CATASAN Is a New Anti-Biofilm Agent Produced by the Marine Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
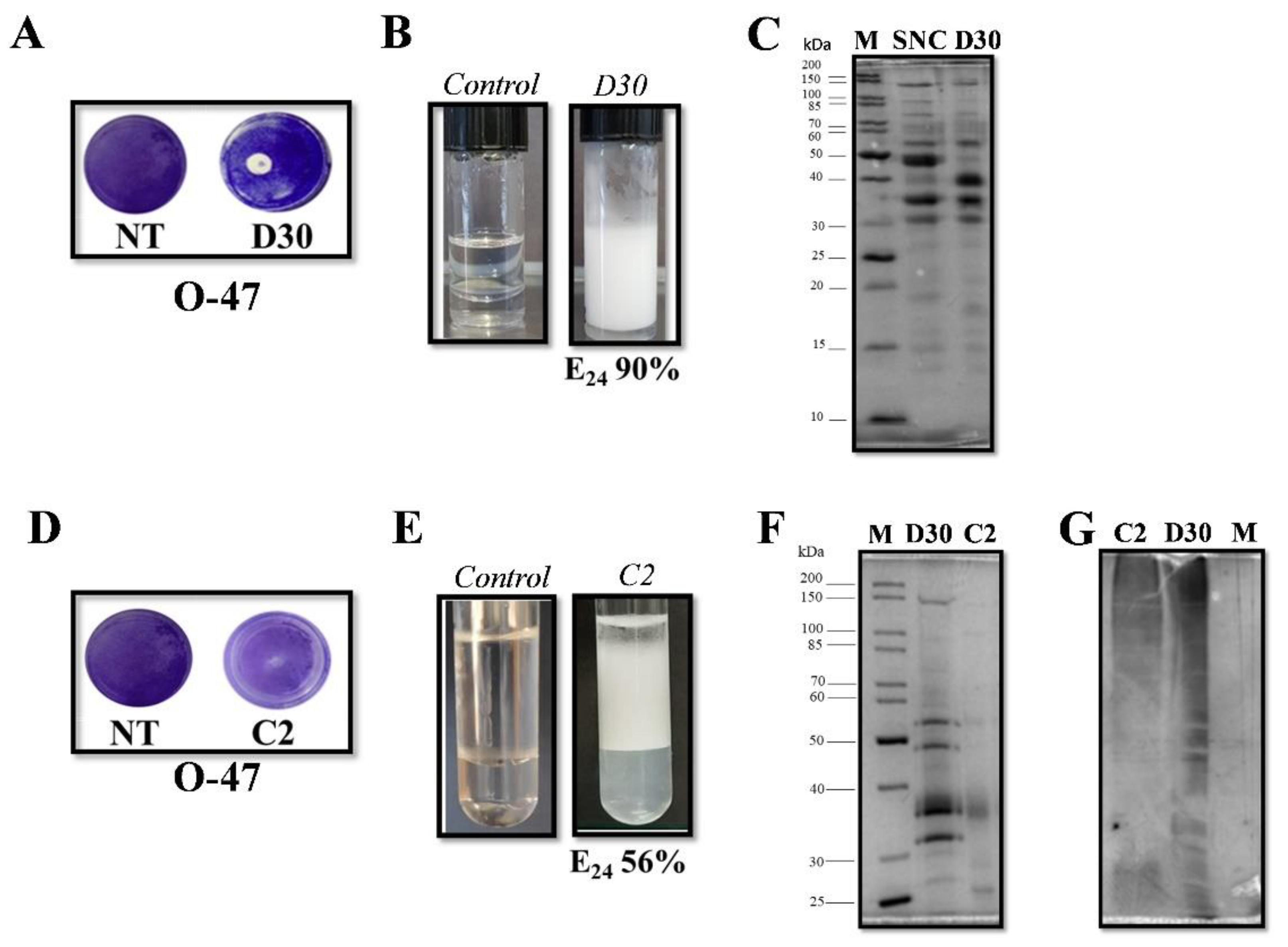
2.1. Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020 Produces Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Adhesive Molecules Active against S. epidermidis Biofilm
2.2. Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020 Supernatant Has a Surfactant and Emulsifier Activity
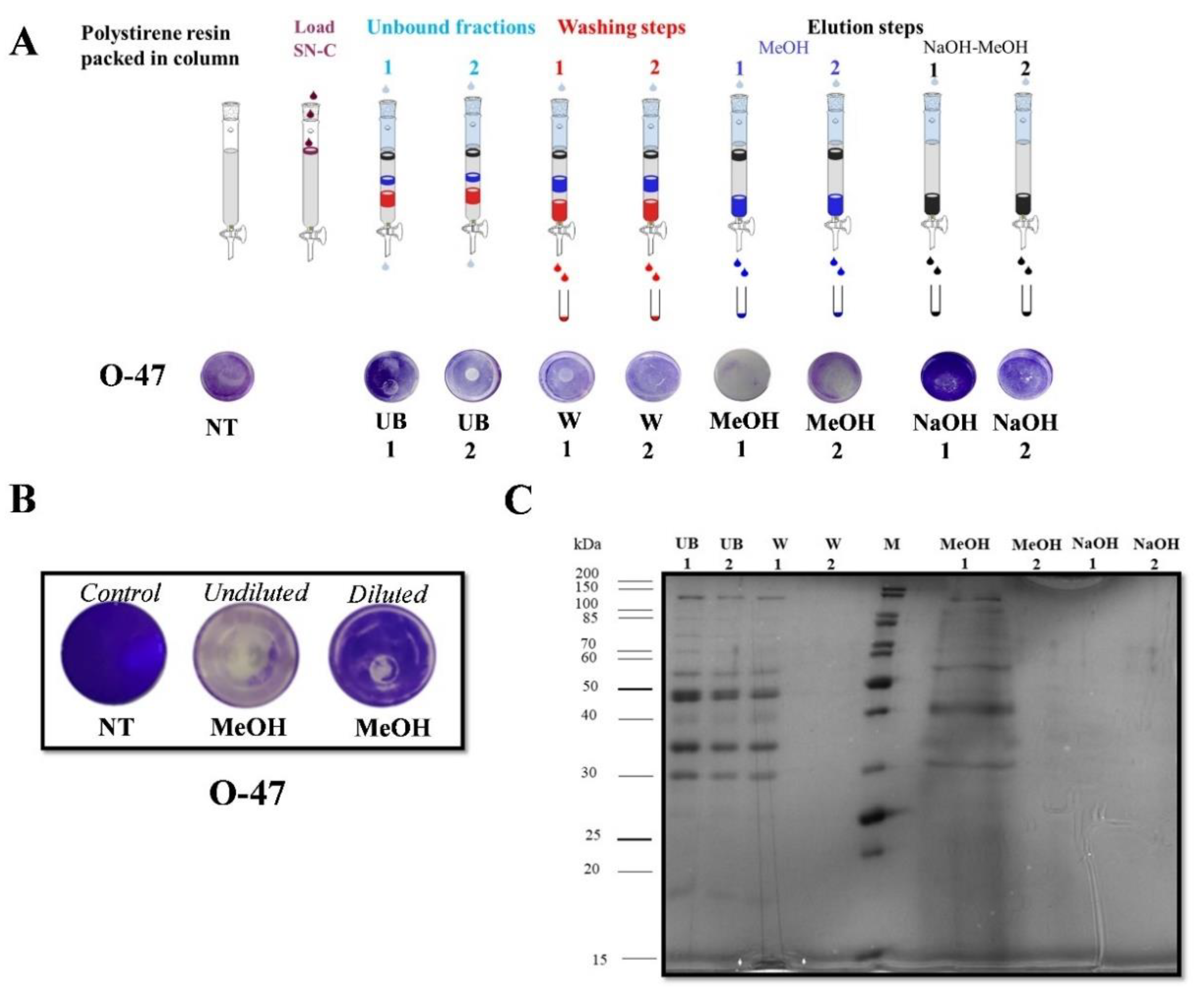
2.3. Purification of Anti-Adhesive and Bioemulsifying Molecules
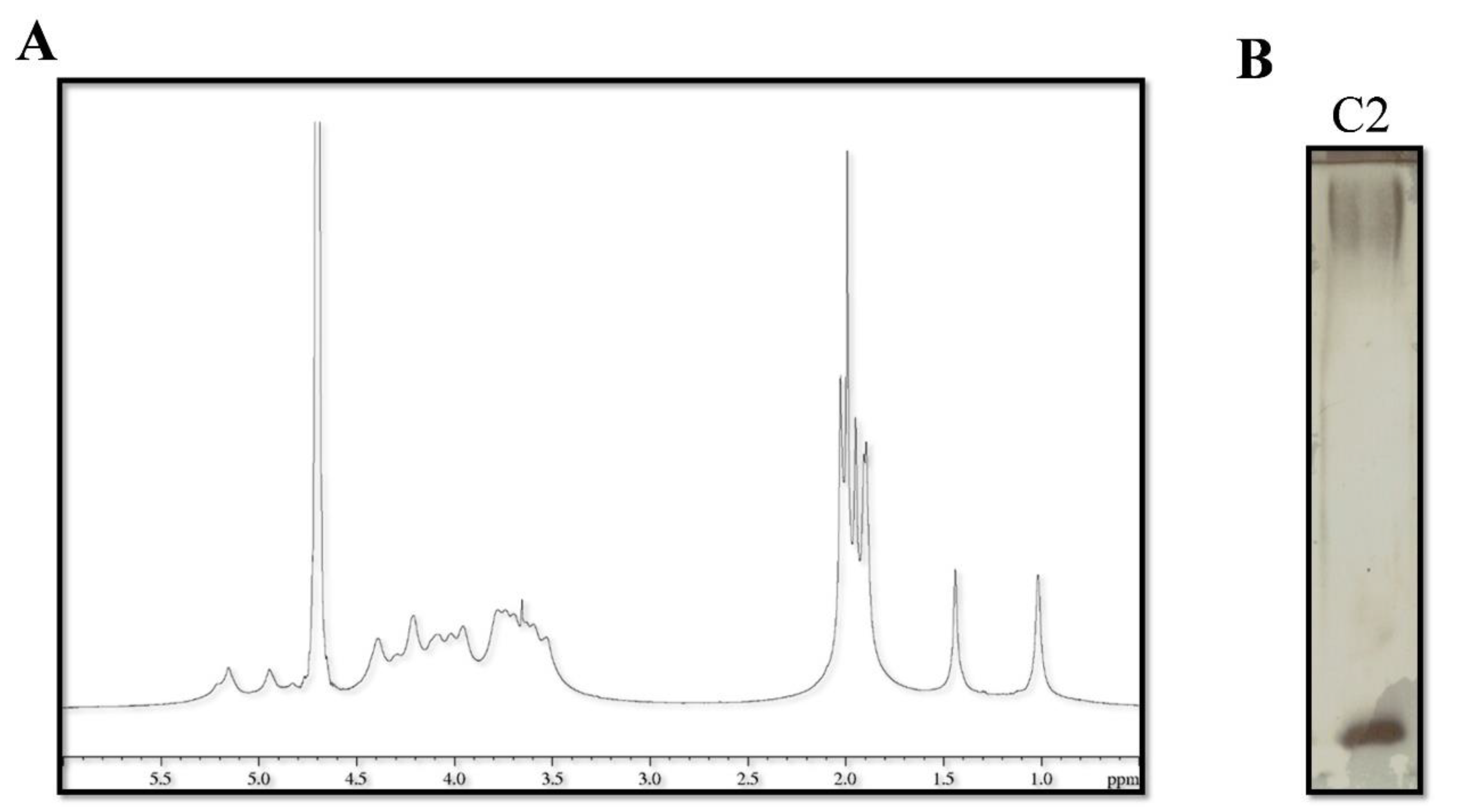
2.4. Catasan Identification
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
5.2. Anti-Adhesive Assay
5.3. Biosurfactant Assays
5.4. Physico-Chemical Properties of Active Compound/S
5.5. Studies of the Bioemulsifier Stability
5.6. SNC_TAE2020 and P_TAE2020 Preparation
5.7. Preliminary Purification of the Active-Compounds
5.8. Large Scale Coultivation of Growth Psycrobacter sp. TAE2020
5.9. SDS PAGE
5.10. DOC PAGE
5.11. Sugar and Fatty Acids Analyses
5.12. NMR Spectroscopy
5.13. Biofilm Inhibiting Assay
5.14. Mature Biofilm Assay
5.15. In-Situ Hydrolysis, LC-MS/MS Analysis and Protein Identification
5.16. Organic Extraction Protocol
5.17. CLSM Analysis
5.18. Statistics and Reproducibility of Results
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| SN_TAE2020 | Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020 cell-free supernatant |
| Gut | Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020 culture medium |
| ExEx TAE2020 | Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020 extracellular extract obtained after the liquid-liquid extraction of cell-free supernatant |
| SNC_TAE2020 | Retentate fraction obtained after the ultrafiltration of TAE2020 cell-free supernatant |
| P_TAE2020 | Permeate fraction obtained after the ultrafiltration of TAE2020 cell-free supernatant |
| NaIO4 | Sodium periodate |
| E24 | Emulsification index after 24 h |
| D30 | SNC_TAE2020 dialyzed against Milli-Q water by a 30kDa PES membrane |
| C2 | Active fraction after the gel filtration chromatography of D30 |
| Ub1, Ub2 | Unbound fractions obtained from adsorption chromatography, |
| W1, W2 | Fractions obtained from adsorption chromatography during the washing steps with Gut medium |
| MeOH1, MeOH2 | Fractions obtained from adsorption chromatography eluted with methanol |
| NaOH1, NaOH2 | Fractions obtained from adsorption chromatography eluted with NaOH in methanol |
References
