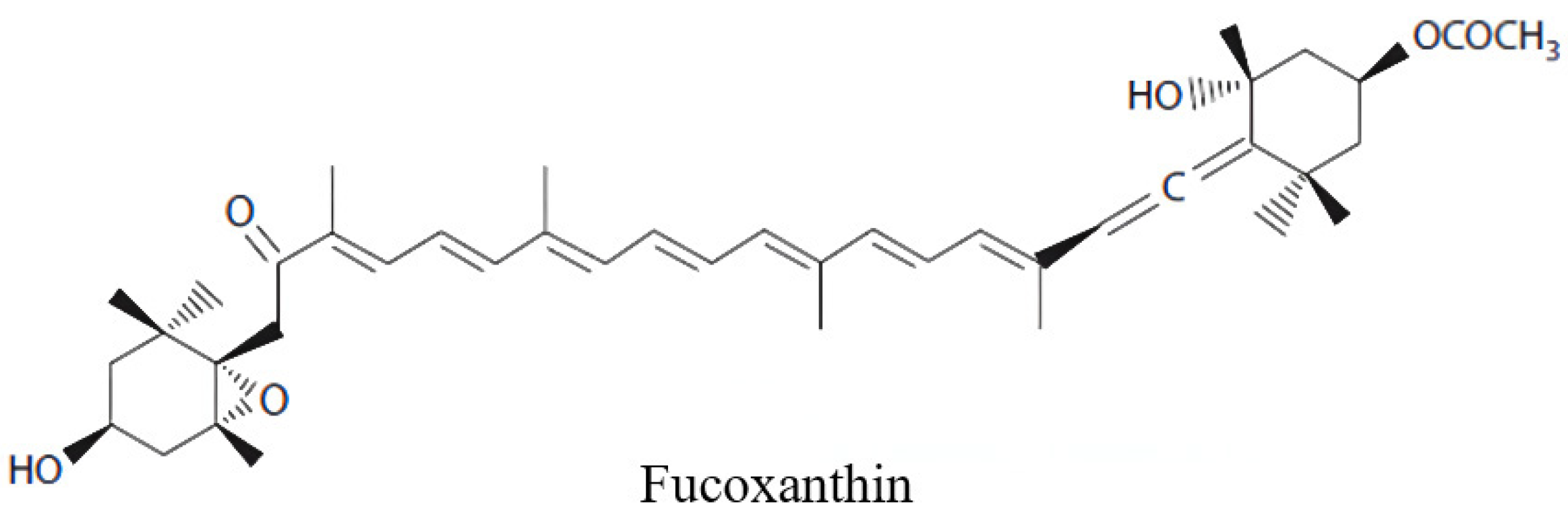
Fucoxanthin Prevents Long-Term Administration l-DOPA-Induced Neurotoxicity through the ERK/JNK-c-Jun System in 6-OHDA-Lesioned Mice and PC12 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Fucoxanthin Showed an Improvement in the Cytotoxicity Triggered by High Concentrations of l-DA Coordinated with 6-OHDA
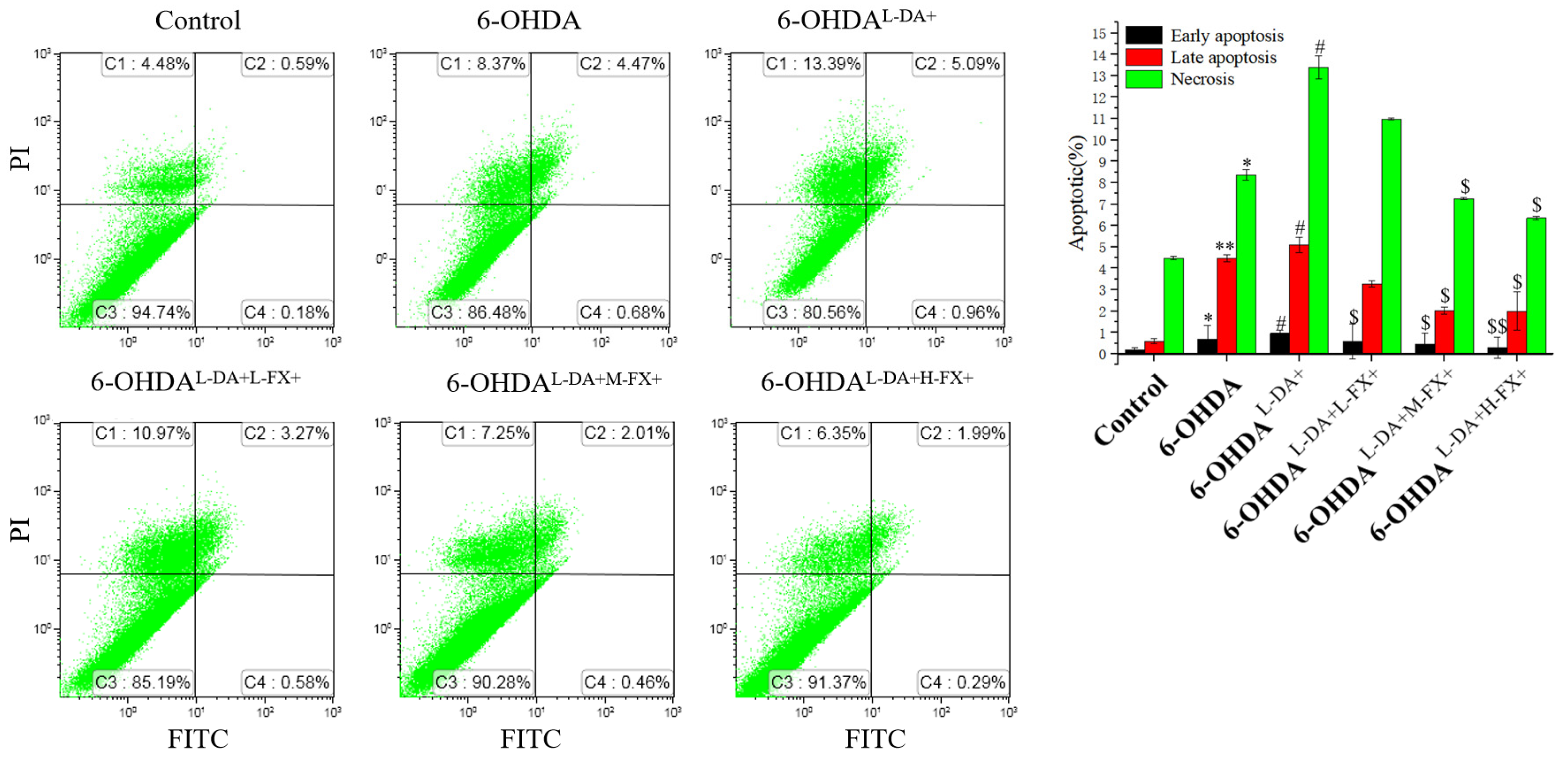
2.2. Apoptosis Induced by High Concentrations of l-DA with 6-OHDA Was Improved by Dose-Dependent Fucoxanthin
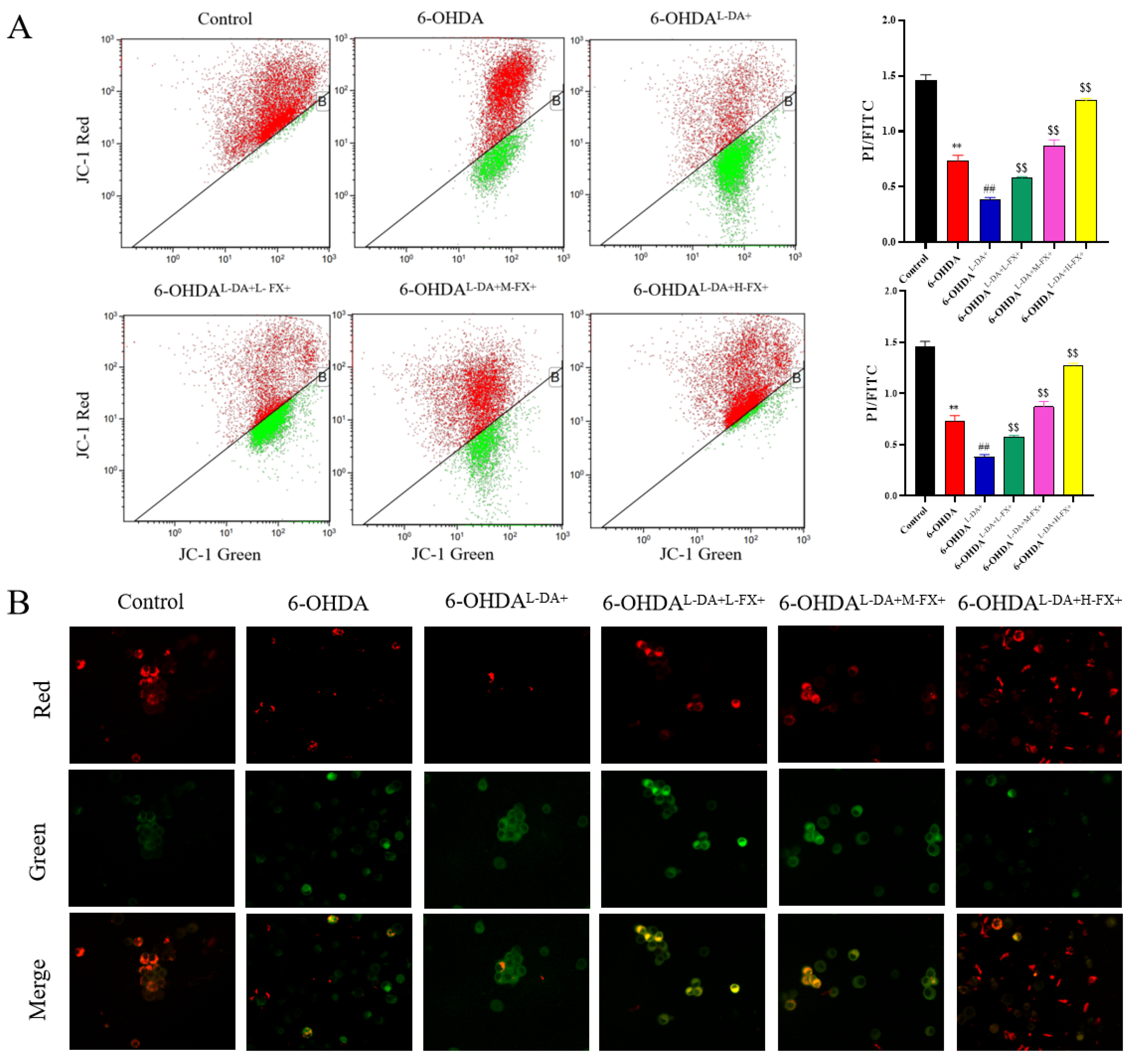
2.3. Mitochondrial Damage Induced by High Concentrations of l-DA and 6-OHDA Could See a Dose-Dependent Improvement by Fucoxanthin
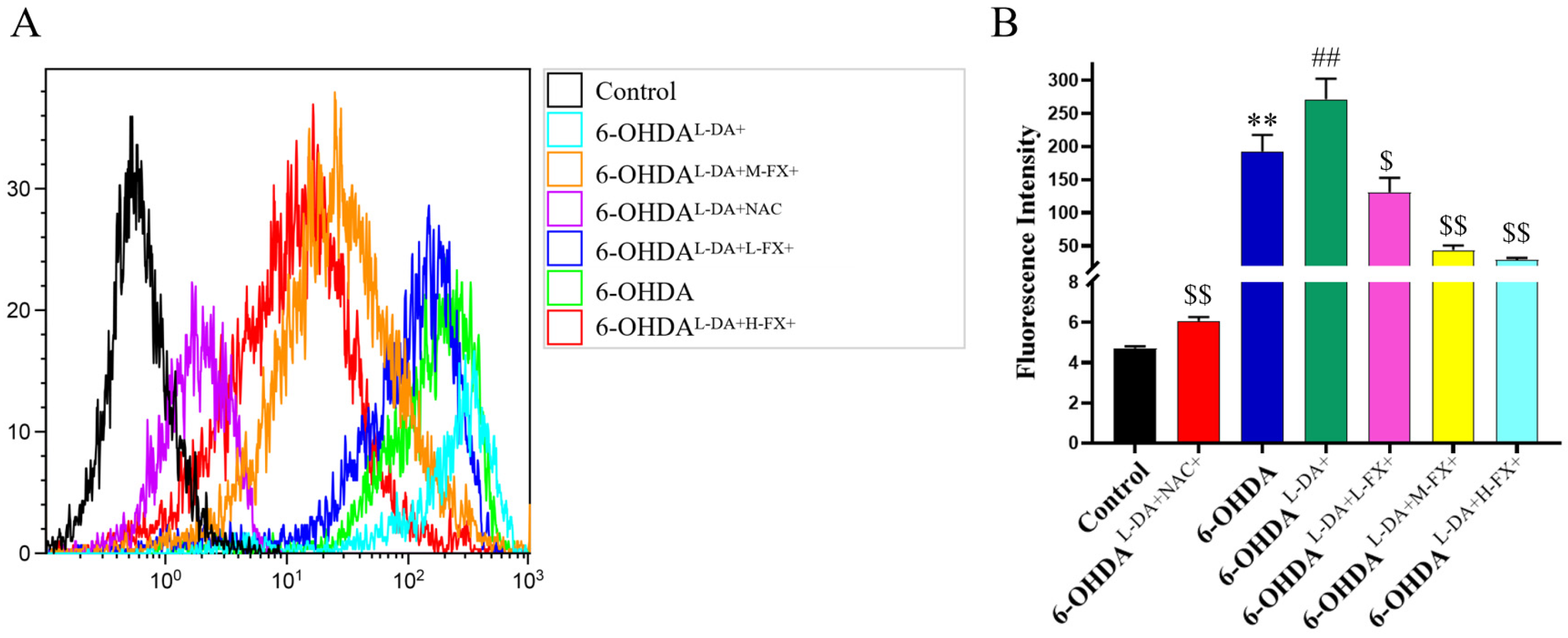
2.4. The Increase in ROS Levels Caused by the Synergy of High Concentrations of l-DA with 6-OHDA Can Be Inhibited by Fucoxanthin Dose Dependence
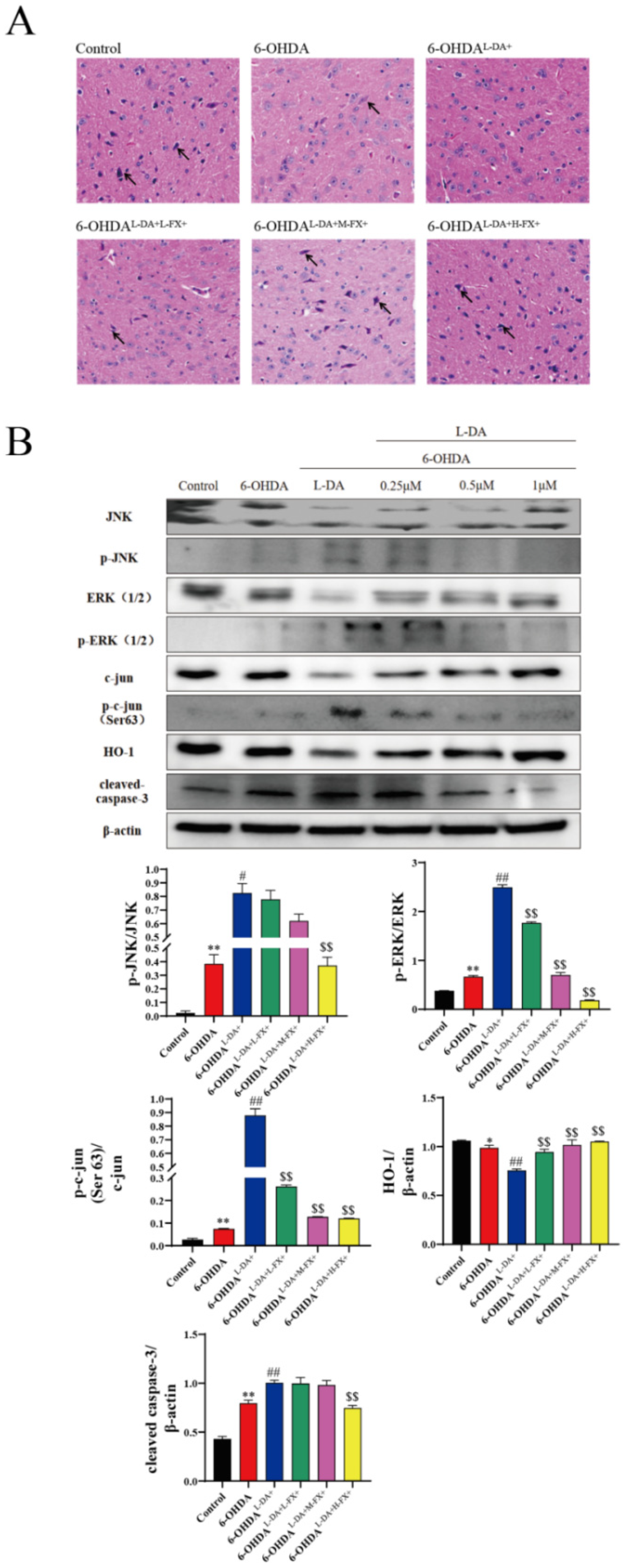
2.5. Fucoxanthin Downregulated the Expression of Apoptotic Proteins by the Inhibition of the ERK/JNK-c-Jun Pathway in the PC12 Cells
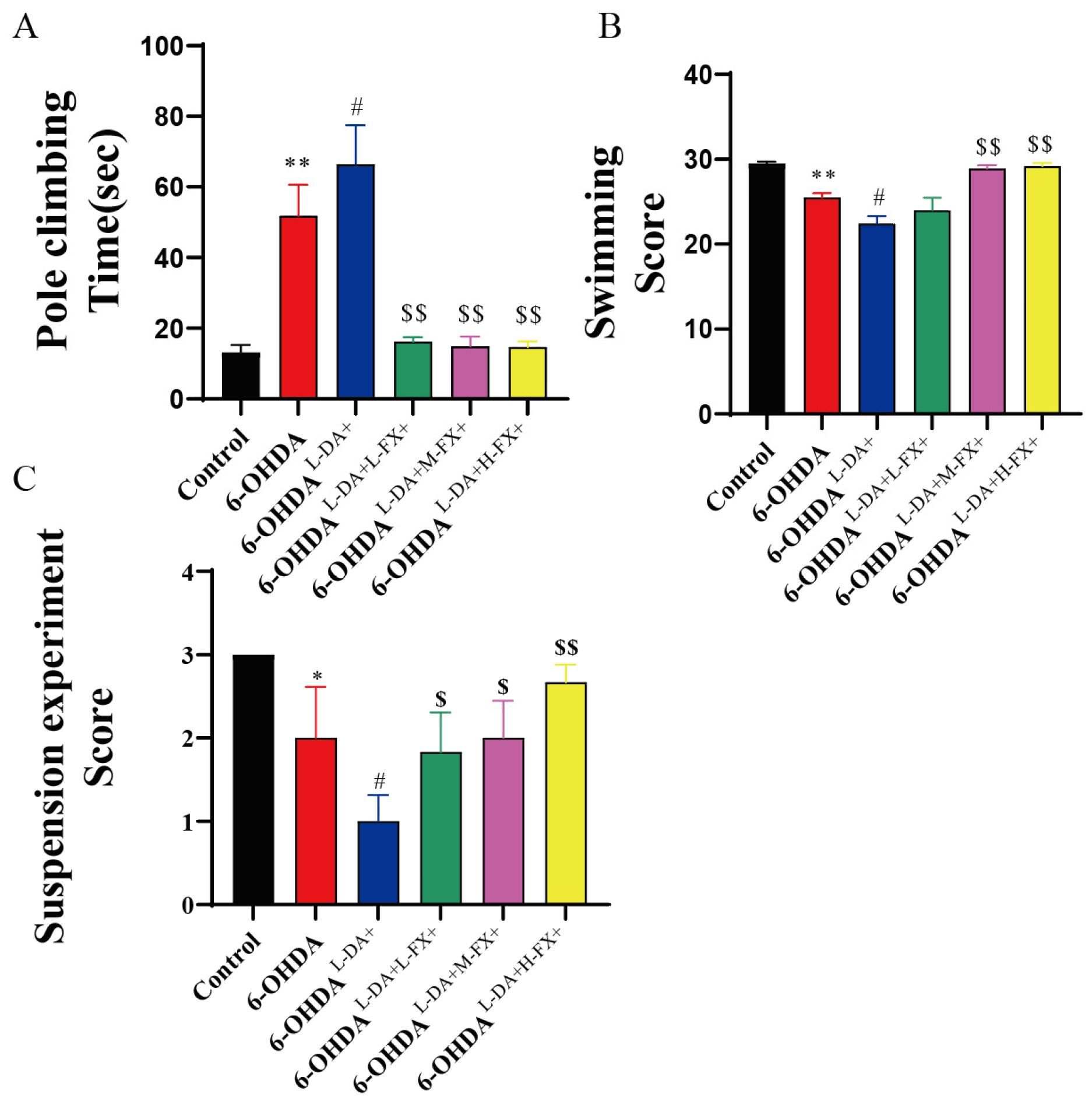
2.6. Exercise Ability of PD Mice Induced by High Concentrations of l-DA Could Be Improved by Fucoxanthin
2.7. Fucoxanthin Was Neuroprotective against Mice with PD Models Induced by High Concentrations of l-DA Synergy with 6-OHDA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Fucoxanthin Preparation
4.2. Experimental Animals and Experimental Procedure
4.3. Cell Viability Assay Was Performed by Using Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8)
4.4. Intracellular ROS Was Measured Using Sensitive Redox Probes (DCFH-DA)
4.5. Apoptosis Was Examined by Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.6. Measurement for Mitochondrial Membrane Potential with Fluorescent Probe JC-1
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Behavioral Tests
