Jellyfish as an Alternative Source of Bioactive Antiproliferative Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
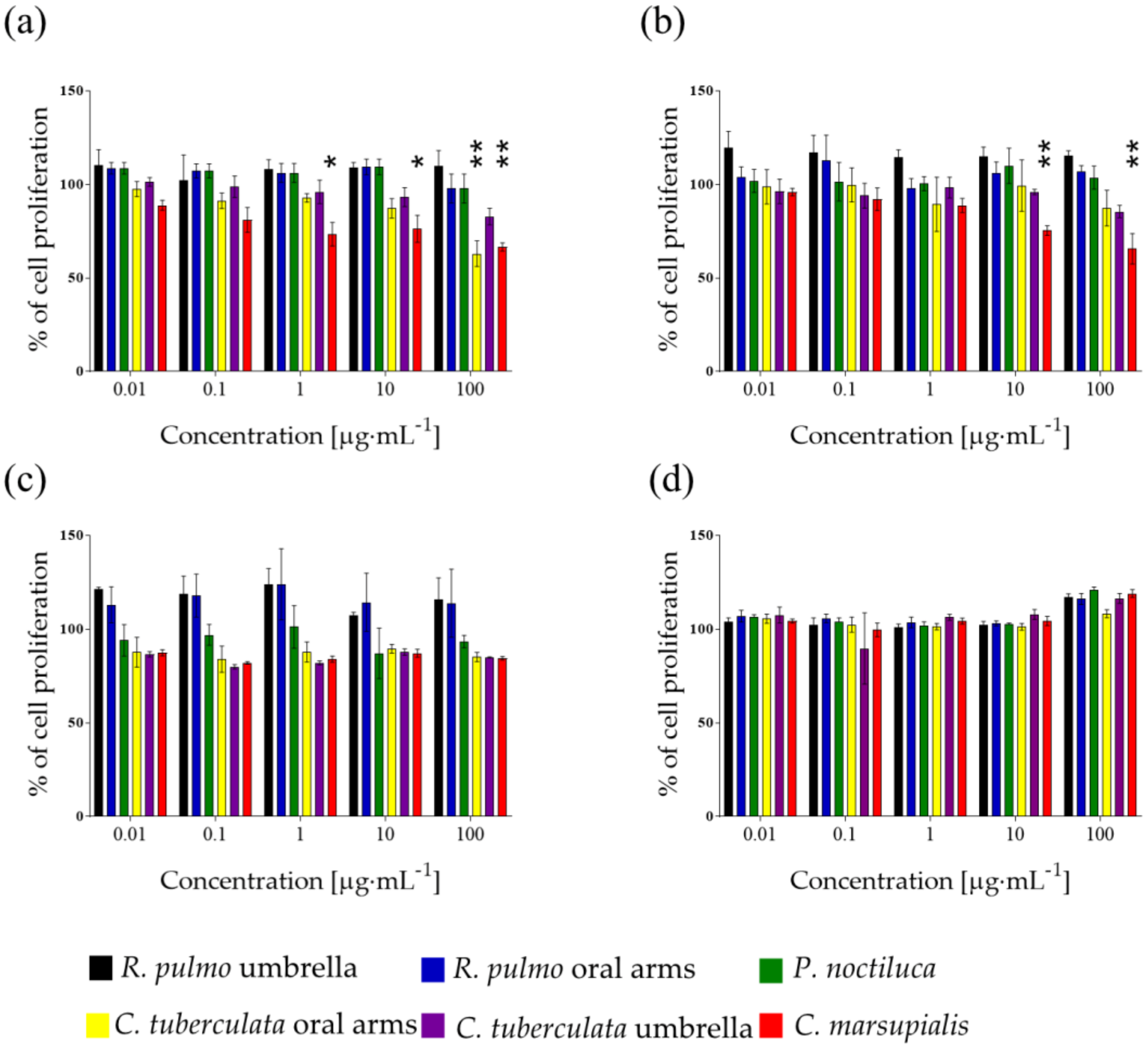
2.1. Raw Extracts Screening
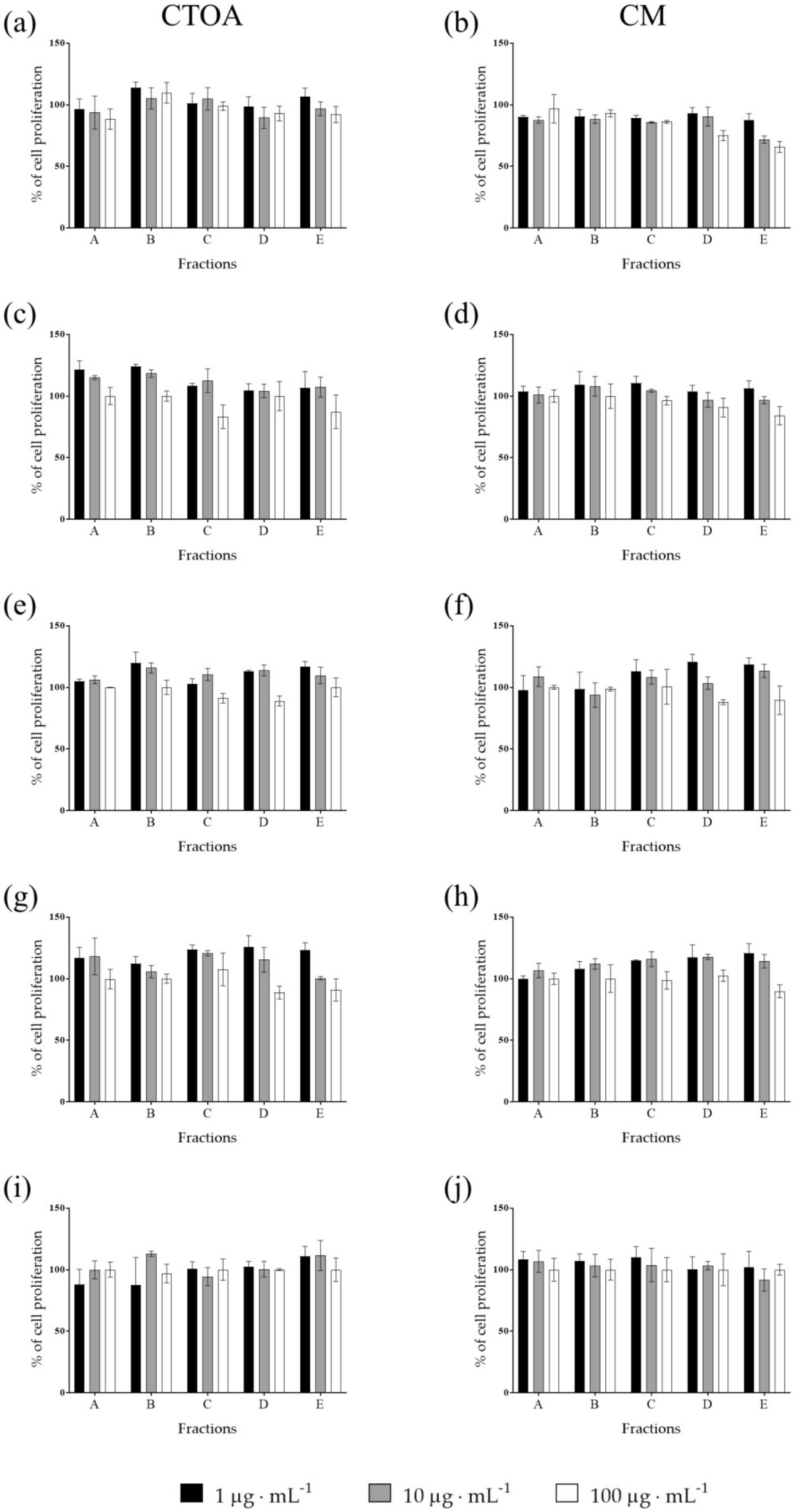
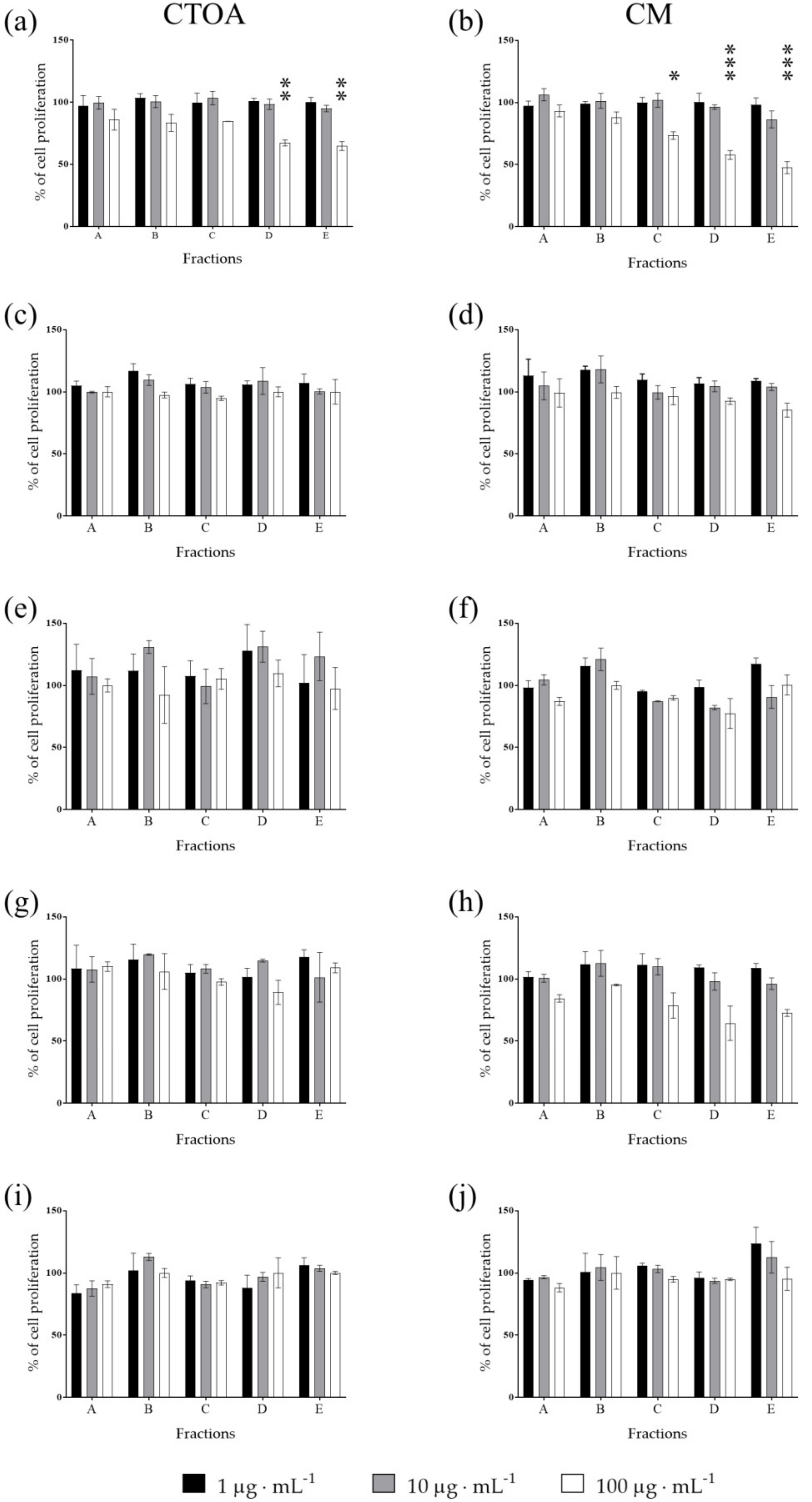
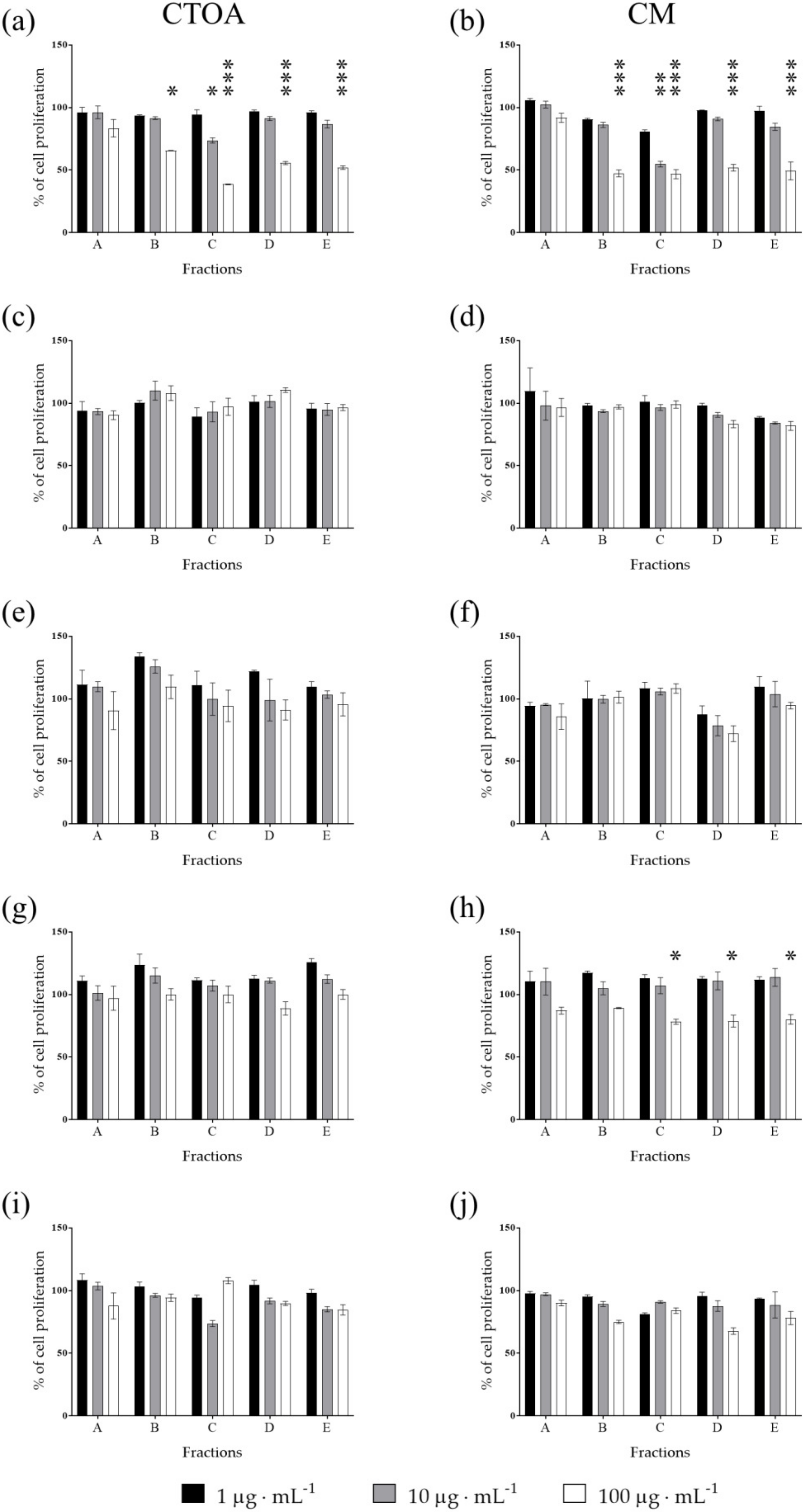
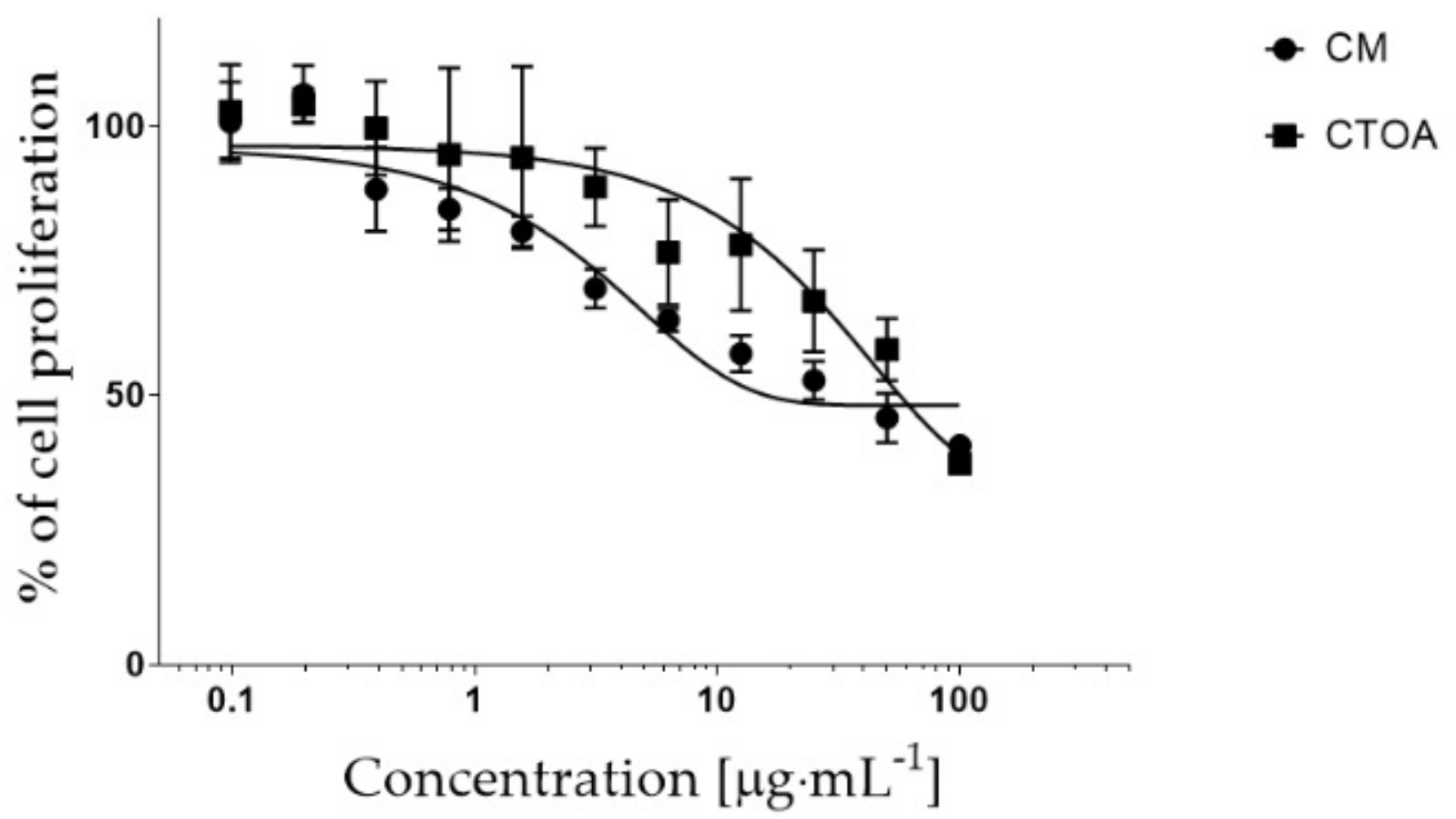
2.2. Bioactivity Testing of CTOA and CM Fractions
2.3. Mechanism of Action of Fraction C of CTOA and CM
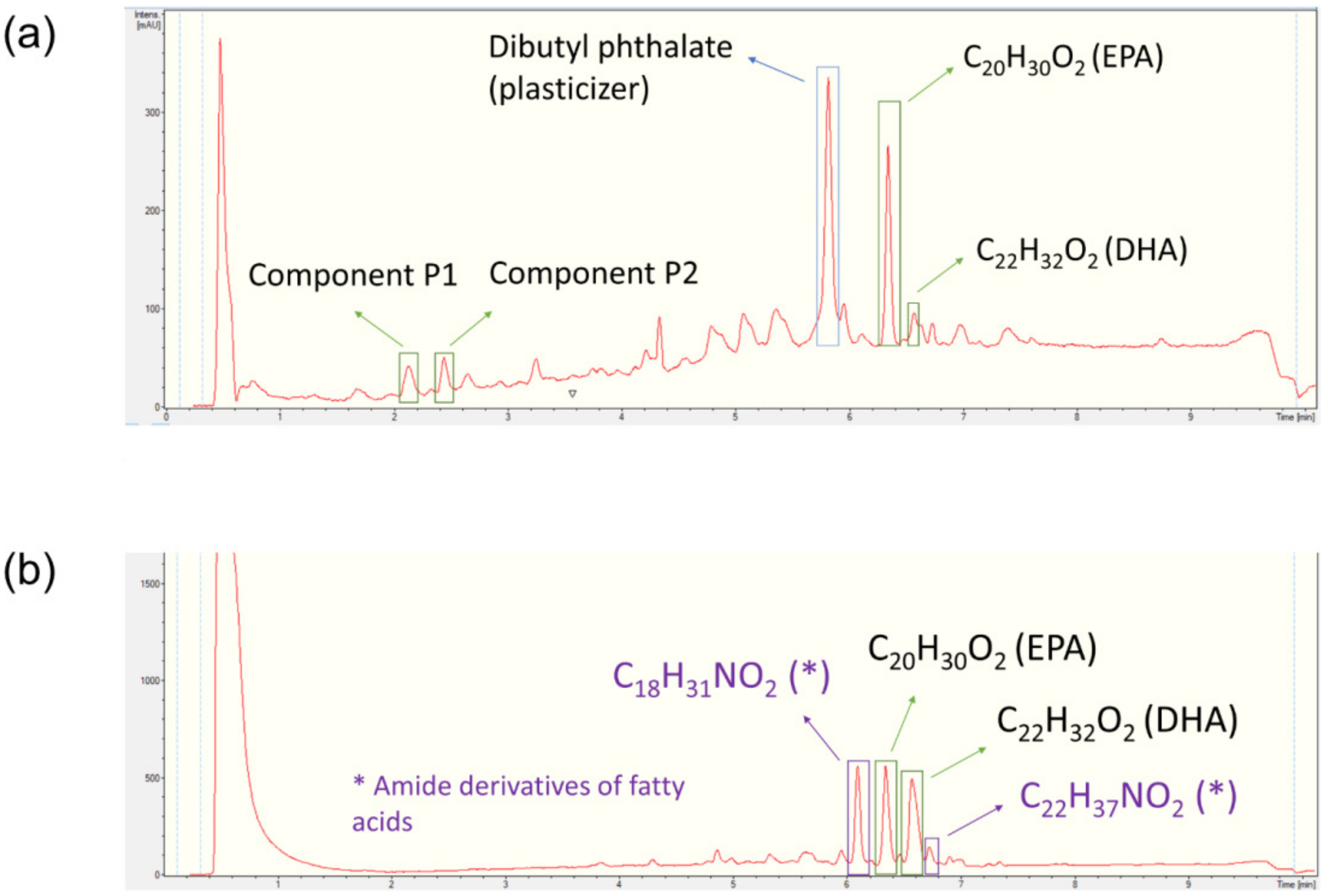
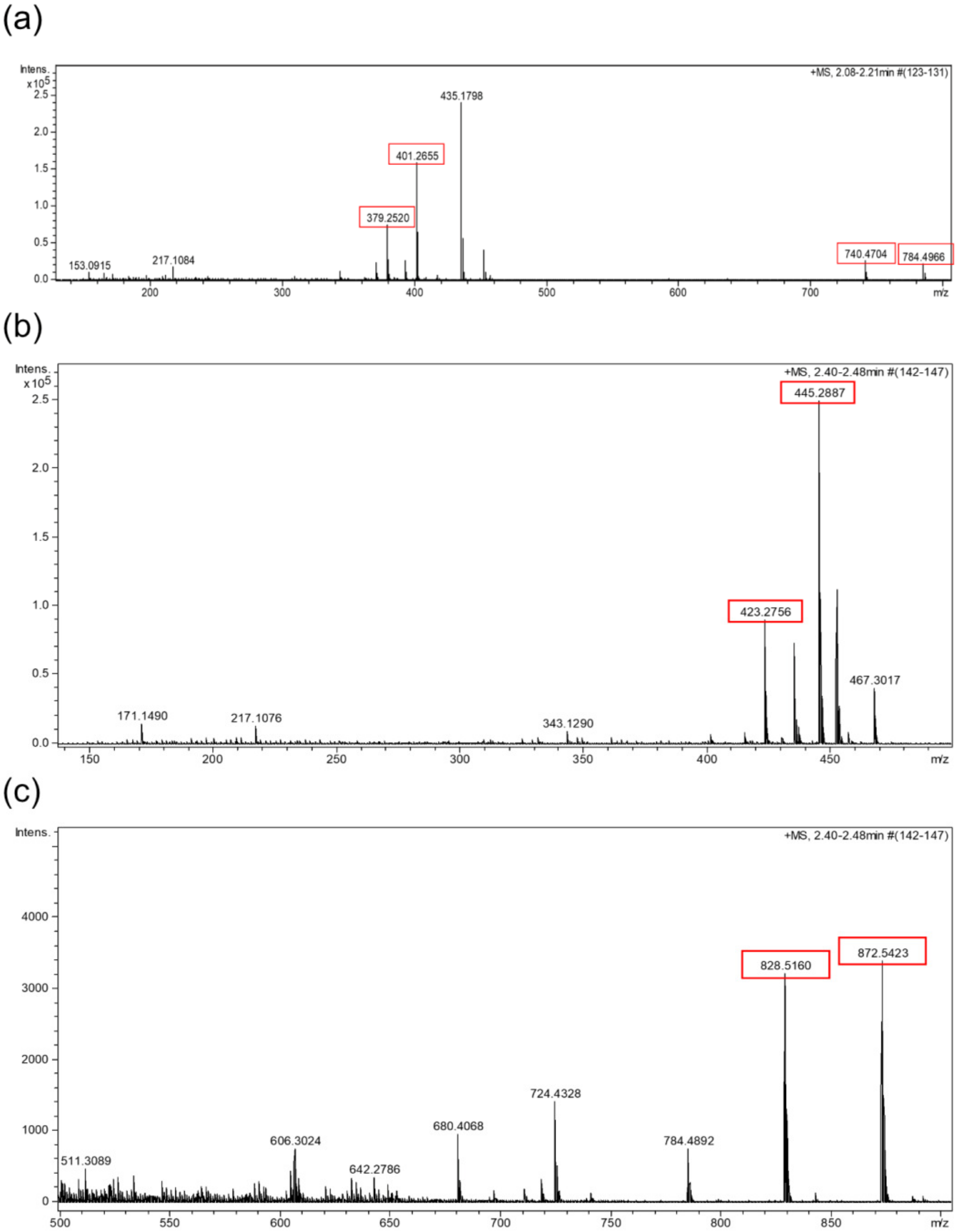
2.4. HPLC-UV-HRMS Dereplication of the Fractions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Processing
4.2. Extract Preparation
4.3. Fractionation of the Raw Extract
4.4. Cell Lines
4.5. In Vitro Antiproliferative Assays
4.6. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
4.7. Dereplication
4.8. Statistics
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaspars, M.; De Pascale, D.; Andersen, J.H.; Reyes, F.; Crawford, A.D.; Ianora, A. The marine biodiscovery pipeline and ocean medicines of tomorrow. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2016, 96, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romano, G.; Costantini, M.; Sansone, C.; Lauritano, C.; Ruocco, N.; Ianora, A. Marine microorganisms as a promising and sustainable source of bioactive molecules. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saide, A.; Martínez, K.A.; Ianora, A.; Lauritano, C. Unlocking the health potential of microalgae as sustainable sources of bioactive compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merquiol, L.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A.; D’Ambra, I. Biotechnological applications of scyphomedusae. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Ambra, I.; Lauritano, C. A Review of toxins from cnidaria. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stabili, L.; Rizzo, L.; Caprioli, R.; Leone, A.; Piraino, S. Jellyfish bioprospecting in the mediterranean sea: Antioxidant and lysozyme-like activities from Aurelia coerulea (cnidaria, scyphozoa) extracts. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.J.; Bakun, A.; Hays, G.C.; Gibbons, M.J. The jellyfish joyride: Causes, consequences and management responses to a more gelatinous future. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.H.P.; Leong, F.M.; Rudloe, J. Jellyfish as food. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Lecci, R.M.; Durante, M.; Meli, F.; Piraino, S. The bright side of gelatinous blooms: Nutraceutical value and antioxidant properties of three Mediterranean jellyfish (Scyphozoa). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4654–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prieto, L.; Enrique-Navarro, A.; Volsi, R.L.; Ortega, M.J. The large jellyfish Rhizostoma luteum as sustainable a resource for antioxidant properties, nutraceutical value and biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morais, Z.B.; Pintao, A.M.; Costa, I.M.; Calejo, M.T.; Bandarra, N.M.; Abreu, P. Composition and in vitro antioxidant effects of jellyfish Catostylus tagi from sado estuary (SW Portugal). J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2009, 18, 90–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, W.; Li, G. Isolation and characterisation of collagens from the skin of largefin longbarbel catfish (Mystus macropterus). Food Chem. 2009, 115, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, S.; De Rinaldis, G.; Paulmery, M.; Piraino, S.; Leone, A. Barrel Jellyfish (Rhizostoma pulmo) as Source of Antioxidant Peptides. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leone, A.; Lecci, R.M.; Milisenda, G.; Piraino, S. Mediterranean jellyfish as novel food: Effects of thermal processing on antioxidant, phenolic, and protein contents. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1611–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mearns-Spragg, A.; Tilman, J.; Tams, D.; Barnes, A. The Biological Evaluation of Jellyfish Collagen as a New Research Tool for the Growth and Culture of iPSC Derived Microglia. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addad, S.; Exposito, J.Y.; Faye, C.; Ricard-Blum, S.; Lethias, C. Isolation, characterization and biological evaluation of jellyfish collagen for use in biomedical applications. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernhardt, A.; Paul, B.; Gelinsky, M. Biphasic scaffolds from marine collagens for regeneration of osteochondral defects. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoyer, B.; Bernhardt, A.; Lode, A.; Heinemann, S.; Sewing, J.; Klinger, M.; Notbohm, H.; Gelinsky, M. Jellyfish collagen scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Munawir, A.; Cha, M.; Sohn, E.T.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.S.; Yoon, W.D.; Lim, D.; Kim, E. Cytotoxicity and hemolytic activity of jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) venom. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 150, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Bae, S.K.; Kim, M.; Pyo, M.J.; Kim, M.; Yang, S.; Won, C.K.; Yoon, W.D.; Han, C.H.; Kang, C.; et al. Anticancer Effect of Nemopilema nomurai Jellyfish Venom on HepG2 Cells and a Tumor Xenograft Animal Model. Evidence-based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 2752716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, I.; Lee, H.; Pyo, M.J.; Heo, Y.; Chae, J.; Yum, S.S.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. Proteomic investigation to identify anticancer targets of Nemopilema nomurai jellyfish venom in human hepatocarcinoma HepG2 cells. Toxins 2018, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boero, F. General Fiaheries Commission for the Mediterranen Review of Jellyfish Blooms in the Mediterranean and Black Sea. In Studies and Reviews. General Fisheries Commission for the Mediterranean; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 92, p. 53. [Google Scholar]