- Westall, F.; De Wit, M.J.; Dann, J.; Van der Gaast, S.; De Ronde, C.E.J.; Gerneke, D. Early Archean Fossil Bacteria and Biofilms in Hydrothermally-Influenced Sediments from the Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Precambrian Res. 2001, 106, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, N.; Birjiniuk, A.; Samad, T.S.; . Doyle, P.S.; Ribbeck, K. Permeability and Mechanics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 78, 36601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daddi Oubekka, S.; Briandet, R.; Fontaine-Aupart, M.P.; Steenkeste, K. Correlative Time-Resolved Fluorescence Microscopy to Assess Antibiotic Diffusion-Reaction in Biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3349–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.S. Antimicrobial Tolerance in Biofilms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cámara, M.; Green, W.; MacPhee, C.E.; Rakowska, P.D.; Raval, R.; Richardson, M.C.; Slater-Jefferies, J.; Steventon, K.; Webb, J.S. Economic Significance of Biofilms: A Multidisciplinary and Cross-Sectoral Challenge. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Xia, G.; Shi, C.; Wan, J.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, M.; He, H.; et al. Therapeutic Strategies against Bacterial Biofilms. Fundam. Res. 2021, 1, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Zhu, X.; Pan, J. Regulatory Mechanisms and Promising Applications of Quorum Sensing-Inhibiting Agents in Control of Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 589640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.; Panda, A.K.; De Mandal, S.; Shakeel, M.; Bisht, S.S.; Khan, J. Natural Anti-Biofilm Agents: Strategies to Control Biofilm-Forming Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 566325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilli, E.; Tedesco, P.; Fondi, M.; Tutino, M.L.; Giudice, A.L.; de Pascale, D.; Fani, R. The Art of Adapting to Extreme Environments: The Model System Pseudoalteromonas. Phys. Life Rev. 2021, 36, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battin, T.J.; Besemer, K.; Bengtsson, M.M.; Romani, A.M.; Packmann, A.I. The Ecology and Biogeochemistry of Stream Biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilli, E.; Tutino, M.L.; Marino, G. Biofilm as an Adaptation Strategy to Extreme Conditions. Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. e Nat. 2022, 33, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artini, M.; Papa, R.; Vrenna, G.; Lauro, C.; Ricciardelli, A.; Casillo, A.; Corsaro, M.M.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E.; Selan, L. Cold-Adapted Bacterial Extracts as a Source of Anti-Infective and Antimicrobial Compounds against Staphylococcus Aureus. Futur. Microbiol. 