Caspase-1 and Cathepsin B Inhibitors from Marine Invertebrates, Aiming at a Reduction in Neuroinflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
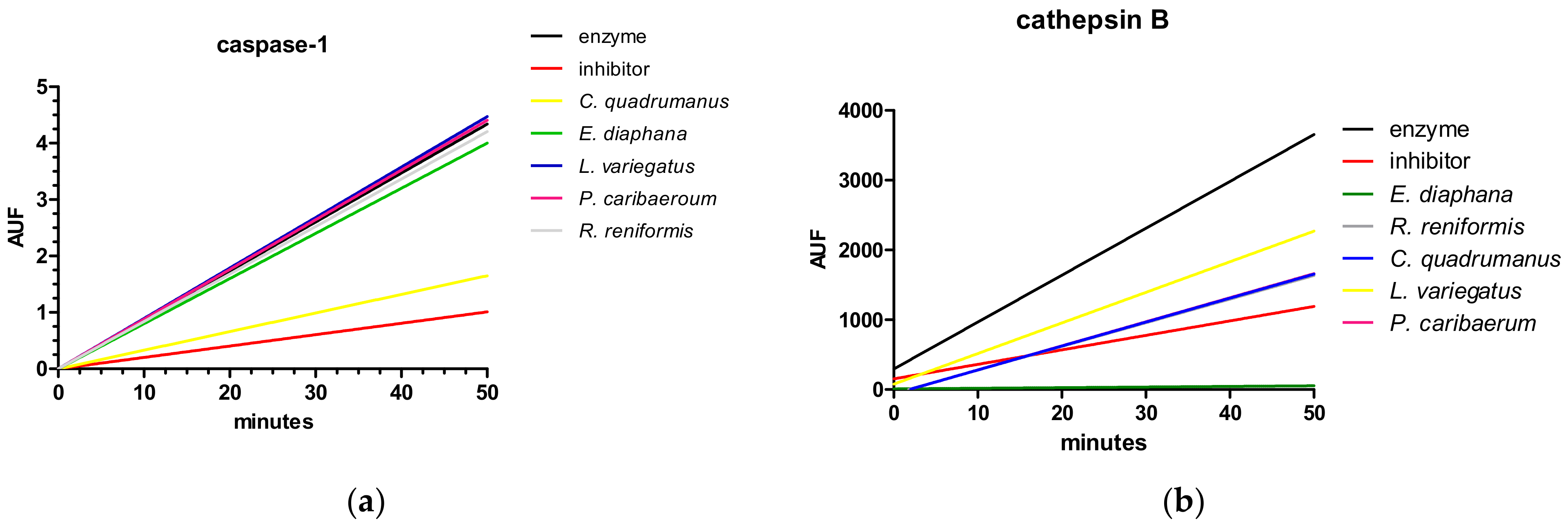
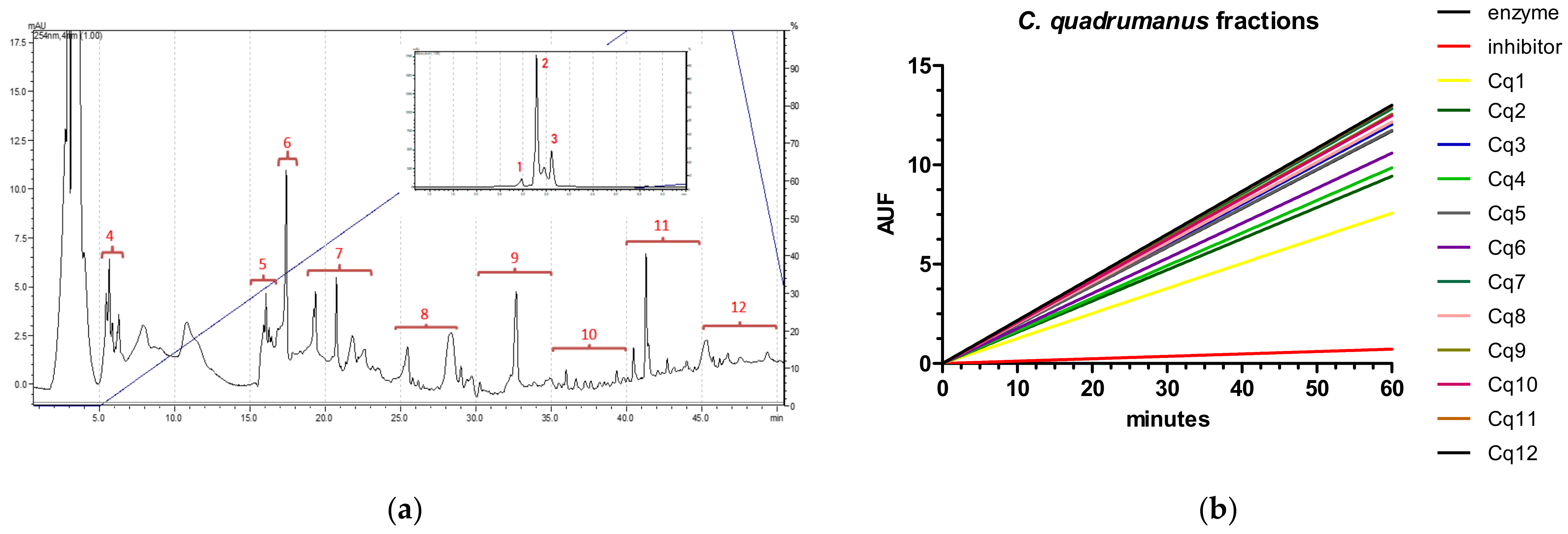
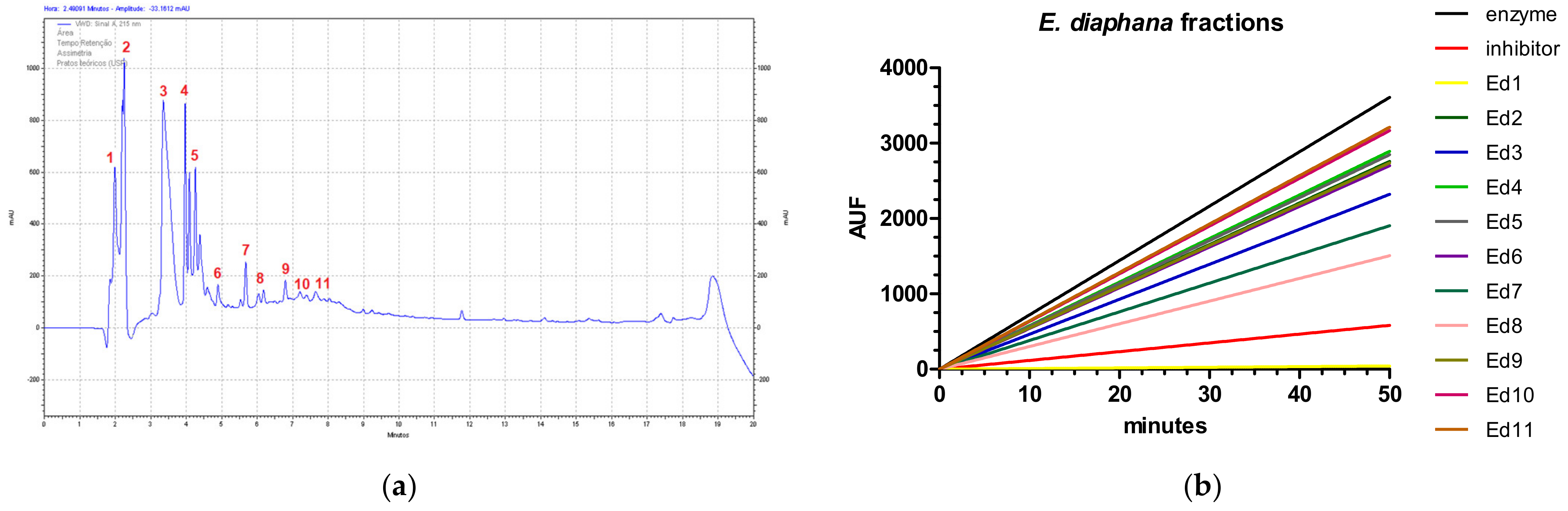
2. Results
2.1. Caspase-1
2.2. Cathepsin B
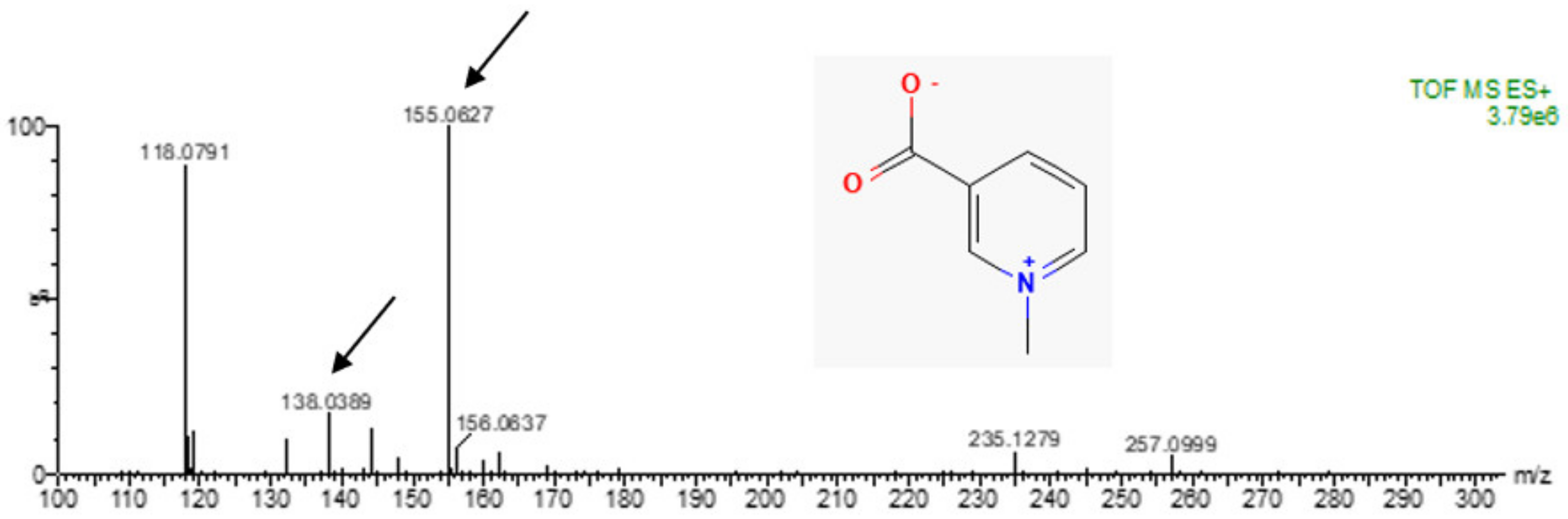
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
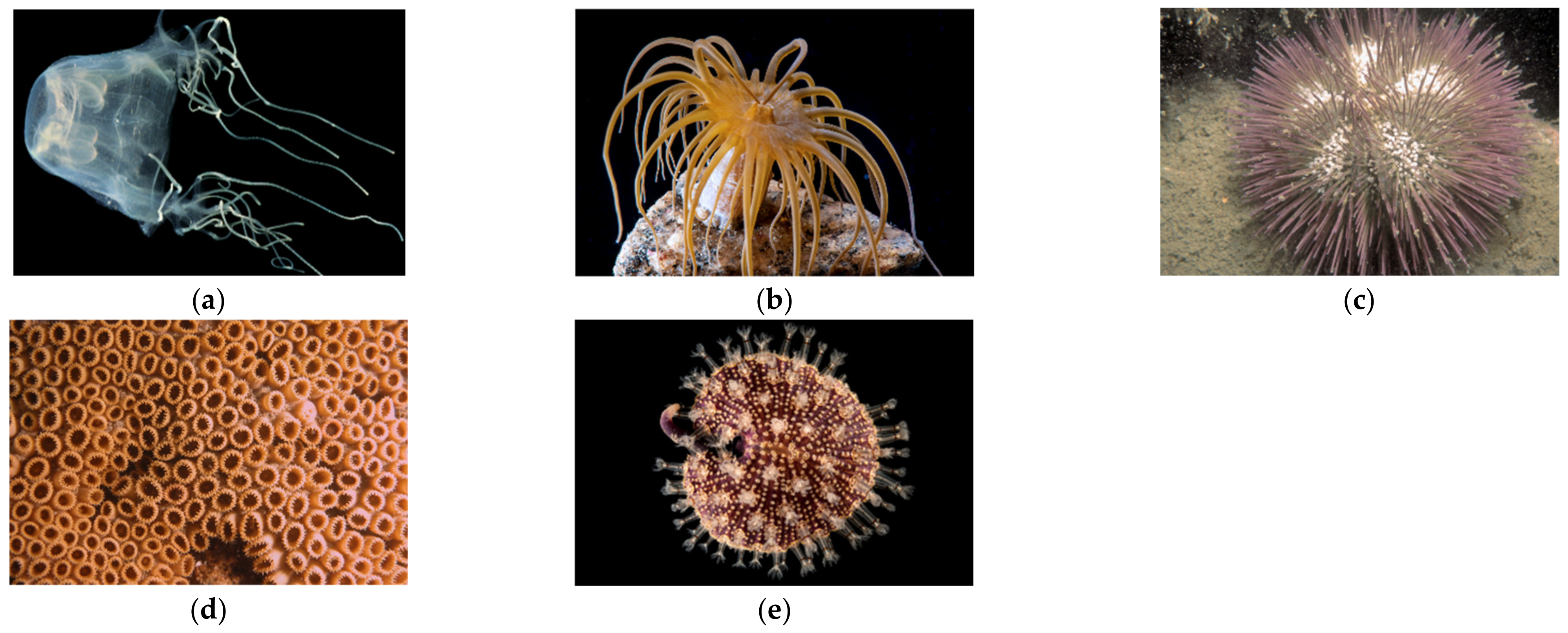
4.1. Species Studied
4.2. Extracts Attainment
4.3. Fractionation
4.4. Mass Spectrometry
4.5. Enzymatic Assays
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- DiSabato, D.J.; Quan, N.; Godbout, J.P. Neuroinflammation: The Devil Is in the Details. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davalos, D.; Grutzendler, J.; Yang, G.; Kim, J.V.; Zuo, Y.; Jung, S.; Littman, D.R.; Dustin, M.L.; Gan, W.-B. ATP Mediates Rapid Microglial Response to Local Brain Injury in Vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, L.C.; Ting, J.P.-Y. The Pathogenic Role of the Inflammasome in Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.K.; Wen, H.; Ting, J.P.-Y. The Inflammasome NLRs in Immunity, Inflammation, and Associated Diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanslik, K.L.; Ulland, T.K. The Role of Microglia and the Nlrp3 Inflammasome in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 570711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Song, W. NLRP3 Inflammasome as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneka, M.T.; Kummer, M.P.; Stutz, A.; Delekate, A.; Schwartz, S.; Vieira-Saecker, A.; Griep, A.; Axt, D.; Remus, A.; Tzeng, T.-C.; et al. NLRP3 Is Activated in Alzheimer’s Disease and Contributes to Pathology in APP/PS1 Mice. Nature 2013, 493, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Xing, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Tian, Y.; Dai, Z. Sevoflurane Aggravates the Progress of Alzheimer’s Disease Through NLRP3/Caspase-1/Gasdermin D Pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 801422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, A.F.; Szabò, I.; Veerhuis, R.; Bubacco, L. The Potential Convergence of NLRP3 Inflammasome, Potassium, and Dopamine Mechanisms in Parkinson’s Disease. NPJ Parkinson’s Dis. 2022, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paldino, E.; Fusco, F.R. Emerging Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome/Pyroptosis in