Preparation and Hepatoprotective Activities of Peptides Derived from Mussels (Mytilus edulis) and Clams (Ruditapes philippinarum)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
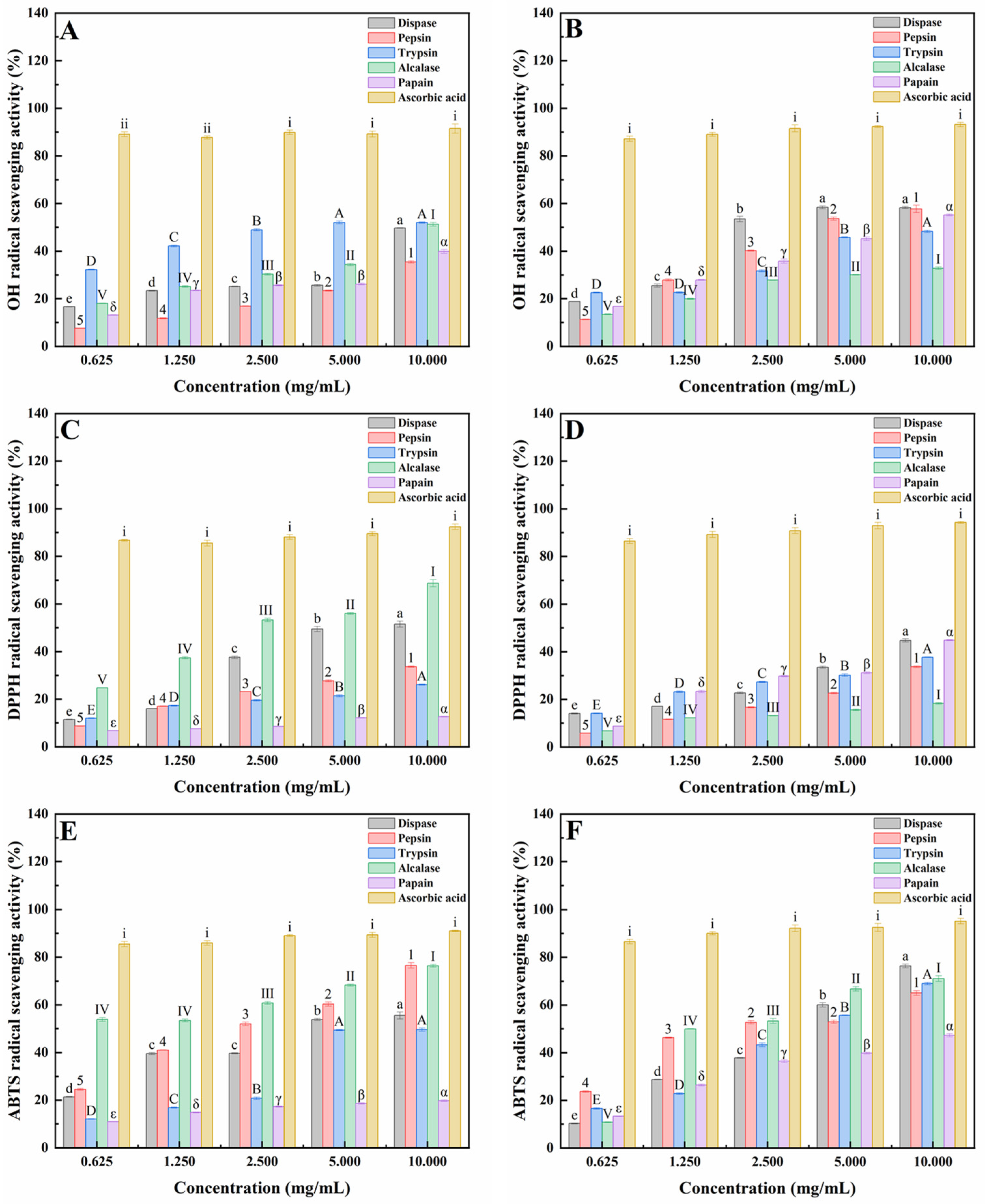
2.1. Antioxidant Activities of Peptides from Mussels (Mytilus edulis) and Clams (Ruditapes philippinarum) Hydrolyzed by Five Proteases
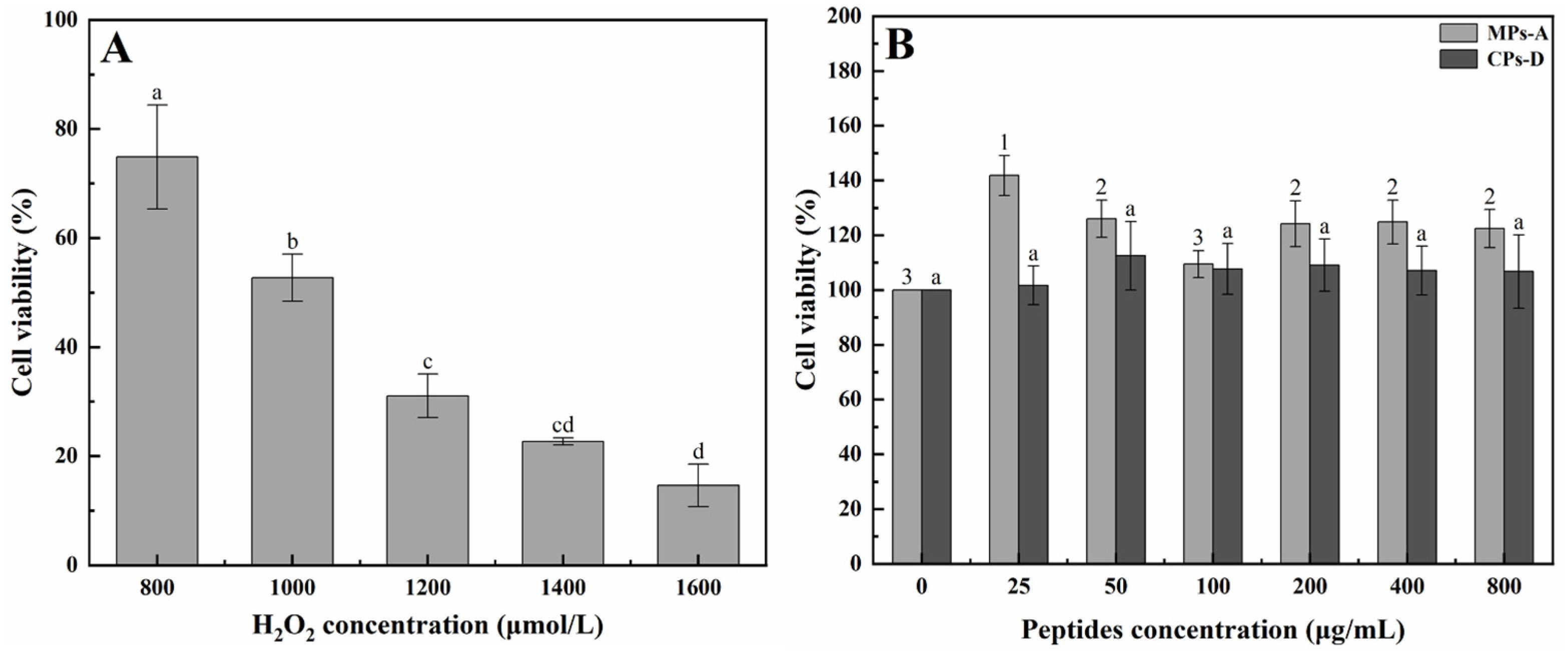
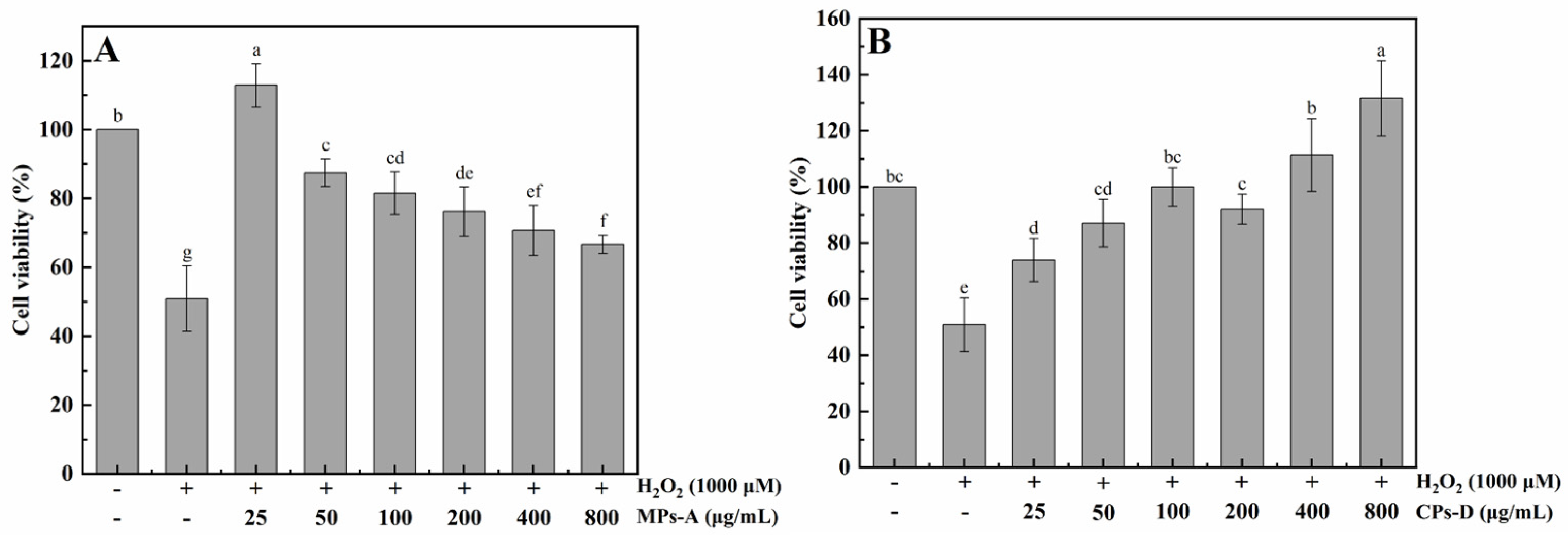
2.2. Hepatoprotective Effect of MPs-A and CPs-D on H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage in HepG2 Cells
2.2.1. Establishment of a HepG2 Cell Model for In Vitro Hepatoprotective Activity Studies
2.2.2. Protective Effects of MPs-A and CPs-D on H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage in HepG2 Cells
2.3. Hepatoprotective Effects of MPs-A and CPs-D on Acute Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice
2.3.1. Effects of MPs-A and CPs-D on Body Weight Gain, Liver Index and Serum Indexes
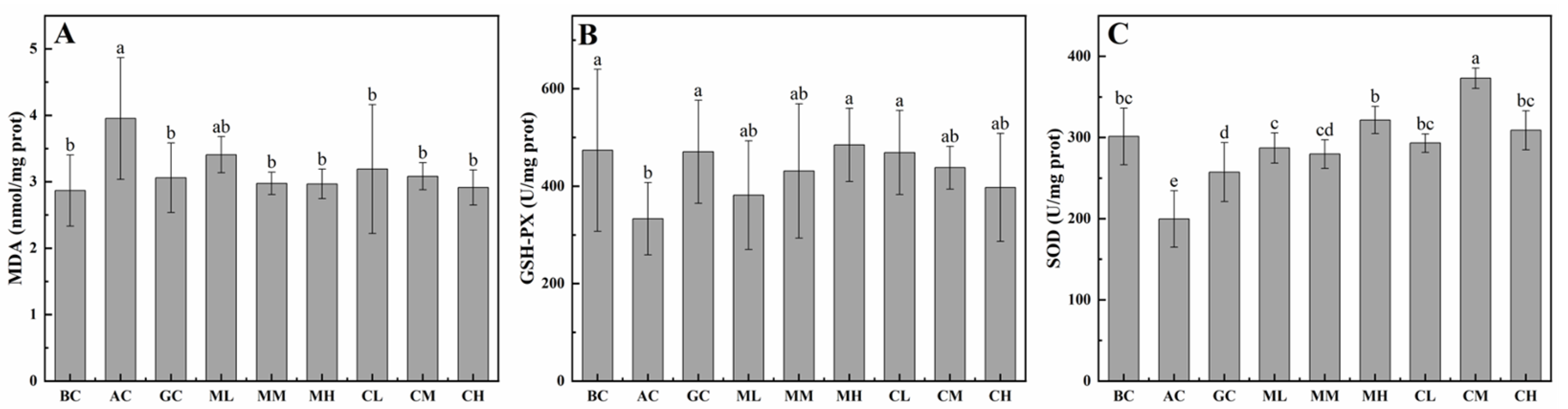
2.3.2. Effects of MPs-A and CPs-D on Hepatic MDA, GSH-PX and SOD
2.3.3. Liver Histological Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Assay Kits
4.3. Cells
4.4. Animals
4.5. Preparation of Peptides from Mussels (Mytilus edulis) and Clams (Ruditapes philippinarum) Hydrolyzed by Five Proteases
4.6. Antioxidant Activities of MPs and CPs
4.6.1. Hydroxyl Radical (OH) Scavenging Activity
4.6.2. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
4.6.3. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
4.7. Hepatoprotective Effect of MPs and CPs on H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage in HepG2 Cells
4.7.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.7.2. Establishment of a H2O2-Induced HepG2 Cell Injury Model
4.7.3. Protective Effects of MPs and CPs on H2O2-Induced Oxidative Damage in HepG2 Cells
4.7.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.8. Hepatoprotective Effects of MPs-A and CPs-D on Acute Alcohol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice
4.8.1. Study Design
4.8.2. Determination of Serum and Hepatic Biomarkers
4.8.3. Histopathologic Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. In Brief to the State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/cc0461zh/online/sofia/2022/aquaculture-production.html (accessed on 2 August 2022).
- Ghazali, F.C.; Edinur, H.A.; Sirajudeen, K.N.S.; Aroyehun, A.Q.B.; Razak, S.A. Medicinal bioactive compounds to functional foods from geochemical signatures marine biomasses: Sea cucumbers, macroalgae and crown of thorns biomasses. Life Sci. Med. Biomed. 2019, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grienke, U.; Silke, J.; Tasdemir, D. Bioactive compounds from marine mussels and their effects on human health. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.T.