A Novel Marine Pyran-Isoindolone Compound Enhances Fibrin Lysis Mediated by Single-Chain Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Fibrinolytic Activity of FGFC1
2.2. FGFC1 Promote FITC-Fibrin Lysis In Vitro
2.3. FGFC1 Effect on Fibrin Fiber Nanostructure by Scanning Electron Microscopy
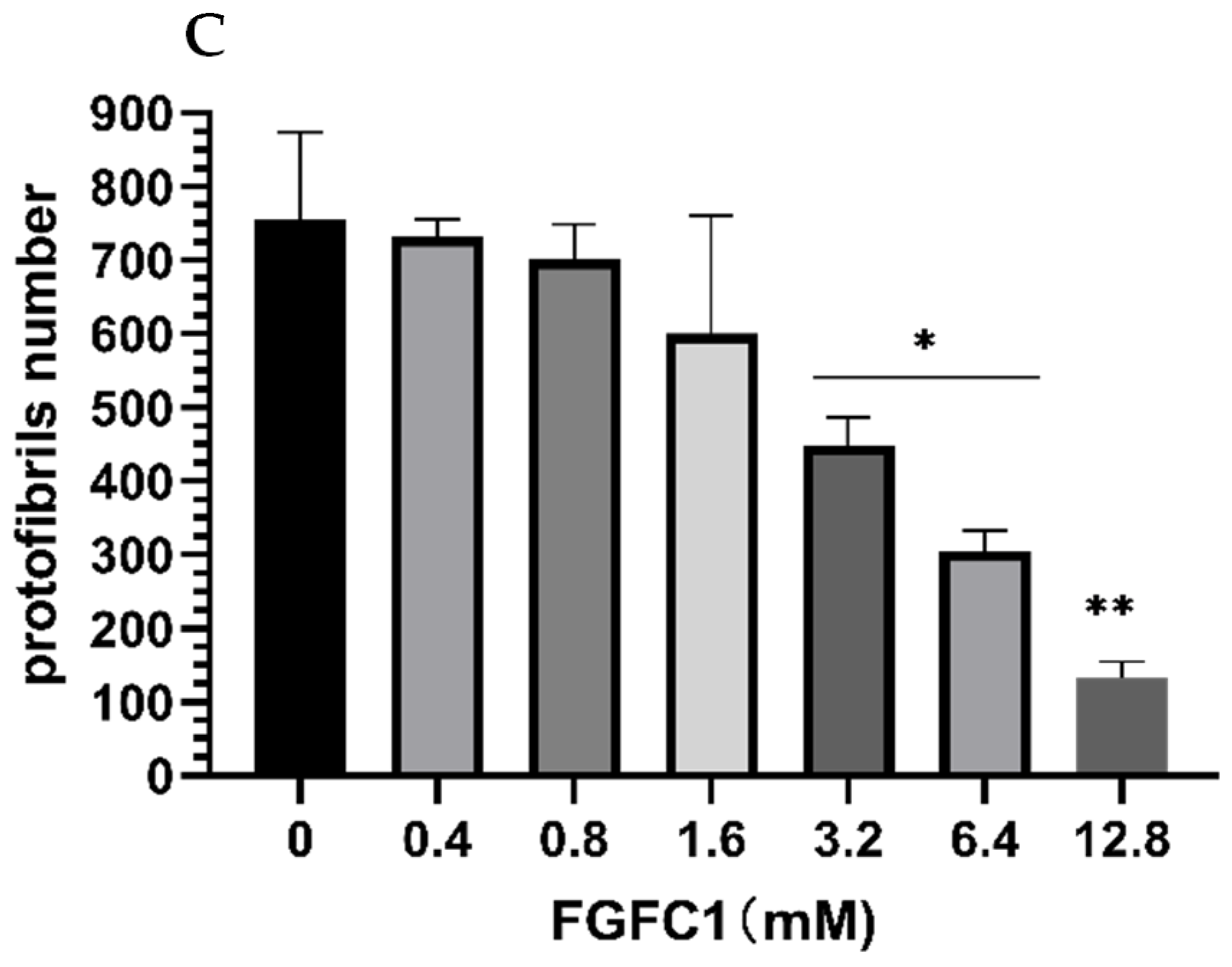
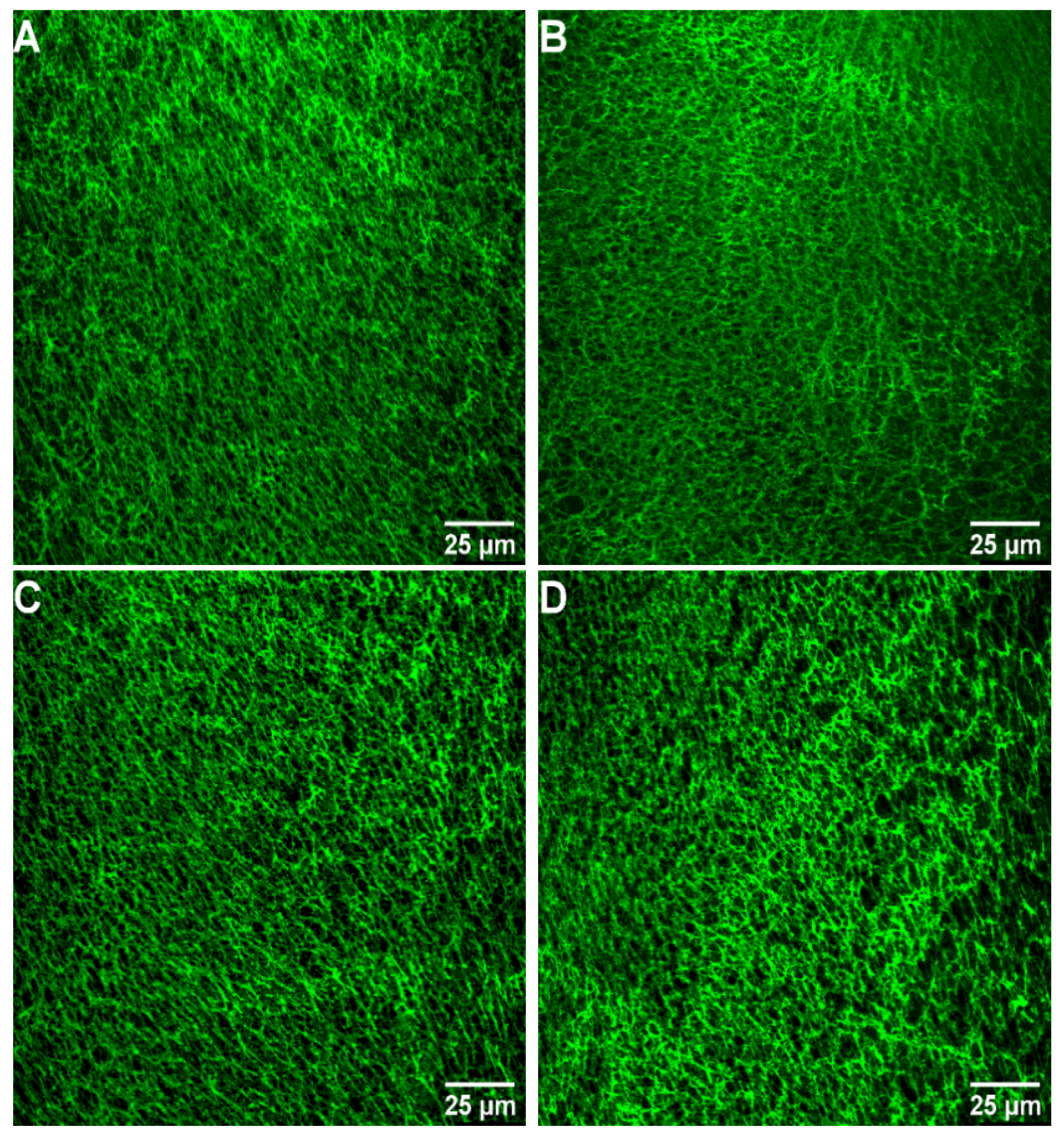
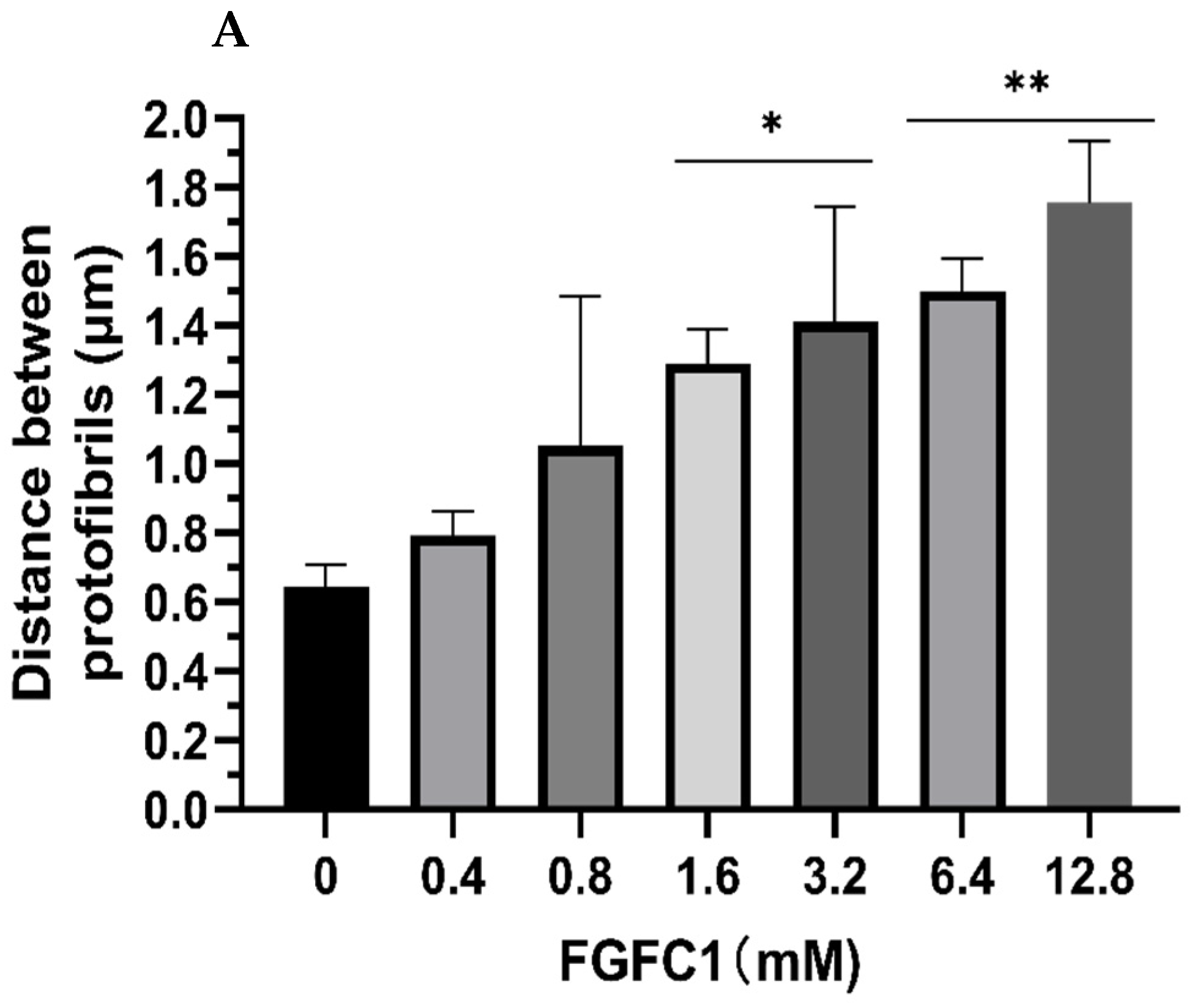
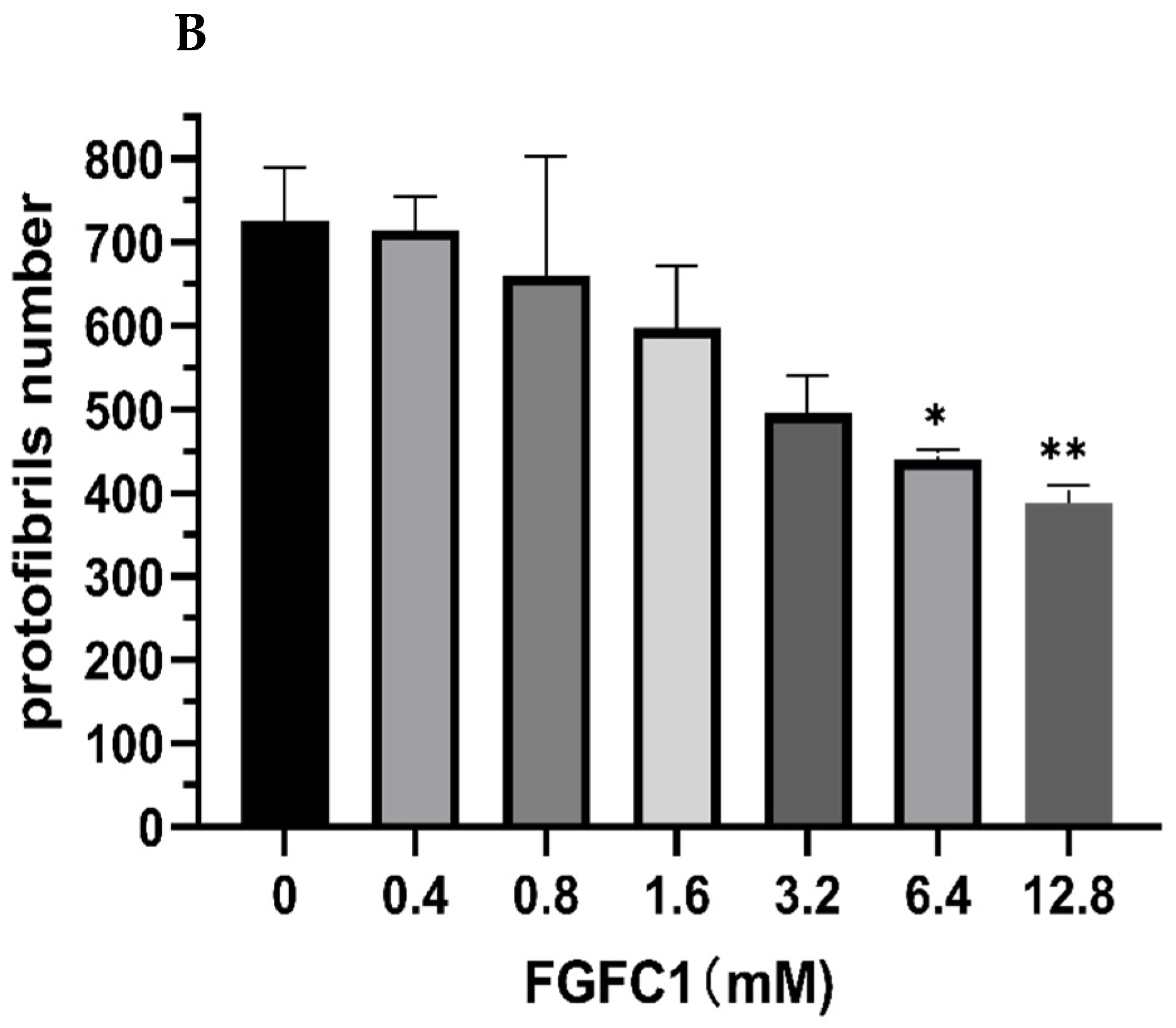
2.4. Images of Fibrin Networks by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Fibrinolytic Activity Measurements of FGFC1
4.3. Preparation of Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)-Labeled Fibrin
4.4. Determination of FITC-Fibrin Dissolution In Vitro
4.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4.6. Confocal Microscopy
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plow, E.F.; Wang, Y.M.; Simon, D.I. The search for new antithrombotic mechanisms and therapies that may spare hemostasis. Blood 2018, 131, 1899–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagarsamy, K.N.; Mathan, S.; Yan, W.; Rafieerad, A.; Sekaran, S.; Manego, H.; Dhingra, S. Carbon nanomaterials for cardiovascular theranostics: Promises and challenges. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2261–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.L.; Tian, Y.B.; Lv, X.; Xiao, X.; Zhan, M.M.; Cheng, K.i.; Li, S.Y.; Liao, C.Z. The selectivity and bioavailability improvement of novel oral anticoagulants: An overview. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 146, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.N.; Chen, H.; Sheng, R.L.; Fu, Z.; Fan, J.T.; Wu, W.H.; Tu, Q.D.; Guo, R.H. Synthesis and Bioactivities of Marine Pyran-Isoindolone Derivatives as Potential Antithrombotic Agents. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, E56–E528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.; Luengo-Fernández, R.; Gray, A.; Petersen, S.; Rayner, M. Economic burden of cardiovascular diseases in the enlarged European Union. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Damiana, T.; Damgaard, D.; Sidelmann, J.J.; Nielsen, C.H.; de Maat, M.P.M.; Munster, A.M.B.; Palarasah, Y. Citrullination of fibrinogen by peptidylarginine deiminase 2 impairs fibrin clot structure. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 501, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunclikova, M.; Simurda, T.; Zolkova, J.; Sterankova, M.; Skornova, I.; Dobrotova, M.; Kolkova, Z.; Loderer, D.; Grendar, M.; Hudecek, J.; et al. Heterogeneity of Genotype–Phenotype in Congenital Hypofibrinogenemia—A Review of Case Reports Associated with Bleeding and Thrombosis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.R.; Laverty, S.M.; Bannish, B.E.; Hudson, N.E. Microscale Structural Changes of Individual Fibrin Fibers during Fibrinolysis. Acta Biomater. 2022, 141, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.A.; Overmyer, K.A.; Selzman, C.H.; Sheridan, B.C.; Wolberg, A.S. Contributions of extravascular and intravascular cells to fibrin network formation, structure, and stability. Blood 2009, 114, 4886–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weisel, J.W.; Litvinov, R.I. Mechanisms of fibrin polymerization and clinical implications. Blood 2013, 121, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Betzabeth, P.; Brazón, J. Aqueous extract from Brownea grandiceps flowers with effect on coagulation and fibrinolytic system. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 160, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, H.; Brash, J.L. Mimicking the fibrinolytic system on material surfaces. Colloids Surf. B 2011, 86, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasche, H. Haemostasis and thrombosis: An overview. Eur. Heart J. Suppl. 2001, 3, Q3–Q7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluft, C.; Sidelmann, J.J.; Gram, J.B. Assessing Safety of Thrombolytic Therapy. Semin. Thromb. Hemostasis. 2017, 43, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotb, E. Activity assessment of microbial fibrinolytic enzymes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 6647–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwaan, H.C. The Role of Fibrinolytic System in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzekaki, E.E.; Tsolaki, M.; Pantazaki, A.A.; Geromichalos, G.; Lazarou, E.; Kozori, M.; Sinakos, Z. The pleiotropic beneficial intervention of olive oil intake on the Alzheimer’s disease onset via fibrinolytic system. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 150, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.L.; Xu, L.N.; Yu, S.J.; Hong, W.J.; Huang, M.D.; Xu, P. Therapeutics targeting the fibrinolytic system. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsen, J.B.; Hvas, A.M. Fibrinolytic Alterations in Sepsis: Biomarkers and Future Treatment Targets. Semin. Thromb. Hemostasis. 2021, 47, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Hua, L.I.; William, X.U.; Luo, J.; Rui-An, X.U. An Overview of the Fibrinolytic Enzyme from Earthworm. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2010, 8, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.S. Progress in Intravenous Thrombolytic Therapy for Acute Stroke. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 928–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simão, F.; Ustunkaya, T.; Clermont, A.C.; Feener, E.P. Plasma kallikrein mediates brain hemorrhage and edema caused by tissue plasminogen activator therapy in mice after stroke. Blood 2017, 129, 2280–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.R.; Zhu, Y.B.; Liu, Z.W.; Chang, L.P.; Bai, X.F.; Kang, L.J.; Cao, Y.L.; Yang, X.; Yu, H.L.; Shi, M.J.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote tPA-induced brain hemorrhage via cGAS in mice with stroke. Blood 2021, 138, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenych, A.; Fournier, L.; Chauvierre, C. Nanomedicine progress in thrombolytic therapy. Biomaterials 2020, 258, 120297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blann, A.D.; Landray, M.J.; Lip, G.Y.H. ABC of antithrombotic therapy: An overview of antithrombotic therapy. BMJ-Br. Med. J. 2002, 325, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruef, J.; Katus, H.A. New antithrombotic drugs on the horizon. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2003, 12, 781–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.X.; Lu, Z.X.; Bie, X.M.; Yao, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Lu, Y.P.; Guo, Y. Purification and characterization of a novel anticoagulant and fibrinolytic enzyme produced by endophytic bacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa EJS-3. Thromb. Res. 2010, 126, E349–E355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, P.M.; Nayak, S.; Lele, S.S. Fibrinolytic enzyme from newly isolated marine bacterium Bacillus subtilis ICTF-1: Media optimization, purification and characterization. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 113, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowthami, K.; Madhuri, R.J. Optimization of Cultural Conditions for Maximum Production of Fibrinolytic Enzymes from the Local Marine Bacterial Isolates and Evaluation of their Wound Healing and Clot Dissolving Properties. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2021, 33, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzkar, N.; Jahromi, S.T.; Vianello, F. Marine Microbial Fibrinolytic Enzymes: An Overview of Source, Production, Biochemical Properties and Thrombolytic Activity. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabu, A. Sources, Properties and Applications of Microbial Therapeutic Enzymes. Deep-Sea Res. Part A 2003, 30, 887–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachikawa, K.; Hasumi, K.; Endo, A. Enhancement of plasminogen binding to U937 cells and fibrin by complestatin. Thromb. Haemostasis. 1997, 77, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.H.; Hasumi, K.; Peng, H.; Hu, X.W.; Wang, X.C.; Bao, B. Fibrinolytic Compounds Isolated from a Brown Alga, Sargassum fulvellum. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shinohara, C.; Hasumi, K.; Hatsumi, W.; Endo, A. Staplabin, a Novel Fungal Triprenyl Phenol which Stimulates the Binding of Plasminogen to Fibrin and U937 Cells. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Wu, W.H.; Zhu, Q.G.; Fu, S.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Hong, S.T.; Guo, R.H.; Bao, B. Identification and Fibrinolytic Evaluation of an Isoindolone Derivative Isolated from a Rare Marine Fungus Stachybotrys longispora FG216. Chin. J. Chem. 2015, 33, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.K.; Zhang, B.; Feng, J.W.; Wu, H.G.; Duan, N.M.; Zhu, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.L.; Shen, S.; Zhang, K.; Wu, W.H.; et al. FGFC1 Selectively Inhibits Erlotinib-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Elevation of ROS Mediated by the EGFR/PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 764699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.W.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, B.; Duan, N.M.; Zhou, R.; Yan, S.K.; Elango, J.; Liu, N.; Wu, W.H. FGFC1 Exhibits Anti-Cancer Activity via Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling Pathway in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Cells. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasumi, K.; Yamamichi, S.; Harada, T. Small-molecule modulators of zymogen activation in the fibrinolytic and coagulation systems. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 3675–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasumi, K.; Suzuki, E. Impact of SMTP Targeting Plasminogen and Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase on Thrombolysis, Inflammation, and Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, S.J.; Chen, H.; Wu, W.H.; Wang, S.Y.; Fang, Y.W.; Sheng, R.L.; Tu, Q.D.; Guo, R.H. Progress in Isoindolone Alkaloid Derivatives from Marine Microorganism: Pharmacology, Preparation, and Mechanism. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraghavan, P.; Arun, A.; Vincent, S.G.P.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A. Cow Dung Is a Novel Feedstock for Fibrinolytic Enzyme Production from Newly Isolated Bacillus sp. IND7 and Its Application in In Vitro Clot Lysis. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijayaraghavan, P.; Vincent, S.G.P.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A. Bioconversion of agro-industrial wastes for the production of fibrinolytic enzyme from Bacillus halodurans IND18: Purification and biochemical characterization. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.P.; Xu, F.; Chen, J.P.; Duan, L.L.; Zhang, T.T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F.J. Breaking the vicious loop between inflammation, oxidative stress and coagulation, a novel anti-thrombus insight of nattokinase by inhibiting LPS-induced inflammation and oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2020, 32, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.L.; Shen, Q.; Tang, P.J.; Cao, Y.L.; Lin, H.W.; Li, B.L.; Sun, P.; Bao, B.; Wu, W.H. In Vitro Study of the Fibrinolytic Activity via Single Chain Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator and Molecular Docking of FGFC1. Molecules 2021, 26, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Kim, S. Fibrinolytic and Thrombolytic Effects of an Enzyme Purified from the Fruiting Bodies of Boletus pseudocalopus (Agaricomycetes) from Korea. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2021, 23, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Q.; Liu, L.Z.; Zeng, X.R. Research progress on the utilisation of embedding technology and suitable delivery systems for improving the bioavailability of nattokinase: A review. Food Struct. 2021, 30, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabayashi, T.; Imoto, Y.; Sakashita, M.; Kato, Y.; Tokunaga, T.; Yoshida, K.; Narita, N.; Ishizuka, T.; Fujieda, S. Nattokinase, profibrinolytic enzyme, effectively shrinks the nasal polyp tissue and decreases viscosity of mucus. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.H.; Duan, D.; Hong, S.T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.S.; Wu, W.H.; Bao, B. A marine fibrinolytic compound FGFC1 stimulating enzymatic kinetic parameters of a reciprocal activation system based on a single chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen. Process Biochem. 2018, 68, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreymann, N.; Wuensche, J.; Sabrowski, W.; Moeller, A.; Czepluch, D.; Van, D.V.; Fuessel, S.; Menger, M.M. Inhibition of Human Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator (uPA) Enzyme Activity and Receptor Binding by DNA Aptamers as Potential Therapeutics through Binding to the Different Forms of uPA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, J.Z.; Skottrup, P.D. Selection and characterization of camelid nanobodies towards urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 65, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, J.M.; Fang, M.H.; Wu, Y.Q. Association of red cell distribution width and D-dimer levels with intracranial hemorrhage in patients with cerebral venous thrombosis. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2022, 214, 107178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; He, H.B.; Fan, G.R.; Wu, Y.T. Determination of porcine fibrinogen in rat and dog plasma after intraperitoneal injection of a porcine-derived fibrin glue by fluorescein-labeled assay method: Comparison with isotope-labeled assay method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 57, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quach, T.; Tippens, M.; Sziam, T.; Van Dyke, R.; Levy, J.H.; Csete, M. Quantitative assessment of fibrinogen cross-linking by epsilon aminocaproic acid in patients with end-stage liver disease. Liver Transpl. 2004, 10, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, C.; Tang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Bao, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, W. A Novel Marine Pyran-Isoindolone Compound Enhances Fibrin Lysis Mediated by Single-Chain Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080495
Gao C, Tang S, Zhang H, Zhang H, Zhang T, Bao B, Zhu Y, Wu W. A Novel Marine Pyran-Isoindolone Compound Enhances Fibrin Lysis Mediated by Single-Chain Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(8):495. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080495
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Chunli, Simin Tang, Haixing Zhang, Huishu Zhang, Tian Zhang, Bin Bao, Yuping Zhu, and Wenhui Wu. 2022. "A Novel Marine Pyran-Isoindolone Compound Enhances Fibrin Lysis Mediated by Single-Chain Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator" Marine Drugs 20, no. 8: 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080495
APA StyleGao, C., Tang, S., Zhang, H., Zhang, H., Zhang, T., Bao, B., Zhu, Y., & Wu, W. (2022). A Novel Marine Pyran-Isoindolone Compound Enhances Fibrin Lysis Mediated by Single-Chain Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator. Marine Drugs, 20(8), 495. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20080495






