | Marine gorgonian coral Rumphella aggregata. | Anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis activity. | [125] |
| Asperheptatide B (273) | Aspergillus versicolor (CHNSCLM-0063) | Marine gorgonian coral Rumphella aggregata. | Anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis activity. | [125] |
| Asperheptatide C (274) | Aspergillus versicolor (CHNSCLM-0063) | Marine gorgonian coral Rumphella aggregata. | - | [125] |
| Asperheptatide D (275) | Aspergillus versicolor (CHNSCLM-0063) | Marine gorgonian coral Rumphella aggregata. | - | [125] |
| Cordyheptapeptide C (276) | Acremonium persicinum SCSIO115 | Marine sediment. | Cytotoxic activity. | [126] |
| Cordyheptapeptide D (277) | Acremonium persicinum SCSIO115 | Marine sediment. | Cytotoxic activity. | [126] |
| Cordyheptapeptide E (278) | Acremonium persicinum SCSIO115 | Marine sediment. | Cytotoxic activity. | [126] |
| Talarolide A (279) | Talaromyces sp. (CMB-TU011) | Marine tunicate. | - | [127] |
| Mortiamide A (280) | Mortierella sp. RKAG 110 | Marine sediment. | - | [128] |
| Mortiamide B (281) | Mortierella sp. RKAG 110 | Marine sediment. | - | [128] |
| Mortiamide C (282) | Mortierella sp. RKAG 110 | Marine sediment. | - | [128] |
| Mortiamide D (283) | Mortierella sp. RKAG 110 | Marine sediment. | - | [128] |
| Unguisin A (284) | Emericella unguis | Stomolopus meliagris (medusa) | Antibacterial activity. | [129] |
| Aspergillus unguis 6-20-6 GDMCC 60337 | Seaweed. | Antibacterial activity. | [130] | |
| Aspergillus unguis IV17-109 | Deep-sea shrimp. | - | [39] | |
| Unguisin B (285) | Emericella unguis | Stomolopus meliagris (medusa). | Antibacterial activity. | [129] |
| Unguisin E (286) | Aspergillus sp. AF119 | Soil of Xiamen beach. | - | [131] |
| Scytalidamide A (287) | Scytalidium sp. CNC-310 | Marine green alga Halimedia sp. | Cytotoxic activity. | [132] |
| Scytalidamide B (288) | Scytalidium sp. CNC-310 | Marine green alga Halimedia sp. | Cytotoxic activity. | [132] |
| Maribasin C (289) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata Nutting. | Antifungal activity. | [50] |
| Maribasin D (290) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata Nutting. | Antifungal activity. | [50] |
| Maribasin E (291) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata Nutting. | Antifungal activity. | [50] |
| Maribasin A (292) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata Nutting. | Antifungal activity. | [50] |
| Maribasin B (293) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata Nutting. | Antifungal activity. | [50] |
| Marihysin A (294) | Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41501 | Marine gorgonian Melitodes squamata Nutting | - | [50] |
| Cyclic nonapeptides | ||||
| Clonostachysin A (295) | Clonostachys rogersoniana (HJK9) | Marine sponge Halicondria japonica. | Anti-dinoflagellate activity. | [133] |
| Clonostachysin B (296) | Clonostachys rogersoniana (HJK9) | Marine sponge Halicondria japonica. | Anti-dinoflagellate activity. | [133] |
| Cyclic decapeptides | ||||
| Auyuittuqamide A (297) | Sesquicillium microsporum RKAG 186 | Marine sediment (intertidal zone). | - | [134] |
| Auyuittuqamide B (298) | Sesquicillium microsporum RKAG 186 | Marine sediment (intertidal zone). | - | [134] |
| Auyuittuqamide C (299) | Sesquicillium microsporum RKAG 186 | Marine sediment (intertidal zone). | - | [134] |