2019, 14, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, R.; Selan, L.; Parrilli, E.; Tilotta, M.; Sannino, F.; Feller, G.; Tutino, M.L.; Artini, M. Anti-Biofilm Activities from Marine Cold Adapted Bacteria against Staphylococci and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casillo, A.; Papa, R.; Ricciardelli, A.; Sannino, F.; Ziaco, M.; Tilotta, M.; Selan, L.; Marino, G.; Corsaro, M.M.; Tutino, M.L.; et al. Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Long-Chain Fatty Aldehyde from Antarctic Pseudoalteromonas Haloplanktis TAC125 against Staphylococcus Epidermidis Biofilm. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, C.; D’Angelo, C.; Calvanese, M.; Ricciardelli, A.; Sellitto, A.; Giurato, G.; Tutino, M.L.; Weisz, A.; Parrilli, E.; Fondi, M. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Pseudomonas Sp. TAE6080, a Strain Capable of Inhibiting Staphylococcus Epidermidis Biofilm. Mar. Genom. 2021, 60, 100887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardi, C.; D’Angelo, C.; Calvanese, M.; Ricciardelli, A.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E.; Fondi, M. Genome Analysis of a New Biosurfactants Source: The Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020. Mar. Genom. 2022, 61, 100922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, R.; Vrenna, G.; D’angelo, C.; Casillo, A.; Relucenti, M.; Donfrancesco, O.; Corsaro, M.M.; Fiscarelli, E.V.; Assanti, V.T.G.; Tutino, M.L.; et al. Anti-Virulence Activity of the Cell-Free Supernatant of the Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter Sp. Tae2020 against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Clinical Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus Epidermidis—The “accidental” Pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranjec, C.; Angeles, D.M.; Mårli, M.T.; Fernández, L.; García, P.; Kjos, M.; Diep, D.B. Staphylococcal Biofilms: Challenges and Novel Therapeutic Perspectives. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, S.; Stevens, N.T.; Humphreys, H.; O’Gara, J.P.; O’Neill, E. Current and Future Approaches to the Prevention and Treatment of Staphylococcal Medical Device-Related Infections. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 21, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haunreiter, V.D.; Boumasmoud, M.; Häffner, N.; Wipfli, D.; Leimer, N.; Rachmühl, C.; Kühnert, D.; Achermann, Y.; Zbinden, R.; Benussi, S.; et al. In-Host Evolution of Staphylococcus Epidermidis in a Pacemaker-Associated Endocarditis Resulting in Increased Antibiotic Tolerance. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- França, A.; Gaio, V.; Lopes, N.; Melo, L.D.R. Virulence Factors in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Pathogens 2021, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowrishankar, S.; Pandian, S.K. Modulation of Staphylococcus Epidermidis (RP62A) Extracellular Polymeric Layer by Marine Cyclic Dipeptide-Cyclo(L-Leucyl-L-Prolyl) Thwarts Biofilm Formation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raue, S.; Fan, S.