Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Hyaluronan-like Exopolysaccharide from the Marine Vibrio MO245 against Pathogenic Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Rheological Characteristics
2.2. Biological Activity of MO245 and HA
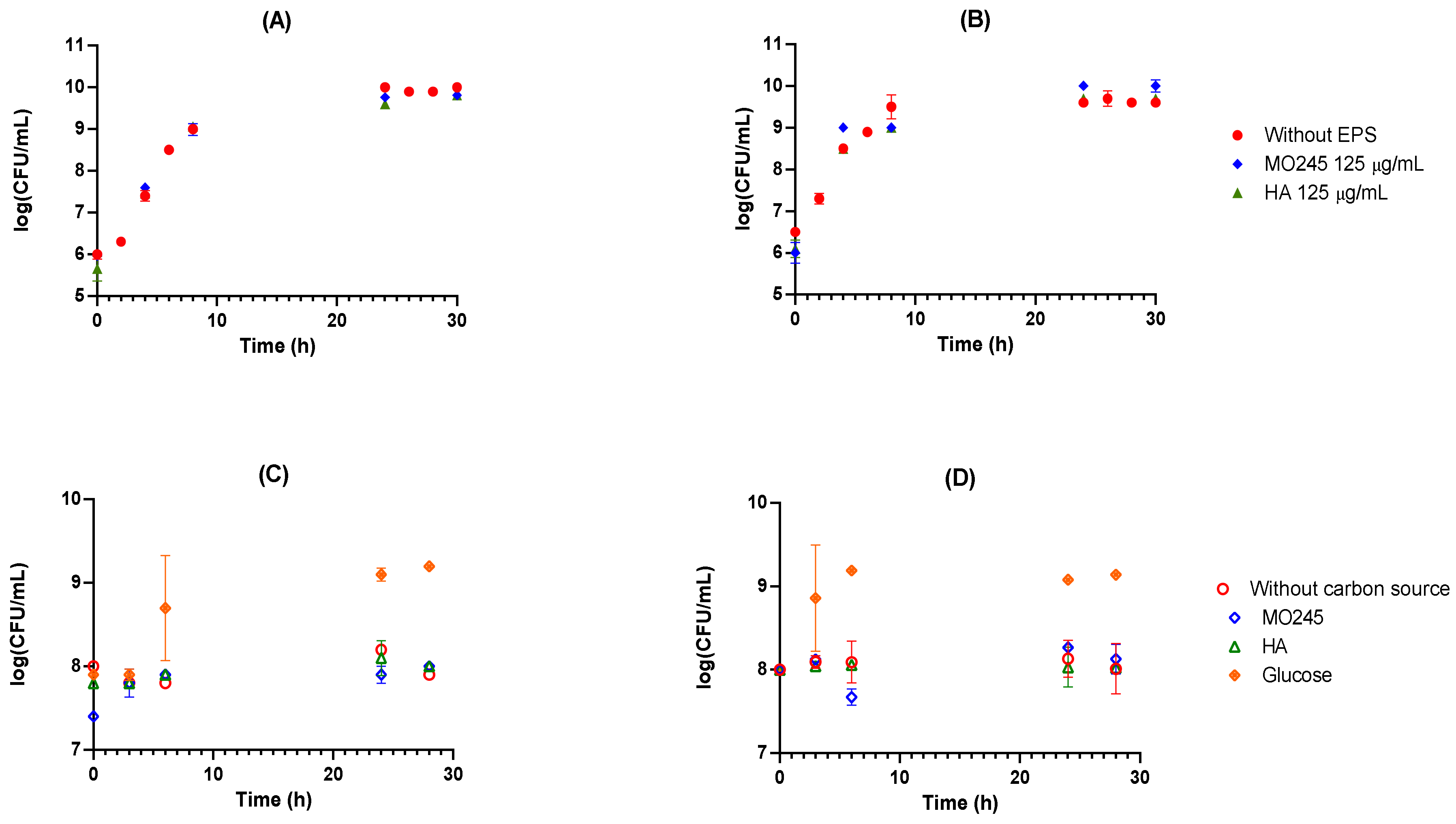
2.2.1. Anti-Bacterial Activity
- 1.
- Bacteriostatic activity
- 2.
- Use of MO245 or HA as a carbon source
- 3.
