A Lymphoid Organ Specific Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor from Litopenaeus vannamei Exhibits Strong Antimicrobial Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequences and Phylogenetic Analysis of LvALF8
2.2. Tissue Distribution of LvALF8 Transcripts
2.3. Expression Profiles of LvALF8 after WSSV or Vibrio Parahaemolyticus Infection
2.4. Anti-Bacterial Activities of LvALF8-LBD Peptide
2.5. In Vivo Anti-Bacterial Function of LvALF8-LBD and FcALF8-LBD
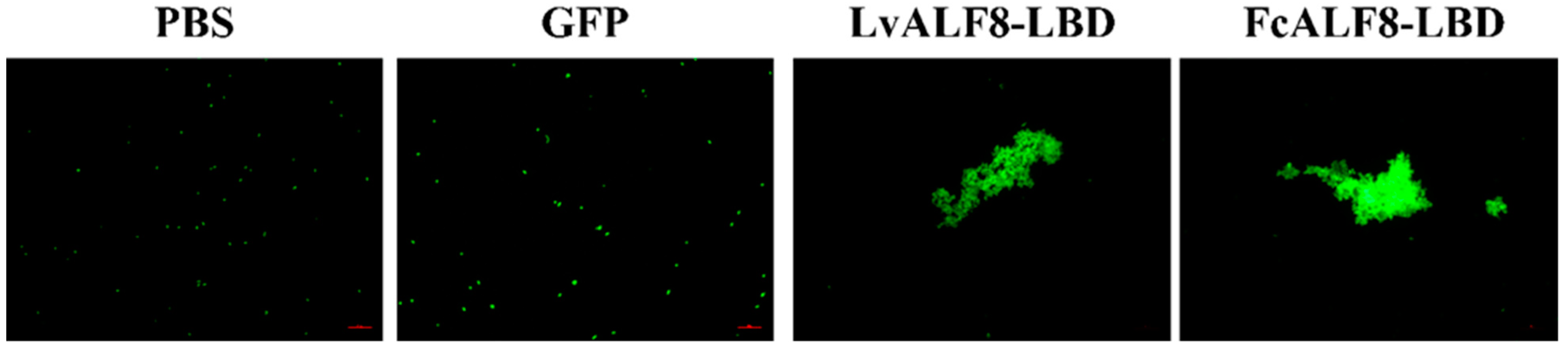
2.6. Agglutination Activity of LvALF8-LBD and FcALF8-LBD
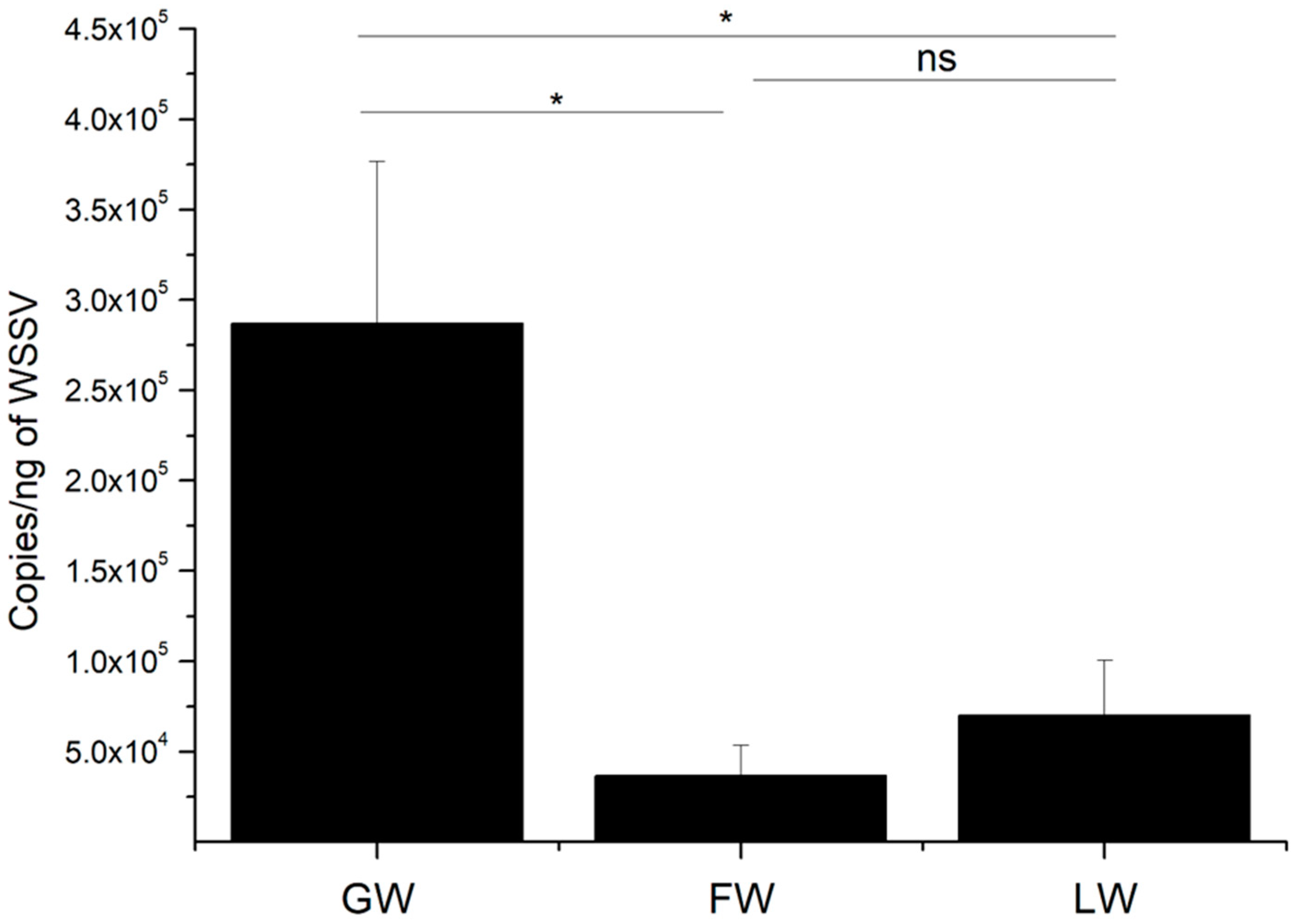
2.7. In Vivo Anti-Virus Function of LvALF8-LBD and FcALF8-LBD
2.8. Structure Analysis of LvALF8-LBD and FcALF8-LBD
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals, Pathogen Stimulation and Tissue Collection
4.2. Total RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
4.3. Sequence Analysis of LvALF8 Gene
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time qPCR
4.5. Synthesis of LvALF8-LBD
4.6. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assay
4.7. Peptide Injection and Pathogens Infection
4.8. Bacterial Count and Strain Identification
4.9. DNA Extraction and WSSV Load Quantification
4.10. Bacterial Agglutination Experiment
4.11. Structure Analysis on the Peptide LvALF8-LBD
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, F.H.; Xiang, J.H. Recent advances in researches on the innate immunity of shrimp in China. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Xiang, J. Signaling pathways regulating innate immune responses in shrimp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2013, 34, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, W.-M. Status of aquaculture of Penaeus vannamei in China. In Proceedings of the Regional Technical Consultation on the Aquaculture of P. vannamei and Other Exotic Shrimps in Southeast Asia, Manila, Philippines, 1–2 March 2005; pp. 84–91. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Dong, L.; Meng, X.; Kong, J.; Luo, K.; Luan, S.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Cao, J.; Wang, M. The difference of tolerance to White spot syndrome virus between Litopenaeus vannamei and Fenneropenaeus chinensis at different temperatures. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2018, 39, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Kong, J.; Luo, K.; Luan, S.; Cao, B.; Liu, N.; Lu, X.; Cao, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; et al. The comparison of the sensitivity to the White spot syndrome virus between Fenneropenaeus chinensis and Litopenaeus vannamei. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2017, 38, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Sui, L. Effect of Salinity on Survival and Growth of Litopenaeus vannamei, Fenneropenaeus chinensis and Penaeus monodon Postlarvae. J. Tianjin Univ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 1, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, R.D.; Barracco, M.A. Antimicrobial peptides in crustaceans. Invert. Surviv. J. 2010, 7, 262–284. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, F. The Anti-lipopolysaccharide Factors in Crustaceans. Subcell. Biochem. 2020, 94, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoess, A.; Watson, S.; Siber, G.R.; Liddington, R. Crystal structure of an endotoxin-neutralizing protein from the horseshoe crab, Limulus anti-LPS factor, at 1.5 A resolution. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 3351–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Inagawa, H.; Kohchi, C.; Nishizawa, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Soma, G.I. Anti-lipopolysaccharide Factor Evokes Indirect Killing of Virulent Bacteria in Kuruma Prawn. In Vivo 2011, 25, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Li, S.; Liu, F.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Identification and function analysis of an anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from the ridgetail prawn Exopalaemon carinicauda. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2017, 70, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, S.H.; Li, F.H.; Lv, X.J.; Xiang, J.H. Recombinant expression and functional analysis of an isoform of anti-lipopolysaccharide factors (FcALF5) from Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 53, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponprateep, S.; Tharntada, S.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Tassanakajon, A. Gene silencing reveals a crucial role for anti-lipopolysaccharide factors from Penaeus monodon in the protection against microbial infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 32, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premruethai, S.; Sirawut, K.; Rath, P.; Ikuo, H.; Takashi, A.; Anchalee, T. Antimicrobial peptides discovered in the black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon using the EST approach. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 61, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Soonthornchai, W.; Chaiyapechara, S.; Klinbunga, S.; Thongda, W.; Tangphatsornruang, S.; Yoocha, T.; Jarayabhand, P.; Jiravanichpaisal, P. Differentially expressed transcripts in stomach of Penaeus monodon in response to AHPND infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 65, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Luan, W.; Song, C.; Nie, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, Q. Three isoforms of anti-lipopolysaccharide factor identified from eyestalk cDNA library of swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 30, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.H.; Guo, S.Y.; Li, F.H.; Xiang, J.H. Functional Diversity of Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor Isoforms in Shrimp and Their Characters Related to Antiviral Activity. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2602–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, Z.; Li, X.; Song, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, S. Molecular cloning, expression pattern and antimicrobial activity of a new isoform of anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from the swimming crab Portunus trituberculatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2012, 33, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.J.; Li, S.H.; Zhang, C.S.; Xiang, J.H.; Li, F.H. Multiple Isoforms of Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors and Their Antimicrobial Functions in the Ridgetail Prawn Exopalaemon carinicauda. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lv, X.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Characterization of a Lymphoid Organ Specific Anti-lipopolysaccharide Factor From Shrimp Reveals Structure-Activity Relationship of the LPS-Binding Domain. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Sun, Z.; Li, F.H.; Xiang, J.H. Transcriptome Analysis on Chinese Shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis during WSSV Acute Infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; He, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. An Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor in Litopenaeus Vannamei Participates in the Immune Defense Against WSSV and Vibrio Anguillarum. J. Crustacean Biol. 2015, 35, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, J. A new anti-lipopolysaccharide factor (ALF) gene with its SNP polymorphisms related to WSSV-resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 39, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, G.X.; Li, F.H. Characterization of two pathogenic Photobacterium strains isolated from Exopalaemon carinicauda causing mortality of shrimp. Aquaculture 2016, 464, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Cheng, W.; Hsu, J.P.; Chen, J.C. Vibrio alginolyticus infection in the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei confirmed by polymerase chain reaction and 16S rDNA sequencing. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2004, 61, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Rodriguez, S.A.; Gomez-Gil, B.; Lozano, R. ‘Bright-red’ syndrome in Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei is caused by Vibrio harveyi. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 92, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.C.; Liu, F.; Bian, H.H.; Liu, J.; HUang, J. Isolation, identification, and pathogenicity analysis of a Vibrio parahaemolyticus strain from Litopenaeus vannamei. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2012, 33, 56–62. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, R.D.; Vergnes, A.; de Lorgeril, J.; Goncalves, P.; Perazzolo, L.M.; Saune, L.; Romestand, B.; Fievet, J.; Gueguen, Y.; Bachere, E.; et al. Functional Divergence in Shrimp Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factors (ALFs): From Recognition of Cell Wall Components to Antimicrobial Activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Lan, J.F.; Sun, J.J.; Jia, W.M.; Zhao, X.F.; Wang, J.X. A novel crustin from Marsupenaeus japonicus promotes hemocyte phagocytosis. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 49, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, S.H.; Li, F.H.; Xiang, J.H. Structure and Bioactivity of a Modified Peptide Derived from the LPS-Binding Domain of an Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor (ALF) of Shrimp. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, C.G.C.; Spaink, H.P.; Zee, M.V.D. The extraembryonic serosa is a frontier epithelium providing the insect egg with a full-range innate immune response. eLife 2014, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; Guarnieri, M.T.; Vasil, A.I.; Vasil, M.L.; Mant, C.T.; Hodges, R.S. Role of peptide hydrophobicity in the mechanism of action of alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, A.L.; Spuches, A.M.; Williams, B.C.; Venugopal, D.; Klapper, D.; Srouji, A.H.; Hicks, R.P. The effect of the placement and total charge of the basic amino acid clusters on antibacterial organism selectivity and potency. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7008–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.Y.; Li, S.H.; Li, F.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Xiang, J.H. Modification of a synthetic LPS-binding domain of anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from shrimp reveals strong structure-activity relationship in their antimicrobial characteristics. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 45, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dathe, M.; Nikolenko, H.; Meyer, J.; Beyermann, M.; Bienert, M. Optimization of the antimicrobial activity of magainin peptides by modification of charge. FEBS Lett. 2001, 501, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangaspero, A.; Sandri, L.; Tossi, A. Amphipathic alpha helical antimicrobial peptides—A systematic study of the effects of structural and physical properties on biological activity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 5589–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Analysis on the dynamic changes of the amount of WSSV in Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis during infection. Aquaculture 2013, 376–379, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-T.; Chen, I.-T.; Yang, Y.-T.; Ko, T.-P.; Huang, Y.-T.; Huang, J.-Y.; Huang, M.-F.; Lin, S.-J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-S.; et al. The opportunistic marine pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus becomes virulent by acquiring a plasmid that expresses a deadly toxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 10798–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

 ) and FcALF8 sequence was marked with a black triangle (▲).
) and FcALF8 sequence was marked with a black triangle (▲).
 ) and FcALF8 sequence was marked with a black triangle (▲).
