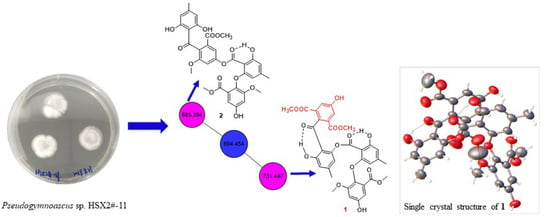
New Polyketides from the Antarctic Fungus Pseudogymnoascus sp. HSX2#-11
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
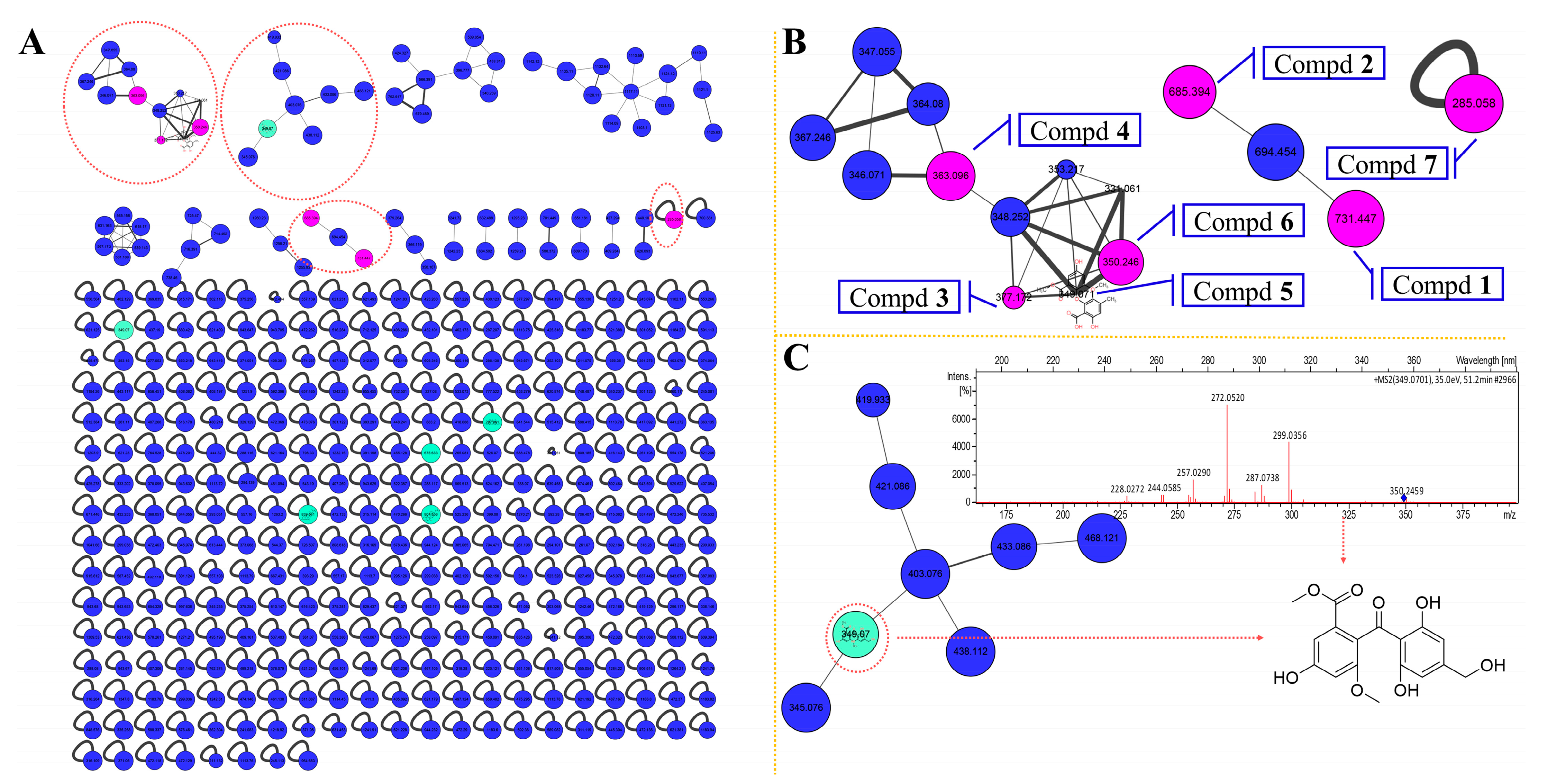
2.1. Secondary Metabolic Profile Visualization through Molecular Networking
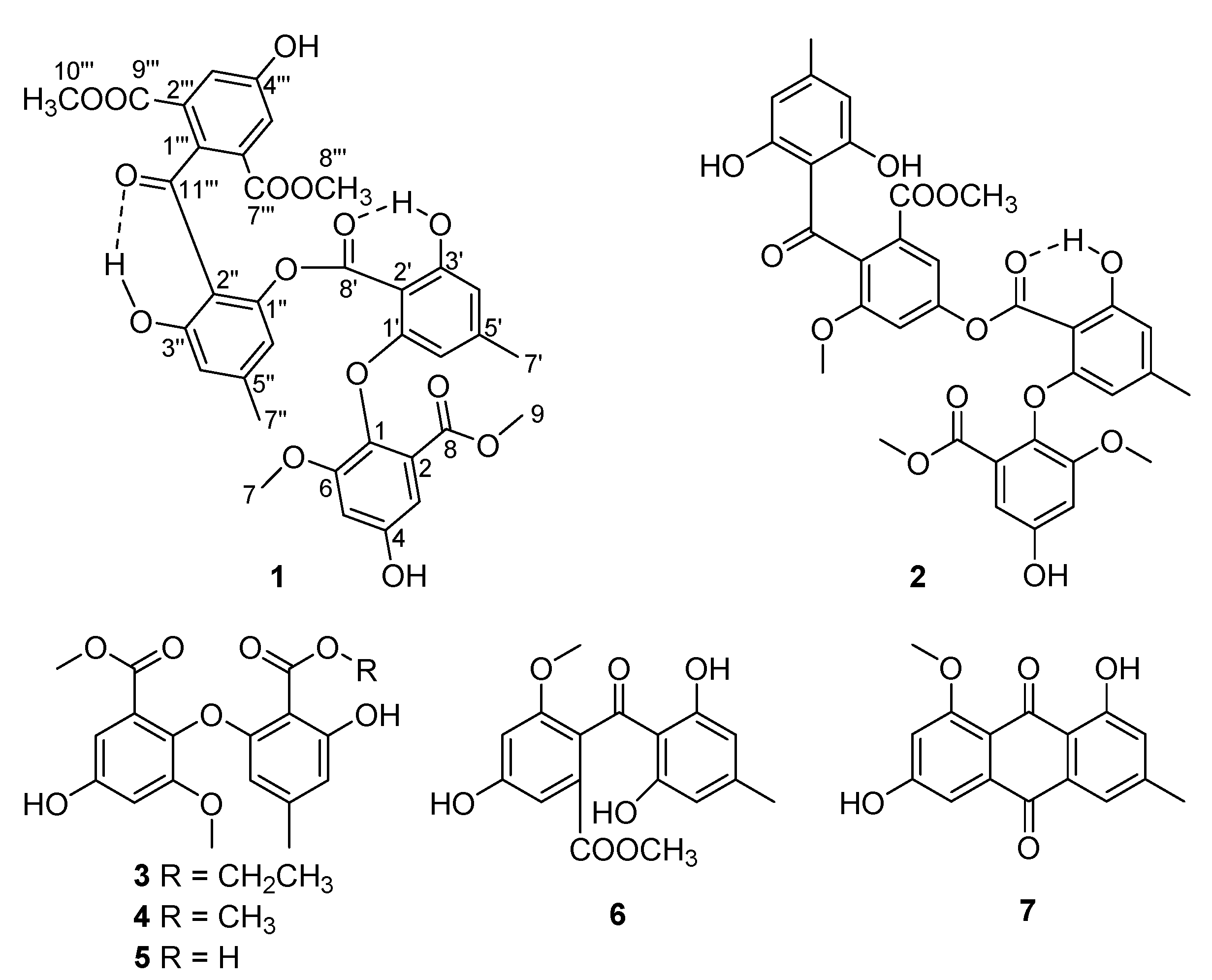
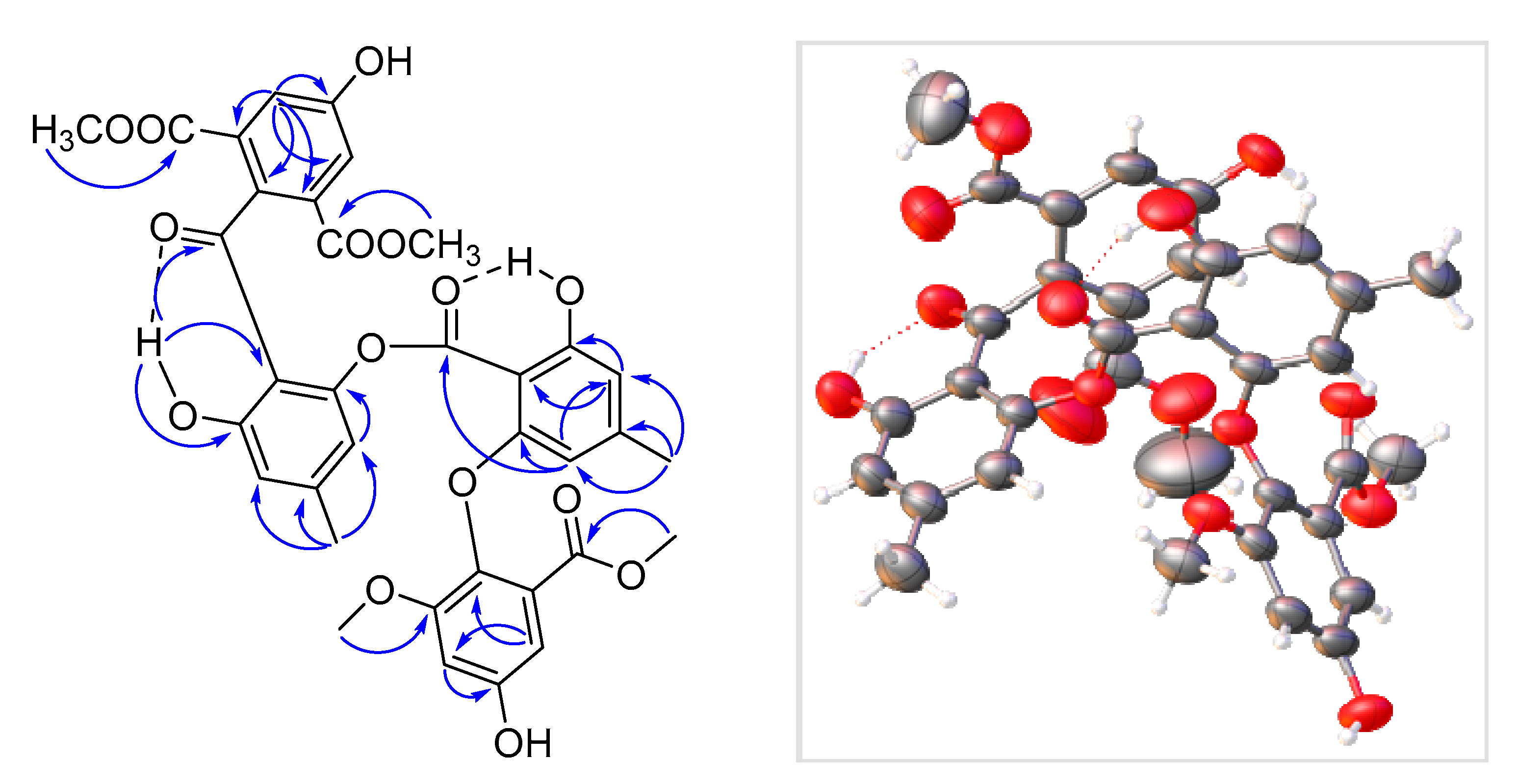
2.2. Structure Elucidation of Pseudophenone A (1)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Materials
3.3. Molecular Networking
3.3.1. UHPLC Parameters
3.3.2. MS/MS Parameters
3.3.3. Molecular Network Analysis
3.4. Extraction and Isolation
3.5. Antibacterial Activity Assay
3.6. Cytotoxic Activity Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mishra, B.B.; Tiwari, V.K. Natural products: An evolving role in future drug discovery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4769–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, C.Y. Metabolites from marine invertebrates and their symbiotic microorganisms: Molecular diversity discovery, mining, and application. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2019, 1, 60–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, B.; Yin, X.; Deng, A.; Shen, J.; Yang, H. Diversity of cultivable microbes from soil of the Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica, and their potential application. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 570836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.; Lee, H.; Ko, W.; Kim, D.C.; Kim, K.W.; Kwon, H.C.; Guo, Y.; Sohn, J.H.; Yim, J.H.; Kim, Y.C. Chemical constituents isolated from Antarctic marine-derived Aspergillus sp. SF-5976 and their anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 and BV2 cells. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 3905–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusman, Y.; Held, B.W.; Blanchette, R.A.; He, Y.; Salomon, C.E. Cadopherone and colomitide polyketides from Cadophora wood-rot fungi associated with historic expedition huts in Antarctica. Phytochemistry 2018, 148, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.H.; Sun, Z.C.; Peng, J.X.; Zhu, M.L.; Che, Q.; Zhang, G.J.; Zhu, T.J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Li, D.H. Secondary metabolites produced by combined culture of Penicillium crustosum and a Xylaria sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2013–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Yu, L.; Zhu, T. Antibacterial cyclic tripeptides from Antarctica-sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus insulicola HDN151418. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, L.; Jiménez, C.; Rodríguez, J.; Areche, C.; Chávez, R.; Henríquez, M.; Mercedes, D.L.C.; Díaz, C.; Segade, Y.; Vaca, I. 3-Nitroasterric acid derivatives from an Antarctic sponge-derived Pseudogymnoascus sp. Fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, Y.Z.; Wei, Q.; Gao, J.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, T.; Hua, H.M.; Hu, Y.C. Metabolites of the psychrophilic fungus Pseudogymnoascus pannorum. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2019, 31, 446–449. [Google Scholar]
- Kevin, P.; Lynsey, M.; Debra, B.; Guemundur, H.; Eva, K.; Margrét, Á.; Louise, Y.; David, G.; Ruangelie, E.E.; Katherine, D. Using molecular networking for microbial secondary metabolite bioprospecting. Metabolites 2016, 6, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Gu, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Hong, B. Exploring novel herbicidin analogues by transcriptional regulator overexpression and MS/MS molecular networking. Microb. Cell Fact. 2013, 18, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Shi, Y.W.; Fang, Y.W.; Shao, C.L. Integrating molecular networking and 1H NMR to target the isolation of chrysogeamides from a library of marine-derived Penicillium fungi. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 84, 1228–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aron, A.T.; Gentry, E.C.; Mcphail, K.L.; Nothias, L.F.; Dorrestein, P.C. Reproducible molecular networking of untargeted mass spectrometry data using GNPS. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1954–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Sun, B.; Jiang, L.; Liu, S. New Compound for Inhibiting Aspergillus fumigatus Activity, Its Preparation Process and Application. CN101372454A, 25 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Sun, B.D.; Liu, S.C.; Jiang, L.H.; Liu, X.Z.; Zhang, H.; Che, Y.S. Bioactive asterric acid derivatives from the Antarctic ascomycete fungus Geomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1643–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, B.