- Bactericidal effect
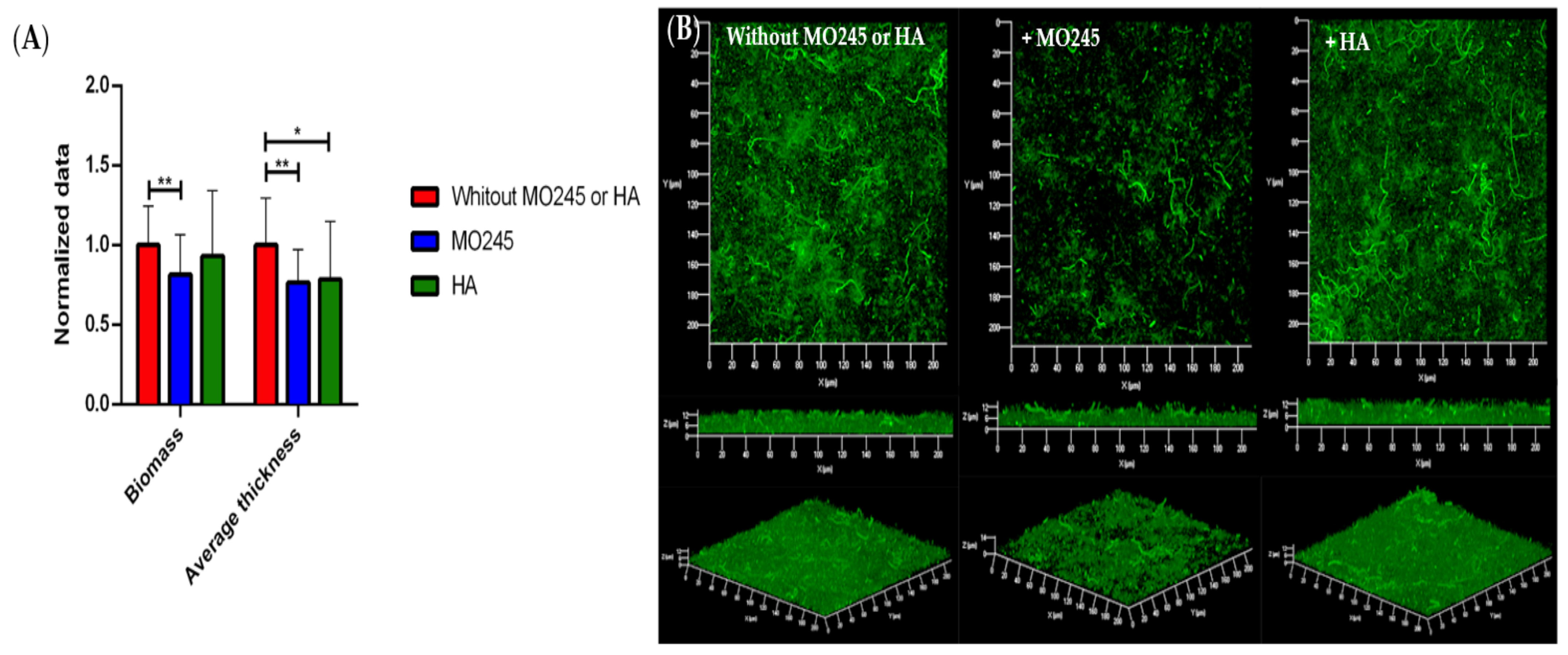
2.2.2. Anti-Adhesion Activity
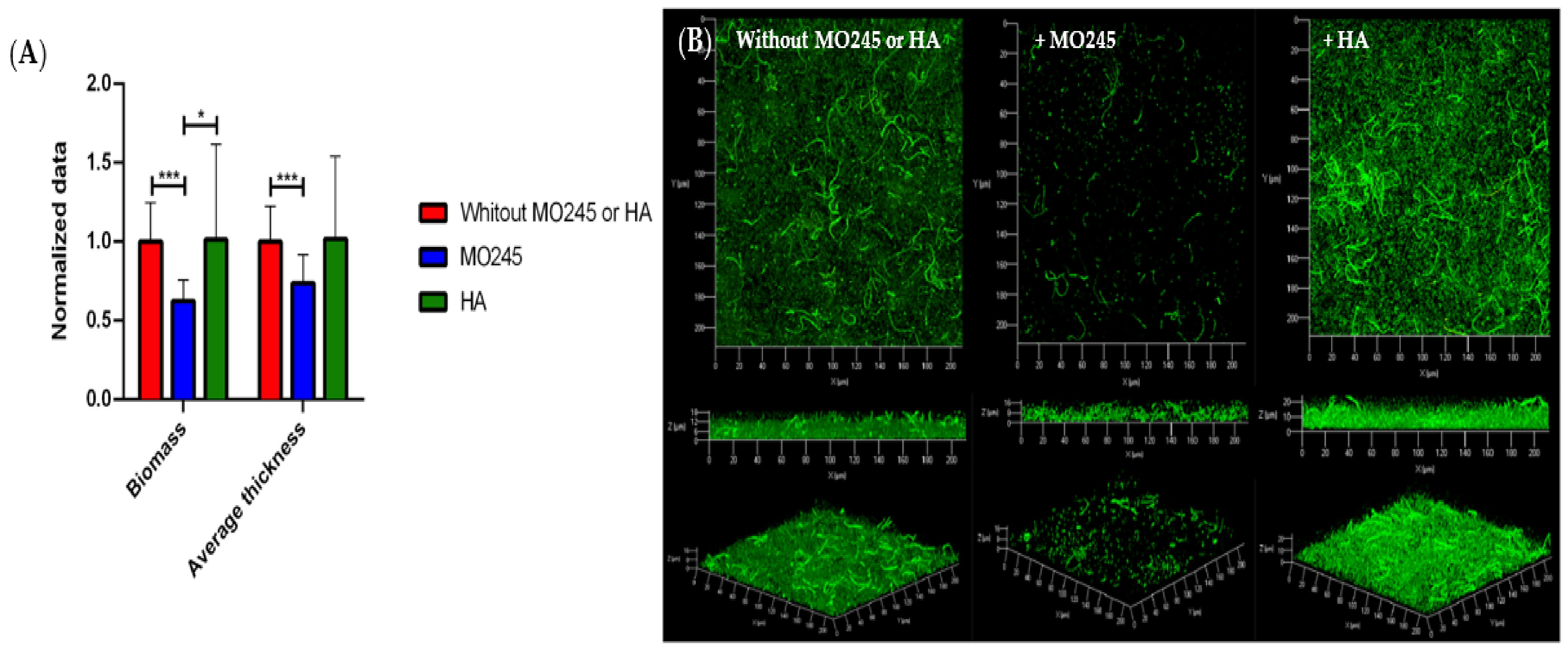
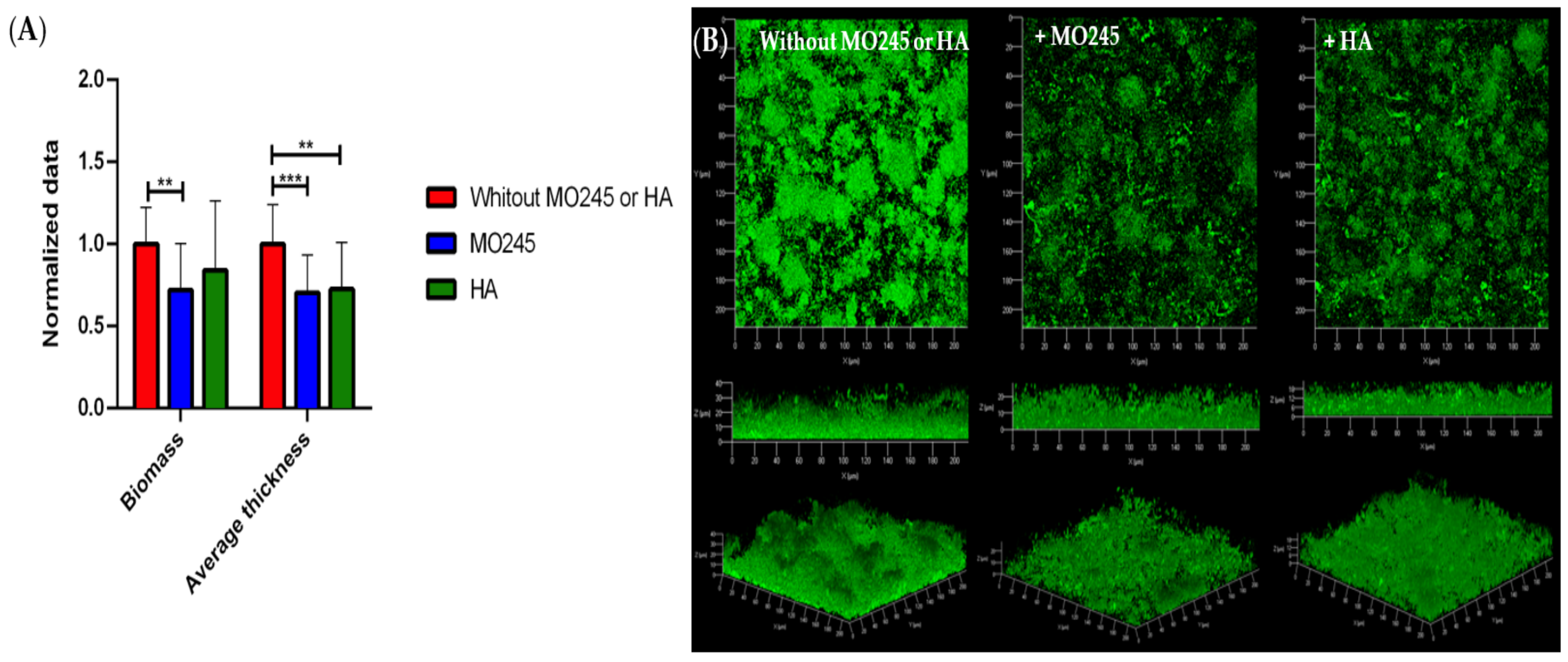
2.2.3. Impact on the Biofilm Maturation
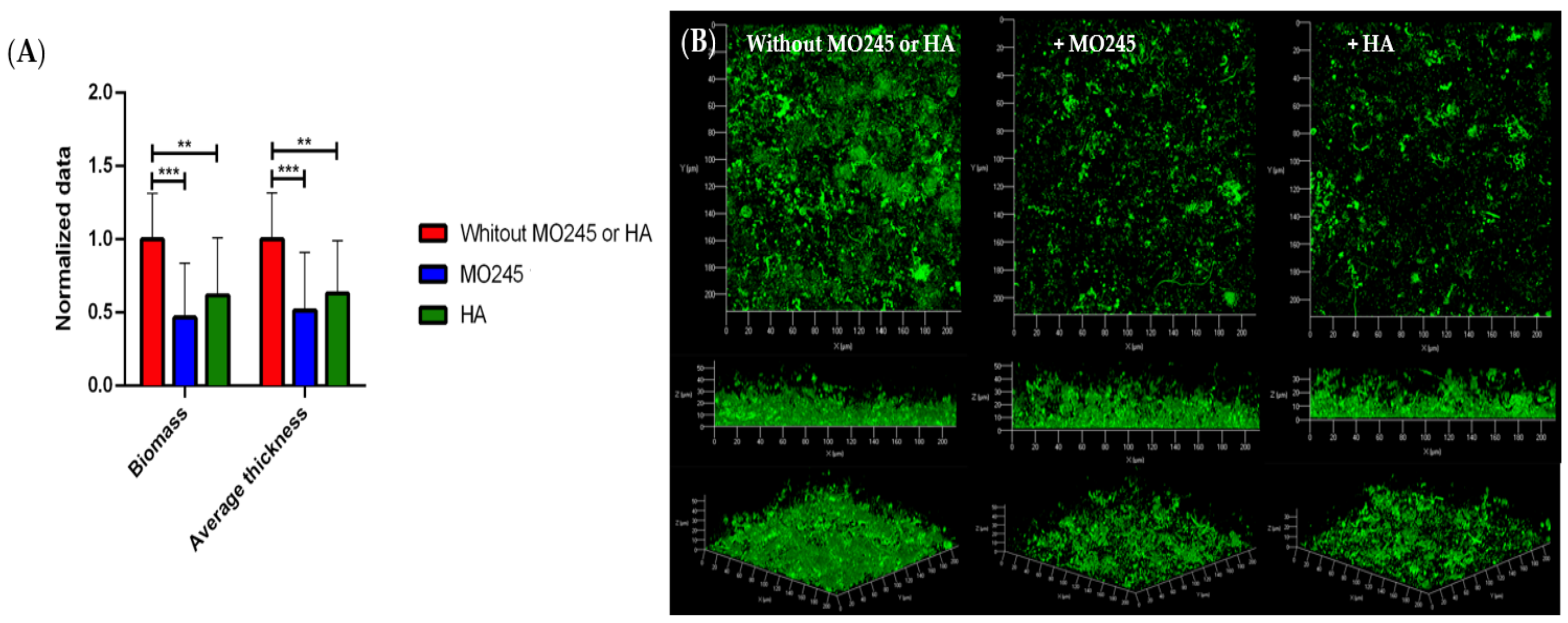
2.2.4. Impact on the Degradation of the Biofilm
2.2.5. Morphological Impact on Bacteria
2.3. Evaluation of the Biological Role of MO245 and HA
2.3.1. Impact on the Bacterial Motility
2.3.2. Anti-Quorum Sensing Properties
2.4. Evaluation of Cell-Surface Interactions
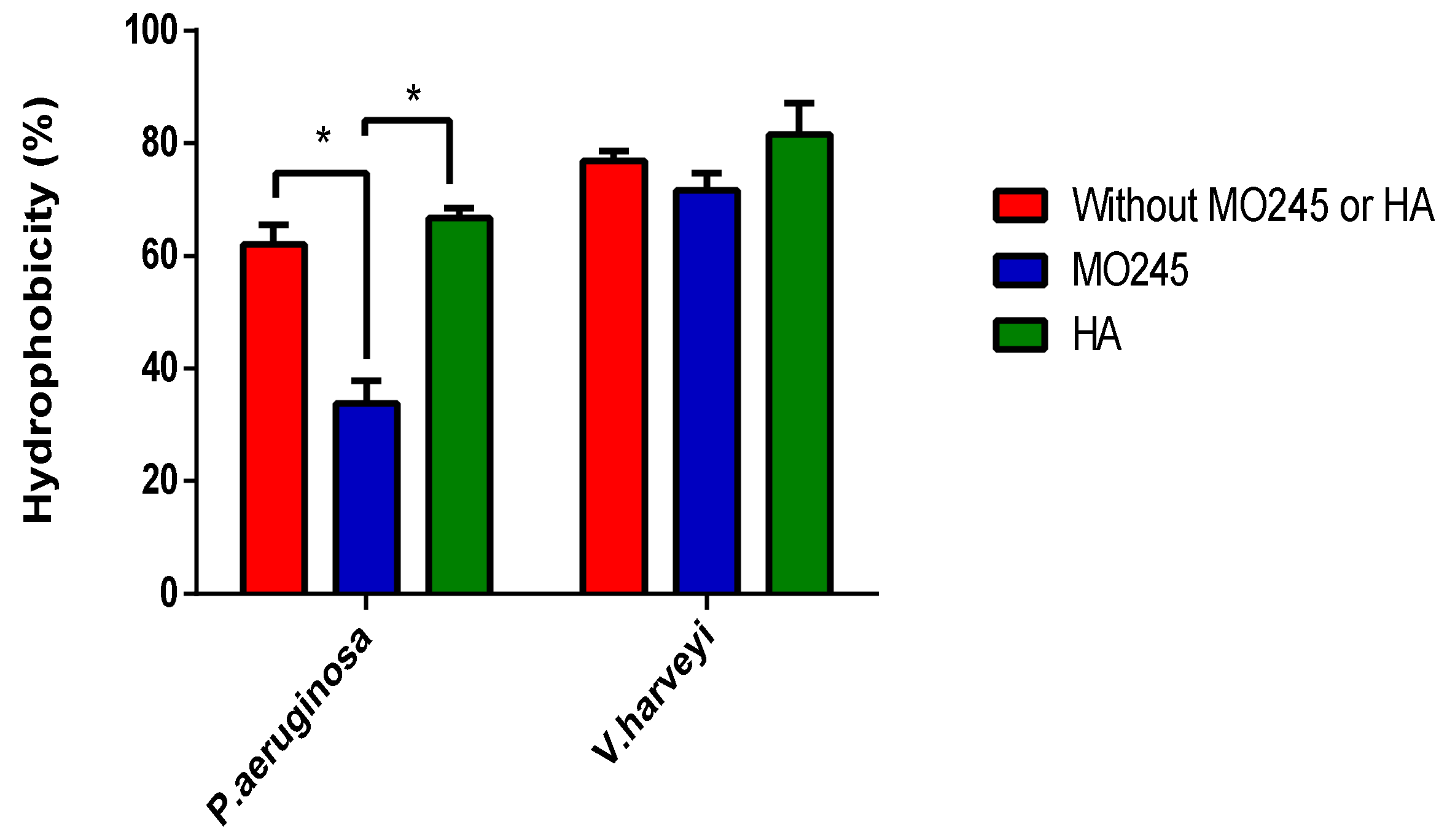
2.4.1. Microbial Adherence to Hydrocarbons (MATH)
2.4.2. Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) Measurements
2.4.3. Water Contact Angle of the Abiotic Surface Interaction with MO245 or HA
2.4.4. Emulsifying Properties
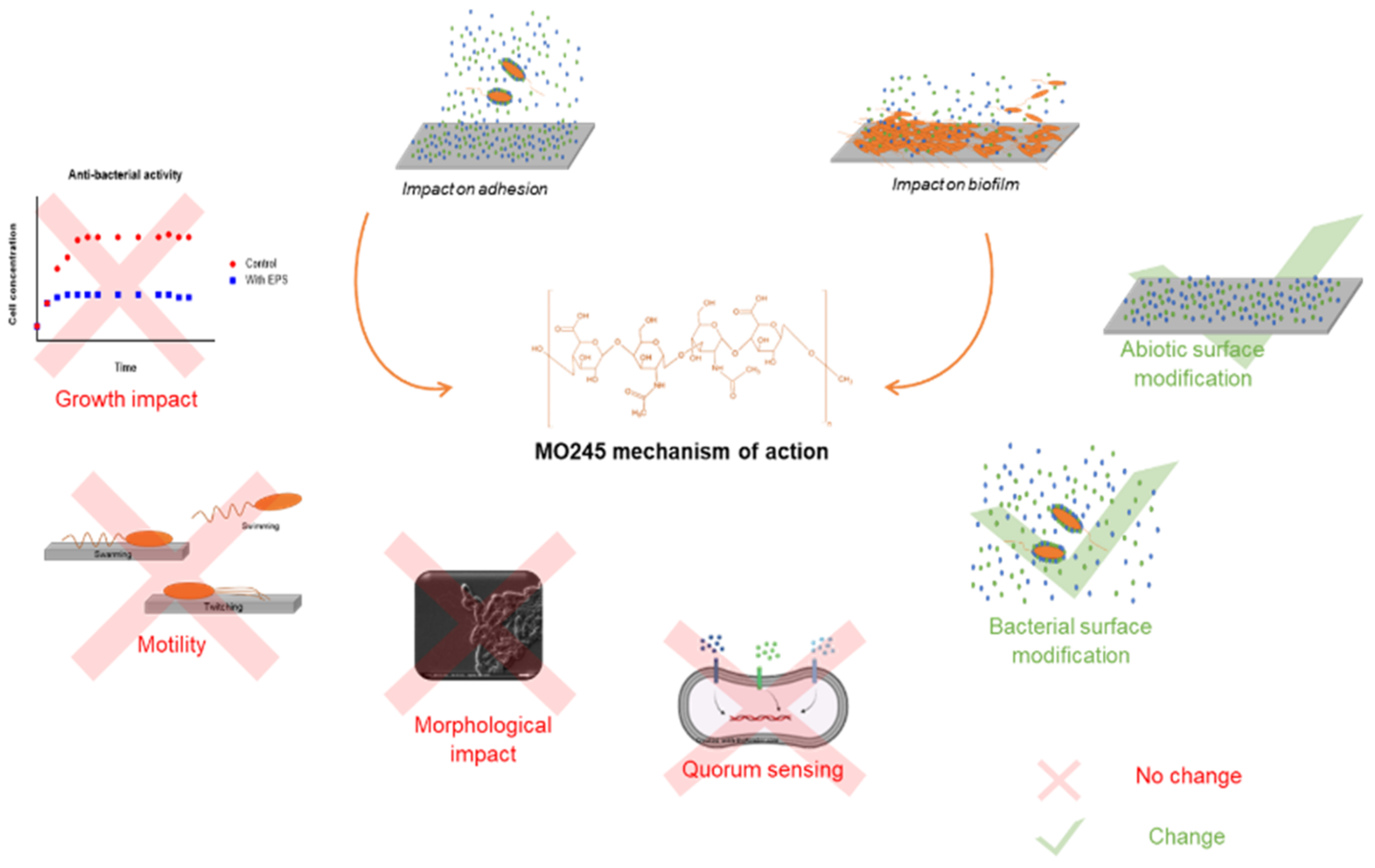
3. Discussion
3.1. Proven Anti-Biofilm Activity for MO245
3.2. The Biological Role of Quorum Sensing of MO245 Was Not Demonstrated
3.3. Is the Anti-Biofilm Activity of MO245 Due to Its Physico-Chemical Properties?
3.4. Complex Physico-Chemical Properties of MO245
3.5. Biotechnological Interests
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Strains and Growth Conditions
4.3. Industrial Production, Extraction, and Purification of MO245
4.4. Anti-Bacterial Activity
4.5. Anti-Adhesion Activity
4.6. Impact on the Biofilm Maturation
4.7. Impact on the Degradation of the Biofilm
4.8. Morphological Impact on Bacteria
4.9. Evaluation of the Biological Role of MO245 and HA
4.9.1. Impact on the Bacterial Motility
4.9.2. Anti-Quorum Sensing Properties of MO245 and HA
4.10. Cell-Surface Interactions
4.10.1. Microbial Adherence to Hydrocarbure (MATH)
4.10.2. QCM Measurements
4.10.3. Cell-Surface Interactions
4.10.4. Emulsifying Properties
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J. The Biofilm Matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial Biofilms: From the Natural Environment to Infectious Diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rendueles, O.; Ghigo, J.-M. Multi-Species Biofilms: How to Avoid Unfriendly Neighbors. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 972–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carniello, V.; Peterson, B.W.; van der Mei, H.C.; Busscher, H.J. Physico-Chemistry from Initial Bacterial Adhesion to Surface-Programmed Biofilm Growth. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 261, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staats, A.; Li, D.; Sullivan, A.C.; Stoodley, P. Biofilm Formation in Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Ann. Jt. 2021, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, L.; Toscano, M. 2-Biofilm Formation and the Biological Response. In Management of Periprosthetic Joint Infections (PJIs); Arts, J.J.C., Geurts, J., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2017; pp. 25–39. ISBN 978-0-08-100205-6. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfmeier, H.; Pletzer, D.; Mansour, S.C.; Hancock, R.E.W. New Perspectives in Biofilm Eradication. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A. Handbook of Antimicrobial Coatings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 978-0-12-811983-9. [Google Scholar]
- Veerachamy, S.; Yarlagadda, T.; Manivasagam, G.; Yarlagadda, P.K. Bacterial Adherence and Biofilm Formation on Medical Implants: A Review. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2014, 228, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limmathurotsakul, D.; Dunachie, S.; Fukuda, K.; Feasey, N.A.; Okeke, I.N.; Holmes, A.H.; Moore, C.E.; Dolecek, C.; van Doorn, H.R.; Shetty, N.; et al. Improving the Estimation of the Global Burden of Antimicrobial Resistant Infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e392–e398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salta, M.; Wharton, J.A.; Blache, Y.; Stokes, K.R.; Briand, J.-F. Marine Biofilms on Artificial Surfaces: Structure and Dynamics. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2879–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannister, J.; Sievers, M.; Bush, F.; Bloecher, N. Biofouling in Marine Aquaculture: A Review of Recent Research and Developments. Biofouling 2019, 35, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepi, M.; Focardi, S. Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Aquaculture and Climate Change: A Challenge for Health in the Mediterranean Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahiner, A.; Yapar, E.A. An Overview on Current Regulation and Evaluation of Biocidal Products. Univers. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 4, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, G.; Jin, W.; Xiu, P.; Sun, C. Antibiofilm and Anti-Infection of a Marine Bacterial Exopolysaccharide against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Li, J.; Han, F.; Duan, G.; Lu, X.; Gu, Y.; Yu, W. Antibiofilm Activity of an Exopolysaccharide from Marine Bacterium Vibrio sp. QY101. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Hao, D.; Jiang, D.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z. Production, Purification, and Antibiofilm Activity of a Novel Exopolysaccharide from Arthrobacter sp. B4. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 45, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanò, A.; Laganà, P.; Visalli, G.; Maugeri, T.L.; Gugliandolo, C. In Vitro Antibiofilm Activity of an Exopolysaccharide from the Marine Thermophilic bacillus licheniformis T14. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 72, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendueles, O.; Kaplan, J.B.; Ghigo, J.-M. Antibiofilm Polysaccharides: Bacterial Antibiofilm Polysaccharides. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, S. Transcriptional Profiling of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 in Response to Anti-Biofilm and Anti-Infection Agent Exopolysaccharide EPS273. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 130, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Pastor, M.; Ferreira, A.S.; Moppert, X.; Nunes, C.; Coimbra, M.A.; Reis, R.L.; Guezennec, J.; Novoa-Carballal, R. Structure, Rheology, and Copper-Complexation of a Hyaluronan-like Exopolysaccharide from Vibrio. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 114999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L.; Brauner, P.; Kolar, J. Hyaluronic Acid (Hyaluronan): A Review. Vet. Med. 2008, 53, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, L.; Cappelletti, L.; De Vecchi, E.; Pignataro, L.; Torretta, S.; Mattina, R. Antiadhesive and Antibiofilm Activity of Hyaluronic Acid against Bacteria Responsible for Respiratory Tract Infections. APMIS 2014, 122, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirnazar, P.; Wolinsky, L.; Nachnani, S.; Haake, S.; Pilloni, A.; Bernard, G.W. Bacteriostatic Effects of Hyaluronic Acid. J. Periodontol. 1999, 70, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolker-Nielsen, T. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Infections: From Molecular Biofilm Biology to New Treatment Possibilities. APMIS 2014, 122, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Liu, Q. A Review: Progress in the Development of Fish Vibrio spp. Vaccines. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 226, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snetkov, P.; Zakharova, K.; Morozkina, S.; Olekhnovich, R.; Uspenskaya, M. Hyaluronic Acid: The Influence of Molecular Weight on Structural, Physical, Physico-Chemical, and Degradable Properties of Biopolymer. Polymers 2020, 12, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norcy, T.L.; Niemann, H.; Proksch, P.; Tait, K.; Linossier, I.; Réhel, K.; Hellio, C.; Faÿ, F. Sponge-Inspired Dibromohemibastadin Prevents and Disrupts Bacterial Biofilms without Toxicity. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Déziel, E.; Comeau, Y.; Villemur, R. Initiation of Biofilm Formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 57RP Correlates with Emergence of Hyperpiliated and Highly Adherent Phenotypic Variants Deficient in Swimming, Swarming, and Twitching Motilities. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishwakarma, J.; VL, S. Unraveling the Anti-Biofilm Potential of Green Algal Sulfated Polysaccharides against Salmonella enterica and Vibrio harveyi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 6299–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayem, S.A.; Manzo, E.; Ciavatta, L.; Tramice, A.; Cordone, A.; Zanfardino, A.; De Felice, M.; Varcamonti, M. Anti-Biofilm Activity of an Exopolysaccharide from a Sponge-Associated Strain of Bacillus licheniformis. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashiya, N.; Padmini, N.; Ajilda, A.A.K.; Prabakaran, P.; Durgadevi, R.; Veera Ravi, A.; Ghosh, S.; Sivakumar, N.; Selvakumar, G. Inhibition of Biofilm Formation and Quorum Sensing Mediated Virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Marine Sponge Symbiont Brevibacterium casei Strain Alu 1. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 150, 104693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Kim, S.-O.; Linardy, E.; Dreaden, E.C.; Zhdanov, V.P.; Hammond, P.T.; Cho, N.-J. Adsorption of Hyaluronic Acid on Solid Supports: Role of PH and Surface Chemistry in Thin Film Self-Assembly. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 448, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Yang, F.; Bick, A.; Oron, G.; Herzberg, M. Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) in a Hybrid Growth Membrane Bioreactor (HG-MBR): Viscoelastic and Adherence Characteristics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8636–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, H. Evaluation of Biosurfactants and Surfactants for Crude Oil Contaminated Sand Washing. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2015, 33, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, P.; Llamas, M.A. Promising Biotechnological Applications of Antibiofilm Exopolysaccharides. Microb. Biotechnol. 2012, 5, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrot, A.V.; Abubakar Mohamed, A.; Faradjeva, E.; Si Jie, L.; Hooi Sze, C.; Arif, A.; Chuan Sean, T.; Norbert Michael, E.; Yeok Mun, C.; Xiao Qi, N.; et al. Mechanisms and Impact of Biofilms and Targeting of Biofilms Using Bioactive Compounds—A Review. Medicina 2021, 57, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanna, S.; Mercier, D.; Gardin, E.; Allion-Maurer, A.; Marcus, P. EPS for Bacterial Anti-Adhesive Properties Investigated on a Model Metal Surface. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 213, 112413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concórdio-Reis, P.; Alves, V.D.; Moppert, X.; Guézennec, J.; Freitas, F.; Reis, M.A.M. Characterization and Biotechnological Potential of Extracellular Polysaccharides Synthesized by Alteromonas Strains Isolated from French Polynesia Marine Environments. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, J.P.M.D.; Yatip, P.; Soowannayan, C.; Maningas, M.B.B. Targeting Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation in the Control of Vibrio harveyi Infections in Penaeus vannamei. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 4919–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentzer, M.; Eberl, L.; Nielsen, J.; Givskov, M. Quorum Sensing. BioDrugs 2003, 17, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindhadevi, K.; LewisOscar, F.; Mylonakis, E.; Shanmugam, S.; Verma, T.N.; Pugazhendhi, A. Biofilm and Quorum Sensing Mediated Pathogenicity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Process Biochem. 2020, 96, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Mao, S.; Wang, H.; Ye, X. The Molecular Architecture of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Quorum-Sensing Inhibitors. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Ye, X.; Emam, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Current Advances in Vibrio harveyi Quorum Sensing as Drug Discovery Targets. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 207, 112741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Datta, S.; Narayanan, K.B.; Rajnish, K.N. Bacterial Exo-Polysaccharides in Biofilms: Role in Antimicrobial Resistance and Treatments. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, S.M.; Aeron, A. Bacterial Biofilm: Dispersal and Inhibition Strategies. Sch. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 1, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadeniz, D.G.; Kaskatepe, B.; Kiymaci, M.E.; Tok, K.C.; Gumustas, M.; Karaaslan, C. Microbial Exopolysaccharide Production of Streptococcus thermophilus and Its Antiquorum Sensing Activity. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 3331–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, R.; Tiwari, M.; Donelli, G.; Tiwari, V. Strategies for Combating Bacterial Biofilms: A Focus on Anti-Biofilm Agents and Their Mechanisms of Action. Virulence 2018, 9, 522–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Manefield, M. Pyocyanin Promotes Extracellular DNA Release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Oh, S.; Kim, S.H. Released Exopolysaccharide (r-EPS) Produced from Probiotic Bacteria Reduce Biofilm Formation of Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 379, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, L.D.; Weibel, D.B. Physicochemical regulation of biofilm formation. MRS Bull. 2011, 36, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fang, D.; Ye, R.; Zhou, C.; Li, P. The Released Polysaccharide Inhibits Cell Aggregation and Biofilm Formation in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Eur. J. Phycol. 