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, A.; Zhao, G.H.; Xie, H.K.; Zhou, D.Y.; Wang, T. Gallic acid and its alkyl esters emerge as effective antioxidants against lipid oxidation during hot air drying process of Ostrea talienwhanensis. LWT 2021, 139, 110551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakhomov, V.; Braginets, S.; Bakhchevnikov, O.; Rudoy, D. Effect of extrusion on nutritional composition of feed containing mussel meat: Experimental study results. In 19th International Scientific Conference Engineering for Rural Development Proceedings. Eng. Rural Dev. 2020, 19, 306–312. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, C.F.; Zhang, J.S.; Wu, C.W.; Xu, M.Y.; Wang, B. Analysis and evaluation of nutrition composition of mussel. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 554–556, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Xie, X. Evaluation of macroalgal detritus as food source for juvenile manila clam, Ruditapes philippinarum: Effects on growth, amino acid content and fatty acid composition. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 3579–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnedy, P.A.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive peptides from marine processing waste and shellfish: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2012, 4, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, L.; Chi, C.F.; Ma, J.H.; Luo, H.Y.; Xu, Y.F. Purification and characterisation of a novel antioxidant peptide derived from blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Tu, M.; Chen, H.; Mao, F.; Yu, C.; Du, M. Identification and in silico prediction of anticoagulant peptides from the enzymatic hydrolysates of Mytilus edulis proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yu, J.; Song, J.; Wang, S.; Cao, T.; Liu, Z.; Gao, X.; Wei, Y. The antihypertensive effect and mechanisms of bioactive peptides from Ruditapes philippinarum fermented with Bacillus natto in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 79, 104411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, J.W.; Lee, J.S.; Moon, S.H.; Jeon, B.T.; Park, P.J. Purification and characterization of a novel anticancer peptide derived from Ruditapes philippinarum. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, M.; Su, G.; Sun, B. Chicken breast muscle hydrolysates ameliorate acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice through alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) activation and oxidative stress reduction. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertola, A.; Mathews, S.; Ki, S.H.; Wang, H.; Gao, B. Mouse model of chronic and binge ethanol feeding (the NIAAA model). Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.S.; Suh, Y.G.; Yi, H.