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.J. Fungal metabolites, asterric acid derivatives inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced tube formation of HUVECs. Cheminform 2002, 55, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.S.; Yan, L.; Ma, L.Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Pan, X.H.; Liu, W.Z.; Lu, Z.H. Diphenyl derivatives from coastal saline soil fungus Aspergillus iizukae. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2014, 38, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, H.; Fujimaki, T.; Okuyama, E.; Yamazaki, M. Immunomodulatory constituents from an ascomycete, Microascus tardifaciens. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Bandeira, N. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appendino, G.; Gibbons, S.; Giana, A.; Pagani, A.; Grassi, G.; Stavri, M.; Smith, E.; Rahman, M.M. Antibacterial cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa: A structure-activity study. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skehan, P.; Storeng, R.; Scudiero, D.; Monks, A.; Mcmahon, J.; Vistica, D.; Warren, J.T.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Boyd, M.R. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Position | δC | δH |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 138.2, C | |
| 2 | 125.5, C | |
| 3 | 108.4, CH | 6.87, d, (2,8) |
| 4 | 153.1, C | |
| 5 | 104.8, CH | 6.67, d, (2.8) |
| 6 | 154.2, C | |
| 7 | 55.9, CH3 | 3.794, s |
| 8 | 165.4, C | |
| 9 | 52.5, CH3 | 3.791, s |
| 1′ | 159.8, C | |
| 2′ | 101.6, C | |
| 3′ | 162.1, C | |
| 4′ | 108.4, CH | 5.87, brs |