4.9. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Score | Training Situation | Number of Replications | Suspension Behavior of the Mice |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Each mouse was trained 3 days before surgery | Each mouse tested three times | Fell immediately |
| 1 | Two hindlimbs were not able to grasp the wire | ||
| 2 | Only one hindlimb was able to grasp the wire | ||
| 3 | Two hindlimbs were able to grasp the wire |
| Score | Testing Time | Number of Replications | Swimming Behavior of the Mice |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10–15 | 1 min | Each mouse tested three times | Hindlimbs occasionally swim and floating on one side of the tank |
| 15–20 | swimming by chance | ||
| 20–25 | Floating time accounts for more than half of the time | ||
| 25–30 | Swimming most of the time, floating by chance | ||
| 30 | Keep swimming for a minute |
References
- Schulz, J.B.; Hausmann, L.; Hardy, J. 199 years of Parkinson disease—What have we learned and what is the path to the future? J. Neurochem. 2016, 139 (Suppl. 1), 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuschl, G.; Beghi, E.; Fazekas, F.; Varga, T.; Christoforidi, K.A.; Sipido, E.; Bassetti, C.L.; Vos, T.; Feigin, V.L. The burden of neurological diseases in Europe: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e551–e567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Yin, P.; Wang, L.; Qu, M.; Kan, G.L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Dong, Z.; et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s Disease: A Community-Based Study in China. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 2940–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, D.; Torch, S.; Lambeng, N.; Nissou, M.; Benabid, A.L.; Sadoul, R.; Verna, J.M. Molecular pathways involved in the neurotoxicity of 6-OHDA, dopamine and MPTP: Contribution to the apoptotic theory in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 65, 135–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauer, W.