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Jeong, W.I. Activation of toll-like receptor 3 attenuates alcoholic liver injury by stimulating Kupffer cells and stellate cells to produce interleukin-10 in mice. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Yu, F.; Wu, Y.; Dai, L.; Feng, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, G.; Ma, H.; Li, X.; Dai, C. Identification of a novel peptide that activates alcohol dehydrogenase from crucian carp swim bladder and how it protects against acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 207, 114426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Park, S.Y.; Han, E.J.; Kim, H.S.; Kang, D.S.; Je, J.Y.; Ahn, C.B.; Ahn, G. Isolation of an antioxidant peptide from krill protein hydrolysates as a novel agent with potential hepatoprotective effects. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 67, 103889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Hsu, C.C.; Yen, G.C. Hepatoprotection by freshwater clam extract against CCl4-induced hepatic damage in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2010, 38, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Ding, G. Ameliorative effect of low molecular weight peptides from the head of red shrimp (Solenocera crassicornis) against cyclophosphamide-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 72, 104185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, J.Y.; Cha, J.Y.; Cho, Y.S.; Ahn, H.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, Y.S.; Ahn, C.B. Hepatoprotective effect of peptic hydrolysate from salmon pectoral fin protein byproducts on ethanol-induced oxidative stress in Sprague-Dawley rats. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruoma, O.I. Free radicals, oxidative stress, and antioxidants in human health and disease. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Yu, S.; Jiang, Z.; Liang, C.; Yu, W.; Li, J.; Du, X.; Wang, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, X. N-acetyl-serotonin protects HepG2 cells from oxidative stress injury induced by hydrogen peroxide. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 310504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamas-Paz, A.; Hao, F.; Nelson, L.J.; Vazquez, M.T.; Canals, S.; Del Moral, M.G.; Martinez-Naves, E.; Nevzorova, Y.A.; Cubero, F.J. Alcoholic liver disease: Utility of animal models. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 5063–5075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandon-Warner, E.; Schrum, L.W.; Schmidt, C.M.; McKillop, I.H. Rodent models of alcoholic liver disease: Of mice and men. Alcohol 2012, 46, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Song, H.; Huang, K.; Li, S.; Guan, X. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptides from enzymatic hydrolysate of mungbean protein. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Shen, M.; Xie, J.; Liu, D.; Du, M.; Lin, L.; Gao, H.; Hamaker, B.R.; Xie, M. Physicochemical characterization, antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Mesona chinensis Benth and their protective effect on injured NCTC-1469 cells induced by H2O2. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.Y.; Sun, Y.X.; Shahidi, F. Preparation and antioxidant activity of tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol esters. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 37, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, D.; Fernandez-Pachon, M.S.; Moya, M.L.; Troncoso, A.M.; Garcia-Parrilla, M.C. Radical scavenging ability of polyphenolic compounds towards DPPH free radical. Talanta 2007, 71, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedare, S.B.; Singh, R.P. Genesis and development of DPPH method of antioxidant assay. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Krishna Chaitanya, R.; Preedy, V.R. Assessment of Antioxidant Potential of Dietary Components. In HIV/AIDS: Oxidative Stress and Dietary Antioxidants; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 239–253. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tan, F.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Liao, W.; Li, Q.; Qin, G.; Liu, W.; Zhao, X. White peony (Fermented Camellia sinensis) polyphenols help prevent alcoholic liver injury via antioxidation. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yu, J.; Hu, X.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Qi, B.; Deng, J. In vitro antioxidant effects of Porphyra haitanensis peptides on H2O2-induced damage in HepG2 cells. J. Ocean Univ. China 2021, 20, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, I.; Prell, E.; Weiwad, M. Assessment of cell death studies by monitoring hydrogen peroxide in cell culture. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 456, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichoz-Lach, H.; Michalak, A. Oxidative stress as a crucial factor in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8082–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzeh, A.; Benjakul, S.; Senphan, T. Comparative study on antioxidant activity of hydrolysates from splendid squid (Loligo formosana) gelatin and protein isolate prepared using protease from hepatopancreas of pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3615–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhang, B.; Deng, S.G. Isolation and characterization of three antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of bluefin leatherjacket (Navodon septentrionalis) heads. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zeng, Y.; He, K.; Luo, Y.; Yu, F. Antioxidant peptides from Mytilus Coruscus on H2O2-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell stress. Food Biosci. 