) and FcALF8 sequence was marked with a black triangle (▲).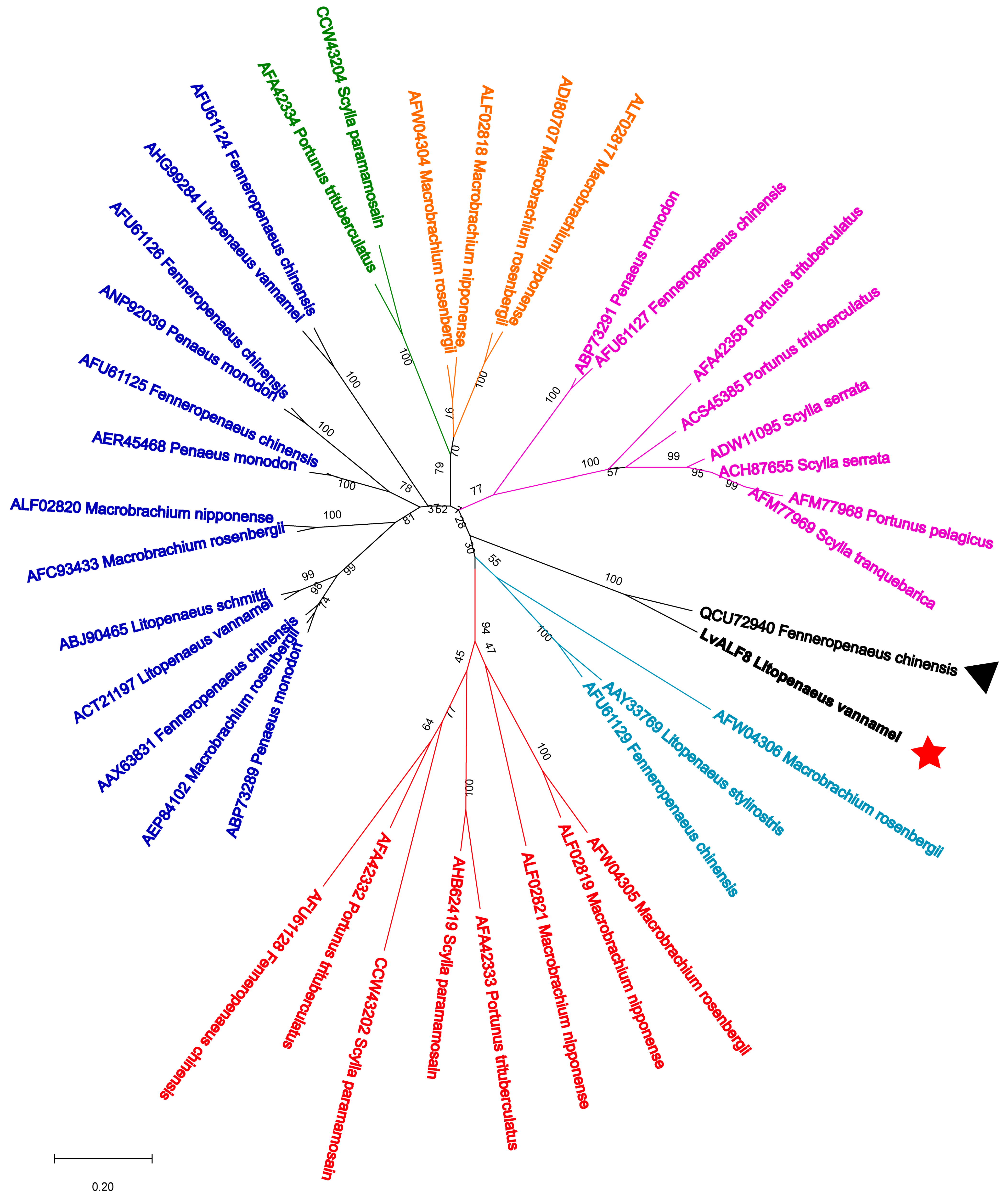




| Species | Gene Name | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|
| Fenneropenaeus chinensis | Antilipopolysaccharide factor isoform 1 | AFU61124 |
| Fenneropenaeus chinensis | Antilipopolysaccharide factor isoform 2 | AFU61125 |
| Fenneropenaeus chinensis | Antilipopolysaccharide factor isoform 3 | AFU61126 |
| Fenneropenaeus chinensis | Antilipopolysaccharide factor isoform 4 | AFU61127 |
| Fenneropenaeus chinensis | Antilipopolysaccharide factor isoform 5 | AFU61128 |
| Fenneropenaeus chinensis | Antilipopolysaccharide factor isoform 6 | AFU61129 |
| Fenneropenaeus chinensis | Antimicrobial peptide (FcALF7) | AAX63831 |
| Fenneropenaeus chinensis | Antilipopolysaccharide factor isoform 8 | MH998632 |
| Macrobrachium nipponense | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor 5 | ALF02821 |
| Macrobrachium nipponense | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor 4 | ALF02820 |
| Macrobrachium nipponense | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor 3 | ALF02819 |
| Macrobrachium nipponense | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor 2 | ALF02817 |
| Macrobrachium nipponense | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor 1 | ALF02818 |
| Portunus trituberculatus | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 7 | AFA42358 |
| Portunus trituberculatus | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 6 | AFA42334 |
| Portunus trituberculatus | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 5 | AFA42332 |
| Portunus trituberculatus | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 4 | AFA42333 |
| Portunus trituberculatus | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 3 | ACS45385 |
| Portunus pelagicus | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor precursor | AFM77968 |
| Scylla serrata | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor | ADW11095 |
| Scylla serrata | Antilipopolysaccharide factor precursor | ACH87655 |
| Scylla paramamosain | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor | AHB62419 |
| Scylla paramamosain | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 4 | CCW43202 |
| Scylla paramamosain | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor-6 | CCW43204 |
| Scylla tranquebarica | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor precursor | AFM77969 |
| Penaeus monodon | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 3 | ABP73289 |
| Penaeus monodon | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 6 | AER45468 |
| Penaeus monodon | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 2 | ABP73291 |
| Penaeus monodon | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 7 | ANP92039 |
| Litopenaeus vannamei | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor isoform 1 | AHG99284 |
| Litopenaeus vannamei | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor AV-K isoform | ACT21197 |