| 5′ | 146.8, C | |
| 6′ | 111.4, CH | 6.37, brs |
| 7′ | 22.2, CH3 | 2.15, s |
| 8′ | 168.9, C | |
| 1″ | 113.7, C | |
| 2″ | 151.1, C | |
| 3″ | 115.1, CH | 6.32, brs |
| 4″ | 147.1, C | |
| 5″ | 116.8, CH | 6.79, brs |
| 6″ | 164.1, C | |
| 7″ | 22.1, CH3 | 2.30, s |
| 1‴ | 124.8, C | |
| 2‴ | 124.8, C | |
| 3‴ | 109.1, CH | 6.83, brs |
| 4‴ | 157.4, C | |
| 5‴ | 103.8, CH | 6.44, brs |
| 6‴ | 124.8, C | |
| 7‴ | 166.0, C | |
| 8‴ | 52.4, CH3 | 3.64, s |
| 9‴ | 166.0, C | |
| 10‴ | 56.2, CH3 | 3.69, s |
| 11‴ | 199.5, C | |
| 6″-OH | 12.75, s |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, T.; Yu, Y.-Y.; Dai, J.-J.; Zhang, Y.-T.; Hu, W.-P.; Zheng, L.; Shi, D.-Y. New Polyketides from the Antarctic Fungus Pseudogymnoascus sp. HSX2#-11. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19030168
Shi T, Yu Y-Y, Dai J-J, Zhang Y-T, Hu W-P, Zheng L, Shi D-Y. New Polyketides from the Antarctic Fungus Pseudogymnoascus sp. HSX2#-11. Marine Drugs. 2021; 19(3):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19030168
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Ting, Yan-Yan Yu, Jia-Jia Dai, Yi-Ting Zhang, Wen-Peng Hu, Li Zheng, and Da-Yong Shi. 2021. "New Polyketides from the Antarctic Fungus Pseudogymnoascus sp. HSX2#-11" Marine Drugs 19, no. 3: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19030168
APA StyleShi, T., Yu, Y.-Y., Dai, J.-J., Zhang, Y.-T., Hu, W.-P., Zheng, L., & Shi, D.-Y. (2021). New Polyketides from the Antarctic Fungus Pseudogymnoascus sp. HSX2#-11. Marine Drugs, 19(3), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19030168