- Goy, J.; Morand, P.; Etienne, M. Long-term fluctuations of Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphomedusa) in the western Mediterranean Sea. Prediction by climatic variables. Deep Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1989, 36, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Mediterranean Action Plan. Jellyfish blooms in the Mediterranean. In Proceedings of the II Workshop on Jellyfish in the Mediterranean Sea, Trieste, Italy, 2–5 September 1987. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Environment Programme. Mediterranean Action Plan. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Jellyfish Blooms in the Mediterranean, Athens, Greece, 31 October–4 November 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Kikinger, R. Cotylorhiza tuberculata (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa)—Life History of a Stationary Population. Mar. Ecol. 1992, 13, 333–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariottini, G.L.; Sottofattori, E.; Mazzei, M.; Robbiano, L.; Carli, A. Cytotoxicity of the venom of Pelagia noctiluca forskål (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). Toxicon 2002, 40, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, Y.; Boussabbeh, M.; Zakhama, W.; Bouaziz, C.; Abid, S.; Bacha, H. Induction of cytotoxicity of Pelagia noctiluca venom causes reactive oxygen species generation, lipid peroxydation induction and DNA damage in human colon cancer cells. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morabito, R.; Costa, R.; Rizzo, V.; Remigante, A.; Nofziger, C.; La Spada, G.; Marino, A.; Paulmichl, M.; Dossena, S. Crude venom from nematocysts of Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) elicits a sodium conductance in the plasma membrane of mammalian cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayed, Y.; Dellai, A.; Mansour, H.B.; Bacha, H.; Abid, S. Analgesic and antibutyrylcholinestrasic activities of the venom prepared from the Mediterranean jellyfish Pelagia noctiluca (Forsskal, 1775). Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2012, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariottini, G.L.; Pane, L. Mediterranean jellyfish venoms: A review on scyphomedusae. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1122–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allavena, A.; Mariottini, G.L.; Carli, A.M.; Contini, S.; Martelli, A. In vitro evaluation of the cytotoxic, hemolytic and clastogenic activities of Rhizostoma pulmo toxin(s). Toxicon 1998, 36, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, A.; Sarkar, A.; Chakrabarty, D. Partial purification and identification of a metalloproteinase with anticoagulant activity from Rhizostoma pulmo (Barrel Jellyfish). Toxicon 2017, 132, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariello, L.; Romano, G.; Spagnuolo, A.; Zanetti, L. Isolation and partial characterization of Rhizolysin, a high molecular weight protein with hemolytic activity, from the jellyfish Rhizostoma pulmo. Toxicon 1988, 26, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Lecci, R.M.; Durante, M.; Piraino, S. Extract from the zooxanthellate jellyfish Cotylorhiza tuberculata modulates gap junction intercellular communication in human cell cultures. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1728–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acevedo, M.J.; Straehler-Pohl, I.; Morandini, A.C.; Stampar, S.N.; Bentlage, B.; Matsumoto, G.I.; Yanagihara, A.; Toshino, S.; Bordehore, C.; Fuentes, V.L. Revision of the genus Carybdea (Cnidaria: Cubozoa: Carybdeidae): Clarifying the identity of its type species Carybdea marsupialis. Zootaxa 2019, 4543, 515–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boero, F.; Minelli, A. First record of Carybdea marsupialis (L., 1758) (Cnidaria, Cubozoa) from the Adriatic Sea. Boll. Mus. Civ. Stor. Nat. Venezia 1986, 35, 179–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gueroun, S.K.M.; Acevedo, M.J.; Kéfi-Daly Yahia, O.; Deidun, A.; Fuentes, V.L.; Piraino, S.; Daly Yahia, M.N. First records of Carybdea marsupialis proliferation (Cnidaria: Cubozoa) along the eastern Tunisian coast (Central Mediterranean). Ital. J. Zool. 2015, 82, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordehore, C.; Fuentes, V.L.; Atienza, D.; Barberá, C.; Fernandez-Jover, D.; Roig, M.; Acevedo-Dudley, M.J.; Canepa, A.J.; Gili, J.M. Detection of an unusual presence of the cubozoan Carybdea marsupialis at shallow beaches located near Denia, Spain (south-western Mediterranean). Mar. Biodivers. Rec. 2011, 4, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rottini, G.; Gusmani, L.; Parovel, E.; Avian, M.; Patriarca, P. Purification and properties of a cytolytic toxin in venom of the jellyfish Carybdea marsupialis. Toxicon 1995, 33, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, J.; Torrens, E.; Segura-Puertas, L. Partial purification and characterization of a novel neurotoxin and three cytolysins from box jellyfish (Carybdea marsupialis) nematocyst venom. Arch. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano-Pérez, F.; Arellano, R.O.; Garay, E.; Arreguín-Espinosa, R.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, J. Electrophysiological activity of a neurotoxic fraction from the venom of box jellyfish Carybdea marsupialis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 191, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anichini, A.; Mortarini, R.; Sensi, M.; Zanon, M. APAF-1 signaling in human melanoma. Cancer Lett. 2006, 238, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshoudeh, M.; Mehdizadeh, K.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Ataei, F. Upregulation of apoptotic protease activating factor-1 expression correlates with anti-tumor effect of taxane drug. Med. Oncol. 2021, 38, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.H.; Leygue, E.R.; Murphy, L.C. Psoriasin (S100A7). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1998, 30, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinquan, T.; Vorum, H.; Larsen, C.G.; Madsen, P.; Rasmussen, H.H.; Gesser, B.; Etzerodt, M.; Honoré, B.; Celis, J.E.; Thestrup-Pedersen, K. Pscoriasin: A novel chemotactic protein. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 107, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hill, S.M.; Wrobel, L.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Post-translational modifications of Beclin 1 provide multiple strategies for autophagy regulation. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, Y.; Hiragi, S.; Fukuda, M. Rab family of small GTPases: An updated view on their regulation and functions. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marat, A.L.; Dokainish, H.; McPherson, P.S. DENN domain proteins: Regulators of Rab GTPases. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 13791–13800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbas, R.; Larisch, S. Targeting XIAP for Promoting Cancer Cell Death-The Story of ARTS and SMAC. Cells 2020, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devi, G.R.; Finetti, P.; Morse, M.A.; Lee, S.; de Nonneville, A.; Van Laere, S.; Troy, J.; Geradts, J.; McCall, S.; Bertucci, F. Expression of X-Linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (XIAP) in Breast Cancer Is Associated with Shorter Survival and Resistance to Chemotherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, I.; Vuolo, M.; Madan, R.; Xue, X.; Levalley, A.J.; Ashton, A.W.; Jasmin, J.F.; Czaja, M.T.; Lin, E.Y.; Armstrong, R.C.; et al. ARC, an apoptosis suppressor limited to terminally differentiated cells, is induced in human breast cancer and confers chemo- and radiation-resistance. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onodera, Y.; Takagi, K.; Neoi, Y.; Sato, A.; Yamaguchi, M.; Miki, Y.; Ebata, A.; Miyashita, M.; Sasano, H.; Suzuki, T. Forkhead box i1 in breast carcinoma as a potent prognostic factor. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2021, 54, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, D.L.; Konstantakopoulos, N.; McInerney, B.V.; Mulvenna, J.; Seymour, J.E.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. Chironex fleckeri (box jellyfish) venom proteins: Expansion of a cnidarian toxin family that elicits variable cytolytic and cardiovascular effects. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 4798–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jouiaei, M.; Casewell, N.R.; Yanagihara, A.A.; Nouwens, A.; Cribb, B.W.; Whitehead, D.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Ali, S.A.