2021, 56, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendueles, O.; Travier, L.; Latour-Lambert, P.; Fontaine, T.; Magnus, J.; Denamur, E.; Ghigo, J.-M. Screening of Escherichia coli Species Biodiversity Reveals New Biofilm-Associated Antiadhesion Polysaccharides. mBio 2011, 2, e00043-11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junter, G.-A.; Thébault, P.; Lebrun, L. Polysaccharide-Based Antibiofilm Surfaces. Acta Biomater. 2016, 30, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.D.; Green, H.; Bjöörn, P.; Kubicki, J.D. Model Bacterial Extracellular Polysaccharide Adsorption onto Silica and Alumina: Quartz Crystal Microbalance with Dissipation Monitoring of Dextran Adsorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7739–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, E.; Liu, L.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Gui, M.; Wu, R.; Li, P. Rheological, Emulsifying and Thermostability Properties of Two Exopolysaccharides Produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LPL061. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ji, J.; Rui, X.; Yu, J.; Tang, W.; Chen, X.; Jiang, M.; Dong, M. Production of Exopolysaccharides by Lactobacillus helveticus MB2-1 and Its Functional Characteristics in Vitro. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavita, K.; Singh, V.K.; Mishra, A.; Jha, B. Characterisation and Anti-Biofilm Activity of Extracellular Polymeric Substances from Oceanobacillus iheyensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndejiko, M.; Wan Dagang, W.R.Z. Methods and Protocol Flow Cells: Technique Used for Studying Microbial Biofilms. J. Teknol. 2016, 78, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Winson, M.K.; Swift, S.; Fish, L.; Throup, J.P.; Jørgensen, F.; Chhabra, S.R.; Bycroft, B.W.; Williams, P.; Stewart, G.S.A.B. Construction and Analysis of LuxCDABE-Based Plasmid Sensors for Investigating N-Acyl Homoserine Lactone-Mediated Quorum Sensing. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1998, 163, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobretsov, S.; Teplitski, M.; Bayer, M.; Gunasekera, S.; Proksch, P.; Paul, V.J. Inhibition of Marine Biofouling by Bacterial Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. Biofouling 2011, 27, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzdrenga, J.; Daudé, D.; Rémy, B.; Jacquet, P.; Plener, L.; Elias, M.; Chabrière, E. Biotechnological Applications of Quorum Quenching Enzymes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 267, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqawi, M.; Gallily, R.; Sionov, R.V.; Zaks, B.; Friedman, M.; Steinberg, D. Cannabigerol Prevents Quorum Sensing and Biofilm Formation of Vibrio harveyi. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavitake, D.; Balyan, S.; Devi, P.B.; Shetty, P.H. Evaluation of Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsifying Properties of Galactan Exopolysaccharide from Weissella confusa KR780676. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Polysaccharide | MW (Da) | Viscosity (mPa·s) | G′ (Pa) (a) | G″ (Pa) (a) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MO245 | 1.5 × 106 | 5 | 0.9 | 20 | [21] |
| HA | 1.1 × 106 | 11.6 | 55.8 | 67.5 | [27] |
| 2.0 × 106 | 107 | 220 | 125 |
| Strain | Percentage of Adhesion Inhibition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Condition | Second Condition | |||
| MO245 | HA | MO245 | HA | |
| P. aeruginosa | −53 ± 15% *** | −6 ± 11% | −44 ± 15% *** | +6 ± 12% |
| V. harveyi | −29 ± 18% *** | 0 ± 15% | −49 ± 17% *** | −4 ± 24% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Champion, M.; Portier, E.; Vallée-Réhel, K.; Linossier, I.; Balnois, E.; Vignaud, G.; Moppert, X.; Hellio, C.; Faÿ, F. Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Hyaluronan-like Exopolysaccharide from the Marine Vibrio MO245 against Pathogenic Bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110728
Champion M, Portier E, Vallée-Réhel K, Linossier I, Balnois E, Vignaud G, Moppert X, Hellio C, Faÿ F. Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Hyaluronan-like Exopolysaccharide from the Marine Vibrio MO245 against Pathogenic Bacteria. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(11):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110728
Chicago/Turabian StyleChampion, Marie, Emilie Portier, Karine Vallée-Réhel, Isabelle Linossier, Eric Balnois, Guillaume Vignaud, Xavier Moppert, Claire Hellio, and Fabienne Faÿ. 2022. "Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Hyaluronan-like Exopolysaccharide from the Marine Vibrio MO245 against Pathogenic Bacteria" Marine Drugs 20, no. 11: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110728
APA StyleChampion, M., Portier, E., Vallée-Réhel, K., Linossier, I., Balnois, E., Vignaud, G., Moppert, X., Hellio, C., & Faÿ, F. (2022). Anti-Biofilm Activity of a Hyaluronan-like Exopolysaccharide from the Marine Vibrio MO245 against Pathogenic Bacteria. Marine Drugs, 20(11), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110728