-H.; Rosenstein, R.; Zabel, S.; Luqman, A.; Nieselt, K.; Götz, F. The Genome of Staphylococcus Epidermidis O47. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, C.; Gerke, C.; Somerville, G.A.; Fischer, E.R.; Otto, M. Quorum-Sensing Control of Biofilm Factors in Staphylococcus Epidermidis. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendaoud, M.; Vinogradov, E.; Balashova, N.V.; Kadouri, D.E.; Kachlany, S.C.; Kaplan, J.B. Broad-Spectrum Biofilm Inhibition by Kingella Kingae Exopolysaccharide. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 3879–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliza, A.; Marcia, Z. Biosurfactants as Agents to Reduce Adhesion of Pathogenic Bacteria to Polystyrene Surfaces: Effect of Temperature and Hydrophobicity. Curr. Microbiol. 2010, 61, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toren, A.; Orr, E.; Paitan, Y.; Ron, E.Z.; Rosenberg, E. The Active Component of the Bioemulsifier Alasan from Acinetobacter Radioresistens KA53 Is an OmpA-like Protein. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toren, A.; Segal, G.; Ron, E.Z.; Rosenberg, E. Structure-Function Studies of the Recombinant Protein Bioemulsifier AlnA. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 4, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walzer, G.; Rosenberg, E.; Ron, E.Z. The Acinetobacter Outer Membrane Protein A (OmpA) Is a Secreted Emulsifier. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 8, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydorn, A.; Nielsen, A.T.; Hentzer, M.; Sternberg, C.; Givskov, M.; Ersbøll, B.K.; Molin, S. Quantification of Biofilm Structures by the Novel Computer Program COMSTAT. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banat, I.M.; De Rienzo, M.A.D.; Quinn, G.A. Microbial Biofilms: Biosurfactants as Antibiofilm Agents. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9915–9929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, L.P.; Castellane, T.C.L.; Polachini, T.C.; de Macedo Lemos, E.G.; Alves, L.M.C. Exopolysaccharides Produced by Pandoraea Shows Emulsifying and Anti-Biofilm Activities. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadra, S.; Chettri, D.; Verma, A.K. Biosurfactants: Secondary Metabolites Involved in the Process of Bioremediation and Biofilm Removal. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liang, X.; Gadd, G.M.; Zhao, Q. Marine Microbial-Derived Antibiotics and Biosurfactants as Potential New Agents against Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzoigwe, C.; Burgess, J.G.; Ennis, C.J.; Rahman, P.K.S.M. Bioemulsifiers Are Not Biosurfactants and Require Different Screening Approaches. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decho, A.W.; Gutierrez, T. Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPSs) in Ocean Systems. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, T.; Mulloy, B.; Black, K.; Green, D.H. Glycoprotein Emulsifiers from Two Marine Halomonas Species: Chemical and Physical Characterization. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 103, 1716–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walzer, G.; Rosenberg, E.; Ron, E.Z. Identification of Outer Membrane Proteins with Emulsifying Activity by Prediction of β-Barrel Regions. J. Microbiol. Methods 2009, 76, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toren, A.; Navon-Venezia, S.; Ron, E.Z.; Rosenberg, E. Emulsifying Activities of Purified Alasan Proteins from Acinetobacter Radioresistens KA53. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navon-Venezia, S.; Zosim, Z.; Gottlieb, A.; Legmann, R.; Carmeli, S.; Ron, E.Z.; Rosenberg, E. Alasan, a New Bioemulsifier from Acinetobacter Radioresistens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 3240–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron, E.Z.; Rosenberg, E. Biosurfactants and Oil Bioremediation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercaldi, M.P.; Dams-Kozlowska, H.; Panilaitis, B.; Joyce, A.P.; Kaplan, D.L. Discovery of the Dual Polysaccharide Composition of Emulsan and the Isolation of the Emulsion Stabilizing Component. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, N.; Zosim, Z.; Rosenberg, E. Reconstitution of Emulsifying Activity of Acinetobacter Calcoaceticus BD4 Emulsan by Using Pure Polysaccharide and Protein. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thraeib, J.Z.; Altemimi, A.B.; Al-manhel, A.J.A.; Abedelmaksoud, T.G.; El-Maksoud, A.A.A.; Madankar, C.S.; Cacciola, F. Production and Characterization of a Bioemulsifier Derived from Microorganisms with Potential Application in the Food Industry. Life 2022, 12, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessôa, M.G.; Vespermann, K.A.C.; Paulino, B.N.; Barcelos, M.C.S.; Pastore, G.M.; Molina, G. Newly Isolated Microorganisms with Potential Application in Biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, R.A.; Darouiche, R.O. Device-Associated Infections: A Macroproblem That Starts with Microadherence. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywicka, M.; Szymańska, J.; Tofil, S.; Malm, A.; Grzegorczyk, A. Surface Properties of Ti6Al7Nb Alloy: Surface Free Energy and Bacteria Adhesion. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerca, N.; Pier, G.B.; Vilanova, M.; Oliveira, R.; Azeredo, J. Quantitative Analysis of Adhesion and Biofilm Formation on Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Surfaces of Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Res. Microbiol. 2005, 156, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sharp, C.E.; Ataeian, M.; Strous, M.; De Beer, D. Role of Extracellular Carbonic Anhydrase in Dissolved Inorganic Carbon Uptake in Alkaliphilic Phototrophic Biofilm. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- e Silva, S.S.; Carvalho, J.W.P.; Aires, C.P.; Nitschke, M. Disruption of Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilms Using Rhamnolipid Biosurfactants. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7864–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, F.; Satpute, S.; Banpurkar, A.; Kumar, A.R.; Zinjarde, S. Biosurfactant from a Marine Bacterium Disrupts Biofilms of Pathogenic Bacteria in a Tropical Aquaculture System. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschel, A.; Otto, M. Phenol-Soluble Modulins and Staphylococcal Infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.Y.; Villaruz, A.E.; Zheng, Y.; He, L.; Fisher, E.L.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ho, T.V.; Yeh, A.J.; Joo, H.S.; Cheung, G.Y.C.; et al. Role of Phenol-Soluble Modulins in Staphylococcus Epidermidis Biofilm Formation and Infection of Indwelling Medical Devices. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3015–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilmann, C.; Gerke, C.; Perdreau-remington, F.; Götz, F. Characterization of Tn917 Insertion Mutants of Staphylococcus epidermidis affected in biofilm formation. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannino, F.; Giuliani, M.; Salvatore, U.; Apuzzo, G.A.; de Pascale, D.; Fani, R.; Fondi, M.; Marino, G.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E. A Novel Synthetic Medium and Expression System for Subzero Growth and Recombinant Protein Production in Pseudoalteromonas Haloplanktis TAC125. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 101, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blesic, M.; DIchiarante, V.; Milani, R.; Linder, M.; Metrangolo, P. Evaluating the Potential of Natural Surfactants in the Petroleum Industry: The Case of Hydrophobins. Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 90, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Errico, G.; Ciccarelli, D.; Ortona, O. Effect of Glycerol on Micelle Formation by Ionic and Nonionic Surfactants at 25 °C. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 286, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the Assembly of the Head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merril, C.R.; Shifrin, S. A Sensitive Silver Stain for Detecting Lipopolysaccharides in Polyacrylamide Gels. Anal. Biochem. 1982, 119, 115–119. [Google Scholar]