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Koludarov, I.; et al. Firing the sting: Chemically induced discharge of cnidae reveals novel proteins and peptides from box jellyfish (Chironex fleckeri) Venom. Toxins 2015, 7, 936–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Kim, E.; Li, J.L.; Xiao, B.; Hong, J.; Yoo, E.S.; Yoon, W.D.; Jung, J.H. A new cyclic tetrapeptide from the jellyfish-derived fungus Phoma sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 1590–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavlaskova, K.; Nedved, J.; Kuzma, M.; Zabka, M.; Sulc, M.; Sklenar, J.; Novak, P.; Benada, O.; Kofronova, O.; Hajduch, M.; et al. Characterization of pseudacyclins A-E, a suite of cyclic peptides produced by Pseudallescheria boydii. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, J.C.; Ackman, R.G. Jellyfish (Cyanea capillata) Lipids: Fatty Acid Composition. J. Fish. Res. Board Canada 1968, 25, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Ye, M.; Xu, J.; Guo, C.; Zheng, H.; Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Yan, X. Lipid Profile in Different Parts of Edible Jellyfish Rhopilema esculentum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8283–8291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenvers, V.; Chi, X.; Javidpour, J. Seasonal variability of the fatty acid composition in Aurelia aurita (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa): Implications for gelativore food web studies. J. Plankton Res. 2020, 42, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Cartwright, C.; Chan, D.; Ding, J.; Felix, E.; Pan, Y.; Pang, J.; Rhea, P.; Block, K.; Fischer, S.M.; et al. Anticancer activity of fish oils against human lung cancer is associated with changes in formation of PGE2 and PGE3 and alteration of Akt phosphorylation. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Newell, M.; Baker, K.; Postovit, L.M.; Field, C.J. A critical review on the effect of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) on cancer cell cycle progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanvir, R.; Javeed, A.; Rehman, Y. Fatty acids and their amide derivatives from endophytes: New therapeutic possibilities from a hidden source. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, B.; McPhail, K.L.; Ligresti, A.; Di Marzo, V.; Gerwick, W.H. Semiplenamides A-G, Fatty Acid Amides from a Papua New Guinea Collection of the Marine Cyanobacterium Lyngbya semiplena. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvin, J.; Shanmughapriya, S.; Gandhimathi, R.; Seghal Kiran, G.; Rajeetha Ravji, T.; Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Hema, T.A. Optimization and production of novel antimicrobial agents from sponge associated marine actinomycetes Nocardiopsis dassonvillei MAD08. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 83, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutignano, A.; Nuzzo, G.; Ianora, A.; Luongo, E.; Romano, G.; Gallo, C.; Sansone, C.; Aprea, S.; Mancini, F.; D’Oro, U.; et al. Development and application of a novel SPE-method for bioassay-guided fractionation of marine extracts. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5736–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haque, F.; Khan, M.S.A.; AlQurashi, N. ROS-Mediated Necrosis by Glycolipid Biosurfactants on Lung, Breast, and Skin Melanoma Cells. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzo, E.; Cutignano, A.; Pagano, D.; Gallo, C.; Barra, G.; Nuzzo, G.; Sansone, C.; Ianora, A.; Urbanek, K.; Fenoglio, D.; et al. A new marine-derived sulfoglycolipid triggers dendritic cell activation and immune adjuvant response. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banchet-Cadeddu, A.; Hénon, E.; Dauchez, M.; Renault, J.H.; Monneaux, F.; Haudrechy, A. The stimulating adventure of KRN 7000. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 3080–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaJeunesse, T.C.; Wiedenmann, J.; Casado-Amezúa, P.; D’Ambra, I.; Turnham, K.E.; Nitschke, M.R.; Oakley, C.A.; Goffredo, S.; Spano, C.A.; Cubillos, V.M.; et al. Revival of Philozoon Geddes for host-specialized dinoflagellates, ‘zooxanthellae’, in animals from coastal temperate zones of northern and southern hemispheres. Eur. J. Phycol. 2022, 57, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djeghri, N.; Pondaven, P.; Stibor, H.; Dawson, M.N. Review of the diversity, traits, and ecology of zooxanthellate jellyfishes. Mar. Biol. 2019, 166, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambra, I.; Merquiol, L. Jellyfish from Fisheries By-Catches as a Sustainable Source of High-Value Compounds with Biotechnological Applications. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Lauritano, C.; Palma Esposito, F.; Riccio, G.; Rizzo, C.; De Pascale, D. Fish Waste: From Problem to Valuable Resource. Mar. Drugs 2022, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, D.; Oliviero, M.; Vitale, G.A.; Lauritano, C.; D’Ambra, I.; Iannace, S.; de Pascale, D. Marine collagen from alternative and sustainable sources: Extraction, processing and applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riccio, G.; Bottone, S.; La Regina, G.; Badolati, N.; Passacantilli, S.; Rossi, G.B.; Accardo, A.; Dentice, M.; Silvestri, R.; Novellino, E.; et al. A Negative Allosteric Modulator of WNT Receptor Frizzled 4 Switches into an Allosteric Agonist. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.; Crespo, G.; González-Menéndez, V.; Pérez-Moreno, G.; Sánchez-Carrasco, P.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Ruiz-Pérez, L.M.; González-Pacanowska, D.; Vicente, F.; Genilloud, O.; et al. MDN-0104, an antiplasmodial betaine lipid from Heterospora chenopodii. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2118–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Victoria, I.; Martín, J.; Reyes, F. Combined LC/UV/MS and NMR Strategies for the Dereplication of Marine Natural Products. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 857–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| UniGEne | RefSeq | Symbol | Description | Fold | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genes up-regulated by CTOA fraction C | |||||