2020, 38, 100762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Du, M.; Qiu, J.; Tang, M.; Sun, X.; Zhu, B. Antioxidative peptides from proteolytic hydrolysates of false abalone (Volutharpa ampullacea perryi): Characterization, identification, and molecular docking. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upata, M.; Siriwoharn, T.; Makkhun, S.; Yarnpakdee, S.; Regenstein, J.M.; Wangtueai, S. Tyrosinase inhibitory and antioxidant activity of enzymatic protein hydrolysate from jellyfish (Lobonema smithii). Foods 2022, 11, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitanggang, A.B.; Putri, J.E.; Palupi, N.S.; Hatzakis, E.; Syamsir, E.; Budijanto, S. Enzymatic preparation of bioactive peptides exhibiting ACE inhibitory activity from soybean and velvet bean: A systematic review. Molecules 2021, 26, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motyan, J.A.; Toth, F.; Tozser, J. Research applications of proteolytic enzymes in molecular biology. Biomolecules 2013, 3, 923–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadzri, F.N.A.; Tawalbeh, D.; Sarbon, N.M. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of enzymatic hydrolysed chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) protein as influence by alcalase and papain enzyme. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 36, 102131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Xie, H.; Liu, Z.; Rakariyatham, K.; Yu, C.; Shahidi, F.; Zhou, D. Antioxidant activity and functional properties of Alcalase-hydrolyzed scallop protein hydrolysate and its role in the inhibition of cytotoxicity in vitro. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Fan, F.; Wu, D.; Yu, C.; Wang, Z.; Du, M. Antioxidant and ACE inhibitory activity of enzymatic hydrolysates from Ruditapes philippinarum. Molecules 2018, 23, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.H.; Zhang, D.; Yu, B.; Zhao, S.P.; Wang, J.W.; Yao, L.; Cao, W.G. Antioxidant activity and optimization of extraction of polysaccharide from the roots of Dipsacus asperoides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.L.; Cai, S.Y.; Gao, M.; Chu, X.M.; Pan, X.Y.; Gong, K.K.; Xiao, C.W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wang, B.; et al. Purification of antioxidant peptides of Moringa oleifera seeds and their protective effects on H2O2 oxidative damaged Chang liver cells. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Noisa, P.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Identification and characterization of tilapia antioxidant peptides that protect AAPH-induced HepG2 cell oxidative stress. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 86, 104662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiriyaphan, C.; Chitsomboon, B.; Roytrakul, S.; Yongsawadigul, J. Isolation and identification of antioxidative peptides from hydrolysate of threadfin bream surimi processing byproduct. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1654–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.M.; Wang, Y.M.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Chi, C.F.; Wang, B. Antioxidant peptides from the protein hydrolysate of monkfish (Lophius litulon) muscle: Purification, identification, and cytoprotective function on HepG2 cells damage by H2O2. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Lv, S.; Jiang, S.; Lu, J.; Lin, L. Radical scavenging activities of peptide from asian clam (Corbicula fluminea) and its protective effects on oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide in HepG2 cells. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.M.; Lu, S.Z.; Li, Y.S.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tu, Z.C. Protective effect of antioxidant peptides from grass carp scale gelatin on the H2O2-mediated oxidative injured HepG2 cells. Food Chem. 2022, 373 Pt B, 131539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, S.; Boyadjieva, N.; Sarkar, D.K. Protective effects of hypothalamic beta-endorphin neurons against alcohol-induced liver injuries and liver cancers in rat animal models. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 38, 2988–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Liu, H.; Hou, Y.; Chan, Z.; Di, W.; Li, L.; Zeng, R. Preparation, characterization and alcoholic liver injury protective effects of algal oligosaccharides from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100 Pt 2, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Han, E.J.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, K.; Kang, D.S.; Ahn, C.B.; Ahn, G. In vivo hepatoprotective effects of a peptide fraction from krill protein hydrolysates against alcohol-induced oxidative damage. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Shi, J.; Wang, K.; Tan, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Protective effects of oyster protein hydrolysates on alcohol-induced liver disease (ALD) in mice: Based on the mechanism of anti-oxidative metabolism. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 8411–8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varatharajalu, R.; Garige, M.; Leckey, L.C.; Reyes-Gordillo, K.; Shah, R.; Lakshman, M.R. Protective role of dietary curcumin in the prevention of the oxidative stress induced by chronic alcohol with respect to hepatic injury and antiatherogenic aarkers. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5017460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goc, Z.; Szaroma, W.; Kapusta, E.; Dziubek, K. Protective effects of melatonin on the activity of SOD, CAT, GSH-Px and GSH content in organs of mice after administration of SNP. Chin. J. Physiol. 