Huntington’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campden, R.I.; Zhang, Y. The Role of Lysosomal Cysteine Cathepsins in NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 670, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brix, K.; Dunkhorst, A.; Mayer, K.; Jordans, S. Cysteine Cathepsins: Cellular Roadmap to Different Functions. Biochimie 2008, 90, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Sloane, B.F. Molecular Regulation of Human Cathepsin B: Implication in Pathologies. Biol. Chem. 2003, 384, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataldo, A.M.; Nixon, R.A. Enzymatically Active Lysosomal Proteases Are Associated with Amyloid Deposits in Alzheimer Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 3861–3865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, V.; Toneff, T.; Bogyo, M.; Greenbaum, D.; Medzihradszky, K.F.; Neveu, J.; Lane, W.; Hook, G.; Reisine, T. Inhibition of Cathepsin B Reduces β-Amyloid Production in Regulated Secretory Vesicles of Neuronal Chromaffin Cells: Evidence for Cathepsin B as a Candidate β-Secretase of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biol. Chem. 2005, 386, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hook, G.; Yu, J.; Toneff, T.; Kindy, M.; Hook, V. Brain Pyroglutamate Amyloid-β Is Produced by Cathepsin B and Is Reduced by the Cysteine Protease Inhibitor E64d, Representing a Potential Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutic. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 41, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Steiner, S.; Zhou, Y.; Arai, H.; Roberson, E.D.; Sun, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, G.; Esposito, L.; Mucke, L.; et al. Antiamyloidogenic and Neuroprotective Functions of Cathepsin B: Implications for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuron 2006, 51, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindy, M.S.; Yu, J.; Zhu, H.; El-Amouri, S.S.; Hook, V.; Hook, G.R. Deletion of the Cathepsin B Gene Improves Memory Deficits in a Transgenic Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model Expressing AβPP Containing the Wild-Type β-Secretase Site Sequence. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2012, 29, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hook, V.; Yoon, M.; Mosier, C.; Ito, G.; Podvin, S.; Head, B.P.; Rissman, R.; O’Donoghue, A.J.; Hook, G. Cathepsin B in Neurodegeneration of Alzheimer’s Disease, Traumatic Brain Injury, and Related Brain Disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2020, 1868, 140428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pišlar, A.; Kos, J. Cysteine Cathepsins in Neurological Disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 49, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundelöf, J.; Sundström, J.; Hansson, O.; Eriksdotter-Jönhagen, M.; Giedraitis, V.; Larsson, A.; Degerman-Gunnarsson, M.; Ingelsson, M.; Minthon, L.; Blennow, K.; et al. Higher Cathepsin B Levels in Plasma in Alzheimer’s Disease Compared to Healthy Controls. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 22, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assfalg-Machleidt, I.; Jochum, M.; Nast-Kolb, D.; Siebeck, M.; Billing, A.G.; Joka, T.; Rothe, G.; Valet, G.K.; Zauner, R.; Scheuber, H.P. Cathepsin B-Indicator for the Release of Lysosomal Cysteine Proteinases in Severe Trauma and Inflammation. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler Supple 1990, 371, 211–222. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Rong, X.; Lu, W.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Translational Study of Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) Biomarkers from Brain Tissues in AβPP/PS1 Mice and Serum of AD Patients. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 45, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlinchey, R.P.; Lee, J.C. Cysteine Cathepsins Are Essential in Lysosomal Degradation of α-Synuclein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 9322–9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halle, A.; Hornung, V.; Petzold, G.C.; Stewart, C.R.; Monks, B.G.; Reinheckel, T.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Latz, E.; Moore, K.J.; Golenbock, D.T. The NALP3 Inflammasome Is Involved in the Innate Immune Response to Amyloid-β. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, J.; Noël, A.; Foveau, B.; Lynham, J.; Lecrux, C.; LeBlanc, A.C. Caspase-1 Inhibition Alleviates Cognitive Impairment and Neuropathology in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, B.A.; Mamik, M.K.; Saito, L.B.; Boghozian, R.; Monaco, M.C.; Major, E.O.; Lu, J.-Q.; Branton, W.G.; Power, C. Caspase-1 Inhibition Prevents Glial Inflammasome Activation and Pyroptosis in Models of Multiple Sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6065–E6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, G.L.M.; Vigerelli, H.; Bufalo, M.C.; Longato, G.B.; Veloso, R.V.; Zambelli, V.O.; Picolo, G.; Cury, Y.; Morandini, A.C.; Marques, A.C.; et al. Box Jellyfish (Cnidaria, Cubozoa) Extract Increases Neuron’s Connection: A Possible Neuroprotector Effect. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 8855248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, M.; Kamal, R. Studies on Trigonelline from Moringa Oleifera and Its in Vitro Regulation by Feeding Precursor in Cell Cultures. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2012, 22, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, D. Über Das Vorkommen von Homarin, Trigonellin Und Einer Neuen Base Anemonin in Der Anthozoe Anemonia sulcata. Hoppe-Seyler’s Z. Physiol. Chem. 1953, 295, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budavari, S. Trigonelline. In The Merck Index; Merck & Co., Inc.: Whitehall, UK, 1996; p. 1651. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer, R.; Berking, S. Control of Formation of the Two Types of Polyps in Thecocodium Quadratum (Hydrozoa, Cnidaria). Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1995, 39, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siefker, B.; Kroiher, M.; Berking, S. Induction of Metamorphosis from the Larval to the Polyp Stage Is Similar in Hydrozoa and a Subgroup of Scyphozoa (Cnidaria, Semaeostomeae). Helgol. Mar. Res. 2000, 54, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, R.X.; Lavoie, S.; Siegel, K.; Gaul, D.A.; Weissburg, M.J.; Kubanek, J. Chemical Encoding of Risk Perception and Predator Detection among Estuarine Invertebrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Du, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J. Trigonelline Inhibits Caspase 3 to Protect β Cells Apoptosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 1 Diabetic Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 836, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohda, C.; Kuboyama, T.; Komatsu, K. Search for Natural Products Related to Regeneration of the Neuronal Network. Neurosignals 2005, 14, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, I.; Radecka, H.; Burza, A.; Radecki, J.; Kaliszan, M.; Kaliszan, R. Association Constants of Pyridine and Piperidine Alkaloids to Amyloid ß Peptide Determined by Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2010, 7, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentze, H.; Lin, X.Y.; Choi, M.S.K.; Porter, A.G. Critical Role for Cathepsin B in Mediating Caspase-1-Dependent Interleukin-18 Maturation and Caspase-1-Independent Necrosis Triggered by the Microbial Toxin Nigericin. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevriaux, A.; Pilot, T.; Derangère, V.; Simonin, H.; Martine, P.; Chalmin, F.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Rébé, C. Cathepsin B Is Required for NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Macrophages, Through NLRP3 Interaction. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Tardivel, A.; Thorens, B.; Choi, I.; Tschopp, J. Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein Links Oxidative Stress to Inflammasome Activation. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Mora, P.; Luna, R.; Colín-Barenque, L. Amyloid Beta: Multiple Mechanisms of Toxicity and Only Some Protective Effects? Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taneo, J.; Adachi, T.; Yoshida, A.; Takayasu, K.; Takahara, K.; Inaba, K. Amyloid β Oligomers Induce Interleukin-1β Production in Primary Microglia in a Cathepsin B- and Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent Manner. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Ye, S.; Chu, A.; Anton, K.; Yi, S.; Vincent, V.A.; von Schack, D.; Chin, D.; Murray, J.; Lohr, S.; et al. Identification of Cathepsin B as a Mediator of Neuronal Death Induced by Aβ-Activated Microglial Cells Using a Functional Genomics Approach. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 5565–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hook, V.Y.H.; Kindy, M.; Hook, G. Inhibitors of Cathepsin B Improve Memory and Reduce β-Amyloid in Transgenic Alzheimer Disease Mice Expressing the Wild-Type, but Not the Swedish Mutant, β-Secretase Site of the Amyloid Precursor Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7745–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, M.; Miyashita, S.; Yokoo, C.; Tamai, M.; Hanada, K.; Hatayama, K.; Towatari, T.; Nikawa, T.; Katunuma, N. Novel Epoxysuccinyl Peptides Selective Inhibitors of Cathepsin B, in Vitro. FEBS Lett. 1991, 280, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, S.; Imae, Y.; Takada, K.; Kikuchi, J.; Nakao, Y.; van Soest, R.W.M.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Shishicrellastatins, Inhibitors of Cathepsin B, from the Marine Sponge Crella (Yvesia) Spinulata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6594–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konno, H.; Kubo, K.; Makabe, H.; Toshiro, E.; Hinoda, N.; Nosaka, K.; Akaji, K. Total Synthesis of Miraziridine A and Identification of Its Major Reaction Site for Cathepsin B. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 9502–9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancey, P.H.; Heppenstall, M.; Ly, S.; Andrell, R.M.; Gates, R.D.; Carter, V.L.; Hagedorn, M. Betaines and Dimethylsulfoniopropionate as Major Osmolytes in Cnidaria with Endosymbiotic Dinoflagellates. Physiol. Biochem. Zool. 2010, 83, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukovskiĭ, I.G.; Kuznetsova, L.P.; Sochilina, E.E.; Dmitrieva, E.N.; Gololobov, I.G.; Bykovskaia, E.I. [Inhibition of Cholinesterases of Varying Origin by Ordinary and Betaine Vinylphosphates]. Ukr. Biokhimicheskii Zhurnal 2010, 68, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yajun, W.; Jin, C.; Zhengrong, G.; Chao, F.; Yan, H.; Weizong, W.; Xiaoqun, L.; Qirong, Z.; Huiwen, C.; Hao, Z.; et al. Betaine Attenuates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis and Angiogenesis in Subchondral Bone. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 723988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, T.; Vancha, S.R.; Kanapathipillai, M. L-proline and Betaine Inhibit Extracellular Enzymes Mediated Abeta 1-42 Aggregation, Oxidative Stress, and Toxicity. Pept. Sci. 2018, 110, e24093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarms, G.; Morandini, A.C. World Atlas of Jellyfish: Scyphozoa except Stauromedusae; Dölling und Galitz Verlag: Hamburg, Germany, 2019; ISBN 9783862180820. [Google Scholar]
- Jaimes-Becerra, A.; Chung, R.; Morandini, A.C.; Weston, A.J.; Padilla, G.; Gacesa, R.; Ward, M.; Long, P.F.; Marques, A.C. Comparative Proteomics Reveals Recruitment Patterns of Some Protein Families in the Venoms of Cnidaria. Toxicon 2017, 137, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grajales, A.; Rodríguez, E. Morphological Revision of the Genus Aiptasia and the Family Aiptasiidae (Cnidaria, Actiniaria, Metridioidea). Zootaxa 2014, 3826, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, Z.M.A.N.; Kikuchi, R.K.P.; Testa, V. Corals and Coral Reefs of Brazil. In Latin American Coral Reefs; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 9–52. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, V.; Vasconcelos, V. Palytoxin and Analogs: Biological and Ecological Effects. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.C. The Global Diversity of Sea Pens (Cnidaria: Octocorallia: Pennatulacea). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavico, E.E.G.; Da Gama, B.A.P.; Soares, A.R.; Cassiano, K.M.; Pereira, R.C. Interaction of Chemical and Structural Components Providing Defences to Sea Pansies Renilla Reniformis and Renilla Muelleri. Mar. Biol. Res. 2013, 9, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, S.A.; McClintock, J.B.; Lawrence, J.M. Lytechinus. In Sea Urchins: Biology and Ecology, 3rd ed.; Lawrence, J.M., Ed.; Elsevier B. V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Sciani, J.M.; Emerenciano, A.K.; Cunha da Silva, J.R.M.; Pimenta, D.C. Initial Peptidomic Profiling of Brazilian Sea Urchins: Arbacia Lixula, Lytechinus Variegatus and Echinometra Lucunter. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 22, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciani, J.M.; Antoniazzi, M.M.; Neves, A.d.C.; Pimenta, D.C. Cathepsin B/X Is Secreted by Echinometra Lucunter Sea Urchin Spines, a Structure Rich in Granular Cells and Toxins. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 19, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreno, R.I.; Zambelli, V.O.; Picolo, G.; Cury, Y.; Morandini, A.C.; Marques, A.C.; Sciani, J.M. Caspase-1 and Cathepsin B Inhibitors from Marine Invertebrates, Aiming at a Reduction in Neuroinflammation. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100614
Moreno RI, Zambelli VO, Picolo G, Cury Y, Morandini AC, Marques AC, Sciani JM. Caspase-1 and Cathepsin B Inhibitors from Marine Invertebrates, Aiming at a Reduction in Neuroinflammation. Marine Drugs. 2022; 20(10):614. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100614
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreno, Rafaela Indalecio, Vanessa O. Zambelli, Gisele Picolo, Yara Cury, André C. Morandini, Antonio Carlos Marques, and Juliana Mozer Sciani. 2022. "Caspase-1 and Cathepsin B Inhibitors from Marine Invertebrates, Aiming at a Reduction in Neuroinflammation" Marine Drugs 20, no. 10: 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100614
APA StyleMoreno, R. I., Zambelli, V. O., Picolo, G., Cury, Y., Morandini, A. C., Marques, A. C., & Sciani, J. M. (2022). Caspase-1 and Cathepsin B Inhibitors from Marine Invertebrates, Aiming at a Reduction in Neuroinflammation. Marine Drugs, 20(10), 614. https://doi.org/10.3390/md20100614