- Fresno, S.; Jiménez, N.; Canals, R.; Merino, S.; Corsaro, M.M.; Lanzetta, R.; Parrilli, M.; Pieretti, G.; Regué, M.; Tomás, J.M. A Second Galacturonic Acid Transferase Is Required for Core Lipopoylsaccharide Biosynthesis and Complete Capsule Association with the Cell Surface in Klebsiella Pneumoniae. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouallegue, A.; Casillo, A.; Chaari, F.; La Gatta, A.; Lanzetta, R.; Corsaro, M.M.; Bachoual, R.; Ellouz-Chaabouni, S. Levan from a New Isolated Bacillus Subtilis AF17: Purification, Structural Analysis and Antioxidant Activities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papa, R.; Parrilli, E.; Sannino, F.; Barbato, G.; Tutino, M.L.; Artini, M.; Selan, L. Anti-Biofilm Activity of the Antarctic Marine Bacterium Pseudoalteromonas Haloplanktis TAC125. Res. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwani, T.; Desai, K.; Patel, D.; Lawani, D.; Bahaley, P.; Joshi, P.; Kothari, V. Effect of Various Solvents on Bacterial Growth in Context of Determining MIC of Various Antimicrobials. Internet J. Microbiol. 2008, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Angelo, C.; Casillo, A.; Melchiorre, C.; Lauro, C.; Corsaro, M.M.; Carpentieri, A.; Tutino, M.L.; Parrilli, E. CATASAN Is a New Anti-Biofilm Agent Produced by the Marine Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120747
D’Angelo C, Casillo A, Melchiorre C, Lauro C, Corsaro MM, Carpentieri A, Tutino ML, Parrilli E. CATASAN Is a New Anti-Biofilm Agent Produced by the Marine Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(12):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120747
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Angelo, Caterina, Angela Casillo, Chiara Melchiorre, Concetta Lauro, Maria Michela Corsaro, Andrea Carpentieri, Maria Luisa Tutino, and Ermenegilda Parrilli. 2022. "CATASAN Is a New Anti-Biofilm Agent Produced by the Marine Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020" Marine Drugs 20, no. 12: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120747
APA StyleD’Angelo, C., Casillo, A., Melchiorre, C., Lauro, C., Corsaro, M. M., Carpentieri, A., Tutino, M. L., & Parrilli, E. (2022). CATASAN Is a New Anti-Biofilm Agent Produced by the Marine Antarctic Bacterium Psychrobacter sp. TAE2020. Marine Drugs, 20(12), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20120747