| Auyuittuqamide D (300) | Sesquicillium microsporum RKAG 186 | Marine sediment (intertidal zone). | - | [134] |
| Linear depsipeptides | ||||
| Waspergillamide A (301) | Aspergillus sp. CMB-W031 | Marine mud dauber wasp Sceliphron sp. | - | [135] |
| Cyclic depsipeptides | ||||
| Saroclide A (302) | Sarocladium kiliense HDN11-112 | Mangrove plant Aricennia marina | Lipid-lowering activity. | [136] |
| Saroclide B (303) | Sarocladium kiliense HDN11-112 | Mangrove plant Aricennia marina | - | [136] |
| Acremolide A (304) | Acremonium sp. (MST-MF588a) | Estuarine sediment. | - | [137] |
| Acremolide B (305) | Acremonium sp. (MST-MF588a) | Estuarine sediment. | - | [137] |
| Acremolide C (306) | Acremonium sp. (MST-MF588a) | Estuarine sediment. | - | [137] |
| Acremolide D (307) | Acremonium sp. (MST-MF588a) | Estuarine sediment. | - | [137] |
| Calcaripeptide A (308) | Calcarisporium sp. strain KF525 | Sea. | - | [138] |
| Calcaripeptide B (309) | Calcarisporium sp. strain KF525 | Sea. | - | [138] |
| Calcaripeptide C (310) | Calcarisporium sp. strain KF525 | Sea. | - | [138] |
| Beauvericin (311) | Aspergillus terreus (no. GX7-3B) | Marine mangrove Bruguiera gymnoihiza (Linn.) Savigny. | Anti-acetylcholinesterase and cytotoxic activity. | [140] |
| Fusarium sp. (No.DZ27) | Marine mangrove. | Cytotoxic activity and induction of apoptosis. | [141] | |
| Guangomide A (312) | Strain No. 001314c | A yellow fan-shaped marine sponge (Coll. No. 00314). | Antibacterial activity. | [142] |
| Guangomide B (313) | Strain No. 001314c | A yellow fan-shaped marine sponge (Coll. No. 00314). | Antibacterial activity. | [142] |
| Homodestcardin (314) | Strain No. 001314c | A yellow fan-shaped marine sponge (Coll. No. 00314). | - | [142] |
| Sansalvamide A (315) | Fusarium sp. | Marine seagrass Halodule wrightii | Cytotoxic activity. | [145,146] |
| N-methylsansalvamide (316) | Fusarium sp. CNL-619 | Marine mangrove green alga Avrainvillea sp. | Cytotoxic activity. | [146] |
| Acremonamide (317) | Acremonium sp. CNQ-049 | Marine sediment. | Wound healing activity. | [147] |
| Zygosporamide (318) | Zygosporium masonii (CNK458) | Marine cyanobacterium. | Cytotoxic activity. | [148] |
| Alternaramide (319) | Altenaria sp. SF-5016 | Marine shoreline sediment. | Antibacterial and inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B activity. | [149] |
| Destruxin A (320) | Metarrhizium sp. (strain number 001103) | Marine sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea (coll. no. 00103). | Cytotoxic activity. | [53] |
| Destruxin B (321) | Metarrhizium sp. (strain number 001103) | Marine sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea (coll. no. 00103). | - | [53] |
| Destruxin B2 (322) | Metarrhizium sp. (strain number 001103) | Marine sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea (coll. no. 00103). | Cytotoxic activity. | [53] |
| Desmethyldestruxin B (323) | Metarrhizium sp. (strain number 001103) | Marine sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea (coll. no. 00103). | Cytotoxic activity. | [53] |
| Destruxin E chlorohydrin (324) | Metarrhizium sp. (strain number 001103) | Marine sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea (coll. no. 00103). | Cytotoxic activity. | [53] |
| Destruxin E2 chlorohydrin (325) | Metarrhizium sp. (strain number 001103) | Marine sponge Pseudoceratina purpurea (coll. no. 00103). | Cytotoxic activity. | [53] |