2017, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, D.; Liu, J. Hepatoprotective effect of albumin peptides from corn germ meal on chronic alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2997–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.H.; Qiu, Y.X.; Li, B.; Peng, C.Y.; Zeng, R.; Wang, W. Kadsura heteroclita stem ethanol extract protects against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice via suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 267, 113496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Liu, X.L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Qu, Y. Antagonistic effect of the glycopeptide from zein on acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 92, 105062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Li, P. Hepatoprotective effect of oyster peptide on alcohol-induced liver disease in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Li, W.J.; Kong, S.Z.; Li, S.D.; Guo, J.Q.; Guo, M.H.; Cai, T.T.; Li, N.; Chen, R.Z.; Luo, R.Q.; et al. Protective effects of collagen polypeptide from tilapia skin against injuries to the liver and kidneys of mice induced by d-galactose. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Saravana, P.S.; Ho, T.C.; Cho, Y.J.; Park, J.S.; Lee, S.G.; Chun, B.S. In vivo protective effect against ethanol metabolism and liver injury of oyster (Crassostrea gigas) extracts obtained via subcritical water processing. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, J.; He, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, S. Hepatoprotective effects of Ganoderma lucidum peptides against D-galactosamine-induced liver injury in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Zhang, F.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Marine collagen peptides protect against early alcoholic liver injury in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bkhairia, I.; Dhibi, S.; Nasri, R.; Elfeki, A.; Hfaiyedh, N.; Amara, I.B.; Nasri, M. Bioactive properties: Enhancement of hepatoprotective, antioxidant and DNA damage protective effects of golden grey mullet protein hydrolysates against paracetamol toxicity. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 23230–23240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, E. Oxidative mechanisms in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2008, 29, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Chi, C.F.; Li, L.; Wang, B. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolysate of scalloped hammerhead (Sphyrna lewini) cartilage. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Chi, C.