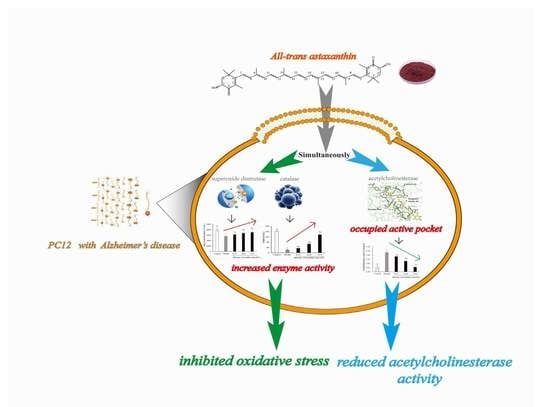
Simultaneous Inhibitory Effects of All-Trans Astaxanthin on Acetylcholinesterase and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
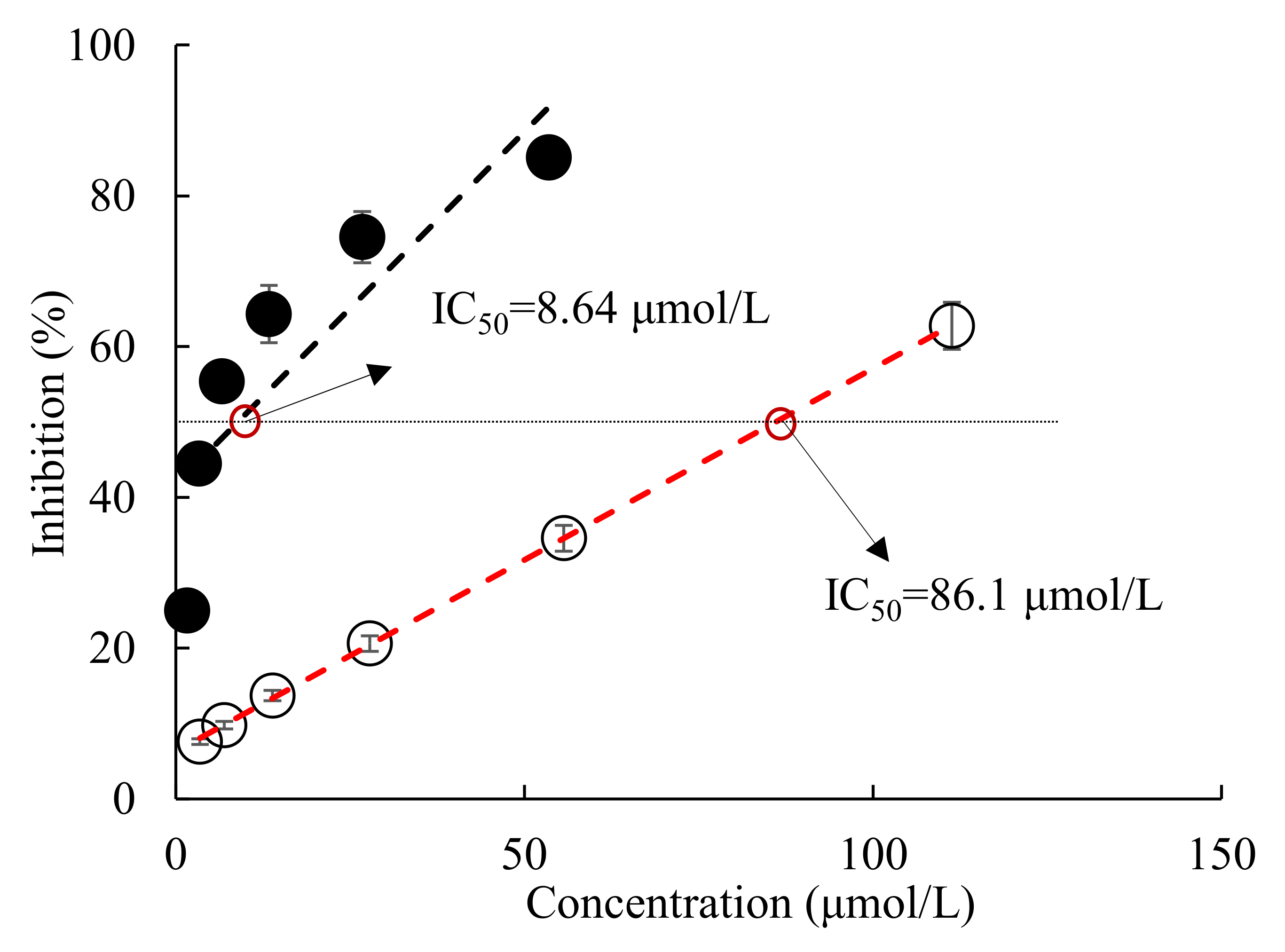
2.1. Effect of All-Trans Astaxanthin on Acetylcholinesterase Activity In Vitro
2.2. Enzyme Kinetic Study
2.3. Changes in Acetylcholinesterase Conformation Based on Circular Dichroism Spectra and Fluorescence
2.4. Effect of All-Trans Astaxanthin Concentration on PC12 Cell Viability
2.5. Effect of All-Trans Astaxanthin on Intracellular Antioxidant Capacity and Acetylcholinesterase Activity
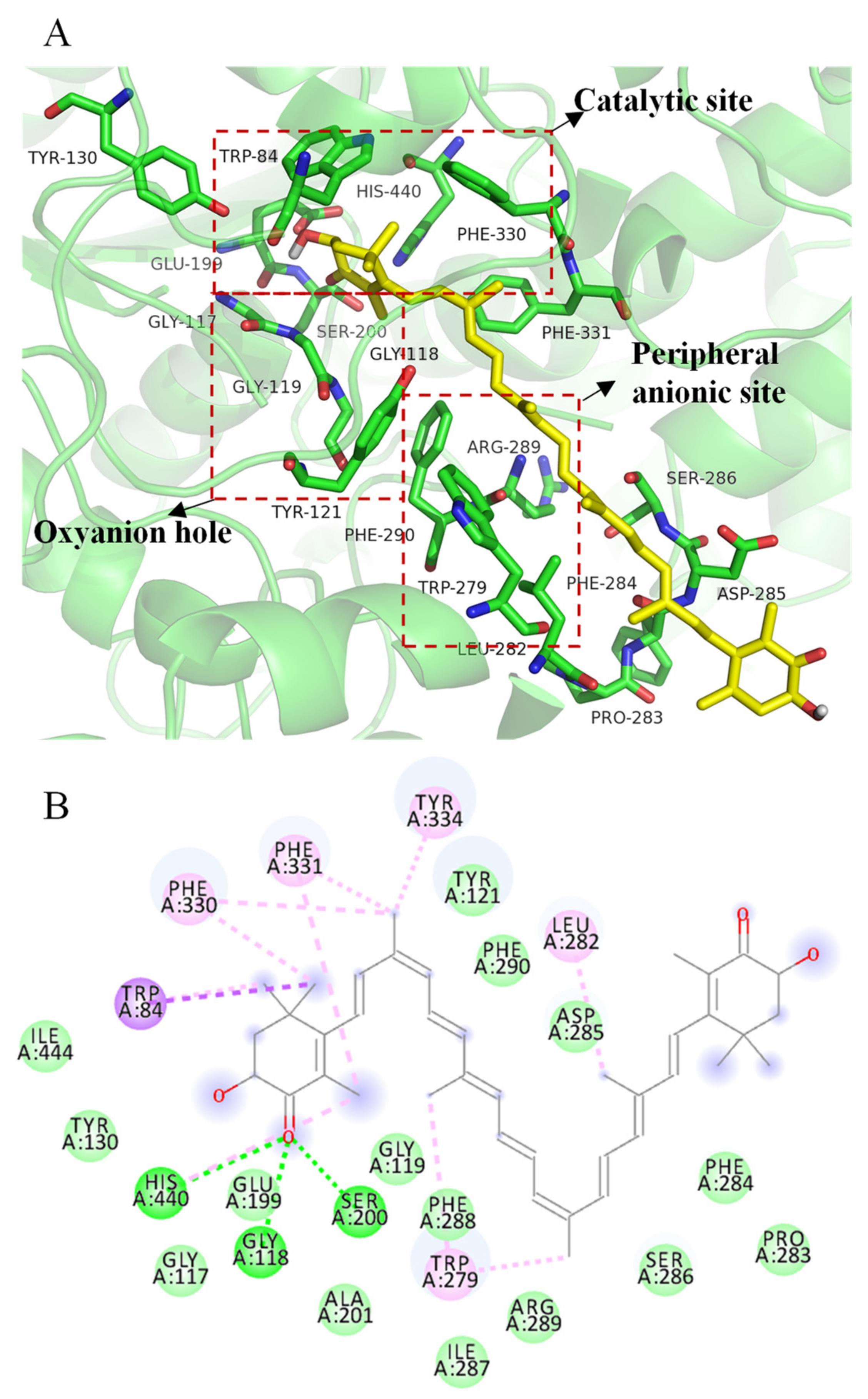
2.6. Molecular Docking Simulation of All-Trans Astaxanthin Binding to Acetylcholinesterase
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Regents
4.2. In Vitro Assay of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition
4.3. Inhibition Kinetic Analysis
4.4. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
4.5. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy Analysis
4.6. MTT Assay
4.7. Cell Pretreatment
4.8. Determination of Malondialdehyde Content and the Activities of Acetylcholinesterase, Superoxide Dismutase, and Catalase
4.9. Molecular Docking Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Key Facts of Dementia. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Gustavsson, A.; Svensson, M.; Jacobi, F.; Allgulander, C.; Alonso, J.; Beghi, E.; Dodel, R.; Ekman, M.; Faravelli, C.; Fratiglioni, L.; et al. Cost of disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. J. Eur. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 21, 718–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maslow, K. 2008 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2008, 4, 110–133. [Google Scholar]
- Colovic, M.B.; Krstic, D.Z.; Lazarevic-Pasti, T.D.; Bondzic, A.M.; Vasic, V.M. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Pharmacology and Toxicology. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holzgrabe, U.; Kapkova, P.; Alptuzun, V.; Scheiber, J.; Kugelmann, E. Targeting acetylcholinesterase to treat neurodegeneration. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartus, R.T.; Dean, R.L.; Beer, B.; Lippa, A.S. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science 1982, 217, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Kumar, V.; Mal, M.; Houghton, P.J. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from plants. Phytomedicine 2007, 14, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, O.; Mandel, S.; Amit, T.; Youdim, M.B.H. Neurological mechanisms of green tea polyphenols in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2004, 15, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzi, G.; Moretti, A. Are reactive oxygen species involved in alzheimers-disease—response. Neurobiol. Aging 1995, 16, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, P.; Maloney, A.J. Selective loss of central cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 1976, 2, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markesbery, W.R. Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1997, 23, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Ekavali, A. review on Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology and its management: An update. Pharmacol. Rep. PR 2015, 67, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Ruiz, P.; Rubio, L.; García-Palomero, E.; Dorronsoro, I.; del Monte-Millán, M.; Valenzuela, R.; Usán, P.; de Austria, C.; Bartolini, M.; Andrisano, V.; et al. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of dual binding site acetylcholinesterase inhibitors: New disease-modifying agents for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 7223–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariot, P.N.; Solomon, P.R.; Morris, J.C.; Kershaw, P.; Lilienfeld, S.; Ding, C. A 5-month, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of galantamine in AD. The Galantamine USA-10 Study Group. Neurol. 2000, 54, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pashkow, F.J.; Watumull, D.G.; Campbell, C.L. Astaxanthin: A novel potential treatment for oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, S58–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.M.; Asoh, S.; Hiranuma, H.; Ohsawa, I.; Iio, K.; Satou, A.; Ishikura, M.; Ohta, S. Astaxanthin protects mitochondrial redox state and functional integrity against oxidative stress. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS function in redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr. Biol. CB 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateos, R.; Lecumberri, E.; Ramos, S.; Goya, L.; Bravo, L. Determination of malondialdehyde (MDA) by high-performance liquid chromatography in serum and liver as a biomarker for oxidative stress. Application to a rat model for hypercholesterolemia and evaluation of the effect of diets rich in phenolic antioxidants from fruits. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 827, 76–82. [Google Scholar]
- Guerin, M.; Huntley, M.E.; Olaizola, M. Haematococcus astaxanthin: Applications for human health and nutrition. Trends Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, A.; Skibsted, L.H.; Sampson, J.; Rice-Evans, C.; Everett, S.A. Comparative mechanisms and rates of free radical scavenging by carotenoid antioxidants. FEBS Lett. 1997, 418, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, R.R.; Phang, S.M.; Ravi, S.; Aswathanarayana, R.G. Astaxanthin: Sources, extraction, stability, biological activities and its commercial applications--a review. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 128–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-j.; Chen, Z.-q.; Lu, W.-q. Hypoglycemic effect of astaxanthin from shrimp waste in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Med. Chem. Res. 2012, 21, 2363–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buesen, R.; Schulte, S.; Strauss, V.; Treumann, S.; Becker, M.; Gröters, S.; Carvalho, S.; van Ravenzwaay, B. Safety assessment of [3S, 3’S]-astaxanthin--Subchronic toxicity study in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2015, 81, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worek, F.; Aurbek, N.; Koller, M.; Becker, C.; Eyer, P.; Thiermann, H. Kinetic analysis of reactivation and aging of human acetylcholinesterase inhibited by different phosphoramidates. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 73, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Su, M.; Sun, H. Spectroscopic investigation on the interaction characteristics and inhibitory activities between baicalin and acetylcholinesterase. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; He, C.; Chen, X.; Zheng, X.; et al. Alkaloids and lignans with acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity from the flower buds of Magnolia biondiiPamp. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 10309–10316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B. Oxidative Stress and the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 316523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolla, N.; Wei, Z.L.; Richardson, J.S.; Li, X.M. Amitriptyline and fluoxetine protect PC12 cells from cell death induced by hydrogen peroxide. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2005, 30, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sultana, R.; Perluigi, M.; Butterfield, D.A. Oxidatively modified proteins in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), mild cognitive impairment and animal models of AD: Role of Abeta in pathogenesis. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 118, 131–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urso, M.L.; Clarkson, P.M. Oxidative stress, exercise, and antioxidant supplementation. Toxicology 2003, 189, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, F.R.; Oliveira, J.T.A.; Martins-Miranda, A.S.; Viégas, R.A.; Silveira, J.A.G. Superoxide dismutase, catalase and peroxidase activities do not confer protection against oxidative damage in salt-stressed cowpea leaves. New Phytol. 2004, 163, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryger, G.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with E2020 (Aricept): Implications for the design of new anti-Alzheimer drugs. Structure 1999, 7, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azman, N.A.N.; Alhawarri, M.B.; Rawa, M.S.A.; Dianita, R.; Gazzali, A.M.; Nogawa, T.; Wahab, H.A. Potential Anti-Acetylcholinesterase Activity of Cassia timorensis DC. Molecules 2020, 25, 4545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, A.; Huang, L.; Lu, C.; He, F.; Li, X. Synthesis biological evaluation and molecular modeling of novel triazole-containing berberine derivatives as acetylcholinesterase and β-amyloid aggregation inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 2298–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harel, M.; Kleywegt, G.J.; Ravelli, R.B.; Silman, I.; Sussman, J.L. Crystal structure of an acetylcholinesterase-fasciculin complex: Interaction of a three-fingered toxin from snake venom with its target. Structure 1995, 3, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Barron, M.G. Development of 3D-QSAR Model for Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors Using a Combination of Fingerprint, Molecular Docking, and Structure-Based Pharmacophore Approaches. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2015, 148, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencsura, A.; Enyedy, I.Y.; Kovach, I.M. Probing the active site of acetylcholinesterase by molecular dynamics of its phosphonate ester adducts. J. Am. Chem. 1996, 118, 8531–8541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.Z.H.; Hou, T. End-Point Binding Free Energy Calculation with MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA: Strategies and Applications in Drug Design. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 9478–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, M.; Bertucci, C.; Cavrini, V.; Andrisano, V. Beta-Amyloid aggregation induced by human acetylcholinesterase: Inhibition studies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Andres, V.; Featherstone, R.M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Bioorganic Chem. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Talbot, S.G.; Li, G.C.; Xu, M. Investigation of the mechanism of enhanced effect of EGCG on huperzine A’s inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity in rats by a multispectroscopic method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, E.; Burke, R.M.; Doig, A.J. Inhibition of toxicity in the beta-amyloid peptide fragment beta -(25–35) using N-methylated derivatives: A general strategy to prevent amyloid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25109–25115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Mu, X. Effect of Quercetin on PC12 Alzheimer’s Disease Cell Model Induced by Aβ (25–35) and Its Mechanism Based on Sirtuin1/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. BioMed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8210578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Du, X.; Jiang, Z.; Ni, H. Simultaneous Inhibitory Effects of All-Trans Astaxanthin on Acetylcholinesterase and Oxidative Stress. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040247
Wang X, Zhang T, Chen X, Xu Y, Li Z, Yang Y, Du X, Jiang Z, Ni H. Simultaneous Inhibitory Effects of All-Trans Astaxanthin on Acetylcholinesterase and Oxidative Stress. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(4):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040247
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xin, Tao Zhang, Xiaochen Chen, Yating Xu, Zhipeng Li, Yuanfan Yang, Xiping Du, Zedong Jiang, and Hui Ni. 2022. "Simultaneous Inhibitory Effects of All-Trans Astaxanthin on Acetylcholinesterase and Oxidative Stress" Marine Drugs 20, no. 4: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040247
APA StyleWang, X., Zhang, T., Chen, X., Xu, Y., Li, Z., Yang, Y., Du, X., Jiang, Z., & Ni, H. (2022). Simultaneous Inhibitory Effects of All-Trans Astaxanthin on Acetylcholinesterase and Oxidative Stress. Marine Drugs, 20(4), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040247