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stednitz, S.J.; Freshner, B.; Shelton, S.; Shen, T.; Black, D.; Gahtan, E. Selective toxicity of l-DOPA to dopamine transporter-expressing neurons and locomotor behavior in zebrafish larvae. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 52 Pt A, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzaldi, K.; Shifren, K. Optimism, Pessimism, Coping, and Depression: A Study on Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Aging Hum. Dev. 2019, 88, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Raymick, J.; Imam, S. Neuroprotective and Therapeutic Strategies against Parkinson’s Disease: Recent Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbulla, L.F.; Song, P.; Mazzulli, J.R.; Zampese, E.; Wong, Y.C.; Jeon, S.; Santos, D.P.; Blanz, J.; Obermaier, C.D.; Strojny, C.; et al. Dopamine oxidation mediates mitochondrial and lysosomal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Science 2017, 357, 1255–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciulla, M.; Marinelli, L.; Cacciatore, I.; Stefano, A.D. Role of Dietary Supplements in the Management of Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, S.; Yu, S.; Qin, J.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Q.; Ke, K.; Ding, F. Neuroprotective effects of pyrroloquinoline quinone against rotenone injury in primary cultured midbrain neurons and in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2016, 108, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Wang, K.; Wan, L.; Li, A.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, C. Production, characterization, and antioxidant activity of fucoxanthin from the marine diatom Odontella aurita. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2667–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Yu, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, J.; Yan, X.; Gerwick, W.H.; et al. Fucoxanthin, a Marine Carotenoid, Attenuates beta-Amyloid Oligomer-Induced Neurotoxicity Possibly via Regulating the PI3K/Akt and the ERK Pathways in SH-SY5Y Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 6792543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Han, H.; Liu, J.; Tang, M.; Wu, X.; Cao, X.; Zhao, T.; Lu, Y.; Niu, T.; Chen, J.; et al. Fucoxanthin Prevents 6-OHDA-Induced Neurotoxicity by Targeting Keap1. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6688708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Waghela, B.; Shah, K.; Vaidya, F.; Mirza, S.; Patel, S.; Pathak, C.; Rawal, R. Silibinin, a Natural Blend in Polytherapy Formulation for Targeting Cd44v6 Expressing Colon Cancer Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16985. [Google Scholar]
- Samantaray, S.; Knaryan, V.H.; Le Gal, C.; Ray, S.K.; Banik, N.L. Calpain inhibition protected spinal cord motoneurons against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion and rotenone. Neuroscience 2011, 192, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Huang, T.; Bu, G.; Xu, H. Dysregulation of protein trafficking in neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurodegener. 2014, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, A.W.; Na, S.J.; Kim, W.K. Antioxidant effects of fucoxanthin rich powder in rats fed with high fat diet. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2013, 7, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niethammer, M.; Tang, C.C.; Feigin, A.; Allen, P.J.; Heinen, L.; Hellwig, S.; Amtage, F.; Hanspal, E.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Poston, K.L.; et al. A disease-specific metabolic brain network associated with corticobasal degeneration. Brain 2014, 137, 3036–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryois, J.; Skene, N.G.; Hansen, T.F.; Kogelman, L.J.A.; Watson, H.J.; Liu, Z.; Eating