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Luo, H.Y. Preparation and evaluation of antioxidant peptides from ethanol-soluble proteins hydrolysate of Sphyrna lewini muscle. Peptides 2012, 36, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, M.; Cheng, L.; Ren, D. Inhibitory effect of low-molecular-weight peptides (0–3 kDa) from Spirulina platensis on H2O2-induced oxidative damage in L02 human liver cells. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Body Weight Gain on the 10th Day (g) | Liver Index (mg/g) | Serum Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT (U/L) | AST (U/L) | TC (mmol/L) | TG (mmol/L) | |||
| WC | 8.82 ± 1.36 a | 42.40 ± 2.19 b | 23.26 ± 5.02 b | 23.88 ± 7.62 bc | 4.12 ± 0.55 c | 1.97 ± 0.41 ab |
| AC | 5.35 ± 0.75 bc | 49.67 ± 5.27 a | 37.27 ± 9.60 a | 34.55 ± 7.98 a | 6.00 ± 1.77 a | 2.25 ± 0.64 a |
| GC | 6.46 ± 1.72 bc | 44.60 ± 1.84 ab | 27.67 ± 7.26 ab | 17.91 ± 2.28 ab | 4.15 ± 0.73 bc | 1.85 ± 0.36 abc |
| ML | 7.01 ± 1.44 ab | 46.70 ± 4.77 ab | 25.10 ± 7.68 b | 20.76 ± 11.21 c | 5.44 ± 0.80 abc | 1.57 ± 0.29 bc |
| MM | 5.84 ± 3.25 bc | 43.40 ± 4.53 b | 23.52 ± 6.58 b | 22.52 ± 7.96 bc | 4.77 ± 1.16 abc | 1.47 ± 0.31 bc |
| MH | 5.67 ± 2.43 bc | 49.75 ± 3.69 a | 23.82 ± 6.59 b | 18.80 ± 4.10 bc | 4.20 ± 0.49 bc | 1.37 ± 0.20 c |
| CL | 4.72 ± 0.91 c | 42.24 ± 8.33 b | 26.85 ± 9.76 ab | 25.23 ± 9.87 bc | 5.67 ± 1.93 ab | 1.79 ± 0.62 abc |
| CM | 4.50 ± 1.47 c | 45.35 ± 2.88 ab | 25.06 ± 8.69 b | 22.00 ± 5.75 bc | 5.64 ± 1.64 abc | 1.68 ± 0.41 bc |
| CH | 4.54 ± 1.93 c | 45.91 ± 1.46 ab | 23.84 ± 5.86 b | 20.33 ± 2.94 bc | 5.00 ± 1.28 abc | 1.69 ± 0.90 bc |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Q.; Liu, F.-J.; Wang, X.-M.; Zhao, G.-H.; Cai, D.; Yu, J.-H.; Yin, F.-W.; Zhou, D.-Y. Preparation and Hepatoprotective Activities of Peptides Derived from Mussels (Mytilus edulis) and Clams (Ruditapes philippinarum). Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110719
Wang Q, Liu F-J, Wang X-M, Zhao G-H, Cai D, Yu J-H, Yin F-W, Zhou D-Y. Preparation and Hepatoprotective Activities of Peptides Derived from Mussels (Mytilus edulis) and Clams (Ruditapes philippinarum). Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(11):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110719
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Qian, Fu-Jun Liu, Xin-Miao Wang, Guan-Hua Zhao, Dong Cai, Jing-Han Yu, Fa-Wen Yin, and Da-Yong Zhou. 2022. "Preparation and Hepatoprotective Activities of Peptides Derived from Mussels (Mytilus edulis) and Clams (Ruditapes philippinarum)" Marine Drugs 20, no. 11: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110719
APA StyleWang, Q., Liu, F.-J., Wang, X.-M., Zhao, G.-H., Cai, D., Yu, J.-H., Yin, F.-W., & Zhou, D.-Y. (2022). Preparation and Hepatoprotective Activities of Peptides Derived from Mussels (Mytilus edulis) and Clams (Ruditapes philippinarum). Marine Drugs, 20(11), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20110719