| Hs.552567 | NM_001160 | APAF1 | Apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 | 2.77 | 0.245 |
| Genes down-regulated by CTOA fraction C | |||||
| Hs.592068 | NM_020655 | JPH3 | Junctophilin 3 | −2.54 | 0.792 |
| Hs.241570 | NM_000594 | TNF | Tumor necrosis factor | −2.22 | 0.227 |
| Hs.654567 | NM_005848 | DENND4A | DENN/MADD domain containing 4A | −2.16 | 0.019 |
| Genes up-regulated by CM fraction C | |||||
| Hs.442337 | NM_176823 | S100A7A | S100 calcium binding protein A7A | 4.28 | 0.917 |
| Hs.552567 | NM_001160 | APAF1 | Apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 | 4.21 | 0.079 |
| Hs.716464 | NM_003766 | BECN1 | Beclin 1 | 2.65 | 0.056 |
| Hs.578973 | NM_015247 | CYLD | Cylindromatosis (turban tumor syndrome) | 2.20 | 0.428 |
| Hs.181301 | NM_004079 | CTSS | Cathepsin S | 2.04 | 0.141 |
| Genes down-regulated by CM fraction C | |||||
| Hs.356076 | NM_001167 | XIAP | X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis | −149.92 | 9.751 |
| Hs.513667 | NM_003946 | NOL3 | Nucleolar protein 3 (apoptosis repressor with CARD domain) | −19.25 | 4.862 |
| Hs.87236 | NM_012188 | FOXI1 | Forkhead box I1 | −6.87 | 1.369 |
| Hs.654567 | NM_005848 | DENND4A | DENN/MADD domain containing 4A | −6.14 | 0.416 |
| Hs.592068 | NM_020655 | JPH3 | Junctophilin 3 | −2.79 | 0.292 |
| Hs.696238 | NM_001166 | BIRC2 | Baculoviral IAP repeat containing 2 | −2.26 | 0.553 |
| Hs.592244 | NM_000074 | CD40LG | CD40 ligand | −2.12 | 0.137 |
| Taxon | Species | Collection Site | Collection Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cubomedusae | Carybdea marsupialis | Gulf of Naples | 23/10/2018 |
| Scyphomedusae | Pelagia noctiluca | Gulf of Naples | 15/05/2019 |
| Rhizostoma pulmo | Gulf of Naples | 27/10/2017 | |
| Cotylorhizatuberculata | Palinuro | 26/08/2019 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riccio, G.; Martinez, K.A.; Martín, J.; Reyes, F.; D’Ambra, I.; Lauritano, C. Jellyfish as an Alternative Source of Bioactive Antiproliferative Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060350
Riccio G, Martinez KA, Martín J, Reyes F, D’Ambra I, Lauritano C. Jellyfish as an Alternative Source of Bioactive Antiproliferative Compounds. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(6):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060350
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiccio, Gennaro, Kevin A. Martinez, Jesús Martín, Fernando Reyes, Isabella D’Ambra, and Chiara Lauritano. 2022. "Jellyfish as an Alternative Source of Bioactive Antiproliferative Compounds" Marine Drugs 20, no. 6: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060350
APA StyleRiccio, G., Martinez, K. A., Martín, J., Reyes, F., D’Ambra, I., & Lauritano, C. (2022). Jellyfish as an Alternative Source of Bioactive Antiproliferative Compounds. Marine Drugs, 20(6), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20060350