Disorders Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; International Headache Genetics Consortium; 23andMe Research Team; Brueggeman, L.; et al. Genetic identification of cell types underlying brain complex traits yields insights into the etiology of Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Hui, Y.; Zhu, C.; Wu, J.; Taylor, D.H.; Ji, J.; Fan, W.; Huang, Z.; Hu, J. Activation of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors protects astrocytes against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis: Implications for Parkinson’s disease. Neuropharmacology 2015, 91, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnen, F.; Cacciatore, I.; Cornacchia, C.; Sozio, P.; Cerasa, L.S.; Iannitelli, A.; Nasuti, C.; Cantalamessa, F.; Sekar, D.; Gabbianelli, R.; et al. Codrugs linking l-dopa and sulfur-containing antioxidants: New pharmacological tools against Parkinson’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, A.; Sozio, P.; Cocco, A.; Iannitelli, A.; Santucci, E.; Costa, M.; Pecci, L.; Nasuti, C.; Cantalamessa, F.; Pinnen, F. l-dopa- and dopamine-(R)-alpha-lipoic acid conjugates as multifunctional codrugs with antioxidant properties. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 1486–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnen, F.; Cacciatore, I.; Cornacchia, C.; Sozio, P.; Iannitelli, A.; Costa, M.; Pecci, L.; Nasuti, C.; Cantalamessa, F.; Di Stefano, A. Synthesis and study of l-dopa-glutathione codrugs as new anti-Parkinson agents with free radical scavenging properties. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Pangestuti, R. Biological activities and potential health benefits of fucoxanthin derived from marine brown algae. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 64, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Hou, L.; Li, X.; Ju, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Y. Neuroprotection of inositol hexaphosphate and changes of mitochondrion mediated apoptotic pathway and alpha-synuclein aggregation in 6-OHDA induced parkinson’s disease cell model. Brain Res. 2016, 1633, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Bakker, A.C.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Beyaert, R.; Jacob, W.A.; Fiers, W. Cytotoxic activity of tumor necrosis factor is mediated by early damage of mitochondrial functions. Evidence for the involvement of mitochondrial radical generation. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 5317–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Beyaert, R.; Vandevoorde, V.; Haegeman, G.; Fiers, W. Depletion of the mitochondrial electron transport abrogates the cytotoxic and gene-inductive effects of TNF. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3095–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, R.; Soares-da-Silva, P. Oxidative and non-oxidative mechanisms of neuronal cell death and apoptosis by L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (l-DOPA) and dopamine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 137, 1305–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Shin, K.S.; Zhao, T.T.; Park, H.J.; Lee, K.E.; Lee, M.K. l-DOPA modulates cell viability through the ERK-c-Jun system in PC12 and dopaminergic neuronal cells. Neuropharmacology 2016, 101, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Sui, G.; Rosa, P.M.; Zhao, W. Radiation-induced c-Jun activation depends on MEK1-ERK1/2 signaling pathway in microglial cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leppa, S.; Saffrich, R.; Ansorge, W.; Bohmann, D. Differential regulation of c-Jun by ERK and JNK during PC12 cell differentiation. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 4404–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Feng, Z.; Porter, A.G. JNK-dependent phosphorylation of c-Jun on serine 63 mediates nitric oxide-induced apoptosis of neuroblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4058–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waetzig, V.; Zhao, Y.; Herdegen, T. The bright side of JNKs-Multitalented mediators in neuronal sprouting, brain development and nerve fiber regeneration. Prog. Neurobiol. 2006, 80, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Y.; Li, J.; Qi, W.Q.; Shen, S.H. Experimental change on dopaminergic neurons in striatum of Parkinson disease rats. Histol. Histopathol. 2007, 22, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, A.; Wang, X.; Siedlak, S.L.; Perry, G.; Smith, M.A.; Zhu, X. c-Jun phosphorylation in Alzheimer disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, L.; Xie, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, W.; Su, X.; Huang, S.; Chen, R.; Zhu, Z.; Mao, Z.; et al. SP600125, a new JNK inhibitor, protects dopaminergic neurons in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 48, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada, A.; Lee, B.Y.; Micevych, P.E. PI3 kinase/Akt activation mediates estrogen and IGF-1 nigral DA neuronal neuroprotection against a unilateral rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Dev. Neurobiol. 2008, 68, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavon, N.; Martin, A.B.; Mendialdua, A.; Moratalla, R. ERK phosphorylation and FosB expression are associated with l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in hemiparkinsonian mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Jin, L.; Zheng, D.; Tang, X.; Yang, J.; Fan, L.; Xie, X. Fucoxanthin Alleviates Oxidative Stress through Akt/Sirt1/FoxO3alpha Signaling to Inhibit HG-Induced Renal Fibrosis in GMCs. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouillet, A.; Levet, C.; Virgone, A.; Robin, M.; Dourlen, P.; Rieusset, J.; Belaidi, E.; Ovize, M.; Touret, M.; Nataf, S.; et al. ER stress inhibits neuronal death by promoting autophagy. Autophagy 2012, 8, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Liu, F.; Lin, J.; Chen, H.; Huang, C.