| Aspergillicin A (326) | Aspergillus carneus (MST-MF156) | Marine estuarine sediment. | - | [71] |
| Aspergillicin B (327) | Aspergillus carneus (MST-MF156) | Marine estuarine sediment. | - | [71] |
| Aspergillicin C (328) | Aspergillus carneus (MST-MF156) | Marine estuarine sediment. | - | [71] |
| Aspergillicin D (329) | Aspergillus carneus (MST-MF156) | Marine estuarine sediment. | - | [71] |
| Aspergillicin E (330) | Aspergillus carneus (MST-MF156) | Marine estuarine sediment. | - | [71] |
| Scopularide A (331) | Scopulariopsis brevicaulis NCPF 2177 | Marine sponge Tethya aurantium. | Cytotoxic activity. | [151] |
| Aspergillus flavus | Marine soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. | Larvicidal and inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity. | [152] | |
| Nigrospora oryzae PF18 | Marine sponge Phakellia fusca | - | [153] | |
| Penicillium chrysogenum (CHSCLM-0003) | Marine gorgonian coral Carijoa sp. (GX-WZ-2010001). | Cytotoxic activity. | [159] | |
| Scopularide B (332) | Scopulariopsis brevicaulis NCPF 2177 | Marine sponge Tethya aurantium. | Cytotoxic activity. | [151] |
| Aspergillus flavus | Marine soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. | Larvicidal and inhibition of pancreatic lipase activity. | [152] | |
| Penicillium chrysogenum (CHSCLM-0003) | Marine gorgonian coral Carijoa sp. (GX-WZ-2010001). | Cytotoxic activity. | [159] | |
| Oryzamide A (333) | Nigrospora oryzae PF18 | Marine sponge Phakellia fusca. | - | [153] |
| Oryzamide B (334) | Nigrospora oryzae PF18 | Marine sponge Phakellia fusca. | - | [153] |
| Oryzamide C (335) | Nigrospora oryzae PF18 | Marine sponge Phakellia fusca. | - | [153] |
| Oryzamide D (336) | Nigrospora oryzae PF18 | Marine sponge Phakellia fusca. | - | [153] |
| Oryzamide E (337) | Nigrospora oryzae PF18 | Marine sponge Phakellia fusca. | - | [153] |
| Isaridin G (338) | Beauveria feline EN-135 | An unidentified marine bryozoan. | Antibacterial activity. | [157] |
| Desmethylisaridin G (339) | Beauveria feline EN-135 | An unidentified marine bryozoan. | Antibacterial activity. | [157] |
| Desmethylisaridin C1 (340) | Beauveria feline EN-135 | An unidentified marine bryozoan. | Antibacterial activity. | [157] |
| Isaridin A (341) | Beauveria feline EN-135 | An unidentified marine bryozoan. | - | [157] |
| Isaridin B (342) | Beauveria feline EN-135 | An unidentified marine bryozoan. | - | [157] |
| Isaridin E (343) | Beauveria feline EN-135 | An unidentified marine bryozoan. | Antibacterial activity. | [157] |
| Beauveria feline SYSU-MS7908 | Marine ascidian Styela plicata. | - | [161] | |
| Chrysogeamide A (344) | Penicillium chrysogenum (CHSCLM-0003) | Marine gorgonian coral Carijoa sp. (GX-WZ-2010001). | Anti-angiogenesis activity. | [159] |
| Chrysogeamide B (345) | Penicillium chrysogenum (CHSCLM-0003) | Marine gorgonian coral Carijoa sp. (GX-WZ-2010001). | Anti-angiogenesis activity. | [159] |
| Chrysogeamide C (346) | Penicillium chrysogenum (CHSCLM-0003) | Marine gorgonian coral Carijoa sp. (GX-WZ-2010001). | - | [159] |
| Chrysogeamide D (347) | Penicillium chrysogenum (CHSCLM-0003) | Marine gorgonian coral Carijoa sp. (GX-WZ-2010001). | - | [159] |
| Chrysogeamide E (348) | Penicillium chrysogenum (CHSCLM-0003) | Marine gorgonian coral Carijoa sp. (GX-WZ-2010001). | - | [159] |