| Litopenaeus vannamei | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor 5 (LvALF8) | AVP74305 |
| Litopenaeus schmitti | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor | ABJ90465 |
| Litopenaeus stylirostris | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor | AAY33769 |
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor | AFC93433 |
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor | AEP84102 |
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor 3 | AFW04306 |
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor 2 | AFW04305 |
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor 1 | AFW04304 |
| Macrobrachium rosenbergii | Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor 2 | ADI80707 |
| Microorganisms | MIC | MBC |
|---|---|---|
| Gram negative bacteria (G−): | ||
| Vibrio parahemolyticus | 1–2 μM | 4–8 μM |
| Vibrio harveyi | 1–2 μM | 4–8 μM |
| Vibrio alginolyticus | 1–2 μM | 4–8 μM |
| Vibrio owensii | 1–2 μM | 4–8 μM |
| Photobacterium damselae | 2–4 μM | 8–16 μM |
| Escherichia coli | 4-8 μM | >64 μM |
| Gram positive bacteria (G+): | ||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 2–4 μM | 32–64 μM |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 4–8 μM | >64 μM |
| Kurthia gibsonii | 4–8 μM | 4–8 μM |
| Peptide | Sequence | NetC a | H b | pI c | GRAVY d | μH e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LvALF8-LBD | Ac-Y(CSYSTRPYFLRWRLKFKSKVWC)P-NH2 | 6 | 0.571 | 10.20 | −0.541 | 0.040 |
| FcALF8-LBD | Ac-Y(CSYSTRPYFIRWQLKFKTKIWC)P-NH2 | 5 | 0.651 | 9.90 | −0.445 | 0.080 |
| GFP | Ac-TTGKLPVPWPTLVTTFSYGVQCFS-NH2 | 1 | 0.732 | 7.86 | 0.3333 | 0.314 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Li, S.; Lv, X.; Xiang, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, F. A Lymphoid Organ Specific Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor from Litopenaeus vannamei Exhibits Strong Antimicrobial Activities. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050250
Sun M, Li S, Lv X, Xiang J, Lu Y, Li F. A Lymphoid Organ Specific Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor from Litopenaeus vannamei Exhibits Strong Antimicrobial Activities. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(5):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050250
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Mingzhe, Shihao Li, Xinjia Lv, Jianhai Xiang, Yuanan Lu, and Fuhua Li. 2021. "A Lymphoid Organ Specific Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor from Litopenaeus vannamei Exhibits Strong Antimicrobial Activities" Marine Drugs 19, no. 5: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050250
APA StyleSun, M., Li, S., Lv, X., Xiang, J., Lu, Y., & Li, F. (2021). A Lymphoid Organ Specific Anti-Lipopolysaccharide Factor from Litopenaeus vannamei Exhibits Strong Antimicrobial Activities. Marine Drugs, 19(5), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19050250