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhang, K.; Jin, J.; et al. Fucoxanthin Inhibits beta-Amyloid Assembly and Attenuates beta-Amyloid Oligomer-Induced Cognitive Impairments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4092–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Tang, M.; Shao, F.; Yang, D.; Chen, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhai, L.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; et al. Fucoxanthin Prevents Long-Term Administration l-DOPA-Induced Neurotoxicity through the ERK/JNK-c-Jun System in 6-OHDA-Lesioned Mice and PC12 Cells. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040245
Liu J, Lu Y, Tang M, Shao F, Yang D, Chen S, Xu Z, Zhai L, Chen J, Li Q, et al. Fucoxanthin Prevents Long-Term Administration l-DOPA-Induced Neurotoxicity through the ERK/JNK-c-Jun System in 6-OHDA-Lesioned Mice and PC12 Cells. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(4):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040245
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jingwangwei, Yujia Lu, Min Tang, Fanghao Shao, Dongzi Yang, Shuchang Chen, Ziyi Xu, Leilei Zhai, Juanjuan Chen, Qian Li, and et al. 2022. "Fucoxanthin Prevents Long-Term Administration l-DOPA-Induced Neurotoxicity through the ERK/JNK-c-Jun System in 6-OHDA-Lesioned Mice and PC12 Cells" Marine Drugs 20, no. 4: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040245
APA StyleLiu, J., Lu, Y., Tang, M., Shao, F., Yang, D., Chen, S., Xu, Z., Zhai, L., Chen, J., Li, Q., Wu, W., & Chen, H. (2022). Fucoxanthin Prevents Long-Term Administration l-DOPA-Induced Neurotoxicity through the ERK/JNK-c-Jun System in 6-OHDA-Lesioned Mice and PC12 Cells. Marine Drugs, 20(4), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20040245