| Chrysogeamide F (349) | Penicillium chrysogenum (CHSCLM-0003) | Marine gorgonian coral Carijoa sp. (GX-WZ-2010001). | - | [159] |
| Chrysogeamide G (350) | Penicillium chrysogenum (CHSCLM-0003) | Marine gorgonian coral Carijoa sp. (GX-WZ-2010001). | - | [159] |
| Nodupetide (351) | Penicillium chrysogenum (CHSCLM-0003) | Marine gorgonian coral Carijoa sp. (GX-WZ-2010001). | Antibacterial and anti-angiogenesis activities. | [159] |
| FJ120DPA (352) | Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis. | Marine sediment. | Inhibition of sortase A (SrtA) activity. | [51] |
| Emericellamide A (353) | Emericella sp. (strain CNL-878) | Marine green alga Halimeda sp. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [160] |
| Emericellamide B (354) | Emericella sp. (strain CNL-878) | Marine green alga Halimeda sp. | Antibacterial and cytotoxic activities. | [160] |
| Scopularide I (355) | Aspergillus sclerotiorum SCSIO41031 | Marine soft coral. | Anti-acetylcholinesterase and cytotoxic activities. | [120] |
| Asperflosamide (356) | Aspergillus flocculosus 16D-1 | Marine sponge Phakellia fusca. | Inhibition of tankyrase1/2 activity. | [113] |
| Isaridin I (357) | Beauveria feline SYSU-MS7908 | Marine ascidian Styela plicata. | - | [161] |
| Isaridin J (358) | Beauveria feline SYSU-MS7908 | Marine ascidian Styela plicata. | Antifungal activity. | [161] |
| Isaridin K (359) | Beauveria feline SYSU-MS7908 | Marine ascidian Styela plicata. | - | [161] |
| Isaridin L (360) | Beauveria feline SYSU-MS7908 | Marine ascidian Styela plicata. | Antifungal activity. | [161] |
| Isaridin M (361) | Beauveria feline SYSU-MS7908 | Marine ascidian Styela plicata. | - | [161] |
| Isaridin N (362) | Beauveria feline SYSU-MS7908 | Marine ascidian Styela plicata. | - | [161] |
| IB-01212 (363) | Clonostachys sp. ESNA-A009 | An unidentified marine sponge. | Cytotoxic activity. | [162] |
| - | - | Anti-parasite activity. | [166] | |
| Phaeosphamides A (364) | Phaeosphaeriopsis sp. Esf-30 | Rhizosphere sediment of a mangrove plant Bruguiera gymnorhiza. | Cytotoxic activity. | [164] |
| Phaeosphamides B (365) | Phaeosphaeriopsis sp. Esf-30 | Rhizosphere sediment of a mangrove plant Bruguiera gymnorhiza. | - | [164] |
| Sch 217048 (366) | Phaeosphaeriopsis sp. Esf-30 | Rhizosphere sediment of a mangrove plant Bruguiera gymnorhiza. | - | [164] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hafez Ghoran, S.; Taktaz, F.; Sousa, E.; Fernandes, C.; Kijjoa, A. Peptides from Marine-Derived Fungi: Chemistry and Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100510
Hafez Ghoran S, Taktaz F, Sousa E, Fernandes C, Kijjoa A. Peptides from Marine-Derived Fungi: Chemistry and Biological Activities. Marine Drugs. 2023; 21(10):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100510
Chicago/Turabian StyleHafez Ghoran, Salar, Fatemeh Taktaz, Emília Sousa, Carla Fernandes, and Anake Kijjoa. 2023. "Peptides from Marine-Derived Fungi: Chemistry and Biological Activities" Marine Drugs 21, no. 10: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100510
APA StyleHafez Ghoran, S., Taktaz, F., Sousa, E., Fernandes, C., & Kijjoa, A. (2023). Peptides from Marine-Derived Fungi: Chemistry and Biological Activities. Marine Drugs, 21(10), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/md21100510